Все способы:
- Размер Виндовс 10 после установки
- Официальная информация
- Реальные цифры
- Windows 10 Home
- Windows 10 Pro
- Windows 10 Enterprise
- Windows 10 Education
- Рекомендации по установке
- Сколько места занимает используемая Виндовс 10
- Заключение
- Вопросы и ответы: 9
Каждая новая версия Windows выдвигает все более высокие требования к железу компьютера, и одним из таковых является наличие свободного пространства на накопителе. «Десятка», ввиду множества функциональных улучшений и переработок, в данном плане является наиболее прожорливым представителем семейства ОС от Майкрософт, и сегодня мы расскажем, сколько конкретно нужно места для установки каждой ее версии и редакции.
Размер Виндовс 10 после установки
Минимальные и рекомендуемые системные требования для инсталляции любой версии Windows можно найти на официальном сайте Microsoft, на упаковке цифровой копии системы, а также на сайтах и в магазинах, где она реализуется официальными дистрибьюторами. Вот только там указаны обобщенные сведения, которые несколько отличаются от реальных. Именно с них мы и начнем.

Официальная информация
Обратившись к любому официальному источнику, предоставляющему возможность приобретения и/или скачивания Виндовс 10, вы увидите следующие сведения:
| Windows 10 32 bit (x86) | 16 Гб |
| Windows 10 64 bit (x64) | 20 Гб |
По сути, это даже не требования, а усредненный размер, который займет система на диске сразу после ее установки и первой настройки. Если же говорить непосредственно о свободном месте, необходимом для работы системы, требования следующие:
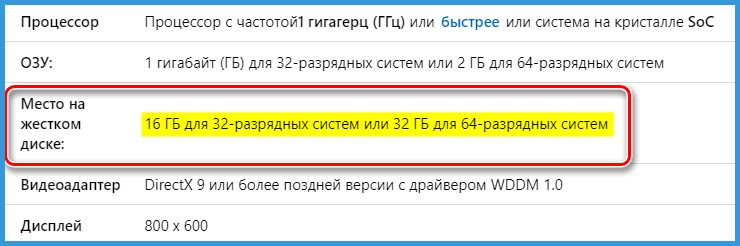
Информация с официального сайта Microsoft
Реальные цифры
В действительности объем занимаемого Виндовс 10 пространства определяется не только ее разрядностью – 32-х или 64-битной – но и редакцией, коих существует четыре:
- Домашняя
- Профессиональная
- Корпоративная (для бизнеса и организаций)
- Образовательная (для образовательных учреждений)
Рядовые пользователи практически всегда останавливают свой выбор либо на первой, либо на второй. Две последних — это по своей сути несколько улучшенные и заточенные под конкретный пользовательский сегмент Про-версии.
Windows 10 Home
| 32 bit | 13 Гб |
| 64 bit | 16 Гб |
То есть Домашняя Виндовс как раз и «упирается» в те рекомендованные значения, которые Майкрософт указывают для всех редакций «десятки».
Windows 10 Pro
| 32 bit | 20 Гб |
| 64 bit | 25 Гб |
А вот Профессиональная, в зависимости от разрядности, либо находится на грани максимальных системных требований, либо выходит за их пределы на целые 25% или 5 Гб в реальных цифрах. Это следует учитывать непосредственно перед ее установкой.
Windows 10 Enterprise
| 32 bit | 16 Гб |
| 64 bit | 20 Гб |
Корпоративная Виндовс, хоть и основывается на Профессиональной, но в плане занимаемого дискового пространства не всегда соответствует указанным разработчиком требованиям. Дело в том, что в данную версию «десятки» интегрировано несколько больше инструментов и функциональных возможностей, чем в Про, а потому уже после первой настройки она вполне может занимать те же 20 – 25 Гб.
Windows 10 Education
| 32 bit | 16 Гб |
| 64 bit | 20 Гб |
Данная редакция Виндовс базируется на Корпоративной, поэтому в действительности размер занимаемого ею пространства (непосредственно после установки) тоже может быть приближен к 20 и 25 Гб для 32-х и 64-разрядной версии соответственно.
Рекомендации по установке
Несмотря на столь скромные по современным меркам минимальные и рекомендуемые системные требования, для комфортного использования и максимально стабильной работы Windows 10, вне зависимости от ее разрядности и версии, требуется около 100 Гб свободного пространства на том диске или разделе, где она установлена. Идеальное решение – SSD от 124 Гб и выше. Связанно это не в последнюю очередь с частыми обновлениями операционной системы, которые тоже должны куда-то скачиваться и сохраняться. Согласитесь, что в заявленные Microsoft и озвученные нами в самом начале статьи 16 (для x86) и 32 Гб (для x64) не «впишется» не то что апдейт, а и даже самая скромная пользовательская папка с документами и файлами.
Сколько места занимает используемая Виндовс 10
Для того чтобы узнать точный размер дискового пространства, занимаемого Windows 10, установленной и используемой на конкретно вашем компьютере или ноутбуке, недостаточно открыть «Этот компьютер» и посмотреть на диск C:. Помимо самой системы на нем хранятся как минимум временные и ваши личные файлы, поэтому для получения точных сведений необходимо действовать следующим образом.
Читайте также:
Как открыть «Проводник» в Windows 10
Как добавить ярлык «Мой компьютер» на рабочий стол Windows 10
- Откройте «Параметры» Виндовс, нажав «WIN+I» на клавиатуре.
- Перейдите к разделу «Система».
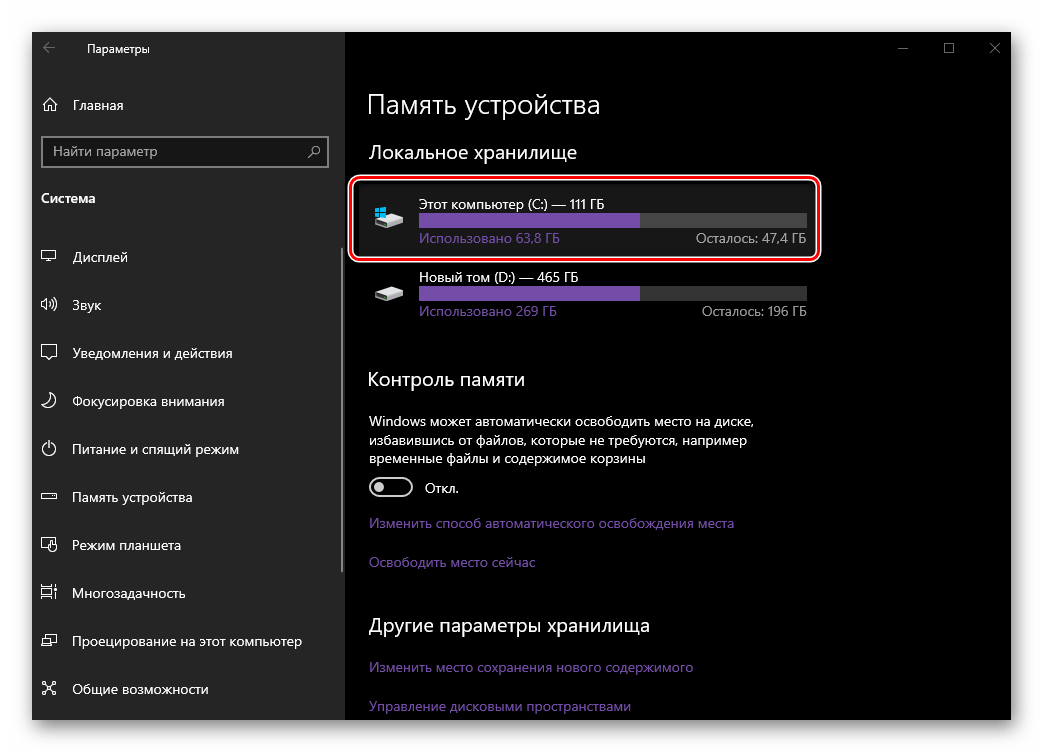
- В боковом меню выберите вкладку «Память устройства».
- В списке дисков и/или разделов (блок «Локальное хранилище») нажмите по тому, на котором у вас установлена операционная система.
- Дождитесь завершения сканирования, после чего обратите внимание на значение, указанное напротив надписи «Системные и зарезервированные». Это и есть тот объем, которые на данный момент занимает конкретно Windows 10, а также дополнительные файлы и компоненты, без которых ее работа невозможна.

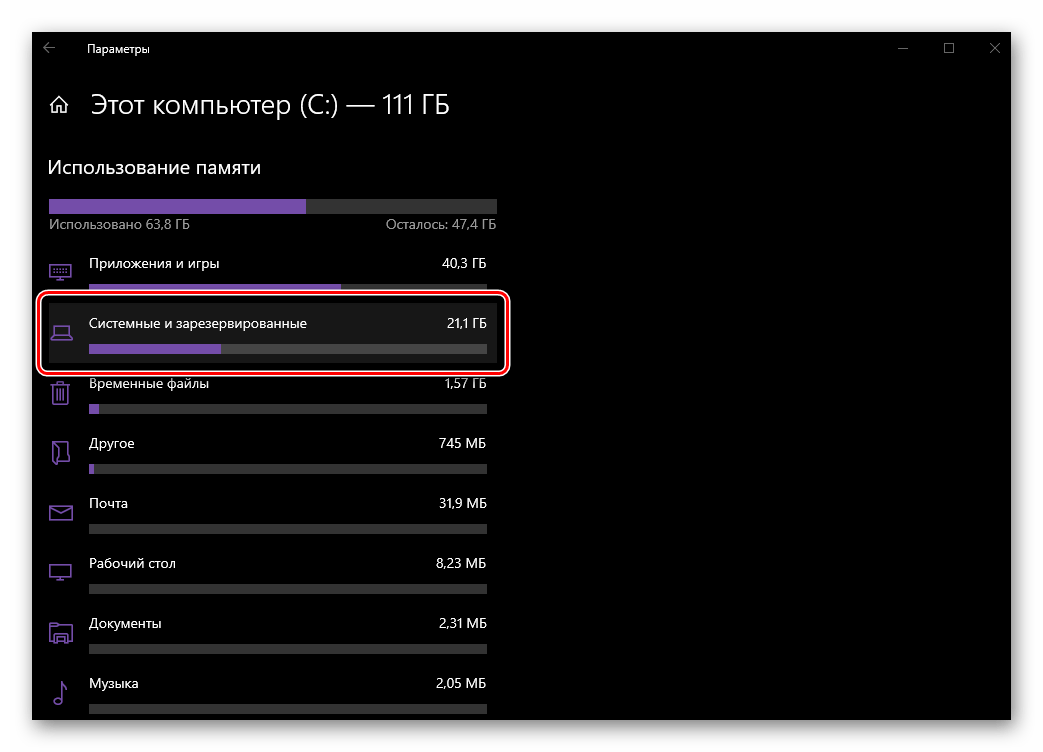
Для получения более детальных сведений просто кликните по этому блоку.

Заключение
Завершая эту небольшую статью, хотим акцентировать внимание на том, что в ней были рассмотрены заявленные и реальные значения только для лицензионной Windows 10, предлагаемой Microsoft и официальными дистрибьюторами. Всевозможные пиратские сборки и ломаные дистрибутивы, которые мы не рекомендуем к использованию, могут занимать как значительно меньше места, так и заметно больше – все зависит от того, что оттуда удалит «автор» или, наоборот, добавит.
Наша группа в TelegramПолезные советы и помощь
-
System requirements for installing Windows 10
Keeping Windows 10 up-to-date
More information on hard drive space requirements to install or update Windows 10
Feature-specific requirements for Windows 10
Language versions
Feature deprecations and removals
These are the basic requirements for installing Windows 10 on a PC. If your device does not meet these requirements, you may not have the great experience intended with Windows 10 and might want to consider purchasing a new PC.
There may be additional requirements over time for updates, as well as requirements to turn on specific features within the OS.
Windows 10 is designed to deliver updates for the supported lifetime of the device. Two types of updates may be provided: quality updates and feature updates. Quality updates include both security and non-security updates and are typically targeted to be released once a month. Feature updates also include security and non-security fixes as well as new features to Windows 10 and are typically provided twice a year. Ensuring that your device receives these updates and is kept up-to-date is important for your device security. Windows 10 periodically checks for updates so you don’t have to. When an update is available—and sufficient free disk space is available on your device—it will be automatically installed. So that Windows 10 continues to stay updated, it’s important to ensure your device has sufficient free space. See additional applicable details in the following notes.
Important notes about updates:
- A device might not be able to receive updates if the device hardware is incompatible, if it lacks current drivers or sufficient available hard drive space, or if it’s otherwise outside of the Original Equipment Manufacturer’s (“OEM”) support period. Visit the Windows Lifecycle Fact Sheet or the Lifecycle FAQ for Windows products to learn more about the servicing timeline for each feature update.
- Some of the disk space needed for installing updates is only temporarily required. Typically, ten days after installing an update, a disk cleanup will be automatically performed to delete copies of the older, unneeded Windows files and free up space again.
- Some of the disk space needed for installing updates is only temporarily required. Typically, ten days after installing an update, a disk cleanup will be automatically performed to delete copies of the older, unneeded Windows files and free up space again.
- Not all features in an update will work on all devices.
- An internet connection is required to perform updates and Internet access (ISP) fees might apply.
- If you need assistance installing an update, Windows 10 Update Assistant may be able to help.
The size of the Windows operating system that comes with your device and the amount of space needed to download and install Windows updates, are highly variable as they depend on a variety of factors. Visit here to learn why. The factors that impact the amount of free hard drive space needed to take an update include: the versions of Windows previously installed on the machine, the amount of disk space available to reuse from Windows files, such as the virtual memory pagefile or hibernation file, which applications are installed on your device and how those applications store data. Starting with the May 2019 Update, the system requirements for hard drive size for clean installs of Windows 10 as well as new PCs changed to a minimum of 32GB. The 32GB or larger drive requirement is set to leave space for users to install apps and to keep data on the device. Installing Windows or updating from a previous version of Windows on devices with less than 32GB storage will continue to work if the device has enough free space available. When updating, Windows will attempt to automatically free up enough hard drive space and guide you through freeing up even more if the automatic cleanup is not sufficient. You can also take steps to free up space on your own. For more information, see Free up space to install the latest Windows 10 update or visit the related FAQ.
In addition to the requirements above that are needed to run Windows, some features have additional requirements. In some cases, features included with updated versions of Windows 10 will be best experienced with newer processors. For specific hardware support please refer to your Original Equipment Manufacturer (OEM). Below are some additional details regarding requirements for key features:
- BitLocker Drive Encryption (available with Windows 10 Pro or Windows 10 Enterprise only) requires a Trusted Platform Module (TPM) 1.2 or higher and Trusted Computing Group (TCG)-compliant BIOS or UEFI. BitLocker can be used on devices without TPM, but you will need to save a startup key on a removable device such as a USB flash drive. TPM 2.0 and InstantGo support is required when you want to automatically encrypt the local drive when joining a device to Azure Active Directory (AAD). Check with your PC manufacturer to confirm if your device supports the correct TPM version and InstantGo for the scenario you want to enable.
- BitLocker To Go requires a USB flash drive (available in Windows 10 Pro and Windows 10 Enterprise only).
- Client Hyper-V requires a 64-bit system with second level address translation (SLAT) capabilities and additional 2 GB of RAM (available in Windows 10 Pro and Windows 10 Enterprise only).
- Copilot in Windows 10 requires greater than 4 GB of RAM and a minimum 720p display resolution. Copilot is currently available in preview in select global markets on compatible Windows 10 Home and unmanaged Pro devices running version 22H2 or higher. It is our intention to add additional markets and compatibility over time.
- Cortana is only currently available on Windows 10 for the United States, United Kingdom, China, France, Italy, Germany, Brazil, Mexico, Japan, Canada, Spain, Australia and India.
- Microsoft account is required for some features.
- Miracast requires a display adapter which supports Windows Display Driver Model (WDDM) 1.3, and a Wi-Fi adapter that supports Wi-Fi Direct.
- Movies & TV application is not available in all regions. For the most up-to-date list of regions, please go to the Movies & TV information page.
- Secure boot requires firmware that supports UEFI v2.3.1 Errata B and has the Microsoft Windows Certification Authority in the UEFI signature database.
- Skype is available only in select countries and regions. Calling to select countries and regions only. Excludes special, premium and non-geographic numbers. For details, visit the Office FAQ page.
- Snap: The number of applications that can be snapped will depend upon the minimum resolution for the application with a limit of two applications in Tablet mode and four applications in Desktop mode.
- Speech recognition will vary by device microphone. For a better speech experience, you will need a:
- High fidelity microphone array
- Hardware driver with microphone array geometry exposed
- Tablet mode is available on tablets and 2-in-1s with GPIO indicators or those that have a laptop and slate indicator will be able to be configured to enter «tablet mode» automatically.
- Touch: To use touch, you need a tablet or a monitor that supports multi-touch.
- Two-factor authentication requires the use of a PIN, Biometric (finger print reader or illuminated infrared camera), or a phone with Wi-Fi or Bluetooth capabilities.
- Windows Hello requires a camera configured for near infrared (IR) imaging or fingerprint reader for biometric authentication. Devices without biometric sensors can use Windows Hello with a PIN or a portable Microsoft compatible security key.
- Xbox application requires an Xbox Live account, which is not available in all regions. For the most up-to-date list of regions, please go to Xbox Live Countries and Regions website.
- Wi-Fi Direct Printing requires a Wi-Fi adapter that supports Wi-Fi Direct and a device that supports Wi-Fi Direct Printing.
Windows 10 full localization languages include: Arabic (Saudi Arabia), Bulgarian (Bulgaria), Chinese (PRC), Chinese (Taiwan), Croatian (Croatia), Czech (Czech Republic), Danish (Denmark), Dutch (Netherlands), English (United Kingdom), English (United States), Estonian (Estonia), Finnish (Finland), French (France), French (Canada), German (Germany), Greek (Greece), Hebrew (Israel), Hungarian (Hungary), Italian (Italy), Japanese (Japan), Korean (Korea), Latvian (Latvia), Lithuanian (Lithuania), Norwegian, Bokmål (Norway), Polish (Poland), Portuguese (Brazil), Portuguese (Portugal), Romanian (Romania), Russian (Russia), Serbian (Latin, Serbia), Slovak (Slovakia), Slovenian (Slovenia), Spanish (Spain), Spanish (Mexico), Swedish (Sweden), Thai (Thailand), Turkish (Turkey), Ukrainian (Ukraine).
Additional languages available as Language Interface Packs
When upgrading to Windows 10 from a previous version of Windows such as Windows 7 or Windows 8.1 as well as when installing a newer update to Windows 10, some features may be deprecated or removed. Please see below for information regarding some of the key removed features:
- Desktop Messaging App: The messaging app on Desktop has a sync feature that can be used to sync SMS text messages received from Windows Mobile and keep a copy of them on the Desktop. Starting with the May 2019 Update (Windows 10, version 1903), the sync feature has been removed from all devices. Due to this change, you will only be able to access messages from the device that received the message.
- Wi-Fi WEP and TKIP: Starting with the May 2019 Update (Windows 10, version 1903), a warning message will appear when connecting to Wi-Fi networks secured with WEP or TKIP, which are not as secure as those using WPA2 or WPA3. In a future release, any connection to a Wi-Fi network using these old ciphers will be disallowed. Wi-Fi routers should be updated to use AES ciphers, available with WPA2 or WPA3.
- Cortana: Cortana has been updated and enhanced in the Windows 10 May 2020 Update (Windows 10, version 2004). With these changes, some previously available consumer skills such as music, connected home, and third-party skills will no longer be available. Get detailed information here.
- Phone Companion: As of the October 2018 Update (Windows 10, version 1809), Phone Companion is removed from your PC. Use the Phone page in the Settings app to sync your mobile phone with your PC. It includes all the Phone Companion features.
- HomeGroup: HomeGroup was removed starting with the April 2018 Update (Windows 10, version 1803), but you still have the ability to share printers, files, and folders. When you update from an earlier version of Windows 10, you won’t see HomeGroup in File Explorer, the Control Panel, or Troubleshoot (Settings > Update & Security > Troubleshoot). Any printers, files, and folders you shared using HomeGroup will continue to be shared. Instead of using HomeGroup, you can now share printers, files, and folders by using features that are built into Windows 10:
- Share your network printers
- Share files in File Explorer
- For Xbox 360 and HomeGroup users, please see more information on streaming media
- People app: In Windows 10, the People app shows mail from Microsoft 365 contacts and contacts from your school or work organization under Conversations. Starting with the April 2018 Update (Windows 10, version 1803), in order to see new mail in the People app from these specific contacts, you need to be online, and you need to have signed in with either a Microsoft 365 account or, for work or school organization accounts, through the Mail, People, or Calendar apps. Please be aware that you’ll only see mail for work and school organization accounts and some Microsoft 365 accounts.
- Reader app: The Reader app was removed from Windows 10 starting with the Fall Creators Update (Windows 10, version 1709). For reading PDF files, Microsoft Edge is the recommended replacement app and offers similar functionality as well as additional features including improved accessibility support, improved Inking, and support for AskCortana. Similarly, Windows XPS Viewer is recommended when reading XPS files and Windows Photos app for viewing TIFF files. Note that users of earlier Windows 10 versions can continue using the Reader app.
- Windows Journal: Windows Journal was removed starting with the Windows 10 Anniversary Update (Windows 10, version 1607). After Windows Journal is removed, you will no longer be able to open or edit Journal files (with .JNT or .JTP extensions). In place of Windows Journal, we encourage you to switch to OneNote. If you need to open or edit your journal files, more information is available here.
- Windows Media Digital Rights Management (WMDRM): WMDRM is no longer supported starting with the Windows 10 Anniversary Update (Windows 10, version 1607). You are no longer able to play music or video files that were protected by this rights management technology. Click here to learn more.
The following changes impact devices that are upgrading to Windows 10 from Windows 7, Windows 8 or Windows 8.1:
- Windows Media Center: If you have Windows 7 Home Premium, Windows 7 Professional, Windows 7 Ultimate, Windows 8 Pro with Media Center, or Windows 8.1 Pro with Media Center and you install Windows 10, Windows Media Center will be removed.
- Mobile Device Management (MDM): MDM functionality will not be available in Windows 10 Home edition.
- Windows 7 desktop gadgets: These will be removed as part of installing Windows 10.
- Solitaire, Minesweeper, and Hearts Games: These games that came pre-installed on Windows 7 will be removed as part of installing the Windows 10 upgrade. Microsoft has released our version of Solitaire and Minesweeper called the «Microsoft Solitaire Collection» and «Microsoft Minesweeper».
- Floppy drives: If you have a floppy drive, you will need to download the latest driver from Windows Update or from the manufacturer’s website.
- If you have Windows Live Essentials installed on your system, the OneDrive application is removed and replaced with the inbox version of OneDrive.
- OneDrive place holder files: OneDrive placeholder files are not supported in Windows 10. Windows 8.1 displayed placeholders for files available in OneDrive but not locally on the device. In Windows 10, users can choose which folders to sync from OneDrive settings.
- Snap: Snap is limited to two applications in Tablet mode.
В данной статье рассмотрим системные требования для различных версий Windows 10 (Pro, Домашняя, Корпоративная и т.п). Каждая версия Windows 10 предназначена для различных задач, соответственно какие-то версии требуют мощных компьютеров за счет множества включенных туда процессов и приложений, а какие-то меньше. Итак, приступим.
Системные требования Windows 10 Pro
Процессор: 1 ГГц или больше
Оперативная память (ОЗУ): 1 ГБ (32-бит) или 2 ГБ (64-бит)
Жесткий диск: 16 ГБ свободного пространства (32-бит) или 32 ГБ (64-бит)
Графика: поддержка DirectX 9 с драйверами WDDM 1.0 или выше
Экран: от 800×600
Приобрести Windows 10 Pro можете в нашем каталоге, а так же скачать дистрибутив.

Системные требования Windows 10 Домашняя (Home)
Процессор: 1 ГГц или больше
Оперативная память (ОЗУ): 1 ГБ (32-бит) или 2 ГБ (64-бит)
Жесткий диск: 16 ГБ свободного пространства (32-бит) или 20 ГБ (64-бит)
Графика: поддержка DirectX 9 с драйверами WDDM 1.0 или выше
Экран: от 800×600
Приобрести Windows 10 Домашняя можете в нашем каталоге, а так же скачать дистрибутив.

Системные требования Windows 10 Корпоративная (Enterprise) LTSC 2019
Процессор: 1 ГГц или больше
Оперативная память (ОЗУ): 1 ГБ (32-бит) или 2 ГБ (64-бит)
Жесткий диск: 16 ГБ свободного пространства (32-бит) или 20 ГБ (64-бит)
Графика: поддержка DirectX 9 с драйверами WDDM 1.0 или выше
Экран: от 800×600
Приобрести Windows 10 Корпоративная (Enterprise) LTSC 2019 можете в нашем каталоге, а так же скачать дистрибутив.

Системные требования Windows 10 Корпоративная (Enterprise) LTSB 2016
Процессор: 1 ГГц или больше
Оперативная память (ОЗУ): 1 ГБ (32-бит) или 2 ГБ (64-бит)
Жесткий диск: 16 ГБ свободного пространства (32-бит) или 20 ГБ (64-бит)
Графика: поддержка DirectX 9 с драйверами WDDM 1.0 или выше
Экран: от 800×600
Приобрести Windows 10 Корпоративная (Enterprise) LTSB 2016 можете в нашем каталоге, а так же скачать дистрибутив.

Системные требования Windows 10 Корпоративная (Enterprise) LTSB 2015
Процессор: 1 ГГц или больше
Оперативная память (ОЗУ): 1 ГБ (32-бит) или 2 ГБ (64-бит)
Жесткий диск: 20 ГБ
Графика: поддержка DirectX 9 с драйверами WDDM 1.0 или выше
Экран: от 800×600
Скачать Windows 10 Корпоративная (Enterprise) LTSB 2015 можете в нашем каталоге.

Системные требования Windows 10 Корпоративная (Enterprise)
Процессор: 1 ГГц или больше
Оперативная память (ОЗУ): 1 ГБ (32-бит) или 2 ГБ (64-бит)
Жесткий диск: 16 ГБ свободного пространства (32-бит) или 20 ГБ (64-бит)
Графика: поддержка DirectX 9 с драйверами WDDM 1.0 или выше
Экран: от 800×600
Приобрести Windows 10 Корпоративная (Enterprise) можете в нашем каталоге, а так же скачать дистрибутив.

Системные требования Windows 10 Для образовательных учреждений (Education)
Процессор: 1 ГГц или больше
Оперативная память (ОЗУ): 1 ГБ (32-бит) или 2 ГБ (64-бит)
Жесткий диск: 16 ГБ свободного пространства (32-бит) или 20 ГБ (64-бит)
Графика: поддержка DirectX 9 с драйверами WDDM 1.0 или выше
Экран: от 800×600
Приобрести Windows 10 Для образовательных учреждений (Education) можете в нашем каталоге, а так же скачать дистрибутив.

Системные требования Windows 10 Для рабочих станций (Pro for WorkStations)
Процессор: 1 ГГц или больше
Оперативная память (ОЗУ): 2 ГБ
Жесткий диск: 20 ГБ
Графика: поддержка DirectX 9 с драйверами WDDM 1.0 или выше
Экран: от 800×600
Приобрести indows 10 Для рабочих станций (Pro for WorkStations) можете в нашем каталоге, а так же скачать дистрибутив.

Лицензионный ключ активации Windows 10 от
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Windows 10 has several editions, all with varying feature sets, use cases, or intended devices. Certain editions are distributed only on devices directly from an original equipment manufacturer (OEM), while editions such as Enterprise and Education are only available through volume licensing channels. Microsoft also makes editions of Windows 10 available to device manufacturers for use on specific classes of devices, including IoT devices, and previously marketed Windows 10 Mobile for smartphones.
Baseline editions are the only editions available as standalone purchases in retail outlets. PCs often come pre-installed with one of these editions.
- Home
- Windows 10 Home is designed for use in PCs, tablets and 2-in-1 PCs. It includes all features directed at consumers.[1][2][3]
- Pro
- Windows 10 Pro includes all features of Windows 10 Home, with additional capabilities that are oriented towards professionals and business environments, such as Active Directory, Remote Desktop, BitLocker, Hyper-V, and Windows Defender Device Guard.[1][2][3]
- Pro for Workstations
- Windows 10 Pro for Workstations is designed for high-end hardware for intensive computing tasks and supports Intel Xeon, AMD Opteron and the latest AMD Epyc processors; up to 4 CPUs; up to 256 cores; up to 6 TB RAM; the ReFS file system; Non-Volatile Dual In-line Memory Module (NVDIMM); and remote direct memory access (RDMA).[4][5][6]
Organizational editions
[edit]
These editions add features to facilitate centralized control of many installations of the OS within an organization. The main avenue of acquiring them is a volume licensing contract with Microsoft.
- Education
- Windows 10 Education is distributed through Academic Volume Licensing. It was based on Windows 10 Enterprise and initially reported to have the same feature set.[1][2][3] As of version 1709, however, this edition has fewer features. See § Comparison chart for details.
- Pro Education
- This edition was introduced in July 2016 for hardware partners on new devices purchased with the discounted K–12 academic license. It was based on the Pro edition of Windows 10 and contains mostly the same features as Windows 10 Pro with different options disabled by default, and adds options for setup and deployment in an education environment. It also features a «Set Up School PCs» app that allows provisioning of settings using a USB flash drive, and does not include Cortana, Microsoft Store suggestions, Windows Sandbox, or Windows Spotlight.[7][8][9]
- Enterprise
- Windows 10 Enterprise provides all the features of Windows 10 Pro for Workstations, with additional features to assist with IT-based organizations.[1][2][3] Windows 10 Enterprise is configurable on two servicing channels, Semi-Annual Channel and Windows Insider Program.[10]
- Enterprise LTSC
- Enterprise LTSC (Long-Term Servicing Channel) is a long-term support variant of Windows 10 Enterprise, released every 2 to 3 years. Each release is supported with security updates for either 5 or 10 years after its release, and intentionally receives no feature updates.[11] Some features, including the Microsoft Store and bundled apps, are not included in this edition.[12][1][3] This edition was first released as Windows 10 Enterprise LTSB (Long-Term Servicing Branch).[13] There are currently 4 releases of LTSC: one in 2015 (RTM), one in 2016 (version 1607), one in 2018 (labeled as 2019, version 1809), and one in 2021 (version 21H2).[14][15]
- Enterprise multi-session
- Windows 10 Enterprise multi-session, a multi-session variant of Enterprise edition, included with Azure Virtual Desktop, allows multiple concurrent interactive sessions. Previously, only Windows Server could do this. A cloud-based alternative to an on-premise Remote Desktop Server (RDS). AVD is deployed in Azure Cloud as a virtual machine. License costs are already included in several Microsoft 365 subscriptions, including Microsoft 365 Business Premium or Microsoft 365 E3.
Since 2018, OEMs can ship Windows 10 Home and Pro in a feature-limited variation named S mode which evolved from the discontinued Windows 10 S. Organizations employing Windows 10 Enterprise or Windows 10 Education can make use of S mode too.[16] S mode is a feature-limited edition of Windows 10 designed primarily for low-end devices in the education market. It has a faster initial setup and login process, and allows devices to be provisioned using a USB drive with the «Set Up School PCs» app.
With the exception of the Microsoft Teams desktop client (which was made available for S mode in April 2019),[citation needed] the installation of software (both Universal Windows Platform (UWP) and Windows API apps) is only possible through the Microsoft Store, and built-in and Microsoft Store-obtained command line programs or shells cannot be run in this mode.[17][18][19][20] System settings are locked to allow only Microsoft Edge as the default web browser with Bing as its search engine.[21] The operating system may be switched out of S mode using the Microsoft Store for free. However, once S Mode is turned off, it cannot be re-enabled.[22][23] All Windows 10 devices in S mode include a free one-year subscription to Minecraft: Education Edition.[citation needed] Critics have compared the edition to Windows RT, and have considered it to be an alternative to ChromeOS.[22][24][25][26][27]
Device-specific editions
[edit]
These editions are licensed to OEMs only, and are primarily obtained via the purchase of hardware that includes it:
- Holographic
- A specific edition used by Microsoft’s HoloLens mixed reality smartglasses.[28][29]
- Team
- A specific edition used by Microsoft’s Surface Hub interactive whiteboard.[30]
Rebranded from Microsoft’s earlier operating system editions in the Windows Embedded family. Binary identical to their non-IoT counterparts with version 1809 and older,[31] while newer versions add support for smaller storage devices.[32][33] Available via OEMs and volume licensing for specific versions.[34]
- IoT Enterprise
- Intended specifically for use in small footprint, low-cost devices and IoT scenarios.[35][36]
- IoT Enterprise LTSC
- Long-Term Servicing Channel variant. Replaces all IoT Core edition variants starting with the 2021 release.[37][38] Furthermore, the 2021 release gains an extra 5 years of support compared to its non-IoT counterpart[39] and is available via volume licensing for the first time.[34]
Discontinued editions
[edit]
The following editions of Windows 10 were discontinued (as of Windows 10 version 21H2). For both Mobile and Mobile Enterprise, Microsoft confirmed it was exiting the consumer mobile devices market, so no successor product is available.[40]
- Mobile
- Windows 10 Mobile was designed for smartphones and small tablets. It included all basic consumer features, including Continuum capability. It was the de facto successor of Windows Phone 8.1 and Windows RT.[1][2]
- Mobile Enterprise
- Windows 10 Mobile Enterprise provided all of the features in Windows 10 Mobile, with additional features to assist IT-based organizations, in a manner similar to Windows 10 Enterprise, but optimized for mobile devices.[1][2]
- IoT Mobile
- A binary equivalent of Windows 10 Mobile Enterprise licensed for IoT applications. Also known as IoT Mobile Enterprise.[41][42]
- IoT Core/IoT Core LTSC
- Windows 10 IoT Core was optimized for smaller and lower-cost industry devices. It was also formerly provided free of charge for use in devices like the Raspberry Pi for hobbyist use. Only UWP apps are supported, and only one at a time at that.[38] Discontinued after version 1809. Support ended on 10 November 2020 for non-LTSC,[43] while IoT Core LTSC (2019/version 1809) support will continue until 9 January 2029.[44][45] Merged into and replaced by IoT Enterprise LTSC starting with the 2021/version 21H2 release.[37][38]
- S
- Windows 10 S was an edition released in 2017 which ultimately evolved into the so-called S mode of Windows 10. In March 2018, Microsoft announced that it would be phasing out Windows 10 S, citing confusion among manufacturers and end-users.[46][47]
- Polaris
- Polaris was made for desktops and laptops; only one build was leaked in 2021. It was known as «Windows OneCore 10» in the Windows Boot Manager.[citation needed]
- Lean
- Lean was meant to be used for cheaper desktops and laptops with a small storage capacity and resources, it could fit even on a 16 GB hard drive; only one build was released in 2018, the setup identifies the edition as «Windows 10 Lean».[48]
- Andromeda
- Andromeda was demonstrated on the Lumia 950.[49] The project was canceled for unknown reasons.
- 10X
- Originally announced for use on dual-screen devices such as the Surface Neo and other potential form factors, 10X featured a modified user interface designed around context specific interactions or «postures» on such devices, including a redesigned Start menu with no tiles, and use of container technology to run Win32 software.[50][51] The platform was described as a more direct competitor to ChromeOS.[52][53] On May 4, 2020, Microsoft announced that Windows 10X would first be used on single-screen devices, and that they would «continue to look for the right moment, in conjunction with our OEM partners, to bring dual-screen devices to market».[54] Microsoft also added anti-theft protection to Windows 10X, just like how Apple’s Activation Lock and anti-theft protection on Android devices and Chromebooks work.[55] On May 18, 2021, Head of Windows Servicing and Delivery John Cable stated that Windows 10X had been cancelled, and that its foundational technologies would be leveraged for future Microsoft products.[56] Several design changes in 10X, notably the centered taskbar and redesigned start menu, would be later introduced in Windows 11.[57]
Regional variations
[edit]
- N/KN
- As with previous versions of Windows since Windows XP, all Windows 10 editions for PC hardware have «N» and «KN» variations in Europe and South Korea that exclude multimedia functionality, in compliance with antitrust rulings.[58] According to details that Microsoft has published, any app that relies on Microsoft multimedia technologies experiences impaired functionality on these editions, unable to even play audio notification tones.[59] Restoring the missing functionality to these editions entails installing the «Media Feature Pack», followed by Skype, Movies & TV, Windows Media Player, Xbox Game Bar, Windows Voice Recorder, and four codecs.[59] The variation cannot be changed without a clean install, and keys for one variation will not work on other variations.
- Home with Bing
- As with Windows 8.1, a reduced-price «Windows 10 with Bing» SKU is available to OEMs; it is subsidized by having Microsoft’s Bing search engine set as default, which cannot be changed to a different search engine by OEMs. It is intended primarily for low-cost devices, and is otherwise identical to Windows 10 Home.[60][61]
- Home Single Language
- In some emerging markets,[citation needed] OEMs preinstall a variation of Windows 10 Home called Single Language without the ability to switch the display language. To change the display language, the user will need to upgrade to the standard editions of Windows 10 Home or Windows 10 Pro. It is otherwise identical to Windows 10 Home. However, it should not be confused with the standard OEM editions of Windows 10, where OEMs and mobile operators can restrict which display languages are preloaded and/or made available for download and installation for their target markets.
- CMIT Government Edition
- In May 2017, it was reported that Microsoft, as part of its partnership with China Electronics Technology Group, created a specially-modified variant of Windows 10 Enterprise («G») designed for use within branches of the Chinese government. This variant is pre-configured to «remove features that are not needed by Chinese government employees», and allow the use of its internal encryption algorithms.[62][63]
- OEM variants (PC and Mobile)
- As with Windows 10 Mobile and previous versions of Windows since Windows Phone 7 for smartphones and Windows 8 for PCs (since its mobile counterpart shares the same Windows NT kernel), device manufacturers (as well as mobile operators for devices with cellular capabilities) who preload Windows 10 can choose not to support certain display languages either during the OOBE process or available as optional downloads via Settings and/or the Microsoft Store based on the target market. For optional downloads, in the first scenario, the option to download the language pack (and any associated supplementary fonts) will not be available; in the second scenario, the installation will be blocked with the message «This app is not compatible with this device,» where the «app» in question is a language pack from the Microsoft Store. Unlike Windows 10 Home Single Language, device manufacturers and mobile operators can support one, some, or even all of the display languages available (though many devices that do not run Single Language editions of Windows will likely support multiple display languages). OEM editions are otherwise identical to their retail counterparts without any other feature restrictions.
Microsoft OEM licensing formula takes display size, RAM capacity and storage capacity into account. In mid-2015, devices with 4 GB RAM were expected to be $20 more expensive than devices with 2 GB RAM.[88]
At the time of launch, Microsoft deemed Windows 7 (with Service Pack 1) and Windows 8.1 users eligible to upgrade to Windows 10 free of charge, so long as the upgrade took place within one year of Windows 10’s initial release date. Windows RT and the respective Enterprise editions of Windows 7, 8, and 8.1 were excluded from this offer.[89]
Windows 10 free upgrade matrix
| Windows version and edition | Windows 10 edition |
|---|---|
| Windows 7 Starter SP1 | Home |
| Windows 7 Home Basic SP1 | |
| Windows 7 Home Premium SP1 | |
| Windows 8.1 with Bing | |
| Windows 8.1 | |
| Windows 7 Professional SP1 | Pro |
| Windows 7 Ultimate SP1 | |
| Windows 8.1 Pro | |
| Windows Phone 8.1 | Mobile |
The following table summarizes possible transition paths (upgrade, downgrade, or migration) that can be taken, provided that proper licenses are purchased.
Windows RT does not appear in this table because it cannot be upgraded to Windows 10.
On September 28, 2023, Microsoft disabled the free upgrade path to Windows 10 from Windows 7 or 8.x, although upgrades from Windows 10 to 11 are still supported.[90][91]
Microsoft releases minor versions of Windows 10 through the free feature updates.[12] Originally, Microsoft released feature updates semiannually. They contained new features as well as changes.[93] With the release of Windows 11, however, Microsoft has changed the release schedule to annual. These feature updates do not contain any noticeable changes.
The pace at which a system receives feature updates depends on the «release channel» (originally, «release branch») from which the system downloads its updates.[12]
Windows Insider is a beta testing program that allows access to pre-release builds of Windows 10, enabling power users, developers, and vendors to test and provide feedback on future feature updates to Windows 10 as they are developed. Before the release of Windows 11, Windows Insider itself consisted of four «rings»:
- The Dev channel (previously «Fast» ring) distributed new builds as they were released.
- The Beta channel (previously «Slow» ring) distributed new builds with a delay following their availability on the Fast ring.
- The «Release Preview» channel distributed release candidate builds.
- The now-closed «Skip Ahead» ring distributed builds of the next feature update while a current release was being finished.
After the release of Windows 11, only the «Release Preview» and «Beta» rings remains active.
General Availability Channel
[edit]
Since 2022, the General Availability Channel (GAC) distributes feature updates annually. To receive these updates, users must either request them manually or wait for their version of Windows 10 to go out of support.
Originally, however, Microsoft distributed feature updates through two distinct channels:[94]
- The «Current Branch» (CB) distributed all feature updates as they graduated from the Windows Insider program. Microsoft only supported the latest build. Windows would automatically install the latest feature update from CB. Users could defer the CB feature update for up to 365 days.[95][96][97][98] Microsoft renamed CB to «Semi-Annual Channel (Targeted)» in version 1709.
- The «Current Branch for Business» (CBB), which was not available in the Home edition, distributed feature updates with a four-month delay. This allowed customers and vendors to evaluate and perform additional testing on new builds before broader deployments. Devices could be switched back to the Current Branch at any time.[12][99] Microsoft renamed CBB to «Semi-Annual Channel» in version 1709.
Since version 1903, Microsoft dismantled the two-channel scheme in favor of a unified «Semi-Annual Channel» (SAC). Microsoft supports each SAC version of Windows for 30 months. Windows no longer installs new feature updates automatically before the expiry of the 30-months support period. With the release of Windows 11, Microsoft changed the release schedule to annual, and change the channel’s name to «General Availability Channel» (GAC).
Long-Term Servicing Channel
[edit]
LTSC exclusively distributes the «Enterprise LTSC», «IoT Core», and «IoT Enterprise LTSC» editions of Windows 10. Microsoft releases a new minor version of these editions every 2–3 years. LTSC builds adhere to Microsoft’s traditional support policy which was in effect before Windows 10, including:
- Five years of mainstream support
- Critical and security updates for ten years after their release (excludes non-IoT editions version 2021 and newer)[100]
- No feature updates from Windows Update
Microsoft discourages the use of LTSC editions outside of «special-purpose devices» that perform a fixed function and thus do not require new user experience features. As a result, these editions do not come with Microsoft Store, most Cortana features, and most bundled apps.[12][1][3] LTSC was originally called the «Long-Term Servicing Branch» (LTSB) until 2016.[13] Later, LTSC editions are included in Windows 11.
- Windows Server 2016, based on Windows 10 version 1607[101]
- Windows Server 2019, based on Windows 10 version 1809
- Windows Server 2022, based on a modified version of Windows 10 version 21H2
- Xbox system software, an operating system now based on the Windows 10 core, designed to run on the Xbox consoles
- Windows 10 version history
- ^ a b c 32-bit architectures like IA-32 and ARM32 have a memory addressing limitation of four gigabytes. In practice, less than 4 GB of memory is addressable as the 4 GB space also includes the memory mapped peripherals.
- ^ Windows 10 utilises processor groups on x86-64 to manage processor affinity and scheduling. The Windows 10 kernel has a hard-coded limit of 20 processor groups, and each processor group can contain up to 64 logical processors. A logical processor is either a physical or SMT core. Processor groups are allocated based on the NUMA topology of the system. One processor group cannot span multiple sockets or NUMA nodes. Processor groups are not available on IA-32; 32-bit builds instead use an older affinity mask implementation with a limit of 32 logical processors. The limit of 20 processor groups does not change between Windows 10 editions. There is no specific limit on the number of physical cores that can be used on Windows 10, unlike Windows Server where physical cores must be additionally licensed.[69][71][72][73]
- ^ There are three (previously four) telemetry levels, in the order of magnitude: Diagnostic data off (Security), Required (Basic), and Optional (Full). The higher the level, the more information that is sent to Microsoft. Previous Windows 10 versions had a level between Required and Optional, and the older names for the levels are shown in the parenthesis.
- ^ Cortana is available only in certain markets. Experience may vary by region and device.
- ^ The only device-encryption feature that is available in Windows 10 Home requires Trusted Platform Module version 2.0.[67]
- ^ BitLocker is available and can be used in the absence of Trusted Platform Module.[67]
- ^ a b This feature was missing from Windows 10 version 1803, but not the prior or next versions.
- ^ Windows Hello requires specialized hardware, such as a fingerprint reader, illuminated IR sensor or other biometric sensor.
- ^ SMB Direct (SMB over Remote Direct Memory Access [RDMA]) is available in cleanly installed Windows 10 Pro 22H2 or later and absent if the operating system has been upgraded from versions prior to 22H2. SMB Direct server capability is absent from all editions of Windows 10, regardless of version.
- ^ On Windows 10 Pro, a Control Panel applet corresponding to this feature appears, but a Windows 10 Enterprise or Education image is still needed.[86][87]
- ^ a b c d e f g h Prophet, Tony (May 13, 2015). «Introducing Windows 10 Editions». Windows Experience Blog. Microsoft.
- ^ a b c d e f Bott, Ed (May 14, 2015). «Windows 10 editions: Everything you need to know». ZDNet. CBS Interactive.
- ^ a b c d e f Foley, Mary Jo (July 2, 2015). «Which Windows 10 editions get which features?». ZDNet. CBS Interactive.
- ^ Diaconu, Klaus (August 10, 2017). «Microsoft announces Windows 10 Pro for Workstations». Windows For Your Business. Microsoft. Archived from the original on August 11, 2017. Retrieved August 12, 2017.
- ^ Foley, Mary Jo (August 10, 2017). «Microsoft confirms new Windows 10 Pro for Workstations edition». ZDNet. CBS Interactive.
- ^ Warren, Tom (August 10, 2017). «Microsoft reveals new Windows 10 Workstations edition for power users». The Verge. Vox Media.
- ^ Foley, Mary Jo (July 27, 2016). «Microsoft to add new Windows 10 Pro Education edition to its line-up». ZDNet. CBS Interactive.
- ^ a b «Windows 10 editions for education customers». Microsoft. Retrieved February 22, 2019.
- ^ a b «Manage Windows 10 and Microsoft Store tips, «fun facts», and suggestions». Microsoft. Retrieved February 22, 2019.
- ^ DaniHalfin. «Assign devices to servicing branches for Windows 10 updates (Windows 10)». docs.microsoft.com. Retrieved May 3, 2017.
- ^ «The next Windows 10 Long Term Servicing Channel (LTSC) release». Microsoft. February 18, 2021. Retrieved July 2, 2021.
- ^ a b c d e «Overview of Windows as a service». Microsoft. Retrieved May 6, 2017.
- ^ a b Brinkmann, Martin (July 28, 2017). «Windows 10 LTSB becomes Windows 10 LTSC». gHacks Technology News.
- ^ Keizer, Gregg. «FAQ: Windows 10 LTSB explained». Computerworld. Archived from the original on January 23, 2018. Retrieved October 3, 2018.
- ^ greg-lindsay. «What’s new in Windows 10 Enterprise LTSC 2021 — What’s new in Windows». docs.microsoft.com. Retrieved November 18, 2021.
- ^ «Windows 10 in S mode FAQ». Windows.com. Microsoft.
- ^ Turner, Rich (May 18, 2017). «Will Linux distros run on Windows 10 S?». Microsoft. Retrieved May 26, 2017.
- ^ Gartenberg, Chaim (May 19, 2017). «Linux distros won’t run on Windows 10 S after all». The Verge. Vox Media.
- ^ Smith, Sharon. «Get clients for Microsoft Teams — Microsoft Teams». docs.microsoft.com. Retrieved May 2, 2021.
- ^ «Update get-clients.md · MicrosoftDocs/OfficeDocs-SkypeForBusiness@5c2ca5a». GitHub. Retrieved May 2, 2021.
- ^ Warren, Tom (May 2, 2017). «Windows 10 S won’t let you change the default browser or switch to Google search». The Verge. Vox Media.
- ^ a b Chacos, Brad. «Meet Windows 10 S, a streamlined, simplified, Microsoft Store-only OS for schools». PC World. IDG.
- ^ Warren, Tom (June 19, 2017). «Microsoft now lets Surface Laptop owners revert back to Windows 10 S». The Verge. Vox Media.
- ^ «Windows 10 S is Microsoft’s answer to Chrome OS». The Verge. Vox Media. May 2, 2017. Retrieved May 2, 2017.
- ^ Bright, Peter (September 14, 2016). «Desktop apps make their way into the Microsoft Store». Ars Technica. Condé Nast.
- ^ «Windows 10 Cloud looks just like Windows 10 in leaked screenshots». The Verge. Vox Media. February 3, 2017. Retrieved March 11, 2017.
- ^ «Leaked Microsoft document confirms Windows 10 Cloud and a Chromebook competitor». PC World. IDG. Retrieved April 23, 2017.
- ^ «Unlock Windows Holographic for Business features». Microsoft Docs. Retrieved May 12, 2021.
- ^ «Microsoft pushes Windows 10 Holographic as the one-stop option for VR and AR». Ars Technica. Retrieved May 12, 2021.
- ^ «Windows 10 Team Anniversary Update now available for Microsoft Surface Hub». Neowin. Retrieved May 3, 2017.
- ^ «Windows Embedded Version Overview» (PDF). PROXIS. Retrieved January 14, 2024.
- ^ «IoT Enterprise FAQ». Microsoft. Retrieved July 2, 2021.
- ^ «IoT Enterprise Features by Release». Microsoft. Retrieved July 2, 2021.
- ^ a b «Windows IoT Enterprise LTSC in Volume License». Microsoft Learn. Microsoft. December 20, 2023. Retrieved January 14, 2024.
- ^ «Windows 10 IoT for your business». Windows for Business. Microsoft. Retrieved January 16, 2016.
- ^ «Windows 10 IoT Enterprise». MS Embedded. Silica. August 14, 2015. Archived from the original on May 8, 2017. Retrieved February 1, 2016.
- ^ a b «Microsoft to combine Windows 10 IoT Core and IoT Enterprise in 2021». ZDNet. Mary Jo Foley. Retrieved January 22, 2022.
- ^ a b c «Windows 10 IoT Core». Arrow Electronics, Inc. Retrieved January 14, 2024.
- ^ «The next Windows 10 Long Term Servicing Channel (LTSC) release». Microsoft. February 18, 2021. Retrieved January 14, 2024.
- ^ Patrizio, Andy (September 29, 2016). «Microsoft is leaving the consumer mobile market». Network World. IDG Publishing. Retrieved August 30, 2018.
- ^ «Windows 10 on Thin Clients: Deliver Best Results with Scout Agents (Part 1 of 2)». Fujitsu. Archived from the original on January 23, 2021. Retrieved August 25, 2020.
- ^ «Supported operating systems and browsers in Intune». Microsoft. Retrieved August 25, 2020.
- ^ «Windows 10 IoT Core lifecycle details». Microsoft Lifecycle. Microsoft. Retrieved January 14, 2024.
- ^ «Windows 10 IoT LTSC 2019 Core lifecycle details». Microsoft Lifecycle. Microsoft. Retrieved January 14, 2024.
- ^ «Windows 10 IoT Core LTSC lifecycle details». Microsoft Lifecycle. Microsoft. Retrieved January 14, 2024.
- ^ «Microsoft admits Windows 10 S was confusing, new ‘S Mode’ upgrades will be free». The Verge. Retrieved March 8, 2018.
- ^ Tung, Liam. «Windows 10 to permit block on apps installing if they’re not from Microsoft Store». ZDNet. Retrieved March 8, 2018.[dead link]
- ^ «What is Windows 10 Lean?». April 24, 2018.
- ^ Bowden, Zac (January 21, 2022). «This is Microsoft’s canceled Andromeda OS running on a Lumia 950». Windows Central. Retrieved October 22, 2023.
- ^ Warren, Tom (October 2, 2019). «Microsoft Surface Neo first look: the future of Windows 10X is dual-screen». The Verge. Retrieved May 4, 2020.
- ^ Hollister, Sean (October 2, 2019). «Windows 10X is Microsoft’s latest stab at a ‘Lite’ operating system, exclusively for dual-screens». The Verge. Retrieved May 4, 2020.
- ^ «Microsoft reportedly shelves Windows 10X, its Chrome OS competitor». The Verge. May 7, 2021. Retrieved May 7, 2021.
- ^ Salter, Jim (May 13, 2021). «Microsoft puts Windows 10X variant on the back burner». Ars Technica. Retrieved May 14, 2021.
- ^ Warren, Tom (May 4, 2020). «Microsoft confirms Windows 10X is coming to laptops amid big jump in Windows usage». The Verge. Retrieved May 4, 2020.
- ^ Ballard, Barclay (January 25, 2021). «This clever Windows 10X feature will prevent thieves from resetting stolen devices». TechRadar. Retrieved January 21, 2023.
- ^ Warren, Tom (May 18, 2021). «Microsoft confirms Windows 10X is dead». The Verge. Retrieved May 18, 2021.
- ^ «Windows 11 Leaks Indicate a Dramatic New Look Is Coming Soon». Gizmodo. June 15, 2021. Archived from the original on June 16, 2021. Retrieved June 16, 2021.
- ^ Ron (August 2, 2015). «Grab the Media Feature Pack for Windows 10 N and Windows 10 KN editions». OnMSFT.com. Retrieved March 11, 2016.
- ^ a b «Media Feature Pack for Windows 10/11 N (February 2023)». Support. Microsoft. Retrieved February 28, 2023.
- ^ Slater-Robins, Max. «Microsoft is helping manufacturers make cheap tablets that can run Windows as well as Android». Business Insider UK. Retrieved April 23, 2016.
- ^ Aaron, Dennis. «Windows Guides». Retrieved June 4, 2023.
- ^ «Microsoft made a version of Windows 10 for the Chinese government». Engadget. May 23, 2017. Retrieved May 28, 2017.
- ^ Myerson, Terry (May 23, 2017). «Announcing Windows 10 China Government Edition and the new Surface Pro». Windows Blog. Microsoft.
- ^ Dudau, Vlad (June 10, 2015). «Microsoft shows OEMs how to market Windows 10; talks features and SKUs». Neowin. Neowin LLC. Retrieved June 19, 2015.
- ^ a b «Compare Windows 10 Pro & Enterprise (E3 & E5) Commercial Editions». microsoft.com. Microsoft. Archived from the original on October 25, 2017.
- ^ a b «Compare Windows 10 Editions & Versions | Home & Pro». microsoft.com. Microsoft. Archived from the original on October 31, 2017.
- ^ a b c «TPM recommendations — Windows Security». microsoft.com. Microsoft. Archived from the original on March 17, 2024.
- ^ Howse, Brett (July 2, 2015). «Windows 10 Editions Compared». AnandTech. Purch.
- ^ a b Graham Sutherland (April 7, 2022). «CPU Socket and Core Count Limits in Windows 10 (And How To Remove Them)». Codeinsecurity. Retrieved April 8, 2022.
- ^ Andre Da Costa (September 15, 2015). «Understanding Windows 10 Editions, Architectures and Builds». groovyPost. Retrieved January 12, 2020.
- ^ «Processor Groups — Win32 Apps — Microsoft Docs». Microsoft Docs. December 30, 2021. Retrieved April 8, 2022.
- ^ «NUMA Support — Win32 Apps — Microsoft Docs». Microsoft Docs. August 19, 2021. Retrieved April 8, 2022.
- ^ Geoff Chappell (December 17, 2019). «KAFFINITY_EX». Geoff Chappell, Software Analyst. Retrieved April 8, 2022.
- ^ «Configure Windows telemetry in your organization». docs.microsoft.com. Microsoft. August 10, 2020.
- ^ «Continuum on Windows 10». July 27, 2015.
- ^ Confirmed by @MicrosoftHelps (Verified) on Twitter
- ^ «Features that are removed or deprecated in Windows 10 Fall Creators Update». Support (28 ed.). Microsoft. October 17, 2017.
- ^ «Windows Insider Program».
- ^ «Windows Insider Program».
- ^ «Windows Insider Program».
- ^ «Windows Insider Program».
- ^ a b «Improve performance of a file server with SMB Direct». Microsoft Learn. Microsoft. August 3, 2023. Retrieved June 27, 2024.
- ^ a b «RDMA Supported Versions of Windows 10/11». Tuxera Documentation. Tuxera. n.d. Retrieved June 27, 2024.
- ^ shortpatti. «DirectAccess». docs.microsoft.com. Retrieved September 1, 2019.
- ^ «DirectAccess and Windows 10 in Education». August 4, 2016.
- ^ Thurrott, Paul (February 10, 2017). «Ask Paul: Is Windows To Go Coming to Windows 10 Pro?». thurrott.com. BWW Media Group.
- ^ Niehaus, Michael; Lich, Brian. «Windows To Go frequently asked questions (Windows 10)». docs.microsoft.com. Microsoft. Retrieved July 30, 2017.
How can Windows To Go be deployed in an organization? [~snip~] A Windows 10 Enterprise or Windows 10 Education image
- ^ «TrendForce Adjusts Notebooks’ Unit Memory Capacity for 2015 Down by 3~5% due to Microsoft’s New License Fee Arrangement for Windows 10». DRAMeXchange. TrendForce Corp. July 27, 2015. Retrieved March 11, 2016.
- ^ Trent, Rod (June 9, 2015). «Windows 10 Upgrade Paths». SuperSite for Windows. Penton.
- ^ «Windows Ends Installation Path for Free Windows 7/8 Upgrade». Microsoft. Retrieved September 29, 2023.
- ^ Tyson, Mark (September 29, 2023). «Microsoft Says the Days of Free Windows 7 to 10 or 11 Updates Are Over». Tom’s Hardware. Retrieved September 29, 2023.
- ^ Lindsay, Greg; Lich, Brian (April 5, 2017). «Windows 10 upgrade paths». Microsoft Docs. Microsoft.
- ^ Warren, Tom (April 20, 2017). «Microsoft will now release major Windows 10 updates every March and September». The Verge. Vox Media.
- ^ «Current Branch». PC Mag.
- ^ «How to Pause Windows 10 Automatic Updates To Avoid Critical Bugs». www.bleepingcomputer.com. Retrieved September 1, 2020.
- ^ «Windows 10 : the case of the missing update deferral options — gHacks Tech News». www.ghacks.net. May 28, 2019. Retrieved June 13, 2019.
- ^ Leonhard, Woody (March 1, 2017). «Put Windows 10 updates on hold—now available in Creators Update build 15046». Computerworld. IDG. Retrieved May 6, 2017.
- ^ Paul, Ian (April 18, 2017). «How to defer future updates in the Windows 10 Creators Update». PC World. IDG.
- ^ Keizer, Gregg (November 17, 2015). «How to defer upgrades and updates in Windows 10 Pro». Computerworld. IDG. Archived from the original on November 18, 2015.
- ^ «What’s new in Windows 10 Enterprise LTSC 2021». Microsoft Learn. Microsoft. December 18, 2023. Retrieved June 9, 2024.
- ^ Woods, Rich (September 24, 2018). «Windows Server 2019 and Windows Server, version 1809 will be generally available in October». Neowin.
Содержание статьи:
- Windows 10 LTSC: где, что, зачем, почему
- В чем отличие LTSC от других версий 10-ки
- Где скачать LTSC версию
- Как добавить русский язык
- Вопросы и ответы: 31
Доброго дня!
А хотели бы вы скачать оптимизированную операционную систему Windows 10 без Store, Edge, Cortana, OneDrive? Как это ни странно, но такая система есть (причем, официальная от Microsoft) — ее оригинальное название «Windows 10 LTSC»!
На мой взгляд это весьма неплохая замена всяким сборкам, внутрь которых могли натолкать всё, что угодно…
Возможно, единственной проблемой для некоторых может стать отсутствие русского языка в меню (но это легко устраняется установкой языкового пакета, причем, тоже официально).
Так что предлагаю присмотреться к этой ОС поближе… 👀
*
👉 В помощь!
Как создать загрузочную флешку с Windows 10 (прим.: далее в статье мы скачаем образ ISO с LTSC, и чтобы установить эту ОС — вам нужно будет подготовить загрузочную флешку…) — https://ocomp.info/sozdat-zagruz-fleshku-v-rufus.html
*
Windows 10 LTSC: где, что, зачем, почему
В чем отличие LTSC от других версий 10-ки
Windows 10 LTSC — это «урезанная» разновидность версии ОС Enterprise (Корпоративная). Основное отличие между Enterprise и LTSC — в количестве приложений (встроенных в систему), и способе получения обновлений.
Например, в LTSC отсутствуют:
- Магазин Microsoft Store;
- браузер Microsoft Edge (есть Internet Explore);
- Среда Windows Ink Workspace;
- Cortana;
- Игровой режим, ночное освещение;
- OneDrive, и ряд др. ПО.
Обратите внимание на скриншот ниже: меню ПУСК (да и в целом панель задач) выглядят непривычно пусто…👀
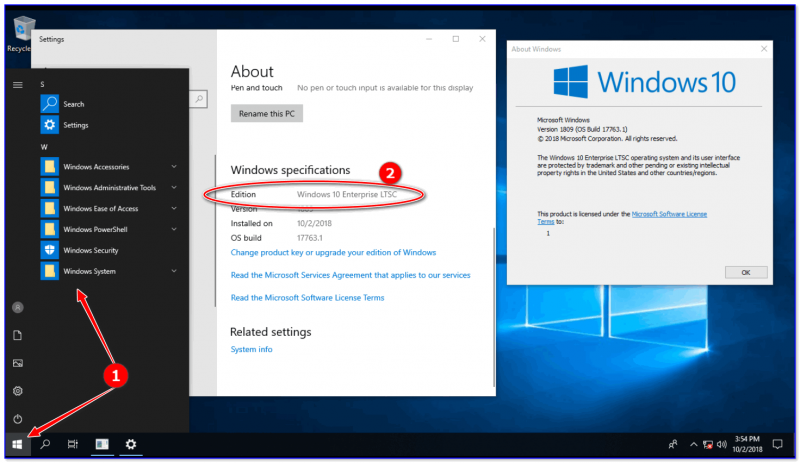
Windows 10 LTSC / Кликабельно
*
👉 Еще одно важное отличие LTSC от других версий Windows — это работа с обновлениями. Дело в том, что в обычных сборках ставятся все подряд обновления (система постоянно «надоедает» этим), в LTSC же обновления касаются только стабильности и безопасности системы (и, как правило, они очень редки: 1-3 в год!).
Предназначена данная ОС, прежде всего, для различных компаний и организаций (кому не нужны различные красивые менюшки…). Впрочем, ничего не мешает ее установить и нам (обычным пользователям), благо что ОС можно бесплатно использовать в течении 90 дней!
*
👉 Ну и пару слов касательно оптимизации
В этом плане система LTSC на порядок быстрее и производительнее, чем Windows 10 Pro или Home. Для работы LTSC будет достаточно 1-1,5 ГБ ОЗУ и около 10 ГБ места на жестком диске! Даже количество процессов по умолчанию не превышает 4-х десятков (в Pro их не менее 70)!
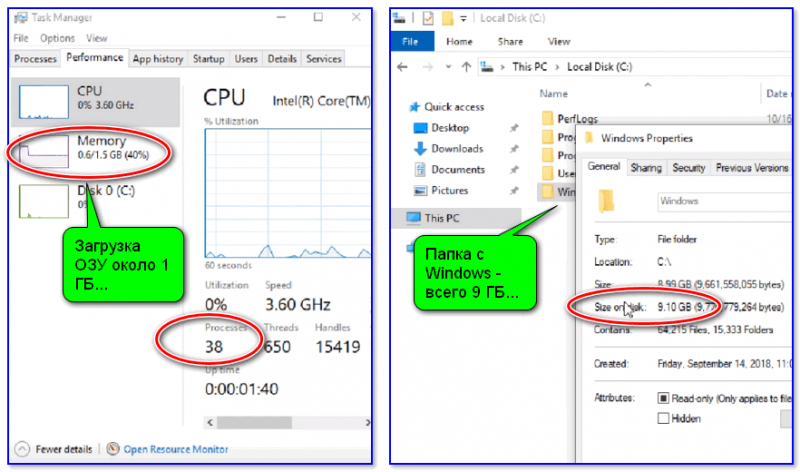
Весьма неплохая оптимизация…
Единственный минус: как уже говорил выше, систему придется устанавливать на английском языке (что у некоторых пользователей может вызвать сильный дискомфорт). Однако, это поправимо…
*
Где скачать LTSC версию
👉 На официальном сайте: https://www.microsoft.com/ru-ru/evalcenter/evaluate-windows-10-enterprise
Перейдя по ссылке выше на официальный сайт Microsoft — нужно будет указать, что вам требуется образ «ISO LTSC» (см. скриншот), далее заполнить форму (с указанием ФИО, телефоном, e-mail адресом).
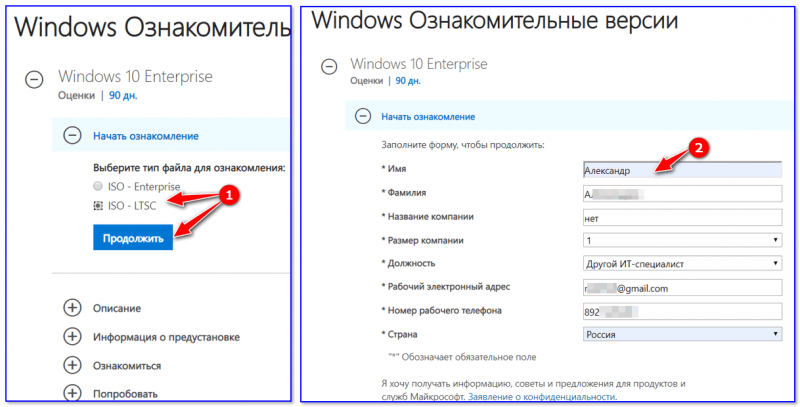
Форма для загрузки ISO
После чего выбрать разрядность системы (32/64 бит), язык и нажать по кнопке «Загрузка».
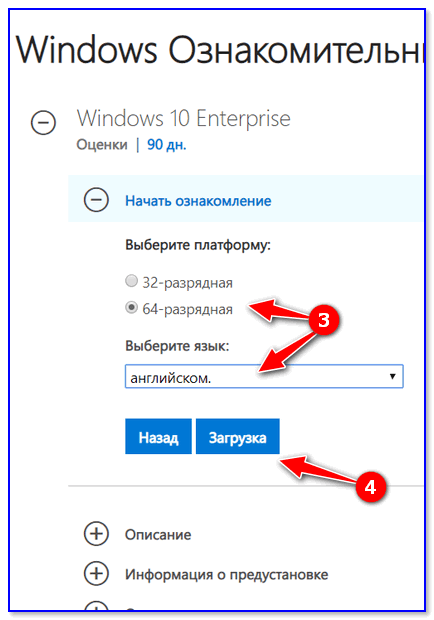
Выбор языка, загрузка ISO
Когда образ ISO будет загружен, его необходимо будет 👉 записать на флешку (и перейти к 👉 установке ОС).
*
Как добавить русский язык
Итак, будем считать, что у вас уже установлена английская Windows 10 LTSC.
1) Сначала нужно нажать сочетание кнопок Win+i (должно появиться окно параметров Windows 10).
2) После зайти в меню «Time & language -> Region & language», нажать по кнопке «Add Language» и добавить русский. Как правило, достаточно загрузить несколько недостающих языковых пакетов. После перезагрузки системы — всё будет на русском…
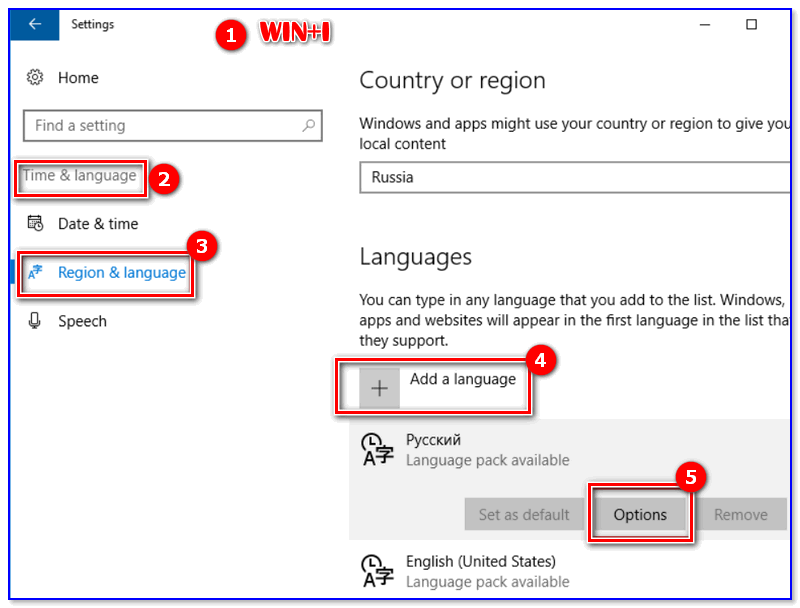
Win+i — параметры Windows 10 / установка русского языка
Русский
👉 Кстати!
Многие пользователи в LTSC не могут найти иконку проводника на панели задач (её и нет, можете не искать 👌). Для запуска проводника используйте либо «Лупу» с поиском, либо сочетание клавиш Win+E.
Проводник
*
Дополнения приветствуются…
Удачной работы!
👋
Первая публикация: 09.10.2019
Корректировка: 11.08.2021
