Dec 28, 2022
Last Updated: Dec 29, 2022
IT Essentials 8
IT Essentials 8.0 Module 11.8.1.2 Windows Configuration Quiz Answers
1. A help desk technician is talking to a user to clarify a technical problem that the user is having. What are two examples of open-ended questions that the technician might use to help determine the issue? (Choose two.)
- What happens when you try to access your files?
- What updates have you performed lately?
- Can you boot the operating system?
- Can you boot up in safe mode?
- Has anyone else used the computer recently?
Explanation: Close-ended questions generally have a fixed or limited set of possible responses, such as “yes” or “no”. Open-ended questions imply no limited or fixed set of replies but rather generally prompt the responder to provide more meaningful feedback.
2. A technician notices that an application is not responding to commands and that the computer seems to respond slowly when applications are opened. What is the best administrative tool to force the release of system resources from the unresponsive application?
- Task Manager
- Add or Remove Programs
- Event Viewer
- System Restore
Explanation: Use the Task Manager Performance tab to see a visual representation of CPU and RAM utilization. This is helpful in determining if more memory is needed. Use the Applications tab to halt an application that is not responding.
3. A technician is designing a hardware preventive maintenance plan for a company. Which strategy should be included in the plan?
- Avoid performing maintenance operations on plug and play devices that are controlled by the operating system.
- Only clean equipment that is requested by the customer.
- Omit performing maintenance operations on components until the equipment malfunctions.
- Schedule and document routine maintenance tasks.
Explanation: The type of tasks that need to be scheduled include operating system and antivirus updates as well as hard drive routines.
4. After solving a problem on a computer, a technician checks the event log to ensure that there are no new error messages. At which step of the troubleshooting process is this action taking place?
- Verify the solution and full system functionality.
- Document the findings.
- Establish a theory of probable cause.
- Determine an exact cause.
Explanation: In this situation, the probable cause has been identified and the exact cause has been acted upon. Documenting the findings is the last action in the process and happens after checking that the problem has been solved by the solution implemented.
5. What is true about restore points?
- Once System Restore is used to restore a system, the change is irreversible.
- Restore points back up personal data files.
- Restore points recover corrupted or deleted data files.
- Restore points should always be created before making changes to a system.
Explanation: Any change from a system restore is reversible. A restore point only contains information about the system and registry settings and therefore cannot be used to backup or recover data files.
6. Which two issues are likely to cause BSOD errors? (Choose two.)
- out-of-date browser
- RAM failing
- device driver errors
- lack of antivirus software
- power supply failure
Explanation: Device driver errors are the most likely cause of BSOD errors. Failing RAM can also create BSOD errors. Software issues such as browsers and antivirus do not produce BSOD errors. A power supply failure would prevent the machine from starting.
7. What are three common causes of operating systems problems? (Choose three.)
- a corrupted registry
- incorrect IP addressing information
- loose cable connections
- failed service pack installation
- CMOS battery problem
- virus infection
Explanation: Typical causes of operating system problems are as follows:
- corrupted or missing system files
- incorrect device driver
- failed update or service pack installation
- corrupted registry
- failing of faulty hard drive
- incorrect password
- virus infection
- spyware
8. Why would an administrator use Windows Remote Desktop and Windows Remote Assistant?
- to provide secure remote access to resources on another network
- to connect to an enterprise network across an unsecured connection and act as a local client of that network
- to enable sharing of files and presentations with a group of users over the Internet
- to connect to a remote computer over the network to control its applications and data
Explanation: Windows Remote Desktop and Remote Assistant allow an administrator to connect a local computer with a remote computer across the network and to interact with it as though it were the local computer. The administrator sees and can interact with the desktop of the remote computer. With Remote Desktop, the administrator logs onto the remote computer using an existing user account and starts a new user session. No user is required at the remoter computer to allow this access. With Remote Assistant, the purpose is for a technician to interact with a remote computer with the assistance of a remote user. The remote user must allow the remote access to the current user session and is able to observe what the technician is doing.
9. A corporation has expanded to include multiple remote offices around the globe. Which technology should be used to allow the remote offices to communicate and share network resources privately?
- VPN
- Remote Desktop
- Administrative share
- Remote Assistance
Explanation: A Virtual Private Network (VPN) is used to connect remote sites together securely over a public network.
10. A user logs into Active Directory on a workstation and the user home directory does not redirect to a network share on a file server. A technician suspects that the group policy setting is incorrect. Which command can the technician use to verify the group policy settings?
- rstrui
- runas
- tasklist
- gpresult
- gpupdate
Explanation: The functions of the listed commands are as follows:
- runas – runs a program or tool with different permissions
- rstrui – starts the System Restore utility
- gpresult – displays group policy settings
- gpupdate – refreshes group policy settings
- tasklist – displays currently running applications
11. What are two file attributes in the Windows environment? (Choose two.)
- details
- archive
- read-only
- security
- general
Explanation: The file attributes are read-only, archive, hidden, and system. Details, security, and general are tabs on the file Properties applet.
12. How many Libraries are created for each user by default on a new Windows 10 installation?
- 2
- 4
- 5
- 6
Explanation: When Windows 10 is installed, it creates six default libraries for each user.
13. A user wants to configure a password on a Windows 10 PC when the PC is woken from hibernation. Where can the user configure this?
- Control Panel, Power Options
- Control Panel, User Accounts
- Settings, Accounts
- Settings, Privacy
Explanation: In Windows 10, the configuration of a password for a PC woken from hibernation or sleep can be set in Settings->Accounts.
14. Match the commands to the task.
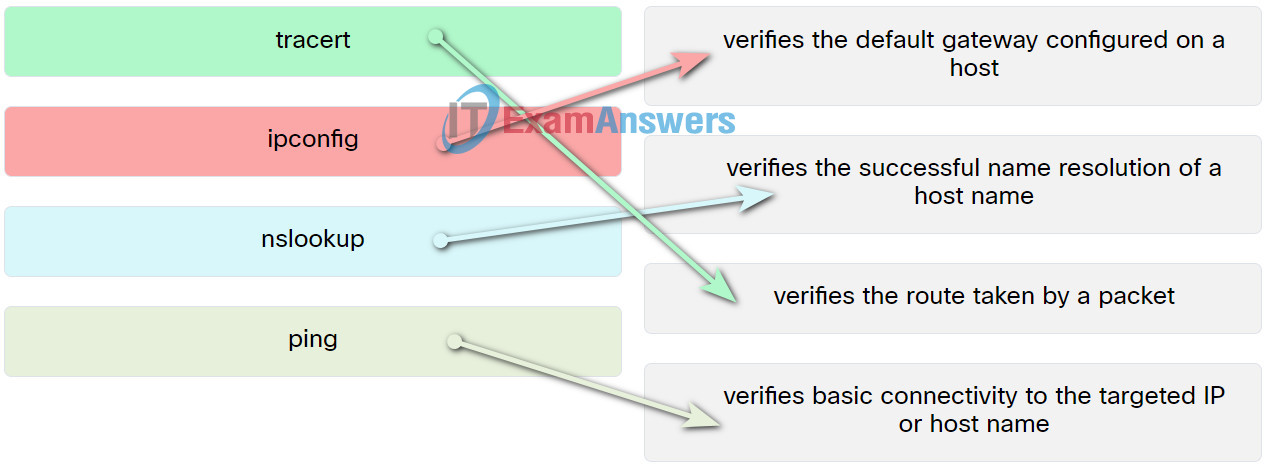
IT Essentials 8.0 Module 11.8.1.2 Windows Configuration Quiz
15. Which TCP port number would be used for remotely connecting to a network switch and configuring it via an unencrypted connection?
- 20
- 22
- 443
- 3389
Explanation: The server listens on TCP port 3389 and UDP port 3389 for remote connections.
16. In which folder are application files for 32-bit programs typically located on a computer that is running a 64-bit edition of Windows 10?
- C:\Users
- C:\Program Files
- C:\Application Data
- C:\Program Files (x86)
Explanation: The C:\users folder contains all the user profiles. The C:\Application Data folder contains application data related to all users. The 32 bit program files are located in the C:\Program Files(x86) folder while 64 bit program files are located in the C:\Program Files folder.
IT Essentials v6.0 A+ Certification Practice 2º Exam Answers 2018
1. A server administrator needs to set up a new server with disk fault tolerance technology. The administrator decides to deploy RAID 0+1 technology. What is the minimum number of disks needed to deploy the disk array setting?
2
3
4*
5
6
2. A user has detected that one of the virtual machines in a computer is infected with a virus. Which statement about the situation is likely to be true?
The host operating system is not necessarily infected with a virus.*
The host machine operating system has a bug.
All of the virtual machines running on the host are infected with a virus.
The host machine antivirus program requires an update.
3. Which fire protection system would be best for a university computer/electronics lab?
an overhead sprinkler system
an electronic ion spreader
a nonwater based fire extinguisher*
fire suppressing hazmat blankets and supressors
4. Why should a technician avoid opening the casing of a power supply?
Power supplies must always be replaced, not repaired.
Hazardous levels of electricity may be present inside the power supply.*
Power supplies are very fragile, expensive, and easy to damage.
Only the power supply manufacturer can open the casing of a power supply.
5. What is the first step a technician should take when preparing to work on the inside of a computer?
Remove the power supply.
Disconnect the computer from power.*
Disconnect the computer from the network.
Remove external devices such as a mouse.
6. What tool can be used to find and attempt to fix file structural errors on a hard disk in Windows 7?
Format
Sfc
Rd
Chkdsk*
7. A customer asks for a solution to a printer problem that is beyond the knowledge level of the technician. What should the technician do?
Try to fix the problem anyway.
Tell the customer to call the printer manufacturer to fix the problem.
Gather as much information as possible and escalate the problem.*
Ask the customer to call again when another technician can provide a solution to the problem.
8. Which statement that is related to running 64-bit software is correct?
64-bit software requires a 64-bit processor but can run on a 32-bit operating system.
64-bit software requires a 64-bit processor and a 64-bit operating system.*
64-bit software can run on a 32-bit processor but requires a 64-bit operating system.
64-bit software can run on a 32-bit processor using a 32-bit operating system but the software performance will be slower.
9. Which statement is correct about installing a 32-bit operating system on a x64 architecture?
The OS will always make use of all the RAM available.
The OS will run correctly.*
The OS can address more than 128 GB of memory.
This combination will provide better security.
10. What action should a technician take before upgrading computers from Vista to Windows 7?
Run Vista Upgrade Analyzer.
Run Windows 7 Upgrade Advisor.*
Uninstall all programs.
Upgrade the video card.
11. What is a possible situation when it might be necessary to boot Windows 7 from a USB device, a CD, or a DVD?
to disable background services
to delete registry keys
to partition the hard drive
to repair the system*
12. What type of partition has the ability to create volumes spanning across more than one disk?
primary
active
extended
dynamic*
13. What type of file system allows the use of files larger than 5 GB and is mostly used on internal hard drives?
FAT32
FAT64
NTFS*
CDFS
exFAT
14. Which user account should be used only to perform system management and not as the account for regular use?
guest
standard user
administrator*
power user
15. Which type of user account is created automatically during a Windows 8.1 installation?
Administrator*
Guest
Remote Desktop user
Standard user
16. A technician is attempting to repair a Windows 7 laptop that has a missing or corrupt OS file that prevents Windows 7 from starting up. The technician reboots the laptop and accesses the WinRE via the F8 key. Which option must the technician choose in the System Recovery menu to locate and fix the missing or corrupt system files?
Startup Repair*
System Restore
System Image Recovery
Windows Memory Diagnostic
17. When would the PXE option be used when repairing a PC?
The display cannot be seen clearly.
There is no response from the mouse or keyboard.
The computer needs a replacement operating system.*
A newly installed application caused the system to perform erratically.
18. A user wants to extend a primary partition formatted with the NTFS file system with the unallocated space on the hard disk. What must the user do after the primary partition is extended to make it usable?
Convert the disk type to dynamic.*
Ensure that the disk type is basic.
Format the disk with the FAT64 file system.
Partition the new space as a basic disk.
19. A user is viewing the Windows Disk Management utility and notices that one of the disks is marked as Foreign. What does this mean?
This is a basic disk that has just been converted to a dynamic disk.
This is a dynamic disk whose partition has been deleted.
This is a dynamic disk from another PC running Windows.*
This is a disk that does not contain a valid signature.
20. What are two file attributes in the Windows environment? (Choose two.)
details
archive*
read-only*
security
general
21. What are two functions of hypervisors? (Choose two.)
to partition the hard drive to run virtual machines
to protect the host from malware infection from the virtual machines
to manage virtual machines*
to allocate physical system resources to virtual machines*
to share the antivirus software across the virtual machines
22. Which Windows utility can be used to schedule a regular backup for preventive maintenance?
Windows Task Scheduler*
Windows Task Manager
Disk Cleanup
System Restore
23. Which statement is correct about applying firmware updates?
Firmware updates are sometimes irreversible.*
It is possible to use the Roll Back feature to reverse the change.
The firmware updates can be installed automatically using the Windows Service Pack utility.
Firmware updates should not be included as part of the preventive maintenance program.
24. What is true about restore points?
Once System Restore is used to restore a system, the change is irreversible.
Restore points back up personal data files.
Restore points recover corrupted or deleted data files.
Restore points should always be created before making changes to a system.*
25. A user has a computer that is infected with spyware. What should be performed before removing the spyware?
Disable System Restore.*
Run Windows Update.
Run a disk defragmentation.
Create a full backup.
26. A technician is troubleshooting a Windows 7 laptop that takes significantly longer than expected when performing a file search. What is the possible cause?
The file system is corrupt.
The disk type is basic.
The disk type is dynamic.
The file permissions are not set.
The index service is not running.*
27. A user reports that a PC is losing files, not opening some files, and is performing slowly. The technician suspects problems with the hard drive. What should be done to protect the data that is on the PC and to determine the source of the problem, without risking total drive failure?
Run the format command, then replace the hard drive.
Run chkdsk, then run format.
Back up all important files, then replace the hard drive.
Back up all important files, then run chkdsk.*
Run chkdsk, then back up all important files.
28. A user logs into Active Directory on a workstation and the user home directory does not redirect to a network share on a file server. A technician suspects that the group policy setting is incorrect. Which command can the technician use to verify the group policy settings?
rstrui
runas
tasklist
gpresult*
gpupdate
29. A company has recently deployed Active Directory and now a workstation cannot connect to a network resource. A technician takes corrective action by modifying group policy settings. Which command should the technician use to make the workstation synchronize with the new settings?
runas
rstrui
tasklist
gpresult
gpupdate*
30. A wired network is undergoing several changes that could leave it vulnerable to connection by unauthorized devices while the work is in progress. Which two temporary measures would enable the authorized devices to continue to have network access but prevent unauthorized devices from connecting? (Choose two.)
Disable DNS.
Disable SSID broadcast.
Disable DHCP.*
Subnet the network.
Assign static IP addresses to the authorized devices.*
31. Refer to the exhibit.
IT Essentials ITE v6 A+ Cert Practice Exam 2 Answers Q31
In what situation would a technician use this tab?
ITE 6.0 Cert Practice Exam 2 001
When the device will not be using the Internet.
When a laptop is used both at work with DHCP and at home with a static IP address.*
When a device is behind a firewall and software is being used that needs access to a remote network.
When the computer will be using a VPN connection and accessing the Internet while connected through the VPN.
32. On a PC that is running Windows 7 Ultimate, a user sets up a home entertainment system and creates a homegroup. The user then joins two other PCs to the workgroup, one PC running Windows 7 Starter and the other running Windows 7 Home Basic. What else must the user do in order to have the user accounts on the Windows 7 Home Basic and Windows 7 Starter PCs access the shares on the home entertainment system?
Users have to be added to the user accounts on the home entertainment PC.
Users on the PC that is running Windows Starter cannot join the homegroup.
Users on the PC that is running Windows Home Basic will have to be manually added to the homegroup.
User accounts on all three PCs have to be added to the homegroup.
Nothing has to be done. All users accounts on all the PCs will automatically be added to the homegroup.*
33. A user is reporting that a file has been shared specifically with another user on the network, but the other user opens the file and is unable to save it once edited. What is the probable cause?
The user shared the document with Read permissions.*
The user forgot to share the parent folder.
The file has the Archive attribute enabled.
The file has been deleted.
34. Which character of the Cloud model provides easy monitoring, controlling, reporting, and billing for both the provider and customers?
rapid elasticity
resource pooling
measured service*
broad network access
on-demand self-service
35. A business organization is configuring security on the mobile devices that are used in the organization. The security policy states that business data on mobile devices should only ever be accessed by employees. Which mobile device security feature can be used to best ensure that business data is rendered completely inaccessible if the device is lost or stolen?
remote lock
remote wipe*
passcode lock
sandbox
36. An administrative assistant tries to link a Bluetooth keyboard and mouse to a computer. The keyboard does not work, but the mouse works fine. What are two issues that could cause this situation? (Choose two.)
Wi-Fi is turned off.
The keyboard battery is dead.*
Bluetooth is turned off.
The Num Lock key has been inadvertently pressed.
The keyboard is too far from the computer.*
37. What is needed from Apple and Google in order for individual programmers to develop apps for iOS and Android devices?
SLA
SDK*
firmware
iOS or Android device
38. Which type of malware is disguised as a legitimate program?
adware
worm
Trojan*
spyware
39. After complaints from users, a technician identifies that the college web server is running very slowly. A check of the server reveals that there are an unusually large number of TCP requests coming from multiple locations on the Internet. What is the source of the problem?
A DDoS attack is in progress.*
The server is infected with a virus.
There is insufficient bandwidth to connect to the server.
There is a replay attack in progress.
40. Which security threat hides the resources that it uses from antivirus programs?
worm
Trojan
rootkit*
spyware
41. A user receives an email requesting verification of the password that is used to access bank files. What type of security threat is this?
virus
social engineering
phishing*
malware
42. A cleaner attempts to enter a computer lab but is denied entry by the receptionist because there is no scheduled cleaning for that day. What type of attack was just prevented?
Trojan
shoulder surfing
war driving
social engineering*
phishing
43. Which two precautions can help prevent social engineering? (Choose two.)
Always ask for the ID of unknown persons.*
Escort all visitors.*
Keep your password securely under your keyboard.
Do not allow any customers into the workplace.
Always require a user name and password to be configured.
44. A company has replaced five desktop computers in the accounting and finance department with new computers. The plan is to donate the recovered computers in a fully functional state to a not-for-profit community organization. How can the company ensure that sensitive financial data cannot be accessed once the computers are donated?
Data wipe the hard drives by using specialized software.*
Perform a high-level format on the hard drives.
Drill holes through the hard drive platters.
Delete all the files and directories on the hard drives.
45. Match the task to the Windows Control Panel utility. (Not all options are used.)

IT Essentials ITE v6 A+ Cert Practice Exam 2 Answers Q45
File attributes are a type of meta-data that describe and may modify how files and/or directories in a filesystem behave. Typical file attributes may, for example, indicate or specify whether a file is visible, modifiable, compressed, or encrypted.
What does the attribute I mean in Windows 10?
“I” indicates that a file is not content indexed. For a list of all the attributes, enter this in a command prompt window: dir /?
Which one is not a file attribute?
4. Which one of the following is not attributes of file? Explanation: rename is not the attribute of file rest all are files attributes.
How do I see file attributes?
To adjust the file attributes in MS-DOS or the Windows command line, use the attrib command.
- Right-click the file that you want to view or change the file attributes.
- Select the Properties option.
- In the file Properties window, you see the attributes under the General tab, as shown in the picture below.
How many file attributes are there?
In operating systems like Linux, there are three main file attributes: read (r), write (w), execute (x). Read – Designated as an “r”; allows a file to be read, but nothing can be written to or changed in the file. Write – Designated as a “w”; allows a file to be written to and changed.
How do you change file attributes?
To view or change the attributes of a file, right-click the file, and then click Properties. In the “Attributes:” section, enabled attributes have checks beside them. Add or remove the checks from Read-only, Archive, or Hidden to enable or disable these options.
How do I remove a file attribute?
Change file attributes in Windows 10
- Open File Explorer and go to the folder that contains your files.
- Select the file whose attributes you want to change.
- On the Home tab of the Ribbon, click on the Properties button.
- In the next dialog, under Attributes, you can set or remove the Read-only and Hidden attributes.
What are file attributes AI?
File attributes are metadata values stored by the file system on disk and are used by the system and are available to developers via various file I/O APIs as described on this link. These attribute symbols might also be helpful: R Read-only file attribute. A Archive file attribute.
Which of the following is not a feature of file attribute *?
D. Explanation: rename is not the attribute of file rest all are files attributes.
What are two file attributes in the Windows environment?
What are two file attributes in the Windows environment? (Choose two.) Explanation: The file attributes are read-only, archive, hidden, and system. Details, security, and general are tabs on the file Properties applet.
How do I change file attributes in Windows 11?
1 Answer
- Right click on the folder that is having trouble saving files and go to Properties.
- On the Security tab, click Edit to change the permissions.
- Select the admin user in the Group or User Names section.
- Put a checkmark on Allow full control.
Can you change file attributes?
How do I remove hidden attributes from a folder?
Open Folder Options by clicking the Start button, clicking Control Panel, clicking Appearance and Personalization, and then clicking Folder Options. Click the View tab. Under Advanced settings, click Show hidden files, folders, and drives, and then click OK.
Which one of the following is not a file attribute in the Windows environment?
What are Windows file attributes?
File attributes are pieces of information associated with every file and directory that includes additional data about the file itself or its contents. They can exist in only one of two states – Set or Cleared; like an On or Off state. Attributes can be in files, directories, volumes and certain system objects.
What is not supported by the content indexing service?
The file or directory is not to be indexed by the content indexing service. The user data stream not to be read by the background data integrity scanner (AKA scrubber). When set on a directory it only provides inheritance.
What does the “file not indexed” flag do?
The file or directory is not to be indexed by the content indexing service. The user data stream not to be read by the background data integrity scanner (AKA scrubber). When set on a directory it only provides inheritance. This flag is only supported on Storage Spaces and ReFS volumes. It is not included in an ordinary directory listing.
What is unsupported attribute?
It is recommended that unsupported attributes be masked off when encountered. A file or directory that is read-only. For a file, applications can read the file but cannot write to it or delete it. For a directory, applications cannot delete it, but applications can create and delete files from that directory.
What does it mean when the file or directory attribute is set?
When this attribute is set, it means that the file or directory is not fully present locally. For a file this means that not all of its data is on local storage (for example, it may be sparse with some data still in remote storage). For a directory it means that some of the directory contents are being virtualized from another location.
Learn what the file attribute letters in Windows and File Explorer attribute columns mean. Discover relations between file permssions and file attributes. We have listed everything about file attributes in Windows, DOS, and other operating systems.
- What Are File Attributes?
- File Attributes in Windows Explorer and Folder Size
- List of All File Attributes
- How are file attributes related to file permissions?
What Are File Attributes?
File attributes are specific properties assigned to files and folders within an operating system. They define their behavior and how the system and applications handle them. These attributes are flags or settings that control various aspects of a file’s accessibility, visibility, and functionality. Understanding file attributes is essential for anyone managing files on a computer. They can significantly impact how files are used, displayed, and protected.
File attributes are crucial in file management, security, and system performance. They help protect important data, optimize storage, and control how files are accessed and displayed. By understanding and properly managing file attributes, you can ensure that your files are used effectively.
Attributes can be modified manually through the file properties dialog in Windows or via command-line tools like attrib. Properly configuring file attributes allows you to tailor the behavior of your files to your needs. Whether you’re ensuring the security of sensitive information or optimizing the storage of large files.
File Attributes in Windows Explorer and Folder Size
File attributes play a vital role in how files are managed, displayed, and secured on your system. They help you understand more about each file’s properties, such as whether it’s hidden, read-only, compressed, or encrypted. These attributes are usually represented by specific letters (such as R for Read-Only, H for Hidden, and S for System). They can be viewed in file management tools like Windows Explorer and the MindGems Folder Size tool.
Understanding File Attributes in Windows Explorer
In Windows Explorer, file attributes are typically displayed in the attributes column. You can quickly see which files are marked with specific properties. For example:
R = Read-Only: Indicates files that cannot be modified or deleted without changing the attribute.
H = Hidden: Marks files that are not visible by default in Explorer.
S = System: Flags essential system files that should not be altered.
A = Archive: Used to mark files that have changed since the last backup.
However, while Windows Explorer provides basic visibility into file attributes, it does have limitations. By default, it does not display hidden and system files. That can make it difficult to get a complete picture of what’s stored on your system. To view these files, you must adjust the settings. Set “Show hidden files, folders, and drives” and uncheck “Hide protected operating system files.”. Even then, navigating through and managing these files can be cumbersome.
The Power of Folder Size for Viewing File Attributes
The MindGems Folder Size tool offers a more robust and comprehensive solution for managing and viewing file attributes. Unlike Windows Explorer, Folder Size allows you to view all file attributes without needing to change any settings. This tool provides a complete view of your files, including hidden and system files. That is crucial for thorough file management and maintenance.

File Attributes in Windows
Here’s why Folder Size is superior to Windows Explorer when it comes to handling file attributes:
Comprehensive Attribute Display
Folder Size lists all file attributes in a clear and accessible manner. Whether a file is hidden, a system file, or has other specific attributes, Folder Size makes it easy to see and manage these properties. The tool ensures that no file is overlooked, giving you full control over your data.
Advanced Filtering and Sorting
With Folder Size, you can filter and sort files based on their attributes. This feature is particularly useful for identifying and managing files that might be hidden or compressed. That helps you optimize your storage space more effectively. Sorting files by attributes allows for quick identification of files that require special attention. Such are those that are system-critical or potentially taking up unnecessary space.
Detailed File Information
Folder Size goes beyond just listing file attributes. It provides in-depth details about each file, including size, date modified, and file type, all in one interface. This comprehensive overview helps you make informed decisions when managing your files. That is especially true when it comes to freeing up space or securing sensitive data.
User-Friendly Interface
The Folder Size tool is designed to be intuitive and easy to use. It is easy even for those who may not be familiar with more advanced file management techniques. The visual representation of file and folder sizes is very helpful. Combined with the clear display of attributes, makes it simple to navigate through your data. As a result, identify where space is being used.
Real-Time Updates
As you manage your files, Folder Size provides real-time updates, ensuring that the information you see is always current. This feature is essential for keeping your system organized. Also for quickly responding to changes, such as new files being added or old ones being deleted.
System Performance Optimization
By providing a clear view of all file attributes, including those that Windows Explorer might hide, Folder Size allows you to better optimize your system’s performance. For example, identifying and managing large compressed files, or recognizing system files that shouldn’t be modified, can help prevent system slowdowns and ensure that your disk space is being used efficiently.
Why Choose Folder Size Over Windows Explorer?
While Windows Explorer is a basic tool that comes with every Windows installation, it falls short in several areas when it comes to advanced file management. Folder Size, on the other hand, is designed specifically to address these shortcomings:
Visibility: Folder Size gives you full visibility into all files, including those that are hidden or system-protected, without requiring any configuration changes.
Efficiency: The ability to sort, filter, and view detailed file information in one place saves time and makes file management more efficient.
Space Management: By understanding file attributes and their impact on storage, you can better manage disk space, particularly when dealing with large volumes of data.
Security: Folder Size helps you keep track of important files and their attributes, ensuring that sensitive data is properly encrypted or protected from unauthorized changes.
In summary, while Windows Explorer offers basic file management capabilities, it lacks the depth and flexibility required for more advanced tasks. The Folder Size tool by MindGems provides a powerful alternative, offering a complete view of your files and their attributes, along with the tools you need to effectively manage and organize your data. Whether you’re looking to optimize disk space, secure sensitive information, or simply keep your system running smoothly, Folder Size is the ideal solution.
Download: Folder Size
List of All File Attributes
File attributes can vary depending on the operating system, but in Windows, some of the most common attributes include:
R = Read-Only:
When a file is marked as read-only, most programs won’t allow it to be deleted or altered. This is fairly straightforward. For example, if you attempt to delete a read-only file in DOS, you’ll receive an “Access denied” message. However, Windows Explorer might still delete it without any issues. Some programs take a middle-ground approach. They’ll permit you to modify or delete the file, but only after confirming that’s what you want to do.
H = Hidden:
This attribute is also straightforward—files marked as hidden won’t be visible under normal circumstances. For instance, when you use the “DIR” command in DOS, hidden files won’t show up. You have to use a specific flag, as shown in the earlier example.
S = System:
This attribute flags files that are essential to the operating system. It is indicating that they should not be tampered with or removed. It’s similar to the read-only flag but carries more importance. Additionally, it acts as a “super-hidden” attribute—even if you set your system to show hidden files, system files marked with this attribute will remain hidden unless you specifically disable the “Hide protected operating system files” option.
D = Directory:
This attribute differentiates between regular files and subdirectories within the current directory. While, in theory, you could change a file to a directory by altering this bit, doing so in practice would cause issues, as directory entries need to follow a specific format.
A = Archive:
This attribute serves as a communication tool between file-modifying applications and backup software. Most backup programs offer an incremental backup option. It lets you back up only the files that have changed since the last backup. The archive bit helps with this—when backup software archives a file, it clears this bit. Any subsequent modifications to the file should set the archive bit again. The next time a backup is performed, the software checks the archive bits to determine which files need to be backed up. While this system works well in most cases, it’s not foolproof. Therefore, you shouldn’t rely on it entirely to ensure your critical files are backed up.
C = Compressed:
When a file or folder is marked as compressed, the data is stored in a way that reduces its size. That frees up storage space. Compression is handled by the file system (such as NTFS), and the data is automatically decompressed when accessed. While this can save significant space, especially for large files, it comes with some limitations. One major restriction is that compressed files and folders cannot be encrypted using the native NTFS encryption (EFS). This is because both compression and encryption alter the way data is stored, and these two processes are incompatible. Therefore, if you need to secure your data, you must choose between compression and encryption.
E = Encrypted:
Encryption is a security measure that encodes the data in a file or folder. It can only be accessed by authorized users. On Windows systems, this is usually handled by the Encrypting File System (EFS). When a file is encrypted, it’s protected against unauthorized access, even if someone physically obtains the storage device. However, like compression, encryption has its own limitations. Encrypted files and folders cannot be compressed. This is because encryption needs to maintain the integrity and security of the data. That conflicts with the way compression alters the data structure to reduce its size.
N = Not Indexed:
The Not Indexed attribute, is often seen as “N” or sometimes “I,”. It indicates that the file or folder should not be indexed by the Windows Search service. Indexing speeds up searches by creating a database of the contents of files on your system. However, you might choose to mark certain files as “Not Indexed”. That will protect their privacy or reduce the size of the search index database. Files marked with this attribute won’t appear in search results as quickly as indexed files. In some cases, they might not appear at all, depending on the search method used.
L = Reparse Points:
A reparse point is a special attribute in the NTFS file system used to extend the file system’s functionality. Reparse points are used by features like symbolic links, junction points, and mounted drives. When a file or folder has the “L” attribute, it means it contains a reparse point. Therefore it acts as a pointer to another location in the file system. This can be useful for redirecting file paths or linking to files in different directories. Reparse points are critical for certain system operations and advanced file management techniques. Unfortunately, they can complicate file operations like copying or moving files, as they don’t behave like standard files or folders.
O = Offline:
The Offline attribute marks files or folders that are not available for immediate access. That is because they have been moved to a different storage tier. For example a remote location, such as a network drive or cloud storage. These files are still listed in the file system, but they may not be physically present on the local disk. When you try to access an offline file, the system may need to retrieve it from its remote location. Unfortunately, that can cause delays. This attribute is commonly used in environments with limited storage. Therefore, less frequently accessed files are offloaded to save space on the primary drive.
P = Sparse File:
A sparse file in the NTFS file system that allows for efficient storage of large empty files. Specifically, those that contain a lot of empty space (zeroes). Instead of storing the zeroes physically on the disk, the file system only stores the actual data. Instead, the empty space is recorded as a placeholder. This can drastically reduce the amount of disk space used by certain types of files. Those are disk images or database snapshots. Sparse files are beneficial in situations where you need to allocate large amounts of space without actually using it all. Certainly, they can be more complex to manage and may not be fully supported by all backup software.
I = Not Content Indexed:
The Not Content Indexed attribute, is similar to “N” for Not Indexed. It specifically prevents the contents of a file or folder from being indexed by the Windows Search service. “Not Indexed” attribute may apply broadly to the file or its metadata. “Not Content Indexed” focuses on the actual data within the file. This is useful for files containing sensitive or personal information that you don’t want to appear in search results. Additionally, marking files as not content-indexed can reduce the load on the indexing service. That improves overall system performance in environments with large amounts of data.
T = Temporary:
The Temporary attribute marks files or folders as temporary. It indicates that they are expected to be used only for a short time. Temporary files are often created by applications during installation, updates, or while performing specific tasks. These files are intended to be deleted once they are no longer needed. Marking a file as temporary can help the operating system or application manage it more efficiently. The file system may choose to prioritize these files for deletion when disk space runs low. However, if not properly managed, temporary files can accumulate and consume significant amounts of storage space over time.
How are file attributes related to file permissions?
File attributes and file permissions are both mechanisms used to manage access to files and directories, but they serve slightly different purposes and function in different ways.
1. File Attributes
File attributes are metadata associated with a file or directory that define specific behaviors or characteristics. These attributes might control how the file is treated by the operating system or applications. Common file attributes include:
- Read-Only: The file cannot be modified.
- Hidden: The file is not visible in the standard directory listing.
- System: The file is used by the operating system and should not be altered by users.
- Archive: Indicates that the file has been modified since the last backup.
- Immutable (Linux-specific): The file cannot be modified, deleted, or renamed.
2. File Permissions
File permissions, on the other hand, are rules associated with a file or directory that determine which users can access the file, and in what way. Permissions generally fall into three categories:
- Read (r): Allows the user to read the contents of the file or directory.
- Write (w): Allows the user to modify or delete the file or directory.
- Execute (x): Allows the user to execute the file, if it is a script or program, or to traverse the directory.
Permissions are usually applied to three different sets of users:
- Owner: The user who owns the file.
- Group: A group of users who are granted similar access rights.
- Others: All other users.
Relationship Between File Attributes and File Permissions
File attributes and file permissions are related in the sense that they both control access to files, but they do so at different levels and in different ways:
- Complementary: Attributes and permissions work together to define how a file can be accessed or modified. For instance, even if a user has write permissions on a file, if the file is marked as read-only (an attribute), the user will not be able to modify it.
- Hierarchical Control: File permissions tend to provide a more granular level of control compared to attributes. While attributes can enforce broad rules (e.g., “this file is hidden”), permissions can specify exactly who can read, write, or execute a file.
- Operating System Specific: Different operating systems handle attributes and permissions differently. For example, Linux has both file permissions (using the
chmodcommand) and attributes (using thechattrcommand), while Windows primarily uses attributes and a different permissions model.
Example (Linux System):
- Permissions: A file might have permissions set to
rwxr-xr--, meaning the owner can read, write, and execute, the group can read and execute, and others can only read. - Attributes: If the file is marked with the
immutableattribute, even the owner will be unable to modify or delete it, regardless of the write permission.
In summary, file attributes and permissions work together to control how files are accessed and manipulated. Attributes tend to enforce broader or more restrictive rules, while permissions provide detailed control over what specific users can do with the file.
Operating Systems store non-volatile information as data files in storage devices like Hard Disks (HDDs) or Solid–State Drives (SSDs).
A File System is the part of an Operating System which defines how files are stored and retrieved from the connected storage devices. Two main Files Systems in Windows Server available currently are NTFS (New Technology File System) and ReFS (Resilient File System). File attributes are metadata (data about data) values stored by the File System on non-volatile storage, Hard Disks (HDDs) or Solid–State Drives (SSDs).
A number of different file attributes are there in NTFS File System in Windows Operating Systems. Following table lists some important File attributes and short description about those File attributes.
| Attribute | Short Description |
|---|---|
| Read-only file (R) | An attribute to specify the file as Read-only file. Not applicable for folders. |
| Hidden (H) | An attribute to specify the file as a hidden file or directory. A hidden file is not displayed in an ordinary folder listing command output. |
| System (S) | An attribute to specify the file as an important System file (Operating System file or directory) |
| Directory | An attribute to specify a folder/directory. |
| Archive (A) | An attribute to specify the file is ready for archive (or backed up). Backup apps use archive attribute. Archive attribute turned on a file means that the file needs to be backed up by the backup apps, or archived. |
| Device | Device attribute is reserved for the system use. |
| Normal | No other attributes are set. |
| Temporary (T) | Temporary storage attribute for a file. |
| Sparse file (P) | Sparse file attribute shows the file is a sparse file. Sparce files does not store the large number of empty bytes on the storage disk. Operating System will regenerate those empty bytes if it is a sparse file. A sparse file’s contents can be partially empty and are non–contiguous. |
| Reparse point | Attribute for a file or directory that has a reparse point, or a symbolic link. |
| Compressed (C) | An attribute to specify the file or folder as a compressed file or folder. |
| Offline (O) | Offline attribute shows offline storage. The data of a file is not available immediately. |
| Not Indexed (I) | The file or directory is not to be indexed by the content indexing service. |
| Encrypted (E) | Attribute for an encrypted file or folder. |
| Integrity (V) | Attribute for the folder or user data stream configured with integrity (ReFS File System). |
| Virtual | Virtual attribute is reserved for the system use. |
| No Scrub Data (X) | Attribute for not to be read by the background data integrity scanner (ReFS File System). |
| Pinned (P) | Pinned attribute is used make the file always available offline. |
| UnPinned (U) | Unpinned attribute is used make the file available only in the cloud. |
| Recall on Data Access (M) | Recall on Data Access attribute is used to specify the data is not fully available locally. |
