,
In this article I’ll show how to recover your Windows Server 2016, 2012 or 2012R2, from a previous system image backup which was created using the Windows Server Backup feature, if Windows fails to start normally.
This article will explain how to restore Server 2016/2012/2012R2, from the Windows Recovery Environment, by using a Windows Server Backup Image, if your server could not start, or if the main hard drive has failure and you have to recover everything on a new hard drive.
Related articles:
- How to Create System Restore Points on Server 2016/2012 using Windows Server Backup.
- How to Restore Server 2016 or 2012 in a Previous System State if Windows can start normally (Online Method)
How to Restore Windows Server 2016/2012/2012R2 from a System Image Backup if Windows could not boot.
The only way to recover your server, if the machine fails to boot, is by using the System Image Recovery option, from the Windows Recovery Environment (WinRE). To be able, to restore your server from WinRE, you will need the following:
Requirements:
1. A Windows Server Installation Media (USB or DVD).
2. A previous System Image backup, that was taken with the Windows Server Backup application.
To recover your Server 2016, 2012 or 2012R2, from a WinRE:
1. Boot your Server from the Windows Server installation Media.
2. Click Next at the first screen.

3. Then click Repair your computer.
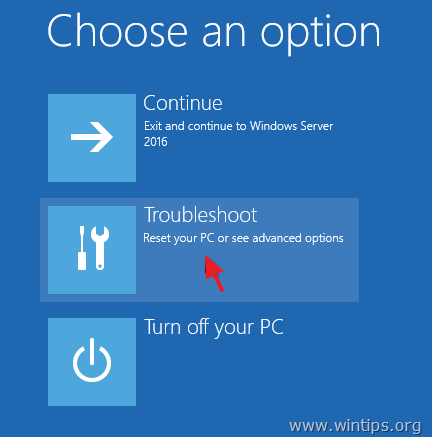
4. At ‘Choose an option’ screen, click Troubleshoot.
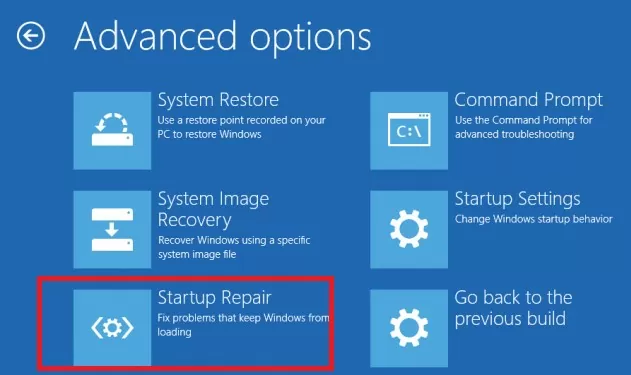
5. At ‘Advanced options’ click System Image Recovery.
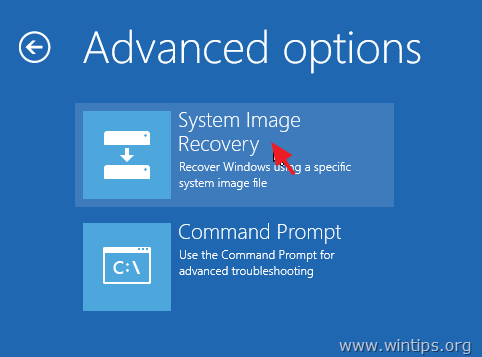
6. At the next screen, choose Windows Server 2016.

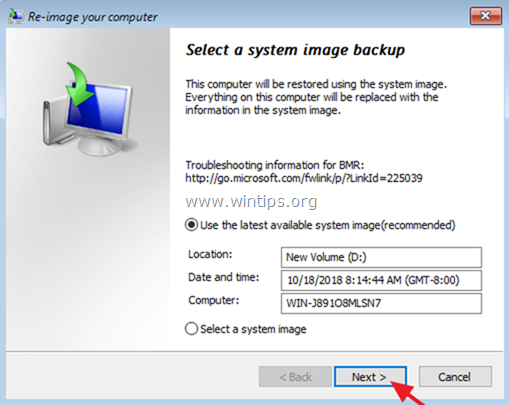
7. At ‘Select a System Image Backup’ screen, you can use the latest available system image to restore your server,* or you can click at «Select a System Image» option to select a different system image. Then click Next to continue.
* Note: Always prefer to recover your server with the most recent system image, in order to restore all the recently changes on your server (policies, network shares, etc.). Keep in mind that any changes made to your server after the system image’s backup date, must be reapplied.
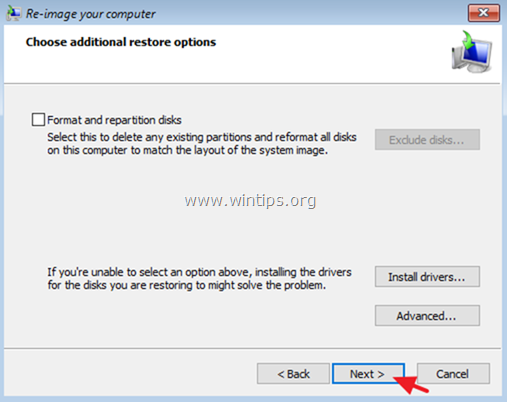
8. At ‘Choose additional restore options’ screen, click Next if you haven’t problems with the disk format or partition, or, select the «Format and repartition disks»* option to delete any existing partitions and reformat all disks on the computer to match the layout of the system image. *
* e.g. Use the «Format and repartition disks» option, only if you have replaced the hard drive on your server (e.g. after a HDD hardware failure, you want to restore your server to a new hard drive.)
9. Review your settings and click Finish to proceed.
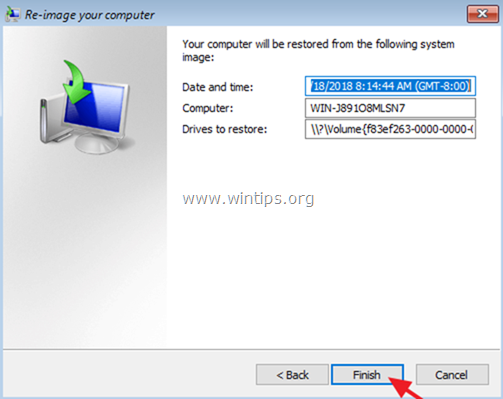
10. Finally, click Yes to restore your server to the selected date/time.
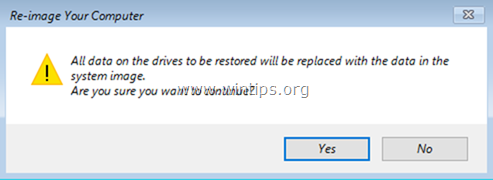
11. After the restoration, remove the Windows Server 2016 installation media and restart the server.
That’s it! Let me know if this guide has helped you by leaving your comment about your experience. Please like and share this guide to help others.
If this article was useful for you, please consider supporting us by making a donation. Even $1 can a make a huge difference for us in our effort to continue to help others while keeping this site free:
- Author
- Recent Posts
Konstantinos is the founder and administrator of Wintips.org. Since 1995 he works and provides IT support as a computer and network expert to individuals and large companies. He is specialized in solving problems related to Windows or other Microsoft products (Windows Server, Office, Microsoft 365, etc.).
Update July 26, 2020
Eight years later this post proves useful once again. During a failed VMware tools upgrade, we had a similar problem as all of those years ago. At first the procedures below didn’t work, but once we remembered that the recovery media (DVD or recovery partition) would not have the VMware Paravirtual SCSI (PVSCSI) driver. Things then fell into place.
In order to get the drivers loaded we mounted the VMwtools ISO /vmimages/tools-isoimages/windows.iso and booted into the recovery partition. Then from the command prompt we loaded the pvscsi driver by using the following drvload "D:\Program Files\VMware\VMware Tools\Drivers\pvscsi\Win8\amd64\pbscsi.inf". Where D was the drive letter of of mounted ISO. Not sure if the next step was necessary, but we ran diskpart and then rescaned for drives. Once it saw all of the drives we were able to use BOOTREC /FIXMBR, and BOOTREC /FIXBOOT. Rebooted and things were good.
I was playing around with a couple of Windows Server 2008 R2 virtual machines today, and accidentally messed up the boot records somehow. After playing around with a number of partition and disk recovery tools. I finally ran across this post called Windows Server 2008 R2 always boots into recovery console that had a solution that worked for me even though my problem was different. I wanted to record the steps I used so that I could find them later.
I used their Method 2 which worked for me. here are the steps:
- Put the Windows Server 2008 R2 installation disc in the disc drive, and then start the computer.
- Press any key when the message indicating “Press any key to boot from CD or DVD …”. appears.
- Select a language, time, currency, and a keyboard or another input method. Then click Next.
- Click Repair your computer.
- Click the operating system that you want to repair, and then click Next.
- In the System Recovery Options dialog box, click Command Prompt.
- Type
bootrec /RebuildBcd, and then press ENTER
Update – April 10, 2017
Last night we had a similar problem, but unfortunately the above steps did not correct the problem. After doing bootrec command it found the boot records, but still didn’t work we then tried running x:\sources\recovery\StartRep.exe which finally resolved our problem.
They also offered up another method to try, but I didn’t need to go that far but here is as well for future reference.
- Put the Windows Server 2008 R2 installation disc into the disc drive, and then start the computer.
- Press a key when the message indicating “Press any key to boot from CD or DVD …”. appears.
- Select a language, a time, a currency, and a keyboard or another input method, and then click Next.
- Click Repair your computer.
- Click the operating system that you want to repair, and then click Next.
- In the System Recovery Options dialog box, click Command Prompt.
- Type
BOOTREC /FIXMBR, and then press ENTER. - Type
BOOTREC /FIXBOOT, and then press ENTER. - Type
Drive:\boot\Bootsect.exe /NT60 All, and then press ENTER.
They also note that the Drive in step 9 is the drive where the Windows Server 2008 R2 installation media is located.
Hopefully I’ll never need to use this again, but if I do now it is documented. Also there is KB article #927392 on Microsoft’s site called How to use the Bootrec.exe tool in the Windows Recovery Environment to troubleshoot and repair startup issues in Windows that details the different options as well.
In this article, we will learn how to repair the Windows bootloader on a modern computer that uses UEFI instead of a classic BIOS and GPT disk partition table (instead of MBR). The corruption of the Windows bootloader can occur after installing a second OS (in Dual Boot configurations), file system corruption, incorrect actions during Windows recovery, removal of some data on hidden partitions, malicious software (virus, ransomware, etc.), and for some other reasons.
This article contains a step-by-step guide for repairing a damaged or deleted bootloader in Windows 11/10/8.1 and Windows Server 2022/2019/2016/2012R2 on computers running in native (non-compatible) UEFI mode. You can use this guide both to repair the binary files of the Windows bootloader, and the bootloader configuration \EFI\Microsoft\Boot\BCD file (in cases where Windows doesn’t boot due to the missing or corrupted BCD boot configuration file).
Contents:
- Windows Boot Error: Boot Configuration Data is Missing (EFI\Microsoft\Boot\BCD)
- Automatic Windows Bootloader Repair with WinRE
- Using BCDBoot to Manually Repair EFI Bootloader in Windows
Windows Boot Error: Boot Configuration Data is Missing (EFI\Microsoft\Boot\BCD)
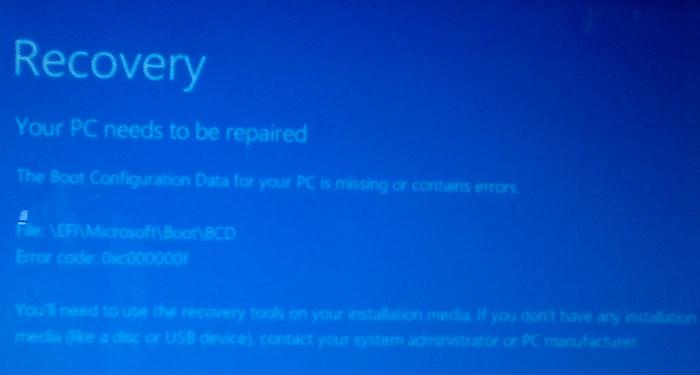
A UEFI computer with Windows installed in native mode will not be able to boot if the Windows EFI bootloader is corrupted. When trying to boot from a disk with a damaged or missing EFI bootloader, the following BSOD (Blue Screen of Death) error appears:
The boot configuration data for your PC is missing or contains errors. File :\EFI\Microsoft\Boot\BCD Error code: 0xc000000f
or:
Error code: 0xc000014c
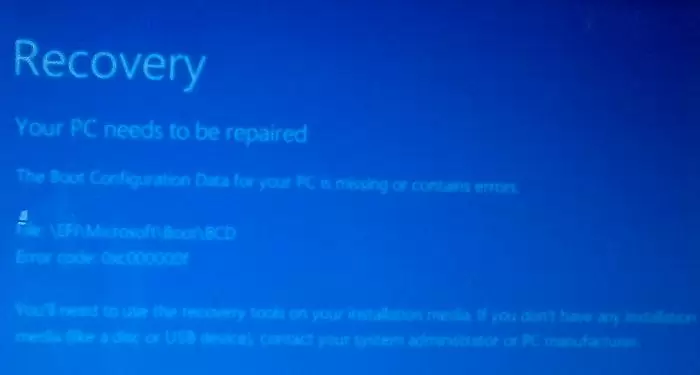
This error indicates that the Windows bootloader configuration (Boot Configuration Data, BCD) has been corrupted or even completely removed. If you try to repair the bootloader on a UEFI computer using bcdedit tool, you will receive an error:
The boot configuration data store could not be found. The requested system device cannot be found.
If Windows 10/11 is installed in native UEFI mode on a GPT disk, then the Windows EFI bootloader (Windows Boot Manager) stores the boot manager and BCD configuration on a separate hidden EFI volume (100 MB in size with the FAT32 file system). The bcdedit tool doesn’t see this EFI partition, and cannot manage the bootloader configuration on it.
If you only see a black screen with the message “An operating system wasn’t found” when you boot your computer, it’s likely that the Windows bootloader has been completely removed. Follow the instructions on the link.
Automatic Windows Bootloader Repair with WinRE
The procedure for the automatic repair of the EFI bootloader used in the Windows Recovery Environment (WinRE) is usually useless in such cases. But it’s still worth a try:
- Boot your device from the recovery disc or Windows 10/11 installation media;
- Click the Restore System on the installation screen;
- Then select Troubleshoot -> Startup Repair and select the OS whose bootloader you want to try to repair;
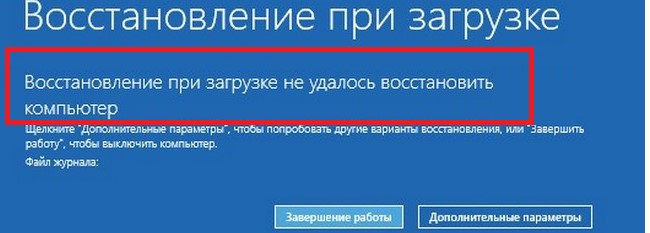
- But most likely the result will be negative:
Automatic Repair couldn’t repair your PC.
Using BCDBoot to Manually Repair EFI Bootloader in Windows
Let’s move on to the procedure for manually repairing the EFI Windows bootloader on a UEFI computer.
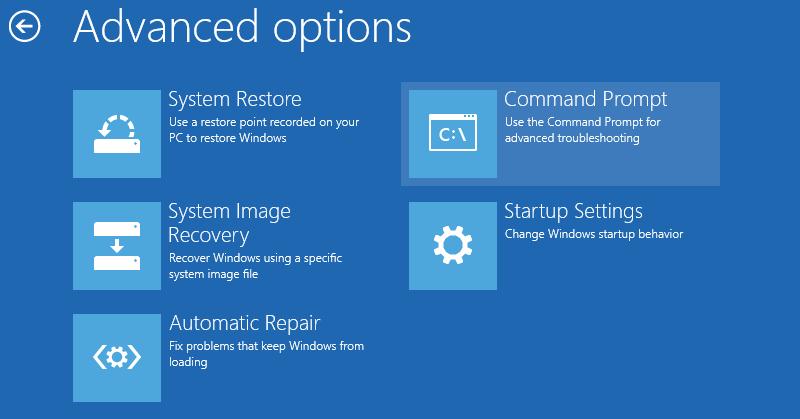
To repair the bootloader configuration (BCD), you have to boot from the original Windows installation media (also, you can use a recovery disk or a special UEFI bootable USB flash drive). After booting into the recovery environment, you need to open a command-line console: select System Restore – > Troubleshoot-> Command Prompt).
You can run the Command Prompt even if you only have a Windows installation media at hand. To do this, it is enough to press the key combination Shift + F10 (or Shift + Fn + F10 on some laptop models) on the first Windows setup screen (when choosing a language and keyboard layout).
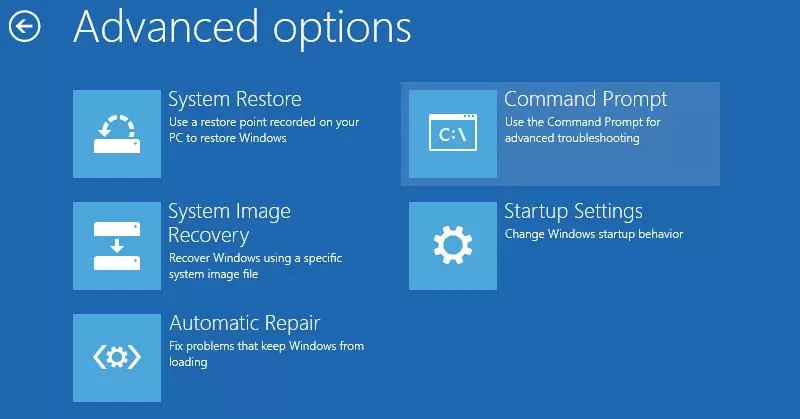
In the command prompt that opens, run the disk management tool:
diskpart
Display the list of drives on the computer:
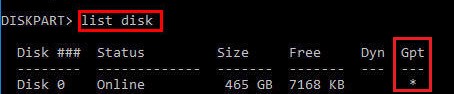
list disk
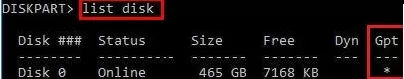
At this stage, it is very important to determine the type of partition table on the disk on which your Windows is installed: MBR or GPT. The point is that the EFI bootloader is used only on disks with a GPT partition table.
If the asterisk (*) is in the Gpt column, then the GPT partition table is used on disk. If not, the MBR is used.
If your disk uses a GPT partition table, follow the steps below in the instructions to repair the Windows EFI bootloader.
If you have an MBR partition table on your disk, this guide won’t work for your computer. Most likely you have a computer with BIOS or Legacy/Compatibility Support Mode (CSM) option enabled in the UEFI settings.
On MBR disks, the Windows bootloader is stored on a separate System Reserved partition, and not on the EFI partition (in any case, don’t convert the MBR partition table to GPT until you fix the Windows bootloader !!). Use another guide to restore the BCD bootloader on a BIOS computer with an MBR (Master Boot Record) disk.
Select the drive where your Windows is installed (if there is only one hard drive in the system, its index should be 0):
sel disk 0
Display the list of partitions and volumes on this disk: list partition
list volume
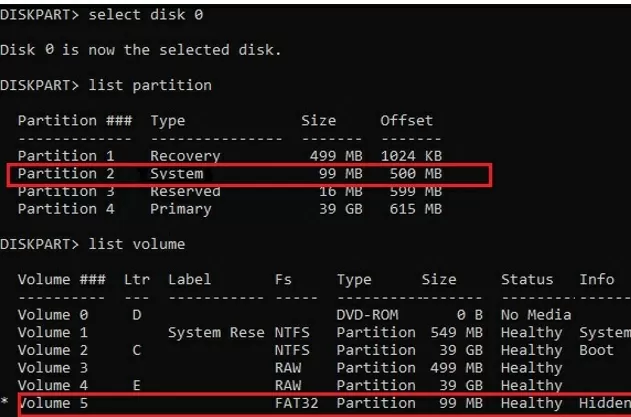
In this example, you can see that the EFI boot partition has the partition 2 index (aka Volume 5 with the Hidden label). The easiest way to identify an EFI partition is by the FAT32 file system and 100 MB in size (this is the standard minimum size of EFI partition for Windows computers; in rare cases, the partition size may differ). The most commonly used label for it is System EFI or ESP/EFI System Partition).
In our example, the main partition on which Windows is installed has a volume 2 index, is formatted in the NTFS file system, and is assigned the drive letter C:.
dir C:\
Make sure that this drive contains the Windows, Program Files, Users, and other directories.
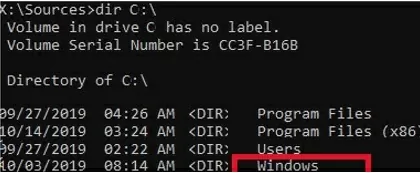
If these directories are missing, then your Windows drive has a different drive letter. Check the contents of drives with different drive letters assigned.
Write down the drive letter assigned to the Windows partition. We will use it as one of the arguments of the bcdboot command a little later.
The partition table must also contain an MSR (Microsoft System Reserved) partition of 16 MB in Windows 10/11 (or 128 MB in Windows 8.1).
Assign the drive letter K: to the hidden EFI volume:
select volume 5
assign letter K:
A message that the drive letter has been successfully assigned to the EFI partition should appear:
DiskPart is successfully assigned the drive letter or mount point.
Close the diskpart:
exit
Go to the bootloader directory on the hidden volume:
cd /d K:\efi\microsoft\boot\
In this case, K: is the drive letter assigned to the EFI partition just above. If the \EFI\Microsoft\Boot\ directory is missing (error The system cannot find the path specified), try the following commands:
cd /d K:\Boot\
or
cd /d K:\ESD\Windows\EFI\Microsoft\Boot\
At this point, many guides recommend running the following commands, which should overwrite the partition boot record, find the installed Windows, and add them to the BCD:
bootrec /fixboot
bootrec /scanos
bootrec /rebuildbcd
or even:
bootrec /FixMbr (preparing MBR record for a GPT disk looks strange)
You can use all these commands only for MBR-based disks. If your computer boots in UEFI mode, then it uses the GPT partition table (as in our case). Therefore, when you run bootrec commands, you will see an error: access is denied
You need to use the BCDBoot.exe tool to restore bootloader files and fix the boot records on the EFI partition by copying them from the system directory on the Windows partition. The BCD bootloader configuration is recreated using the %WINDIR%\System32\Config\BCD-Template file.
Use the attrib command to remove the hidden, read-only, and system attributes from the BCD file:
attrib BCD -s -h -r
Delete the current BCD configuration file by renaming it (this will keep the old boot configuration as a backup): ren BCD BCD.bak
Using the bcdboot tool, you need to copy the critical files of the UEFI boot environment from the system directory to the EFI boot partition and recreate the BCD bootloader config file:
bcdboot C:\Windows /l en-us /s k: /f ALL
- C:\Windows – the path to the root Windows system directory on the disk (this is your disk on which your Windows is installed, we determined it earlier using the diskpart command);
- f ALL –means that you need to copy the Windows Boot Environment files, including those for UEFI and BIOS computers (theoretically able to boot both on UEFI and BIOS computers). To copy only the EFI bootloader, use the /f UEFI command;
- /l en-us —specifies the system locale that is used when initializing the BCD store. By default, en-us – English (USA) is used;
- /s K: — copy the bootloader EFI files to the specified partition;
- /c – this is a new BCDBoot option in Windows 10 that allows you to overwrite existing boot records (including debugsettings). Use this option to ignore old boot settings and create a clean BCD configuration;
- /v – used to enable BCDBoot verbose output.
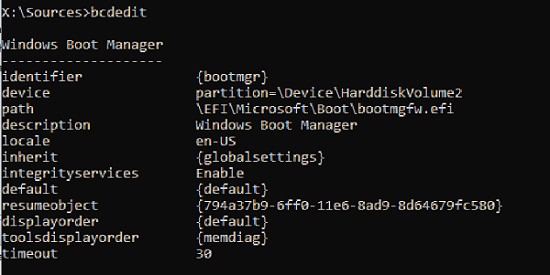
Now, if you run the bcdedit command, you will see the following :
An entry should appear in the Windows Boot Manager section containing the full path to the UEFI boot file (\EFI\MICROSOFT\BOOT\BOOTMGFW.EFI).In this example, it is located on volume 5 (partition=\Device\HarddiskVolume5).
Windows Boot Manager
--------------------
identifier {bootmgr}
device partition=\Device\HarddiskVolume5
path \EFI\Microsoft\Boot\bootmgfw.efi
description Windows Boot Manager
locale en-US
inherit {globalsettings}
bootshutdowndisabled Yes
default {CURRENT}
resumeobject {xxxxxxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxxxxxxxxxx}
displayorder {default}
toolsdisplayorder {memdiag}
timeout 30
Windows Boot Loader
-------------------
identifier {current}
device partition=C:
path \Windows\system32\winload.efi
description Windows 10
locale en-US
inherit {bootloadersettings}
recoverysequence {xxxxxxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxxxxxxxxxx}
recoveryenabled Yes
isolatedcontext Yes
allowedinmemorysettings 0x15000075
osdevice partition=C:
systemroot \Windows
resumeobject {xxxxxxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxxxxxxxxxx}
The Windows Boot Manager section must contain the path to the EFI partition (=\Device\HarddiskVolume5 ) and the path to the boot manager file (bootmgfw.efi). The Windows Boot Loader section contains the Windows partition info and the path to the Windows EFI bootloader ( \Windows\system32\winload.efi). When you turn it on, your computer will pass control to the EFI bootloader, which will start the Windows bootloader.
Possible errors:
Now you need to restart your computer and disconnect the bootable media. If you did everything correctly, the Windows Boot Manager should appear in the list of bootable devices, where you can choose a desired operating system to boot. Your EFI bootloader and BCD configuration have been restored successfully!
In some cases, after repairing the BCD bootloader, when Windows boots, a BAD SYSTEM CONFIG INFO error appears. To fix the error:
Make sure you haven’t made any recent changes to UEFI settings. Undo all changes.
Boot your computer from the installation/bootable flash drive and change the bootloader configuration with the commands:
bcdedit /deletevalue {default} numprocbcdedit /deletevalue {default} truncatememory
В этой статье мы разберемся, как восстановить загрузчик Windows 10 или 11 на современном компьютере, на котором используется UEFI интерфейс вместо классического BIOS и таблица разделов диска GPT (вместо MBR). Повреждение загрузчика Windows может быть вызвано установкой второй ОС (Dual Boot — конфигурация), повреждением файловой систему, некорректным восстановлении Windows после сбоя, удалением скрытых разделов, вирусом-вымогателем и рядом других причин.
Данная статья содержит подробную пошаговую процедуру восстановления поврежденного или удаленного загрузчика ОС в Windows 11/10/8.1 и Windows Server 2022/2019/2016/2012R2 на компьютерах, которые работают в нативном (не legacy) режиме UEFI. Инструкцию можно использовать как для восстановления бинарных файлов загрузчика Windows, так и конфигурационного файла загрузчика EFI\Microsoft\Boot\BCD (в случаях, когда Windows не загружается из-за отсутствия или повреждения файла конфигурацией загрузка BCD.
Содержание:
- Не загружается Windows: Boot configuration data is missing EFI\Microsoft\Boot\BCD
- Автоматическое восстановление загрузчика Windows
- Ручное восстановление загрузчика Windows с помощью BCDBoot
Не загружается Windows: Boot configuration data is missing EFI\Microsoft\Boot\BCD
UEFI компьютер с Windows, установленной в наивном режиме, не сможет загрузиться при повреждении EFI загрузчика Windows. При попытке загрузиться с диска с повреждённым или отсутствующим EFI загрузчиком появится BSOD (синий экран смерти) с ошибкой:
The boot configuration data for your PC is missing or contains errors. File :\EFI\Microsoft\Boot\BCD Error code: 0xc000000f
или
Error code: 0xc000014c
В русской версии Windows ошибка может быть такая:
Ваш компьютер нуждается в ремонте Данные конфигурации загрузки для вашего ПК отсутствуют или содержат ошибки Файл:\EFI\Microsoft\Boot\BCD Код ошибки: 0xc000000f
Эта ошибка говорит о повреждении или даже полном удалении конфигурации загрузчика Windows — Boot Configuration Data (BCD). Если вы попытаетесь восстановить загрузчик на UEFI компьютере с помощью утилиты
bcdedit
, вы получите такую ошибку:
The boot configuration data store could not be found. The requested system device cannot be found.
Дело в том, что если Windows 10/11 установлена в нативном режиме UEFI на GPT диск, то EFI загрузчик Windows (Windows Boot Manager) хранит программу управления загрузкой и конфигурацию BCD на отдельном скрытом разделе EFI (размером 100 мб с файловой системой FAT32). Утилита bcdedit не видит этот EFI раздел, и соответственно не может управлять конфигурацией загрузчика на нем.
Если при загрузке Windows появляется только черный экран с надписью “Operating System not found”, скорее всего у вас полностью удален загрузчик Windows. Следуйте инструкции по ссылке.
Автоматическое восстановление загрузчика Windows
Процедура автоматического восстановления загрузчика, зашитая в среду восстановления Windows (WinRe), как правило, в таких случаях бессильна. Но попробовать все-же стоит:
- Загрузитесь с диска загрузочного диска, диска восстановления или установочной флешки с Windows 10 или 11;
- На экране установки нажмите кнопку Восстановление системы;
- Затем выберите пункт Поиск и устранение неисправностей -> Восстановление при загрузке и выберите ОС, загрузчик которой нужно попытаться восстановить;
- Но скорее всего результат будет отрицательный: Восстановление при загрузке не удалось восстановить компьютер
Ручное восстановление загрузчика Windows с помощью BCDBoot
Перейдем к процедуре ручного восстановления EFI загрузчика Windows на UEFI компьютере.
Для восстановления конфигурации загрузчика (BCD), вам нужно загрузить компьютер с оригинального установочного диска с Windows (диска восстановления или специально подготовленной установочной USB флешки с Windows ). После загрузки в среде восстановления нужно открыть окно командной строки: выберите Восстановление системы -> Диагностика -> Командная строка (System Restore -> Troubleshoot -> Command Prompt).
Командную строку также можно запустить, если у вас под рукой есть только установочный диск с Windows. Для этого достаточно на самом первом этапе установки Windows (при выборе языка и раскладки клавиатуры) нажать комбинацию клавиш Shift+F10 (или Shift+Fn+F10 на некоторых моделях ноутбуков).
В открывшейся командной строке выполните запустите утилиту управления дисками, набрав команду:
diskpart
Выведите список дисков в системе:
list disk
На этом этапе очень важно определить тип таблицы разделов на диске, на котором установлена Windows: MBR или GPT. Дело в том, что EFI загрузчик используется только на дисках с GPT разметкой.
Если у диска в столбце Gpt указана звездочка (
*
), тогда на диске используется таблица разделов GPT, если нет – MBR.
Если с помощью diskpart вы определили, что на вашем диске используется GPT разметка, следуйте дальнейшим шагам инструкции по восстановлению загрузчика.
Если у вас разметка MBR, тогда данная инструкция не применима к вашему компьютеру. Скорее всего у вас компьютер с BIOS, или в настройках UEFI включен режим совместимости Legacy/Compatibility Support Module/CSM.
На MBR дисках загрузчик хранится на отдельном разделе System Reserved, а не на EFI разделе (ни в коем случае не конвертируйте таблицу разделов MBR в GPT, пока не исправите загрузчик!!) Используйте другую инструкцию по восстановлению BCD загрузчика на MBR (Master Boot Record) диске.
Выберите диск, на котором установлена ваша Windows (если жесткий диск в системе один, его индекс должен быть равен 0):
sel disk 0
Выведите список томов и разделов в системе:
list partition
list volume
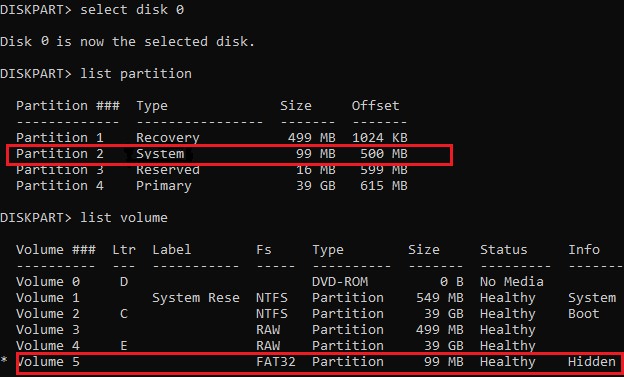
В нашем примере видно, что загрузочный раздел EFI имеет индекс Partition2 (он же Volume 5 с меткой Hidden). Проще всего определить EFI размер по файловой системе FAT32, размеру 100 Мб (это стандартный минимальный размер для Windows компьютеров, в редких случая размер раздела может быть). Чаще всего для него используется метка — System EFI или ESP/ EFI System Partion).
В нашем примере основной раздел, на который установлена Windows, имеет индекс volume 2, отформатирован в файловая система NTFS и ему назначена буква C:.
В вашем случае назначенная буква диске может отличаться. Это зависит, как вы загрузили свой компьютер в среде WinPE. Проще всего определить его по размеру. Если вы не уверены, нужно проверить что на этом диске есть каталог Windows. Выйдите из утилиты diskpart (команда exit) и выполните команду:
dir C:\
Убедитесь, что на этом диске есть каталоги
Windows
,
Program Files
,
Users
и прочие.
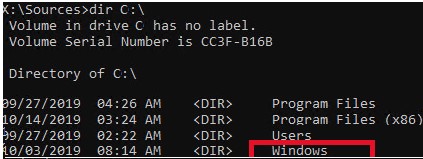
Если этих каталогов нет, значит вашему диску с Windows назначена другая буква диска. Проверьте содержимоет дисков с другими буквами.
Запомните букву диска, назначенную разделу с Windows, чуть ниже мы будем использовать ее в качестве одного из аргументов команды bcdboot.
В таблице также обязательно должен быть раздел MSR (Microsoft System Reserved) размером 16 мб в Windows 10/11 (или 128 Мб в Windows 8.1).
Назначьте скрытому EFI разделу произвольную букву диска (например, M:):
select volume 5
assign letter M:
Должна появится строка, свидетельствующая об успешном назначении буквы диска разделу EFI:
DiskPart successfully assigned the drive letter or mount point.
Завершите работу с diskpart:
exit
Перейдите в каталог с загрузчиком на скрытом разделе:
cd /d m:\efi\microsoft\boot\
В данном случае M: это буква диска, присвоенная разделу EFI чуть выше. Если каталог \EFI\Microsoft\Boot\ отсутствует
The system cannot find the path specified
), попробуйте следующие команды:
cd /d M:\Boot\
или
cd /d M:\ESD\Windows\EFI\Microsoft\Boot\
На этом этапе многие рекомендуют выполнить следующие команды, которые должны перезаписать загрузочную запись раздела, найти установленные Windows и добавить их в BCD:
bootrec /fixboot
bootrec /scanos
bootrec /rebuildbcd
или даже:
bootrec /FixMbr
(восстановление MBR записи для GPT диска выглядит странным)
Все эти команды применимы только для дисков с MBR. Если ваш компьютер загружается в UEFI режиме, то на нем обязательно используется таблица разделов GPT (как раз наш случай). Поэтому при запуске команд
bootrec
вы увидите ошибку:
access is denied
Для исправления загрузочных записей на EFI разделе нужно использовать утилиту
BCDBoot
, а не bootrec.
Утилита BCDBoot позволяет восстановить файлы загрузчика на EFI разделе, скопировав их системного каталога на разделе с Windows. Конфигурация загрузчика BCD пересоздается с помощью шаблона %WINDIR%\System32\Config\BCD-Template.
С помощью команды
attrib
снимите атрибуты скрытый, read-only и системный с файла BCD:
attrib BCD -s -h -r
Удалите текущий файл с конфигурацией BCD, переименовав его (так вы сохраните старую конфигурацию в качестве резервной копии):
ren BCD BCD.bak
С помощью утилиты bcdboot.exe нужно скопировать из системного каталога критические файлы среды загрузки UEFI в загрузочный EFI раздел и пересоздать конфигурацию загрузчика в хранилище BCD:
bcdboot C:\Windows /l en-us /s M: /f ALL
где,
- C:\Windows – путь к корневому системному каталогу Windows на диске (это ваш диск, на который была установлена ваша Windows, мы узнали его ранее с помощью команды diskpart);
- /f ALL – означает, что необходимо скопировать файлы среды загрузки Windows, включая файлы для компьютеров с UEFI и BIOS (теоретическая возможность загружаться на EFI и BIOS системах). Чтобы скопировать только EFI загрузчик, используйте команду /f UEFI;
- /l en-us — определяет языковой стандарт, который используется при инициализации хранилища BCD. По умолчанию используется en-US — английский язык (США);
- /s M: — скопировать файлы EFI загрузчика на указанный раздел;
- /с – эта новая опция BCDBoot в Windows 10, которая позволяет перезатереть имеющиеся загрузочные записи при создании нового хранилища (в том числе debugsettings). Используйте этот параметр, чтобы игнорировать старые настройки и создать полностью чистую конфигурацию BCD загрузчика;
- /v – используется для включения режима вывода подробной информации BCDBoot..
Теперь, если выполнить команду bcdedit, вы увидите следующую картину:
В секции диспетчера загрузки Windows (Windows Boot Manager) должна появится запись, указывающая на полный путь к файлу управления загрузкой UEFI. В этом примере он находится на разделе 2 (
partition=\Device\HarddiskVolume2
), путь
\EFI\MICROSOFT\BOOT\BOOTMGFW.EFI
.
Windows Boot Manager
--------------------
identifier {bootmgr}
device partition=\Device\HarddiskVolume2
path \EFI\Microsoft\Boot\bootmgfw.efi
description Windows Boot Manager
locale en-US
inherit {globalsettings}
bootshutdowndisabled Yes
default {CURRENT}
resumeobject {xxxxxxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxxxxxxxxxx}
displayorder {default}
toolsdisplayorder {memdiag}
timeout 30
Windows Boot Loader
-------------------
identifier {current}
device partition=C:
path \Windows\system32\winload.efi
description Windows Server 10
locale en-US
inherit {bootloadersettings}
recoverysequence {xxxxxxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxxxxxxxxxx}
recoveryenabled Yes
isolatedcontext Yes
allowedinmemorysettings 0x15000075
osdevice partition=C:
systemroot \Windows
resumeobject {xxxxxxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxxxxxxxxxx}
В секции Windows Boot Manager должен быть указан путь к EFI разделу (
=\Device\HarddiskVolume2
), путь к файлу управления загрузкой (bootmgfw.efi). В секции Windows Boot Loader указан раздел Windows и путь к EFI загрузчику Windows (
\Windows\system32\winload.efi
). При включении компьютер передаст управление диспетчеру загрузки EFI, который запустит загрузчик Windows.
Возможные ошибки:
Перезагрузите компьютер, отключите загрузочный диск. Если вы все сделали правильно, в выборе устройств загрузки должен появиться пункт Windows Boot Manager в котором можно выбрать загрузку нужной операционной системы. Ваш EFI загрузчик и конфигурация BCD успешно восстановлены!
В некоторых случаях после восстановления BCD загрузчика, при загрузке Windows появляется ошибка
BAD SYSTEM CONFIG INFO
. Чтобы исправить ошибку:
Убедитесь, что вы не вносили недавно изменения в настройки UEFI
Загрузитесь с установочной/загрузочной флешки и измените конфигурацию загрузчика командами:
-
bcdedit /deletevalue {default} numproc -
bcdedit /deletevalue {default} truncatememory