Storage Spaces Direct (S2D) – новая технология распределенного хранения данных, представленная в Windows Server 2016. Благодаря использованию Storage Spaces Direct локальные диски нескольких серверов можно организовать в отказоустойчивое, масштабируемое хранилище, защищенное от выхода из строя как отдельных дисков, так и целых серверов. Цена такого «программного» хранилища получается значительно меньше, чем стоимость организации полноценного SAN или NAS, а за счет простого масштабирования (до 16 серверов и 400 дисков) и возможности использовать различных накопителей (в том числе SSD и NVMe) можно обеспечить значительную производительность.
Содержание:
- Что такое Storage Spaces Direct (S2D)
- Требования к Storage Spaces Direct
- Включаем Storage Spaces Direct
Что такое Storage Spaces Direct (S2D)
S2D является дальнейшим развитием технологии Storage Spaces и позволяет объединить локальные диски узлов (серверов) кластер Hyper-V в пулы хранения (Storage Pool). На данных пулах можно создать виртуальные тома (диски) и использовать их в качестве общего тома кластера Cluster Shared Volume (CSV) для хранения файлов виртуальных машин Hyper-V и файловых шар SOFS-серверов. При необходимости расширить размер хранилища достаточно добавить в S2D новый сервер или накопитель. По сути, технология Storage Spaces Direct является ответом Microsoft на VMware vSAN.
Требования к Storage Spaces Direct
В S2D поддерживаются следующие типы устройств хранения:
- Обычные HDD диски (SAS)
- SATA / SAS SSD диски
- NVMe (Non-Volatile Memory Express) — SSD диски, подключенные не через классический интерфейс SATA/SAS, а через более скоростную шину PCI Express
В дальнейшем разные типы дисков можно комбинировать в различные массивы (по скорости и емкости), например, логично расположить кэш и транзакционные логи приложений на скоростных NVMe SSD, медленные и недорогие диски лучше использовать для хранения больших файлов, доступ к которым не требует повышенной производительности и т.д.
Для работы S2D нужно организовать отказоустойчивый кластер, к узлам которого выдвигаются следующие требования:
Требования к узлам кластера S2D
- Редакция Windows Server 2016 — DataCenter
- На серверах нужно установить следующие компоненты: роли Hyper-V, File Services и фичу Failover Clustering
Примечание. Не забудьте отключить SMB 1:
Remove-WindowsFeature –Name FS-SMB1 -Verbose -Restart - Как минимум два сервера в кластере (в идеале не менее 4 для обеспечения высокой отказоустойчивости)
- Наличие дисков. Помимо системного должен иметь как минимум один физический диск на каждом узле. Все диски, которые планируется добавить в хранилище Storage Spaces Direct должны быть не размечены (не должны быть разбиты и не содержать таблицы разделов)
Итак, предполагаем, что у нас уже собран отказоустойчивый кластер из двух серверов с Windows Server 2016 (можно собрать такой кластер даже в рабочей группе).
Примечание. Если в кластере четное число серверов, придется настроить ресурс-свидетель. Если количество узлов нечетное – свидетель не нужен.
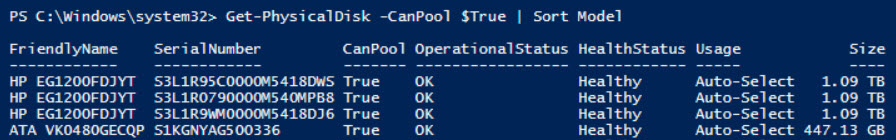
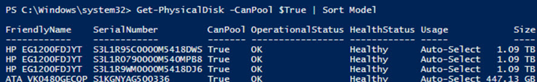
Перед тем, как включить Storage Spaces Direct, проверьте, что ваши диски можно объединить в такой пул.
Get-PhysicalDisk –CanPool $True | Sort Model
Включаем Storage Spaces Direct
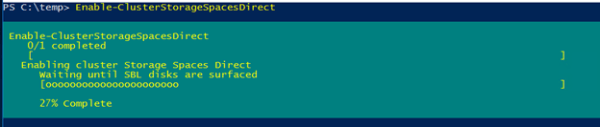
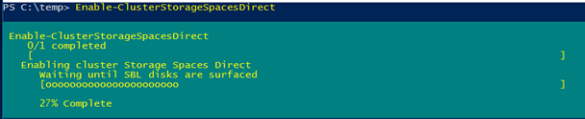
Активируем S2D с помощью командлета:
Enable-ClusterStorageSpacesDirect
Командлет отрабатывает довольно долго (около 10 минут), в течении которых будет проанализированы все доступные диски и их производительность, и автоматически создан кластерный пул. Также автоматически создаются два тира: Performance и Capacity с разным типом отказоустойчивости хранения: mirror и parity соответственно.
Всего поддерживаются 3 типа организации отказоустойчивого хранения данных:
- Mirrored (3) – данные синхронно реплицируются между 3 (или 2 в минимальной конфигурации) узлами. Высокая скорость чтения обеспечивается распределением операции между всеми серверами.
- Parity (2) – данные с хранением четности распределены между разными дисками. Данные хранятся более эффективно, т.к. не надо как в первом случае хранить несколько копий одних и тех же данных.
- Tiered (1) – используется комбинация обоих техник.
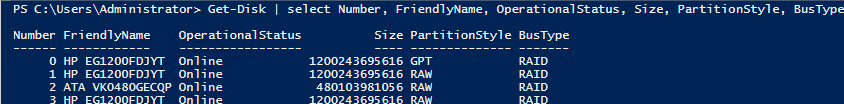
Примечание 1. В том случае, если при выполнении команды Enable-ClusterS2D появится ошибка «no disks with supported bus types found to be used for S2D», скорее всего тип шины (BusType) ваших дисков – RAID (что с точки зрения S2D – неподдерживаемая конфигурация). Проверим тип шины
Get-Disk | select Number, FriendlyName, OperationalStatus, Size, PartitionStyle, BusType | sort Number | ft -AutoSize
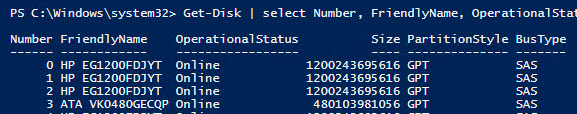
Так и есть – во всех случаях это RAID. Решение — обновить драйверы/ firmware контроллеров (в случае серверов HP установить последний HPE Support Pack). Проверим тип BusType еще раз (теперь он сменился на SAS).
Кроме того, есть небольшой трюк позволяющий в реестре изменить тип шины на SATA для нужного типа контроллера:HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\arcsas\Parameters
«BusType»=dword:0000000b (вместо 00000008)Другие примеры использования командлетов PowerShell для управления локальными дисками приведены в статье Управление дисками и разделами из PowerShell.
Примечание 2. Если в массиве обнаружен диск типа дисков SSD, NVMe, он автоматически используется в качестве диска для хранения кэша. Если таких дисков нет, в процессе создания S2D будут появляться предупреждения. Можно отключить кэш с помощью параметра
-CacheState Disabled
.
Откроем консоль управления кластером и убедимся, что в разделе Storage новый появился Cluster Pool 1.
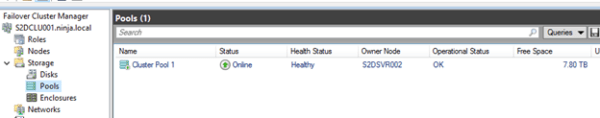
Выбрав пул, можно увидеть из каких дисков он состоит.
В случае необходимости, имя пула можно изменить:
Set-StoragePool –FriendlyName “Cluster Pool 1” –NewFriendlyName “S2D”
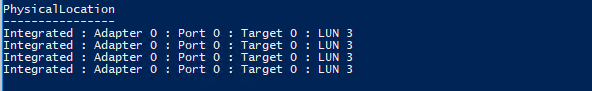
Если нужно создать том из определенных дисков, можно воспользоваться к примеру, такой командой. Сначала выбираем все диски с LUN 3, а затем собираем из них пул.
$HDDs = Get-PhysicalDisk | ? PhysicalLocation -like "*LUN 3"
New-StoragePool -StorageSubSystemFriendlyName *Cluster* -FriendlyName S2DPool -ProvisioningTypeDefault Fixed -PhysicalDisk $HDDs
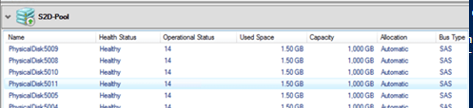
Вывести список дисков в пуле:
Get-StoragePool -FriendlyName S2D | Get-PhysicalDisk | ft PhysicalLocation
Добавить в пул новый диск:
$HDDs = Get-PhysicalDisk | ? PhysicalLocation -like "*LUN 4"
Add-PhysicalDisk -PhysicalDisks $HDDs -StoragePoolFriendlyName S2D
Диски, помеченные как S2D, в консоли управления дисками более не отображаются, это нормально.
При наличии разнородных накопителей можно использовать тиринг (не обязательно). Тир типа зеркало из SSD дисков создается так:
New-StorageTier -StoragePoolFriendlyName S2D -FriendlyName "Mirror_Tier" -MediaType SSD -ResiliencySettingName Mirror
Тир из обычных HDD с хранением четности:
New-StorageTier -StoragePoolFriendlyName S2D -FriendlyName "Parity_Tier" -MediaType HDD -ResiliencySettingName Parity
Теперь можно создать том CSV (Cluster Shared Volume):
New-Volume –StoragePoolFriendlyName S2D –FriendlyName CSV001 –PhysicalDiskRedudancy 2 -FileSystem CSVFS_ReFS -Size 200GB
Список томов и типом избыточности можно вывести так
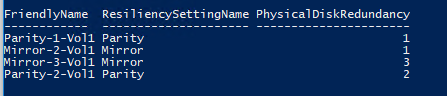
Get-VirtualDisk | ft FriendlyName, ResiliencySettingName, PhysicalDiskRedundancy
Новый CSV том появится в консоли управления дисками.
Данный том можно использовать для размещения виртуальных машин Hyper-V или сетевого хранилища Scale-out File Server.
Итак, при использовании Storage Spaces Direct из нескольких серверов с локальными дисками можно с легкостью создать программное сетевое хранилище данных. За счет технологии S2D обеспечивается как защита от одновременного выхода из строя любых двух дисков или двух серверов (4+ нодовый кластер). Кластер S2D автоматически запускает процесс перераспределения данных между оставшимися устройствами в случае обнаружения неполадок с дисками или серверами. В тестовой среде можно убедится, что при отключении двух любых дисков хранилище продолжает быть доступным, а ВМ, запущенные на нем штатно работают. Процедура замены неисправного диска в хранилище S2D описана в следующей статье.
Copilot is your AI companion
Always by your side, ready to support you whenever and wherever you need it.
Storage Spaces Direct Management Pack for Windows Server 2016 and above
Storage Spaces Direct Management Pack for Windows Server 2016 and above
Important! Selecting a language below will dynamically change the complete page content to that language.
-
File Name:
Storage Spaces Direct MP Guide.docx
Microsoft System Center Management Pack for StorageSpacesDirect.msi
Microsoft SC MP for Storage Spaces Direct.TRK.msi
Microsoft SC MP for Storage Spaces Direct.SVE.msi
Microsoft SC MP for Storage Spaces Direct.RUS.msi
Microsoft SC MP for Storage Spaces Direct.PTG.msi
Microsoft SC MP for Storage Spaces Direct.PTB.msi
Microsoft SC MP for Storage Spaces Direct.PLK.msi
Microsoft SC MP for Storage Spaces Direct.NLD.msi
Microsoft SC MP for Storage Spaces Direct.KOR.msi
Microsoft SC MP for Storage Spaces Direct.JPN.msi
Microsoft SC MP for Storage Spaces Direct.ITA.msi
Microsoft SC MP for Storage Spaces Direct.HUN.msi
Microsoft SC MP for Storage Spaces Direct.FRA.msi
Microsoft SC MP for Storage Spaces Direct.ESN.msi
Microsoft SC MP for Storage Spaces Direct.DEU.msi
Microsoft SC MP for Storage Spaces Direct.CSY.msi
Microsoft SC MP for Storage Spaces Direct.CHT.msi
Microsoft SC MP for Storage Spaces Direct.CHS.msi
File Size:
496.9 KB
1.5 MB
540.0 KB
536.0 KB
544.0 KB
536.0 KB
536.0 KB
544.0 KB
536.0 KB
552.0 KB
544.0 KB
536.0 KB
544.0 KB
536.0 KB
536.0 KB
540.0 KB
536.0 KB
536.0 KB
536.0 KB
The System Center Operations Manager (SCOM) Management Pack for Storage Spaces Direct on Windows Server 2016 and above that provides a straightforward monitoring solution for your Storage Spaces Direct configurations. It’s designed for use with Windows Server 2016 and later versions, extending SCOM’s monitoring capabilities to various components of your storage infrastructure.
Key Features:
- Storage Pool Monitoring: Track the health and performance of storage pools.
- Storage Node Monitoring: Monitor the operational status of storage nodes.
- Physical Disk Monitoring: Keep an eye on the health and availability of physical disks.
- File Shares Monitoring: Ensure file shares are accessible and performing well.
- Volumes Monitoring: Monitor the status and performance of volumes.
- Storage Subsystems Monitoring: Gain an overview of the storage subsystems’ performance and health.
This Management Pack integrates seamlessly with System Center Operations Manager (SCOM), aiding administrators in keeping Storage Spaces Direct environments well-monitored and managed.
-
Supported Operating Systems
Windows Server 2016, Windows Server 2019, Windows Server 2022
Supported SCOM Versions
- System Center Operations Manager 2022
- System Center Operations Manager 2019
- System Center Operations Manager 2016
Technology description
Storage Spaces enables cost-effective, highly available, scalable, and flexible storage solutions for business-critical (virtual or physical) deployments. Storage Spaces delivers sophisticated storage virtualization capabilities, which empower customers to use industry-standard storage for single computer and scalable multi-node deployments. It is appropriate for a wide range of customers, including enterprise and cloud hosting companies, which use Windows Server for highly available storage that can cost-effectively grow with demand.
With Storage Spaces the Windows storage stack has been fundamentally enhanced to incorporate two new abstractions:
- Storage pools. A collection of physical disks that enable you to aggregate disks, expand capacity in a flexible manner, and delegate administration.
- Storage spaces. Virtual disks created from free space in a storage pool. Storage spaces have such attributes as resiliency level, storage tiers, fixed provisioning, and precise administrative control.
Storage Spaces is integrated with failover clustering for high availability, and it’s integrated with cluster shared volumes (CSV) for scale-out file server deployments. You can manage Storage Spaces through:
- System Center Virtual Machine Manager
- Failover Cluster Manager
- Server Manager
- Windows PowerShell
- Windows Management Instrumentation (WMI)
Important functionality Storage Spaces includes the following features:
- Storage pools. Storage pools are the fundamental building blocks for Storage Spaces. Storage administrators are already familiar with this concept, obviating the need to learn a new model. They can flexibly create storage pools based on the needs of the deployment. For example, given a set of physical disks, an administrator can create one pool (by using all the available physical disks) or multiple pools (by dividing the physical disks as required). Furthermore, to maximize the value from storage hardware, the administrator can combine hard disks and solid-state drives (SSDs) in the same pool, using storage tiers to move frequently accessed portions of files to SSD storage, and using write-back caches to buffer small random writes to SSD storage. Pools can be expanded dynamically by simply adding additional disks, thereby seamlessly scaling to cope with data growth.
- Resilient storage. Storage Spaces provides three storage layouts (also known as resiliency types):
- Mirror. Writes data in a stripe across multiple disks while also writing one or two extra copies of the data. Use the mirror layout for most workloads – it helps protect your data from disk failures and provides great performance, especially when you add some SSDs to your storage pool and use storage tiers.
- Parity. Writes data in a stripe across physical disks while also writing one or two copies of parity information. Use the parity layout for archival and streaming media workloads, or other workloads where you want to maximize capacity and you’re OK with lower write performance.
- Simple (no resiliency). Writes data in a stripe across physical disks without any extra copies or parity information. Because the simple layout doesn’t provide any protection from disk failures, use it only when you require the highest performance and capacity and you’re OK with losing or recreating the data if a disk fails. You can also use the simple layout when your application provides its own data protection.
Additionally, Storage Spaces can automatically repair mirror and parity spaces in which a disk fails by using dedicated disks that are reserved for replacing failed disks (hot spares), or more rapidly by using spare capacity on other disks in the pool. Storage Spaces also includes background scrubbing and intelligent error correction to allow continuous service availability despite storage component failures. In the event of a power failure or cluster failover, the integrity of data is preserved so that recovery happens quickly without lost data.
- Continuous availability. Storage Spaces is integrated with failover clustering, which allows it to deliver continuously available service deployments. One or more pools can be clustered across multiple nodes within a single cluster. Storage spaces are accessed by one node, and the storage will seamlessly fail over to a different node when necessary (in response to failure conditions or due to load balancing). Integration with CSVs permits scale-out access to data.
- Storage tiers. Storage tiers combine the best attributes of SSDs and hard disk drives (HDDs) by letting you create virtual disks with two tiers of storage – an SSD tier for frequently accessed data, and a HDD tier for less-frequently accessed data. New data is generally written to the HDD tier and then Storage Spaces transparently moves data at a sub-file level between the two tiers based on how frequently data is accessed. As a result, storage tiers can dramatically increase performance for the most used (“hot”) data by moving it to SSD storage, without sacrificing the ability to store large quantities of data on inexpensive HDDs.
- Write-back cache. Storage Spaces in Windows Server 2016 supports creating a write-back cache that uses a small amount of space on existing SSDs in the pool to buffer small random writes. Random writes, which often dominate common enterprise workloads, are directed to SSDs and later are written to HDDs.
- Operational simplicity. The Windows Storage Management API, WMI, and Windows PowerShell permit full scripting and remote management. Storage Spaces can also be easily managed through the File and Storage Services role in Server Manager and through System Center Virtual Machine Manager. Storage Spaces also provides notifications when the amount of available capacity in a storage pool hits a configurable threshold.
- Multitenancy. Administration of storage pools can be controlled through access control lists (ACLs) and delegated on a per-pool basis, thereby supporting hosting scenarios that require tenant isolation. Storage Spaces follows the familiar Windows security model; therefore, it can be fully integrated with Active Directory Domain Services.
For this Demo, I’m using my DC-CLOUD.Windows.ae server.
So lets get started. be patient.. this going to be a long step by step,
01 – Create a storage from six disks on Hyper-v server. (Please Refer to the Pictures)
1 – Hard Drive and click Add.

2 – Now we need to create a new virtual hard disk. Click new to create new virtual harddisk.

3 – Just Click Next.

4 – You have three options to choose disk type – Fixed Size, dynamically expanding and Differencing. In this case, I am going with dynamically.

5 – Specify Name and location.


6 – You can create a blank virtual hard disk or copy the contents of an existing physical disk.

7 – Summary of your new virtual hard disk which we are creating and click
Okay below to create your new virtual hard disk.

8 – Once Hyper-V completed it process of creating new virtual hard disk, this is how you should see the end result.

02 – Create a storage pool from six disks that are attached to the server
1 – On Dc-CLOUD, click Start, and then click Server Manager.

2 – In Server Manager, in the left pane, click File and Storage Services, and then in the Servers pane, click Storage Pools.

3 – In the STORAGE POOLS pane, click TASKS, and then, in the TASKS drop-down list, click New Storage Pool.

4 – In the New Storage Pool Wizard, on the Before you begin page, click Next.

5 – On the Specify a storage pool name and subsystem page, in the Name text box, type
StoragePool1, and then click Next.

6 – On the Select physical disks for the storage pool page, select the first six disks in the Physical disks list and then click Next.


7 – On the Confirm selections page, click Create.

8 – On the View results page, wait until the task completes, and then click Close.

03 – Create a three-way mirrored virtual disk (need at least five physical disks)
1 – On DC-CLOUD, in Server Manager, in the Storage Pools pane, click StoragePool1.

2 – In the VIRTUAL DISKS pane, click TASKS, and then, from the TASKS drop-down list, click New Virtual Disk.

3 – Click Okay.

4 – In the New Virtual Disk Wizard, on the Before you begin page, click Next.

5 – On the Specify the virtual disk name page, in the Name text box, type Mirrored Disk, and then click Next.

6 – On the Specify enclosure resiliency page, click Next.

7 – On the Select the storage layout page, in the Layout list, click Mirror, and then click Next.

8 – On the Configure the resiliency settings page, click Three-way mirror, and then click Next.

9 – On the Specify the provisioning type page, click Thin, and then click Next.

10 – On the Specify the size of the virtual disk page, in the Specify size text box, type 10, and then click Next.

11 – On the Confirm selections page, click Create.

12 – On the View results page, wait until the task completes.

Ensure that the Create a volume when this wizard closes check box is selected, and then click Close.
13 – In the New Volume Wizard window, on the Before you begin page, click Next.

14 – On the Select the server and disk page, in the Disk pane, click the Mirrored Disk virtual disk, and then click Next.

15 – On the Specify the size of the volume page, click Next to confirm the default selection.

16 – On the Assign to a drive letter or folder page, in the Drive letter drop-down list, ensure that E is selected, and then click Next.

17 – On the Select file system settings page, in the File system drop-down list, click ReFS, in the Volume label text box, type New Volume, and then click Next.

18 – On the Confirm selections page, click Create.

19 – On the Completion page, wait until the creation completes, and then click Close.

04 – Copy a file to the volume, and verify it is visible in File Explorer
1 – On DC-CLOUD, click Start, on the Start screen, type command prompt, and then press Enter.

2 – When you receive the command prompt, type the following command, and then press Enter:
Copy C:\windows\system32\write.exe E:\
3 – Close Command Prompt.

4 – On the taskbar, click the File Explorer icon.

5 – In the File Explorer window, in the navigation pane, click New Volume (E:). and Verify that write.exe is visible in the file list.

Close File Explorer.
05 – Remove a physical drive to simulate drive failure (Please Refer to the Pictures)
1 – On the host computer, open Hyper-V Manager. the Virtual Machines pane, right-click DC-Server=Win 2016, and then click Settings.

2 – In Settings for DC-Server=Win 2016, in the Hardware pane, click the hard drive that begins with DC-Server=Win 2016–Hard Disk 06.

4 – In the Hard Drive pane, click Remove, click OK, and then click Continue.



06 – Verify that the file is still available
1 – Switch to DC-CLOUD SERVER, and On the taskbar, click the File Explorer icon.

2 – In the File Explorer window, in the navigation pane, click New Volume (E:).

In the file list pane, verify that write.exe is still available. then Close File Explorer.
3 – In Server Manager, in the STORAGE POOLS pane, on the menu bar, click Refresh “Storage Pools”.

4 – In the VIRTUAL DISK pane, right-click Mirrored Disk, and then click Properties.

5 – In the Mirrored Disk Properties dialog box, in the left pane, click Health.

Notice that the Health Status indicates a warning. The Operational Status should indicate one or more of the following: Incomplete, Unknown, or Degraded.
07 – Add a new disk to the storage pool and remove the broken disk
1 – On DC-CLOUD, in Server Manager, in the STORAGE POOLS pane, on the menu bar, click Refresh “Storage Pools”, In the STORAGE POOLS pane, right-click StoragePool1, and then click Add Physical Disk.

2 – In the Add Physical Disk window, click the first disk in the list, and then click OK.

3 – Right-click Start, and then click Windows PowerShell (Admin).

4 – In Windows PowerShell, type the following command, and then press Enter:
Get-PhysicalDisk
5 – Note the FriendlyName for the disk that shows an OperationalStatus of Lost Communication.

6 – In Windows PowerShell, type the following command, and then press Enter:
$Disk = Get-PhysicalDisk -FriendlyName “diskname”

Replace diskname with the name of the disk that you noted in Step 6.
7 – In Windows PowerShell, type the following command, and then press Enter:
Remove-PhysicalDisk -PhysicalDisks $disk -StoragePoolFriendlyName StoragePool1

8 – In Windows PowerShell, type A, and then press Enter.

9 – In Server Manager, in the STORAGE POOLS pane, on the menu bar, click the Refresh “Storage Pools” button to see the warnings disappear.

Results: After completing this exercise, you will have successfully created a storage pool and added five disks to it. Additionally, you should have created a three-way mirrored, thinly-provisioned virtual disk from the storage pool. You also should have copied a file to the new volume and then verified that it is accessible. Next, after removing a physical drive, you should have verified that the virtual disk was still available and that you could access it. Finally, you should have added another physical disk to the storagepool.
that’s all for now.., any Doubts type a commend.. 🙂
Storage Spaces Direct (S2D) is a new distributed data storage technology that appeared in Windows Server 2016. Due to Storage Spaces Direct, you can turn local drives of several servers into fault-tolerant, scalable storage protected from failure of both separate disks and entire servers. The cost of this software storage is much less than that of a SAN or NAS due to simplified scaling (up to 16 servers and 400 drives) and the opportunity to use different drives (including SSDs and NVMes) enables significant performance.
Contents:
- What Is Storage Spaces Direct (S2D)
- Storage Spaces Direct Requirements
- How to Enable Storage Spaces Direct
- How to Replace a Failed Physical Disk in Storage Spaces Direct
What Is Storage Spaces Direct (S2D)
S2D is the further development of Storage Spaces technology and allows to merging the local drives of the Hyper-V cluster nodes into Storage Pools. You can create virtual volumes (disks) on these drives and use them as common Cluster Shared Volume (CSV) to store Hyper-V virtual machines files and SOFS file shares. If you need to expand the storage size, just add a new server or drive to S2D. In general, Storage Spaces Direct is the answer of Microsoft to VMware vSAN.
Storage Spaces Direct Requirements
S2D supports the following storage device types:
- Common HDDs (SAS);
- SATA / SAS SSDs;
- NVMe (Non-Volatile Memory Express) are SSDs connected through a faster PCI Express bus instead of the classic SATA/SAS interface.
Later different types of disks can be combined in various arrays (by speed or size). For example, it is reasonable to locate the cache and application transaction logs on faster NVMe SSDs, and it is better to use slower and less expensive disks to store large files that do not require high performance to access them, etc.
For S2D to work, you have to create a failover cluster with the following requirements to its nodes.
Requirements for S2D cluster nodes:
- Windows Server 2016 Datacenter edition;
- The following components must be installed on the servers: Hyper-V, File Services roles, and Failover Clustering feature.
Note. Don’t forget to disable SMB 1.0:
Remove-WindowsFeature –Name FS-SMB1 -Verbose –Restart - At least two servers in a cluster (ideally, at least 4 hosts to ensure high fault tolerance);
- In addition to the system drive, there must be at least one physical disk in each node. All disks that you are going to add to the Storage Spaces Direct must be unformatted (i.e. not partitioned and containing no partition table).
Suppose that you have created a failover cluster of two servers running Windows Server 2016 (you can create it even in a workgroup).
Note. If there is an even number of nodes in a cluster, you will have to configure a witness node. If there is an uneven number of nodes, you don’t need a witness.
Before enabling Storage Spaces Direct, make sure that your disks can be joined into this pool.
Get-PhysicalDisk –CanPool $True | Sort Model
How to Enable Storage Spaces Direct
Activate S2D using the following cmdlet:
Enable-ClusterStorageSpacesDirect
The cmdlet is being processed long enough (about 10 minutes), all available disks and their performance will be analyzed and a cluster pool will automatically be created. Also, two tiers are created automatically: Performance and Capacity, having different failover types: mirror and parity, respectively.
3 types of providing fault tolerance of the data storage are supported:
- Mirrored (3) – the data are synchronously replicated between 3 (or 2 in minimal configuration) nodes. High reading speed is reached due to distributing the operation between all servers.
- Parity (2) – the data with parity information are distributed among different disks. Data storage is more efficient since you don’t need to store several copies of the same data.
- Tiered (1) – a combination of both above mentioned methods.
Note 1. If there appears an error “no disks with supported bus types found to be used for S2D” when running the Enable-ClusterS2D command, the bus type (BusType) of your disks is likely RAID (it is an unsupported configuration from S2D). Let’s check the bus type:
Get-Disk | select Number, FriendlyName, OperationalStatus, Size, PartitionStyle, BusType | sort Number | ft -AutoSize
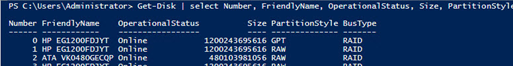
It is true – in all cases it is RAID. The solution is to update the drivers or firmware of the controllers (if you have HP servers, install the latest HPE Support Pack). Check the BusType again. (now it’s changed to SAS).
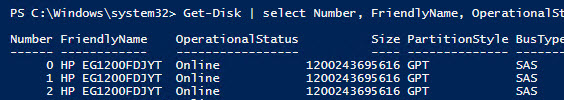
Also, there is a little trick that allows to change the bus type to SATA for the specific type of controller:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\arcsas\Parameters
"BusType"=dword:0000000b (instead of 00000008)
Note 2. If an SSD or NVMe type of disk is detected in the array, it will be automatically used as a cache storage. If there are no such disks, some warnings will appear during S2D creation. You can disable the cache using the -CacheState Disabled parameter.
Open the Failover Cluster Manager and make sure that Cluster Pool 1 has appeared in the Storage section.
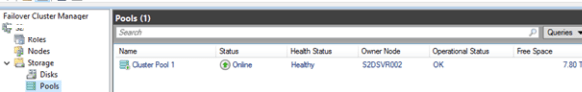
After selecting the pool, you can see what disks it consists of.
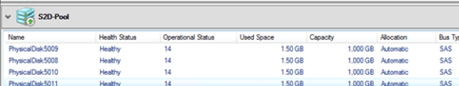
If necessary, the pool name may be changed:
Set-StoragePool –FriendlyName “Cluster Pool 1” –NewFriendlyName “S2D”
If you have to create a volume from the specific disks, you can use this command. First, select all LUN 3 disks and collect them into the pool.
$HDDs = Get-PhysicalDisk | ? PhysicalLocation -like "*LUN 3"
New-StoragePool -StorageSubSystemFriendlyName *Cluster* -FriendlyName S2DPool -ProvisioningTypeDefault Fixed -PhysicalDisk $HDDs
Display the list of disks in the pool:
Get-StoragePool -FriendlyName S2D | Get-PhysicalDisk | ft PhysicalLocation
Add a new disk to the pool:
$HDDs = Get-PhysicalDisk | ? PhysicalLocation -like "*LUN 4"
Add-PhysicalDisk -PhysicalDisks $HDDs -StoragePoolFriendlyName S2D
Disks marked as S2D are not displayed in the Disk Management console anymore, and it is OK.
If you have different types of drives you can use storage tiering (optional). A mirror-type tier of SSDs is created as follows:
New-StorageTier -StoragePoolFriendlyName S2D -FriendlyName "Mirror_Tier" -MediaType SSD -ResiliencySettingName Mirror
A parity tier of common HDDs:
New-StorageTier -StoragePoolFriendlyName S2D -FriendlyName "Parity_Tier" -MediaType HDD -ResiliencySettingName Parity
Now you can create a CSV (Cluster Shared Volume):
New-Volume –StoragePoolFriendlyName S2D –FriendlyName CSV001 –PhysicalDiskRedudancy 2 -FileSystem CSVFS_ReFS -Size 200GB
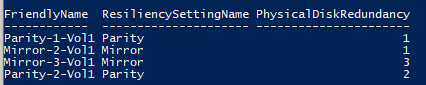
You can display the list of volumes and their redundancy types like this:
Get-VirtualDisk | ft FriendlyName, ResiliencySettingName, PhysicalDiskRedundancy
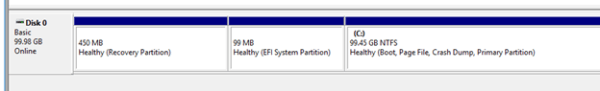
A new CSV will appear in the Disk Management.
This volume can be used to host Hyper-V virtual machines or Scale-out File Server shares.
How to Replace a Failed Physical Disk in Storage Spaces Direct
Check the status of the disks in a S2D pool using PowerShell:
Get-StoragePool *S2D* | Get-PhysicalDisk
Find failed physical drives:
$Disk = Get-PhysicalDisk |? OperationalStatus -Notlike ok
Prevent further write attempts to this disk:
Set-PhysicalDisk -InputObject $Disk -Usage Retired
Remove the failed disk from the storage pool:
Get-StoragePool *S2D* | Remove-PhysicalDisk –PhysicalDisk $Disk
To make it easier to identify a disk in a server rack, enable the LED light of a disk:
Get-PhysicalDisk |? OperationalStatus -Notlike OK | Enable-PhysicalDiskIdentification
Replace a failed disk with a new one.
You can now turn off the backlight:
Get-PhysicalDisk |? OperationalStatus -like OK | Disable-PhysicalDiskIdentification
Make sure that the OS has detected the new disk:
$Disk = Get-PhysicalDisk | ? CanPool –eq True
Add the new disk to a pool:
Get-StoragePool *S2D* | Add-PhysicalDisk –PhysicalDisks $Disk –Verbos
S2D will automatically start the data redistribution between the disks in a cluster.
So, using Storage Spaces Direct of several servers with local disks, you can easily create a software network storage. Due to S2D, fault tolerance of any pair of disks or servers (4+ node cluster) is provided. S2D cluster automatically starts the process of data reallocating between the rest devices if any faults of disks or servers are detected. In the test environment, you can make sure that when you disconnect any two disks, the storage is still available, and VMs on it are running.
Время на прочтение6 мин
Количество просмотров35K
Пока некоторые читатели (да что уж там, и писатели — например, я) наслаждались в отпуске теплыми летними денечками, известный автор нашего англоязычного блога Адам Бертрам подготовил краткий обзор Windows Storage Spaces. В него он включил, в частности, сведения о настройке Windows Storage Spaces на популярных конфигурациях. Перевод его статьи я и предлагаю вашему вниманию.
Во многих дата-центрах и серверных фермах для хранения данных используются HDD и SSD. Статистика, однако, сообщает о том, что после трёх лет работы 10% дисков становятся негодными.
Конечно, те организации, которые заботятся о целостности и сохранности своих данных, держат руку на пульсе, а также отслеживают и другие факторы риска — будь то человеческий фактор, железо или софт. И тут тем, кто работает с Windows-инфраструктурой, могут помочь Windows Storage Spaces. Ведь их RAID-подобная функциональность (то, что мы видим в File Explorer как виртуальные диски) весьма полезна в деле обеспечения резерва мощностей хранения.

Гибкие возможности масштабирования тоже привлекательны: можно объединить 3 и более драйвов в единый сторадж-пул и затем формировать на его основе “стораджики” нужного размера. А поскольку при работе с пулом формируются и сохраняются дополнительные копии для ваших данных, то проблемы с одним из дисков не приведут к потере всего и вся. А если понадобилось больше места? Просто добавь воды еще дисков в пул.
Storage Spaces для Windows 10
— Он забирается на самую высокую сосну и оттуда планирует.
— Ага, простите, что планирует?
— Он прыгает и планирует.
(“День радио”)
Даже если сценарий развертывания, который вы хотите воплотить, входит в число самых популярных, и инструкция к нему коротка и вроде даже сходу понятна, этап подготовки и планирования все равно никто не отменял. Итак:
Если вы используете дисковые пространства Storage Spaces на машине с Windows 10, то рекомендуется обеспечить наличие минимум 2 дисков помимо системного. Эти диски могут быть как встроенными, так и внешними. Поддерживаются SSD; можно комбинировать SATA, USB и SAS.
Количество дисков рассчитывается исходя из того, какой метод обеспечения отказоустойчивости вы хотите применить. Есть вот такие варианты:
-
Simple (простой) — требует наличия минимум двух дисков. Хоть этот метод и дает хорошую производительность, но ничем вам не поможет в случае отказа. Его можно использовать, например, если вы настраиваете storage space для хранения временных данных (например, файлов видео-рендеринга, файлов-черновиков в графических редакторах, и так далее).
-
Mirror (зеркальный) — позволяет сохранять несколько копий данных на случай отказа. Так, Two-way mirror spaces хранят две копии данных, и с ними вы переживете отказ одного из дисков. Для их организации потребуется минимум два диска. Three-way mirror spaces позволят пережить отказ двух дисков, а для их организации потребуется минимум пять. Зато хранить в таких storage spaces можно самые разнообразные данные.
-
Parity (с контролем четности) — рекомендуется для хранения архивных и стриминговых данных. Хранят несколько копий на случай отказа. Если вы хотите обеспечить отказоустойчивость в случае проблемы с одним диском, то в сценарии с Parity spaces вам понадобится минимум три диска, а на случай проблемы с двумя — минимум семь дисков.
После того, как вы все рассчитали и подготовили, можно организовать собственно Storage Spaces. Для этого в Windows 10 нужно выполнить вот такие шаги:
-
Проверить, что диски, которые вы планируете задействовать, у вас подключены.
Важно! Если вы укажете, что в сторадж-пул хотите включить размеченный диск, имейте в виду, что Windows безвозвратно удалит все разделы и файлы на нём. До начала работы сделайте резервную копию всего, что вам дорого на этом диске!
-
Для простоты в поле поиска в панели задач вводим Storage Spaces и из полученного списка выбираем Storage Spaces.
-
Кликаем Create a new pool and storage space.
-
Выберем нужные нам диски и затем кликнем Сreate new storage pool.
-
Указываем имя, буквенное обозначение и файловую систему для нового сторадж пула.
-
На случай сбоя рекомендуется выбрать метод обеспечения отказоустойчивости (Resiliency) как одну из следующих опций: Two-way mirror, Three-way mirror или Parity.
Важно! Помните про количество дисков, которые потребуются в каждом из указанных вариантов, о чем мы говорили выше. Если, допустим, вы предпочтете Two-way mirror, то для нового storage space будет создаваться две копии данных. Так что для такого сценария понадобится минимум два диска (помимо системного).
-
Затем задайте максимальный размер стораджа для Storage Spaces.
Примечание: Можно указать значение, превышающее размер сторадж-пула — когда место будет заканчиваться, вы просто добавите еще один диск.
-
Когда с настройками покончено, нажимаем Create storage space.
Оптимизация работы
Рекомендуется своевременно оптимизировать работу с дисками. Вот что советует делать Microsoft:
При добавлении новых дисков в существующий пул рекомендуется оптимизировать использование диска. При этом некоторые данные будут перемещены на новый диск, чтобы оптимизировать использование емкости пула. Это стандартное действие при добавлении нового диска в обновленный пул в Windows 10: флажок Optimize to spread existing data across all drives будет установлен по умолчанию.
Однако если вы сняли этот флажок или добавили диски до обновления пула, вам нужно вручную оптимизировать использование диска. Для этого в поле поиска на панели задач введите Storage Spaces, выберите Storage Spaces из списка результатов поиска, а затем щелкните Optimize drive usage.
Автономный сервер
Если у вас один отдельно взятый сервер, то для настройки на нем дисковых пространств Storage Spaces есть подробная инструкция от Microsoft, на русском языке и даже с картинкой. Storage Spaces поддерживаются для Windows Server 2019, Windows Server 2016, Windows Server 2012 R2 и Windows Server 2012.
Обратите внимание: до начала настройки нужно обеспечить наличие одного или нескольких пулов, а также проверить конфигурацию на соответствие ряду требований (они перечислены в разделе «Предварительные условия»).
На базе сторадж-пула можно создать несколько виртуальных дисков. (Windows идентифицирует их как обычные диски, которые могут быть отформатированы.)
Для их создания можно использовать File and Storage Services; в настройках можно указать thin provisioning либо fixed provisioning, а также размер. Дополнительные настройки можно задать с помощью команд PowerShell.
Кластеры и Storage Spaces Direct
Если вы работаете с кластером и используете для каждой его ноды СХД с прямым подключением (DAS), то Storage Spaces Direct могут оказаться вполне разумным и эффективным вариантом по сравнению с NAS и SAN. Storage Spaces Direct отличаются хорошей масштабируемостью и возможностями управления. Технология Storage Spaces работает наряду с кэшированием, RDMA и поддержкой СХД для разных уровней (tiers). Помимо этого, поддерживаются диски NVMe.
Storage Spaces Direct поддерживаются для Windows Server 2019 Datacenter, 2016 Datacenter и Insider Preview Builds. Можно создать конвергентное или гипер-конвергентное пространство.
Вкратце, основные этапы развертывания Storage Spaces Direct — это:
-
Развертывание Windows Server — установка и настройка ОС, добавление доменных учеток, настройка ролей и необходимых фич.
-
Настройка сети (этот этап не относится к сценарию развертывания Storage Spaces Direct на виртуальных машинах).
-
Конфигурация собственно Storage Spaces Direct — очистка дисков и разделов, настройка кластеров, настройка Storage Spaces Direct, создание томов, развертывание необходимых виртуальных машин.
-
Для конвергентной инфраструктуры — развертывание масштабируемых файловых серверов, настройка ролей, создание шар, настройка ограниченного делегирования Kerberos.
Все эти этапы очень подробно описаны здесь (на русском языке).
Возможен сценарий, при котором все физические диски содержатся в enclosures с общим доступом — это т.н. JBOD enclosure. Такая инфраструктура должна соответствовать требованиям Windows Certification, а также включать в себя идентичные SAS HBA (имеющие сертификацию Storage Spaces). Такие диски в кластере не должны иметь встроенную функциональность RAID.
Storage Spaces vs. RAID
Как водится, у Windows Storage Spaces и RAID есть свои преимущества и свои недостатки. Об этом уже написана не одна сотня строк (например, здесь). Вкратце:
-
У RAID есть два аспекта: аппаратный и программный — а Windows Storage Spaces, так сказать, является software-driven, настраивается целиком через графический интерфейс или командную строку.
-
Для программных RAID, как и для Storage Spaces отсутствуют ограничения по числу сокетов (у традиционных RAID они есть).
-
ОС по-разному “видит” диски в RAID и в Storage Spaces — диски RAID предстают как цельный юнит (даже если у физических дисков разная емкость), что может приводить к неоптимальному использованию свободного пространства. Для Storage Spaces такой проблемы нет, так как есть доступ к отдельным дискам.
-
Если говорить о производительности, то RAID 0 превосходит Storage Spaces с режимом simple mode примерно вдвое. Однако на скоростях 4K они уже сравнимы. RAID 1 быстрее выполняет последовательные операции чтения, зато Storage Spaces в режиме two-way mirror mode вдвое быстрее выполняет операции записи, нежели RAID 1. Что касается hardware RAID, то операции чтения и записи для них гораздо быстрее, чем Storage Spaces в режиме parity mode.
Ссылки
Общие сведения о дисковых пространствах Storage Spaces
Развертывание Storage Space Direct
Дисковые пространства в Windows 10
Кейс о развертывании Storage Space Direct компанией-провайдером Veeam
