Содержание
- Что такое OEM-лицензия: простыми словами
- Основные преимущества и недостатки OEM-лицензий
- Виды OEM-лицензий:
- OEM_COA (Certificate of Authenticity)
- OEM_SLP (System Locked Pre-installation)
- OEM_Non-SLP
- OEM_COEM (Commercial OEM)
- Подтверждение OEM-лицензии: наклейка COA и другие варианты
- Способы узнать, что ваша Windows — OEM
- Установка и переустановка Windows с OEM-лицензией
- Автоматическая активация
- Повторная при переустановке
- Замена материнской платы и OEM-лицензия: что происходит
- Перенос и продажа ПК: остаётся ли лицензия новому владельцу
- Можно ли купить OEM-лицензию отдельно без ПК
- Ограничения от Microsoft для производителей и сборщиков
- Почему OEM-лицензия такая дешёвая
- Безопасная покупка OEM-лицензий и риски «серых» каналов
- Корпоративное развёртывание и OEM-лицензия: совместимы ли?
- Где купить лицензию Windows 10 OEM
- OEM-лицензии от крупных производителей и сборщиков: различия
- Сколько раз можно активировать OEM-лицензию
- Как удалить OEM-лицензию Windows
- Как удалить OEM-лицензию из BIOS
- Как перенести OEM-лицензию на другой компьютер
- Как узнать OEM-ключ лицензионной Windows
- Как определить OEM или Retail-версию Windows
- Как узнать, вшита ли в BIOS лицензия Windows
- Чем отличается OEM от коробочной версии
Что такое OEM-лицензия
OEM — это сокращение от «Original Equipment Manufacturer», что переводится как «Производитель оригинального оборудования». Если сказать совсем просто, OEM-лицензия — это та, что поставляется вместе с новым компьютером, ноутбуком или готовым системным блоком. Она уже «зашита» производителем и предназначена для использования именно на том «железе», с которым изначально поставлялась.

Зачем вообще покупать лицензию?
- Легальное использование Windows: безопасно, без угроз блокировки.
- Полноценная поддержка от Microsoft: обновления, техподдержка, отсутствие «пиратских» проблем.
- Соблюдение закона: при проверках лицензионное ПО — это спокойствие и уверенность.
Если вам интересно узнать больше об активации, то почитайте статью: Что такое активация Windows и Office.
Читайте тут, если вы ищите способ активации Windows бесплатно.
Основные преимущества и недостатки OEM-лицензий
Как и у любого типа лицензии, у OEM-версии есть сильные стороны и слабые места.
Плюсы OEM-лицензии:
- Низкая стоимость. OEM-версия стоит дешевле розничной (Retail) благодаря отсутствию дополнительных затрат на упаковку, маркетинг и более жёстким условиям использования.
- Предустановленная Windows. Если вы покупаете ноутбук или ПК с уже установленной OEM-лицензией, система, как правило, сразу активирована. Не нужно тратить время и деньги на отдельную установку.
- Полная функциональность. По функционалу OEM не отличается от розничной версии Windows.
- Поддержка от производителя. При приобретении компьютера от крупных брендов (Dell, HP, Lenovo и др.) в комплекте идёт пакет драйверов и фирменных утилит, упрощающих настройку системы.
Минусы OEM-лицензии:
- Привязка к материнской плате. При замене «материнки» без гарантийного случая лицензия формально утрачивает свою силу.
- Отсутствие возможности переноса. OEM-лицензию нельзя (по лицензии Microsoft) легально «отвязать» и перенести на другой компьютер.
- Ограниченная поддержка Microsoft. В ряде случаев при возникновении проблем Microsoft может перенаправить вас к производителю устройства для решения вопросов, связанных с лицензией.
- Сложности при покупке отдельно. OEM-лицензии предназначены для поставки с новым компьютером или для сборщиков (System Builder). Приобретать такую лицензию отдельно бывает затруднительно (и не всегда легально, если речь об OEM для крупных брендов).
Подробнее о том, зачем нужна активация Windows, читайте здесь.
Виды OEM-лицензий: сравнение System Builder и «обычных» OEM
На рынке встречаются два основных типа OEM-лицензий:
- Предустановленные OEM (от производителя) — эти идут вместе с готовым компьютером от HP, Dell, Acer и т. д.
- System Builder OEM — вариант для небольших сборщиков, а также энтузиастов, которые сами собирают компьютеры.
| Критерий | OEM от производителя | System Builder OEM |
|---|---|---|
| Способ приобретения | В комплекте с ПК от брендов (HP, Dell и др.) | Отдельно или через сборщика |
| Поддержка | Производитель «железа» | Ограниченная поддержка через Microsoft |
| Возможность самосборки | Нет | Да, можно установить на «самопальный» ПК |
| Цена | Может быть «включена» в стоимость ПК | Дешевле, чем розничная, но не всегда дешевле, чем «брендовая» OEM |
Чем System Builder OEM-лицензии отличаются от обычных OEM-лицензий?
System Builder лицензии формально предназначены для сборщиков компьютеров. В ряде регионов Microsoft разрешает купить такую лицензию конечному пользователю. Разница в том, что пользователь выступает как «System Builder» (то есть сборщик), устанавливает Windows сам и несёт ответственность за поддержку.
Сравнение OEM-лицензий
OEM-лицензии бывают нескольких видов:
OEM_COA (Certificate of Authenticity)
- Это классическая OEM-лицензия, которая привязывается к материнской плате.
- Требует ручного ввода ключа (в отличие от SLP).
- Если меняется материнская плата – потребуется новый ключ.
- Применяется для индивидуальных сборщиков ПК и системных интеграторов.
OEM_SLP (System Locked Pre-installation)
- Используется крупными производителями (HP, Dell, Lenovo и т. д.).
- Автоматически активируется на заводе при установке Windows.
- Не требует интернет-активации – проверка идет через BIOS (SLIC).
- Не требует ввода ключа – ключ встроен в BIOS.
- Не работает на других ПК, кроме тех, где была предустановлена.
OEM_Non-SLP
- Это OEM-лицензия без привязки к BIOS (SLIC).
- Требует ручной активации через интернет или по телефону.
- Применяется в небольших сборках и у локальных поставщиков.
OEM_COEM (Commercial OEM)
- Почти то же, что и обычный OEM, но с некоторыми отличиями:
- Может поставляться в виде отдельного установочного носителя.
- Используется независимыми сборщиками (не крупными брендами, а локальными продавцами ПК).
- Привязывается к железу, как и обычный OEM.
OEM_VLK (Volume License Key)
- Корпоративные OEM-лицензии, предназначенные для массовой установки.
- Обычно активируются через KMS-сервер организации.
- Не привязываются к железу, но требуют регулярного обновления активации.
- Применяются в офисах, школах, университетах и других учреждениях.
Сравнительная таблица:
| Лицензия | Привязка к железу | Ключ в BIOS | Интернет-активация | Используется кем? |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| OEM_COA | Да, к мат. плате | Нет | Да | Индивидуальные сборщики |
| OEM_SLP | Да, к мат. плате | Да | Нет | Крупные бренды (HP, Dell) |
| OEM_Non-SLP | Да, к железу | Нет | Да | Небольшие сборщики |
| OEM_COEM | Да, к железу | Нет | Да | Независимые продавцы |
| OEM_VLK | Нет | Нет | KMS (локальная сеть) | Корпорации, офисы |
Подтверждение OEM-лицензии: наклейка COA и другие варианты
Чтобы убедиться, что ваша OEM Windows подлинна, Microsoft использует COA (Certificate of Authenticity) — специальную наклейку с голограммой и серийным номером.

- Где должна располагаться наклейка?
- На корпусе стационарного ПК (обычно сбоку или сзади).
- На нижней панели ноутбука или под аккумулятором (в более старых моделях).
- У современных ноутбуков нередко лишь голограмма Microsoft на нижней крышке.
Что должно быть на наклейке?
- Логотип Windows (например, Windows 10).
- Серийный номер продукта (может быть спрятан под защитным слоем).
- Голограммная полоса или элементы, подтверждающие подлинность.
В случае Windows 8, 8.1 и 10 ключ часто «вшит» в BIOS, и физическая наклейка лишь подтверждает принадлежность лицензии, но не содержит ключ как таковой.
Способы узнать, что ваша лицензия Windows — OEM
Иногда мы не уверены, какая у нас лицензия — Retail или OEM. Самый простой способ — воспользоваться командой в Windows:
- Нажмите
Win + R - Введите CMD и нажмите Enter
- В командной строке введите: slmgr /dli
- Нажмите Enter и дождитесь всплывающего окна. Если написано OEM — значит OEM-лицензия.
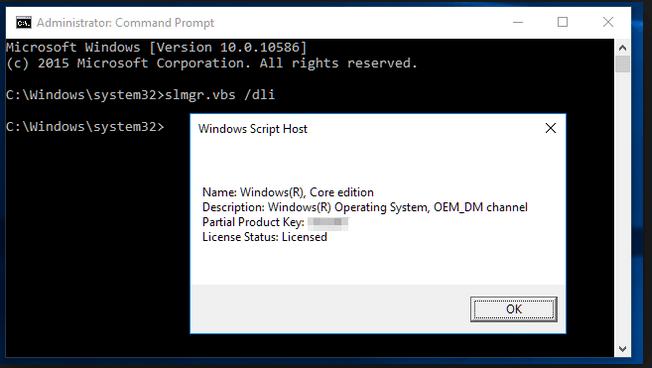
Существует и другой вариант:
- Открыть «Параметры» → «Система» → «О системе» (для Windows 10/11). Часто в разделе «Активация» указывается, какой у вас тип ключа (но не всегда).
Если у вас есть сомнения, обратитесь к официальной поддержке Microsoft с вопросом или посмотрите инструменты от производителя ПК.
Как переустановить Windows с OEM-лицензией
Рано или поздно наступает момент, когда нужно переустановить операционную систему. Проблема ли это для OEM? Совсем нет, если вы переустанавливаете на том же самом компьютере.
Первичная активация на новом ПК
- При первом включении компьютера с предустановленной ОС, система уже будет активирована.
- Если система напишет что не активирована, то нажмите Активировать сейчас — Устранение неполадок — Нажать на исправление — Перезагрузить и снова проверить.
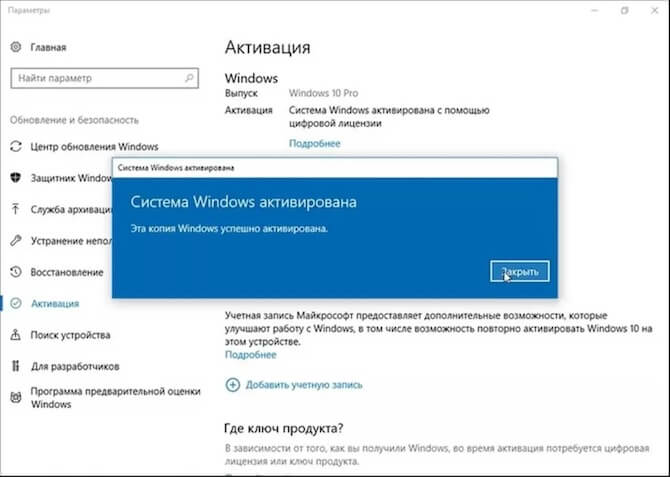
Повторная активация после переустановки
Если вы решили переустановить Windows (например, с нуля) на том же ПК (без смены материнской платы), то:
- Скачайте образ с сайта Microsoft или используйте установочную флешку.
- Установите Windows.
- Если ключ вшит в BIOS — всё активируется автоматически. Или спользуйте устарнение ошибок из предыдущего шага.
- Если автоматическая активация не сработала, используйте телефонную активацию или поддержку Microsoft.
Переход от другой редакции Windows к OEM
Если у вас была, скажем, Retail-версия Windows 10 Home, а вы хотите установить OEM Windows 10 Pro, то розничный ключ не подойдёт для OEM Pro. Приобретите соответствующую OEM-лицензию и активируйте систему новым ключом (купить можно электронную лицензия через Microsoft Store или в коробочную лицензию в магазинах вашего города).
Таблица сравнений
| Этап | Действия | Методы активации | Ограничения |
|---|---|---|---|
| Первичная активация | При первом включении Windows активируется автоматически. Если нет — используйте «Устранение неполадок». | Автоматически при установке, устранение неполадок | Нельзя менять материнскую плату без потери активации |
| Повторная активация | Если ключ в BIOS — активация пройдет автоматически, иначе используйте устранение ошибок или поддержку Microsoft. | Автоматически (BIOS), устранение ошибок, телефонная активация, поддержка Microsoft | Нельзя менять материнскую плату без потери активации |
| Переход к OEM-версии | Розничный ключ не подходит для OEM. Купите новый ключ и активируйте Windows. | Ввод нового OEM-ключа | Требуется покупка новой OEM-лицензии. Можно менять материнскую плату. |
Что произойдёт с OEM лицензией при замене материнской платы
Привязка к материнской плате — главный камень преткновения OEM-лицензии.
- Если вы меняете материнскую плату по гарантии (поломка), обычно Microsoft позволяет сохранить лицензию. Нужно связаться с поддержкой, объяснить ситуацию и при необходимости предоставить документы на замену.
- Если меняете материнскую плату для апгрейда (улучшение производительности), то официально лицензия теряется и её нужно покупать заново.
Почему так? Потому что OEM-лицензия юридически закреплена за конкретным устройством. С точки зрения Microsoft, новая материнка = новый компьютер.
Перенос и продажа ПК: остаётся ли лицензия новому владельцу
Если вы продаёте компьютер, на котором установлена OEM-лицензия, лицензия переходит вместе с «железом». Новый владелец продолжает пользоваться активированной Windows. При этом сама лицензия не может быть «отвязана» и «прикреплена» к другому компьютеру.
Можно ли купить OEM-лицензию отдельно без ПК

В теории OEM-лицензию Microsoft разрешает продавать только вместе с новым компьютером или как System Builder для сборщиков. На практике в некоторых магазинах вы можете найти System Builder версии Windows 10/11 по привлекательной цене. Формально вы приобретаете её как «сборщик» для себя.
Однако покупать «чистую OEM» от крупных брендов (Dell, HP) отдельно нельзя — это нарушение лицензионных соглашений. Часто на онлайн-площадках (сюрприз!) всё равно встречаются подобные ключи. Будьте осторожны: велика вероятность проблем с активацией и законом.
Ограничения от Microsoft для производителей и сборщиков
Компания Microsoft накладывает ряд условий, которые должны соблюдать OEM-партнёры (предприятий, которые получают лицензии на крупных условиях):
- Установка Windows только на новый компьютер.
- Предоставление поддержки пользователям (в том числе гарантийной).
- Публикация драйверов и фирменных утилит для корректной работы.
- Наличие COA (наклейки или голограммы).
Небольшие сборщики (System Builder) тоже обязаны вкладывать в каждый собранный ПК соответствующие материалы (документацию, наклейку COA и т. д.), а также следовать процедурам активации.
Почему OEM-лицензия дешевле остальных
В магазинах можно найти цены на Windows 10 стоимостью 10–12 тысяч рублей, а OEM — 6–8 тысяч (а то и дешевле)?
Вот почему:
- Отсутствие коробки. Никаких «бумажек», DVD-дисков и прочих «прелестей».
- Нет маркетинговых наценок. Коробочная версия часто рекламируется, продаётся в ритейле. OEM же распространяют напрямую производителям.
- Жёсткие ограничения на перенос, поддержку и прочее. За счёт этого цена ниже.
Безопасная покупка OEM-лицензий и риски «серых» магазинов
Покупка дешёвых О ЕМ лицензий не безопаска и вот почему:
- Выкупленные из утилизированных ПК ключи (нелегально).
- Студенческие (MSDN) ключи, продаваемые с нарушением правил.
- Украденные ключи.
В итоге вы рискуете получить заблокированную или «призрачную» лицензию, которая перестанет работать при ближайшем обновлении.
Безопаснее покупать у:
- Авторизованных реселлеров.
- Официальных магазинов.
- Надёжных ритейлеров (DNS, М.Видео, Ситилинк и т. д.).
Поддельные наклейки COA легко штампуются в подпольных условиях, но при проверке Microsoft такие наклейки могут всплыть как невалидные.
Корпоративное развёртывание и OEM-лицензия: совместимы ли?
В больших компаниях, где развёртывание Windows идёт на десятки или сотни машин, часто используют Volume Licensing (например, Microsoft Volume License). Это даёт централизованную активацию и гибкость в перемещении лицензий.
OEM-лицензии не очень подходят для корпоративного развёртывания, потому что каждая копия «привязана» к железу и не позволяет гибко переносить лицензию между ПК.
- Однако есть случаи, когда малый бизнес покупает несколько готовых ПК с предустановленным OEM Windows — это легально, но не так удобно, как Volume Licensing.
Где купить лицензию Windows 10 OEM
Чтобы купить Windows 10 OEM, обратитесь к:
- Официальным партнёрам Microsoft (которых можно найти на сайте).
- Крупным розничным сетям техники (DNS, Ситилинк, М.Видео и др.).
- Онлайн-магазинам с хорошей репутацией.
При покупке смотрите, чтобы была пометка System Builder или «OEM DSP». Убедитесь, что магазин не предлагает «странно дешёвые» ключи.
Какие различия OEM-лицензий от крупных производителей и сборщиков
- Dell, HP, Lenovo — устанавливают проприетарные утилиты, драйверы, а ключ уже «вшит» в BIOS. Откат системы часто делается через встроенный recovery-раздел.
- Мелкие сборщики — используют System Builder OEM. Активацию делает сам сборщик или покупатель.
С точки зрения активации, особых отличий нет — ключи одинаково «привязаны» к материнке. Различия лишь в методах восстановления и техподдержке.
Сколько раз можно активировать OEM-лицензию
OEM-лицензия активируется неограниченное число раз, но только на том же «железе». Вы можете хоть 10 раз переустановить систему, если не меняете материнскую плату. Если вдруг потребуются телефонные активации (случается при смене диска, памяти и т. д.), Microsoft обычно идёт навстречу.
Как удалить OEM-лицензию Windows
Бывает, что нужно «очистить» систему от лицензионного ключа, например, перед продажей без ОС. Для этого:
- Откройте командную строку от имени администратора.
- Введите команду: slmgr /upk
- Это удалит установленный в системе ключ (Uninstall Product Key).
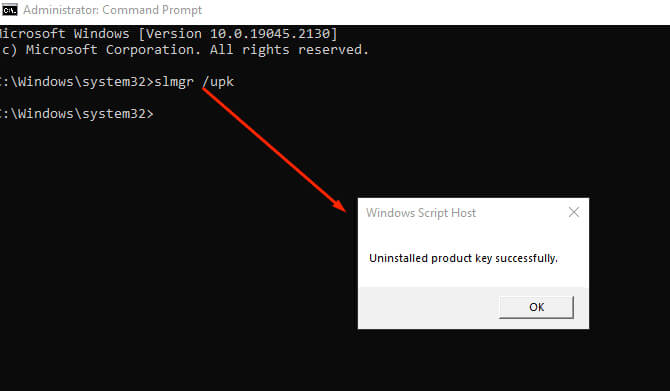
Учтите, что это удалит ключ из текущей системы, но не из BIOS. Если ключ был вшит в BIOS, при следующей установке Windows он может подхватиться автоматически.
Как удалить OEM-лицензию из BIOS
Официально удалить OEM-лицензию из BIOS без специальных утилит и перепрошивок невозможно. Производители записывают ключ в раздел ACPI (SLIC-таблица), и пользовательский инструмент для этого не предусмотрен.
- Теоретически, при перепрошивке BIOS модифицированной прошивкой можно удалить SLIC-запись, но это нарушение гарантий, лицензионных соглашений и большая вероятность «убить» материнскую плату.
- Microsoft не предоставляет легальных инструментов для удаления ключа из BIOS.
Как перенести OEM-лицензию на другой компьютер
Официально перенос OEM-лицензии на другой компьютер не разрешён. Вы можете использовать её только на том устройстве, с которым она изначально поставлялась (или на котором впервые была активирована в случае System Builder).
Если необходимо переносить Windows, придётся купить Retail (коробочную) версию или другую подходящую лицензию.
Как узнать OEM-ключ лицензионной Windows
Если ключ хранится в BIOS, его можно узнать:
- Откройте PowerShell или командную строку от имени администратора.
- Введите: wmic path softwarelicensingservice get OA3xOriginalProductKey
- Нажмите Enter. Если ключ вшит, он появится.
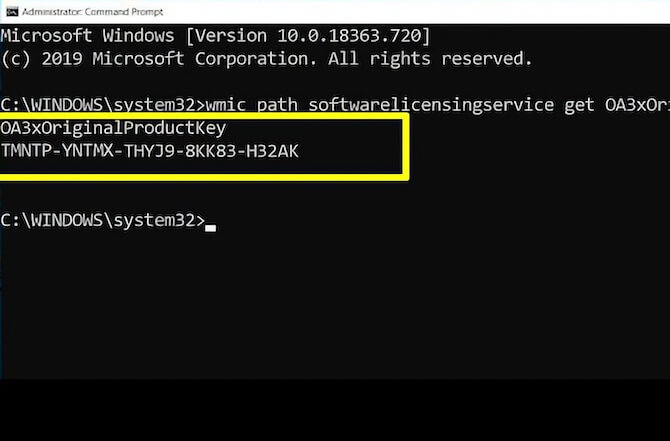
Если же ключ не вшит, посмотрите наклейку COA или используйте программы вроде ShowKeyPlus.
Как определить OEM или Retail-версию Windows
Самый простой путь — уже описанная команда slmgr /dli. Она показывает тип канала лицензии:
- OEM_COA, OEM_SLP, OEM_DM — OEM-лицензия.
- Retail — розничная версия.
- Volume — корпоративная.

Как узнать, вшита ли в BIOS лицензия Windows
Для проверки, есть ли в BIOS (UEFI) SLIC-таблица, существуют утилиты вроде «RWEverything» или «SLIC Toolkit». Но это довольно продвинутая процедура.
Проще всего:
- Вызвать PowerShell и ввести команду
wmic path softwarelicensingservice get OA3xOriginalProductKey. - Если ключ отобразится — значит, он вшит.

Чем отличается OEM-лицензия от коробочной
- Цена: OEM дешевле, Retail дороже.
- Привязка к ПК: у OEM она жёсткая, у Retail можно переносить на другой компьютер (при соблюдении ряда условий).
- Поддержка: OEM — поддержка через производителя железа, Retail — через Microsoft.
- Физическая упаковка: OEM — без «коробок», Retail — с коробкой, диск/флешка и документация.
Заключение
Оригинальная OEM-лицензия — отличный выбор, если вы покупаете новый компьютер или собираете его самостоятельно в качестве «System Builder». Она дешевле розничной, но «привязана» к материнской плате. Если вам нужно часто менять комплектующие или переносить систему на новые устройства, лучше подумать о коробочной версии.
Какие-то вопросы остались? Ознакомьтесь с другими лицензиями Windows — там вы найдёте ответы на многие технические нюансы.
Помните, что лицензионная Windows — это не только вопрос закона, но и вашей безопасности и стабильности работы системы. Не гонитесь за подозрительно низкими ценами, чтобы потом не пришлось писать жалобу, что «опять всё слетело».
Для работы проектов iXBT.com нужны файлы cookie и сервисы аналитики.
Продолжая посещать сайты проектов вы соглашаетесь с нашей
Политикой в отношении файлов cookie
Я думаю, уже каждый сталкивался с предложением купить дешевый ключ Windows (или другой программы) за цену гораздо ниже, чем в официальных магазинах. И многие эти ключи даже покупали. Давайте вместе попробуем разобраться, что это за ключи и почему их покупать не стоит.

Содержание
- Что такое OEM-лицензия
- Какую лицензию может легально купить обычный пользователь?
- Чем грозит использование ОЕМ-ключа?
Для примера возьмём ключи для Windows 10 Pro. На многих площадках их продают по цене от 50 рублей. Цена зависит только от жадности продавца.
А вот если зайти на Яндекс.Маркет и вбить туда «лицензионный ключ Windows», то мы видим следующую картину:
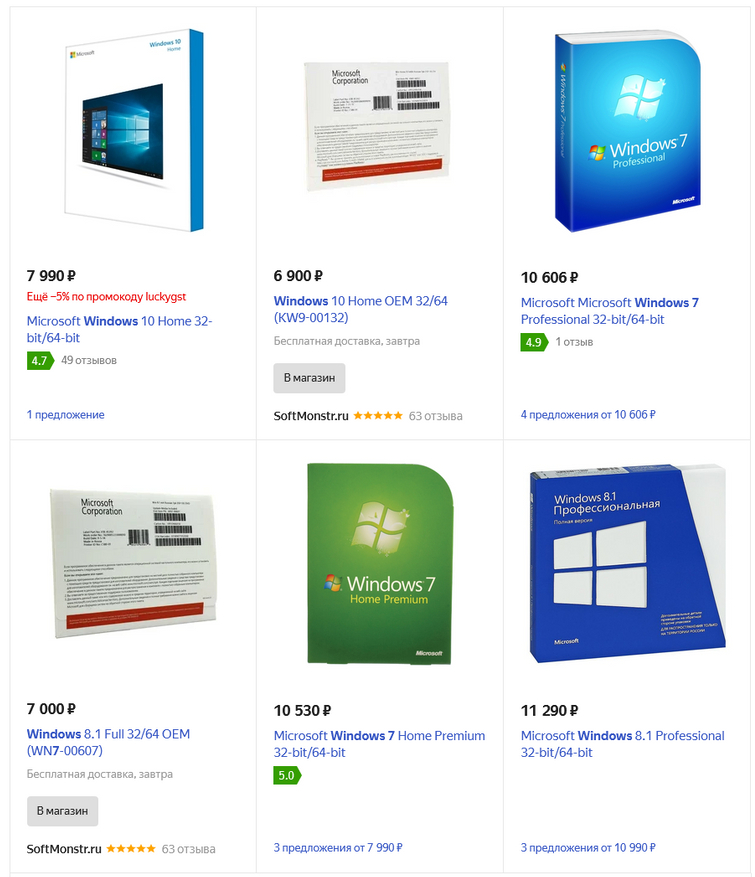
Обычный пользователь, конечно же, скажет, что это очень дорого. Ведь можно зайти на Aliexpress или Ebay, вбить там «windows 10 key» и купить ключ за 100-600 рублей:
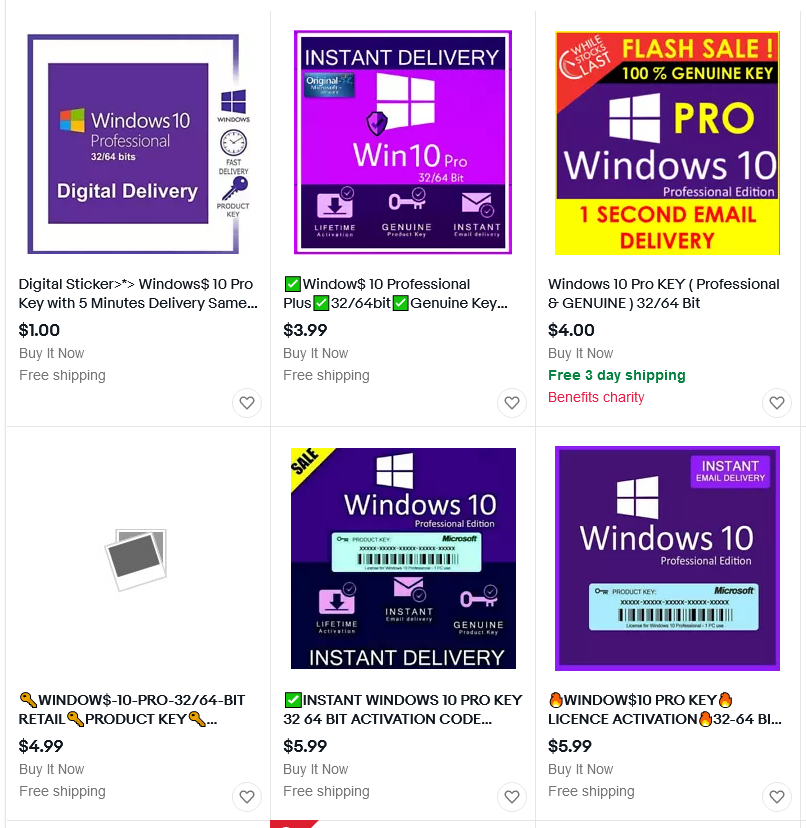
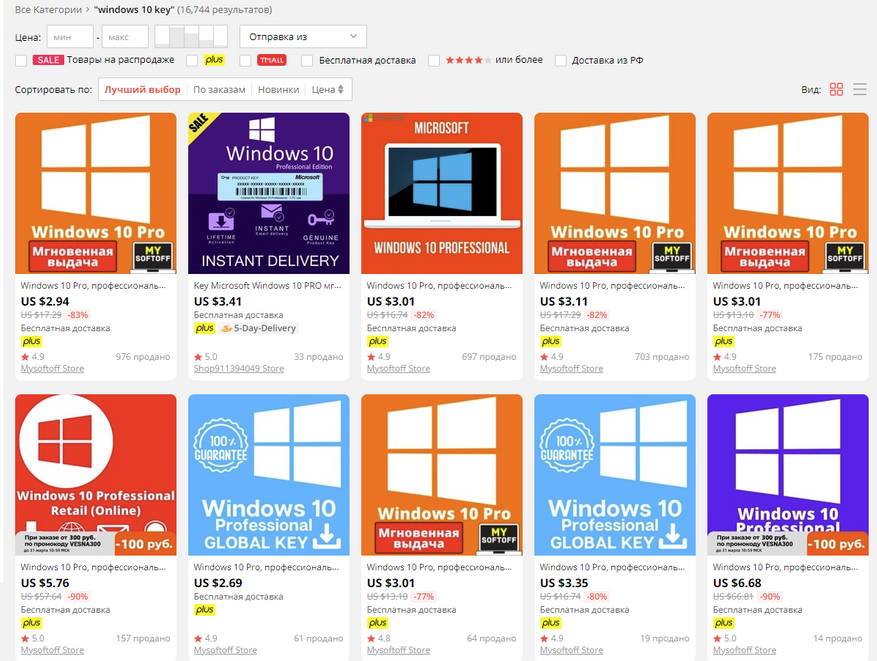
Эти ключи активно продаются, покупаются и используются. Но на самом деле ли они лицензионные?
Сразу скажу: НЕТ! Эти ключи — не лицензия. И ниже попробую объяснить, почему именно.
Некоторые ключи могли быть куплены с помощью украденных кредитных карт. Когда кредитные карты блокируются и банки отменяют платежи по ним, Microsoft дезактивирует проданные ключи, и использовать их становится нельзя. А вот деньги, заплаченные за такой ключ мошеннику, уже не вернуть.
В лучшем случае это так называемые ключи «серого рынка». Например, «региональные». Они настоящие, но выдавались только для определенного региона, в котором стоят значительно дешевле. Либо это ключи «образовательные», то есть, предназначенные для студентов (и только для них). Еще на площадках появляются ключи «корпоративные», купленные оптом одной организацией. Перепродажа таких ключей нарушает условия лицензионного соглашения Microsoft. Но большая часть дешевых ключей — это OEM-лицензии, которые перепродавать тоже нельзя.
Что такое OEM-лицензия
Сначала разберемся, что же это за ключи такие. Они выдаются корпорацией Microsoft сборщикам систем (железа). Аббревиатура OEM расшифровывается как Original Equipment Manufacturer (с английского «Оригинальный производитель оборудования»). Такие ключи должны быть привязаны к определенной конфигурации железа. То есть, если вы купили ноутбук с подобным ключом, который на заводе был установлен производителем — это абсолютно легальная лицензия. А если вы просто купили ключ и поставили на свой комп, то получили «серый» ключ, который нарушает условия лицензионного соглашения Microsoft.
Корпорация Microsoft предоставляет сборщику определенное количество OEM-ключей для произведенных устройств по цене ниже рыночной. Чтобы получить скидку, производитель берет на себя обязанности по установке, настройке и последующем обслуживании устройства и установленной на него ОС. Как следствие, каждый ОЕМ-ключ должен быть жестко привязан к конфигурации железа и не может быть активирован на случайном устройстве.
Но что делают недобросовестные дельцы? Они покупают ОЕМ-ключи у Microsoft, притворяясь производителями, и просто перепродают их на площадках типа Авито, OLX, Ebay, Aliexpress и прочих. Некоторые даже делают отдельные сайты под продажу дешевых ключей Windows.

При этом они обманывают сразу всех. Во-первых, корпорацию Microsoft, обещая продавать готовые ПК с предустановленной системой и получая за это большую скидку. А во-вторых — покупателей, которые и рады обмануться и потратить небольшие деньги на пиратский по своей сути ключ.
Напомню один известный тезис: Незнание официально опубликованного закона не освобождает от ответственности за его несоблюдение. Это значит, что, покупая дешевый ОЕМ-ключ, мы также нарушаем лицензионное соглашение.
Какую лицензию может легально купить обычный пользователь?
Для обычного пользователя не существует законного способа получить ключ продукта Windows за 12$.
Обычный пользователь может легально купить ОС только у сертифицированного продавца по фиксированной цене в виде коробочной или цифровой версии. Причём в условиях лицензионного соглашения Windows указано, что, по сути, мы покупаем не операционную систему, а право на использование операционной системы в единственном количестве на одном ПК:
2. Права установки и использования
а. Лицензия. Программное обеспечение не продается, а предоставляется по лицензии. В рамках настоящего соглашения мы предоставляем вам право установить и запустить один экземпляр программного обеспечения на устройстве (лицензированное устройство) для одновременного использования одним лицом, если вы соблюдаете все условия настоящего соглашения.
Теперь вернемся к ОЕМ-ключам. Да, формально они работают и проходят проверку роботом, который не может знать откуда у вас взялся ключ. Но фактически такой ключ ничем не отличается от ключа, сгенерированного в генераторах ключей и KMS-активаторах. Никто вам не даст гарантии, что завтра эти ключи не будут заблокированы.
А блокируются такие ключи очень часто: стоит скомпрометировать пару-тройку лицензий из выданного производителем диапазона, и договор со «сборщиком» разорван, а активация всех выданных ключей отозвана. А все пользователи, купившие эти ключи, после очередного обновления обнаруживают на своих компьютерах вот такое сообщение:
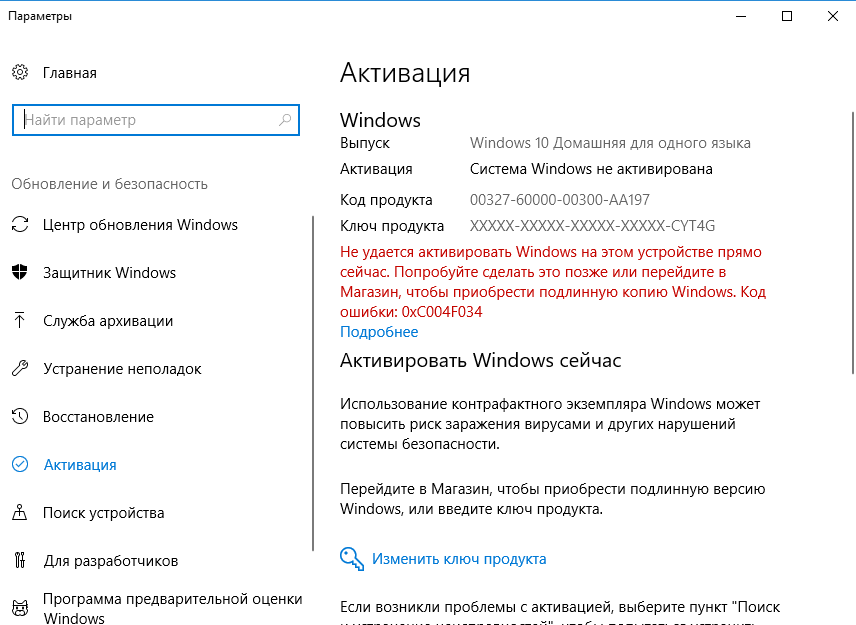
И вот вы потратили свои деньги на покупку воздуха и поддержали копеечкой мошенника. И если вы думаете, что не обеднели от 1-5$, то представьте, что таких как вы, ежедневно у мошенника 10/100/1000 человек. Это уже более ощутимые суммы. И вы, получается, являетесь одним из спонсоров мошенников и из своего кармана оплачиваете мошеннические схемы.
Чем грозит использование ОЕМ-ключа?
Формально, если вы обычный пользователь домашнего ПК, то ничем — с юридической точки зрения. Никто ведь не придет к вам домой для проверки вашего компьютера на лицензионность (хочется ведь на это надеяться?). Максимум, что может быть, это массовая блокировка массива ключей, выданных определенному ОЕМ и — как следствие — потеря лицензии на вашем ПК. Ну и, естественно, потеря ваших денег.
А вот если такие ОЕМ-ключи будет использовать некая фирма, то при проверке, если выяснится, что у них нет официально купленной ОС, OEM будут приравниваться к пиратским ключам. И штрафы за такое пиратство в РФ довольно ощутимые:
Согласно статье 7.12 КоАП РФ — «Нарушение авторских и смежных прав, изобретательских и патентных прав». Для физических лиц штраф составляет от 1500 до 2000 рублей, для должностных — от 10 до 20 тысяч, для юридического лица штраф составляет от 30 до 40 тысяч рублей.
Это не так уж и мало. Согласитесь.

И вот теперь можно подводить итоги.
Естественно, весь материал носит информационно рекомендательный характер. Не думаю, что читатель сейчас же побежит сносить со своего ПК пиратский ключ. Но надеюсь, что статья поможет определиться с понятиями и даст пищу для размышлений.
Какой лицензией пользуется сам автор? У меня ноутбук с уже установленной ОС, который был приобретен в Китае. И да, на нем как раз установлена лицензия ОЕМ. Но она привязана к железу и конфигурации моего ноутбука, и не нарушает условия лицензионного соглашения. А что касается другого софта, то я предпочитаю пользоваться условно-бесплатными программами: LibreOffice для документов, PhotoScape для работы с фотографиями, стандартные плееры для просмотра мультимедиа-файлов. К чему призываю и читателей, если нет возможности купить лицензии.
Кстати, в Конференции IXBT есть несколько тем с обсуждением таких лицензий:
- Самый дешевый способ стать владельцем лицензионной Windows 10
- OEM ключи Windows

Windows is the most used operating system in the entire world. Each version of it brings us new, unique and sometimes even surprising features. At the same time, each of these versions has some subversions designed for a specific audience and a specific task.
Both of these versions are the OEM version and the Retail version. But, what is the difference between these two? Most people are not clear about it. In this Windows 10 Oem vs Retail, we’ll clarify all the differences and decide which one is for you.

|
Windows 10 OEM |
Windows 10 Retail |
|
|
Cost – Official prices |
Official: $85 for Windows 10 Home and $113 for Pro version. RoyalCDKeys price: €2,50 for Windows 10 Home and €2,81 for Windows 10 Pro version. |
$139 for the Windows 10 Home Edition, and $199 for the Pro version. RoyalCDKeys price: €3,90 for Windows 10 Home and €2,40 for Windows 10 Pro version. |
|
License |
OEM licenses are tied to the first computer you activate it on. This version cannot be used to upgrade from an older Windows OS. |
You can transfer Retail version to another computer, as long as you deactivate the old device. There is no limit on hardware. |
|
Support |
OEM version does not offer any free Microsoft direct support from Microsoft support personnel. |
You can contact Microsoft Support directly to get help when you encounter activation issues. |
|
Hardware Replacement |
You can replace hardware or a part of your computer, except for the motherboard. |
You can freely replace any part of your PC, and your operating system will still be activated. |
What Is OEM Windows 10?
The OEM version of Windows – OEM means Original Equipment Manufacturer – is a version of Windows designed for small PC makers. This system builder is mainly used by large computer manufacturers as well as individuals and local computer shops that build their own computers.
It’s very common for computer enthusiasts to use OEM Windows 10 on their workstation PCs. Besides, your OEM version of Windows 10 will be tied to your single PC forever. Anyway, you can uninstall and reinstall this version as many times you want, but only on one PC.
In general, when we talk about OEM builds, they have a slower performance since their parts are sold in bulk to OEMs. OEM companies use these parts in their systems. Thus, most consumers end up with a computer that runs slower than it should.

What is Windows 10 Retail?
This Retail license refers to that version or copy of Windows 10 you acquire from authorized retailers or directly from the Microsoft Store. Any Retail key you buy is a Windows full version as well as a standard “consumer” version.
Anytime you head to a virtual store or online retailer and see a version of Windows 10, it’s a retail version of Windows. This version of Windows and all the features it integrates are designed for users who want to upgrade their computer or buy a new license in the future.
A significant advantage of any retail Windows key is that you can install it on any computer you want, and you can also transfer it to a different computer quickly, as long as you deactivate the old device. Besides, it comes with full support from Microsoft.

What Are the Main Differences Between Retail and OEM Licensing?
Both OEM software and Retail software offer the same OS but with subtle differences. In general, the major difference has to do with the price, but still, there are others worth mentioning.
Features
Regarding use, there is no difference between OEM Windows 10 and Retail Windows 10. Both versions have all the basic features of the operating system. You can enjoy all the tools, upgrades, data, and functionality you expect from Windows.

OEM License vs Retail License
The second major difference between OEM and Retail versions is related to licenses. In a few words, you cannot transfer OEM keys of Windows 10 to other devices. However, you can transfer the retail license from one machine to another.
OEM License
OEM is short for Original Equipment Manufacturer. When original equipment manufacturers produce computers, they always pre-install OEM Windows before selling them. When you buy these PCs, you will get a Windows OEM license and don’t need to pay extra money.
It seems that the Windows 10 OEM license does not cost you money, but actually, its cost is already included in the computer cost. Despite this, it is still cheaper than Windows 10 Retail license.
The Windows 10 OEM license is customized for OEM Windows 10 users. Once it is first activated in the OEM PC, it is locked to the hardware. The product key isn’t transferable, and you can’t use it to activate another installation.
In a few words, OEM licenses are tied to the first computer you activate it on. Also, OEM versions cannot be used to upgrade from an older Windows OS.
Retail License
A Windows 10 Retail license refers to the license you obtain when buying a copy of Windows 10 from the Microsoft store or an authorized retailer. If you have a Windows 10 Retail license, you can transfer it to another computer, as long as you deactivate the old device. There is no limit on hardware.
Oem or Retail Versions Support
Here’s the big difference between both windows licenses.
If you have a Windows 10 Retail version, you’ll be able to contact Microsoft Support directly to get help when you encounter activation issues or run into problems with hardware compatibility.
In short, the OEM version does not offer any free Microsoft direct support from Microsoft support personnel.
On the other hand, if you buy an OEM copy of Windows 10, Microsoft will tell you to contact the device’s manufacturer to get technical support and solve your problems.
What’s more, you will still receive updates from Microsoft Update; you just won’t be able to connect to them directly for support. Generally speaking, though, retail is best.

Hardware Replacement
If you have a Windows 10 OEM license and think of getting new hardware or replacing a part of your machine, you can do it except for the motherboard. It is where the Software Licensing Internal Code (SLIC) is stored in BIOS. If SLIC is missing, the OEM Windows can’t be activated.
Changing a part of your PC with a Windows 10 Retail copy is easier. If you have this license type, you can freely replace any part of your PC, and your operating system will still be activated.
System Upgrade
Whether you are using Windows Retail (FPP) version or the Windows OEM version, you can upgrade your system to Windows 10 as long as you have an official license. Although the free upgrade is already over, some users report they can still upgrade to Windows 10 for free.
Anyway, the process of upgrading is similar in both versions. Just reserve your free update on the official Windows website. Then, when you receive the notification, install it right away. Now, the upgrade is yours!

Availability and Price
As you can imagine, the OEM version of Windows is much cheaper than the retail version, but it’s also far more limited. This isn’t necessarily bad if you’re building your own workstation PC, and every dollar counts.
If you look for the retail Windows license on the official site of Microsoft, the company very likely will charge you around $139 for the Windows 10 Home Edition, and $199 for the Pro version.
On the other hand, if you look in online stores, the price is much lower, probably 10 or 20 USD.
However, an OEM Key License is much cheaper. You very likely can find it for $85 for Windows 10 Home and $113 for Pro.
Here, at RoyalCDKeys, you can find Microsoft Windows 10 Home OEM Key and Microsoft Windows 10 Home Retail Key at the best price on the market (€2,50 and €2,10 at the moment of writing, respectively!). Click on the click before and check the offer we have for you!
Windows 10 OEM and Retail Conclusions
In general, Windows users that have genuine computers or laptops purchased in stores or websites use an OEM version, while those who assemble their own PC prefer to use a Retail version.
However, at this point of the article, we have to mention a couple of tips to help you decide which is the best version for your purpose.
- If you have a computer with a pre-installed Windows 10, and you don’t need to make a hardware change, including the motherboard, keep using the OEM license that your computer already has.
- If you want to build a new PC, or your machine does not have a preinstalled Windows 10, we don’t recommend you to buy OEM copies. It’s much better if you purchase a Retail version due to its privileges.
If this is your choice, get Microsoft Windows 10 Home Retail Key here, at RoyalCDKeys. You’ll get all the benefits of this version we’ve mentioned in this post at a really cheap price.

FAQ
How Do I Know if My Windows 10 Is OEM or Retail?
Open a PowerShell or Command Prompt and type in Slmgr –dli. You can also use Slmgr /dli. Wait a few seconds for the Windows Script Manager to appear. It is going to tell you which license type you have.
Which Is Better, OEM or Retail Windows 10?
Both full versions are good for different purposes and services. The OEM version is cheaper, more simple, but it lacks features. Retail has more tools and highlights regarding technical support and general solutions.
Windows 10 has several editions, all with varying feature sets, use cases, or intended devices. Certain editions are distributed only on devices directly from an original equipment manufacturer (OEM), while editions such as Enterprise and Education are only available through volume licensing channels. Microsoft also makes editions of Windows 10 available to device manufacturers for use on specific classes of devices, including IoT devices, and previously marketed Windows 10 Mobile for smartphones.
Baseline editions are the only editions available as standalone purchases in retail outlets. PCs often come pre-installed with one of these editions.
- Home
- Windows 10 Home is designed for use in PCs, tablets and 2-in-1 PCs. It includes all features directed at consumers.[1][2][3]
- Pro
- Windows 10 Pro includes all features of Windows 10 Home, with additional capabilities that are oriented towards professionals and business environments, such as Active Directory, Remote Desktop, BitLocker, Hyper-V, and Windows Defender Device Guard.[1][2][3]
- Pro for Workstations
- Windows 10 Pro for Workstations is designed for high-end hardware for intensive computing tasks and supports Intel Xeon, AMD Opteron and the latest AMD Epyc processors; up to 4 CPUs; up to 256 cores; up to 6 TB RAM; the ReFS file system; Non-Volatile Dual In-line Memory Module (NVDIMM); and remote direct memory access (RDMA).[4][5][6]
Organizational editions
edit
These editions add features to facilitate centralized control of many installations of the OS within an organization. The main avenue of acquiring them is a volume licensing contract with Microsoft.
- Education
- Windows 10 Education is distributed through Academic Volume Licensing. It was based on Windows 10 Enterprise and initially reported to have the same feature set.[1][2][3] As of version 1709, however, this edition has fewer features. See § Comparison chart for details.
- Pro Education
- This edition was introduced in July 2016 for hardware partners on new devices purchased with the discounted K–12 academic license. It was based on the Pro edition of Windows 10 and contains mostly the same features as Windows 10 Pro with different options disabled by default, and adds options for setup and deployment in an education environment. It also features a «Set Up School PCs» app that allows provisioning of settings using a USB flash drive, and does not include Cortana, Microsoft Store suggestions, Windows Sandbox, or Windows Spotlight.[7][8][9]
- Enterprise
- Windows 10 Enterprise provides all the features of Windows 10 Pro for Workstations, with additional features to assist with IT-based organizations.[1][2][3] Windows 10 Enterprise is configurable on two servicing channels, Semi-Annual Channel and Windows Insider Program.[10]
- Enterprise LTSC
- Enterprise LTSC (Long-Term Servicing Channel) is a long-term support variant of Windows 10 Enterprise, released every 2 to 3 years. Each release is supported with security updates for either 5 or 10 years after its release, and intentionally receives no feature updates.[11] Some features, including the Microsoft Store and bundled apps, are not included in this edition.[12][1][3] This edition was first released as Windows 10 Enterprise LTSB (Long-Term Servicing Branch).[13] There are currently 4 releases of LTSC: one in 2015 (RTM), one in 2016 (version 1607), one in 2018 (labeled as 2019, version 1809), and one in 2021 (version 21H2).[14][15]
- Enterprise multi-session
- Windows 10 Enterprise multi-session, a multi-session variant of Enterprise edition, included with Azure Virtual Desktop, allows multiple concurrent interactive sessions. Previously, only Windows Server could do this. A cloud-based alternative to an on-premise Remote Desktop Server (RDS). AVD is deployed in Azure Cloud as a virtual machine. License costs are already included in several Microsoft 365 subscriptions, including Microsoft 365 Business Premium or Microsoft 365 E3.
Since 2018, OEMs can ship Windows 10 Home and Pro in a feature-limited variation named S mode which evolved from the discontinued Windows 10 S. Organizations employing Windows 10 Enterprise or Windows 10 Education can make use of S mode too.[16] S mode is a feature-limited edition of Windows 10 designed primarily for low-end devices in the education market. It has a faster initial setup and login process, and allows devices to be provisioned using a USB drive with the «Set Up School PCs» app.
With the exception of the Microsoft Teams desktop client (which was made available for S mode in April 2019),[citation needed] the installation of software (both Universal Windows Platform (UWP) and Windows API apps) is only possible through the Microsoft Store, and built-in and Microsoft Store-obtained command line programs or shells cannot be run in this mode.[17][18][19][20] System settings are locked to allow only Microsoft Edge as the default web browser with Bing as its search engine.[21] The operating system may be switched out of S mode using the Microsoft Store for free. However, once S Mode is turned off, it cannot be re-enabled.[22][23] All Windows 10 devices in S mode include a free one-year subscription to Minecraft: Education Edition.[citation needed] Critics have compared the edition to Windows RT, and have considered it to be an alternative to ChromeOS.[22][24][25][26][27]
Device-specific editions
edit
These editions are licensed to OEMs only, and are primarily obtained via the purchase of hardware that includes it:
- Holographic
- A specific edition used by Microsoft’s HoloLens mixed reality smartglasses.[28][29]
- Team
- A specific edition used by Microsoft’s Surface Hub interactive whiteboard.[30]
Rebranded from Microsoft’s earlier operating system editions in the Windows Embedded family. Binary identical to their non-IoT counterparts with version 1809 and older,[31] while newer versions add support for smaller storage devices.[32][33] Available via OEMs and volume licensing for specific versions.[34]
- IoT Enterprise
- Intended specifically for use in small footprint, low-cost devices and IoT scenarios.[35][36]
- IoT Enterprise LTSC
- Long-Term Servicing Channel variant. Replaces all IoT Core edition variants starting with the 2021 release.[37][38] Furthermore, the 2021 release gains an extra 5 years of support compared to its non-IoT counterpart[39] and is available via volume licensing for the first time.[34]
Discontinued editions
edit
The following editions of Windows 10 were discontinued (as of Windows 10 version 21H2). For both Mobile and Mobile Enterprise, Microsoft confirmed it was exiting the consumer mobile devices market, so no successor product is available.[40]
- Mobile
- Windows 10 Mobile was designed for smartphones and small tablets. It included all basic consumer features, including Continuum capability. It was the de facto successor of Windows Phone 8.1 and Windows RT.[1][2]
- Mobile Enterprise
- Windows 10 Mobile Enterprise provided all of the features in Windows 10 Mobile, with additional features to assist IT-based organizations, in a manner similar to Windows 10 Enterprise, but optimized for mobile devices.[1][2]
- IoT Mobile
- A binary equivalent of Windows 10 Mobile Enterprise licensed for IoT applications. Also known as IoT Mobile Enterprise.[41][42]
- IoT Core/IoT Core LTSC
- Windows 10 IoT Core was optimized for smaller and lower-cost industry devices. It was also formerly provided free of charge for use in devices like the Raspberry Pi for hobbyist use. Only UWP apps are supported, and only one at a time at that.[38] Discontinued after version 1809. Support ended on 10 November 2020 for non-LTSC,[43] while IoT Core LTSC (2019/version 1809) support will continue until 9 January 2029.[44][45] Merged into and replaced by IoT Enterprise LTSC starting with the 2021/version 21H2 release.[37][38]
- S
- Windows 10 S was an edition released in 2017 which ultimately evolved into the so-called S mode of Windows 10. In March 2018, Microsoft announced that it would be phasing out Windows 10 S, citing confusion among manufacturers and end-users.[46][47]
- Polaris
- Polaris was made for desktops and laptops; only one build was leaked in 2021. It was known as «Windows OneCore 10» in the Windows Boot Manager.[citation needed]
- Lean
- Lean was meant to be used for cheaper desktops and laptops with a small storage capacity and resources, it could fit even on a 16 GB hard drive; only one build was released in 2018, the setup identifies the edition as «Windows 10 Lean».[48]
- Andromeda
- Andromeda was demonstrated on the Lumia 950.[49] The project was canceled for unknown reasons.
- 10X
- Originally announced for use on dual-screen devices such as the Surface Neo and other potential form factors, 10X featured a modified user interface designed around context specific interactions or «postures» on such devices, including a redesigned Start menu with no tiles, and use of container technology to run Win32 software.[50][51] The platform was described as a more direct competitor to ChromeOS.[52][53] On May 4, 2020, Microsoft announced that Windows 10X would first be used on single-screen devices, and that they would «continue to look for the right moment, in conjunction with our OEM partners, to bring dual-screen devices to market».[54] Microsoft also added anti-theft protection to Windows 10X, just like how Apple’s Activation Lock and anti-theft protection on Android devices and Chromebooks work.[55] On May 18, 2021, Head of Windows Servicing and Delivery John Cable stated that Windows 10X had been cancelled, and that its foundational technologies would be leveraged for future Microsoft products.[56] Several design changes in 10X, notably the centered taskbar and redesigned start menu, would be later introduced in Windows 11.[57]
- N/KN
- As with previous versions of Windows since Windows XP, all Windows 10 editions for PC hardware have «N» and «KN» variations in Europe and South Korea that exclude multimedia functionality, in compliance with antitrust rulings.[58] According to details that Microsoft has published, any app that relies on Microsoft multimedia technologies experiences impaired functionality on these editions, unable to even play audio notification tones.[59] Restoring the missing functionality to these editions entails installing the «Media Feature Pack», followed by Skype, Movies & TV, Windows Media Player, Xbox Game Bar, Windows Voice Recorder, and four codecs.[59] The variation cannot be changed without a clean install, and keys for one variation will not work on other variations.
- Home with Bing
- As with Windows 8.1, a reduced-price «Windows 10 with Bing» SKU is available to OEMs; it is subsidized by having Microsoft’s Bing search engine set as default, which cannot be changed to a different search engine by OEMs. It is intended primarily for low-cost devices, and is otherwise identical to Windows 10 Home.[60][61]
- Home Single Language
- In some emerging markets,[citation needed] OEMs preinstall a variation of Windows 10 Home called Single Language without the ability to switch the display language. To change the display language, the user will need to upgrade to the standard editions of Windows 10 Home or Windows 10 Pro. It is otherwise identical to Windows 10 Home. However, it should not be confused with the standard OEM editions of Windows 10, where OEMs and mobile operators can restrict which display languages are preloaded and/or made available for download and installation for their target markets.
- CMIT Government Edition
- In May 2017, it was reported that Microsoft, as part of its partnership with China Electronics Technology Group, created a specially-modified variant of Windows 10 Enterprise («G») designed for use within branches of the Chinese government. This variant is pre-configured to «remove features that are not needed by Chinese government employees», and allow the use of its internal encryption algorithms.[62][63]
- OEM variants (PC and Mobile)
- As with Windows 10 Mobile and previous versions of Windows since Windows Phone 7 for smartphones and Windows 8 for PCs (since its mobile counterpart shares the same Windows NT kernel), device manufacturers (as well as mobile operators for devices with cellular capabilities) who preload Windows 10 can choose not to support certain display languages either during the OOBE process or available as optional downloads via Settings and/or the Microsoft Store based on the target market. For optional downloads, in the first scenario, the option to download the language pack (and any associated supplementary fonts) will not be available; in the second scenario, the installation will be blocked with the message «This app is not compatible with this device,» where the «app» in question is a language pack from the Microsoft Store. Unlike Windows 10 Home Single Language, device manufacturers and mobile operators can support one, some, or even all of the display languages available (though many devices that do not run Single Language editions of Windows will likely support multiple display languages). OEM editions are otherwise identical to their retail counterparts without any other feature restrictions.
Microsoft OEM licensing formula takes display size, RAM capacity and storage capacity into account. In mid-2015, devices with 4 GB RAM were expected to be $20 more expensive than devices with 2 GB RAM.[88]
At the time of launch, Microsoft deemed Windows 7 (with Service Pack 1) and Windows 8.1 users eligible to upgrade to Windows 10 free of charge, so long as the upgrade took place within one year of Windows 10’s initial release date. Windows RT and the respective Enterprise editions of Windows 7, 8, and 8.1 were excluded from this offer.[89]
Windows 10 free upgrade matrix
| Windows version and edition | Windows 10 edition |
|---|---|
| Windows 7 Starter SP1 | Home |
| Windows 7 Home Basic SP1 | |
| Windows 7 Home Premium SP1 | |
| Windows 8.1 with Bing | |
| Windows 8.1 | |
| Windows 7 Professional SP1 | Pro |
| Windows 7 Ultimate SP1 | |
| Windows 8.1 Pro | |
| Windows Phone 8.1 | Mobile |
The following table summarizes possible transition paths (upgrade, downgrade, or migration) that can be taken, provided that proper licenses are purchased.
Windows RT does not appear in this table because it cannot be upgraded to Windows 10.
On September 28, 2023, Microsoft disabled the free upgrade path to Windows 10 from Windows 7 or 8.x, although upgrades from Windows 10 to 11 are still supported.[90][91]
Microsoft releases minor versions of Windows 10 through the free feature updates.[12] Originally, Microsoft released feature updates semiannually. They contained new features as well as changes.[93] With the release of Windows 11, however, Microsoft has changed the release schedule to annual. These feature updates do not contain any noticeable changes.
The pace at which a system receives feature updates depends on the «release channel» (originally, «release branch») from which the system downloads its updates.[12]
Windows Insider is a beta testing program that allows access to pre-release builds of Windows 10, enabling power users, developers, and vendors to test and provide feedback on future feature updates to Windows 10 as they are developed. Before the release of Windows 11, Windows Insider itself consisted of four «rings»:
- The Dev channel (previously «Fast» ring) distributed new builds as they were released.
- The Beta channel (previously «Slow» ring) distributed new builds with a delay following their availability on the Fast ring.
- The «Release Preview» channel distributed release candidate builds.
- The now-closed «Skip Ahead» ring distributed builds of the next feature update while a current release was being finished.
After the release of Windows 11, only the «Release Preview» and «Beta» rings remains active.
General Availability Channel
edit
Since 2022, the General Availability Channel (GAC) distributes feature updates annually. To receive these updates, users must either request them manually or wait for their version of Windows 10 to go out of support.
Originally, however, Microsoft distributed feature updates through two distinct channels:[94]
- The «Current Branch» (CB) distributed all feature updates as they graduated from the Windows Insider program. Microsoft only supported the latest build. Windows would automatically install the latest feature update from CB. Users could defer the CB feature update for up to 365 days.[95][96][97][98] Microsoft renamed CB to «Semi-Annual Channel (Targeted)» in version 1709.
- The «Current Branch for Business» (CBB), which was not available in the Home edition, distributed feature updates with a four-month delay. This allowed customers and vendors to evaluate and perform additional testing on new builds before broader deployments. Devices could be switched back to the Current Branch at any time.[12][99] Microsoft renamed CBB to «Semi-Annual Channel» in version 1709.
Since version 1903, Microsoft dismantled the two-channel scheme in favor of a unified «Semi-Annual Channel» (SAC). Microsoft supports each SAC version of Windows for 30 months. Windows no longer installs new feature updates automatically before the expiry of the 30-months support period. With the release of Windows 11, Microsoft changed the release schedule to annual, and change the channel’s name to «General Availability Channel» (GAC).
Long-Term Servicing Channel
edit
LTSC exclusively distributes the «Enterprise LTSC», «IoT Core», and «IoT Enterprise LTSC» editions of Windows 10. Microsoft releases a new minor version of these editions every 2–3 years. LTSC builds adhere to Microsoft’s traditional support policy which was in effect before Windows 10, including:
- Five years of mainstream support
- Critical and security updates for ten years after their release (excludes non-IoT editions version 2021 and newer)[100]
- No feature updates from Windows Update
Microsoft discourages the use of LTSC editions outside of «special-purpose devices» that perform a fixed function and thus do not require new user experience features. As a result, these editions do not come with Microsoft Store, most Cortana features, and most bundled apps.[12][1][3] LTSC was originally called the «Long-Term Servicing Branch» (LTSB) until 2016.[13] Later, LTSC editions are included in Windows 11.
- Windows Server 2016, based on Windows 10 version 1607[101]
- Windows Server 2019, based on Windows 10 version 1809
- Windows Server 2022, based on a modified version of Windows 10 version 21H2
- Xbox system software, an operating system now based on the Windows 10 core, designed to run on the Xbox consoles
- Windows 10 version history
- ^ a b c 32-bit architectures like IA-32 and ARM32 have a memory addressing limitation of four gigabytes. In practice, less than 4 GB of memory is addressable as the 4 GB space also includes the memory mapped peripherals.
- ^ Windows 10 utilises processor groups on x86-64 to manage processor affinity and scheduling. The Windows 10 kernel has a hard-coded limit of 20 processor groups, and each processor group can contain up to 64 logical processors. A logical processor is either a physical or SMT core. Processor groups are allocated based on the NUMA topology of the system. One processor group cannot span multiple sockets or NUMA nodes. Processor groups are not available on IA-32; 32-bit builds instead use an older affinity mask implementation with a limit of 32 logical processors. The limit of 20 processor groups does not change between Windows 10 editions. There is no specific limit on the number of physical cores that can be used on Windows 10, unlike Windows Server where physical cores must be additionally licensed.[69][71][72][73]
- ^ There are three (previously four) telemetry levels, in the order of magnitude: Diagnostic data off (Security), Required (Basic), and Optional (Full). The higher the level, the more information that is sent to Microsoft. Previous Windows 10 versions had a level between Required and Optional, and the older names for the levels are shown in the parenthesis.
- ^ Cortana is available only in certain markets. Experience may vary by region and device.
- ^ The only device-encryption feature that is available in Windows 10 Home requires Trusted Platform Module version 2.0.[67]
- ^ BitLocker is available and can be used in the absence of Trusted Platform Module.[67]
- ^ a b This feature was missing from Windows 10 version 1803, but not the prior or next versions.
- ^ Windows Hello requires specialized hardware, such as a fingerprint reader, illuminated IR sensor or other biometric sensor.
- ^ SMB Direct (SMB over Remote Direct Memory Access [RDMA]) is available in cleanly installed Windows 10 Pro 22H2 or later and absent if the operating system has been upgraded from versions prior to 22H2. SMB Direct server capability is absent from all editions of Windows 10, regardless of version.
- ^ On Windows 10 Pro, a Control Panel applet corresponding to this feature appears, but a Windows 10 Enterprise or Education image is still needed.[86][87]
- ^ a b c d e f g h Prophet, Tony (May 13, 2015). «Introducing Windows 10 Editions». Windows Experience Blog. Microsoft.
- ^ a b c d e f Bott, Ed (May 14, 2015). «Windows 10 editions: Everything you need to know». ZDNet. CBS Interactive.
- ^ a b c d e f Foley, Mary Jo (July 2, 2015). «Which Windows 10 editions get which features?». ZDNet. CBS Interactive.
- ^ Diaconu, Klaus (August 10, 2017). «Microsoft announces Windows 10 Pro for Workstations». Windows For Your Business. Microsoft. Archived from the original on August 11, 2017. Retrieved August 12, 2017.
- ^ Foley, Mary Jo (August 10, 2017). «Microsoft confirms new Windows 10 Pro for Workstations edition». ZDNet. CBS Interactive.
- ^ Warren, Tom (August 10, 2017). «Microsoft reveals new Windows 10 Workstations edition for power users». The Verge. Vox Media.
- ^ Foley, Mary Jo (July 27, 2016). «Microsoft to add new Windows 10 Pro Education edition to its line-up». ZDNet. CBS Interactive.
- ^ a b «Windows 10 editions for education customers». Microsoft. Retrieved February 22, 2019.
- ^ a b «Manage Windows 10 and Microsoft Store tips, «fun facts», and suggestions». Microsoft. Retrieved February 22, 2019.
- ^ DaniHalfin. «Assign devices to servicing branches for Windows 10 updates (Windows 10)». docs.microsoft.com. Retrieved May 3, 2017.
- ^ «The next Windows 10 Long Term Servicing Channel (LTSC) release». Microsoft. February 18, 2021. Retrieved July 2, 2021.
- ^ a b c d e «Overview of Windows as a service». Microsoft. Retrieved May 6, 2017.
- ^ a b Brinkmann, Martin (July 28, 2017). «Windows 10 LTSB becomes Windows 10 LTSC». gHacks Technology News.
- ^ Keizer, Gregg. «FAQ: Windows 10 LTSB explained». Computerworld. Archived from the original on January 23, 2018. Retrieved October 3, 2018.
- ^ greg-lindsay. «What’s new in Windows 10 Enterprise LTSC 2021 — What’s new in Windows». docs.microsoft.com. Retrieved November 18, 2021.
- ^ «Windows 10 in S mode FAQ». Windows.com. Microsoft.
- ^ Turner, Rich (May 18, 2017). «Will Linux distros run on Windows 10 S?». Microsoft. Retrieved May 26, 2017.
- ^ Gartenberg, Chaim (May 19, 2017). «Linux distros won’t run on Windows 10 S after all». The Verge. Vox Media.
- ^ Smith, Sharon. «Get clients for Microsoft Teams — Microsoft Teams». docs.microsoft.com. Retrieved May 2, 2021.
- ^ «Update get-clients.md · MicrosoftDocs/OfficeDocs-SkypeForBusiness@5c2ca5a». GitHub. Retrieved May 2, 2021.
- ^ Warren, Tom (May 2, 2017). «Windows 10 S won’t let you change the default browser or switch to Google search». The Verge. Vox Media.
- ^ a b Chacos, Brad. «Meet Windows 10 S, a streamlined, simplified, Microsoft Store-only OS for schools». PC World. IDG.
- ^ Warren, Tom (June 19, 2017). «Microsoft now lets Surface Laptop owners revert back to Windows 10 S». The Verge. Vox Media.
- ^ «Windows 10 S is Microsoft’s answer to Chrome OS». The Verge. Vox Media. May 2, 2017. Retrieved May 2, 2017.
- ^ Bright, Peter (September 14, 2016). «Desktop apps make their way into the Microsoft Store». Ars Technica. Condé Nast.
- ^ «Windows 10 Cloud looks just like Windows 10 in leaked screenshots». The Verge. Vox Media. February 3, 2017. Retrieved March 11, 2017.
- ^ «Leaked Microsoft document confirms Windows 10 Cloud and a Chromebook competitor». PC World. IDG. Retrieved April 23, 2017.
- ^ «Unlock Windows Holographic for Business features». Microsoft Docs. Retrieved May 12, 2021.
- ^ «Microsoft pushes Windows 10 Holographic as the one-stop option for VR and AR». Ars Technica. Retrieved May 12, 2021.
- ^ «Windows 10 Team Anniversary Update now available for Microsoft Surface Hub». Neowin. Retrieved May 3, 2017.
- ^ «Windows Embedded Version Overview» (PDF). PROXIS. Retrieved January 14, 2024.
- ^ «IoT Enterprise FAQ». Microsoft. Retrieved July 2, 2021.
- ^ «IoT Enterprise Features by Release». Microsoft. Retrieved July 2, 2021.
- ^ a b «Windows IoT Enterprise LTSC in Volume License». Microsoft Learn. Microsoft. December 20, 2023. Retrieved January 14, 2024.
- ^ «Windows 10 IoT for your business». Windows for Business. Microsoft. Retrieved January 16, 2016.
- ^ «Windows 10 IoT Enterprise». MS Embedded. Silica. August 14, 2015. Archived from the original on May 8, 2017. Retrieved February 1, 2016.
- ^ a b «Microsoft to combine Windows 10 IoT Core and IoT Enterprise in 2021». ZDNet. Mary Jo Foley. Retrieved January 22, 2022.
- ^ a b c «Windows 10 IoT Core». Arrow Electronics, Inc. Retrieved January 14, 2024.
- ^ «The next Windows 10 Long Term Servicing Channel (LTSC) release». Microsoft. February 18, 2021. Retrieved January 14, 2024.
- ^ Patrizio, Andy (September 29, 2016). «Microsoft is leaving the consumer mobile market». Network World. IDG Publishing. Retrieved August 30, 2018.
- ^ «Windows 10 on Thin Clients: Deliver Best Results with Scout Agents (Part 1 of 2)». Fujitsu. Archived from the original on January 23, 2021. Retrieved August 25, 2020.
- ^ «Supported operating systems and browsers in Intune». Microsoft. Retrieved August 25, 2020.
- ^ «Windows 10 IoT Core lifecycle details». Microsoft Lifecycle. Microsoft. Retrieved January 14, 2024.
- ^ «Windows 10 IoT LTSC 2019 Core lifecycle details». Microsoft Lifecycle. Microsoft. Retrieved January 14, 2024.
- ^ «Windows 10 IoT Core LTSC lifecycle details». Microsoft Lifecycle. Microsoft. Retrieved January 14, 2024.
- ^ «Microsoft admits Windows 10 S was confusing, new ‘S Mode’ upgrades will be free». The Verge. Retrieved March 8, 2018.
- ^ Tung, Liam. «Windows 10 to permit block on apps installing if they’re not from Microsoft Store». ZDNet. Retrieved March 8, 2018.[dead link]
- ^ «What is Windows 10 Lean?». April 24, 2018.
- ^ Bowden, Zac (January 21, 2022). «This is Microsoft’s canceled Andromeda OS running on a Lumia 950». Windows Central. Retrieved October 22, 2023.
- ^ Warren, Tom (October 2, 2019). «Microsoft Surface Neo first look: the future of Windows 10X is dual-screen». The Verge. Retrieved May 4, 2020.
- ^ Hollister, Sean (October 2, 2019). «Windows 10X is Microsoft’s latest stab at a ‘Lite’ operating system, exclusively for dual-screens». The Verge. Retrieved May 4, 2020.
- ^ «Microsoft reportedly shelves Windows 10X, its Chrome OS competitor». The Verge. May 7, 2021. Retrieved May 7, 2021.
- ^ Salter, Jim (May 13, 2021). «Microsoft puts Windows 10X variant on the back burner». Ars Technica. Retrieved May 14, 2021.
- ^ Warren, Tom (May 4, 2020). «Microsoft confirms Windows 10X is coming to laptops amid big jump in Windows usage». The Verge. Retrieved May 4, 2020.
- ^ Ballard, Barclay (January 25, 2021). «This clever Windows 10X feature will prevent thieves from resetting stolen devices». TechRadar. Retrieved January 21, 2023.
- ^ Warren, Tom (May 18, 2021). «Microsoft confirms Windows 10X is dead». The Verge. Retrieved May 18, 2021.
- ^ «Windows 11 Leaks Indicate a Dramatic New Look Is Coming Soon». Gizmodo. June 15, 2021. Archived from the original on June 16, 2021. Retrieved June 16, 2021.
- ^ Ron (August 2, 2015). «Grab the Media Feature Pack for Windows 10 N and Windows 10 KN editions». OnMSFT.com. Retrieved March 11, 2016.
- ^ a b «Media Feature Pack for Windows 10/11 N (February 2023)». Support. Microsoft. Retrieved February 28, 2023.
- ^ Slater-Robins, Max. «Microsoft is helping manufacturers make cheap tablets that can run Windows as well as Android». Business Insider UK. Retrieved April 23, 2016.
- ^ Aaron, Dennis. «Windows Guides». Retrieved June 4, 2023.
- ^ «Microsoft made a version of Windows 10 for the Chinese government». Engadget. May 23, 2017. Retrieved May 28, 2017.
- ^ Myerson, Terry (May 23, 2017). «Announcing Windows 10 China Government Edition and the new Surface Pro». Windows Blog. Microsoft.
- ^ Dudau, Vlad (June 10, 2015). «Microsoft shows OEMs how to market Windows 10; talks features and SKUs». Neowin. Neowin LLC. Retrieved June 19, 2015.
- ^ a b «Compare Windows 10 Pro & Enterprise (E3 & E5) Commercial Editions». microsoft.com. Microsoft. Archived from the original on October 25, 2017.
- ^ a b «Compare Windows 10 Editions & Versions | Home & Pro». microsoft.com. Microsoft. Archived from the original on October 31, 2017.
- ^ a b c «TPM recommendations — Windows Security». microsoft.com. Microsoft. Archived from the original on March 17, 2024.
- ^ Howse, Brett (July 2, 2015). «Windows 10 Editions Compared». AnandTech. Purch.
- ^ a b Graham Sutherland (April 7, 2022). «CPU Socket and Core Count Limits in Windows 10 (And How To Remove Them)». Codeinsecurity. Retrieved April 8, 2022.
- ^ Andre Da Costa (September 15, 2015). «Understanding Windows 10 Editions, Architectures and Builds». groovyPost. Retrieved January 12, 2020.
- ^ «Processor Groups — Win32 Apps — Microsoft Docs». Microsoft Docs. December 30, 2021. Retrieved April 8, 2022.
- ^ «NUMA Support — Win32 Apps — Microsoft Docs». Microsoft Docs. August 19, 2021. Retrieved April 8, 2022.
- ^ Geoff Chappell (December 17, 2019). «KAFFINITY_EX». Geoff Chappell, Software Analyst. Retrieved April 8, 2022.
- ^ «Configure Windows telemetry in your organization». docs.microsoft.com. Microsoft. August 10, 2020.
- ^ «Continuum on Windows 10». July 27, 2015.
- ^ Confirmed by @MicrosoftHelps (Verified) on Twitter
- ^ «Features that are removed or deprecated in Windows 10 Fall Creators Update». Support (28 ed.). Microsoft. October 17, 2017.
- ^ «Windows Insider Program».
- ^ «Windows Insider Program».
- ^ «Windows Insider Program».
- ^ «Windows Insider Program».
- ^ a b «Improve performance of a file server with SMB Direct». Microsoft Learn. Microsoft. August 3, 2023. Retrieved June 27, 2024.
- ^ a b «RDMA Supported Versions of Windows 10/11». Tuxera Documentation. Tuxera. n.d. Retrieved June 27, 2024.
- ^ shortpatti. «DirectAccess». docs.microsoft.com. Retrieved September 1, 2019.
- ^ «DirectAccess and Windows 10 in Education». August 4, 2016.
- ^ Thurrott, Paul (February 10, 2017). «Ask Paul: Is Windows To Go Coming to Windows 10 Pro?». thurrott.com. BWW Media Group.
- ^ Niehaus, Michael; Lich, Brian. «Windows To Go frequently asked questions (Windows 10)». docs.microsoft.com. Microsoft. Retrieved July 30, 2017.
How can Windows To Go be deployed in an organization? [~snip~] A Windows 10 Enterprise or Windows 10 Education image
- ^ «TrendForce Adjusts Notebooks’ Unit Memory Capacity for 2015 Down by 3~5% due to Microsoft’s New License Fee Arrangement for Windows 10». DRAMeXchange. TrendForce Corp. July 27, 2015. Retrieved March 11, 2016.
- ^ Trent, Rod (June 9, 2015). «Windows 10 Upgrade Paths». SuperSite for Windows. Penton.
- ^ «Windows Ends Installation Path for Free Windows 7/8 Upgrade». Microsoft. Retrieved September 29, 2023.
- ^ Tyson, Mark (September 29, 2023). «Microsoft Says the Days of Free Windows 7 to 10 or 11 Updates Are Over». Tom’s Hardware. Retrieved September 29, 2023.
- ^ Lindsay, Greg; Lich, Brian (April 5, 2017). «Windows 10 upgrade paths». Microsoft Docs. Microsoft.
- ^ Warren, Tom (April 20, 2017). «Microsoft will now release major Windows 10 updates every March and September». The Verge. Vox Media.
- ^ «Current Branch». PC Mag.
- ^ «How to Pause Windows 10 Automatic Updates To Avoid Critical Bugs». www.bleepingcomputer.com. Retrieved September 1, 2020.
- ^ «Windows 10 : the case of the missing update deferral options — gHacks Tech News». www.ghacks.net. May 28, 2019. Retrieved June 13, 2019.
- ^ Leonhard, Woody (March 1, 2017). «Put Windows 10 updates on hold—now available in Creators Update build 15046». Computerworld. IDG. Retrieved May 6, 2017.
- ^ Paul, Ian (April 18, 2017). «How to defer future updates in the Windows 10 Creators Update». PC World. IDG.
- ^ Keizer, Gregg (November 17, 2015). «How to defer upgrades and updates in Windows 10 Pro». Computerworld. IDG. Archived from the original on November 18, 2015.
- ^ «What’s new in Windows 10 Enterprise LTSC 2021». Microsoft Learn. Microsoft. December 18, 2023. Retrieved June 9, 2024.
- ^ Woods, Rich (September 24, 2018). «Windows Server 2019 and Windows Server, version 1809 will be generally available in October». Neowin.
Похожие новости
Инструкция по активации Windows 10
Инструкция по активации Windows 10 Активация позволит подтвердить подлинность вашей …
Читать подробнее
Инструкция по активации Microsoft Office через учетную запись
Инструкция по активации Microsoft Office Активация Microsoft Office позволяет подтвердить …
Читать подробнее
Понравилась статья?
Поделись!
Чтобы легально использовать Windows 10, нужна официальная лицензия. Это обязательное требование, продиктованное пользователю компанией Microsoft. Разработчик блокирует все попытки использования ОС без соблюдения этого правила и называет такие копии своего продукта пиратскими.
Если пользователь не ввел и не проверил электронный ключ (или цифровую лицензию при обновлении до «Десятки» с «Семерки»), он не может выбрать и установить обои рабочего стола и системные звуки, скрыть сообщение о необходимости активации копии Виндовс. На сегодня существуют способы, как бесплатно устранить эти ограничения (например, скачать программу Universal Watermark Disabler для удаления водяных знаков Виндовс 10 с экрана или активатор, проверяющий подлинность копии без ключа). Эти утилиты нелегально используют для персональной или корпоративной версии «Десятки». Перечисленные программы дают временное решение, могут заразить компьютер вредоносными приложениями и строго запрещены к использованию компанией Майкрософт. Для корректной работы операционной системы пользователю стоит купить и использовать официальную лицензию.
Далее расскажем об основных видах лицензий для персональных и корпоративных пользователей. Надеемся, эта информация поможет вам подобрать подходящую лицензию для легального использования программного продукта.
Что такое OEM лицензия?
Чтобы легально установить и использовать «Десятку» на личном ПК, нужно иметь одну из следующих лицензий:
- ОЕМ (Original Equipment Manufacturer, или производитель оригинального оборудования) – самый дешевый и «скрытый» тип. Копию Виндовс устанавливает производитель оборудования, а потом наклеивает соответствующий сертификат подлинности на корпус данной техники. То есть лицензионная операционная система предоставляется вместе с устройством, на котором она установлена. Пользователь просто включает ПК с «Десяткой» и начинает работать. Но у этого типа лицензии есть серьезные ограничения:
- пользователь не имеет права покупать и устанавливать OEM license Виндовс 10;
- категорически нельзя переносить на другое устройство;
- возникают сбои активации после замены материнской платы и других компонентов техники;
- нельзя делать перепрошивку BIOS;
- ОЕМ не может быть подарком, установленным отдельно от компьютера, собранного производителем.
Если пользователь установил такую лицензию отдельно на работающий ПК, любая серьезная проверка покажет нарушения соглашения с компанией Майкрософт. Это может обернуться серьезными проблемами (особенно для юрлиц, но физлиц это тоже касается).
- FPP (Full Packaged Product, или полный укомплектованный продукт) – коробочная версия лицензии, которую можно покупать в фирменном магазине или у сертифицированного партнера Майкрософт и самостоятельно установить на ПК. Права на использование ОС не привязаны к устройству. Пользователь может создать аккаунт Майкрософт, привязать license к нему и использовать Виндовс 10 после замены компонентов ПК, покупки нового компьютера или переезда в другую страну. Также он может оставлять заявку для техподдержки через официальный сайт разработчика. Главным недостатком FFP остается высокая цена.
- GGK (Get Geniune Kit, или получить подлинный комплект) – компромиссное решение, предложенное Майкрософт для пользователей, которые случайно стали использовать нелегальную копию. Благодаря лицензированию объекты малого бизнеса и отдельные пользователи могут работать на Виндовс 10 без последствий.
Также ESD (Electronic Software Distribution, или электронное распространение программного продукта) ошибочно принимают за отдельный вид лицензий. Сами представители компании Microsoft настаивают на том, что это способ распространения лицензии, а не отдельный тип разрешений.
Этот канал предполагает отправку Product Key по электронной почте, поэтому лицензионная копия «Десятки» стоит дешевле и распространяется быстрее. Чтобы восстановить ключ, пользователю достаточно найти письмо на почте и скопировать 25-символьный шифр активации. Таким способом можно легально активировать любую версию «Десятки» (Pro, Home, Enterprise).
Среди корпоративных лицензий выделяются такие разновидности:
- OL (открытая лицензия) – электронная license на корпоративные продукты, которая позволяет купить легальные копии ОС дешевле. Не предполагает ограниченный срок действия и строгие обязательства. Компания должна приобрести не менее 5 разрешений при одновременной покупке.
- OV (открытая ценность) – программа для образовательных учреждений и среднего бизнеса, позволяющая отдельно покупать подписки на веб-службы.
- OVS (подписка на открытую ценность) предполагает, что компания использует ПО, пока действует соглашение с разработчиком. Отличается низкими затратами.
- SPLA (лицензионное соглашение поставщика услуг) – партнерская программа, которая предполагает оплату только за используемое ПО.
- GGWA (получить соглашение на подлинную копию Виндовс) – именная лицензия для организации, которая случайно установила нелицензионное ПО ранее. Предполагает Downgrade, 1 key многократной установки. Чтобы загрузить дистрибутив, стоит перейти на официальный сайт разработчика.
Теперь вы ознакомились с основными типами лицензий и можете делать собственный выбор программы для личного или корпоративного пользования. Существует единый стандарт – легально использовать ОС без license нельзя. Пользователь может убрать водяной знак и скачать активатор и подключиться к KMS server, но от этого не получится превратить пиратскую копию в официальную. Через какое-то время Майкрософт обязательно обнаружит такую копию, и сообщение о нелегальной копии появится снова вместе с черным экраном вместо заставки.
Выбирайте лицензию для вашей копии (Хоум, Про, Корпоративная) и продлевайте ее, если она истекает, чтобы иметь возможность пользоваться всеми возможностями «Десятки».
Преимущества электронного распространения лицензии
Электронное распространение ключей (ESD) – это удобная и популярная форма приобретения лицензий на ОС Виндовс 10. Она не предполагает материальное доказательство покупки (карточку с 25-символьным шифром).
Однако, обладает весомыми преимуществами:
- стоит дешевле, чем при покупке коробочной версии;
- отсутствие привязки к технике (не нужно запоминать ключ при добавлении license в аккаунт Майкрософт);
- допустимый перенос на другое устройство (если ключ удален из реестра на первом компьютере);
- может быть подарком;
- предполагает доставку ключа по электронной почте.
Также пользователь может приобрести 2-3 ключа для активации ОС в офисе частного предпринимателя или на нескольких личных устройствах. Дистрибутив подходящей версии Виндовс можно скачать на официальном сайте разработчика бесплатно. Активация занимает около 3 минут. При использовании дистрибутива системные ошибки не возникнут.
Покупка электронных ключей удобна и предприятиям, и частным лицам. Доставка лицензии в таком случае мгновенная.
