Обновлено:
Опубликовано:
Тематические термины: iPerf, Linux, CentOS, Windows
iPerf является кроссплатформенным приложением и может быть установлен на любую популярную операционную систему. В данной инструкции будет рассмотрена установка сервера на Linux CentOS и клиента как на последнем, так и Microsoft Windows.
Установка и запуск
Запуск клиента и проверка сервера
Ключи
Автозапуск
Примеры
Версия для Windows
iPerf и iPerf3
Публичные сервера
Свой публичный сервер
Возможные проблемы
Установка сервера/клиента
По сути, нет отдельного iPerf для сервера или клиента — это один и тот же программный продукт, который может запускаться в режиме сервера или выполнять клиентские команды.
Для начала выполняем установку расширенного репозитория:
yum install epel-release
Устанавливаем iPerf:
yum install iperf3
Открываем порт в брандмауэре:
firewall-cmd —permanent —add-port=5201/tcp
firewall-cmd —permanent —add-port=5201/udp
firewall-cmd —reload
* в данном примере мы открыли порт 5201 (для iPerf по умолчанию) для пакетов TCP и UDP.
Запускаем сервер:
iperf3 -s
На экране появится:
————————————————————
Server listening on 5201
————————————————————
Сервер ждет запросов.
Клиентские запросы и проверка сервера
Напомню, что клиент может быть установлен на любую систему. Также, как в первом случае, выполняем установку клиента на другой компьютер в сети.
После можно сразу выполнить команду:
iperf3 -c 192.168.0.15
* где 192.168.0.15 — iPerf сервер.
На клиенте мы увидим что-то подобное:
[ 4] local 192.168.0.20 port 47068 connected to 192.168.0.15 port 5201
[ ID] Interval Transfer Bandwidth Retr Cwnd
[ 4] 0.00-1.00 sec 104 MBytes 873 Mbits/sec 10 391 KBytes
[ 4] 1.00-2.00 sec 110 MBytes 921 Mbits/sec 4 393 KBytes
[ 4] 2.00-3.00 sec 111 MBytes 928 Mbits/sec 1 478 KBytes
[ 4] 3.00-4.00 sec 104 MBytes 875 Mbits/sec 5 423 KBytes
* где:
- 192.168.0.20 — адрес клиента
- 192.168.0.15 — адрес сервера
- ID — идентификатор запросов, нужен для ориентирования, если к серверу идет несколько обращений.
- Interval — промежуток времени в секундах, на протяжении которого выполнялась передача данных.
- Transfer — сколько было передано данных за интервал времени.
- Bandwidth — средняя скорость передачи данных за интервал времени.
- Retr — количество повторно отправленных TCP-сегментов.
- Cwnd — одновременно переданных данных.
Все ключи запуска iPerf
Общие для сервера и клиента:
| Ключ | Описание |
|---|---|
| -p | Определить порт, на котором будет слушать сервер или отправлять запросы клиент |
| -f | Формат отчетов — kmgKMG (Kbits, Mbits, KBytes, MBytes, …) |
| -i | Задать интервал, в течение которого выполняется одна проверка |
| -F | Указать файл, из которого будут взяты входные данные для запуска |
| -A | Степень нагрузки на процессор |
| -B | Указать, через какой сетевой интерфейс работать |
| -V | Детализированные сообщения в консоли |
| -J | Вывод в формате json |
| —logfile | Весь вывод в отдельный лог-файл |
| -d | Режим отладки (много сообщений) |
| -v | Показать версию программы |
| -h | Вызвать справку по работе с программой |
Для сервера:
| Ключ | Описание |
|---|---|
| -s | Запустить iPerf в режиме сервера |
| -D | Запустить как демона (как службу) |
| -I | Указать pid-файл |
| -1 | Принять запрос от одного клиента и завершить работу |
Для клиента:
| Ключ | Описание |
|---|---|
| -c | Запустить iPerf в режиме клиента |
| -u | Отправлять UDP-пакеты |
| -b | Формат отчетов для bandwidth (средней скорости) |
| -t | Количество секунд, в течение которых будет идти проверка скорости |
| -n | Объем данных для проверки (применяется вместо времени -t) |
| -k | Количество пакетов для проверки (вместо -t или -n) |
| -l | Длина буфера записи/чтения |
| -P | Число параллельных запросов |
| -R | Обратный режим — сервер отправляет, клиент принимает |
| -w | Размер сетевого окна |
| -C | Установить алгоритм управления перегрузкой TCP |
| -M | Задать максимальный размер MTU |
| -4 | Работать только для IPv4 |
| -6 | Работать только для IPv6 |
| -Z | Использовать метод «нулевой копии» для отправки данных |
| -O | Опустить первые n секунд |
| -T | Задать префикс для каждой строки вывода |
Также самый свежий список ключей можно получить командой:
man iperf3
Автозапуск сервера (создание сервиса в systemd)
По умолчанию, программу нужно запускать вручную. Если мы хотим, чтобы сервер запускался автоматически и работал как служба systemd, выполняем инструкцию ниже.
Создаем юнит в systemd со следующим содержимым:
vi /etc/systemd/system/iperfd.service
[Unit]
Description=iPerf Service
After=network.target
[Service]
Type=forking
PIDFile=/run/iperf3.pid
ExecStart=-/bin/iperf3 -s -D -I /run/iperf3.pid
ExecReload=/bin/kill -HUP $MAINPID
Restart=always
[Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.target
* где
- Description — описание юнита;
- After указывает на юнит, после которого может загружаться наш сервис;
- Type — тип службы;
- PIDFile — путь к pid файлу, в котором хранится номер процесса;
- ExecStart — команда, которую нужно выполнить при старте сервиса (в данном примере запускается iPerf в режиме сервера как демон и создает pid-файл);
- ExecReload — команда для перезапуска службы;
- Restart=always — опция, позволяющая автоматически перезапускать сервис, если он перестанет работать;
- опция WantedBy=multi-user.target позволяет установить для автозапуска службу в обычном многопользовательском режиме.
Перезапускаем systemd:
systemctl daemon-reload
Разрешаем созданный сервис:
systemctl enable iperfd
Запускаем его:
systemctl start iperfd
Проверяем:
systemctl status iperfd
Примеры использования iPerf
Рассмотрим некоторые команды запросов к серверу для проверки скорости соединения.
Использование UDP
iperf3 -c 192.168.0.15 -u
* сам сервер не нужно запускать в UDP-режиме, так как он принимает любые запросы.
Альтернативные порты
Для этого необходимо сначала запустить сервер на нужном порту:
iperf3 -s -p 443
* кстати, можно запустить несколько процессов iperf одновременно, которые будут слушать на разных портах.
* стоит не забывать по настройки брандмауэра. В данном примере понадобиться ввести команды firewall-cmd —permanent —add-port=443/tcp и firewall-cmd —reload.
Теперь можно запускать клиента:
iperf3 -c 192.168.0.15 -p 443
Проверка скорости в течение 30 секунд с интервалами по 2 секунды
iperf3 -c 192.168.0.15 -t 30 -i 2
Несколько параллельных запросов
iperf3 -c 192.168.0.15 -P 3
Отправляем на проверку 3 Гб данных
iperf3 -c 192.168.0.15 -n 3G
Клиент/сервер для Windows
Скачиваем iPerf под Windows с официального сайта. Распаковываем архив и запускаем командную строку (cmd). Переходим в распакованную папку (команда cd).
Можем работать с iperf. Команды такие же, как для Linux, например:
iperf3.exe -c 192.168.0.15
GUI
Для работы с iPerf в графическом интерфейсе есть различные утилиты, например Iperf3-Cygwin-GUI. Скачиваем архив, распаковываем его и запускаем iperf3cygwingui.bat.
В открывшемся окне для простой проверки нужно только прописать адрес iPerf-сервера и нажать кнопку Run Iperf3:

Однако, на моей практике, программа не заработала, а после запуска зависала (или не запускался iperf3.exe). Проблему удалось решить с помощью скачанного с официального сайта клиента (файлов iperf3.exe и cygwin1.dll), которыми я заменил одноименные файлы в папке bin.
При желании, программу можно также запустить в режиме сервера:

jPerf
Для работы в графическом интерфейсе также есть популярная программа jperf. Ее можно скачать с сайта sourceforge. Однако, она создана с использованием старой версии iperf, поэтому я не стал уделять ей много внимания. В целом, процесс и внешний вид не сильно отличается от Iperf3-Cygwin-GUI.
Совместимость iPerf и iPerf3
Клиент и сервер совместимы, но нужно знать, что по умолчанию, рабочий порт для iPerf — 5001, для iPerf3 — 5201.
Поэтому либо необходимо запускать сервер:
iperf3 -s -p 5001
* также не забываем настроить брандмауэр.
Либо запускаем клиентские запросы командой:
iperf -c 192.168.0.15 -p 5201
Публичные сервера iPerf
Актуальные публичные сервера iPerf можно найти на официальном сайте программы. Внимательно смотрите на описания серверов и рабочие порты.
Пример проверки с использованием сервера во Франции:
iperf3 -c bouygues.testdebit.info -p 5200
или в Индонезии:
iperf3 -c iperf.biznetnetworks.com
Свой публичный сервер
Сервер iPerf может обрабатывать только одно подключение одновременно на порту. Поэтому, в условиях публичного использования необходим его запуск на множестве портов одновременно.
Мы настроим сервер при помощи systemd. Ранее мы уже создавали один юнит для запуска iperf. Повторяем процедуру с небольшими изменениями.
Создаем юнит со следующим содержимым:
vi /etc/systemd/system/iperfd5205.service
[Unit]
Description=iPerfService on port %i
After=network.target
[Service]
Type=forking
PIDFile=/var/run/iperf3.5205.pid
ExecStart=-/bin/iperf3 -s -p 5205 -D -I /var/run/iperf3.5205.pid
ExecReload=/bin/kill -HUP $MAINPID
Restart=always
RuntimeMaxSec=3600
[Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.target
* если сравнить с ранее созданным юнитом, мы добавили запуск сервера на порту 5205.
Перезапускаем systemd:
systemctl daemon-reload
Разрешаем юнит и запускаем сервис:
systemctl enable iperfd5205
systemctl start iperfd5205
Повторяем шаги для других портов — создаем для каждого отдельный юнит в systemd. Для публичного сервера лучше создать побольше.
Возможные ошибки
the server is busy running a test. try again later
В данный момент сервер обрабатывает другой запрос или он завис. Если мы являемся администратором сервера, перезагружаем его, в противном случае, ждем.
Iperf – кроссплатформенная консольная утилита с открытым исходным кодом, предназначенная для тестирования пропускной способности сети между двумя узлами. Утилита iperf позволяет генерировать нагрузочный TCP и UDP трафик между хостами. С помощью iperf вы можете быстро измерить максимальную пропускную способность сети между сервером и клиентом, провести нагрузочное тестирование канала связи, маршрутизатора, сетевого шлюза (файервола), вашей Ethernet или Wi-Fi сети.
В этой статье мы покажем, как установить и использовать утилиту iPerf для проверки скорости сети в Windows, Linux и VMware ESXi (есть версии iperf для Android, MacOS, RouterOS от MikroTik и других платформ).
Содержание:
- Установка и использование iPerf в Windows
- Установка iPerf в Linux
- Запуск iPerf в VMware ESXi
- Проверка пропускной способности сети с помощью iPerf
Утилита iPerf является кроссплатформенной и не требует установки, достаточно скопировать и запустить ее на двух устройствах, пропускную способность сети между которыми нужно оценить. iPerf работает в режиме клиент-сервер. На первом компьютере утилита iPerf запускается в режиме сервера (ожидает трафик от клиента). На втором компьютере iPerf запускается в режиме клиента, начинает генерировать TCP/UDP трафик и выполнять измерение максимальной скорости передачи данных. В большинстве случаев сейчас используется версия iPerf3 (поддерживает высокоскоростное UDP тестирование, по умолчанию используется порт 5201 TCP/UDP).
Установка и использование iPerf в Windows
Вы можете скачать iperf 3.1 для Windows по ссылке https://iperf.fr/iperf-download.php или версию iperf2. Достаточно скачать архив iperf и распаковать в локальный каталог на диске. Установка утилиты не требуется. В архиве всего два файла: cygwin1.dll и iperf3.exe.
Вы можете скачать архив iPerf и распаковать его на диск с помощью команд PowerShell:
$iPerfZip = "https://iperf.fr/download/windows/iperf-3.1.3-win64.zip"
$TargetFolder = Join-Path $env:TEMP "iperf.zip"$iPerfPath = Join-Path $env:TEMP "iperf"
if (!(Test-Path $iPerfPath))
{ Invoke-WebRequest -Uri $iPerfZip -OutFile $TargetFolder
Expand-Archive -Path $TargetFolder -DestinationPath $iPerfPath
}
Iperf это консольная утилита и для ее запуска нужно использовать командную строку. Откройте командную строку (cmd.exe) и перейдите в каталог с утилитой. Например:
cd c:\tools\iperf
Если вы запустить программу iperf3.exe без параметров, она выведет список доступных опций.
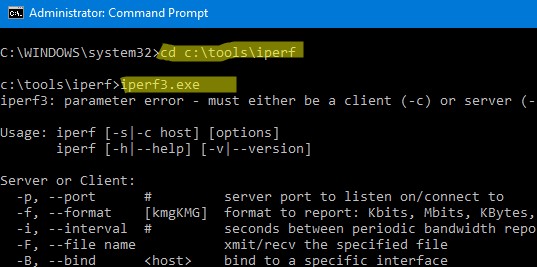
Утилита iPerf может работать в режиме сервера (параметр -s) или клиента (-c). Если вы запускаете iPerf сервер на Windows, нужно открыть входящие порт 5201 для протоколов TCP и UDP. Можно открыть порты через графический интерфейс Windows Defender Firewall или с помощью команд PowerShell. Создайте и включите правила файервола так:
New-NetFirewallRule -DisplayName 'iPerf-Server-Inbound-TCP' -Direction Inbound -Protocol TCP -LocalPort 5201 -Action Allow | Enable-NetFirewallRule
New-NetFirewallRule -DisplayName 'iPerf-Server-Inbound-UDP' -Direction Inbound -Protocol UDP -LocalPort 5201 -Action Allow | Enable-NetFirewallRule

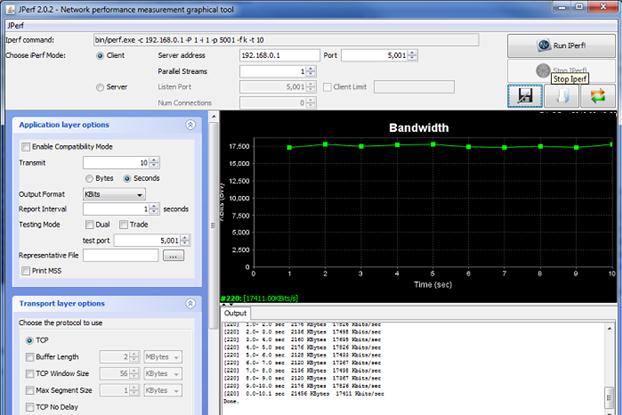
Для Windows есть несколько реализаций графического интерфейса. Например, Iperf3-Cygwin-GUI и jperf.
Утилита jperf написана на Java (для работы на компьютере должна быть установлена Java-машина). Помимо графических рюшечек к CLI интерфейсу, Jperf умеет в реальном времени строить графики пропускной способности канала связи.
Для использования достаточно указать адрес сервера iPerf и запустить проверку.
В галерее скриптов PowerShell есть отдельный модуль iPerfAutomate, который можно использовать для получения данных измерения производительности сети из скриптов PowerShell. Вы можете установить модуль так:
Install-Module -Name iPerfAutomate
Установка iPerf в Linux
В дистрибутивах CentOS/RHEL/Fedora 8 пакет iperf3 включен в состав базового репозитория AppStream (в CentOS 7 iperf3 есть в EPEL). Вы можете установить его стандартной командой yum/dnf:
# dnf install iperf3
В дистрибутивах Debian/Ubuntu вы можете установить утилиту iperf3 командой:
$ sudo apt install iperf3
Если данный Linux сервер планируется использовать в качестве сервере iperf3, нужно открыть порт 5201 в firewalld (или iptables):
# firewall-cmd --permanent --add-port=5201/tcp
# firewall-cmd --permanent --add-port=5201/udp
# firewall-cmd --reload
Запуск iPerf в VMware ESXi
VMware удалила утилиту iPerf в ESXi 6.7, но вернула его в 6.7U1. Проверьте, что на вашем хосте ESXi установлен iPerf. Подключитесь к консоли ESXi по SSH, перейдите в каталог
/usr/lib/vmware/vsan/bin
и проверьте, есть ли в нем файл iperf или iperf3.
Если iPerf не установлен, вы можете вручную скачать offline bundle с iperf здесь (http://vibsdepot.v-front.de/depot/bundles/iperf-2.0.5-1-offline_bundle.zip), скопируйте его на ESXi хост и установить командой:
# esxcli software vib install -d /iperf-2.0.5-1-offline_bundle.zip –no-sig-check
Утилита будет установлена в каталог /opt/iperf/bin и для ее запуска нужно указывать команду:
# /opt/iperf/bin/iperf3
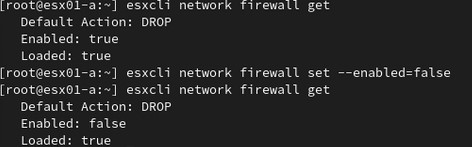
Если вы запускаете iPerf сервер на хосте ESXi, нужно открыть порты 5201. По умолчанию эти порты запрещены в файерволе ESXi. Чтобы открыть их, можно временно отключить файервол:
# esxcli network firewall get# esxcli network firewall set --enabled=false
# esxcli network firewall get
Не забудьте включить файервол ESXi после окончания проверки пропускной способности сети:
# esxcli network firewall set --enabled true
При запуске iPerf в ESXi его нужно привязывать к интерфейсу vmkernel:
# esxcli network ip interface ipv4 get
Проверку доступности между хостами ESXi можно выполнить с помощью:
# vmkping IP address
Запускайте iPerf на полученном IP адресе:
# iperf -s -B 192.168.31.50
Проверка пропускной способности сети с помощью iPerf
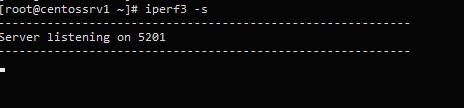
Рассмотрим теперь несколько примеров использования iperf для тестирования пропускной способности сети. В этом примере мы будем использовать сервер с CentOS в качестве сервера iperf. Запустим утилиту iperf в серверном режиме:
# iperf3 –s
Сервер iperf запущен, он ожидает соединения на порту TCP/5201.
Server listening on 5201
Важно. Аргументы утилиты iperf регистрозависимы!
Можно запустить iperf сервер с большим размером TCP окна и на другом порту:
# iperf3 -s -w 32768 –p 5203
-w 32768 – зададим размер окна TCP в 32 KB (по умолчанию около 8 Кб)
–p 5203 – порт, на котором ожидает подключения iperf (напоминаю, что iperf2 по умолчанию слушает на порту 5001).
Можно запустить сервер iPerf в режиме службы Windows с помощью ключа -D.
В качестве клиента iperf я использую компьютер с Windows 10. Запустите командную строку и перейдите в каталог с исполняемым файлом iperf:
cd c:\tools\iperf
Чтобы запустить проверку сети со стороны клиента, укажите адрес (имя) хоста, где запущен сервер iperf:
iperf3.exe -c 192.168.1.202
Клиент начнет генерировать сетевой трафик и выполнит тестирование канала в течении 10 секунд и выведет примерно такую таблицу:
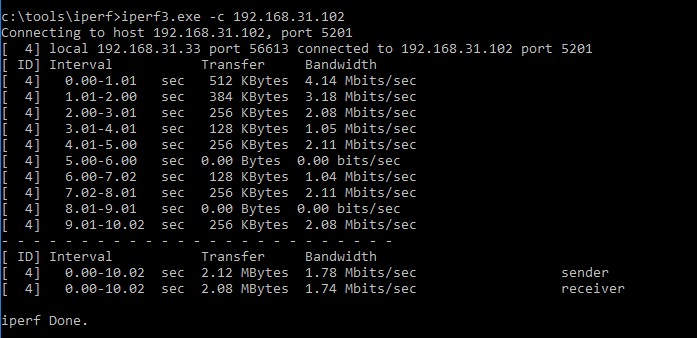
- Interval – промежуток тестирования (в сек.);
- Transfer – размер переданных данных за это время;
- Bandwidth – средняя скорость передачи данных.
Если вы запустили сервер iperf с увеличенным размером TCP окна, вы можете использовать следующую команду для получения максимальной нагрузки на сеть:
iperf3.exe -c 192.168.1.202 -P 8 -t 30 -w 32768 -i 5 -f g
- -c 192.168.1.202 – IP адрес сервера iperf;
- -w 32768 — увеличиваем размер TCP окна;
- -t 30 – время в секундах, в течении которого выполняется тестирование (по умолчанию 10 секунд);
- -P 8 — число параллельных потоков (подключений), используется для получения максимальной нагрузки на канал;
- -i 5 – выводить статистику на экран каждые 5 секунд. Параметр удобно использовать при продолжительных тестах (несколько минут, часов);
- -f m — выводить результаты в Мбит/с. Здесь можно использовать атрибуты kmgKMG (килобиты, мегабиты, мегабайты и т.д.).
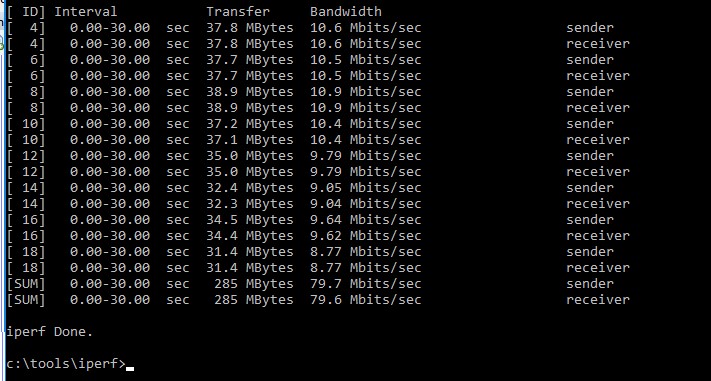
В нашем примере тестирование длилось 30 секунд. В итоговом отчете нас интересует значения столбца Bandwidth в последней строке [SUM]. Здесь указаны средняя скорость отправки (sender) и получения данных по сети (receiver).
В нашем случае средняя пропускная способность сети между двумя узлами – 79,7 Мбит/с. Было передано 285 Мб данных (столбец Transfer).
Можно запустить iperf в обратном режиме (сервер отправляет данные, а клиент принимает), для этого на клиенте указывается опция –R.
По-умолчанию утилита генерирует TCP трафик, если вам нужно проверить скорость сети для UDP пакетов, необходимо использовать ключ –u (сервер при этом запускается командой:
iperf3 -s –u
).
Если вам нужно проверить ваш интернет-канал (предоставляемый провайдером), можно воспользоваться одним из публичных iperf серверов (список доступен здесь):
iperf3 -c iperf.it-north.net
Обратите внимание, что iperf3 не поддерживает несколько одновременных тестов. Если сервер iperf сейчас выполняет тестирование с одним клиентов, то при попытке подключиться к нему с другого вы получите ошибку: iperf3: error — the server is busy running a test. try again later.
Если нужно оценить пропускную способность сети в обоих направлениях (в дуплексном режиме), дополнительно на клиенте нужно указать опцию –d:
iperf3.exe -c IP -P 8 -t 30 -w 32768 -d
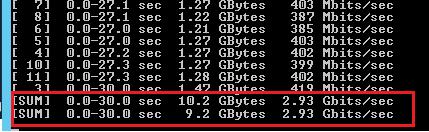
Во время выполнения теста сете с помощью iperf вы можете следить за нагрузкой на сетевой интерфейс компьютера через Task Manager.
Важно отметить, что при тестировании Iperf используем всю доступную пропускную способность канала связи между клиентом и сервером, что может негативно повлиять на продуктивные приложения и пользователей.
Полный список опций утилиты iperf можно получить так:
iperf3 –help
Iperf – простая и удобная сетевая утилита, которая поможет вам измерить производительность сетевого подключения и максимальную скорость передачи данных между двумя устройствами.
Iperf is a great networking tool for performing end-to-end throughput tests. These tests can be layer two or layer three. But as simple the use of Iperf is, it is only popular among experienced network engineers. In this post, we will look at how to install and use Iperf on Windows for throughput test.
The Iperf tool is a freeware that can be run as executable file either in server or client mode. It is purely command line and that explains the reason why only a few people use it. Iperf is available for Windows, Arch Linux, Ubuntu, Android, iOS, and more. Since this post is about how to install and use Iperf on Windows, I limit my explaination to installing and using Iperf on a Windows 7/8 computers with 32/64-bit processors respectively. The process is fairly thesame for other versions of Windows.

Downloading Iperf
To download Iperf, simply look up the word “Iperf” on Google and click on the first option in the results or click here. You can check the speed of your internet connection at www.speedcheck.org to see if your bandwidth is good enough. A connection speed of 3 -5mbps will be just fine. If you are downloading for a Windows computer, click on the first option named Iperf for Windows. choose the one for your Windows version and Iperf will be downloaded. Now, by default, it goes into your download folder. To simplify the execution process, copy the Iperf folder from your download folder to your desktop and unzipped the folder to extract the executable file named iperf3.
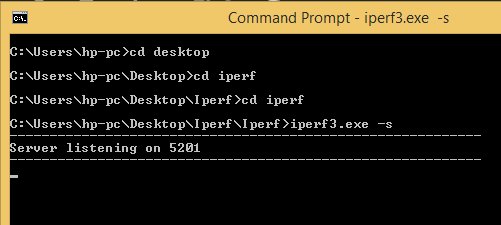
Running Iperf in server mode
To run the Iperf executable file, open the command prompt. This can be done by typing the “cmd” into the search field after you have clicked on the start button. Next, change your directory to the directory housing the Iperf folder. To change your directory to desktop, simply type “cd desktop” and hit the enter key. See image below

To move into the Iperf folder, change your directory once more to the Iperf folder by typing “cd Iperf” as shown below. Since I have another folder named Iperf, I will furthermore change my directory to Iperf once more. Now, what is left is the executable file named iperf3. To run Iperf in server mode, I will type the command “iperf3.exe -s from the Iperf directory. See image below:
Running Iperf in client mode
On the client side, simply use the command as shown in the image below to run Iperf in client mode. Note that the IP address on the server side must be included in the command.
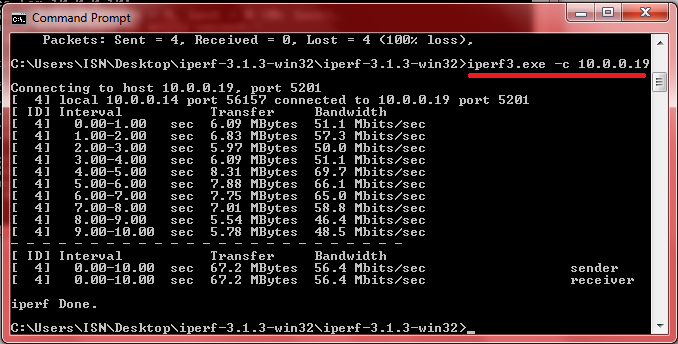
From the result of the test, can see the bandwith available to us at different Megabytes of data transferred. The average is 56.4 Mbps on both upload and download for 67.2 Megabytes of data sent or received.
In this tutorial you will learn how to use iPerf3 to measure throughput and simulate network loads on your networking infrastructure. iPerf3 is a useful, simple command-line tool for testing network throughput and performance. We will provide step-by-step instructions as well as a few common examples and use cases of ways to effectively use iPerf in your environment.
Install iPerf on Windows
iPerf can be installed on and ran from any windows based machine including Windows 10, Windows 11, and Windows Server.
Step 1. Download the latest iPerf3 package for your operating system from https://iperf.fr/iperf-download.php

Step 2. Extract the zip file.
Step 3. Copy the iperf3 executable and any required DLLs to the computers you want to use for testing. One computer will act as the server and the other the client. Here I created a folder named ‘TEMP’ on each machine.

Install iPerf on Linux (Ubuntu in this Case)
Step 1. Update the package repository:
sudo apt update
Step 2. Install iperf3 package:
sudo apt install iperf3
Step 3. Verify iperf3 is installed:
iperf3 -v
You should see output like:
iperf 3.1.3
Step 4. To start iperf3 in server mode:
iperf3 -s
Step 5. To start iperf3 in client mode, connect to a server IP:
iperf3 -c SERVER_IP
Replace SERVER_IP with the IP address of your iperf3 server.
Fun fact, you can even run iperf directly on some networking equipment such as Cisco’s Cat9k series switches.
Run iPerf
To test network throughput between two computers using iPerf, you will need to set up one computer as the iPerf server and the other as the iPerf client. You do this by specifying command-line parameters to indicate which system will assume the role of the server and which will become the client.

On the iPerf Server:
Step 1. Open a command prompt or terminal and navigate to the folder containing iperf3.exe.
C:\Users\Chase>cd C:\TEMP\
C:\TEMP>dir
Volume in drive C has no label.
Volume Serial Number is C44B-B620
Directory of c:\TEMP
08/23/2023 03:08 PM <DIR> .
08/23/2023 03:08 PM 3,539,372 cygwin1.dll
08/23/2023 03:08 PM 468,748 iperf3.exe
2 File(s) 4,008,120 bytes
1 Dir(s) 567,597,051,904 bytes free
C:\TEMP>
Step 2. Type the command iperf3 -s to start the iPerf server.
C:\TEMP\iperf3 -s
-------------------------------------------------------------------
Server listening on 5201
-------------------------------------------------------------------
Step 3. The server will display “server listening on 5201” when ready.
On the iPerf Client:
Step 1. Open a command prompt or terminal and navigate to the iperf3 executable.
Step 2. Type iperf3 -c SERVER-IP-OR-NAME to start the iPerf client, replacing SERVER-IP-OR-NAME with the IP address or hostname of the iPerf server.
C:\TEMP\iperf3 -c 10.2.0.10 Connecting to host 10.2.0.10, port 5201 [ 4] local 10.2.0.89 port 32777 connected to 10.2.0.10 port 5201 [ ID] Interval Transfer Bandwidth [ 4] 0.00-1.00 sec 109 MBytes 916 Mbits/sec
The test will run for 10 seconds by default and display results when finished. If you’re on a windows machine you can open Task Manager and see the bandwidth utilization on the performance tab.

Interpreting iPerf Test Results
The iPerf output will display report intervals and throughput information. Key stats:
- Interval – The periodic reporting interval.
- Transfer – The bytes transferred during this interval.
- Bandwidth – The throughput measured over this interval.
- Transfer Total – Total bytes transferred and the average bandwidth over the whole test.
- Bandwidth Average – Average throughput throughout the duration of the test.

Useful iPerf Options
iPerf comes with multiple command switches you can use for adjusting settings and performing various tests. Here are some common iPerf options to tweak your throughput tests:
- -i – Sets the interval time between periodic bandwidth reports in seconds. Useful for longer tests.
- -t – Sets the total time in seconds to transmit for. Default is 10 seconds.
- -p – Changes the listening port on the server..
- -u – Use UDP instead of TCP.
- -b – Limit bandwidth to a specified amount. Useful for not saturating a network.
- -R – Reverse direction – server sends data, client receives.
- -bidir – Bidirectional – data transmitted from both server and client in the same test.
See the official documentation or ‘iperf3 –help‘ for the complete list of options.
C:\TEMP> iperf3 --help
Usage: iperf [-s|-c host] [options]
iperf [-h|--help] [-v|--version]
Server or Client:
-p, --port # server port to listen on/connect to
-f, --format [kmgKMG] format to report: Kbits, Mbits, KBytes, MBytes
-i, --interval # seconds between periodic bandwidth reports
-F, --file name xmit/recv the specified file
-B, --bind <host> bind to a specific interface
-V, --verbose more detailed output
-J, --json output in JSON format
--logfile f send output to a log file
-d, --debug emit debugging output
-v, --version show version information and quit
-h, --help show this message and quit
Server specific:
-s, --server run in server mode
-D, --daemon run the server as a daemon
-I, --pidfile file write PID file
-1, --one-off handle one client connection then exit
Client specific:
-c, --client <host> run in client mode, connecting to <host>
-u, --udp use UDP rather than TCP
-b, --bandwidth #[KMG][/#] target bandwidth in bits/sec (0 for unlimited)
(default 1 Mbit/sec for UDP, unlimited for TCP)
(optional slash and packet count for burst mode)
-t, --time # time in seconds to transmit for (default 10 secs)
-n, --bytes #[KMG] number of bytes to transmit (instead of -t)
-k, --blockcount #[KMG] number of blocks (packets) to transmit (instead of -t or -n)
-l, --len #[KMG] length of buffer to read or write
(default 128 KB for TCP, 8 KB for UDP)
--cport <port> bind to a specific client port (TCP and UDP, default: ephemeral port)
-P, --parallel # number of parallel client streams to run
-R, --reverse run in reverse mode (server sends, client receives)
-w, --window #[KMG] set window size / socket buffer size
-M, --set-mss # set TCP/SCTP maximum segment size (MTU - 40 bytes)
-N, --no-delay set TCP/SCTP no delay, disabling Nagle's Algorithm
-4, --version4 only use IPv4
-6, --version6 only use IPv6
-S, --tos N set the IP 'type of service'
-Z, --zerocopy use a 'zero copy' method of sending data
-O, --omit N omit the first n seconds
-T, --title str prefix every output line with this string
--get-server-output get results from server
--udp-counters-64bit use 64-bit counters in UDP test packets
[KMG] indicates options that support a K/M/G suffix for kilo-, mega-, or giga-
Now, let’s step through a few common examples of using iPerf to test network bandwidth.
Practical iPerf Examples
Here are a few examples that provide a mix of TCP and UDP tests, with options to adjust duration, direction, bandwidth, ports, and parallel streams.
Example 1. Basic iperf3 TCP test
Run a simple 10 second TCP test between iperf3 server and client.
Command:
Server: iperf3 -s
Client: iperf3 -c SERVER_IP
Example 2. 60 second TCP test
Extend the test duration to 60 seconds.
Command:
Server: iperf3 -s
Client: iperf3 -c SERVER_IP -t 60
Example 3. UDP test
Switch to UDP instead of TCP.
Command:
Server: iperf3 -s
Client: iperf3 -c SERVER_IP -u
Once the server receives a udp packet from the client it will switch to listening on udp.
Example 4. Reverse direction
Reverse the direction so the server sends and client receives data.
Command:
Server: iperf3 -s
Client: iperf3 -c SERVER_IP -R
Example 5. Limit bandwidth
Limit bandwidth to 50 megabits per second.
Command:
Server: iperf3 -s
Client: iperf3 -c SERVER_IP -b 50M
By default iPerf target bandwidth for UDP connections is 1Mbps, and the default target bandwidth for TCP connections is unlimited. It’s a good idea to set a custom bandwidth limit when testing so you don’t saturate the links and bring down the network (unless that’s your intention).
Example 6. Change port
Use port 5002 instead of default 5201.
Command:
Server: iperf3 -s -p 5002
Client: iperf3 -c SERVER_IP -p 5002
Notice that the port needs to be changed on both the server and the client for the connection to work.
Example 7. Parallel streams
Use 5 parallel streams.
Command:
Server: iperf3 -s
Client: iperf3 -c SERVER_IP -P 5
Example 8. Change interval
Set the test interval to 5 seconds.
Command:
Server: iperf3 -s
Client: iperf3 -c SERVER_IP -i 5
When changing the interval, it’s a good idea to change the test time as well if you want to get much data.
Use cases for using iPerf
iPerf has come in handy numerous times for me as a Network Engineer. Off the top of my head some of the things I’ve used iPerf for that were particular handy have been:
- Running iPerf between VMs or systems in different data centers to test latency and throughput
- Verifying I was getting the bandwidth we were paying for from our ISP
- Testing the speed between wireless clients and access points
- Benchmarking NAS and SAN performance
- Generate TCP and UDP traffic to load test applications and infrastructure
- Checking the impact of network or firewall changes
- Troubleshooting slow networks
- Checking for packet loss ( UDP tests will show packet loss percentage if there is any)
- Showing clients actual measured throughput during a site visit
What about you? Have any interesting use cases where iPerf has come in handy for you?
Recommended Tool: ManageEngine OpManager

- Multi-vendor Network Monitoring
- Simple Installation & Setup
- Intuitive UI
- Complete Visibility
- Intelligent Detections
- Easy Resolutions
Network Engineer III
I am a Senior Network Engineer who has spent the last decade elbow deep in enterprise System Administration and Networking in the local government and energy sectors. I can usually be found trying to warm up behind the storage arrays in the datacenter.
This article describes how to setup iPerf server and client on both Windows and Linux machine.
Table of Contents
- Solution
- Installing iPerf in a Windows machine.
- Installing iPerf in a Linux Machine.
- Windows as an iPerf Server.
- Windows as an iPerf client.
- Linux as an iPerf server.
- Linux as an iPerf client.
- FortiGate as an iPerf client.
Solution
Installing iPerf in a Windows machine.
Download the iPerf3 installer from: https://iperf.fr/iperf-download.php
Extract the iPerf3 installer to a folder.
Installing iPerf in a Linux Machine.
Execute yum install iperf3 command:
Windows as an iPerf Server.
Step 1: Open a command prompt.
Step 2: Navigate to the iperf folder location.
Step 3: Run the command: iperf3.exe -s
Windows as an iPerf client.
Step 1: Open a command prompt.
Step 2: Navigate to the iperf folder location.
Step 3: Run the command: iperf3.exe -c 161.142.100.30, where the IP address set is the iperf server’s.
Linux as an iPerf server.
Step 1: Open a Terminal.
Step 2: Execute the command: iperf3 -s
Linux as an iPerf client.
Step 1: Open a Terminal.
Step 2: Execute the command: iperf3 -c 192.168.100.253
It is possible to change protocol, ports among other settings of iPerf.
Note: FortiGate can only be iPerf client.
