To remove all files in a directory using the command prompt, you can use the following command, which will delete all files without affecting subdirectories:
del *.*
Understanding CMD Commands
What is Command Prompt?
Command Prompt (CMD) is a command-line interpreter application available in most Windows operating systems. It allows users to execute commands, run scripts, and perform various administrative tasks directly from the command line interface. CMD is an essential tool for power users, IT professionals, and anyone who prefers to manage their system through textual commands, rather than relying solely on the graphical user interface (GUI).
Why Use CMD for File Management?
Using CMD for file management provides efficiency and speed that GUI methods often lack. When you’re dealing with a large number of files, executing a command directly can save time and reduce the chance of errors. CMD also gives you the flexibility to create batch scripts, allowing for complex operations and automation.

Cmd Remove Directory With Files: A Quick Guide
Preparing for File Deletion
Precautions to Take
Before proceeding with any file deletion operation, it’s crucial to take precautions. Always double-check the target directory to prevent unintentional loss of important files. If you are unsure about what files you might need later, consider making a backup of the directory or specific files before executing deletion commands.
How to Access Command Prompt
To access CMD in Windows, follow these steps:
- Press Windows key + R to open the Run dialog.
- Type `cmd` and press Enter.
Alternatively, you can search for «Command Prompt» in the start menu. For advanced users, you can also open it as an administrator by right-clicking and selecting «Run as administrator.»

Cmd Echo Current Directory: A Simple Guide
Basic Command Structure
The fundamental command for removing all files in a directory is structured as follows:
del <path>\*.*
Let’s break down this command:
- `del` is the command used to delete files.
- `<path>` should be replaced with the actual file path to the directory.
- `.` is a wildcard that signifies all files in that directory, regardless of their extension.
Example of Deleting All Files
To remove all files within a specified folder, you would use:
del C:\Path\To\Your\Folder\*.*
This command deletes every file in the given folder. The wildcard `.` effectively states: «Delete all files of any type.»
Additional Options with `del`
To Delete Specific File Types
If your goal is to delete only certain types of files (for instance, all `.txt` files), you can modify the command like this:
del C:\Path\To\Your\Folder\*.txt
This targets only text files within the specified directory, leaving other types intact.
Force Deletion Without Prompt
When executing file deletions, CMD will generally prompt you for confirmation. If you want to bypass this confirmation prompt, use the `/Q` flag to enter quiet mode:
del /Q C:\Path\To\Your\Folder\*.*
This command will silently delete all files in the specified folder without asking for confirmation, streamlining the process.
How to Delete All Files in a Directory Including Subdirectories
Using `rd` to Delete Folder and Files
Sometimes, users want to delete not only the files within a directory but the directory itself along with its contents. The `rd` (remove directory) command is suitable for this purpose:
rd /S /Q C:\Path\To\Your\Folder
In this command:
- `/S` specifies that all files and subdirectories within the specified directory should be deleted.
- `/Q` again runs the command in quiet mode, eliminating confirmation prompts.
Caution: Using the `rd` command is permanent. Once executed, it cannot easily be reversed.

Cmd Get Current Directory: A Handy Guide
Alternative Commands for Deleting Files and Directories
Using File Explorer vs. CMD
While using CMD is a powerful approach, many users still prefer the graphical interface of File Explorer for file deletion. However, CMD offers benefits such as batch processing, which can be a game-changer when dealing with vast numbers of files. Choose the method that aligns with your comfort and the complexity of the task.
Using PowerShell as an Alternative
For users who are more familiar with scripting and advanced tasks, PowerShell may provide a more versatile option. PowerShell commands for file deletions can sometimes offer features that CMD lacks, such as the ability to filter by specific attributes and perform more complex scripting tasks.

How to Cmd Show Current Directory in Style
Best Practices for File Deletion Using CMD
Final Checks Before Executing
Always perform a final review of your target path. Employing `dir <path>` before executing the delete command can help verify what files will be affected.
Use with Caution
Given the permanent nature of file deletions in CMD, avoid executing deletion commands unless you are absolutely certain it is safe to do so. It’s easy to mistakenly target important files, so caution is paramount.

Mastering Cmd Current Directory with Ease
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Access Denied Errors
If you encounter «Access Denied» errors, it might be due to insufficient permissions. To resolve this, ensure you run CMD as an administrator or take ownership of the files or directories.
Files in Use
Sometimes, files may be in use and cannot be deleted. In such cases, identify the application currently using the file, close it, and then attempt the deletion again. You could also use tools like Task Manager to force-quit any processes holding onto the file.

Cmd See All Devices on Network: A Simple Guide
Conclusion
Mastering the command to cmd remove all files in directory signifies an important step towards effective file management through CMD. By understanding the commands, their options, and best practices, you can efficiently manage your files with confidence.
Effortless File Transfers: Cmd Move Files Made Easy
Call to Action
For those eager to dive deeper into CMD commands, stay tuned for more insightful articles that will enhance your command line proficiency. Consider downloading our comprehensive CMD cheat sheet to keep essential commands at your fingertips!

Sometimes it’s just faster to do things with the command line.
In this quick tutorial we’ll go over how to open Command Prompt, some basic commands and flags, and how to delete files and folders in Command Prompt.
If you’re already familiar with basic DOS commands, feel free to skip ahead.
How to open Command Prompt
To open Command Prompt, press the Windows key, and type in «cmd».
Then, click on «Run as Administrator»:
After that, you’ll see a Command Prompt window with administrative privileges:
Screenshot of Command Prompt window
If you can’t open Command Prompt as an administrator, no worries. You can open a normal Command Prompt window by clicking «Open» instead of «Run as Administrator».
The only difference is that you may not be able to delete some protected files, which shouldn’t be a problem in most cases.
How to delete files with the del command
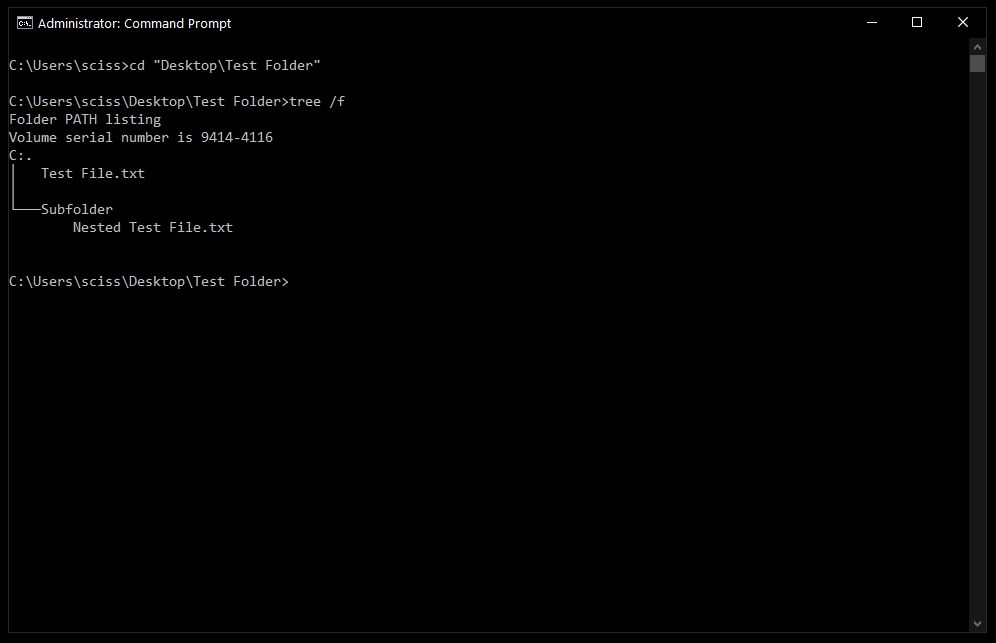
Now that Command Prompt is open, use cd to change directories to where your files are.
I’ve prepared a directory on the desktop called Test Folder. You can use the command tree /f to see a, well, tree, of all the nested files and folders:
To delete a file, use the following command: del "<filename>".
For example, to delete Test file.txt, just run del "Test File.txt".
There may be a prompt asking if you want to delete the file. If so, type «y» and hit enter.
Note: Any files deleted with the del command cannot be recovered. Be very careful where and how you use this command.
After that, you can run tree /f to confirm that your file was deleted:

Also, bonus tip – Command Prompt has basic autocompletion. So you could just type in del test, press the tab key, and Command Prompt will change it to del "Test File.txt".
How to force delete files with the del command
Sometimes files are marked as read only, and you’ll see the following error when you try to use the del command:
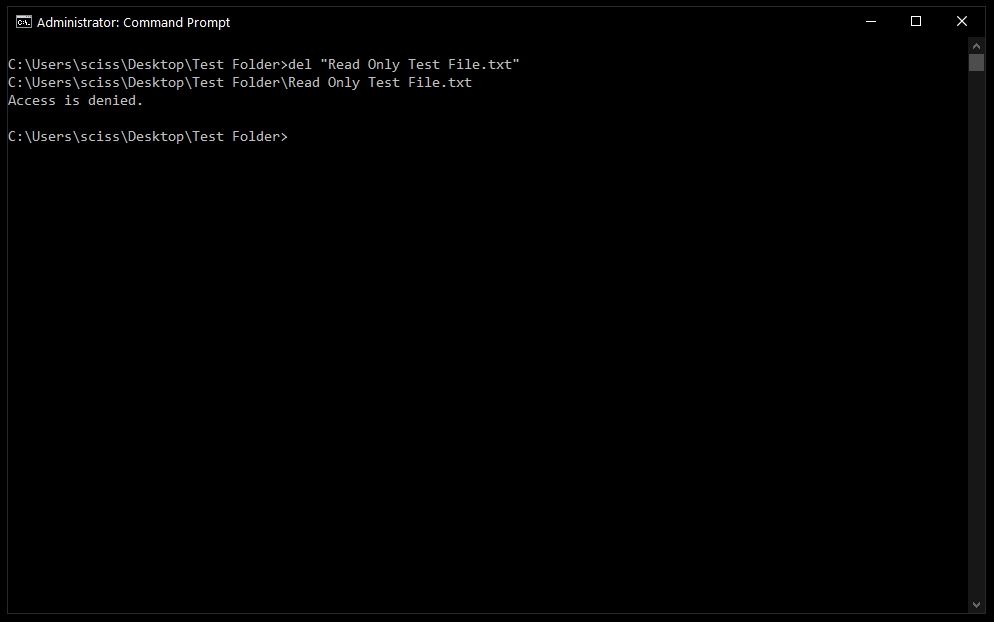
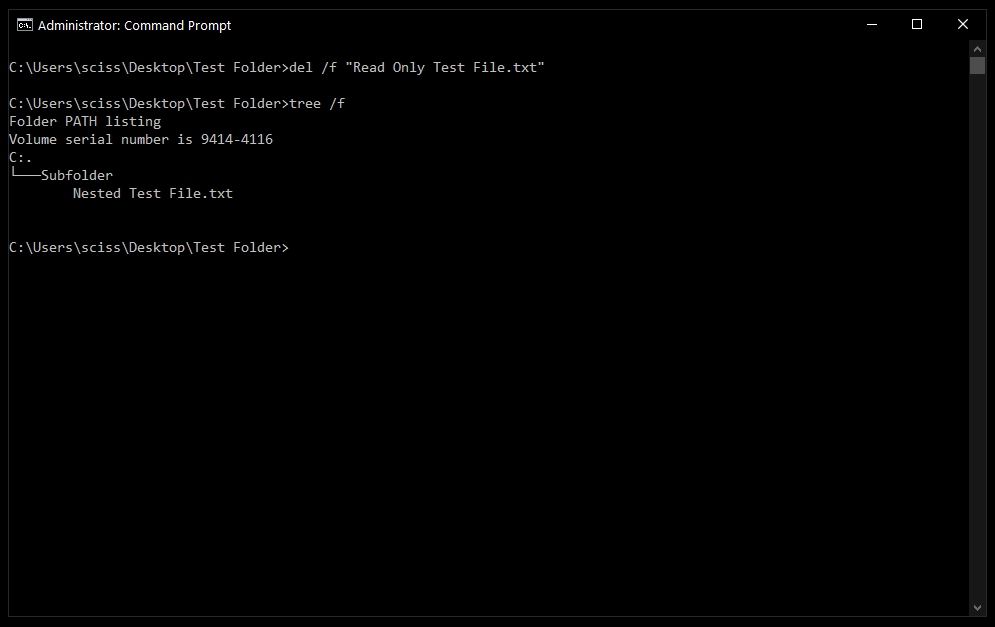
To get around this, use the /f flag to force delete the file. For example, del /f "Read Only Test File.txt":
How to delete folders with the rmdir command
To delete directories/folders, you’ll need to use the rmdir or rd command. Both commands work the same way, but let’s stick with rmdir since it’s a bit more expressive.
Also, I’ll use the terms directory and folder interchangeably for the rest of the tutorial. «Folder» is a newer term that became popular with early desktop GUIs, but folder and directory basically mean the same thing.
To remove a directory, just use the command rmdir <directory name>.
Note: Any directories deleted with the rmdir command cannot be recovered. Be very careful where and how you use this command.
In this case I want to remove a directory named Subfolder, so I’ll use the command rmdir Subfolder:
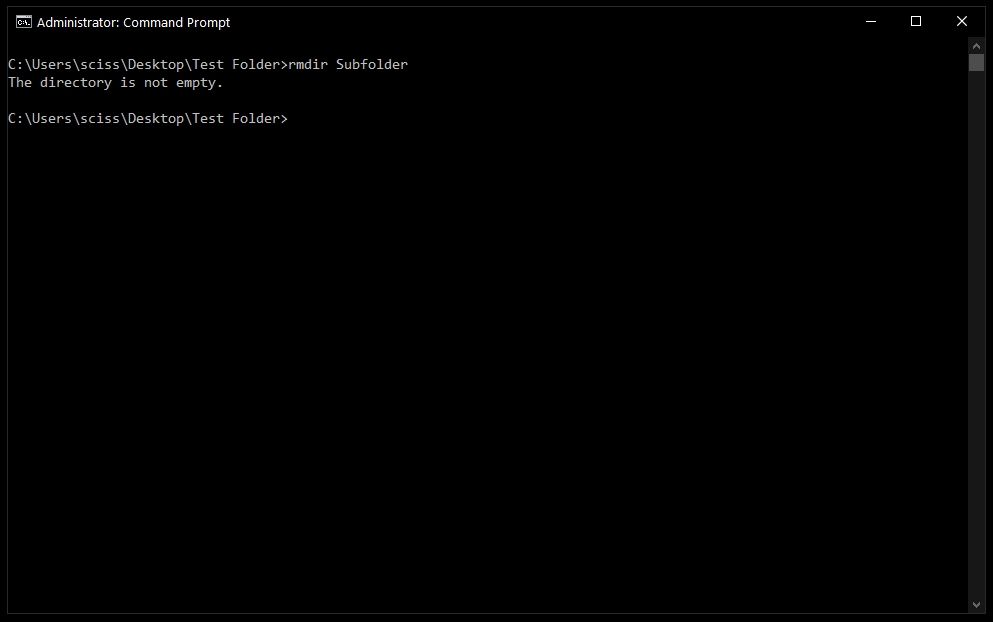
But, if you remember earlier, Subfolder has a file in it named Nested Test File.
You could cd into the Subfolder directory and remove the file, then come back with cd .. and run the rmdir Subfolder command again, but that would get tedious. And just imagine if there were a bunch of other nested files and directories!
Like with the del command, there’s a helpful flag we can use to make things much faster and easier.
How to use the /s flag with rmdir
To remove a directory, including all nested files and subdirectories, just use the /s flag:
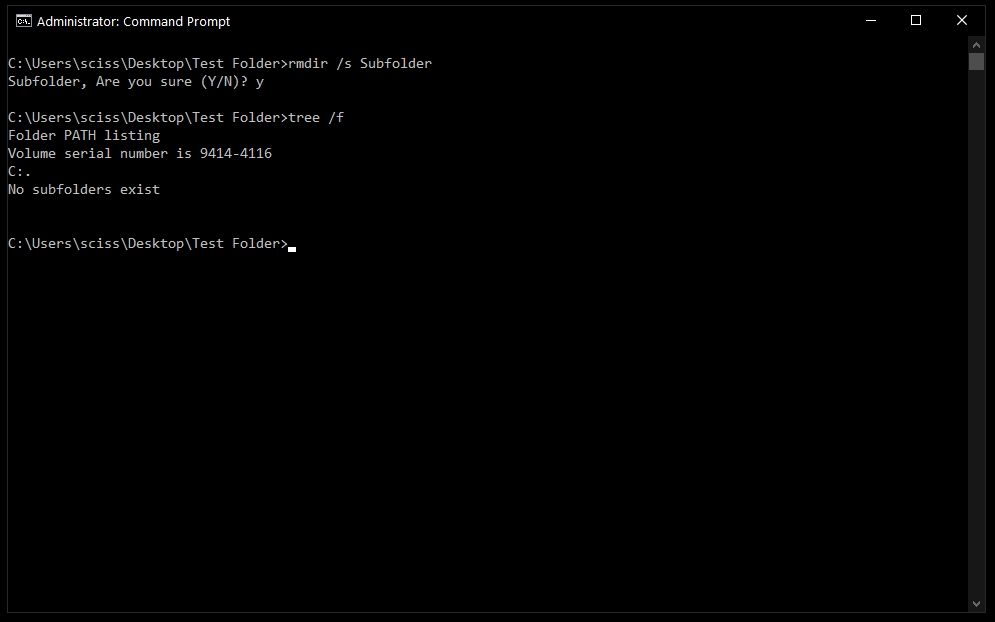
There will probably be a prompt asking if you want to remove that directory. If so, just type «y» and hit enter.
And that’s it! That should be everything you need to know to remove files and folders in the Windows Command Prompt.
All of these commands should work in PowerShell, which is basically Command Prompt version 2.0. Also, PowerShell has a bunch of cool aliases like ls and clear that should feel right at home if you’re familiar with the Mac/Linux command line.
Did these commands help you? Are there any other commands that you find useful? Either way, let me know over on Twitter.
Learn to code for free. freeCodeCamp’s open source curriculum has helped more than 40,000 people get jobs as developers. Get started
Key Takeaways:
- You can use the “del” command to delete a single file, multiple files, files that contain a specific word, files with a specific extension, and all files in a folder at once.
- The Command Prompt can also help remove or delete stubborn files that you cannot delete from File Explorer.
- Deleting files using commands is also helpful when you want to delete a large number of files.
Generally, deleting a file in Windows is a simple process. All you have to do is select the file you want to delete and press the “Delete” key on your keyboard or right-click on the file and select the “Delete” option.
If you cannot delete a file using File Explorer, you can use the Command Prompt to delete files in Windows 10 and 11. The Command Prompt offers a quick and easy way to delete a single file, multiple files, files with a specific extension, or read-only files. The best thing is that this works even if the file is locked, in use, or blocked from deletion.
In this short tutorial, let me walk you through the process of deleting a file using cmd.
Table of contents:
- How to delete a file using CMD
- How to delete all files in a folder using CMD
- How to delete files with a specific extension using CMD
- How to delete read-only files using CMD
- Conclusion
Important note: Files deleted using cmd will skip the Recycle Bin. That means you cannot restore a deleted file from the Recycle Bin. So, be careful while using Command Prompt to delete files in Windows.
How to delete a file using CMD
To delete a single file, all you need to do is execute a single command with the file name.
- Select the “Start” icon on the taskbar.
- Search for “Command Prompt.”
- Click on the “Run as administrator” option.
- Use the “cd C:\path\to\folder” to navigate to the folder.
- Run the “del filename.ext” command to delete the file. Replace “filename.ext” with the actual file name and extension.
Steps with more details:
First, search for “cmd” in the start menu, right-click on Command Prompt and select “Run as administrator.” This action will open an elevated command prompt.
Note: The elevated Command Prompt is required to delete locked files, files belonging to other user accounts, etc.
Once the Command Prompt window opens, use the “cd” command to go to the folder where the files you want to delete are located. For instance, the files I want to delete are in a folder named “del” on my desktop. So, I use the following command.
Note: If the folder is located in another partition, like the D drive, execute the “DriveLetter:” command while replacing “DriveLetter” with the actual drive letter. For example, to change the directory to D drive, you have to execute the “D:” command. Once in the drive, you can use the “cd” command to navigate to the target directory.
cd c:\users\vamsi\desktop\del

Once you are in the folder, run the below command to delete a file. Don’t forget to replace <filename> with the actual file name along with its file extension. In my case, the file name is image-1.jpg.
del <filename>

If the file is locked in some way, use the below command to force delete the file.
del /f <filename>
On successfully deleting the file, you will not see any confirmation message. So, that’s a good thing. If there is a problem, the command prompt will show an error message.
How to delete all files in a folder using CMD
The Command Prompt offers a simple command to delete multiple files in a folder at once. Whether you need to delete specific files or all files in a folder, cmd provides the option to do so. I will show how to use the command to delete multiple files in both situations. Follow the one that best suits your needs.
Here’s the cmd to delete multiple files:
First of all, open Command Prompt as administrator from the Start menu.
Once the command window opens, use the “cd C:\folder\path” to go to the folder with the files you want to delete.
Next, to delete multiple specific files at once, execute the below command while replacing <filname1>, <filename2>, etc., with the actual file names along with the file extension. You can specify as many file names as you want.
del <filename1> <filename2>

You can use the “*” (wildcard) character to delete all the files in a folder. Here’s the command to remove all files in a directory.
del *
Since we are deleting all the files in a folder, the Command Prompt window will warn you. Simply type “Y” and press “Enter” to confirm file deletion.

You can also use the wildcard character to delete all files that start with a specific name in a folder. For that, use the below syntax. For instance, the below command will delete all the files in a folder that start with the name “image.”
del image*

Alternatively, you can also delete files that contain a specific word. The below command will delete all the files with the name that contains the “tFile” word.
del *word*

How to delete files with a specific extension using CMD
Sometimes, you might want to delete all the files with a specific extension. For instance, maybe you want to delete all the “.png” files in a folder. In that case, we can use the same wildcard character.
Here’s the command to delete files that have a specific file extension, then you can use below command. Don’t forget to replace “fileExtension” with the actual file extension, like png, jpg, zip, etc.
del *.fileExtension
For example, to delete all the PNG files in a folder, the command looks something like this.
del *.png

Use the below command to delete all files with a specific name and extension. Don’t forget to replace the file name and extension to match your needs.
del filename*.png

How to delete read-only files using CMD
Unlike regular files, read-only files are protected and difficult to delete by design. If you try to delete a read-only file using the normal commands shown above, you will receive the “Access is denied” error message.

First, open the command prompt from the Start menu and use the “cd C:\path\to\folder” command to go to the folder with the read-only file.
Once you are here, use one of the below commands to delete the read-only file. Replace <filename> with the actual filename and extension.
del /f <filename>
or
del /a:r <filename>

CMD to delete files in Windows – Conclusion
As you can see, commands to delete files in Windows are pretty simple and straightforward. With the commands and flags shown in this tutorial, you can delete individual files, read-only files, multiple files, or even all files in a folder. You can also use the Command Prompt to delete files that are locked, in use, or blocked from deletion. The steps shown above are handy when you need to delete a large number of files or when you cannot delete a file using the traditional File Explorer method.
I hope this simple and easy Windows how-to guide helped you.
If you are stuck or need help, send an email, and I will try to help as much as possible.
If you like this article, you might also want to know how to force delete locked files in Windows and how to delete a single URL from Chrome and Firefox’s auto-complete history.
on August 5, 2015
Deleting files is one of the frequently done operation from Windows command prompt. This post explains how to use ‘del’ command from CMD for different use cases like deleting a single file, deleting files in bulk using wild cards etc. Before we start to look at the syntax, note that the command works only for files and can’t handle folders.
How to delete a file
Run del command with the name of the file to be deleted, you are done!
del filename
You do not see message after running the command if the file is deleted successfully. Error message is shown only when something goes wrong.
Delete files in bulk
Del command recognizes wildcard(*) and so can be used to delete files in bulk from CMD. Some examples below.
To delete all the files in current folder
del *
To delete all the files with ‘log’ extension
del *.log
Delete all files having the prefix ‘abc’
del abc*
Delete all files having ‘PIC’ somewhere in the file name.
del *PIC*
The above are the basic use cases of del command. Continue to read below for non trivial use cases.
Delete multiple files
‘Del’ command can accept multiple files as argument
del filename1 filename2 filename3 filename4....
Example:
D:\>dir /s /b 1.pdf 2.pdf 3.pdf D:\>del 1.pdf 2.pdf 3.pdf D:\> D:\>dir /s /b D:\>
Delete Read only files
We can’t delete a read-only file using simple‘del’ command. We get access denied error in this scenario.
c:\>attrib readonlyfile.txt A R C:\readonlyfile.txt c:\>del readonlyfile.txt c:\readonlyfile.txt Access is denied. c:\>
A read-only file can be deleted by adding /F flag.
del /F readonlyfile.txt
Alternatively, we can use the below command too
del /A:R readonlyfile.txt

The CMD del command is used to delete files from the command line in the Windows operating system.
del file-nameWe can delete multiple files at once:
del file1.txt file2.txtNotes
- The
delcommand removes files permanently without sending them to the Recycle Bin. - If you use the
/poption, thedelcommand prompts for confirmation before deleting each file. - There is another command, the
erasecommand, and it is identical to thedelcommand, and the syntax is similar. - To force delete read-only files, use the
/Foption. - We can use the wildcard (*) character to remove all files in a directory.
- To delete folders, use the rmdir command.
DEL Command Examples
Remove the file file1.txt in the current directory:
del file1.txtRemove the file file1.txt in the c:\data directory:
del C:\data\file1.txtThe following command uses the /F option to force delete file1.txt if it is a read-only file:
del /f file1.txtRemove all files in the c:\data directory:
del /q *Remove all text files (files with .txt extension) in the current directory:
del *.txtDelete all files with the pattern file.* (e.g., file1.txt, file2.txt, file1.doc, etc.) in the c:\data directory:
del file*When using the wildcard character, the del command prompts for confirmation by default. You can use the \Q option to suppress the confirmation message.
In the following example, The windows del command deletes all files from c:\data and all subdirectories. The /S option is used to remove the specified file(s) from all subdirectories.
del /s /q C:\data\*However, the del command does not remove subdirectories, only files inside subdirectories.

The del command does not delete hidden files by default. To include hidden files, use the /a:h switch:
del /a:h file1.txtThe following command deletes all hidden files in the current directory:
del /a:h *The /a switch is used to delete files based on their attributes (H represents hidden files). To see a list of all options, type del /?.
