Многие пользователи Windows 11 предпочитают для работы с ОС графический интерфейс, но командная строка предоставляет непревзойденный контроль над системой. Освоив несколько основных команд, вы сможете быстрее перемещаться по файловой системе, диагностировать проблемы и эффективно выполнять административные задачи, экономя свое время и усилия.
Прежде чем мы перейдем к командам, давайте разберемся с некоторыми терминами:
- Командная строка – текстовый интерфейс для взаимодействия с операционной системой, в отличие от графического. Вы вводите команды, и система их выполняет.
- Каталог (папка) – место хранения файлов и других папок.
cd(сменить каталог) помогает перемещаться между ними. - Путь – это маршрут к файлу или папке в файловой системе. Например:
C:\Users\YourName\Documents. - Корневой каталог — это основание файловой системы, обычно диск
C:\. - Атрибуты файла — свойства файла, например, «скрытый», «только для чтения» или «системный».
- IP-адрес — уникальный адрес компьютера в сети.
- DNS-сервер — сервер, преобразующий доменные имена (например, google.com) в IP-адреса.
- Пакет – небольшой блок данных, отправляемый по сети.
- PID (Идентификатор процесса) – уникальный номер, присвоенный каждому выполняющемуся процессу.
- Модуль (DLL) — это библиотека программного кода, которую используют другие программы.
- Служба — программа, как правило работающая в фоновом режиме, без прямого взаимодействия с пользователем.
Для использования команд, откройте «Командную строку» Windows, это можно легко сделать нажав сочетание клавиш Win+R , в диалоговом окне «Выполнить» введите cmd и нажмите «ОК», или запустите приложение «Windows Terminal», а затем откройте вкладку «Командная строка».
-
cd (Сменить каталог)
Команда
cdпозволяет перемещаться между папками.- Пример:
cd C:\Users\YourName– переходит в папку вашей учетной записи. cd ..– перемещает вас на один уровень вверх.cd \– перемещает вас в корневой каталог текущего диска.cd /– (в некоторых системах) также переводит вас в корневой каталог.
- Пример:
-
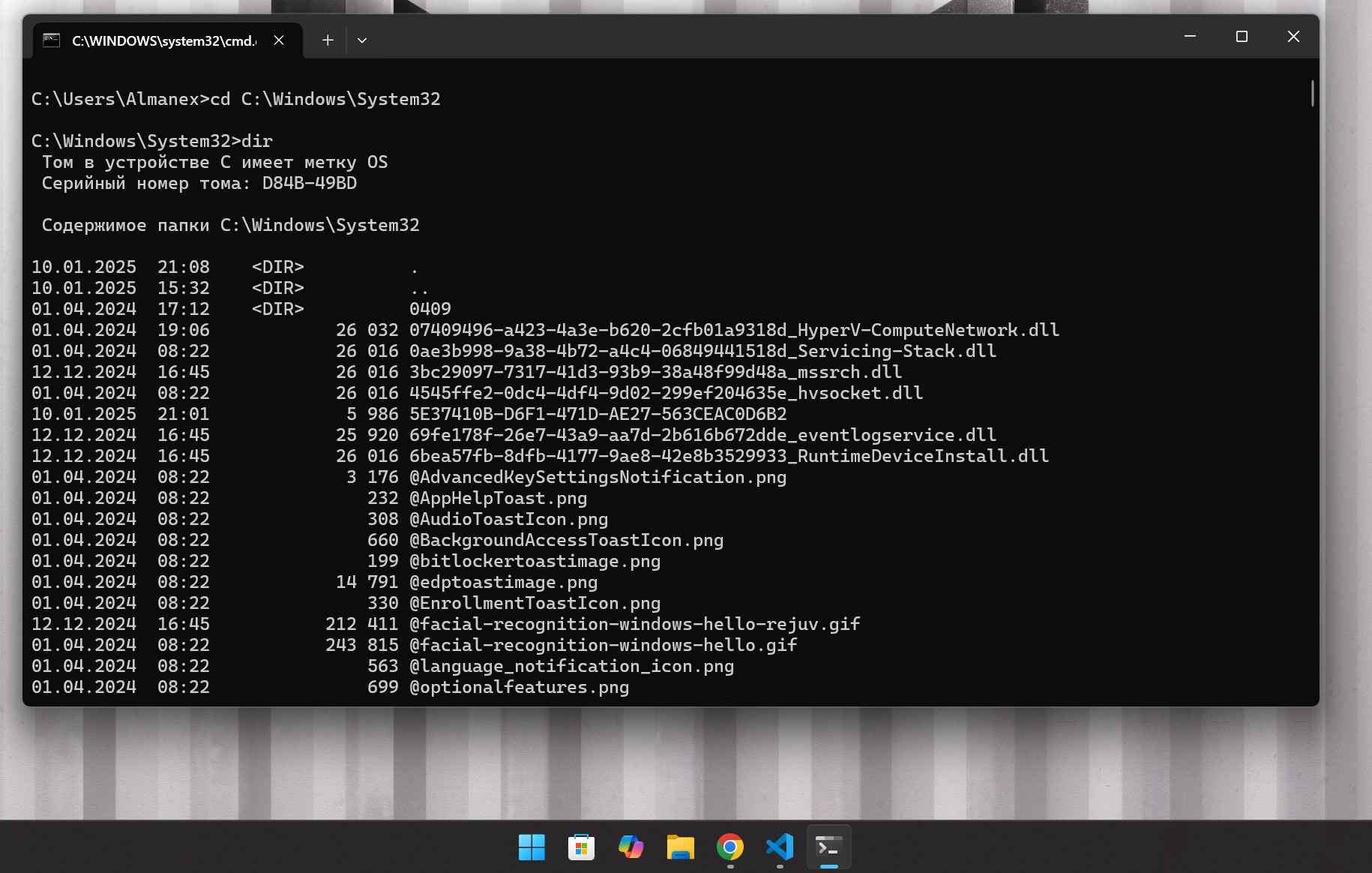
dir (Каталог)
Команда
dirпоказывает содержимое текущего каталога.- Пример:
dir– выводит список содержимого текущего каталога. dir /P– выводит список содержимого с паузами после каждого заполнения экрана.dir /AH– показывает все скрытые файлы.
Особые случаи:
/P: Приостанавливает вывод после каждого заполнения экрана./W: Отображает вывод в широком формате./A: Отображает файлы с определенными атрибутами. Например:/A:Dпоказывает только каталоги./A:Hпоказывает скрытые файлы./A:Rпоказывает файлы только для чтения./A:Sотображает системные файлы.
/O: Сортирует вывод. Например:/O:Nсортирует по имени (в алфавитном порядке)./O:Dсортирует по дате/времени./O:Sсортирует по размеру.
/S: Отображает список всех файлов и подкаталогов.
- Пример:
-
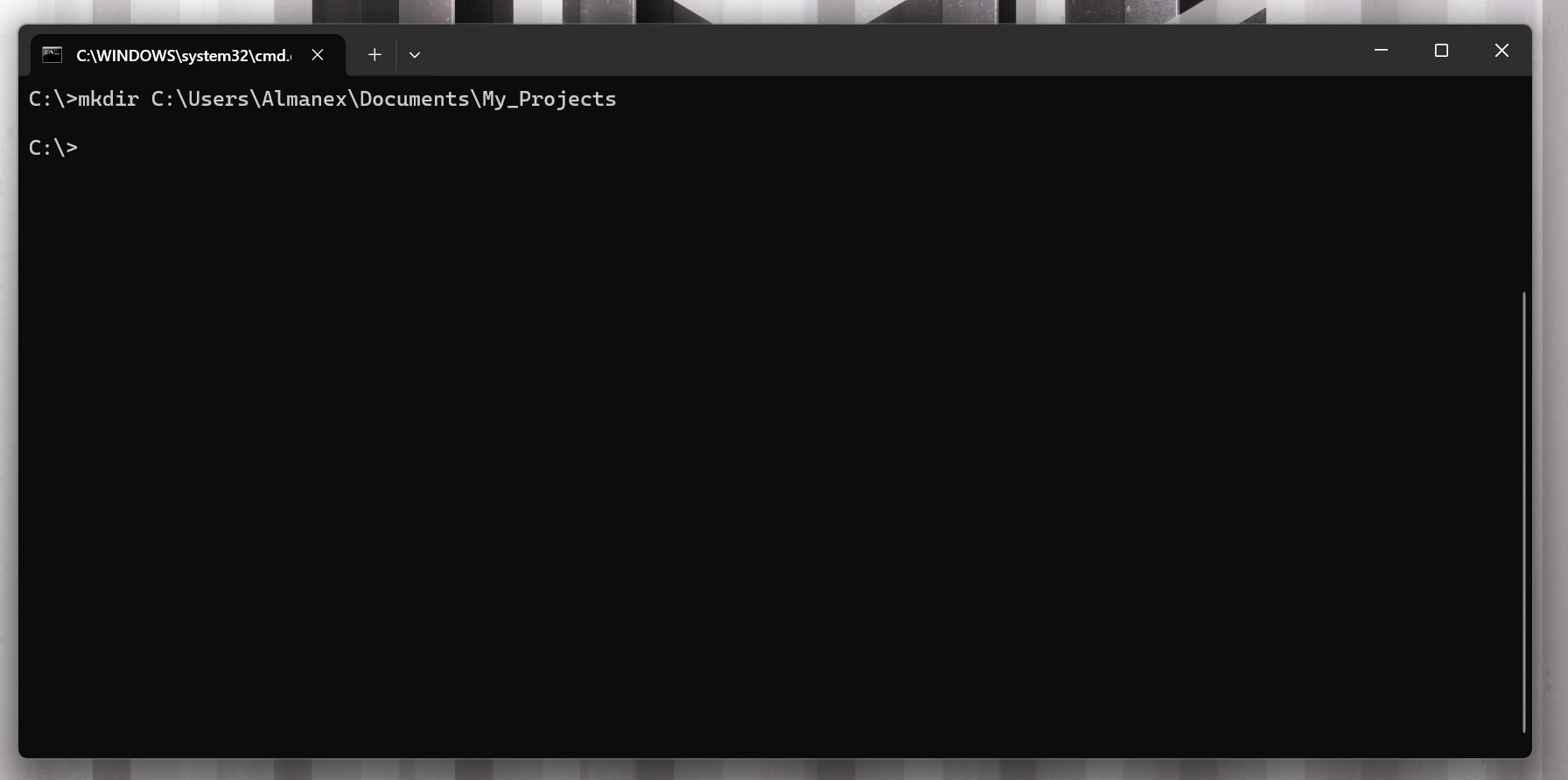
mkdir (Создать каталог)
Команда
mkdirсоздает новые каталоги/папки.- Пример:
mkdir «My_Projects»– создает папку «My_Projects» в текущем каталоге. - Пример:
mkdir «C:\Users\YourName\Documents\My_Projects»– создает папку «My_Projects» в папке «Documents».
- Пример:
-
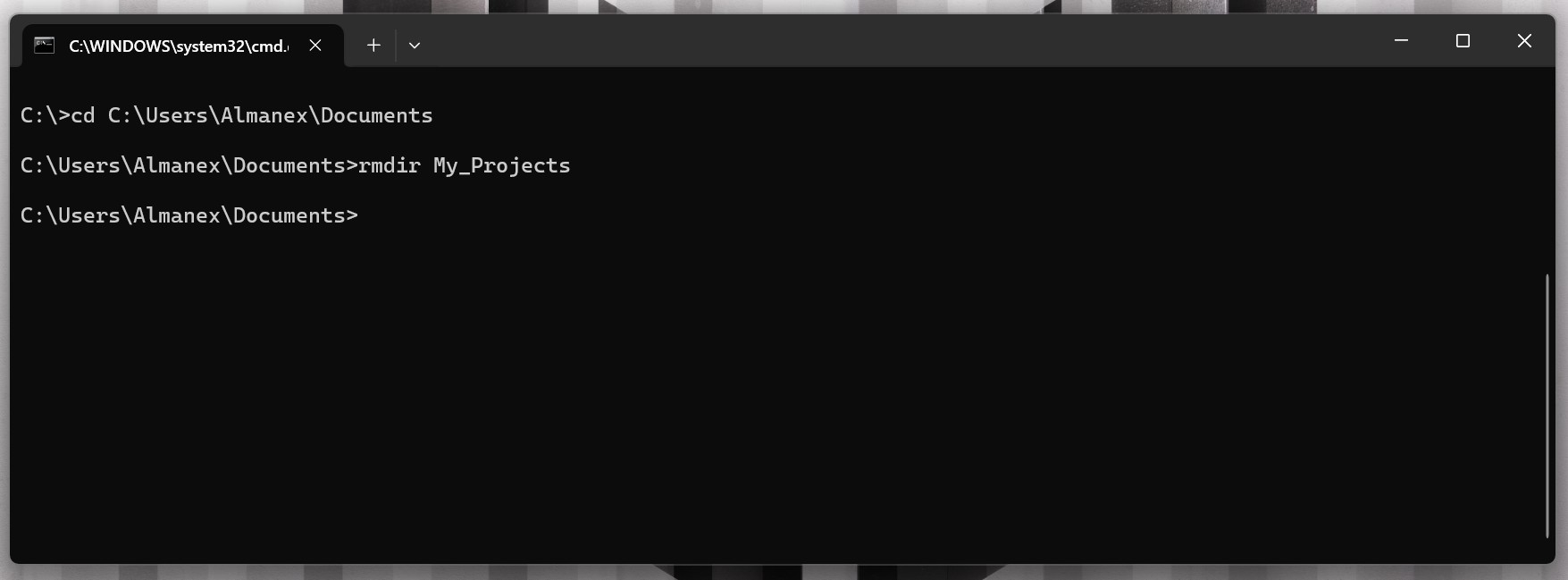
rmdir (Удалить каталог)
Команда
rmdirудаляет пустые каталоги.- Пример:
rmdir «My_Projects»– удаляет папку «My_Projects», если она пуста. - Пример:
rd /s /q «My_Projects»– удаляет папку «My_Projects» и ее содержимое. Внимание: Используйте с осторожностью!
- Пример:
-
copy (Копировать)
Команда
copyкопирует файлы из одного места в другое.- Пример:
copy file1.txt C:\Backup– копируетfile1.txtв папкуC:\Backup. - Пример:
copy *.jpg C:\Backup– копирует все файлы.jpgв папкуC:\Backup. - Пример:
copy D:\My_Files\Report.docx C:\Users\YourName\Documents– копирует файлReport.docx. - Пример:
copy file1.txt C:\Backup /Y– копирует, перезаписывая существующие файлы.
- Пример:
-
del (Удалить)
Команда
delудаляет файлы.- Пример:
del file1.txt– удаляетfile1.txt. - Пример:
del *.jpg– удаляет все файлы.jpg. - Пример:
del *.jpg /f– принудительно удаляет файлы «только для чтения».
Внимание: Файлы удаляются безвозвратно, минуя Корзину.
- Пример:
-
ren (Переименовать)
Команда
renпереименовывает файлы или папки.- Пример:
ren old_file.txt new_file.txt– переименовываетold_file.txtвnew_file.txt. - Пример:
ren «old_folder» «new_folder»– переименовывает папкуold_folderвnew_folder.
- Пример:
-
cls (Очистить экран)
Команда
clsочищает содержимое экрана.Пример:
cls -
ipconfig (Конфигурация интернет-протокола)
Команда
ipconfigпоказывает информацию о сетевых подключениях.- Пример:
ipconfig– выводит основную сетевую информацию. - Пример:
ipconfig /all– выводит более подробную информацию. - Пример:
ipconfig /release– освобождает текущий IP-адрес. - Пример:
ipconfig /renew– запрашивает новый IP-адрес. - Пример:
ipconfig /flushdns– очищает кэш DNS.
Обычно, для обновления конфигурации сети используйте последовательность:
ipconfig /release, а затемipconfig /renew. - Пример:
-
ping
Команда
pingпроверяет сетевое подключение к указанному адресу.- Пример:
ping google.com– проверяет подключение к google.com. - Пример:
ping 8.8.8.8– проверяет подключение к публичному DNS-серверу Google.
Успешный
pingпоказывает время отклика, а неудачный — сообщение «Превышен интервал ожидания для запроса». - Пример:
-
tracert (Трассировка маршрута)
Команда
tracertпоказывает путь, который проходят пакеты данных до места назначения.- Пример:
tracert google.com– отслеживает маршрут к серверам Google.
- Пример:
-
shutdown (Выключение)
Команда
shutdownуправляет выключением и перезапуском компьютера.shutdown /s– немедленно выключает компьютер.shutdown /s /t 60– выключает компьютер через 60 секунд.shutdown /r– немедленно перезагружает компьютер.shutdown /r /t 30– перезагружает компьютер через 30 секунд.shutdown /L– выходит из текущей учетной записи.shutdown /a– отменяет ожидающее выключение или перезагрузку.
-
tasklist (Список задач)
Команда
tasklistотображает список активных процессов.- Пример:
tasklist– показывает список процессов с основными данными. - Пример:
tasklist /V– показывает список процессов с подробными данными. - Пример:
tasklist /M ИМЯ-МОДУЛЯ– показывает процессы, использующие указанный модуль (например, DLL). - Пример:
tasklist /SVC– показывает службы, размещенные в каждом процессе. - Пример:
tasklist /FI ФИЛЬТР– фильтрует вывод по критериям.
- Пример:
-
taskkill (Завершить задачу)
Команда
taskkillзавершает выполняющиеся процессы.- Пример:
taskkill /IM notepad.exe– завершает процесс «notepad.exe». - Пример:
taskkill /PID 1237– завершает процесс с PID 1237. - Пример:
taskkill /F /IM explorer.exe– принудительно завершает процесс «explorer.exe».
- Пример:
-
chkdsk (Проверка диска)
Команда
chkdskпроверяет диск на наличие ошибок и поврежденных секторов.- Пример:
chkdsk C: /f– проверяет дискC:и исправляет ошибки. - Пример:
chkdsk C: /r– проверяет дискC:, исправляет ошибки и восстанавливает данные. - Пример:
chkdsk C: /x– отключает диск перед запуском проверки.
Проверка диска, особенно с параметром
/r, может занять значительное время. - Пример:
-
sfc /scannow (Проверка системных файлов)
Команда
sfc /scannowсканирует и восстанавливает поврежденные системные файлы.Пример:
sfc /scannow -
help (Справка)
Команда
helpпредоставляет информацию о других командах.- Пример:
help dir– показывает справку по командеdir. - Пример:
help– показывает список доступных команд.
- Пример:
-
exit (Выход)
Команда
exitзакрывает текущее окно командной строки.Пример:
exit -
winget (Диспетчер пакетов Windows)
Команда
wingetупрощает установку, обновление и управление приложениями.- Пример:
winget search firefox– ищет приложения, соответствующие запросу «firefox». - Пример:
winget install «Mozilla Firefox»– устанавливает браузер Mozilla Firefox. - Пример:
winget upgrade «Mozilla Firefox»– обновляет браузер Mozilla Firefox. - Пример:
winget uninstall «Mozilla Firefox»– удаляет браузер Mozilla Firefox.
- Пример:
-
sudo (Выполнить от имени суперпользователя)
Команда
sudoпозволяет запускать команды от имени администратора.Пример:
sudo del file.txtПримечание: Эта функция по умолчанию отключена. Для ее включения нужно перейти в Параметры > Система > Для разработчиков и активировать переключатель «Включить sudo».
Командная строка Windows 11 – мощный инструмент, который открывает расширенные возможности управления вашей системой. Используя эти 20 основных команд, вы сможете эффективнее работать, диагностировать проблемы и выполнять различные задачи с большей гибкостью. Помните, что практика – ключ к успеху. Экспериментируйте с командами, и вы быстро станете уверенным пользователем командной строки.
Командная строка Windows (CMD) — мощный инструмент, который предоставляет доступ к широкому набору команд для выполнения различных задач, от работы с файлами до настройки сети и автоматизации процессов. В статье рассмотрим 100 популярных команд CMD, которые пригодятся как новичкам, так и опытным пользователям. Для удобства они разделены по категориям.

Разделы
- Общие команды CMD
- Сетевые команды CMD
- Команды для управления процессами
- Команды для управления файловой системой
- Команды для управления пользователями
- Команды для управления безопасностью
- Команды для диагностики и устранения неполадок
- Команды для скриптинга и автоматизации
- Команды для управления сетевыми подключениями
- Команды для управления печатью
- Дополнительные команды в Windows
Общие команды командной строки (CMD) позволяют пользователям управлять ОС Windows через интерфейс командной строки. Они нацелены на различные задачи – от получения справочной информации до управления процессами.
- hel — выводит список всех доступных команд и их краткое описание, что полезно для получения информации о базовых командах.
- cls — очищает экран командной строки. Если в окне CMD много текста, этой командой можно убрать весь вывод и начать работу «с чистого листа».
- exit — завершает текущую сессию командной строки и закрывает окно CMD.
- echo — выводит сообщения в консоль или включает/выключает отображение команд в пакетных файлах – echo Hello, World! выведет Hello, World! на экран.
- ver — отображает версию операционной системы Windows.
- title — изменяет заголовок окна командной строки. Например, title Моя Командная Строка изменит заголовок на «Моя Командная Строка».
- pause — временно приостанавливает выполнение скрипта, но при нажатии любой клавиши можно продолжить работу.
- date — позволяет узнать или изменить текущую дату в системе.
- time — отображает или изменяет текущее время в системе.
- tasklist — выводит список всех запущенных процессов с их PID (идентификатором процесса).
- powercfg — управляет настройками энергопотребления и профилями питания.
- fc — сравнивает два файла и отображает их различия.
Сетевые команды CMD
В разделе собраны основные сетевые команды CMD, которые помогут управлять подключениями, диагностировать сетевые проблемы и выполнять разнообразные операции с сетью. Они незаменимы для системных администраторов и пользователей, нуждающихся в решении сетевых задач.
- ping — проверяет связь с удаленным узлом, отправляя ему пакеты данных. Например, ping google.com проверит доступность сервера Google.
- ipconfig — отображает конфигурацию сетевых интерфейсов системы (IP-адреса, маску подсети и шлюзы).
- netstat — выводит информацию о сетевых соединениях и открытых портах
- netstat -an — показывает все активные соединения.
- tracert — отслеживает маршрут пакета до целевого узла – tracert yandex.ru покажет все узлы, через которые проходит запрос.
- nslookup — используется для проверки информации о DNS-серверах.
- nslookup example.com — отображает IP-адрес сайта example.com.
- arp — выводит или изменяет записи ARP (Address Resolution Protocol) –: arp -a покажет текущие записи ARP.
- route — управляет таблицей маршрутизации сети – route print выведет все существующие маршруты в системе.
- net use — подключает сетевые диски. Например, net use Z: \\server\folder подключит сетевой ресурс как диск Z:.
- netsh — позволяет настраивать различные параметры сети через командную строку.
- netsh wlan show profiles — отображает сохраненные профили Wi-Fi.
Команды для управления процессами
Команды ниже позволяют эффективно управлять процессами и службами на вашем ПК: помогают запускать службы, планировать задачи, управлять активными процессами, а также выключать или перезагружать систему. С их помощью можно автоматизировать выполнение задач, получать информацию о состоянии системы и контролировать её работоспособность.
- sc — управляет службами Windows. Пример: sc start servicename запустит службу с именем servicename.
- schtasks — управляет планировщиком задач. Так, schtasks /create /tn «Моя Задача» /tr notepad.exe /sc once /st 12:00 создаст задачу для запуска.
- start — запускает программу или команду в новом окне. Например, start notepad откроет блокнот.
- wmic — взаимодействует с системой через Windows Management Instrumentation – wmic process list brief покажет список процессов.
- shutdown — выключает, перезагружает или завершает работу системы. Так, shutdown /s /f /t 0 немедленно выключит компьютер.
- systeminfo — выводит информацию о системе, включая версию Windows, параметры оборудования и установленные обновления.
Команды для управления файловой системой
Команды для управления файловой системой в CMD позволяют работать с файлами и папками: просматривать содержимое директорий, перемещаться между папками, создавать и удалять файлы и каталоги, копировать данные с использованием различных опций.
- dir — отображает список файлов и каталогов в указанной директории. Пример: dir C:\Windows выведет содержимое папки Windows.
- cd — меняет текущий каталог. Так, cd C:\Users перейдет в папку пользователей.
- md NewFolder — создает новую папку.
- rd — удаляет пустую папку. Пример: rd NewFolder удалит папку NewFolder.
- copy — копирует файлы из одного места в другое.
- move — перемещает файлы или папки.
- del — удаляет файлы. Например, del file.txt удалит файл file.txt.
- xcopy — копирует файлы и директории, включая их структуру. Так, xcopy C:\Source D:\Destination /s /e скопирует все файлы и папки из Source в Destination.
- robocopy — более продвинутая версия xcopy, используется для надежного копирования данных. Например, robocopy C:\Source D:\Destination /mir синхронизирует две папки.
Команды для управления пользователями
Команды для управления пользователями предоставляют средства для администрирования учетных записей, настройки групповых прав и управления политиками безопасности. А также позволяют администраторам эффективно управлять пользователями в системе, добавлять новых пользователей, изменять их права и настраивать параметры учетных записей.
- net user — управляет учетными записями пользователей.
- net user UserName /add — добавляет нового пользователя с именем UserName.
- net localgroup — управляет локальными группами пользователей.
- net localgroup Administrators UserName /add — добавляет пользователя в группу администраторов.
- whoami — выводит имя текущего пользователя и информацию о его правах.
- runas — позволяет запускать программы от имени другого пользователя. Так, runas /user:administrator cmd запустит CMD с правами администратора.
- net accounts — управляет параметрами учетных записей, например, минимальной длиной пароля и периодом его действия.
- gpupdate — обновляет групповые политики на локальном компьютере, что полезно для администраторов, управляемых сетей.
- taskview — открывает таймлайн Windows, показывая историю активности пользователя, полезно для управления и поиска ранее использованных файлов и приложений.
- msg — отправляет сообщение пользователям, подключенным к системе. Пример: msg «Система будет перезагружена через 5 минут» отправит сообщение всем пользователям.
Команды для управления безопасностью
Команды для управления безопасностью предназначены для обеспечения защиты данных и управления доступом к файлам и системным ресурсам, что позволяет шифровать файлы, проверять целостность системных файлов и управлять правами доступа.
- cipher — управляет шифрованием файлов на дисках NTFS.
- cipher/e — зашифровывает файлы в указанной директории.
- sfc — проверяет целостность системных файлов и автоматически восстанавливает их при обнаружении повреждений.
- sfc /verifyonly — проверяет системные файлы на наличие повреждений, но не исправляет их автоматически.
- sfc /scannow — выполняет полную проверку системы.
- cacls — изменяет права доступа к файлам. Пример: cacls file.txt /g UserName:F даст пользователю полный доступ к файлу.
- icacls — расширяет возможности команды cacls и предоставляет дополнительные параметры для управления правами доступа.
- takeown — позволяет взять владение файлом или директорией. Так, takeown /f file.txt предоставит доступ к файлам.
- attrib — изменяет атрибуты файлов и папок. Например, attrib +r file.txt сделает файл доступным только для чтения.
Команды для диагностики и устранения неполадок
Команды из раздела помогают находить и устранять неполадки в системе, восстанавливать загрузочные параметры и проверять целостность данных на диске, а также они позволяют решать проблемы, связанные с запуском операционной системы или со сбоями на уровне файловой системы.
- chkdsk — проверяет диск на наличие ошибок и исправляет их. Так, chkdsk C: /f выполнит проверку диска C.
- bootrec — восстанавливает загрузочный сектор.
- bcdedit — управляет параметрами загрузки системы.
- bcdedit /set {current} safeboot minimal — включает безопасный режим.
Команды для скриптинга и автоматизации
Команды, приведенные ниже, предназначены для создания сложных сценариев выполнения команд, что позволяет автоматизировать повседневные задачи и более эффективно управлять процессами.
- for — создает цикл для выполнения команд. Например, for %i in (1 2 3) do echo %i выведет числа 1, 2, 3.
- if — выполняет условное выполнение команд.
- goto — перенаправляет выполнение скрипта к определенной метке.
- call — вызывает другую команду или скрипт.
Команды для управления сетевыми подключениями
Команды для управления сетевыми подключениями предоставляют возможности для настройки, диагностики и оптимизации сетевых параметров и соединений, позволяя управлять IP-адресами, подключаться и отключаться от сетей.
- ipconfig /release — освобождает текущий IP-адрес, назначенный DHCP сервером, что позволяет при необходимости сбросить сетевое подключение.
- ipconfig /renew — обновляет IP-адрес, полученный от DHCP сервера. Часто используется после команды ipconfig /release для восстановления подключения.
- ipconfig /flushdns — очищает кэш DNS, если изменился DNS-сервер или необходимо устранить проблемы с доступом к сайтам.
- ipconfig /displaydns — выводит содержимое кэша DNS, часто используется для диагностики проблем с DNS.
- netsh interface ip set address — используется для назначения статического IP-адреса сетевому интерфейсу. Пример: netsh interface ip set address Ethernet static 192.168.1.100 255.255.255.0 192.168.1.1.
- netsh wlan show drivers — выводит информацию о драйверах беспроводной сети, что полезно при настройке Wi-Fi подключения.
- netsh wlan show interfaces — отображает текущие активные беспроводные подключения и их параметры, например, мощность сигнала.
- netsh wlan connect — подключает к указанной Wi-Fi сети. Для этого нужно ввести: netsh wlan connect name=MyWiFi.
- netsh wlan disconnect — отключает текущее беспроводное подключение.
- netsh advfirewall set allprofiles state — управляет состоянием брандмауэра Windows – netsh advfirewall set allprofiles state off отключает брандмауэр для всех профилей.
- netsh int ip reset — сбрасывает настройки IP стека (TCP/IP) к значениям по умолчанию, помогая при сетевых неполадках.
- route add — добавляет маршрут в таблицу маршрутизации. Например, route add 192.168.2.0 mask 255.255.255.0 192.168.1.1 добавит маршрут для подсети 192.168.2.0 через шлюз 192.168.1.1.
- route delete — удаляет указанный маршрут из таблицы маршрутизации.
- netsh interface show interface — выводит список всех сетевых интерфейсов в системе, включая их состояние и тип.
- net view — отображает список компьютеров в локальной сети – net view \\server покажет общие ресурсы на указанном сервере.
- net use /delete — удаляет существующее подключение к сетевому ресурсу. Так, net use Z: /delete отключает сетевой диск Z:.
- ftp — открывает FTP-клиент для передачи файлов между локальной и удаленной системами. Например, по команде ftp ftp.example.com ПК подключится к FTP-серверу.
- telnet — используется для подключения к удаленным системам через Telnet-протокол. Так, telnet example.com 23 подключит ПК к серверу на порту 23.
- getmac — выводит MAC-адреса всех сетевых интерфейсов компьютера.
Команды для управления печатью
В этом разделе команды для управления печатью позволяют эффективно управлять процессом печати (включая очередью на печать), настройками принтеров и заданиями на печать.
- print — отправляет файл на печать. Например, print C:\Documents\file.txt отправит текстовый файл на принтер по умолчанию.
- rundll32 printui.dll,PrintUIEntry — открывает диалоговое окно для установки или управления принтерами – rundll32 printui.dll,PrintUIEntry /in /n\\server\printer установит сетевой принтер.
- net print — отображает список заданий на печать – net print \\server\printer покажет очередь печати на указанном принтере.
- net stop spooler — останавливает службу диспетчера очереди печати (spooler), особенно когда требуется устранить зависшие задания печати.
- net start spooler — запускает службу диспетчера очереди печати после её остановки.
- wmic printer list brief — выводит список установленных принтеров с краткой информацией о каждом из них.
- wmic printer where default=true get name — выводит имя принтера, установленного по умолчанию.
- wmic printer where name=’PrinterName’ delete — удаляет указанный принтер из системы.
- wmic printerconfig — отображает информацию о конфигурации принтера, включая его настройки и параметры печати.
- cscript prnjobs.vbs — используется для управления заданиями печати через скрипт prnjobs.vbs, который можно использовать для удаления, приостановки или возобновления заданий.
Дополнительные команды в Windows
В дополнение к основным инструментам для управления системой, командная строка Windows предоставляет ряд дополнительных команд, которые расширяют возможности администрирования и диагностики.
- wevtutil — управляет журналами событий Windows. Например, wevtutil qe System выведет события из системного журнала.
- tzutil — управляет настройками часовых поясов. tzutil /s Pacific Standard Time установит часовой пояс на Тихоокеанское стандартное время.
- taskkill — завершает процесс по его PID или имени. Так, taskkill /F /PID 1234 завершит процесс с PID 1234.
- powercfg /hibernate off — отключает режим гибернации.
- powercfg /energy — создает отчет об использовании энергии системой.
Learn essential Windows 11 CMD commands to enhance your productivity and manage your system effectively.
ipconfig /all
Getting Started with Windows 11 CMD
What is CMD?
CMD, short for Command Prompt, is a command-line interpreter application available in most Windows operating systems, including Windows 11. It allows users to execute commands to perform tasks within the system, which can be faster and more efficient than using a graphical user interface (GUI). Understanding how to navigate and utilize CMD is crucial for both novice and advanced users, as it grants powerful access to system operations, diagnostics, and automation.
How to Access CMD in Windows 11
To effectively use Windows 11 CMD commands, you first need to know how to access the Command Prompt. Here’s how:
- Using the Start Menu: Click on the Start button, type «cmd,» and select «Command Prompt» from the search results.
- Using the Run Dialog: Press `Windows + R`, type `cmd`, and hit Enter.
- Using Windows Terminal: If you have Windows Terminal installed, you can open it and select Command Prompt from the dropdown menu.
CMD User Interface
The CMD window presents a straightforward interface where users can input commands. While it’s relatively basic, customization options are available. You can adjust the font size and color settings by right-clicking on the title bar, selecting «Properties,» and modifying the appearance to suit your preferences.

Windows Cmd Commands List PDF: Quick Reference Guide
Basic CMD Commands
Navigating Directories
Understanding how to navigate directories is essential when using Windows 11 CMD commands.
-
`cd` (Change Directory) is a command that allows users to navigate through folders.
Syntax:
cd [directory_path]Example:
To change to a specific directory:cd C:\Users\YourUsername\DocumentsTo go back to the previous directory:
cd .. -
`dir` (Directory) lists all files and folders in the current directory, along with additional details about each item.
Syntax:
dir [directory_path]Example:
To list files in the current directory:dir
File Manipulation Commands
CMD also provides powerful commands for managing files, which can greatly streamline your workflow.
-
`copy` (Copy files) allows you to duplicate files.
Syntax:
copy [source] [destination]Example:
To copy a file to another directory:copy C:\file.txt D:\ -
`move` (Move files) is used for relocating files.
Syntax:
move [source] [destination]Example:
To move a file to another folder:move C:\file.txt C:\NewFolder\ -
`del` (Delete files) is a straightforward command to remove files.
Syntax:
del [file_path]Example:
Permanently delete a file:del C:\file.txt

Windows Repair Cmd Commands: Quick and Easy Guide
Advanced CMD Commands
System Information and Maintenance
CMD is also instrumental in obtaining system information and maintaining performance.
-
`ipconfig` provides detailed information about network configurations, including IP addresses and subnet masks.
Example:
To check your IP address:ipconfig -
`ping` is a command that tests the reachability of a host on an IP network, helpful for troubleshooting connectivity issues.
Syntax:
ping [hostname]Example:
To ping a website:ping www.example.com
Disk Management Commands
Managing disk spaces and verifying their integrity can be effectively performed through CMD.
-
`chkdsk` (Check Disk) checks the file system and file system metadata of a volume for logical and physical errors.
Syntax:
chkdsk [volume:] [/f] [/r]Example:
To check and fix errors on the C: drive:chkdsk C: /f -
`format` is used to format a disk, preparing it for use by erasing the data.
Syntax:
format [volume:] [/fs:file_system]Example:
To format a USB drive as FAT32:format E: /fs:FAT32

Unlocking Windows XP Cmd Exe Commands: A Quick Guide
CMD Scripting Basics
Introduction to Batch Files
Batch files are a series of commands saved in a single script file with a `.bat` extension. They facilitate automation of repetitive tasks, thus improving efficiency.
Creating a Simple Batch File
To create your first batch file, follow these simple steps:
- Open Notepad or any text editor.
- Type the commands you want to run:
echo off echo Hello, World! pause - Save the file with a `.bat` extension, such as `hello.bat`.
- Run the batch file by double-clicking it.

Unlocking Common Cmd Commands for Quick Mastery
Troubleshooting Common CMD Issues
Even veteran CMD users encounter roadblocks. Here are a few tips to troubleshoot common issues:
- Check Command Syntax: Always ensure your command is typed correctly without unnecessary spaces or typos.
- Permissions: Some commands require administrative privileges; if you face issues, try running CMD as an administrator.
Recommended commands for diagnostics include `tracert` (Trace Route) to check the path packets take to a target and `netstat` to view active network connections.
Windows Cmd Clear: Refresh Your Command Line Effortlessly
CMD Tricks and Tips
Enhancing Workflow with Shortcuts
Utilizing keyboard shortcuts can significantly enhance your productivity in CMD. A few useful ones include:
- `Ctrl + C`: Cancel command execution.
- `Up Arrow`: Retrieve previous command.
- `Tab`: Auto-complete file and directory names.
Custom Aliases and Commands
Creating custom commands can save you time when regularly using long commands. You can add them to your `profile` to make them available whenever CMD is opened.
Example: To create a custom shortcut for clearing the screen, add the following line in your batch script:
alias cls = clear

Directory Cmd Commands Made Easy for Beginners
Conclusion
Utilizing Windows 11 CMD commands can significantly enhance your efficiency and control over your system. From basic file navigation to advanced scripts, mastering these commands empowers you to streamline your workflow and troubleshoot effectively. Practice these commands regularly, and consider enrolling in our courses for deeper learning and using CMD like a pro!

Mastering the Virus Cmd Command in Quick Steps
Additional Resources
For further development of your CMD skills, consider exploring recommended reading materials, online forums, and tutorials. Also, don’t forget to check out the offerings from our company to take your knowledge of CMD to the next level!
Windows Command Prompt is not only useful but also a tool that you should give more respect to by knowing these cool cmd commands. Here is a list of the most used commands in the CMD window or prompt commands that you can type to perform certain tasks in windows.
Command Prompt is one of the most powerful tools in Windows, also known as CMD. CMD is the command-line interpreter on Windows operating systems. Command Prompt interacts with the user through a command-line interface.
Things were not always like this, but with the advent of GUI-based operating systems, people started feeling that computing through command-based tools was boring. This ultimately leads the command prompt into obscurity.
However, the command prompt is not useless. It can be pretty helpful. This article provides some excellent tricks, secrets, and hacks that will make you realize that the Windows Command Prompt is useful and a tool you should give more respect to by knowing these cool cmd commands. Here you will find lots of basic cmd commands, cmd commands for the network, cmd commands tricks, etc.
Also Read: How To Remove Computer Viruses Using CMD
To Open CMD, you need to search for CMD in the Search box, or you can press Windows Key + R, which will eventually open the Run window, where you need to type CMD and hit enter.
1. Accessibility Controls – zaccess.cpl 2. Accessibility Wizard – accwiz 3. Add Hardware Wizard – hdwwiz.cpl 4. Add/Remove Programs – appwiz.cpl 5. Administrative Tools – control admintools 6. Automatic Updates – wuaucpl.cpl 7. Bluetooth Transfer Wizard – fsquirt 8. Calculator – calc 9. Certificate Manager – certmgr.msc 10. Character Map – charmap 11. Check Disk Utility – chkdsk 12. Clipboard Viewer – clipbrd 13. Command Prompt – cmd 14. Component Services – dcomcnfg 15. Computer Management – compmgmt.msc 16. Control Panel – control 17. Date and Time Properties – timedate.cpl 18. DDE Shares – ddeshare 19. Device Manager – devmgmt.msc 20. Direct X Troubleshooter – dxdiag 21. Disk Cleanup Utility – cleanmgr 22. Disk Defragment – dfrg.msc 23. Disk Management – diskmgmt.msc 24. Disk Partition Manager – diskpart 25. Display Properties – control desktop 26. Display Properties – desk.cpl 27. Dr. Watson System Troubleshooting Utility – drwtsn32 28. Driver Verifier Utility – verifier 29. Event Viewer – eventvwr.msc 30. Files and Settings Transfer Tool – migwiz 31. File Signature Verification Tool – sigverif 32. Findfast – findfast.cpl 33. Firefox – firefox 34. Folders Properties – control folders 35. Fonts – control fonts 36. Fonts Folder – fonts 37. Free Cell Card Game – freecell 38. Game Controllers – joy.cpl 39. Group Policy Editor (for xp professional) – gpedit.msc 40. Hearts Card Game – mshearts 41. Help and Support – helpctr 42. HyperTerminal – hypertrm 43. Iexpress Wizard – iexpress 44. Indexing Service – ciadv.msc 45. Internet Connection Wizard – icwconn1 46. Internet Explorer – iexplore 47. Internet Properties – inetcpl.cpl 48. Keyboard Properties – control keyboard 49. Local Security Settings – secpol.msc 50. Local Users and Groups – lusrmgr.msc 51. Logs You Out Of Windows – logoff 52. Malicious Software Removal Tool – mrt 53. Microsoft Chat – winchat 54. Microsoft Movie Maker – moviemk 55. Microsoft Paint – mspaint 56. Microsoft Syncronization Tool – mobsync 57. Minesweeper Game – winmine 58. Mouse Properties – control mouse 59. Mouse Properties – main.cpl 60. Netmeeting – conf 61. Network Connections – control netconnections 62. Network Connections – ncpa.cpl 63. Network Setup Wizard – netsetup.cpl 64. Notepad – notepad 65. Object Packager – packager 66. ODBC Data Source Administrator – odbccp32.cpl 67. On Screen Keyboard – osk 68. Outlook Express – msimn 69. Paint – pbrush 70. Password Properties – password.cpl 71. Performance Monitor – perfmon.msc 72. Performance Monitor – perfmon 73. Phone and Modem Options – telephon.cpl 74. Phone Dialer – dialer 75. Pinball Game – pinball 76. Power Configuration – powercfg.cpl 77. Printers and Faxes – control printers 78. Printers Folder – printers 79. Regional Settings – intl.cpl 80. Registry Editor – regedit 81. Registry Editor – regedit32 82. Remote Access Phonebook – rasphone 83. Remote Desktop – mstsc 84. Removable Storage – ntmsmgr.msc 85. Removable Storage Operator Requests – ntmsoprq.msc 86. Resultant Set of Policy (for xp professional) – rsop.msc 87. Scanners and Cameras – sticpl.cpl 88. Scheduled Tasks – control schedtasks 89. Security Center – wscui.cpl 90. Services – services.msc 91. Shared Folders – fsmgmt.msc 92. Shuts Down Windows – shutdown 93. Sounds and Audio – mmsys.cpl 94. Spider Solitare Card Game – spider 95. SQL Client Configuration – cliconfg 96. System Configuration Editor – sysedit 97. System Configuration Utility – msconfig 98. System Information – msinfo32 99. System Properties – sysdm.cpl 100. Task Manager – taskmgr 101. TCP Tester – tcptest 102. Telnet Client – telnet 103. User Account Management – nusrmgr.cpl 104. Utility Manager – utilman 105. Windows Address Book – wab 106. Windows Address Book Import Utility – wabmig 107. Windows Explorer – explorer. 108. Managing the Boot Configuration Data - bcdedit 109. Editing Boot Settings - bootcfg 110. Encrypting or Decrypting Files/folders - cipher 111. Clearing the screen - cls 112. Managing stored usernames/passwords - cmdkey 113. Changing CMD Color - color 114. Compressing one or more files - compress 115. Converting FAT drives to NTFS - convert 116. Delete files - del 117. Deleting User Profiles - delprof 118. Displaying the list of files and folders - dir 119. Displaying Message On Screen - echo 120. Deleting one or more files - erase 121. Opening the windows Explorer - explorer 122. Formatting a disk - format 123. Knowing file extension - ftype 124. Displaying the Mac Address - getmac 125. Online help - help 126. Displaying the host name - hostname 127. Editing disc label - label 128. Log a user off - logoff 129. Get a log time in a file - logtime 130. Creating .cab files - makecab 131. Creating new folders- md 132. Opening Windows Installer - msiexec 133. Managing the network resources - net 134. Knowing the permissions for a user - perms 135. Testing a network connecting - ping 136. Printing a text file - print 137. Shutdown computer - psshutdown 138. Checking free disk space - freedisk 139. Know the file and volume utilities - fsutil 140. File transfer protocl - ftp 141. Showing the space used in folders - diskuse 142. Deleting a folder and all subfolders - deltree 143. Importing or Exporting Active directory data - csvde 144. Displaying the resultant set of Policy information - gpresult 145. Updating the Group policy settings - gpupdate 146. Replacing the files that are currently in use by the os - inuse 147. Comparing two files - fc 148. Finding a text string in a file - find 149. Finding for a strings in file - findstr 150. Displaying the memory usage - mem 151. Remote desktop protocol - mstsc 152. Managing the domain - netdom 153. Manage the Background intelligent Transfer Service - bitsadmin 154. Enable Or disable Break Capability in CMD - break 155. Change the permissions of files - cacls 156. Call another batch program using one - call 157. Manage the certification authority files and services - certutil 158. Change the folder or go to a specific one - cd 159. Check the NTFS file system - chkntfs 160. Copy one or more files to other location - copy 161. show the mapping inbetween logical and physical processor - coreinfo 162. Import/Export data of an active directory - csvde 163. Display the date or change it - date 164. Display disk usage - diruse 165. View used space in folder - diskuse 166. Show the list of device drivers - driverquery 167. View objects in active directory - dsget 168. Modify objects in an active directory - dsmod 169. Display the print queue status - lpq 170. Display open files - open files 171. Monitor performance in CMD - perfmon 172. Shows remote Access service status - rasdial 173. Managing RAS connections - rasphone 174. Send A Message - msg 175. Create a symbolic Link - mklink 176. Send email from command line - mapisend 178. Manage the performance monitor logs - logman 179. Uncompress the CAB files - expand 180. Loop command - all options files, directory, and list - for 181. Move an active Directory Object - dsmove 182. In order to view items in the Active directory - dsget 183. View the Active directory ACLs - DSACLs 184. Client-side caching for offline files - CSCcmd 185. Monitor and log system activity (Windows event log) - sysmon 186. Edit file and folder permissions - subinacl 187. Save and change the current directory - pushd 188. Display user session - quser 189. Read, export, delete and set keys and values - reg registry 190. Register or unregister a DLL - regsvr32 191. Batch process multiple files - forfiles 192. Search for Items in Active directory - dsquery 193. Cleanup temp file, recycle bin - cleanmgr 194. Compare the contents of two sets of files - comp 195. show the map between logical and physical processor - coreinfo 196. Manage RAS connections - rasdial 197. kill process by process and name id - pskill 198. Disconnect the remote desktop session - tsdiscon 199. Edit the service principal name - setspn 200. Share a folder or printer rmtshare 201. Change the registry permissions - regini 202. Execute a program from different user account - runas
So, these are the best cmd commands. I hope these cmd commands will help you a lot. If you know some other cmd commands, let us know by commenting on the comment box below. Feel free to share this post with your friends!
The Windows Command Prompt (CMD) is a powerful tool that allows users to interact with their operating system through text-based commands. Whether you’re a beginner exploring CMD for the first time, an expert troubleshooting advanced issues, or just looking for utility-focused tasks, this guide has you covered.
In this guide, we will provide you with some of the most useful commands for the following:
- CMD Commands for Beginners
- CMD Commands for Experts
- CMD Commands for Utility
- CMD Commands for Troubleshooting
- CMD Commands for Students
- CMD Commands for Programmers
CMD Commands for Beginners
These commands are essential for users who are new to CMD and provide basic functionalities to help them navigate and perform simple tasks.
1. View Directory ‘dir‘
- Function: Displays the contents of the current directory.
- How to use: Type
dirand press Enter. Usedir /sto include subdirectories. - Use case: Quickly view files and folders in your current location.
Syntax: dir
2. Change Directories ‘cd’
- Function: Lets you navigate between folders.
- How to use: Type
cd [folder_name]to move into a directory. Usecd ..to go up one level. - Use case: Navigate to specific directories to manage files or execute commands
Syntax: cd [folder name]
3. Create a New Directory ‘mkdir’ or ‘md’
- Function: Allows you to create a new directory
- How to use: Type mkdir [file_name]– Here the new directory name is GFG
- Use case: When you need a new directory for any separate work, you may create a new directory
Syntax: mkdir [GFG]
4. Rename a File ‘ren’
- Function: Helps in renaming any file or directory.
- How to use: Type
renorrename [old_name] [new_name]and press Enter. - Use case: Discover new method of renaming file or any directory.
Syntax: ren xyz.txt newxyz.txt
5. Delete a File ‘del’
- Function: Lets you to remove one or more files
- How to use: Type del [file_name]– This will erase the provided file name
- Use case: This function allows you to erase any file if you’re unable to fetch
Syntax: del[file_name]
6. Close ‘exit’
- Function: Closes the Command Prompt window.
- How to use: Type
exitand press Enter. - Use case: Ends your session with CMD.
Syntax: exit
7. Clear Screen ‘cls’
- Function: Clears all text from the CMD window.
- How to use: Type
clsand press Enter. - Use case: Removes clutter after multiple commands
Syntax: cls
8. View Available Command ‘help’
- Function: Lists all available commands and their descriptions.
- How to use: Type
helpand press Enter. - Use case: Discover new commands and learn their functions.
Syntax: help
9. Display or Set the System time ‘time’
- Function: Lets you set the system time or display the current time.
- How to use: Type
time [new_time] and press Enter. - Use case: Allows the user to set their system’s time without additional navigation
Syntax: time [new_time]
10. Copy Files ‘copy’
- Function: Lists all available commands and their descriptions.
- How to use: Type
copy [source1] [destination2] and press Enter. - Use case: Discover new commands and learn their functions.
Syntax: copy file.txt Backup\
| Command | Description | Syntax | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
dir |
View the contents of a directory | dir |
dir C:\Users\Documents |
cd |
Change the current working directory | cd [directory_name] |
cd Downloads |
mkdir |
Create a new directory | mkdir [directory_name] |
mkdir NewProject |
ren |
Rename a file | ren [old_name] [new_name] |
ren draft.txt final.txt |
del |
Delete a file | del [file_name] |
del unwanted.txt |
exit |
Close the Command Prompt | exit |
exit |
cls |
Clear the Command Prompt screen | cls |
cls |
help |
View available CMD commands and their descriptions | help |
help |
time |
Display or set the system time | time |
time 14:30:00 |
copy |
Copy files from one location to another | copy [destination] |
copy report.docx D:\Backup\ |
CMD Commands for Experts
These commands are more advanced and suitable for users comfortable with troubleshooting and system management tasks.
1. System File Checker ‘sfc’
- Function: Scans and repairs corrupted system files.
- How to use: Type
sfc /scannowin CMD (run as administrator). - Use case: Fix system errors related to missing or corrupted files.
Syntax: sfc /scannow
2. Disk Error ‘chkdsk’
- Function: Scans the hard drive for bad sectors and file system errors.
- How to use: Type
chkdsk [drive letter]: /f(e.g.,chkdsk C: /f) in CMD. - Use case: Identify and fix disk issues.
Syntax: chkdsk C: /f
3. View Running Processor ‘tasklist’
- Function: Displays all running processes and their details.
- How to use: Type
tasklistto list processes. Usetasklist /fi "imagename eq [process name]"to filter. - Use case: Identify resource-heavy or unresponsive processes.
Syntax: tasklist /fi "imagename eq [process name]
4. Restart ‘shutdown’
- Function: Allows you to shut down or restart the computer via CMD.
- How to use:
- Shutdown:
shutdown /s /f /t [seconds]. - Restart:
shutdown /r /f /t [seconds].
- Shutdown:
- Use case: Automate shutdown or restart tasks
Syntax:
Shutdown: shutdown /s /f /t [seconds].
Restart: shutdown /r /f /t [seconds].
5. Network Statistics ‘netstat’
- Function: Displays active connections and listening ports.
- How to use: Type
netstatto view all active connections. - Use case: Diagnose network-related issues or monitor network activity.
Syntax: netstat
6. Kill a Running Process ‘taskkill’
- Function: Lets you terminate a process using its process ID (PID)
- How to use: Type
taskkill /[PID] /F to terminate - Use case: Can be helpful for terminating any dedicated PID.
Example (PID: 1124)
Syntax: taskkill /PID 11234 /F
7. View Saved Passwords ‘netsh wlan show profiles’
- Function: Retrieve the password of a saved Wi-Fi network.
- How to use: Type netsh wlan show profile name=”WiFi-Name” key=clear
- Use case: Discover new commands and learn their functions.
Example: netsh wlan show profile name="MyHomeWiFi" key=clear
| Command | Description | Syntax | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
sfc |
System File Checker – Scans and repairs system files | sfc /scannow |
sfc /scannow |
chkdsk |
Check Disk – Scans and fixes disk errors | chkdsk [drive]: /f /r |
chkdsk C: /f /r |
tasklist |
View running processes | tasklist |
tasklist |
shutdown |
Shutdown or restart the system | shutdown /r /t [seconds] |
shutdown /r /t 10 (Restart in 10 seconds) |
netstat |
View network statistics and active connections | netstat -a |
netstat -an (Show all connections numerically) |
taskkill |
Kill a running process using its process ID (PID) | taskkill /PID [PID] /F |
taskkill /PID 4567 /F (Kill process with ID 4567) |
netsh wlan show profiles |
View saved Wi-Fi network names | netsh wlan show profiles |
netsh wlan show profiles |
CMD Commands for Utility
These commands are focused on specific tasks and utilities to enhance productivity and system performance.
1. Network Configuration ‘ipconfig’
- Function: Displays IP address, subnet mask, and gateway information.
- How to use:
- Basic: Type
ipconfig. - Detailed: Type
ipconfig /all.
- Basic: Type
- Use case: Troubleshoot internet connectivity issues.
Syntax: ipconfig
2. Network Connectivity ‘ping’
- Function: Sends packets to test communication with another device or website.
- How to use: Type
ping[destination] - Use case: Check if a device or website is reachable.
Syntax: ping geeksforgeeks.org
3. System Information ‘systeminfo’
- Function: Displays detailed information about your computer.
- How to use: Type
systeminfo. - Use case: Quickly access system specifications for troubleshooting or reporting.
Syntax: systeminfo
4. Trace Route ‘tracert’
- Function: Shows the path packets take to reach a specific destination.
- How to use: Type
tracert[destination] - Use case: Identify network bottlenecks or connectivity issues.
Syntax: tracert geeksforgeeks.org
5. Manage Drives ‘diskpart’
- Function: Opens a command-line utility for managing disk partitions.
- How to use: Type
diskpartto enter the disk management interface. - Use case: Create, delete, or modify partitions on your drives.
Syntax: diskpart
6. Delete a Directory ‘rmdir’
- Function: Removes directory from the origin
- How to use: Type rmdir [directory_name] and press Enter.
- Use case: Discover new commands and learn their functions.
Example: GFG – Directory name
Syntax: rmdir GFG
7. View ‘rmdir’
- Function: Removes directory from the origin
- How to use: Type rmdir [directory_name] and press Enter.
- Use case: Discover new commands and learn their functions.
Example: GFG - Directory name
8. Manage User Account ‘net user’
- Function: To list all the user accounts
- How to use: Type net user and press Enter.
- Use case: Discover new commands and learn their functions.
Syntax: net user username password /add
9. View Startup Programs ‘wmic startup get caption,command’
- Function: To check what programs launch on startup.
- How to use: Type wmic startup get caption,command, and press Enter.
- Use case: Discover new commands and learn their functions.
Syntax: wmic startup get caption,command
| Command | Description | Syntax | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
ipconfig |
View network configuration, including IP address, subnet mask, and gateway | ipconfig |
ipconfig /all (Displays detailed network info) |
ping |
Test network connectivity by sending packets to a host | ping [host or IP] |
ping google.com (Check connection to Google) |
systeminfo |
Display detailed system information, including OS version, installed memory, and processor | systeminfo |
systeminfo |
tracert |
Trace the route packets take to a network destination | tracert [hostname or IP] |
tracert google.com (View network path to Google) |
diskpart |
Manage disk partitions, including creating, formatting, and deleting partitions | diskpart |
diskpart → list disk → select disk 1 → create partition primary |
rmdir |
Delete a directory (folder) | rmdir [directory_name] |
rmdir /s /q OldFolder (Delete a folder and its contents without confirmation) |
dir |
View contents of a directory | dir |
dir C:\Users\Documents (List files in a specific directory) |
net user |
Manage user accounts, including adding, modifying, or deleting users | net user |
net user John password123 /add (Create a new user account) |
wmic startup get caption,command |
View startup programs and their commands | wmic startup get caption,command |
wmic startup get caption,command |
CMD Commands for Troubleshooting
1. File Comparison ‘fc’
- Function: Compares two files and highlights differences.
- How to use: Type
fc [file1] [file2]to compare files. - Use case: Detect changes or errors in files
Syntax: fc 1 2
2. Advanced Network Diagnostics ‘pathping’
- Function: Combines
pingandtracertfunctionalities to provide detailed network path diagnostics. - How to use: Type
pathping[destination] - Use case: Troubleshoot complex network issues.
Syntax: pathping geeksforgeeks.org
3. Registry Editor ‘regedit’
- Function: Launches the Windows Registry Editor.
- How to use: Type
regeditto open the registry. - Use case: Modify registry keys for advanced configuration or troubleshooting.
Syntax: regedit
4. View MAC ‘getmac’
- Function: Displays the MAC address of your network adapter.
- How to use: Type
getmacto view the MAC address. - Use case: Identify your device’s hardware address for network configurations
Syntax: getmac
5. Power Configuration ‘powercfg’
- Function: Displays and manages power settings.
- How to use: Type
powercfg/[option] - Use case: Optimize power usage and troubleshoot battery issues.
Syntax: powercfg /energy for a detailed power usage report
6. Enable Boot Manager ‘bcdedit’
- Function: Used to modify boot configuration settings
- How to use: Type
bcdedit/ set current - Use case: Discover new commands and learn their functions.
Syntax: bcdedit /set {current} bootmenupolicy standard
7. Format a Drive ‘format’
- Function: To erase any specific drive.
- How to use: Type format [drive]: /FS:NTFS and press Enter.
- Use case: Discover new commands and learn their functions.
Syntax: format D: /FS:NTFS
| Command | Description | Syntax | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
fc |
Compare two files and highlight differences | fc [file1] [file2] |
fc file1.txt file2.txt (Compare two text files) |
pathping |
Perform advanced network diagnostics with packet loss details | pathping [destination] |
pathping google.com (Analyze network route to Google) |
regedit |
Open the Windows Registry Editor (GUI) | regedit |
regedit (Opens the registry editor – use with caution!) |
getmac |
Display the MAC (Media Access Control) address of your network adapters | getmac |
getmac /v /fo list (View MAC addresses in detailed format) |
powercfg |
Manage and analyze power configurations | powercfg /[option] |
powercfg /batteryreport (Generate a battery usage report) |
bcdedit |
Enable, disable, or modify Windows Boot Configuration | bcdedit /set {current} [option] |
bcdedit /set {current} bootmenupolicy standard (Enable boot menu in Windows 10/11) |
format |
Format a drive (erase all data) | format [drive]: /FS:[filesystem] |
format D: /FS:NTFS (Format drive D: with NTFS file system) |
CMD Commands for Students
Students can use these commands to manage files, perform simple calculations, and even help with tasks like coding and studying.
1. Calculator ‘calc’
- Function: Opens the Windows Calculator application.
- How to use: Type
calcand press Enter. - Use case: Quickly open the calculator for
Syntax: calc
CMD Commands for Programmers
Programmers often use CMD to automate tasks, compile code, and test network functionality. These commands can be especially useful for developers working in command-line environments.
1. Compile Java Code ‘javac’
- Function: Compiles Java source files into bytecode.
- How to use: Type
javac [file name].javato compile Java code. - Use case: Compile and test Java programs directly from the command line.
Syntax: javac
2. Version Control ‘git’
- Function: Interacts with Git repositories from the command line.
- How to use: Type
git [command] - Use case: Manage version control, clone repositories, or push commits from the command line.
Syntax: git clone [repository URL]
3. Execute Python Script ‘python’
- Function: Runs Python scripts in the command prompt.
- How to use: Type
python [script.py]to execute a Python program. - Use case: Test and run Python code directly in the command line.
Syntax: python [script.py]
4. Run Node.js Scripts ‘node’
- Function: Executes Node.js scripts.
- How to use: Type
node [script.js]to run a JavaScript file using Node.js. - Use case: Run backend scripts and test JavaScript programs in the command line.
Syntax: node [script.js]
5. Node Package Manager ‘npm’
- Function: Installs and manages JavaScript packages.
- How to use: Type
npm install [package]to install a package. - Use case: Manage dependencies and libraries in Node.js applications.
Syntax: npm install [package]
| Command | Description | Syntax | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
javac |
Compile Java source code into bytecode (.class files) | javac [filename].java |
javac HelloWorld.java (Compile a Java file) |
git |
Version control system for tracking changes in files | git [command] |
git clone https://github.com/user/repo.git (Clone a repository) |
python |
Execute a Python script or enter interactive mode | python [script.py] |
python script.py (Run a Python script) |
node |
Execute JavaScript code using Node.js | node [script.js] |
node app.js (Run a Node.js script) |
npm |
Manage Node.js packages and dependencies | npm [command] |
npm install express (Install the Express.js package) |
Bonus: CMD Tricks and Tips
To make CMD usage even more efficient, here are some bonus tips:
1. Save CMD Output to a File
Use the > operator to save the output of a command to a text file.
2. Open CMD in a Specific Directory
Instead of navigating manually, you can directly open CMD in a folder by typing cmd in the File Explorer’s address bar.
3. Use && for Multiple Commands
You can run multiple commands sequentially:
ipconfig && ping google.com
Conclusion
Mastering the most useful CMD commands in Windows can empower you to perform tasks more efficiently, troubleshoot problems, and gain deeper control over your system. By familiarizing yourself with these essential CMD commands, you’ll be better equipped to handle a variety of situations, from simple file management to advanced system configurations. Whether you’re a beginner or an experienced user, these commands are invaluable tools to have at your disposal.