IT Essentials (Version 8.0) – IT Essentials 8.0 Chapter 10 Exam Answers (10.5 Module Exam)
How to find: Press “Ctrl + F” in the browser and fill in whatever wording is in the question to find that question/answer. If the question is not here, find it in Questions Bank.
NOTE: If you have the new question on this test, please comment Question and Multiple-Choice list in form below this article. We will update answers for you in the shortest time. Thank you! We truly value your contribution to the website.
1. A support technician wants to upgrade a system to Windows 10 but is unsure whether the hardware and software on the existing system are compatible. What tool or utility would be the best choice for the user?
- Windows Easy Transfer
- Cortana Virtual Assistant
- Get Windows 10 app
- User State Migration Tool
2. True or False? When a user is working on a system that uses a network file system, there is no difference between accessing a file stored locally or on another computer on the network.
- True
- False
3. Which file system is used to access files over a network?
- NFS
- CDFS
- FAT
- NTFS
Explanation: NFS (Network File System) is used to access files on other computers across a network. Windows operating systems support several file systems. FAT, NTFS, and CDFS are used to access files stored on drives installed in the computer.
4. Which command line utility was developed by Microsoft to allow users to transfer files and settings to a new edition of Windows OS during an upgrade to Windows 10?
- Windows Upgrade Assistant
- Windows Easy Transfer
- User State Migration Tool
- PCmover Express
Explanation: The User State Migration Tool (USMT) is a command line utility program developed by Microsoft that allows users to transfer files and settings between Windows PCs. Windows Easy Transfer is not available in Windows 10. PCmover Express is third party software. Windows Upgrade Assistant is used to prepare a computer for upgrading by checking for compatibility issues and downloading all necessary files to start the installation process.
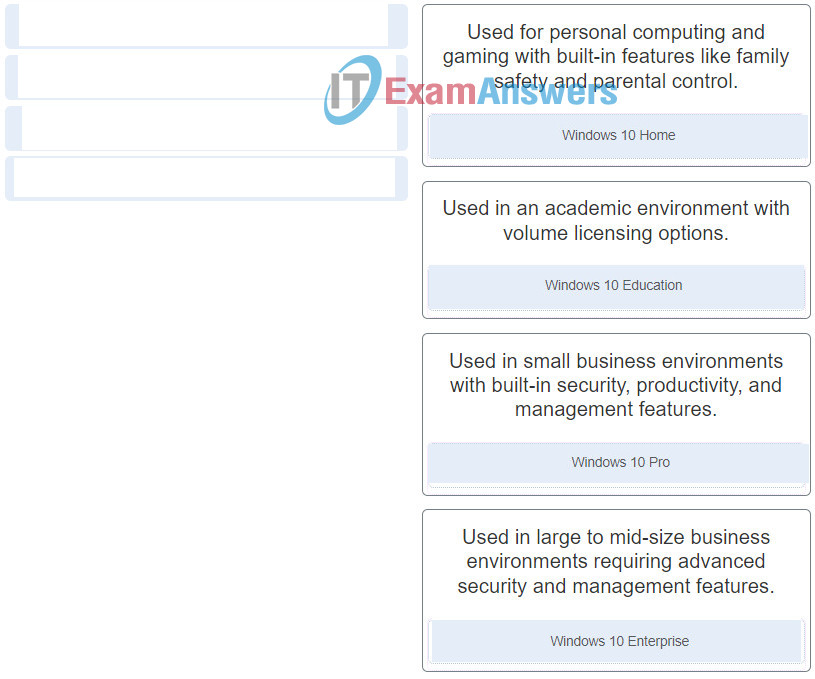
5. Select the Windows 10 version that best meets the described use.
6. Match the steps that will lead to the loading of bootmgr.exe in a 32 bit Windows 10 environment.
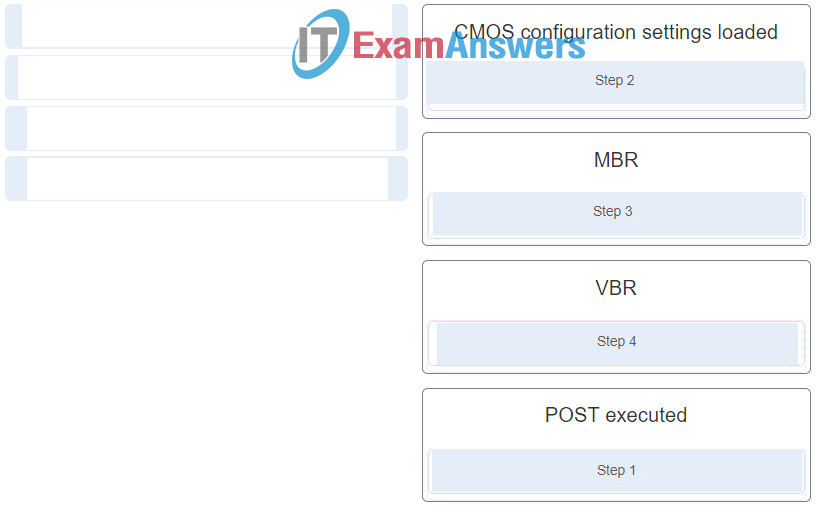
IT Essentials ( Version 8.0) – IT Essentials 8.0 Chapter 10 exam Q6
7. What term is used to describe a logical drive that can be formatted to store data?
- volume
- partition
- cluster
- track
- sector
Explanation: Hard disk drives are organized by several physical and logical structures. Partitions are logical portions of the disk that can be formatted to store data. Partitions consist of tracks, sectors, and clusters. Tracks are concentric rings on the disk surface. Tracks are divided into sectors and multiple sectors are combined logically to form clusters
8. When would the PXE option be used when repairing a PC?
- The display cannot be seen clearly.
- There is no response from the mouse or keyboard.
- A newly installed application caused the system to perform erratically.
- The computer needs a replacement operating system.
Explanation: The Preboot eXecution Environment (PXE, but pronounced pixie) BIOS boot option is used to install an operating system from a remote network location.
9. Which statement describes dynamic disks in a PC that is running Windows 10 Pro?
- A partition created on a dynamic disk can be shrunk without deleting the partition first.
- More space can be added to a partition by extending it into adjacent, unallocated space, as long as it is contiguous.
- Free space can only be added from the same disk to extend the volume.
- They have the ability to create volumes that span across more than one disk.
Explanation: A dynamic disk has the ability to create volumes that span across more than one disk. The size of the partitions can be changed after they have been set, even if the unallocated space is noncontiguous. However, the partition size cannot be reduced without loss of data.
10. What are two types of computer user interface? (Choose two.)
- CLI
- OpenGL
- PnP
- API
- GUI
Explanation: Two types of computer operating system user interfaces are CLI and GUI. CLI stands for command-line interface. In a command-line interface, a user enters commands at a prompt using a keyboard. The second type is the GUI, or graphical user interface. With this type of user interface, a user interacts with the operating system by working with icons and menus. A mouse, finger, or stylus can be used to interact with a GUI. PnP is the name of a process by which an OS assigns resources to different hardware components of a computer. The other answers are examples of Application Programming Interfaces, or APIs.
11. Which key, when pressed during the boot process, will allow the user to choose to start Windows in safe mode?
- Esc
- Windows
- F8
- F1
Explanation: Pressing the F8 key during the boot process will allow the user to choose to start the computer in Safe mode.
12. Which statement accurately describes the GUID partition table?
- It cannot be used in a multiboot environment.
- It is not supported by Windows 10 Home edition.
- It is commonly used in computers with UEFI firmware.
- It is 512 bytes long and contains the boot loader.
Explanation: The GUID partition table, also referred to as GPT, expands on the limitations of the MBR and is commonly used in systems with UEFI firmware.
13. Match the file system with the respective description.
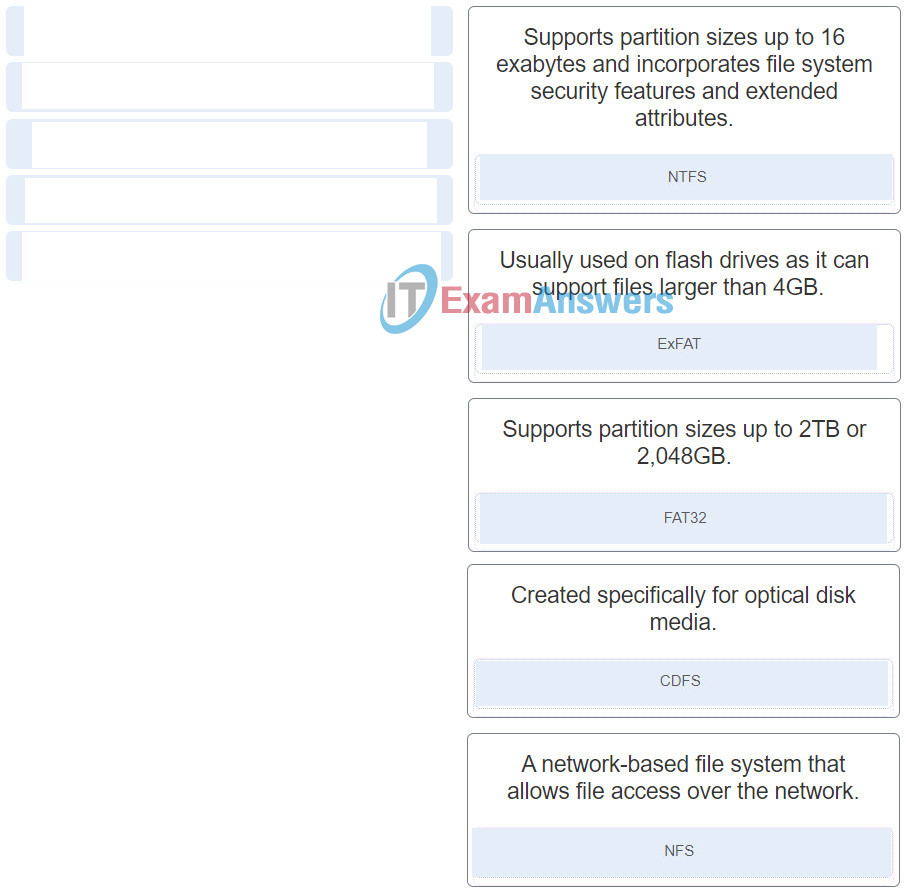
IT Essentials ( Version 8.0) – IT Essentials 8.0 Chapter 10 exam Q13
14. A technician wishes to deploy Windows 10 Pro upgrade to a group of employee PCs on the network and ensure that the user state migrates successfully. Which tool would the technician use to do this?
- Windows 10 Update Assistant
- Windows Easy Transfer
- User State Migration
- PCmover Express
Explanation: USMT (User Migration State tool) is part of the Windows Assessment and Deployment Kit that can be used to streamline and simplify user state migration during large deployments of Windows operating systems.
15. What feature of an operating system allows it to support two or more CPUs?
- multitasking
- multiprocessing
- multiuser support
- multithreading
Explanation: Multiprocessing allows an operating system to use two or more CPUs. Support for two or more users is provided by the multiuser feature. Multitasking allows multiple applications to run at the same time. Multithreading allows different parts of the same program to run at the same time.
16. A user installs a new sound card driver in a computer that is working properly. After the installation of the drivers for the new sound card, the computer fails to boot. Which quick fix can the user implement to return to the previous working state?
- Boot to Emergency Recovery State.
- Boot to Start Windows Normally.
- Boot to Last Known Good Configuration.
- Boot to Recovery Console.
Explanation: The last known Good Configuration is a copy of the last registry that is saved on successful login. Care should be exercised never to log in when you suspect any system instability because once you log in successfully, the Last Known Good Configuration will be overwritten with the current one.
17. Which term best describes the process of breaking a program into smaller parts that can be loaded as needed by the operating system?
- multiuser
- multiprocessing
- multitasking
- multithreading
Explanation: Thread is a small piece of a program in execution. Multi-processing is related to a system with more than one processor. Multi-user is related to a system that supports more than one user at the same time. Multi-task is a system that can perform more than one task at the same time.
18. Which component of a CPU architecture allows the CPU immediate access to data?
- RAM
- CMOS
- registers
- cache
Explanation: Registers are memory locations that are part of the architecture of a CPU. They provide a storage location for the logical functions performed on data.
19. What are two default account types provided by Windows 10? (Choose two.)
- Guest
- DefaultAccount
- Standard User
- Administrator
- Users
Explanation: Windows 10 offers two account types, namely, Administrator and Standard User. Guest is a built-in user account. DefaultAccount is a user account managed by the system. Users is a user group.
20. Which operation in Windows 10 is limited to users with Administrator privileges only?
- Run applications.
- Install software programs.
- Change system settings.
- Modify user settings.
Explanation: Administrator accounts have complete control over a computer. Standard user accounts have limited control over a computer. They can run applications, but cannot install programs. A standard user account can change system settings but only settings that do not affect other user accounts.
21. Which statement describes formatting?
- It is used to boot an operating system by default.
- It is a section of an extended partition on an MBR. It can be used to separate information for administrative purposes.
- It is a process to create a file system in a partition or volume for file storage.
- It is often used to organize data storage by subdividing it into as many as 23 logical sections.
22. What is a possible situation when it might be necessary to boot Windows 7 from a USB device, a CD, or a DVD?
- to disable background services
- to delete registry keys
- to repair the system
- to partition the hard drive
Explanation: Disabling background services, deleting registry keys, and partitioning the hard drive do not require rebooting a PC. It might be necessary to boot a computer from a USB drive in order to repair the system in some situations.
23. Which statement describes a primary partition?
- It is a section of an extended partition on an MBR. It can be used to separate information for administrative purposes.
- It is a type of disk with the ability to create volumes that span across more than one disk even if the unallocated space is noncontiguous.
- It is a physical section of a hard disk. It can contain an operating system to boot the system and cannot be subdivided.
- It is often used to organize data storage by subdividing it into as many as 23 logical sections.
24. Which program file is loaded by the boot manager in a Windows boot process?
- sysprep.exe
- ntoskrnl.exe
- winlogon.exe
- winload.exe
Explanation: During a Windows boot process, once the boot manager, bootmgr.exe, has the control of the boot process, it first loads the Windows boot loader, winload.exe.
25. Which tab would be used to set the priority for a process in Windows 10 Task Manager?
- Performance
- Startup
- Details
- Services
Explanation: The Windows 10 Task Manager has seven tabs. The Details tab allows setting a priority for a process.
26. True or False? Multithreading describes an operating system that can support two or more CPUs.
- False
- True
27. What is the default file system used during a fresh installation of Windows 7?
- HPFS
- NTFS
- FAT16
- FAT32
Explanation: While Windows XP can use either FAT or NTFS, Vista and Windows 7 can only be installed on an NTFS partition.
28. True or False? Smartphones require an operating system before they can be operated.
- True
- False
29. A manager wants to install Windows 10 directly onto a computer and needs help with the setup process. What tool or utility would be the best choice for the user?
- User State Migration Tool
- Windows Easy Transfer
- Windows Boot Manager
- Upgrade Assistant
30. Which statement describes the active partition?
- It is a section of an extended partition on an MBR. It can be used to separate information for administrative purposes.
- It is used to boot an operating system by default.
- It is a type of disk with the ability to create volumes that span across more than one disk even if the unallocated space is noncontiguous.
- It is often used to organize data storage by subdividing it into as many as 23 logical sections.
31. Which statement describes the active partition?
- It is a section of the disk, that is inaccessible to the user, containing an image that can be used to restore the computer to its original configuration.
- It is a process to create a file system in a partition or volume for file storage.
- It is used to boot an operating system by default.
- It is a type of disk with the ability to create volumes that span across more than one disk even if the unallocated space is noncontiguous.
32. Which statement describes an extended partition?
- It is a section of the disk, that is inaccessible to the user, containing an image that can be used to restore the computer to its original configuration.
- It is a process to create a file system in a partition or volume for file storage.
- It is a type of disk with the ability to create volumes that span across more than one disk even if the unallocated space is noncontiguous.
- It is often used to organize data storage by subdividing it into as many as 23 logical sections.
33. Which statement describes the master boot record (MBR)?
- It is a section of the disk, that is inaccessible to the user, containing an image that can be used to restore the computer to its original configuration.
- It is a process to create a file system in a partition or volume for file storage.
- It takes the first 512 bytes on the disk and contains the boot loader, an executable program that allows a user to choose from multiple operating systems.
- It is a type of disk with the ability to create volumes that span across more than one disk even if the unallocated space is noncontiguous.
34. True or False? Multitasking describes a computer operating system that is capable of running multiple applications at the same time.
- True
- False
35. Which statement describes a logical drive?
- It is a section of the disk, that is inaccessible to the user, containing an image that can be used to restore the computer to its original configuration.
- It is a process to create a file system in a partition or volume for file storage.
- It is a section of an extended partition on an MBR. It can be used to separate information for administrative purposes.
- It is a type of disk with the ability to create volumes that span across more than one disk even if the unallocated space is noncontiguous.
36. Which statement describes the master boot record (MBR)?
- It takes the first 512 bytes on the disk and contains the boot loader, an executable program that allows a user to choose from multiple operating systems.
- It is a process to create a file system in a partition or volume for file storage.
- It is a type of disk with the ability to create volumes that span across more than one disk even if the unallocated space is noncontiguous.
- It is a section of an extended partition on an MBR. It can be used to separate information for administrative purposes.
37. True or False? The registry is a database that only contains information about the device drivers on a computer.
- False
- True
38. A technician has just purchased a new Windows 10 PC and wants to transfer selected files, folders, profiles, and applications from the old Windows PC. What tool or utility would be the best choice for the user?
- Upgrade Assistant
- User State Migration Tool
- PCmover Express
- Windows Task Manager
Explanation: PCmover Express is the software tool recommended by Microsoft to automatically moves files, settings, and user profiles from an old PC to a new one. The free version is no longer available, and there is a cost to use it from LapLink.
39. A technician needs to capture the company user accounts, files, operating system settings, and application settings for migration into the new Windows 10 installation. What tool or utility would be the best choice for the user?
- User State Migration Tool
- Upgrade Assistant
- Windows Easy Transfer
- WinLoad
40. True or False? DirectX is a collection of APIs related to multimedia tasks for Microsoft Windows.
- True
- False
41. Which operating system does not support Windows Easy Transfer to transfer information from one computer to another?
- Windows 8
- Windows 10
- Windows Vista
- Windows 7
Explanation: Windows Easy Transfer is not supported in Windows 10 and is replaced with PCmover Express.
42. An analyst is running Windows 7 on the PC and is planning to migrate to Windows 8.1. The analyst wants help migrating the personal files and settings into the newer version. What tool or utility would be the best choice for the user?
- Upgrade Assistant
- User State Migration Tool
- Application manager
- Windows Easy Transfer
43. True or False? Modern operating systems boot the computer, manage the file system, and support only one user, task, or CPU.
- False
- True
44. At the end of the boot process of Windows 10, the login program file winlogon.exe loads. Which program loads winlogon.exe?
- hal.dll
- winload.exe
- sysprep.exe
- ntoskrnl.exe
Explanation: During a Windows 10 boot process, after the Windows kernel, ntoskrnl.exe, takes over the process, it starts the login file, winlogon.exe and displays the Windows Welcome screen.
45. True or False? When a hardware device is installed, the operating system needs to use a device driver to access and use that hardware.
- True
- False
46. True or False? Windows 10 64-bit version can be installed on as little as 1GB of hard drive space.
- False
- True
47. Which statement is a feature of the Windows 8 operating system?
- It uses the Aero user interface.
- It supports a touch screen interface.
- It can be directly upgraded from Windows XP.
- It is a 128-bit operating system.
Explanation: One of the features introduced with the Windows 8 operating system was the support for a touch screen interface to allow use on phones and tablets.
48. True or False? A 32-bit operating system can address up to a maximum of 4 GB of RAM.
- True
- False
49. Which statement describes a recovery partition?
- It is a section of the disk, that is inaccessible to the user, containing an image that can be used to restore the computer to its original configuration.
- It is a process to create a file system in a partition or volume for file storage.
- It is a type of disk with the ability to create volumes that span across more than one disk even if the unallocated space is noncontiguous.
- It is a section of an extended partition on an MBR. It can be used to separate information for administrative purposes.
A dynamic disk in Windows 10 is a type of disk storage that offers advanced features and capabilities compared to a basic disk. Unlike a basic disk, a dynamic disk allows for the creation of dynamic volumes, such as striped volumes, mirrored volumes, and spanned volumes, which enhance the storage and performance capabilities of your system.
Dynamic disks also provide features like disk spanning and fault tolerance, allowing for improved data management and protection. With dynamic disks, you can easily resize volumes, add or remove drives without the need for reformatting, and create fault-tolerant environments for mission-critical data. This flexibility makes dynamic disks an ideal choice for users who require efficient storage management and enhanced data protection.
A dynamic disk in Windows 10 is a type of storage that offers more advanced features compared to a basic disk. It allows for disk spanning, disk striping, and fault tolerance through RAID configurations. With a dynamic disk, you can create volumes that span multiple disks or combine free space from different disks to form a single logical volume. This enables more efficient utilization of storage capacity and enhanced data protection. Dynamic disks are ideal for larger storage needs and server environments.

Understanding Dynamic Disks in Windows 10
In the world of computer storage, dynamic disks are an essential component that plays a significant role in managing disk volumes efficiently. Windows 10, the latest operating system from Microsoft, offers dynamic disk support to provide advanced features and capabilities for disk management. This article will explore what dynamic disks are, their benefits, and how they differ from basic disks. We will dive into the technical aspects of dynamic disks, their functionality, and how they can enhance your Windows 10 experience.
What Are Dynamic Disks?
A dynamic disk, in simple terms, is a type of disk storage in Windows 10 that offers advanced features such as disk spanning, fault tolerance, and software-based RAID functionality. Unlike basic disks, which are the traditional disks used in earlier versions of Windows, dynamic disks allow for more flexibility in managing disk volumes. With dynamic disks, you can create and resize volumes on-the-fly, without the need to reboot your computer.
Dynamic disks support a variety of features that make disk management more efficient. These features include:
- Spanned volumes: Dynamic disks allow you to combine multiple physical disks into a single logical volume, increasing storage capacity.
- Striped volumes: Also known as RAID-0, striped volumes distribute data across multiple disks, improving read and write speeds.
- Mirrored volumes: Mirrored volumes, or RAID-1, duplicate data across multiple disks for redundancy and fault tolerance.
- RAID-5 volumes: Dynamic disks support RAID-5, which provides fault tolerance and data redundancy by distributing parity information across multiple disks.
- Volume sets: Dynamic disks can be used to create large volumes that span across multiple disks, providing increased storage capacity.
These features give you more control over your disk storage, enabling you to create fault-tolerant and high-performance storage solutions.
Differences Between Dynamic and Basic Disks
While dynamic disks provide advanced features not found in basic disks, it is important to understand the key differences between the two. Basic disks are the traditional storage method used in older versions of Windows, while dynamic disks were introduced to offer enhanced functionality.
The main differences between dynamic and basic disks are:
- Volume management: Basic disks use primary and extended partitions to manage disk space, while dynamic disks use volume sets and dynamic volumes for more flexible management.
- Flexibility: Dynamic disks allow for on-the-fly volume resizing and the creation of spanned, striped, mirrored, and RAID-5 volumes, providing more options for managing storage space.
- Compatibility: Dynamic disks are not compatible with older versions of Windows, such as Windows 7 or earlier. Basic disks, on the other hand, are compatible with all Windows operating systems.
It is important to note that once you convert a basic disk to a dynamic disk, you cannot revert it back to a basic disk without erasing all data on the disk. Therefore, it is recommended to carefully consider your disk management needs before converting to dynamic disks.
How to Convert Disks to Dynamic in Windows 10
If you decide to utilize the advanced features of dynamic disks in Windows 10, you can convert your basic disks to dynamic disks using the Disk Management tool. Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you through the process:
| Step | Description |
|---|---|
| 1 | Open the Disk Management tool. You can do this by right-clicking on the Start button, selecting «Disk Management» from the menu, or by searching for «Disk Management» in the Windows search bar. |
| 2 | Locate the disk you want to convert to dynamic. Right-click on the disk and select «Convert to Dynamic Disk.» |
| 3 | Choose the disks you want to include in the dynamic disk setup, and select the desired partition style (MBR or GPT). |
| 4 | Follow the on-screen instructions to complete the conversion process. |
Once the conversion is complete, you can start taking advantage of the advanced features offered by dynamic disks.
Limitations and Considerations
While dynamic disks provide a range of benefits for disk management, they also have certain limitations and considerations:
- Compatibility: Dynamic disks are not compatible with older Windows operating systems, so if you plan to use the disk in a different operating system, you may need to convert it back to a basic disk.
- Dual-boot configurations: Dynamic disks may pose challenges when using dual-boot configurations with other operating systems, as non-Windows operating systems may not recognize the dynamic disk format.
- Data recovery: In the event of disk failure or data corruption, data recovery from dynamic disks can be more challenging compared to basic disks.
- Complexity: Dynamic disks introduce additional complexity in disk management, so it is important to have a good understanding of the features and functionality before making the switch.
Considering these limitations and considering your specific needs is crucial when deciding whether to utilize dynamic disks in Windows 10.
Conclusion
In conclusion, dynamic disks offer advanced features and capabilities for efficient disk management in Windows 10. They provide flexibility in creating and managing disk volumes, allowing for fault-tolerant, high-performance, and expansive storage solutions. However, it is important to carefully consider the limitations and compatibility issues associated with dynamic disks before converting your disks. If you are looking to maximize your disk management capabilities on Windows 10, dynamic disks are worth exploring.

Understanding Dynamic Disks on Windows 10
In the realm of Windows 10 storage, a dynamic disk is a popular option that offers enhanced flexibility and functionality compared to basic disks. Unlike basic disks, dynamic disks allow for the creation of multiple volumes and offer advanced features such as disk spanning, mirroring, and striping.
The primary benefit of dynamic disks is the ability to create spanned, striped, and mirrored volumes that provide increased data redundancy, performance optimization, and storage expansion options. Dynamic disks also support dynamic volumes, which can be resized and extended without losing data.
It is important to note that dynamic disks are not supported on all Windows 10 editions. The feature is limited to the Professional, Enterprise, and Education editions of Windows 10. Additionally, converting a basic disk to a dynamic disk requires the disk to be empty, so it is advisable to back up data before making any changes.
In conclusion, dynamic disks offer advanced storage capabilities on Windows 10 for professionals who require increased flexibility and performance. Understanding the features and limitations of dynamic disks ensures efficient utilization and management of storage resources.
Key Takeaways
- A dynamic disk is a storage type in Windows 10 that offers advanced features for managing disk space.
- Dynamic disks allow you to create volumes that span multiple physical disks.
- With dynamic disks, you can create fault-tolerant volumes using RAID technology.
- Dynamic disks support features like volume expansion and the ability to extend existing volumes.
- One drawback of dynamic disks is that they are not compatible with other operating systems.
Frequently Asked Questions
A dynamic disk in Windows 10 refers to a type of disk storage that provides advanced features and flexibility compared to basic disks. It allows for the creation of volumes that can span multiple disks and provides options for fault tolerance and dynamic volume expansions.
1. What is the difference between a dynamic disk and a basic disk in Windows 10?
A basic disk is the traditional disk storage type in Windows 10, while a dynamic disk offers more advanced features and flexibility. Unlike basic disks, dynamic disks allow the creation of volumes that can span multiple physical disks, known as spanned volumes or striped volumes. Dynamic disks also support fault tolerance options like mirrored volumes and RAID-5 volumes.
In contrast, basic disks can only have partitions that are limited to a single physical disk and do not offer the same level of flexibility and fault tolerance as dynamic disks.
2. How do I convert a basic disk to a dynamic disk in Windows 10?
To convert a basic disk to a dynamic disk in Windows 10, follow these steps:
- Open the Disk Management tool by right-clicking on the Start button and selecting «Disk Management.»
- Identify the basic disk you want to convert to dynamic.
- Right-click on the disk and select «Convert to Dynamic Disk.»
- Follow the on-screen instructions to complete the conversion process.
It’s important to note that converting a basic disk to a dynamic disk is a one-way process. Once converted, you cannot revert back to a basic disk without deleting all the volumes on the dynamic disk.
3. What are the advantages of using dynamic disks in Windows 10?
Using dynamic disks in Windows 10 offers several advantages:
- Spanned volumes: Dynamic disks allow you to create volumes that span multiple physical disks, increasing the available storage capacity.
- Striped volumes: You can create striped volumes that enhance read and write performance by distributing data across multiple disks.
- Fault tolerance: Dynamic disks support fault tolerance options like mirrored volumes and RAID-5 volumes, providing data redundancy in case of disk failures.
- Dynamic volume expansions: You can easily extend dynamic volumes to utilize additional disk space without the need to recreate or delete existing volumes.
4. Can I upgrade from a basic disk to a dynamic disk without data loss?
Yes, you can upgrade from a basic disk to a dynamic disk in Windows 10 without data loss. However, it’s always recommended to create a backup of your important data before performing any disk-related operations, as unexpected issues can occur.
5. Are dynamic disks supported on all versions of Windows 10?
No, dynamic disks are not supported on all versions of Windows 10. Dynamic disks are only supported on Windows 10 Pro, Enterprise, and Education editions. Windows 10 Home edition does not support dynamic disks.
To conclude, a dynamic disk in Windows 10 is a storage solution that offers increased flexibility and functionality compared to a basic disk. It allows for advanced features such as creating mirrored volumes for redundancy, extending volumes without any downtime, and creating fault-tolerant disk arrays using RAID technology.
By converting a basic disk to a dynamic disk in Windows 10, users gain access to these advanced features and can better manage their storage needs. It’s important to note that dynamic disks are not compatible with all Windows operating systems, so it’s crucial to ensure compatibility before making the switch. Overall, dynamic disks provide a powerful and efficient storage solution for Windows 10 users.
For a long time, people have been accustomed to basic partitioning which on the other hand has its own host of advantages and disadvantages. If you are reading this, there are high chances you are beginning to show interest in dynamic disks.

If you are looking for a better way to manage disk volumes in your Windows 10 computer, then it is the right time to read about Dynamic Disk in Windows 10. In this guide, we share more details about the Dynamic Disk management scheme.
Generally, when you install Windows OS, it creates basic partitions on your hard disk. Afterwards, you can decide to create dynamic partitions with the Windows Disk manager tool. Read more about dynamic disk invalid error by following this link. Note that both the basic disk and dynamic disk support master boot record (MBR) partition styles.
Page Contents
To give you a straightforward definition, a Dynamic Disk is a hard drive with dynamic partitions. It is a more flexible option compared to the basic disk partitioning scheme. It creates partitions and logical drives for file storage. Each partition is labeled using a different drive letter.
Alternatively, we can define a dynamic disk as a physical disk that manages its volumes by using an LDM (Logical Disk Manager) database. LDM is a 1MB hidden database at the end of the dynamic disk. It records all information about the volumes on a single disk including related information on each dynamic disk such as volume size and drive letter.
All dynamic disks are interrelated and this allows you to see a “Missing” disk. This information appears in the Windows Disk Management and is saved in the LDM database.
Once dynamic partitions are created, they can be formatted with FAT, FAT32 or NTFS (new Technology File System). One way you can quickly do this is with a Disk Drill from Cleverfiles. Furthermore, dynamic disks are better than basic disks since they create volumes that span multiple physical disks also known as spanned or striped volumes.
It is however unfortunate that spanned or striped volumes are not fault-tolerant. However, you can also create fault tolerant volumes in a similar way as spanned ones.
Differences Between Basic and Dynamic Disk in Windows
Let’s now look at the differences between basic disks and dynamic disks.
Basic Disk Storage
Below are the major elements of basic disk storage.
- Uses normal partition tables
- Contains basic volumes such as extended partitions, primary partitions, and logical drives
- They include multi-disk volumes created using Windows NT 4.0 or earlier editions
Dynamic Disk Storage
Below are the major elements of dynamic storage.
- Contains dynamic volumes such as spanned volumes, simple volumes, striped volumes, RAID-5 volumes, and mirrored volumes
- Does not require Windows restart to perform disk and volume management
- Not supported on portable computers
- Storage types are separated from file system types
In addition, there are five major operations that distinguish dynamic from basic partitioning. These are:
- Dynamic schemes can reactivate missing hard drives
- They support spanning or extending partitions across different physical disks
- Can repair mirrored or RAID-5 volumes using information in the database
- Can remove mirrored volumes or even break them into two volumes
- They can create and delete simple, spanned, mirrored and RAID-5 volumes
Dynamic Disk Features
So far, you can figure out how dynamic disks work. We will now discuss the features in detail to give you a better understanding.
Dynamic disks use dynamic volume
Volume also means partition and they mainly use the NTFS file system, although they can also use the older FAT and FAT32 file systems. The volume can be split, converted or even expanded after they are created.
On the same hard drive, you can create up to 2,000 dynamic volumes regardless of whether it uses GPT or MBR partition schemes. This makes them more immune to disk corruption. It is however recommended to have just 32 dynamic volumes or even less for better disk management.
Information on partitions is managed using a database
The dynamic partition scheme takes care of the information contained in the many partitions. This is done by the VDS and LDM database. They provide a user interface that helps in analyzing disk volumes, formats and sizes.
The database sends constant queries to the disk and receives their responses. It then uses these responses to draw graphical representations of disk volumes.
Creates up to 5 types of volumes
You can create up to 5 types of partitions with a dynamic disk scheme. These are simple volumes, Mirrored, Striped, Spanned, and RAID-5. Note that mirrored volumes are fault tolerant. By “fault tolerant,” this is to say that in case one of the physical disks fails, it can be replaced and the mirrored volume recovered.
Only available in Windows OS
Dynamic disk management scheme is only available in Windows 8.1, 10, 11, and Windows Server 2008, 2012, 2016, and 2022.
How Does Dynamic Disk Work?
For basic partitions, they keep track of the information contained in its partitions using a partition table. On the other hand, a dynamic scheme does not use partition tables to keep the information about the disk.
MBR partition style keeps their database in the last 1MB space of the disk. On the other hand, GPT partitions keep their database in a reserved partition of 1MB size too.
Both LDM and VDS (virtual disk service) retrieves configuration information of the disk. They are the Windows APIs (application programming interface).
Dynamic volumes can repair damaged databases using the information derived from the database of another volume. This makes it easier to fix hard drives without formatting. This is because each dynamic disk stores a copy of each dynamic database file.
Pros and Cons of Dynamic Disk
Pros
- Can create or delete different volumes
- More space and improved performance
- Creates fault-tolerant volumes
- Easier to manage disk volumes
- Unlimited number of partitions
Cons
- Does not support dual operating systems
- Cannot be detected by a machine other than the one creating it
- Files can be lost when converting back to basic disk
- Lack of tools that can repair corrupted sectors
Wrap Up
It is without doubt that dynamic disks are a better way to manage disk space in Windows 10. If after reading this article you developed more interest in using a dynamic disk scheme, we wish you success in your next move. You can also read more on how Disk Drill can help you secure databases in your new data management system.
Dynamic disks are a significant component of the Windows 10 operating system, providing advanced storage options that enhance the overall functionality and flexibility of disk management. With the increasing need for efficient data handling and organization, understanding dynamic disks becomes essential for both casual users and IT professionals. This article will explore what dynamic disks are, how they differ from basic disks, their advantages, potential drawbacks, and practical applications.
Basic vs. Dynamic Disks
Before diving into dynamic disks, it’s essential to grasp the foundational concepts surrounding them. Windows partitions storage drives into two main categories: basic disks and dynamic disks.
Basic Disks
Basic disks are the most commonly used type of storage in Windows. They utilize partition tables to manage disk space, dividing the drive into primary partitions and logical drives. Characteristics of basic disks include:
- Partition Limit: A basic disk can contain up to four primary partitions or three primary partitions and one extended partition (which can contain several logical drives).
- File System Support: Basic disks typically support major file systems like NTFS, FAT32, and exFAT.
- Simplicity: The management of basic disks is relatively straightforward through the Disk Management utility in Windows.
Dynamic Disks
Dynamic disks, on the other hand, offer a more advanced approach to disk management. They are not limited to partitions but instead allow for volumes that can span multiple disks, provide redundancy, and adapt to growing storage requirements.
The following features distinguish dynamic disks:
- Volume Types: Dynamic disks support several volume types, including simple, spanned, striped, mirrored, and RAID-5 volumes.
- Flexibility: Dynamic disks can be expanded or shrunk without the need for reformatting or partitioning.
- Multi-Disk Configurations: These disks enable users to set up volumes that span across multiple physical drives, which can lead to more efficient data management.
Understanding Dynamic Disks
Dynamic disks are essentially an enhancement of the Windows storage model. They allow users to create and manage volumes in a way that enhances performance, redundancy, and scalability.
How Dynamic Disks Work
When a disk is converted from a basic to a dynamic disk, the Windows operating system changes the way it manages data on the disk. Dynamic disks utilize a technology that includes:
- Logical Unit Numbers (LUNs): A LUN is a unique identifier assigned to a logical disk, allowing the operating system to distinguish between multiple disks easily.
- Disk Groups: For configurations requiring multiple disks, dynamic disks may be grouped. This grouping allows for easier management of multiple dynamic disks, especially in a RAID setup.
Types of Dynamic Volumes
Dynamic disks allow for the creation of various types of volumes, each with its unique characteristics. Here are the primary types of dynamic volumes:
-
Simple Volume
- A simple volume uses space from a single dynamic disk and is the most basic type of dynamic volume. It is analogous to a partition on a basic disk.
-
Spanned Volume
- A spanned volume combines unallocated space from multiple disks into one large volume. This configuration can increase storage capacity, but it does not provide redundancy. If one disk fails, the entire volume is compromised.
-
Striped Volume (RAID 0)
- Striped volumes divide data evenly across multiple disks, providing improved performance due to concurrent read/write operations. However, similar to spanned volumes, if one disk fails, all data on the striped volume is lost.
-
Mirrored Volume (RAID 1)
- A mirrored volume duplicates the data onto two separate disks. This setup offers redundancy—if one disk fails, the data remains accessible from the other disk.
-
RAID-5 Volume
- This configuration combines data striping with parity information, allowing for redundancy without excessive storage overhead. RAID-5 requires a minimum of three disks and can tolerate the failure of one disk while still maintaining data integrity.
Advantages of Dynamic Disks
Dynamic disks come with several key advantages, making them suitable for various use cases:
Enhanced Flexibility
Dynamic disks allow users to create and manage complex volume arrangements. You can expand or shrink volumes without losing data, providing flexibility through changing storage needs.
Improved Performance
Depending on how they are configured, dynamic disks can optimize system performance. For instance, striped volumes can accelerate data access by reading and writing data across multiple disks simultaneously.
Redundancy and Data Protection
Dynamic disks enable users to implement mirrored volumes and RAID configurations, providing an additional layer of data protection against hardware failure. This is particularly crucial for businesses that rely on data integrity and availability.
Shared Storage Options
Dynamic disks allow for the creation of volumes that can be accessed over a network, which is essential in collaborative environments. This allows multiple users to access shared data efficiently.
Disadvantages of Dynamic Disks
Though dynamic disks have numerous advantages, they also present some drawbacks that must be considered:
Complexity
Dynamic disks can be more complex to manage than basic disks, especially for inexperienced users. The various volume types and configurations necessitate a more in-depth understanding of disk management.
Limited Compatibility with Other Operating Systems
Dynamic disks are specifically designed for Windows operating systems. If a user attempts to access a dynamic disk on a non-Windows OS, the disk may be unrecognized. This limitation can pose challenges when using dual-boot setups or external drives that need to be read by different systems.
Potential for Data Loss
Converting basic disks to dynamic disks and creating or modifying volumes involves risks. Incorrect management can result in data loss or corruption, making it imperative to back up data before making any significant changes.
Converting Basic Disks to Dynamic Disks
If you decide to take advantage of dynamic disks and their capabilities, you will need to convert a basic disk into a dynamic disk. This process can be performed through the Disk Management utility in Windows.
Steps to Convert to Dynamic Disk
-
Open Disk Management:
- Right-click the Start menu and select Disk Management.
-
Identify the Disk:
- Locate the basic disk you want to convert.
-
Convert to Dynamic Disk:
- Right-click on the disk (where it says “Disk X”) and select Convert to Dynamic Disk. Follow the on-screen prompts to complete the process.
-
Create Dynamic Volumes:
- After conversion, you can create various types of dynamic volumes by right-clicking on unallocated space or existing volumes.
Important Considerations
- Always back up important data before converting a disk type.
- Be cautious of the volume structures you create—make sure they align with your data management needs.
Managing Dynamic Disks
Once you have created dynamic disks and volumes, managing them becomes your next priority. Windows provides various options to manage your dynamic disks effectively.
Expanding and Shrinking Volumes
Dynamic volumes can be resized to accommodate changes in data storage requirements:
-
To Expand a Volume:
- Right-click on the volume you want to expand.
- Select Extend Volume and follow the wizard to allocate additional space.
-
To Shrink a Volume:
- Right-click on the volume and select Shrink Volume.
- Specify the amount of space to shrink and proceed with the operation.
Removing Dynamic Disks and Volumes
If necessary, you can remove dynamic volumes to reclaim space or reconfigure your disk setup:
- To Delete a Dynamic Volume:
- Right-click the desired volume.
- Select Delete Volume.
Keep in mind that deleting a volume will erase all data contained within, so always ensure you have a backup before proceeding.
Converting Back to Basic Disk
If you find that dynamic disks do not meet your needs, you may convert them back to basic disks:
-
Delete All Dynamic Volumes:
- Before converting back, remove all dynamic volumes from the disk.
-
Convert to Basic Disk:
- Right-click the disk and select Convert to Basic Disk.
Monitoring Disk Health
Maintaining an eye on the health of dynamic disks is vital. Use tools such as Windows’ built-in Error Checking utility to scan for issues and keep your drives in optimal condition.
When to Use Dynamic Disks
Dynamic disks cater to particular scenarios that require greater flexibility and advanced features. Here are some considerations for when to use dynamic disks:
For Professionals and IT Environments
Dynamic disks are geared toward those who require robust data management capabilities, such as IT administrators and network professionals. Implementing dynamic disks in servers can benefit organizations managing large data volumes.
For RAID Configurations
If you want to set up RAID arrays for redundancy and improved performance, dynamic disks are the ideal choice.
For Flexible Storage Solutions
Dynamic disks provide a means for users who have fluctuating storage requirements to manage their disks more effectively without undergoing tedious re-partitioning tasks.
Conclusion
Dynamic disks represent a powerful feature of Windows 10, offering users several advanced disk management options that enhance performance, provide data redundancy, and cater to flexible storage requirements. While they may not be necessary for every user, understanding their capabilities can significantly benefit those with specific data management needs.
In our increasingly data-driven world, the ability to manage storage effectively is crucial. Dynamic disks provide an additional layer of versatility that can adapt to the evolving landscape of technology and data handling, making them a valuable tool for both personal and professional use. Whether you’re a casual user looking to optimize your storage or an IT professional responsible for managing complex networks, mastering dynamic disks ensures you’re equipped to manage your data with efficiency and resilience.
In the realm of computer storage systems, understanding the differences between various disk configurations is crucial for both casual users and IT professionals. One such concept, which is often overlooked yet immensely useful, is that of dynamic disks in Windows 10. This article will delve deeply into what dynamic disks are, how they differ from basic disks, their advantages and disadvantages, the scenarios in which they should be used, and a step-by-step guide on how to convert basic disks to dynamic disks.
Understanding Disk Types
Before diving into dynamic disks, it’s essential to understand the two primary types of disks within the Windows operating system: basic disks and dynamic disks.
-
Basic Disks: Basic disks utilize traditional partitioning methods and come with a straightforward structure. These disks use partition tables to define the partitions, allowing administrators to create primary and extended partitions. Each partition functions independently, making them well-suited for simple drive setups.
-
Dynamic Disks: In contrast, dynamic disks allow for more advanced configurations. They support features like dynamic volumes, which can span multiple disks, create fault-tolerant setups with mirrored volumes, and allow for increased flexibility in managing storage.
What Is a Dynamic Disk?
A dynamic disk is a type of disk in Windows that provides added functionality over basic disks. Introduced with Windows 2000, dynamic disks enable the creation of more complex storage structures called dynamic volumes. These volumes can be formatted with various file systems and can span multiple physical disk drives, offering various benefits in terms of performance, redundancy, and functionality.
When you convert a basic disk to a dynamic disk, Windows will manage its space in a way that allows for advanced volume creation. Dynamic disks support the following types of dynamic volumes:
- Simple Volume: A basic storage unit that can be located on a single dynamic disk.
- Spanned Volume: Combines unallocated space from multiple disks into a single volume, allowing for larger storage solutions.
- Striped Volume: Increases performance by spreading data across multiple disks. It effectively allows for much quicker read and write speeds.
- Mirrored Volume: Provides redundancy by duplicating all data on two disks. If one disk fails, the other continues to function, ensuring data availability (a form of fault tolerance).
- RAID-5 Volume: Requires at least three disks and provides both redundancy and improved performance. Data and parity information are striped across all disks.
Key Features of Dynamic Disks
Understanding the features of dynamic disks can help users leverage their capabilities effectively:
- Flexibility: Dynamic disks allow users to adjust volumes and disks easily. You can create, delete, and resize dynamic volumes much easier than with basic disks.
- Performance: With striped volumes, users can benefit from increased performance due to data being read from and written to multiple disks simultaneously.
- Fault Tolerance: Dynamic disks can enhance data protection through mirrored volumes, ensuring that there is a backup if one disk fails.
- Volume Spanning: Spanned volumes enable users to extend storage beyond the limits of a single disk, as data can be spread across several disks.
- Dynamic Volume Management: Windows Disk Management provides a graphical interface to handle dynamic disks and volumes, making it user-friendly.
Differences Between Basic and Dynamic Disks
The distinction between basic and dynamic disks is essential for users looking to optimize their data storage strategies. The following table outlines essential differences between the two disk types:
| Feature | Basic Disk | Dynamic Disk |
|---|---|---|
| Disk Configuration | Uses simple partition structures | Supports advanced volume types |
| Volume Types | Primary/Extended | Simple, Spanned, Striped, Mirrored, RAID-5 |
| Disk Management | Limited flexibility | More flexibility and control |
| Fault Tolerance | Not supported | Mirrored and RAID volumes |
| Performance | Basic read/write speeds | Enhanced through striping |
| Conversion | Can convert to dynamic directly | Can convert back to basic |
Advantages of Using Dynamic Disks
1. Enhanced Storage Management
Dynamic disks provide a more sophisticated way to manage disk space, allowing users to create volumes that span more than one disk. This feature is particularly advantageous for users who need to expand storage quickly without the hassle of moving data.
2. Performance Boosting
Striped volumes can significantly enhance data transfer speeds, making dynamic disks ideal for applications that require high performance, such as video editing and server environments.
3. Data Redundancy
For mission-critical systems, having multiple copies of data is crucial. Mirrored volumes allow users to maintain a duplicate of their data, providing peace of mind in case of hardware failure.
4. RAID Functionality
Dynamic disks can implement RAID configurations, increasing data redundancy and performance. RAID-5, in particular, can be highly beneficial for servers and databases.
Disadvantages of Using Dynamic Disks
1. Complexity
Managing dynamic disks can be more complicated than basic disks. Users must understand the implications of each volume type and how their configurations affect overall performance and storage.
2. Compatibility Issues
Not all operating systems support dynamic disks; for example, some versions of Linux may have difficulty reading or writing to them. This becomes a crucial factor if dual-booting with another OS.
3. Data Recovery Challenges
If a dynamic disk becomes corrupted, recovery can be more complicated than with basic disks due to the various volume types and interdependencies.
When to Use Dynamic Disks
Dynamic disks may not be necessary for all users, but they are the perfect solution in certain scenarios:
-
Server Environments: For businesses running servers that require high availability and redundancy, dynamic disks offer features like RAID configurations and mirroring.
-
Advanced Users: Users who understand how to manage their volumes and require advanced configurations will find dynamic disks extremely beneficial.
-
High-Performance Applications: Users who work with applications that demand significant read/write speeds, such as video editing software or databases, can leverage striped volumes effectively.
How to Convert a Basic Disk to a Dynamic Disk
If you decide that dynamic disks are right for you, converting a basic disk to a dynamic disk is a straightforward process. Here’s how to do it:
Step 1: Open Disk Management
- Right-click on the Start Menu button or press Win + X.
- Select Disk Management from the menu.
Step 2: Identify the Disk to Convert
- In the Disk Management window, locate the basic disk you want to convert.
- Ensure that you have backed up any important data on the disk, as while converting is generally safe, data loss can occur if something goes wrong.
Step 3: Convert the Disk
- Right-click on the disk label (the area showing “Disk 1”, “Disk 2”, etc.).
- Select Convert to Dynamic Disk… from the context menu.
- A new window will appear, providing a list of disks to convert. Ensure the correct disks are selected.
- Click OK to proceed, and then confirm the operation in the next prompt.
Step 4: Finishing Up
Once the conversion process is complete, the disk will now appear as a dynamic disk, and you can begin creating dynamic volumes as needed.
Conclusion
Dynamic disks in Windows 10 offer a wealth of advantages, enabling better storage management, performance enhancements, and data redundancy. However, they come with their complexities and are not suited for all users. Understanding the differences between basic and dynamic disks can aid in making informed decisions for both personal and professional use.
For those who require sophisticated storage configurations and performance enhancements, dynamic disks present an effective solution. However, it’s critical to weigh the advantages against the potential drawbacks, as well as to be prepared for the intricacies of managing a dynamic disk setup. Ultimately, with the right application and understanding, dynamic disks can transform the way users handle and store data in Windows 10.
