Last Updated :
09 Apr, 2025
Open ports on your Windows computer act like doors for data-letting information in and out. While necessary for apps and services, unprotected ports can become security risks. Checking which ports are open helps you spot vulnerabilities, fix connection issues, and keep your system safe.
Using Command Prompt (CMD), you can quickly see active ports with simple built-in commands—no extra tools needed. This guide walks you through the steps to check open ports in Windows, understand the results, and close any unnecessary ones.
Whether you’re troubleshooting a network problem or guarding against threats, these CMD techniques give you control over your system’s security.

How to Check Open Ports Using CMD in Windows
Make sure that the essential ports are allowed or blocked by your firewall system configuration. The Control Panel’s Windows Firewall settings allow you to control all the initial processes for system requirements. If you discover the open ports that ought to be closed within the system, you might want to halt the related service or change the in-build configuration of the program that opened the port manually.
Now, see the below-mentioned steps and implement them to Check Open Ports Using CMD in Windows.
Step 1: Open CMD or Command Prompt
- Press Win + R from your keyboard > Type cmd > Click on the Enter button
Step 2: Implement the «netstat» Command
An effective tool for keeping an eye on open ports within the system and configured network connections is the netstat command to simplify. It offers comprehensive details on all open connections and system servers, such as the protocol in use, and local and international addresses to control or verify all the connection’s status.
- Type the below command in the cmd to check the open port functions > Press Enter
netstat -an | find "LISTEN"
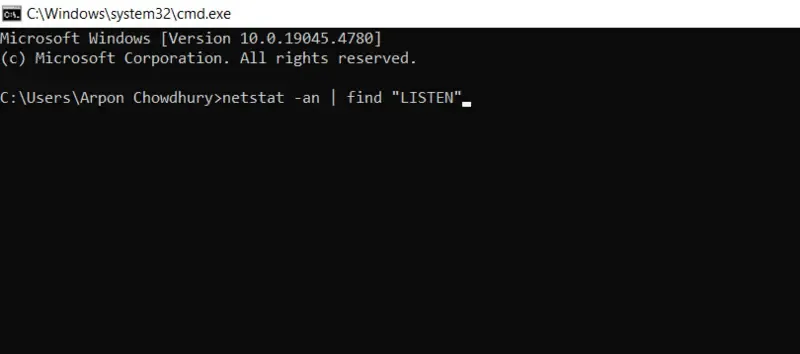
- See the output below
TCP 0.0.0.0:135 0.0.0.0:0 LISTENING
TCP 0.0.0.0:445 0.0.0.0:0 LISTENING
TCP 0.0.0.0:902 0.0.0.0:0 LISTENING
In this case, 0.0.0.0 designates that all pre-processed network interfaces are listening on the port, which is open for the internal system server. The port number is the number that comes after the colon of the system commands (e.g., 135, 445, 3389).
Step 3: Observe the functional Process Using the Port
- Write the following command to identify which application or process is using a specific port within the system.
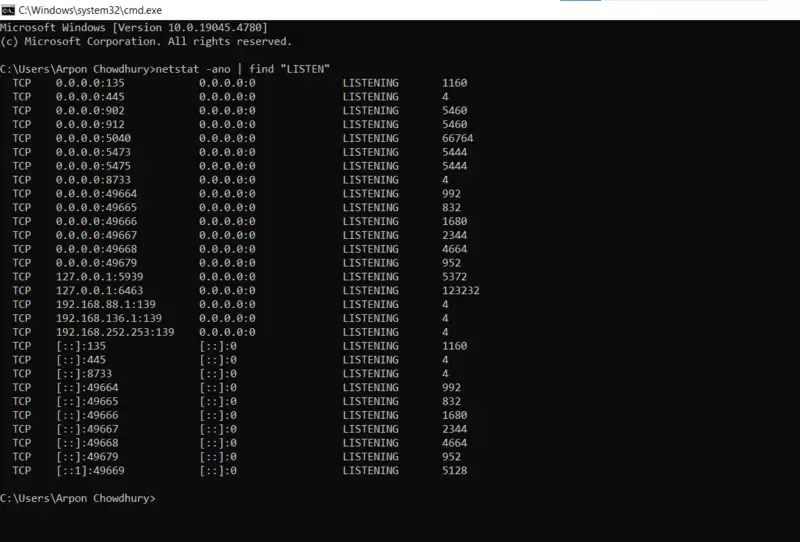
netstat -ano | find "LISTEN"
An extra -o flag is included with this command while processed, which shows the Process ID (PID) connected to each port manually.
- See the output within a PID column
TCP 0.0.0.0:135 0.0.0.0:0 LISTENING 1160
TCP 0.0.0.0:445 0.0.0.0:0 LISTENING 4
- Search and Open Task Manager > Go to Details option > See the PID column
Step 4: Check Specific Port in cmd
- You can change the implemented command to focus on a particular port if you want to see if it’s open or not within the system configuration. For instance, use this to see if port 60 is open to identify the process:
netstat -an | find ":60"
- See the final entry below —
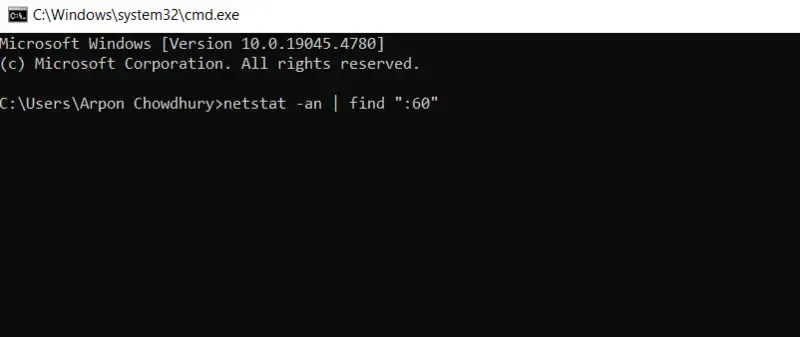
TCP 0.0.0.0:40 0.0.0.0:0 LISTENING
Conclusion
Using Windows’ CMD to check all the internal open ports is a simple yet effective method for network management, security control, and troubleshooting issues identification. You can safeguard your system from external potential dangers and make sure your connected network is operating efficiently by routinely checking open ports within the system. The netstat command is an invaluable resource for any IT professional or developer toolset, especially when paired with a basic understanding of ports and processes of all the initial implementations.
Also Read
- How to check Active Network Connections in Windows?
- Ways to Find Out List of All Open Ports in Linux
Обмен данными по локальной сети или через интернет осуществляется путем подключения друг к другу двух компьютеров. Чтобы получить данные с удаленного сервера, требуется соблюсти несколько условий – наличие IP-адреса у источника и получателя, выбор конкретного протокола приема-передачи и открытые порты на обоих компьютерах.
Что такое порт компьютера
Порт – это виртуальное дополнение к сетевому адресу, которое позволяет разделить запросы разных приложений и обрабатывать их автономно. Часть постоянно занята системными службами Windows или другой операционки, остальные свободны для использования прикладными программами, в том числе запускаемыми на удаленных серверах.
Особенности портов:
- Иногда порты путают с разъемами на материнской плате (формально они и являются ими, но там речь идет о подключении физических устройств).
- Общее количество портов составляет 65535. Они имеют определенное назначение, например, 20-21 «по умолчанию» используется для соединения по FTP, а 110 выделен под почтовый протокол POP3.
- Сочетание IP-адреса и порта принято называть сокетом или файловым дескриптором, при помощи которого программа передает данные.
Перед подключением к какому-либо порту рекомендуется проверить, свободен ли он. Если нет, то операционная система выдаст ошибку, и соединение прервется. Многие программы делают проверку в автоматическом режиме и сами пытаются менять номера в поиске незанятого подключения. Но в ряде случаев это требуется сделать вручную, например, при отладке собственного кода.
Комьюнити теперь в Телеграм
Подпишитесь и будьте в курсе последних IT-новостей
Подписаться
Как проверить, открыт ли порт для подключения
Порты присутствуют у всех сетевых устройств, включая маршрутизаторы и роутеры, поэтому при анализе среды важно понимать, какой именно узел проверяется. На этом отчасти основаны системы безопасности, когда ради блокировки вероятных хакерских атак закрываются все свободные сокеты и открываются только те, которые используются корпоративным софтом.
Существует три основных способа проверки открытых портов:
- Специализированные онлайн-сервисы.
- Прикладные приложения, запускаемые на компьютере.
- Встроенные в операционную систему утилиты.
Выбор решения зависит от задач. Так, если требуется открыть доступ к своему компьютеру извне, можно воспользоваться сервисами 2ip.ru или portscan.ru. При локальных работах удобнее приложения типа Portforward Network Utilities или штатная утилита TELNET. Она поставляется в «стандартной» сборке Windows и доступна для запуска в консоли CMD.
Перечень открытых портов на локальном компьютере
Открытый порт на домашнем или рабочем компьютере – это фактически «дыра» в безопасности и риски утраты контроля над ситуацией. Именно через них проникают трояны и иные вирусы, которые имеют цель предоставить злоумышленнику возможность удаленного подключения к ПК без разрешения владельца.
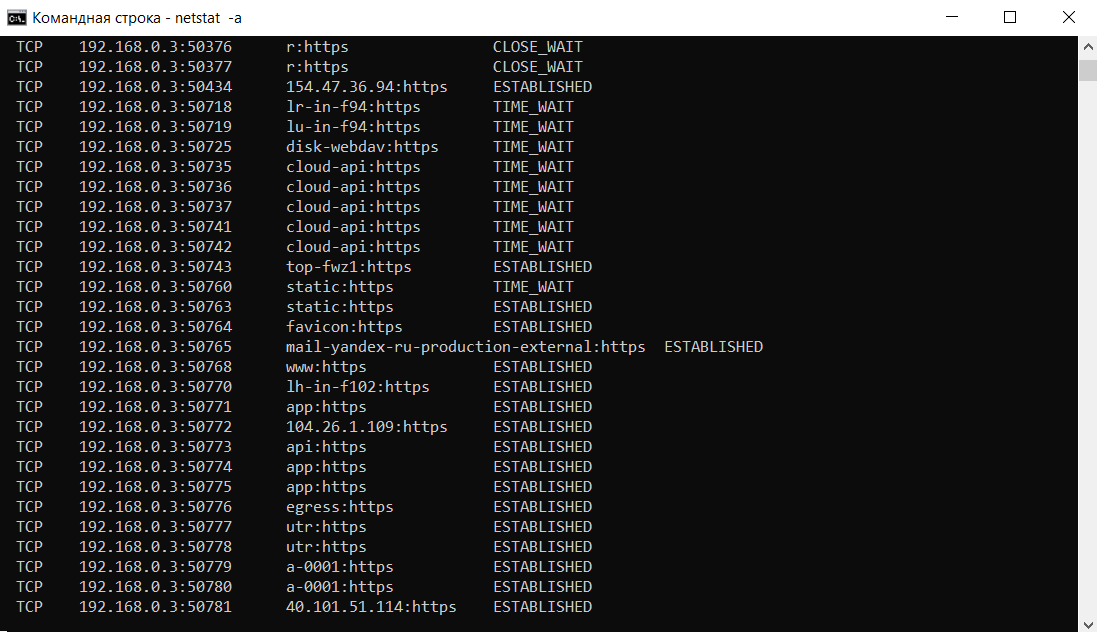
Проверить занятые порты легко:
- Нужно нажать комбинацию клавиш <Win+R>.
- Ввести команду CMD и нажать кнопку Enter.
- Ввести команду netstat –a и повторно нажать Enter.
В консоли отобразится перечень занятых портов с указанием, какое приложение или служба ими «распоряжается». Такой вариант проверки интересен тем, что он дает объективную картину. Если рассчитывать только на онлайн-сервисы, иногда создается впечатление, что открытых портов нет. Эффект создается из-за блокировки внешних запросов брандмауэром Windows или другим ПО.
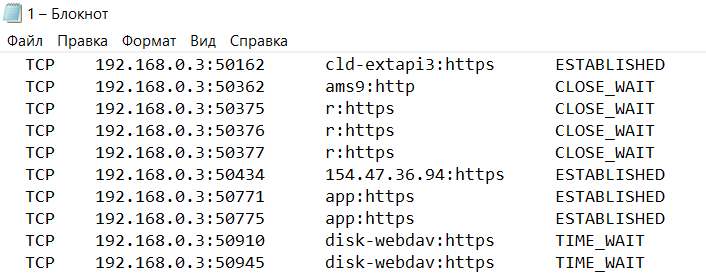
Если хочется изучить список на предмет «посторонних» программ, его лучше выгрузить в файл при помощи команды netstat –a >имя.txt. По умолчанию список сохраняется в каталоге пользователя, в аккаунте которого происходил запуск утилиты (типа C:\\Пользователи\User\). При желании перед запуском утилиты можно перейти в корень диска командой cd c:\.

Просмотр открытых портов на удаленном компьютере
При взаимодействии с удаленным сервером используется другая утилита – TELNET. В Windows она по умолчанию отключена, потому что не относится к пользовательским приложениям. Перед первым запуском придется провести «активацию». Существует два способа включения – в консоли или через графический интерфейс.
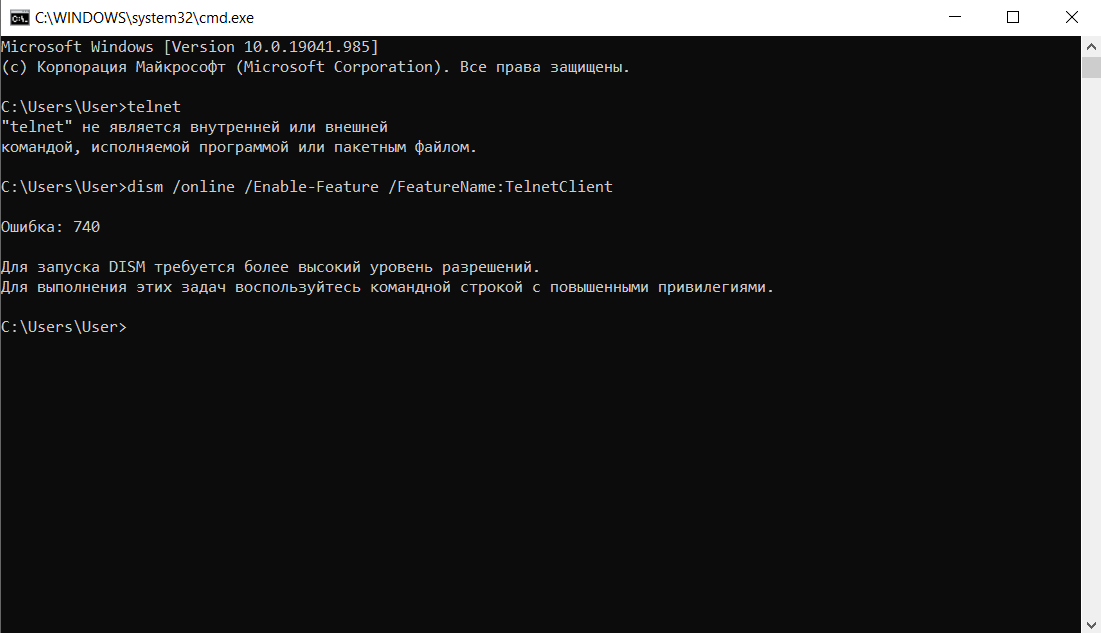
Активация заключается во вводе специальной команды:
dism /online /Enable-Feature /FeatureName:TelnetClient
Она сработает только при запуске консоли с правами администратора. Схема открытия приложения несколько иная:
- Нажать комбинацию клавиш <Win+X>.
- Выбрать пункт «Командная строка (администратор)».
- В открывшемся окне ввести команду активации telnet.
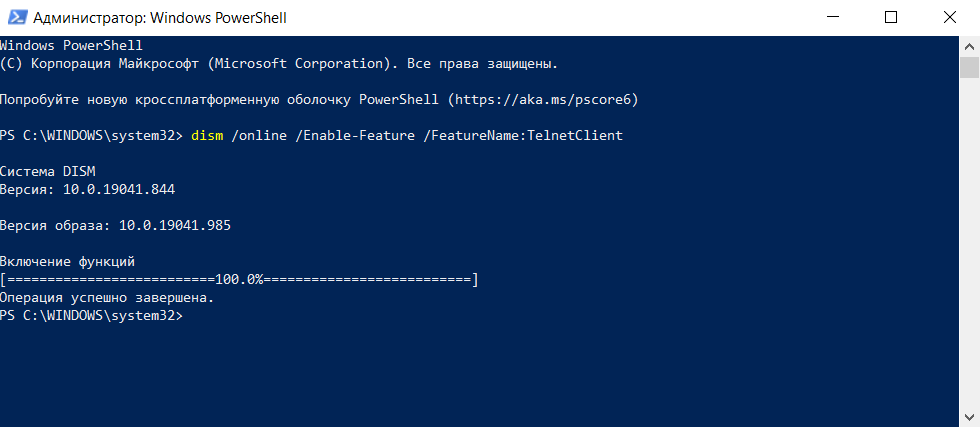
Если пользователь предпочитает управлять компьютером через графический интерфейс, нужно запустить панель управления, а в ней утилиту «Удаление программы». В открывшемся окне нужно перейти в раздел «Включение или отключение компонентов Windows», далее в общем списке найти строку «Telnet», поставить в ней галочку и нажать кнопку ОК. Все, служба активирована и готова к использованию (даже в консоли).
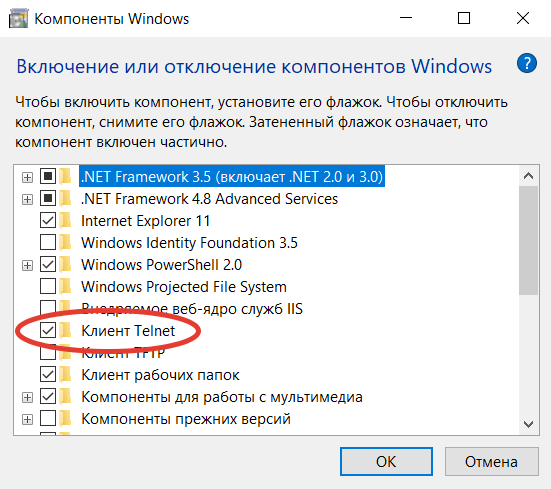
Синтаксис:
telnet опции хост порт
Хост – это домен или его IP-адрес, порт – виртуальное дополнение для образования сокета, опции же позволяют менять режим подключения. Их основные варианты:
- -4 – использовать адреса стандарта IPV4;
- -6 – использовать адреса стандарта IPV6;
- -8 – применять 8-битную кодировку типа Unicode;
- -E – отключение поддержки Escape-последовательностей;
- -a – вход с именем пользователя из переменного окружения User;
- -b – использовать локальный сокет;
- -d – включить режим отладки;
- -p – режим эмуляции rlogin;
- -e – задать символ начала Escape-последовательности;
- -l – пользователь для авторизации на удаленном сервере.
Простейший вариант проверки открытых портов – это ввод команды без опций:
telnet 10.0.119.127 80
Если на экран будет выведено сообщение «Сбой подключения», порт закрыт, нужно подбирать другой номер. Если порт открыт, пользователь увидит пустой экран или приглашение со стороны сервера ввести логин и пароль.
In this article, you will see the procedure to Check Open Ports in Windows 11 or 10 Using CMD (or Command Prompt). When an app uses a TCP/IP port on your device in order to access a network, that port would be locked out – no other program may be able to use it. And while everything related to ports and traffic is usually taken care of on its own by the system, there might be situations when you might have to know the application that is blocking a specific port.
Here you can find some built-in ways to do so- specifically the ways to check open ports using CMD or Command Prompt. Apart from using the Command Prompt, you can even consider using some third-party applications that can easily list the ports and the apps or processes that are using them.
Way to Check Open Ports in Windows 11 and 10 Using CMD
Here is how to check open Ports in Windows 11 or 10 Using CMD –
To find port-use with process names
Follow along with these steps to get the list of ports in use and the names of the processes tied up with them respectively.
Step-1: Open Run dialog box by pressing Win+R hotkeys. Type cmd in the text box and hit Shift + Ctrl + Enter keys altogether.
Step-2: Hit Yes on the UAC prompt.
Step-3: This will let you access an elevated Command Prompt on the screen. Here, type in or copy-paste the below-given code and hit Enter.
Netstat -ab
Wait for the entire result to load. Once you successfully run this command, simply scroll down to the port number you want to check. As shown below, you’ll be able to see the process’ name respectively below the port it is linked to.
To find port-use with the process identifiers
Usually, identifying the application represented by a specific process name can be tricky. This method might help you identify the application that a process relates to.
Here also, first of all, launch the “Command Prompt” with admin rights using any of your preferred methods.
Copy-paste or type the below code and ensure to hit Enter.
netstat -aon
Finally, the result now will contain the “PID” or the process identifiers instead of the names. Simply scroll down to the port you want to check and note the PID corresponding to it.
Moving ahead, open Task Manager. To do so, perform a right-click on the taskbar and select the option namely “Task Manager”.
Go to the Processes tab. Right-click on the Name column and choose PID (see snapshot).
You just need to find the PID you note earlier. The ‘Name’ column corresponding to the PID must reveal the application associated with the port.
That’s all!!
1) How to Flush DNS Cache in Windows 10 Using CMD
2) How Run System Restore Using Command Prompt (CMD) in Windows 10
3) How to Get BitLocker Recovery Key from CMD in Windows 10
4) How to Open Device Manager Using Command Prompt in Windows 10
5) How to Get IP Address using PowerShell on Windows PC
Как посмотреть список открытых портов в Windows
Статья обновлена: 10 сентября 2021
ID: 101
Чтобы посмотреть список открытых портов:
- Откройте командную строку. Инструкция в статье.
- Выполните команду:
netstat -a
- Нажмите Enter на клавиатуре.
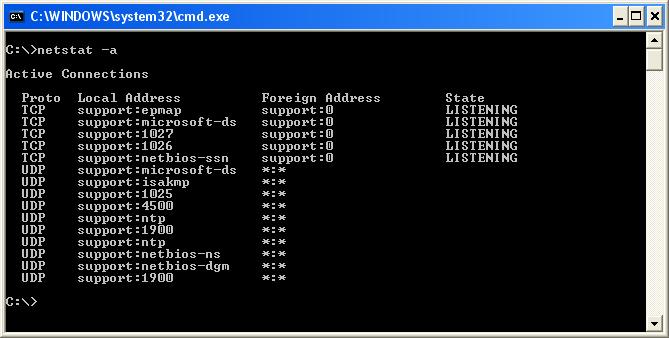
Вы получите список открытых портов в Windows.
Спасибо за ваш отзыв, вы помогаете нам становиться лучше!
Спасибо за ваш отзыв, вы помогаете нам становиться лучше!

In this tutorial, we will learn how to run the netstat command to check open ports in Windows Operating System. We will also look at command options and how to use the findstr command (similar to grep) to filter the netstat output.
To check open ports, open a command prompt (or PowerShell) as administrator and run the netstat command as follows:
netstat -aonThe command displays lots of information. What you should pay attention to are Local Addresses that are in the LISTENING state.

As you can see in the previous screenshot, In my Windows 10 computer, port 22 (SSH) is open.
Administrators can run the following command to show opened ports only without all other details:
netstat -aon | findstr /i listeningOne important point is that the Windows Firewall may block a port even if it is in the listening state. In the Windows Defender Firewall with Advanced Security, there has to be a corresponding inbound firewall rule to match the listening port (Anything with a green checkmark is an open rule).

The Foreign Address column of the output shows the IP address and port of the computer/server at the remote end of the connection.
To check that the port is open from a remote computer, an administrator can run the telnet command from a remote computer against the IP address of the Windows computer.
For example, to check if port 22 is open, I will run the telnet command from a remote computer as follows:
telnet IP_ADDRESS 22Replace IP_ADDRESS with the actual IP Address of the Windows computer.

Filtering netstat using findstr
Administrators can use the findstr CMD command (which is similar to grep) to filter netstat command data based on string patterns.
For example, run the following command to check TCP connections in TIME_WAIT State.
netstat -a | findstr /i TIME_WAITThe /I option is for the case insensitive matching.

Command Options
Windows netstat command, without any command-line arguments, displays active TCP connections.
It also includes some useful command options to show network connections and ports in various forms, such as show connections and opened ports based on the protocol, find the process id of a connection/port, view network statics, and find the application that utilizes connections and ports.
| -a | displays all network connections and ports on which Windows is listening (include both IPv4 or IPv6 addresses). |
| -b | The output shows you which applications are using each active connection and ports (need administrative privileges). |
| -e | Displays network statistics, such as the Errors, the number of bytes, and packets sent and received. |
| -n | Displays addresses and ports in numerical format. |
| -f | When used, the output will contain Fully Qualified Domain Names (FQDNs) of IP addresses, if available. |
| -o | Displays an additional column that contains the Process ID (PID). |
| -p | Display data for a specific protocol (e.g., -p TCP). The Protocol can be one of the following: TCP, UDP, TCPv6, or UDPv6. If combined with the -s option, Protocol can be TCP, UDP, ICMP, IP, TCPv6, UDPv6, ICMPv6, or IPv6. |
| -r | Check Windows routing table. |
| -s | Displays detailed network statistics for each protocol (IPv4, IPv6, ICMPv4, ICMPv6, TCP, and UDP). |
| interval | Sets Time interval (in seconds) to automatically update the output. See examples to learn more. |
Examples: Using the netstat command
List all Active TCP connections:
netstatCheck open ports:
netstat -aon | findstr /i listeningOnly want to see information about TCP protocol:
netstat -a -p tcpShow network statistics:
netstat -sReal-time network monitoring — In the following example, we set a 5 second time interval to check active network connections in real-time. The number 5 causes the command to repeat every five seconds (Press CTRL+C to quit).
netstat -n 5If you need more information about the Windows netstat command, type netstat \? in the command prompt.
