Environment variables are key-value pairs a system uses to set up a software environment. The environment variables also play a crucial role in certain installations, such as installing Java on your PC or Raspberry Pi.
In this tutorial, we will cover different ways you can set, list, and unset environment variables in Windows 10.
Prerequisites
- A system running Windows 10
- User account with admin privileges
- Access to the Command Prompt or Windows PowerShell
Check Current Environment Variables
The method for checking current environment variables depends on whether you are using the Command Prompt or Windows PowerShell:
List All Environment Variables
In the Command Prompt, use the following command to list all environment variables:
set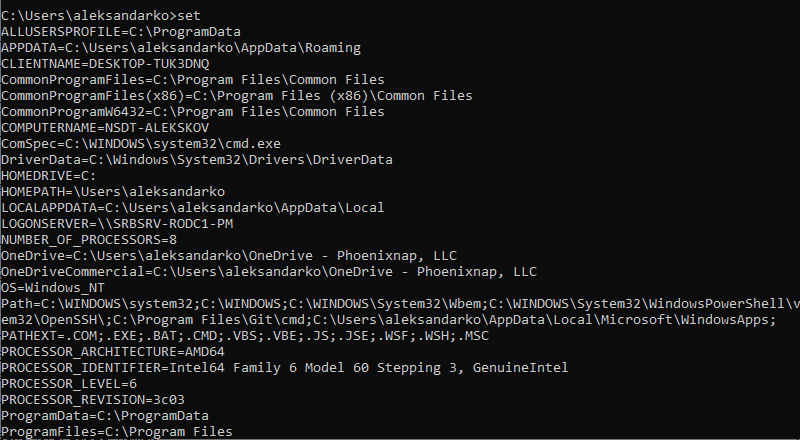
If you are using Windows PowerShell, list all the environment variables with:
Get-ChildItem Env: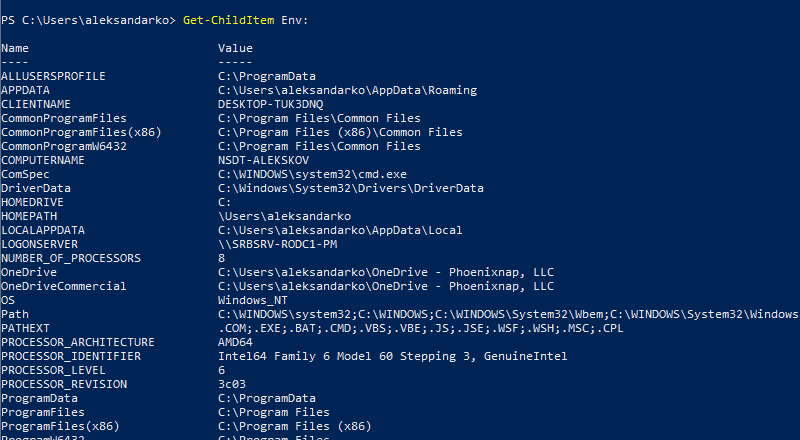
Check A Specific Environment Variable
Both the Command Prompt and PowerShell use the echo command to list specific environment variables.
The Command prompt uses the following syntax:
echo %[variable_name]%
In Windows PowerShell, use:
echo $Env:[variable_name]
Here, [variable_name] is the name of the environment variable you want to check.
Set Environment Variable in Windows via GUI
Follow the steps to set environment variables using the Windows GUI:
1. Press Windows + R to open the Windows Run prompt.
2. Type in sysdm.cpl and click OK.
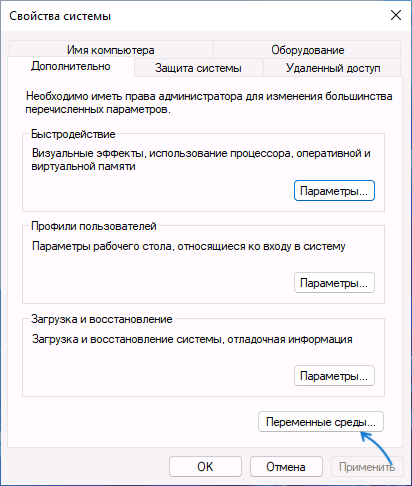
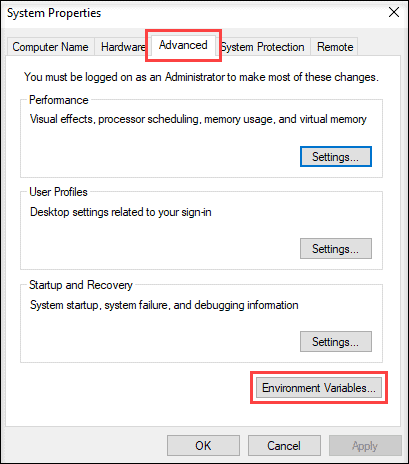
3. Open the Advanced tab and click on the Environment Variables button in the System Properties window.
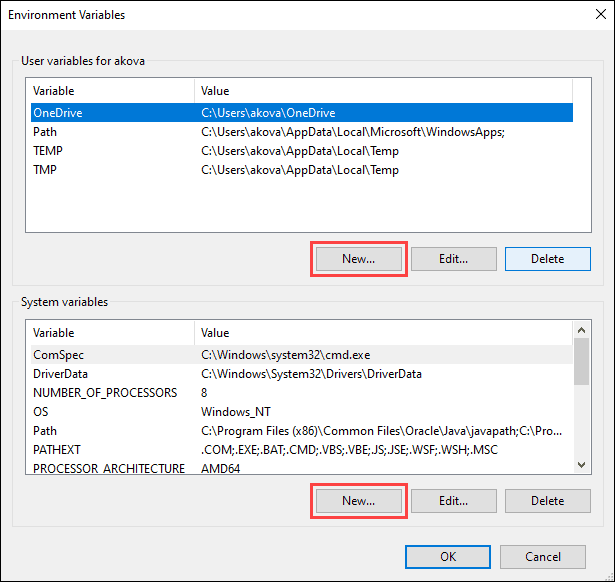
4. The Environment Variables window is divided into two sections. The sections display user-specific and system-wide environment variables. To add a variable, click the New… button under the appropriate section.
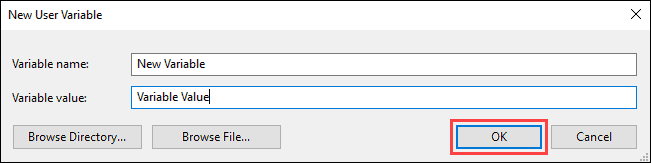
5. Enter the variable name and value in the New User Variable prompt and click OK.
Set Environment Variable in Windows via Command Prompt
Use the setx command to set a new user-specific environment variable via the Command Prompt:
setx [variable_name] "[variable_value]"Where:
[variable_name]: The name of the environment variable you want to set.[variable_value]: The value you want to assign to the new environment variable.
For instance:
setx Test_variable "Variable value"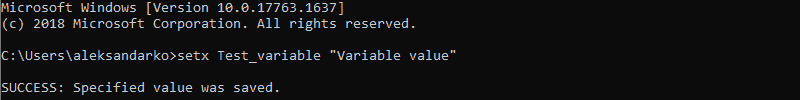
Note: You need to restart the Command Prompt for the changes to take effect.
To add a system-wide environment variable, open the Command Prompt as administrator and use:
setx [variable_name] "[variable_value]" /M
Unset Environment Variables
There are two ways to unset environment variables in Windows:
Unset Environment Variables in Windows via GUI
To unset an environment variable using the GUI, follow the steps in the section on setting environment variables via GUI to reach the Environment Variables window.
In this window:
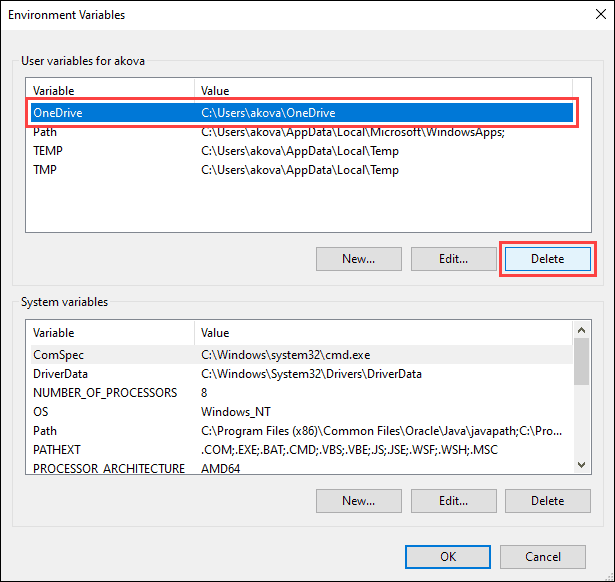
1. Locate the variable you want to unset in the appropriate section.
2. Click the variable to highlight it.
3. Click the Delete button to unset it.
Unset Environment Variables in Windows via Registry
When you add an environment variable in Windows, the key-value pair is saved in the registry. The default registry folders for environment variables are:
- user-specific variables: HKEY_CURRENT_USEREnvironment
- system-wide variables: HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESYSTEMCurrentControlSetControlSession ManagerEnvironment
Using the reg command allows you to review and unset environment variables directly in the registry.
Note: The reg command works the same in the Command Prompt and Windows PowerShell.
Use the following command to list all user-specific environment variables:
reg query HKEY_CURRENT_USEREnvironment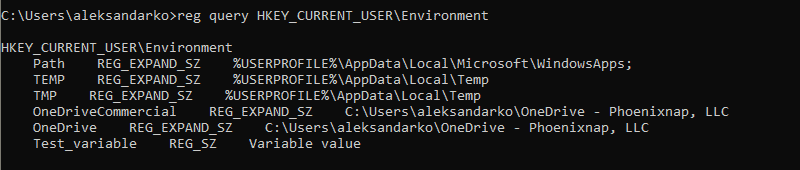
List all the system environment variables with:
reg query "HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESYSTEMCurrentControlSetControlSession ManagerEnvironment"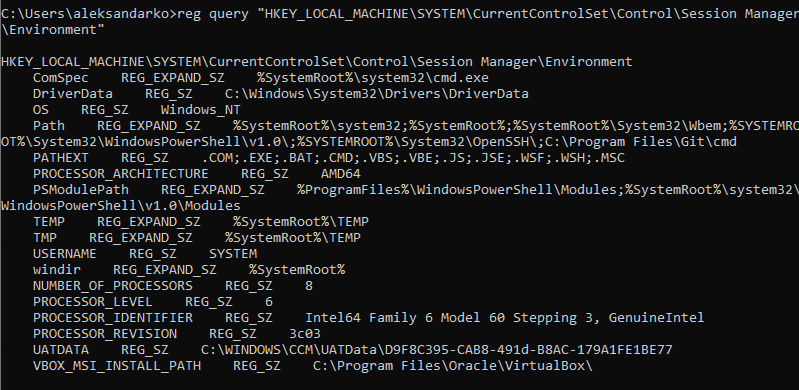
If you want to list a specific variable, use:
reg query HKEY_CURRENT_USEREnvironment /v [variable_name]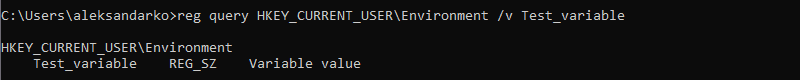
or
reg query "HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESYSTEMCurrentControlSetControlSession ManagerEnvironment" /v [variable_name]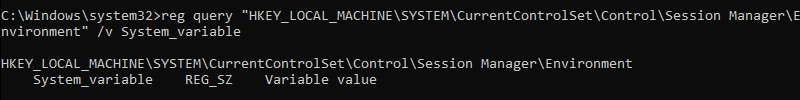
Where:
/v: Declares the intent to list a specific variable.[variable_name]: The name of the environment variable you want to list.
Use the following command to unset an environment variable in the registry:
reg delete HKEY_CURRENT_USEREnvironment /v [variable_name] /f
or
reg delete "HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESYSTEMCurrentControlSetControlSession ManagerEnvironment" /v [variable_name] /f
Note: The /f parameter is used to confirm the reg delete command. Without it, entering the command triggers the Delete the registry value EXAMPLE (Yes/No)? prompt.
Run the setx command again to propagate the environment variables and confirm the changes to the registry.
Note: If you don’t have any other variables to add with the setx command, set a throwaway variable. For example:
setx [variable_name] trash
Conclusion
After following this guide, you should know how to set user-specific and system-wide environment variables in Windows 10.
Looking for this tutorial for a different OS? Check out our guides on How to Set Environment Variables in Linux, How to Set Environment Variables in ZSH, and How to Set Environment Variables in MacOS.
Was this article helpful?
YesNo
Настройка переменных среды Windows может помочь сократить время, необходимое для набора команд в командной строке или, если вы часто пишете скрипты для собственных задач, сделать их более читаемыми. В большинстве случаев обычные пользователи добавляют записи в системную переменную среды PATH, хотя бывают и другие задачи.
В этой пошаговой инструкции базовая информация о том, как открыть переменные среды Windows 11 и Windows 10, создать или отредактировать их.
Что такое переменные среды
Переменные среды в Windows — записи о расположении системных папок, свойствах системы и другие, которые доступны для любой программы или скрипта.
Одна из наиболее часто используемых переменных среды — PATH, указывающая на папки, в которых выполняется поиск файлов, вызываемых в командной строке, терминале Windows, файле bat или из других источников. В качестве примера её назначения:
- Если вы откроете командную строку (или диалоговое окно «Выполнить»), введёте regedit и нажмете Enter — вы сможете запустить редактор реестра, не указывая полный путь к файлу regedit.exe, поскольку путь C:\Windows добавлен в переменную среды Path.
- Если же тем же образом в командной строке написать имя программы, путь к которой не добавлен в Path (chrome.exe, adb.exe, pip и другие), вы получите сообщение «Не является внутренней или внешней командой, исполняемой программой или пакетным файлом».
Если предположить, что вы часто используете команды adb.exe (например, для установки приложений Android в Windows 11), pip install (для установки пакетов Python) или любые другие то для того, чтобы не писать каждый раз полный путь к этим файлам, имеет смысл добавить эти пути в переменные среды.
Также вы можете добавлять и иные переменные среды (не обязательно содержащие пути), а в дальнейшем получать и использовать их значения в сценариях BAT (командной строки) или PowerShell. Пример получения и отображения значения системной переменной PATH для обоих случаев:
echo %PATH% echo $Env:PATH
Получить список всех переменных среды в командной строке и PowerShell соответственно можно следующими командами:
set ls env:
Редактирование переменных среды Windows 11/10
Прежде чем приступать, учтите: изменение системных переменных среды по умолчанию может привести к проблемам в работе системы, не удаляйте уже имеющиеся переменные среды. Возможно, имеет смысл создать точку восстановления системы, если вы не уверены в своих действиях.
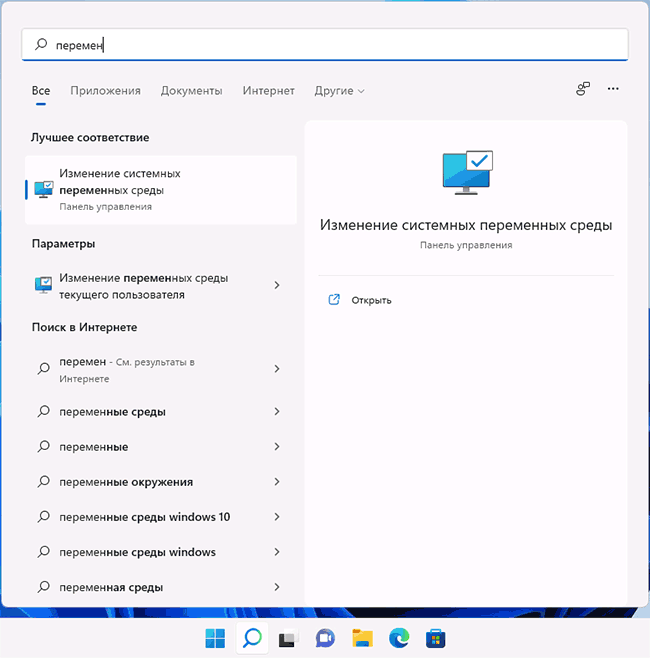
- Чтобы открыть переменные среды Windows вы можете использовать поиск в панели задач (начните вводить «Переменных» и откройте пункт «Изменение системных переменных среды») или нажать клавиши Win+R на клавиатуре, ввести sysdm.cpl и нажать Enter.
- На вкладке «Дополнительно» нажмите кнопку «Переменные среды…»
- В разделе «Переменные среды пользователя» (если требуется изменение только для текущего пользователя) или «Системные переменные» выберите переменную, которую нужно изменить и нажмите «Изменить» (обычно требуется именно это), либо, если необходимо создать новую переменную — нажмите кнопку «Создать». В моем примере — добавляем свои пути в системную переменную Path (выбираем эту переменную и нажимаем «Изменить»).
- Для добавления нового значения (пути) в системную переменную в следующем окне можно нажать кнопку «Создать», либо просто дважды кликнуть по первой пустой строке, затем — ввести нужный путь к папке, содержащей нужные нам исполняемые файлы.
- Также вы можете использовать кнопку «Изменить текст», в этом случае окно изменения системной переменной откроется в ином виде: имя переменной, а ниже — её значение. В случае указания путей значение будет представлять собой все пути, хранящиеся в переменной, разделенные знаком «точка с запятой».
- При создании новой переменной среды окно будет тем же, что и в 5-м шаге: необходимо будет указать имя системной переменной в верхнем поле, а её значение — в нижнем.
После создания или изменения переменной среды и сохранения сделанных настроек, переменная или обновленные значения сразу становятся доступны для текущего пользователя или в системе в целом в зависимости от того, какие именно переменные редактировались или создавались. Также есть методы добавления переменных среды в командной строке или PowerShell, подробнее в статье: Как добавить путь в переменную среды PATH
Переменные окружения (среды) в Windows содержат различную информацию о настройках системы и среды пользователя. Различают переменные окружения пользователя, системы и процессов.
Самый простой способ просмотреть содержимое переменных окружения в Windows – открыть свойства системы (sysdm.cpl) -> Дополнительно -> Переменные среды. Как вы видите, в открывшемся есть две секции: в верхней содержатся переменные окружения пользователя, в нижнем – системные.
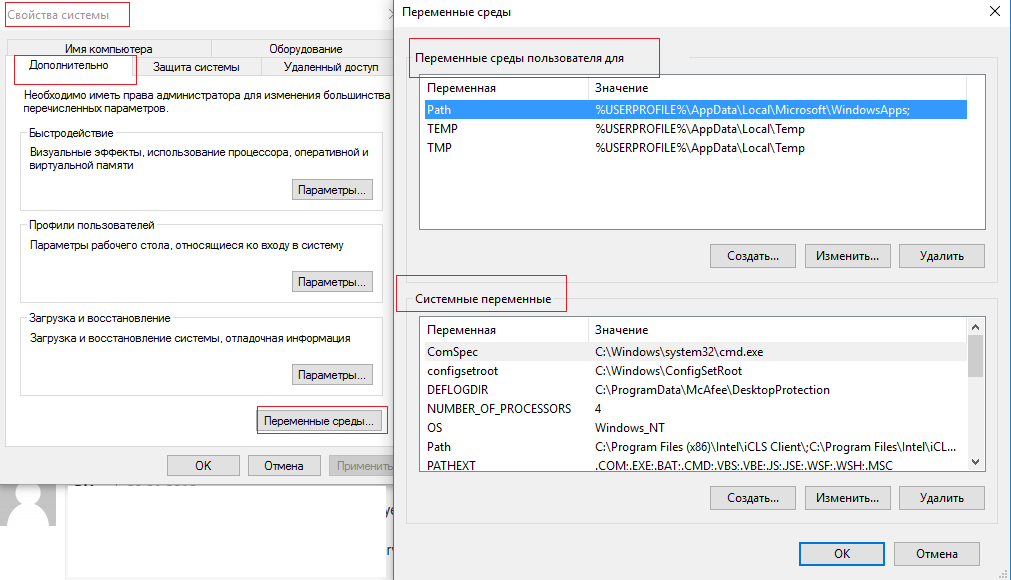
Кроме того, переменные среды хранятся в реестре системы. Пользовательские переменные хранятся в разделе HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Environment. Системные – в HKLM\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\Session Manager\Environment.
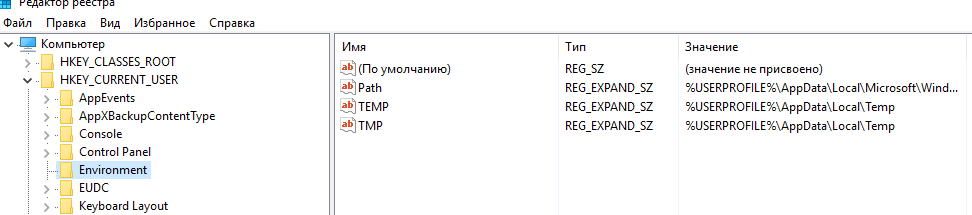
Вывести значения всех переменных окружения можно в командной строке Windows. Команда простая:
Set
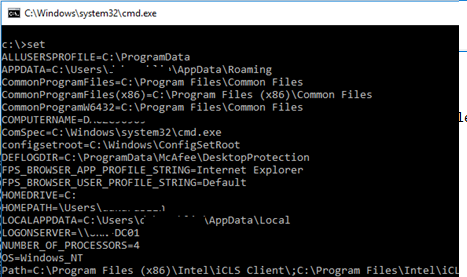
Команда выведет список переменных среды и их значения.
В PowerShell для вывод всех переменных окружения можно использовать команду:
ls env:
Если нужно вывести значение только одной переменной, нужно воспользоваться командой echo, причем имя переменной нужно заключить в знаки процентов. Например,
Echo %systemroot%
Чтобы сохранить все переменные среды и их значения в текстовый файл, воспользуйтесь командой:
set > c:\tmp\env_var.txt
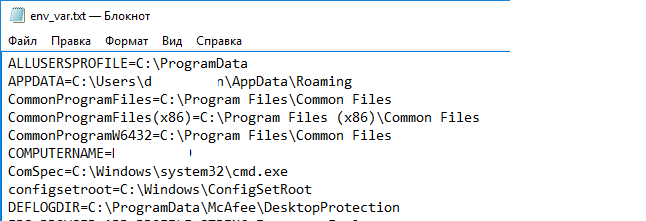
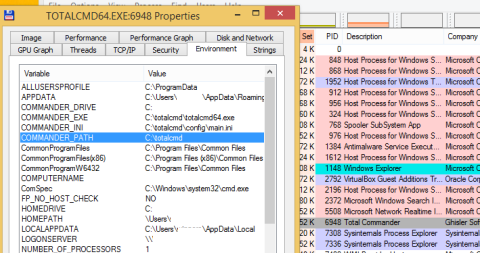
Переменные окружения конкретного процесса можно получить с помощью бесплатной утилиты Process Explorer (от Sysinternals). Достаточно открыть свойства процесса и перейти на вкладку Environment.
What is an environment variable in Windows? An environment variable is a dynamic “object” containing an editable value which may be used by one or more software programs in Windows.
In this note i am showing how to list environment variables and display their values from the Windows command-line prompt and from the PowerShell.
Cool Tip: Add a directory to Windows %PATH% environment variable! Read More →
The environment variables in Windows can be printed using the Windows command-line prompt (CMD) or using the PowerShell.
Windows Command-Line Prompt (CMD)
List all Windows environment variables and their values:
C:\> set
“Echo” the contents of a particular environment variable:
C:\> echo %ENVIRONMENT_VARIABLE%
Windows PowerShell
Print all Windows environment variables (names and values):
PS C:\> gci env:* | sort-object name
Show the contents of a particular environment variable:
PS C:\> echo $env:ENVIRONMENT_VARIABLE
Cool Tip: Set environment variables in Windows! Read More →
Was it useful? Share this post with the world!

Overview – Check
Environment Variables in Windows
Environment variables in Windows are used to store information that are used by applications and services. The Windows operating system defines a number of environment variables, and user applications and services can also further add additional environment variables.
When you start a Windows program, the operating system creates several environment variables that the program can use. These variables include the path to the application’s directory and any additional folders that the program requires access to.
It seems that you want to check compatibility issues among the numerous environment variables stored on your computer. By the end of this article, you’ll be able to list all environment variables in Windows:
Using System Properties
Using Command Prompt
Using PowerShell
Using Batch Script
Using System Information
Using Registry Editor
1. Check Environment
Variables using System Properties
Step 1: In the Start menu, search for “Edit the system environment variables” (without quotation marks) and hit the enter key.

Edit System Environment Variables
Step 2: In the “Advanced” tab, click the “Environment Variables” button and all the environment variables on your system will be visible..

“Environment Variables” Button

List of All Environment variables – Both User and System Environment Variables
2. Check Environment
Variables using Command Prompt
Step 1: Run the Command Prompt as an administrator from the Start menu.
Command Prompt (CMD) Icon
Step 2: To list all the environment variables using Command Prompt, type the command “set” (without quotation marks).

Command To List Environment Variables using CMD
3. Check Environment
Variables using PowerShell
Step 1: Run the PowerShell as an administrator from the Start menu.
PowerShell App Icon
Step 2: To list all the environment variables using PowerShell, type the command: “gci env:” (without quotation marks).

Command To List Environment Variables using PowerShell
4. Check Environment
Variables using Batch Script
Step 1: Right-click the desktop and add a new “Text Document”.

Create New Document
Step 2: Copy and Paste the following script in the text document:
@ECHO OFF
set
pause

Batch Script To Show Environment Variables In Windows
Step 3: Click the “File” button on the top left corner of the window and click the “Save As” option.

“File” Button > “Save as” Button
Step 4: Change the file extension to “File-Name.bat’ (.bat is the new extension), choose the desired location where you want to save the file and click the “Save” button.

File Extension from “.txt” to “.bat”
Step 5: Once the file is saved, double-click it to execute and you’ll see the environment variables listed in command prompt.

Running Batch Script To Show Environment Variables
NOTE: If copying and pasting the script above doesn’t work, type the script in the text document instead.
5. Check Environment
Variables using System Information
Step 1: In the Start menu, search for System Information and open it or press the “Windows Logo Key + R” key combination to open Windows Run, type “msinfo32” (without quotation marks) and hit the enter key.
System Configuration Icon
Step 2: In the left sidebar, expand the “Software Environment” section by clicking the “+” icon, click the environment variables button and you’ll see the environment variables listed on the right pane.

“+” Button > “Environment Variables” Button
6. Check Environment
Variables using Registry Editor
1. Check
System Environment Variables using Registry Editor
Step 1: In the Start menu, search for Registry Editor and hit the enter key or press the “Windows Logo Key + R” key combination on the keyboard, type: regedit and hit the enter key.
Step 2: To Check System Variables, navigate to the following path: Computer\HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\Session Manager\Environment and you’ll find the system variables listed on the right pane.

System Environment Variables in Registry Editor
2.
Check Environment Variables for Current User using Registry Editor
Step 1: In the Start menu, search for Registry Editor and hit the enter key or press the “Windows Logo Key + R” key combination on the keyboard, type: regedit and hit the enter key.
Step 2: To check user variables, navigate to the following path: Computer\HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Environment and you’ll find the user variables listed on the right pane.

User Environment Variables in Registry Editor
FAQs Related to
Environment Variables
How does environment
variables work in Windows?
Environment variables are the dynamic objects in form of key/value pairs that are responsible for instructing the programs to search for user profile settings, install files, and store temporary files in appropriate location in Windows.
What are types of
environmental variables?
There are two types of environment variables: User environment variables and system environment variables. The system variables are shared and applied to all users on the computer, but the user variables are exclusive to each profile.
Where are
environment variables stored in Windows?
In Windows, the user environment variables are stored in HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Environment in the registry editor and the system variables are stored in HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\Session Manager\Environment in the registry editor.
Next
Steps
We’ve covered how to check environment variables in Windows 11. To list environment variables in Windows, you can use any one of the methods listed above.
Further, configure the environment variables and other settings by referring the related articles below.