Download Article
Easily run .BAT files in Windows and troubleshoot common problems
Download Article
- Running from the Batch File’s Folder
- Running from Anywhere
- Troubleshooting
- Other Ways to Run Batch Files
- Video
- Expert Q&A
- Warnings
|
|
|
|
|
|
If you need to run a batch file at the Windows Command Prompt, you’ll just need to know the location of the batch file. To run the file at the command line, simply type the full path to the batch file and press Enter. Or, if you don’t want to type the full path to the file, you can use the cd command to enter the folder containing the .BAT file, type the batch file’s name, and then press Enter. This wikiHow guide will teach you 2 simple ways to run a batch file from the Command Prompt in Windows, help you fix common errors, and show you a few other cool ways to run batch files on your PC.
Things You Should Know
- Use the «cd» command to enter the folder that contains your batch file.
- To run the batch file, type its name and press «Enter.»
- You can also type the full path to the batch file from any folder to run batch files from anywhere.
-
If your batch file performs administrative tasks, open Command Prompt as an administrator. If the batch file only requires access to files in your user account, you don’t need to start it as an administrator.[1]
- Press the Windows key on your keyboard.
- Type cmd.
- If your batch file doesn’t need administrator rights, click Command Prompt.
- If your batch file does require administrator rights:
- Right-click Command Prompt.
- Select Run as administrator.
- Click Yes.
-
The cd command stands for «change directories.» For example:
- If the file is at D:\Music\MP3s\Unsorted, you’d type cd D:\Music\MP3s\Unsorted.
- If the batch file is on your desktop, you’d type cd \Users\YourLoginName\Desktop.
- If you use OneDrive to automatically back up your personal files, you’d use cd \Users\YourLoginName\OneDrive\Desktop instead.
- If you don’t know your login name, type cd \Users and press Enter. Then, type dir and press Enter to see a list of users.
Advertisement
-
This will move you into the folder containing your batch file.
- Type dir and press Enter to see a list of all files in the current folder. You should see your batch file (ending with .bat) here.
-
For example, if your batch file is called program.bat, type program.bat and press Enter. This runs the batch file.
Advertisement
-
If you want to run a batch file without using cd to enter its folder first, you’ll just need to know the full path to the file. For example, C:\Users\wikiHow\Scripts\mybatchfile.bat. Here’s an easy way to find the full path to your batch file:
- Navigate to your batch file. If you’re not sure where you saved it, you can search for it.
- If you’re using Windows 11, right-click the file and select Copy as path (Windows 11).
- On Windows 10 and earlier, right-click the file and select Properties. Highlight the path next to «Location» and press Ctrl + C to copy it to your clipboard.
-
If your batch file performs administrative tasks, open Command Prompt as an administrator. If it only requires access to files in your user account, you don’t need to start it as an administrator.[2]
- Press the Windows key on your keyboard.
- Type cmd.
- If your batch file doesn’t need administrator rights, click Command Prompt.
- If your batch file does require administrator rights:
- Right-click Command Prompt.
- Select Run as administrator.
- Click Yes.
-
To paste the path you copied earlier, press Ctrl + V.
- Alternatively, you can type the full path to your file manually (e.g., C:\Users\wikiHow\Scripts\mybatchfile.bat).
- Because the .BAT extension is executable, you don’t need to type any commands before pasting or entering the path to the file.
-
The batch file will now run. Any commands in the batch file will execute as specified in the script.
Advertisement
-
Depending on the commands in your batch file, you may not see confirmation or output when you run a .BAT file from Command Prompt. You’ll only see output if there’s a command in the batch file that’s supposed to display output.
- For example, if the batch file is just working with files on your PC, such as moving, renaming, and/or deleting, you won’t see the commands as they run unless @echo on is at the top of the .BAT file.[3]
- You can also add echo "your text here" to your batch file to display a custom message when run.
- For example, if the batch file is just working with files on your PC, such as moving, renaming, and/or deleting, you won’t see the commands as they run unless @echo on is at the top of the .BAT file.[3]
-
This means that there’s an error with one of the commands in the batch file. The error could be due to missing or incorrect symbols, leaving out a flag required by a command, or even missing quotation marks around paths. Open the batch file in an editor like Notepad and inspect the code for errors.
-
This error also indicates an error in the batch file. But in this case, the error occurs because a command in the batch file is not recognized by Command Prompt. Fortunately, the error tells you exactly which command is failing, so it should be simple to fix.
- For example, if a command in the .BAT file is misspelled or incorrect (e.g., «ifconfig» instead of «ipconfig»), or trying to start a program using its name instead of its full path.
-
If double-clicking your .BAT file quickly opens and closes a Command Prompt window, it just means the batch file doesn’t have a «pause» at the end. If you want to keep the window open after the commands have run, just add «pause» to the end of the batch file.
- Right-click the batch file.
- Select Open with > Notepad (Windows 10) or Show more options > Edit (Windows 11).
- Add «pause» to the last line of the batch file.
- Save the file and run it again. Now, when you run the batch file, the window will stay open while displaying «Press any key to continue…» Once you press a key, the window will close.[4]
Advertisement
-
If you don’t want to use the Command Prompt, you can easily run a batch file from any location on your Windows PC just by double-clicking it.
- If double-clicking the batch file opens and closes a window without showing you any details, see this troubleshooting tip.
-
To call up a batch script from the Run dialog:
- Press Windows key + R to open Run.
- Click Browse.
- Navigate to and select your batch file.
- Click Open.
- Click OK to run the batch file.
-
Use Windows Task Scheduler to automatically run a batch file at the time and date of your choice. You can have the batch file run once or on a regular schedule.
- Press the Windows key and type task scheduler.
- Click Task Scheduler.
- Expand the «Task Scheduler Library» folder.
- Create a new folder: Right-click Task Scheduler Library, click New Folder…, type a name, and click OK.
- Right-click your new folder and select Create basic task. Type a name for your task and click Next.
- Choose when (and how often) you want the batch file to run. For example, if you want it to run at a certain date, select the date. Then, click Next.
- Select Start a program, click Next, and then click Browse to select your .BAT file.
- Click Finish. The batch file will now run automatically at the selected time and date.
-
If you want the batch file to start automatically when your PC boots into Windows, you can copy or move the file to your Windows startup scripts folder. Here’s how:[5]
- Press Windows key + R to open the Run dialog.
- Type shell:startup and click OK. This opens a File Explorer window to your Startup folder.
- Drag or copy the .BAT file into the folder.
Advertisement
Add New Question
-
Question
After I run the batch script, it just opens another line and nothing happens.
Nicole Levine is a Technology Writer and Editor for wikiHow. She has more than 20 years of experience creating technical documentation and leading support teams at major web hosting and software companies. Nicole also holds an MFA in Creative Writing from Portland State University and teaches composition, fiction-writing, and zine-making at various institutions.
wikiHow Technology Writer
Expert Answer
Many batch scripts won’t display any confirmation that the commands have run. If you wrote the batch script yourself, you can switch the value of «echo» to «on» to display the commands at the prompt as they run. You can also add «pause» to the end of the script to make it prompt the user to press a key to continue. But in general, as long as you don’t see an error, that means the batch script executed properly.
-
Question
What does this error mean? ‘.’ is not recognized as an internal or external command, operable program or batch file.
This answer was written by one of our trained team of researchers who validated it for accuracy and comprehensiveness.
wikiHow Staff Editor
Staff Answer
The batch script is trying to run «.» as a command, which is not a recognized command. Look for the extra period somewhere in the script and remove it.
-
Question
How do I get out after I run my batch file ?
This answer was written by one of our trained team of researchers who validated it for accuracy and comprehensiveness.
wikiHow Staff Editor
Staff Answer
Just click the »’X»’ at the top corner of the command prompt window to close it. Or, if the batch script is hung on a process and not letting you go to the next line, you can press Ctrl + C to stop the batch file from running.
See more answers
Ask a Question
200 characters left
Include your email address to get a message when this question is answered.
Submit
Advertisement
Video
Thanks for submitting a tip for review!
-
Never run a .BAT file as an administrator unless you know exactly what the file does. If the batch file is malicious, running it as an administrator could steal your data, install malware and viruses, and other dirty deeds.
-
Be careful when downloading .BAT files from the web or as email attachments. Make sure your PC is always protected by Microsoft Defender (or your preferred antivirus software) before running files from unknown sources.
Advertisement
About This Article
Article SummaryX
1. Press the Windows + R keys.
2. Click Browse.
3. Select the .bat file.
4. Click Open.
5. Click OK.
Did this summary help you?
Thanks to all authors for creating a page that has been read 594,142 times.
Is this article up to date?
On Windows 10, a batch file typically has a «.bat» extension, and it is a special text file that contains one or multiple commands that run in sequence to perform various actions with Command Prompt.
Although you can type commands manually to execute a particular task or change system settings on Windows 10, a batch file simplifies the work of having to re-type the commands, saving you time and avoiding mistakes.
You can also use other tools like PowerShell to write even more advanced scripts. However, running batch files in Command Prompt is still relevant for executing commands to change settings, automate routines, and launch apps or web pages on your computer.
This guide will walk you through the steps to create and run a batch file on Windows 10. Also, we will outline the steps to create advanced scripts and rum them automatically on schedule using the Task Scheduler.
How to create a batch file on Windows 10
The process of writing a batch file is not complicated. You only need Notepad or another text editor and some basic knowledge of typing commands in Command Prompt. These instructions will help you create a basic and advanced batch file to query system settings.
Create basic Windows 10 batch file
To create a basic batch file on Windows 10, use these steps:
All the latest news, reviews, and guides for Windows and Xbox diehards.
- Open Start.
- Search for Notepad and click the top result to open the text editor.
- Type the following lines in the text file to create a batch file:
@ECHO OFF
ECHO Hello World! Your first batch file was printed on the screen successfully.
PAUSE
The above script outputs the phrase, «Hello World! Your first batch file was printed on the screen successfully,» on the screen.
- @ECHO OFF — Shows the message on a clean line disabling the display prompt. Usually, this line goes at the beginning of the file. (You can use the command without the «@» symbol, but it’s recommended to include it to show a cleaner return.)
- ECHO — The command prints the text after the space on the screen.
- PAUSE — Allows the window to stay open after the command has been executed. Otherwise, the window will close automatically as soon as the script finishes executing. You can use this command at the end of the script or after a specific command when running multiple tasks and wanting to pause between each line.
- Click the File menu.
- Select the Save as option.
- Confirm a name for the script — for example, first_basic_batch.bat.
- Quick note: While batch files typically use the .bat file extensions, you can also find them using the .cmd or .btm file extensions.
Once you complete the steps, double-click the file to run it. Alternatively, you can use the steps below to learn how to run a batch file with Command Prompt, File Explorer, or Task Scheduler.
Create advanced Windows 10 batch file
To create an advanced Windows batch file with multiple commands, use these steps:
- Open Start.
- Search for Notepad and click the top result to open the text editor.
- Type the following lines in the text file to create a more advanced Windows 10 batch file:
@ECHO OFF
:: This batch file details Windows 10, hardware, and networking configuration.
TITLE My System Info
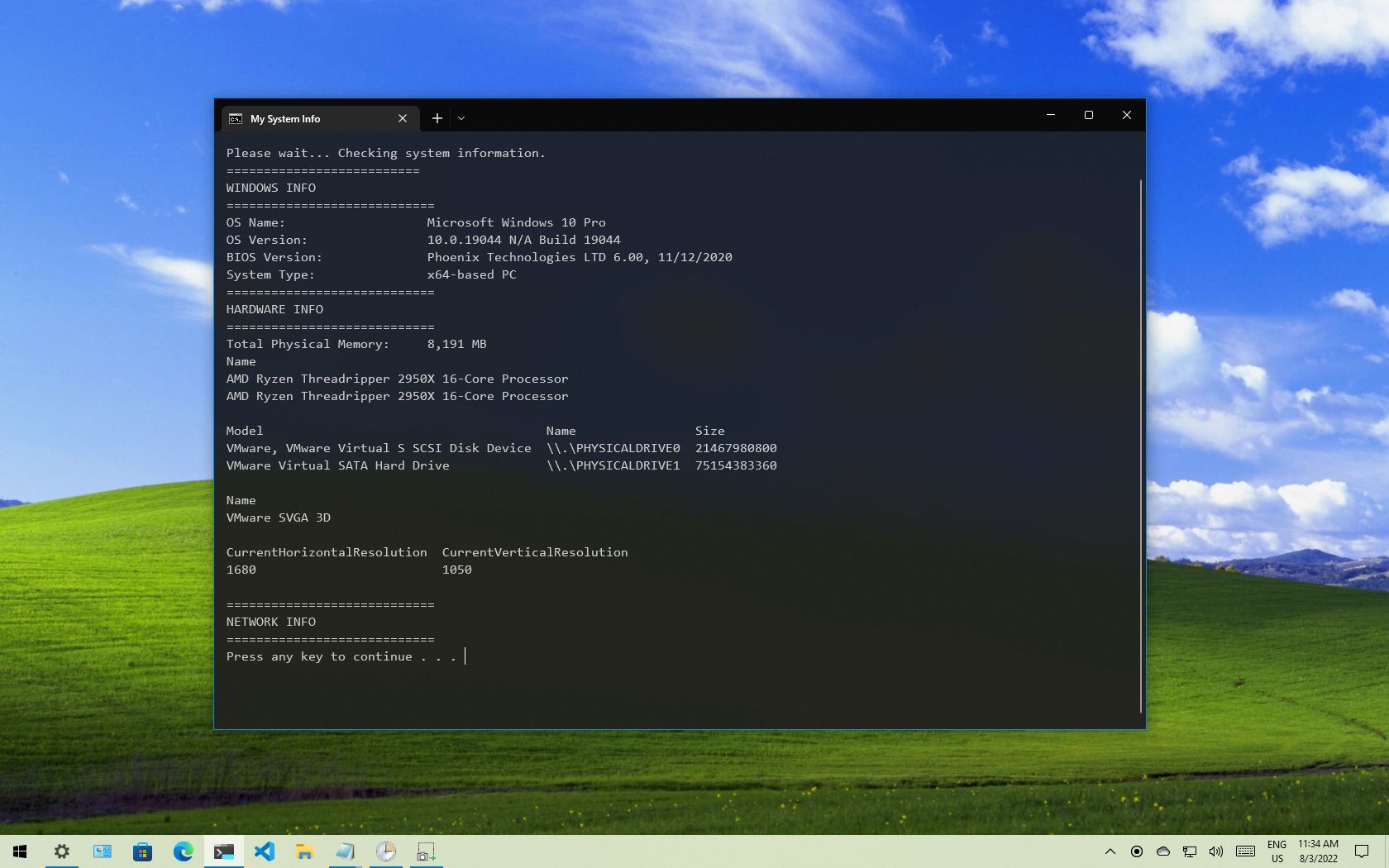
ECHO Please wait… Checking system information.
:: Section 1: Windows 10 information
ECHO ==========================
ECHO WINDOWS INFO
ECHO ============================
systeminfo | findstr /c:»OS Name»
systeminfo | findstr /c:»OS Version»
systeminfo | findstr /c:»System Type»
:: Section 2: Hardware information.
ECHO ============================
ECHO HARDWARE INFO
ECHO ============================
systeminfo | findstr /c:»Total Physical Memory»
wmic cpu get name
wmic diskdrive get name,model,size
wmic path win32_videocontroller get name
wmic path win32_VideoController get CurrentHorizontalResolution,CurrentVerticalResolution
:: Section 3: Networking information.
ECHO ============================
ECHO NETWORK INFO
ECHO ============================
ipconfig | findstr IPv4ipconfig | findstr IPv6
START https://support.microsoft.com/en-us/windows/windows-10-system-requirements-6d4e9a79-66bf-7950-467c-795cf0386715
PAUSE
The above script runs each line to query a series of system details, and the result will be divided into three categories, including «WINDOWS INFO,» «HARDWARE INFO,» and «NETWORK INFO.» Also, the «START» command will open the web browser in the official support page outlining the Windows 10 system requirements, which you can check against your information.
- @ECHO OFF — Shows the message on a clean line disabling the display prompt. Usually, this line goes at the beginning of the file.
- TITLE — Prints a custom name in the title bar of the console window.
- :: — Allows writing comments and documentation information. These details are ignored when the system runs the batch file.
- ECHO — Prints the text after the space on the screen.
- START — Opens an app or website with the default web browser.
- PAUSE — Tells the console window to stay open after running the command. If you do not use this option, the window will close automatically as soon as the script finishes executing.
- Click the File menu.
- Select the Save as option.
- Type a name for the script — for example, first_advanced_batch.bat.
After you complete the steps, double-click the .bat file to run it or use the steps below to execute the script with Command Prompt, File Explorer, or Task Scheduler.
Create actionable Windows 10 batch file
You can also write batch scripts for any task that does not require user interaction. For instance, to map a network drive, install an application, change system settings, and more.
To create a non-interactive batch file on Windows 10, use these steps:
- Open Start.
- Search for Notepad and click the top result to open the text editor.
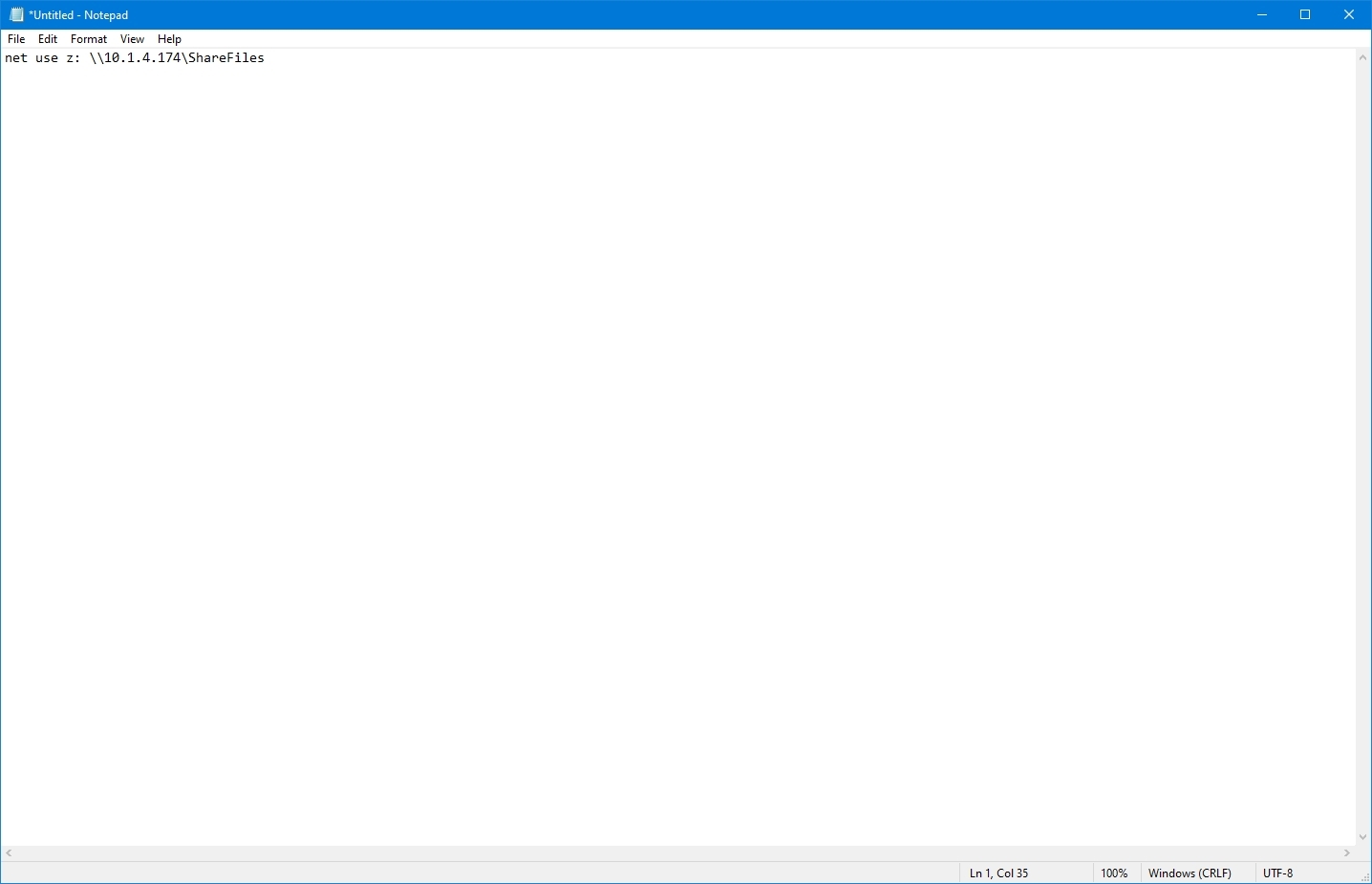
- Type the following command to map a network drive in the text file: net use z: \\PATH-NETWORK-SHARE\FOLDER-NAME /user:YOUR-USERNAME YOUR-PASSWORD
In the command, replace the «\\PATH-NETWORK-SHARE\FOLDER-NAME» for the folder network path to mount on the device and «YOUR-USERNAME YOUR-PASSWORD» with the username and password that authenticates access to the network share.
This example maps a network folder as a drive inside File Explorer using the «Z» drive letter: net use z: \\10.1.4.174\ShareFiles
- Quick note: If you are accessing the files from another computer that uses a specific username and password, do not forget to use the /user: option with the correct credentials.
- Click the File menu.
- Select the Save as option.
- Confirm a name for the script — for example, mount-z-network-drive.bat.
Once you complete the steps, the batch file will map the network folder without opening a Command Prompt window.
We only demonstrate a script with a single command, but you can include as many as you like, as long as you write them one per line.
How to run a batch file on Windows 10
Windows 10 has at least three ways to write batch files. You can run them on-demand using Command Prompt or File Explorer. You can configure the script using the Task Scheduler app to run it on schedule. Or you can save the batch files in the «Startup» folder to let the system run them as soon as you sign into the account.
Run batch file on-demand
If you want to run a script on-demand, you can use File Explorer or Command Prompt.
Command Prompt
To run a script file with Command Prompt on Windows 10, use these steps:
- Open Start.
- Search for Command Prompt, right-click the top result, and select the Run as administrator option.
- Type the following command to run a Windows 10 batch file and press Enter: C:\PATH\TO\FOLDER\BATCH-NAME.bat
In the command, make sure to specify the path and name of the script.
This example runs the batch file located in the «scripts» folder inside the «Downloads» folder: C:\Users\UserAccount\Downloads\first_basic_batch.bat
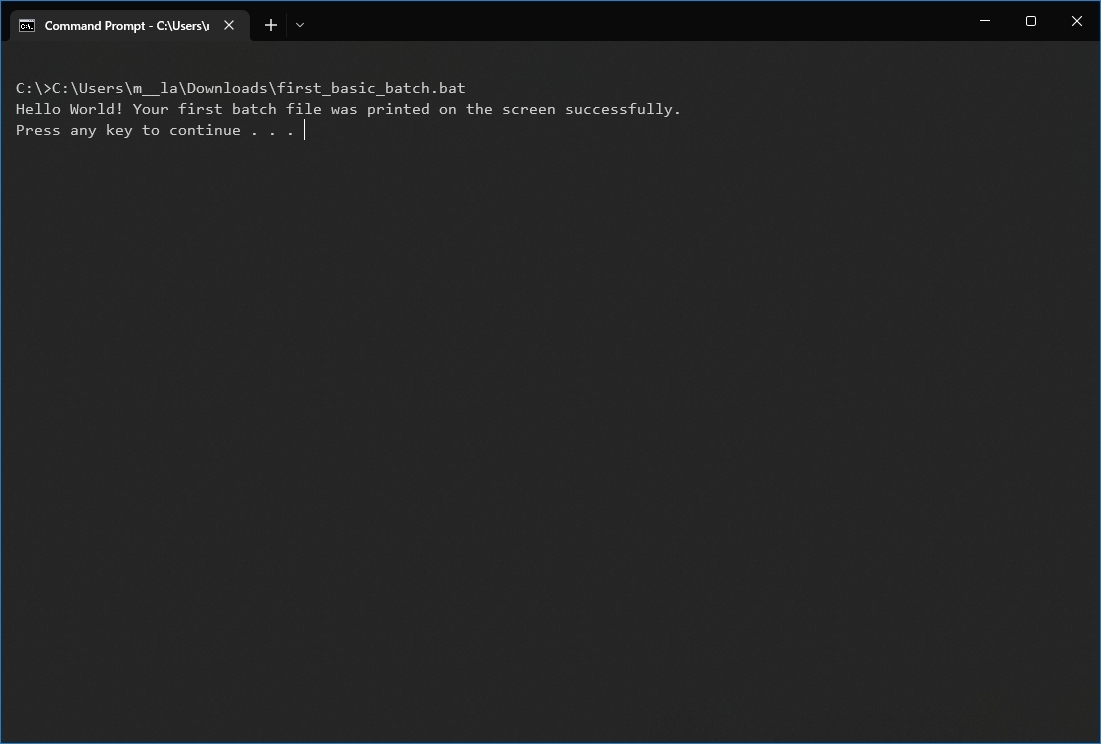
After you complete the steps, the console will return the results, and the window won’t close even if the script does not include the «PAUSE» command since you are invoking the script from within a console session that was already open.
File Explorer
To run a batch file with File Explorer, use these steps:
- Open File Explorer.
- Browse to the folder with the batch file.
- Double-click the script file to run it.
- (Optional) If a command in the batch file requires administrator privileges, you will have to run the script as an admin by right-clicking the file and selecting the Run as administrator option.
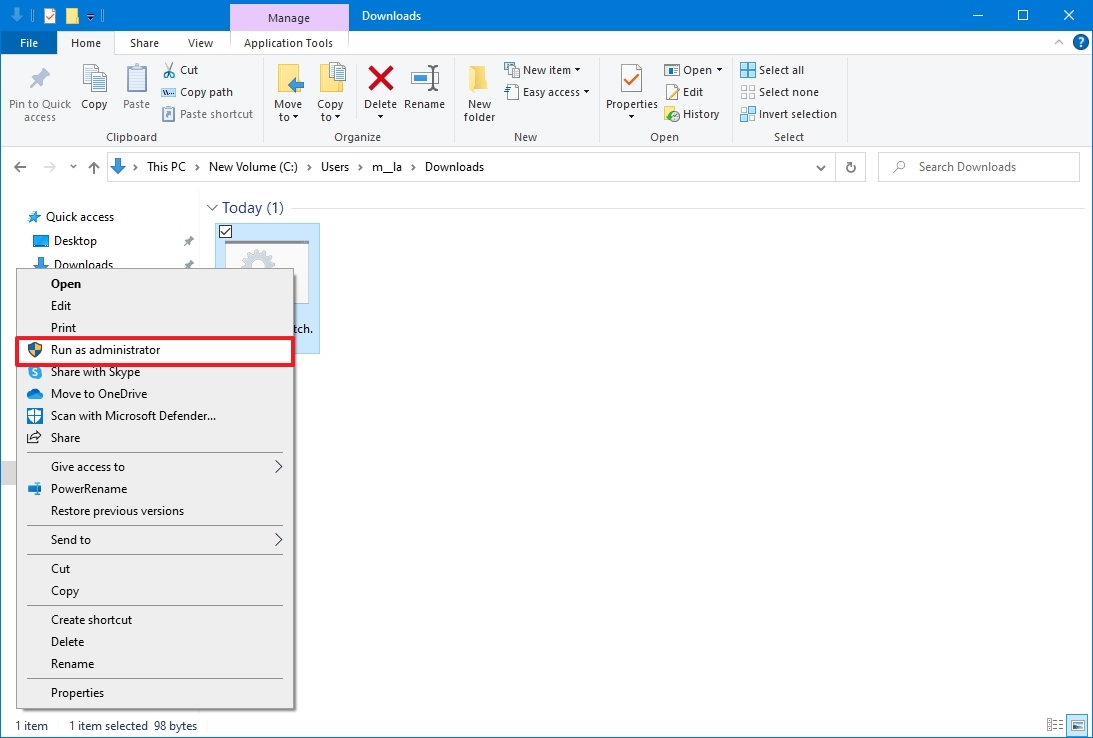
- Click the Yes button
Once you complete the steps, the script will run each command in sequence, displaying the results in the console window.
Run batch files on startup
Windows 10 also features a known folder called «Startup,» which the system checks every time it starts to run applications, shortcuts, and scripts automatically without the need for extra configuration.
To run a script on the Windows 10 startup, use these steps:
- Open File Explorer.
- Open the folder containing the batch file.
- Right-click the batch file and select the Copy option.
- Use the Windows key + R keyboard shortcut to open the Run command.
- Type the following command: shell:startup
- Click the OK button.
- Click the Paste option from the «Home» tab in the Startup folder. (Or click the Paste shortcut button to create a shortcut to the batch file.)
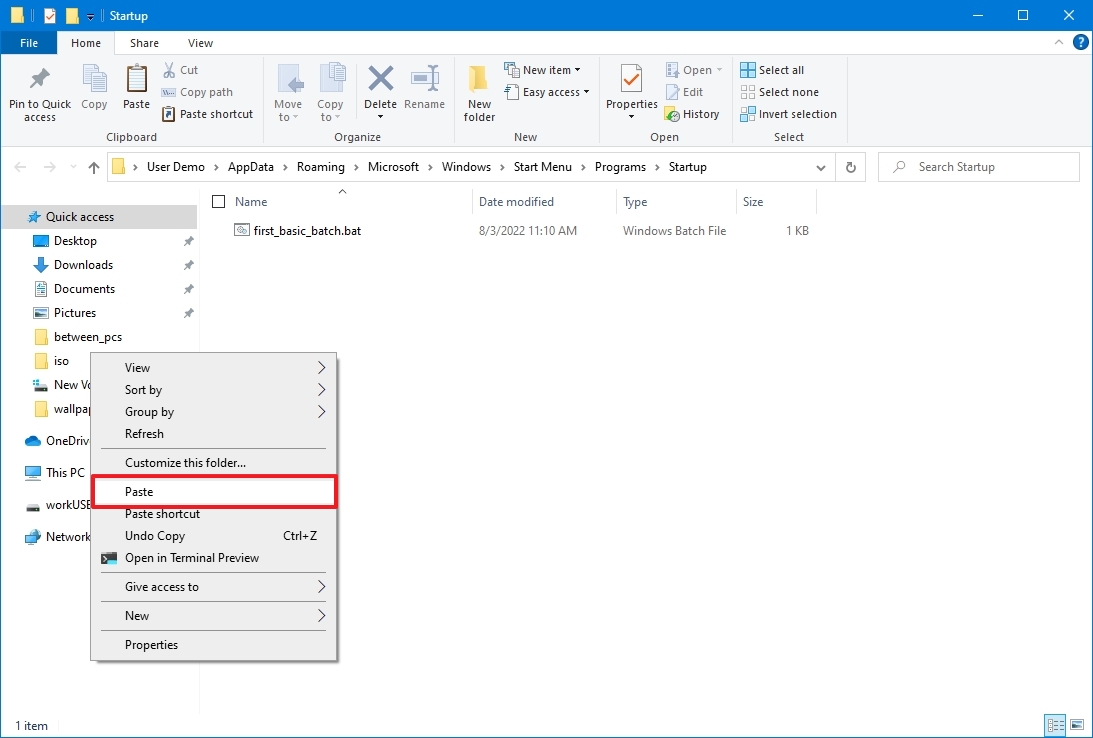
After you complete the steps, the batch file will execute automatically every time you log into your account.
Run batch file with Task Scheduler
To use Task Scheduler to run the batch file automatically at a specific time, use these steps:
- Open Start.
- Search for Task Scheduler and click the top result to open the app.
- Right-click the «Task Scheduler Library» branch and select the New Folder option.
- Confirm a name for the folder — for example, MyScripts.
- Quick note: You don’t need to create a folder, but keeping the system and your tasks separate is recommended.
- Click the OK button.
- Expand the «Task Scheduler Library» branch.
- Right-click the MyScripts folder.
- Select the Create Basic Task option.
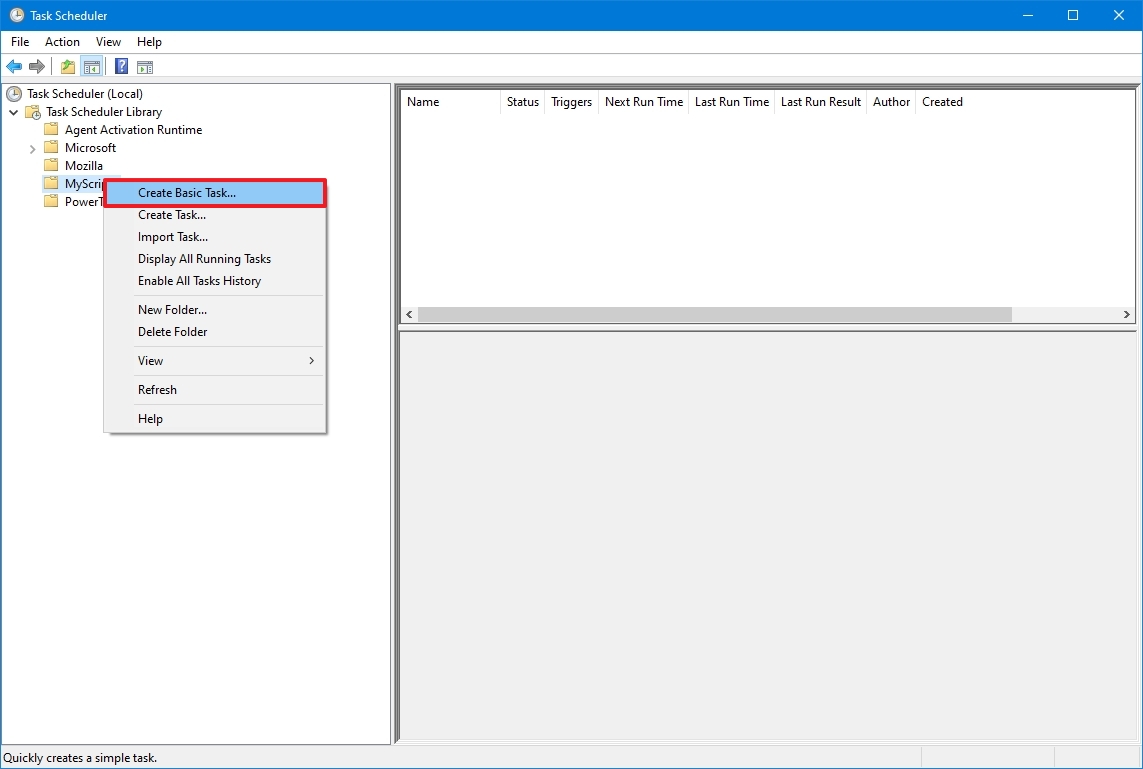
- In the «Name» field, confirm a name for the task — for example, SystemInfoBatch.
- (Optional) In the «Description» field, write a description for the task.
- Click the Next button.
- Select the Monthly option.
- Quick note: Task Scheduler lets you choose from different triggers, including a specific date, during startup, or when a user logs in to the computer. In this example, we will select the option to run a task every month, but you may need to configure additional parameters depending on your selection.
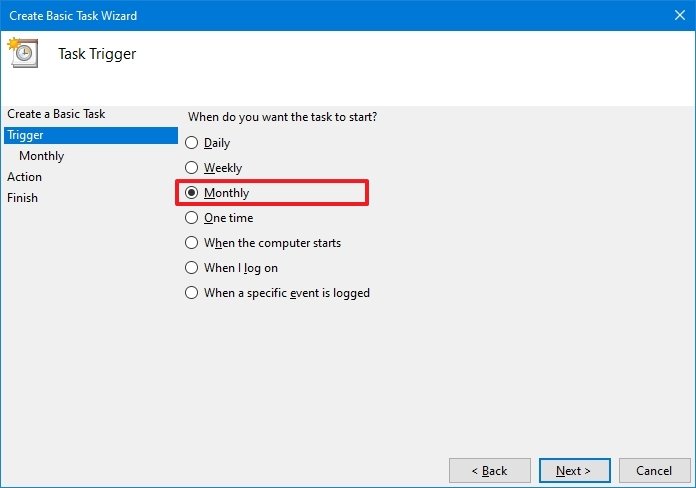
- Click the Next button.
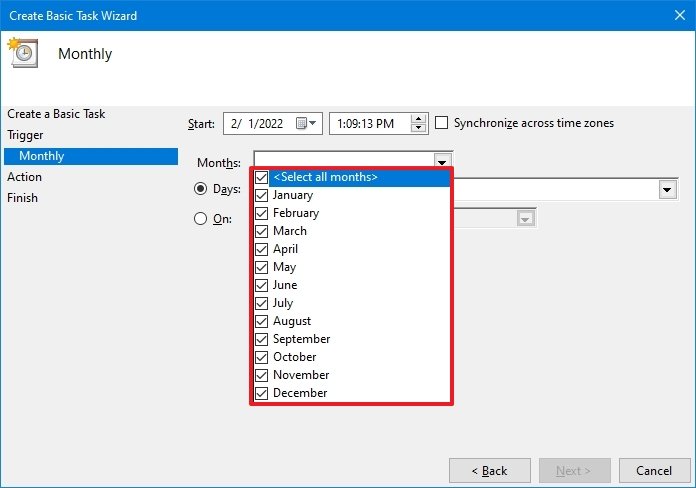
- Use the «Start» settings to confirm the day and time to run the task.
- Use the «Monthly» drop-down menu to pick the months of the year to run the task.
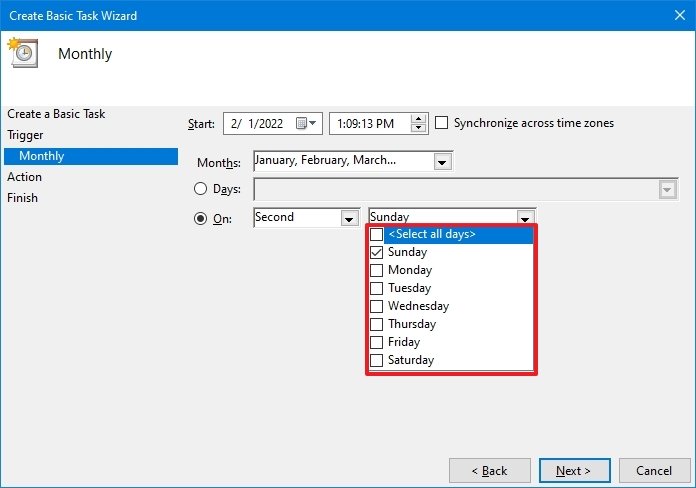
- Use the «Days» or «On» drop-down menu to confirm the days to run the task.
- Click the Next button.
- Select the Start a program option to run the batch file.
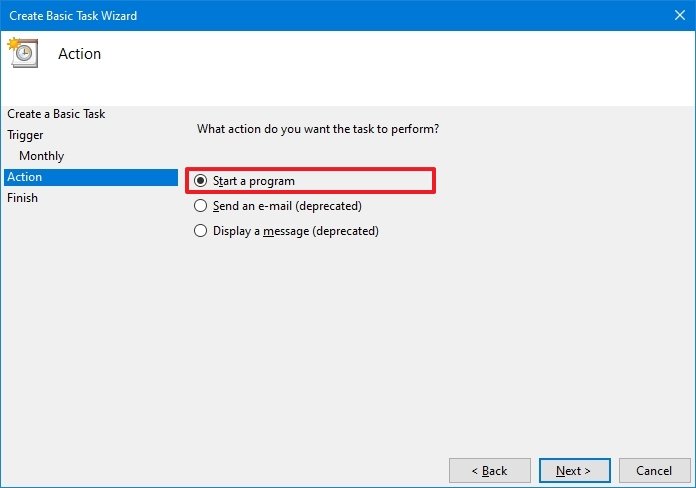
- In the «Program/script» field, click the Browse button.
- Select the batch file you want to execute.
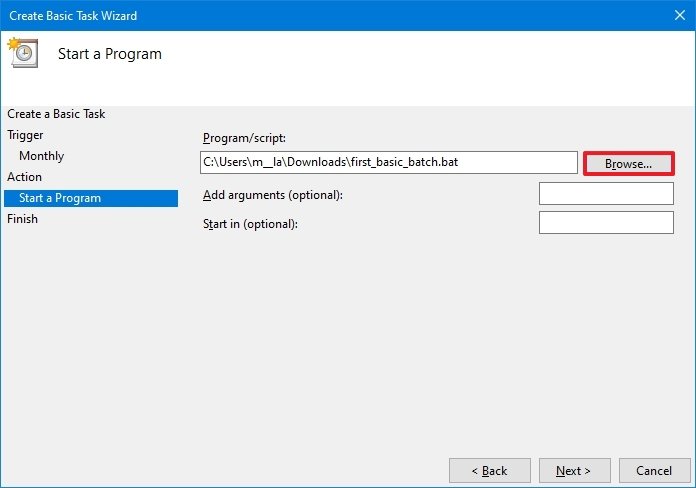
- Click the Finish button.
Once you complete the steps, the task will run the script during the configured time and date or action.
The above instructions are meant to schedule only a basic task. You can use these instructions to create a more customizable task with the Task Scheduler.
This guide focuses on Windows 10, but the same steps will also work for older versions, including Windows 8.1 and 7. Also, you can refer to these instructions if you have Windows 11 installed on your computer.
More Windows resources
For more helpful articles, coverage, and answers to common questions about Windows 10 and Windows 11, visit the following resources:
- Windows 11 on Windows Central — All you need to know
- Windows 10 on Windows Central — All you need to know
Mauro Huculak has been a Windows How-To Expert contributor for WindowsCentral.com for nearly a decade and has over 15 years of experience writing comprehensive guides. He also has an IT background and has achieved different professional certifications from Microsoft, Cisco, VMware, and CompTIA. He has been recognized as a Microsoft MVP for many years.
-
Quick Links:
- Introduction
- What is a Batch File?
- Setting Up Your Environment
- Creating a Batch File
- Running a Batch File from CMD
- Common Issues & Troubleshooting
- Advanced Uses of Batch Files
- Case Studies & Examples
- Expert Insights
- FAQs
Introduction
Running a Windows batch file from the command line (CMD) is an essential skill for users looking to automate repetitive tasks, manage system processes, or streamline workflows. This guide will take you through the steps necessary to create, modify, and execute batch files effectively.
What is a Batch File?
A batch file is a text file containing a series of commands that are executed by the Windows command line interpreter. The file extension typically used for batch files is .bat. When a batch file is run, it executes each command in the order they are written, making it a powerful tool for automation.
Characteristics of Batch Files
- Simple to create and edit using any text editor.
- Can execute multiple commands in sequence.
- Supports conditional statements and loops.
- Useful for automating repetitive tasks.
Setting Up Your Environment
Before you can run batch files from CMD, ensure your environment is properly set up:
1. Open Command Prompt
To open CMD, press Win + R, type cmd, and hit Enter.
2. Set the Path (Optional)
If your batch files are located in a specific directory, you can add that directory to your system’s PATH variable. This allows you to run the batch files from any location in CMD without specifying the full path.
How to Add a Directory to PATH
- Right-click on
This PCand selectProperties. - Click on
Advanced system settings. - In the
System Propertieswindow, click onEnvironment Variables. - Under
System variables, findPath, and clickEdit. - Add your directory path and click
OK.
Creating a Batch File
Now that your environment is set up, let’s create a simple batch file.
Step-by-Step Guide to Create a Batch File
- Open Notepad or any text editor.
- Type the following commands:
- Save the file with a
.batextension, e.g.,hello.bat.
@echo off
echo Hello, World!
pause
Running a Batch File from CMD
To run the batch file you just created, follow these steps:
Step-by-Step Execution
- Open Command Prompt.
- Navigate to the directory where your batch file is located using the
cdcommand. For example: - Type the name of the batch file and hit
Enter:
cd C:\path\to\your\batchfile
hello.bat
You should see «Hello, World!» printed in the command prompt.
Common Issues & Troubleshooting
When running batch files, you may encounter some common issues:
1. Command Not Found
This usually occurs if the command is misspelled or the executable is not in the system’s PATH.
2. Permission Denied
If your batch file tries to access files or folders that require administrative privileges, run CMD as an administrator.
Advanced Uses of Batch Files
Batch files can do much more than just echo messages. Here are some advanced uses:
Automating System Tasks
Batch files can automate tasks like disk cleanup, software installations, and backups. For example:
@echo off
echo Cleaning temporary files...
del /q /f C:\Windows\Temp\*
Scheduling Batch Files
Use Windows Task Scheduler to run batch files at specific intervals. This can be useful for backups or system maintenance.
Case Studies & Examples
Here are a couple of examples illustrating the power of batch files:
Example 1: Daily Backup Script
A business needed to back up its data daily. They created a batch file that copied files from their main directory to an external hard drive. The script looked like this:
@echo off
xcopy C:\Users\YourName\Documents D:\Backup\Documents /E /I
Example 2: System Cleanup
A user wanted to automate system cleanup. They created a batch file to delete temporary files and clear cache:
@echo off
del /q /f C:\Users\YourName\AppData\Local\Temp\*
rd /s /q C:\Windows\Temp
Expert Insights
According to industry experts, batch files remain relevant despite the rise of more sophisticated scripting languages. They are lightweight, easy to learn, and effective for simple automation tasks.
Experts recommend keeping batch files organized and well-documented to avoid confusion, especially in a corporate environment.
FAQs
1. What is the difference between a batch file and a script?
A batch file is specific to Windows and uses the command interpreter, while scripts can refer to any programming language, including Python, JavaScript, and more.
2. Can I run a batch file from another batch file?
Yes, you can call another batch file within a batch file using its name.
3. Are there any risks associated with running batch files?
Yes, batch files can execute harmful commands. Always review the content before running unknown batch files.
4. Can I schedule a batch file to run automatically?
Yes, you can use Windows Task Scheduler to schedule batch files to run at specific times or intervals.
5. What command is used to pause a batch file?
The command pause is used to pause execution and wait for user input to continue.
6. How do I make a batch file executable from anywhere?
Add the folder containing your batch file to the system PATH variable.
7. Can batch files run PowerShell scripts?
Yes, you can call PowerShell scripts from within a batch file using the powershell command.
8. What is the purpose of @echo off?
This command prevents the commands in the batch file from being displayed in the command prompt during execution.
9. Can I pass arguments to a batch file?
Yes, you can pass arguments to a batch file and access them using %1, %2, etc.
10. Where can I find more resources on batch scripting?
Websites like Computer Hope and SS64 provide comprehensive resources on batch scripting.
Random Reads
- Boosting bass windows mac
- Bring back viridian city gym leader fire red
- How to delete recent documents in word excel
- How to collapse columns in excel
- How to close google chrome
- How to paint wood
- How to paint pvc
- How to paint plastic furniture
- How to do the pokemon shop questionnaire
- How to remove grout
- Overview
- Part 1 – Getting Started
- Part 2 – Variables
- Part 3 – Return Codes
- Part 4 – stdin, stdout, stderr
- Part 5 – If/Then Conditionals
- Part 6 – Loops
- Part 7 – Functions
- Part 8 – Parsing Input
- Part 9 – Logging
- Part 10 – Advanced Tricks
Getting Started with Windows Batch Scripting
Windows batch scripting is incredibly accessible – it works on just about any modern Windows machine. You can create and modify batch scripts on just about any modern Windows machine. The tools come out of the box: the Windows command prompt and a text editor like Notepad.exe. It’s definitely far from
the best shell scripting langauge, but, it gets the job done. It’s my “duct tape” for Windows.
Launching the Command Prompt
Windows gurus launch the command prompt using the keyboard shortcut Windows Logo Key+R (i.e., “Run”) > Type cmd.exe then Enter. This is way faster than navigating the Windows Start Menu to find the Command Prompt.
Editing Batch Files
The universal text editor for batch files is Notepad (Windows Logo Key + R > Type notepad then Enter). Since batch files are just ASCII text, you can probably use just about any text editor or word processor. Very few editors do anything special for Batch files like syntax highlighting or keyword support, so notepad is good enough fine and will likely be installed on just about every Windows system you encounter.
Viewing Batch Files
I would stick with Notepad for viewing the contents of a batch file. In Windows Explorer (aka, “My Computer”), you should be able to view a batch file in Notepad by right clicking the file and seleting Edit from the context menu. If you need to view the contents within a command prompt window itself, you can use a DOS command like TYPE myscript.cmd or MORE myscript.cmd or EDIT myscript.cmd
Batch File Names and File Extensions
Assuming you are using Windows XP or newer, I recommend saving your batch files with the file extension .cmd. Some seriously outdated Windows versions used .bat, though I recommend sticking with the more modern .cmd to avoid some rare side effects with .bat files.
With the .cmd file extension, you can use just about filename you like. I recommend avoiding spaces in filenames, as spaces only create headaches in shell scripting. Pascal casing your filenames is an easy way to avoid spaces (e.g., HelloWorld.cmd instead of Hello World.cmd). You can also use punctuation characters like . or - or _ (e.g. Hello.World.cmd, Hello-World.cmd, Hello_World.cmd).
Another thing with names to consider is avoiding names that use the same name of any built-in commands, system binaries, or popular programs. For example, I would avoid naming a script ping.cmd since there is a widely used system binary named ping.exe. Things might get very confusing if you try to run ping and inadvertently call ping.cmd when you really wanted ping.cmd. (Stay tuned for how this could happen.) I might called the script RemoteHeartbeat.cmd or something similar to add some context to the script’s name and also avoid any naming collisions with any other executable files. Of course, there could be a very unique circumstance in which you want to modify the default behavior of ping in which this naming suggestion would not apply.
Saving Batch Files in Windows
Notepad by default tries to save all files as plain jane text files. To get Notepad to save a file with a .cmd extension, you will need to change the “Save as type” to “All Files (.)”. See the screenshot below for an example of saving a script named “HelloWorld.cmd” in Notepad.
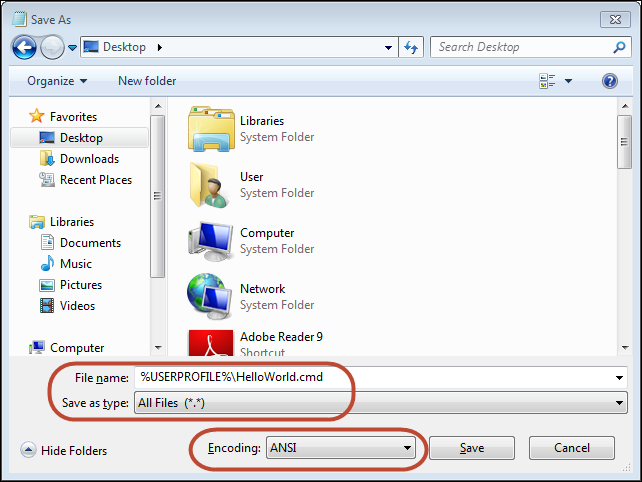
SIDEBAR: I’ve used a shortcut in this screenshot that you will learn more about later. I’ve saved the file to my “user profile folder” by naming
the file%USERPROFILE%\HelloWorld.cmd. The%USERPROFILE%keyword is the Windows environmental variable for the full path
to your user profile folder. On newer Windows systems, your user profile folder will typically beC:\Users\<your username>. This shortcut
saves a little bit of time because a new command prompt will generally default the “working directory” to your user profile folder. This lets you run
HelloWorld.cmdin a new command prompt without changing directories beforehand or needing to specify the path to the script.
Running your Batch File
The easy way to run your batch file in Windows is to just double click the batch file in Windows Explorer (aka “My Computer”). Unfortunately, the command prompt will not give you much of a chance to see the output and any errors. The command prompt window for the script will disappear as soon as the script exits. (We will learn how to handle this problem in Part 10 – Advanced Tricks ).
When editing a new script, you will likely need to run the batch file in an existing command window. For newbies, I think the easiest foolproof way to
run your script is to drag and drop the script into a command prompt window. The command prompt will enter the full path to your script on the
command line, and will quote any paths containing spaces.
Some other tips to running batch files:
- You can recall previous commands using the up arrow and down arrow keys to navigate the command line history.
- I usually run the script as
%COMPSPEC% /C /D "C:\Users\User\SomeScriptPath.cmd" Arg1 Arg2 Arg3
This runs your script in a new command prompt child process. The/Coption instructs the child process to quit when your script quits.
The/Ddisables any auto-run scripts (this is optional, but, I use auto-run scripts). The reason I do this is to keep the command prompt
window from automatically closing should my script, or a called script, call theEXITcommand. TheEXITcommand automatically closes
the command prompt window unless theEXITis called from a child command prompt process. This is annoying because you lose any messages
printed by your script.
Comments
The official way to add a comment to a batch file is with the REM (Remark) keyword:
REM This is a comment!
The power user method is to use ::, which is a hack to uses the the label operator : twice, which is almost always ignored.
Most power authors find the :: to be less distracting than REM. Be warned though there are a few places where :: will cause errors.
:: This is a comment too!! (usually!)
For example, a FOR loop will error out with :: style comments. Simply fall back to using REM if you think you have a situation like this.
Silencing Display of Commands in Batch Files
The first non-comment line of a batch file is usually a command to turn off printing (ECHO’ing) of each batch file line.
@ECHO OFF
The @ is a special operator to suppress printing of the command line. Once we set ECHO’ing to off, we won’t need the @ operator again
in our script commands.
You restore printing of commands in your script with:
ECHO ON
Upon exit of your script, the command prompt will automatically restore ECHO to it’s previous state.
Debugging Your Scripts
Batch files invole a lot of trial and error coding. Sadly, I don’t know of any true debugger for Windows batch scripts. Worse yet, I don’t
know of a way to put the command processor into a verbose state to help troubleshoot the script (this is the common technique for Unix/Linux
scripts.) Printing custom ad-hoc debugging messages is about your only option using the ECHO command. Advanced script writers can do
some trickery to selectively print debugging messages, though, I prefer to remove the debugging/instrumentation code once my script is
functioning as desired.
<< Overview
Part 2 – Variables >>
-
Method 1: Running Batch Files Directly in CMD
-
Method 2: Running Batch Files Using Python
-
Method 3: Running Batch Files with Command Line Arguments
-
Conclusion
-
FAQ

Running a Batch (.bat) file in Command Prompt (CMD) is a fundamental skill for Windows users, especially for those who want to automate tasks or execute scripts efficiently. Whether you’re a beginner or have some experience with command-line operations, this tutorial will guide you through the process of running Batch files seamlessly. We’ll cover different methods, including how to do this using Python, making it easier for you to integrate Batch file execution into your workflows. By the end of this article, you will have a clear understanding of how to run Batch files in CMD, along with practical code examples to enhance your skills.
Method 1: Running Batch Files Directly in CMD
The simplest way to run a Batch file is to execute it directly from the Command Prompt. To do this, you need to know the path of your Batch file. Here’s how to do it:
- Open Command Prompt by typing “cmd” in the Windows search bar and hitting Enter.
- Navigate to the directory containing your Batch file using the
cdcommand. For example, if your Batch file is located in the “Scripts” folder on your desktop, you would type:
cd C:\Users\YourUsername\Desktop\Scripts
- Once you’re in the correct directory, type the name of your Batch file, including the .bat extension, and press Enter:
Output:
Batch file is executed successfully.
This method is straightforward and doesn’t require any additional software. It’s perfect for quick executions or testing scripts. Just ensure that you have the correct path and file name. If your Batch file contains commands that require administrative privileges, make sure to run CMD as an administrator by right-clicking on the Command Prompt icon and selecting “Run as administrator.”
Method 2: Running Batch Files Using Python
If you’re looking to integrate Batch file execution into a Python script, you can easily do this using the subprocess module. This method is particularly useful for developers who want to automate tasks or incorporate Batch files into larger applications. Here’s a simple example:
import subprocess
subprocess.run(["C:\\Path\\To\\YourBatchFile.bat"])
In this code, we import the subprocess module, which is a powerful tool for spawning new processes and connecting to their input/output/error pipes. The run() function is then used to execute the specified Batch file. Make sure to replace C:\\Path\\To\\YourBatchFile.bat with the actual path of your Batch file.
Output:
Batch file executed from Python.
This method allows you to run Batch files as part of a larger Python program, which can be very handy when you want to perform multiple tasks in sequence or manage file operations programmatically. The subprocess module provides additional functionalities, such as capturing output and handling errors, making it a versatile choice for script automation.
Method 3: Running Batch Files with Command Line Arguments
Sometimes, you may want to pass arguments to your Batch file when executing it. This can be done easily from CMD or within a Python script. Here’s how you can do it in both scenarios.
Using CMD
You can pass arguments directly in CMD by adding them after the Batch file name. For example:
YourBatchFile.bat arg1 arg2
Output:
Arguments received: arg1, arg2
Using Python
To run a Batch file with arguments in Python, you can modify the subprocess.run() function like this:
import subprocess
subprocess.run(["C:\\Path\\To\\YourBatchFile.bat", "arg1", "arg2"])
In this example, arg1 and arg2 are passed to the Batch file as command-line arguments. Inside your Batch file, you can access these arguments using %1, %2, etc.
Output:
Arguments received: arg1, arg2
This method is particularly useful when you need to customize the execution of your Batch file based on user input or other dynamic data. It opens up a range of possibilities for making your scripts more interactive and functional.
Conclusion
Running Batch files in CMD is a valuable skill that can enhance your productivity and streamline various tasks on your Windows system. Whether you choose to execute them directly in Command Prompt or integrate them into a Python script, the methods we’ve discussed provide flexibility and efficiency. By understanding how to run Batch files and pass arguments, you can automate repetitive tasks and manage system operations effectively. With practice, you’ll become proficient in using Batch files, making your workflow smoother and more organized.
FAQ
-
how do I create a Batch file?
You can create a Batch file by opening Notepad, writing your commands, and saving the file with a .bat extension. -
can I run a Batch file from a USB drive?
Yes, you can run a Batch file from a USB drive by navigating to the drive in CMD and executing the file. -
what if my Batch file doesn’t execute?
Ensure that the file path is correct and that you have the necessary permissions to run the file. -
can I schedule a Batch file to run automatically?
Yes, you can use Windows Task Scheduler to schedule Batch files to run at specific times or events. -
how can I debug a Batch file?
You can debug a Batch file by addingechostatements to print variable values or usingpauseto stop execution at certain points.
Enjoying our tutorials? Subscribe to DelftStack on YouTube to support us in creating more high-quality video guides. Subscribe
















