Брандмауэр Microsoft Defender Firewall встроен во все современные версии Windows и Windows Server и позволяет настраивать правила фильтрации входящего и/или исходящего сетевого трафика на компьютере. Правила Windows Firewall можно настраивать локально на компьютере пользователя (с помощью консоли
wf.msc
, команды
netsh
или встроенного PowerShell модуля NetSecurity). На компьютерах Windows, которые добавлены в домен Active Directory вы можете централизованно управлять правилами и настройками Microsoft Defender Firewall с помощью групповых политик.
В крупных организациях правила фильтрации портов обычно выносятся на уровень маршрутизаторов, L3 коммутаторов или выделенных межсетевых экранах. Однако ничего не мешает вам распространить ваши правила ограничения сетевого доступа Windows Firewall к рабочим станциям или серверам Windows.
Содержание:
- Включить Windows Defender с помощью GPO
- Создать правила файервола Windows с помощью групповой политики
- Применить политики брандмауэра Microsoft Defender к компьютерам Windows
- Импорт и экспорт правил брандмауэра Windows в GPO
- Доменные и локальные правила Microsoft Defender
Включить Windows Defender с помощью GPO
Запустите консоль управления доменными групповыми политиками (Group Policy Management Console,
gpmc.msc
), создайте новую GPO с именем gpoFirewallDefault и перейдите в режим редактирования (Edit).
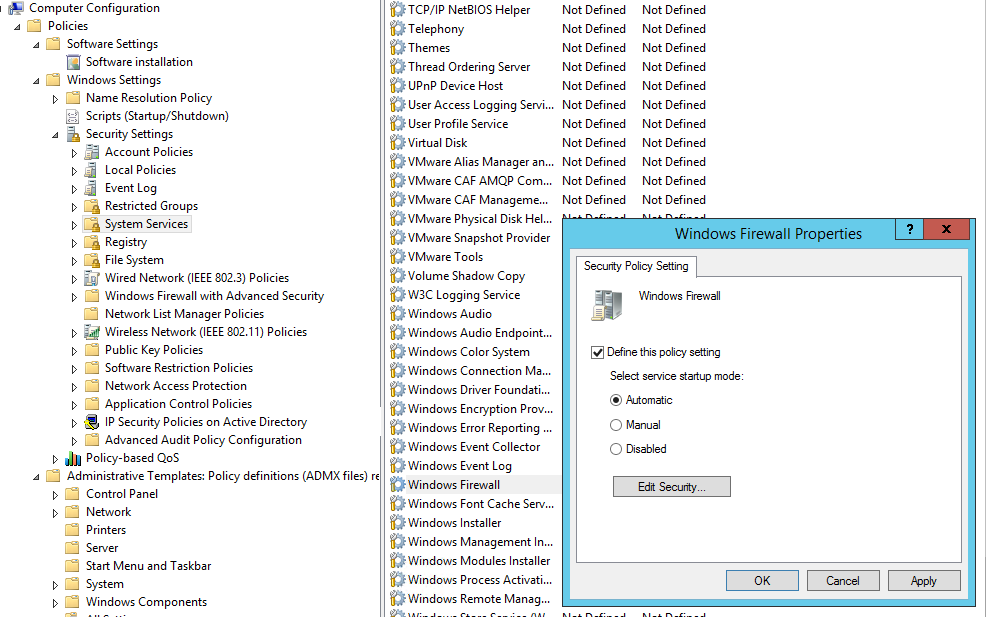
Чтобы пользователи (даже с правами локального админа) не могли выключить службу брандмауэра, желательно настроить автоматический запуск службы Windows Firewall через GPO. Для этого перейдите в раздел Computer Configuration -> Windows Settings -> Security Settings -> System Services. Найдите в списке служб Windows Firewall и измените тип запуск службы на автоматический (Define this policy setting -> Service startup mode Automatic). Убедитесь, что у пользователей нет прав на остановку служб.
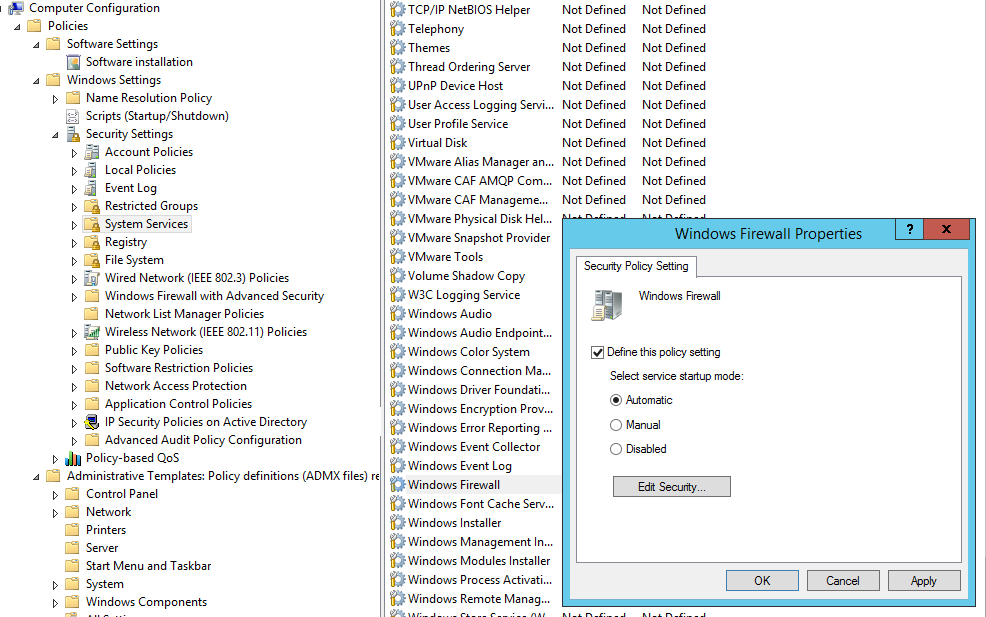
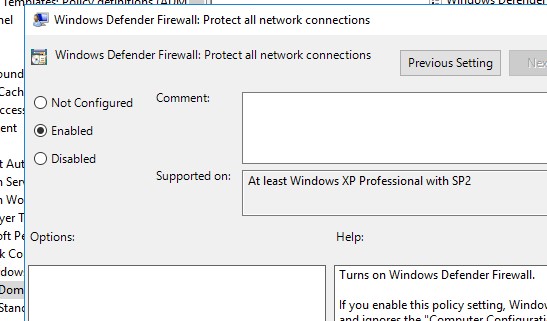
Затем перейдите в раздел Computer Configuration -> Policies -> Administrative Templates -> Network -> Network Connections -> Windows Defender -> Firewall -> Domain Profile и включите политику Windows Defender Firewall: Protect all network connections.
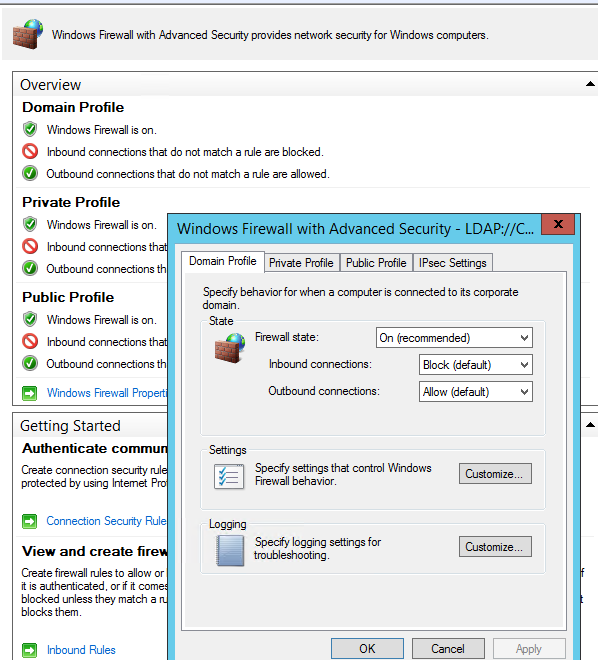
Откройте свойства Windows Firewall with Advanced Security в разделе GPO Computer Configuration -> Windows Settings -> Security Settings.
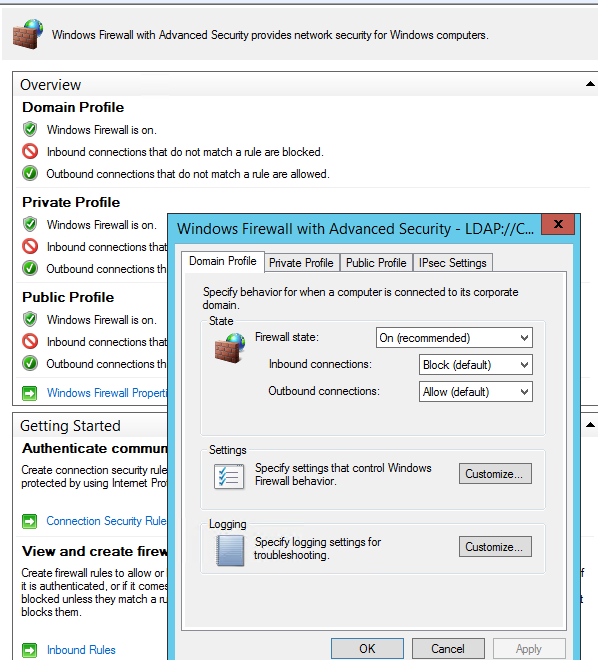
На всех трех вкладках Domain Profile, Private Profile и Public Profile (что такое профиль сети в Windows) измените состояние Firewall state на On (recommended). В зависимости от политик безопасности в вашей организации вы можете указать, что все входящие подключения по умолчанию запрещены (Inbound connections -> Block), а исходящие разрешены (Outbound connections -> Allow). Сохраните изменения.
В целях отладки правил файервола вы можете включить запись логов Windows Defender в текстовый файл %systemroot%\system32\logfiles\firewall\pfirewall.log (по умолчанию). Можно включить логирование отклоненных пакетов (Log dropped packets) или пакетов, который были разрешены правилами файервола (Log successfully connections). По-умолчанию логирование сетевых соединений в Windows отключено.
Создать правила файервола Windows с помощью групповой политики
Теперь рассмотрим, как создать правила файервола Microsoft Defender с помощью GPO. Для настройки правил, перейдите в раздел Computer Configuration -> Windows Settings -> Security Settings -> Windows Firewall with Advanced Security.
Интерфейс этого раздела напоминает локальную консоль управления брандмауэром Windows и состоит из трех секций:
- Inbound rules
- Outbound rules
- Connection security rules
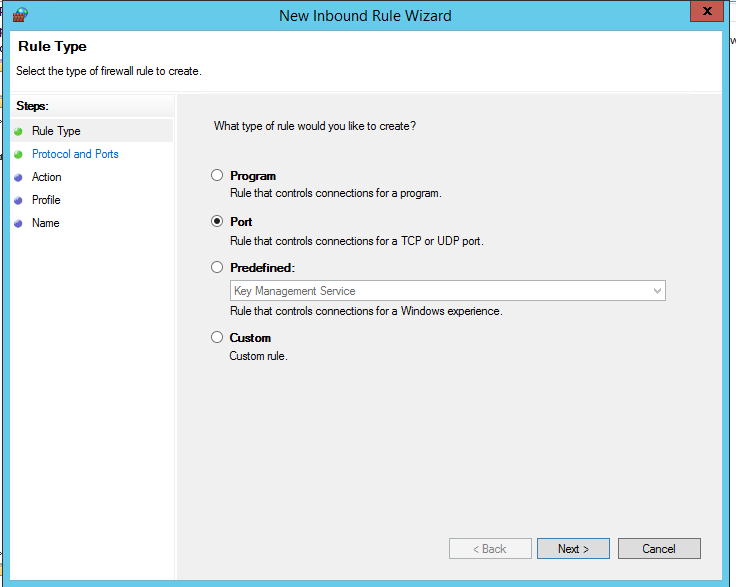
Попробуем создать разрешающее входящее правило файервола. Например, мы хотим разрешить подключение к компьютерам по RDP (порт по умолчанию TCP 3389). Щелкните ПКМ по разделу Inbound Rules и выберите пункт меню New Rule. Запустится мастер создания нового правила брандмауэра.
Выберите тип правила. Можно разрешить доступ для:
- Программы (Program) – можно выбрать исполняемый exe программы;
- Порта (Port) – выбрать TCP/UDP порт или диапазон портов;
- Преднастроенное правило (Predefined) – выбрать одно из стандартных правил Windows, в которых уже имеются правила доступа (описаны как исполняемые файлы, так и порты) к типовым службам (например, AD, Http, DFS, BranchCache, удаленная перезагрузка, SNMP, KMS, WinRM и т.д.);
- Собственное правило (Custom) – здесь можно указать программу, протокол (другие протоколы помимо TCP и UDP, например, ICMP, GRE, L2TP, IGMP и т.д.), IP адреса клиентов или целые IP подсети.
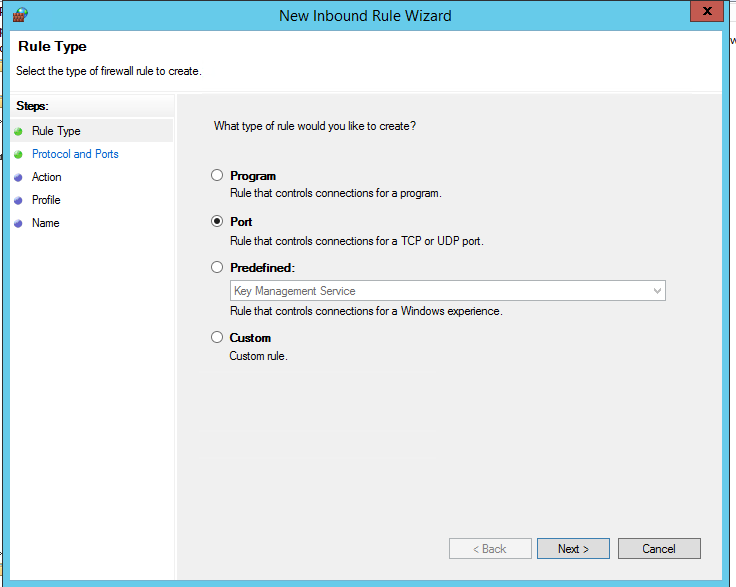
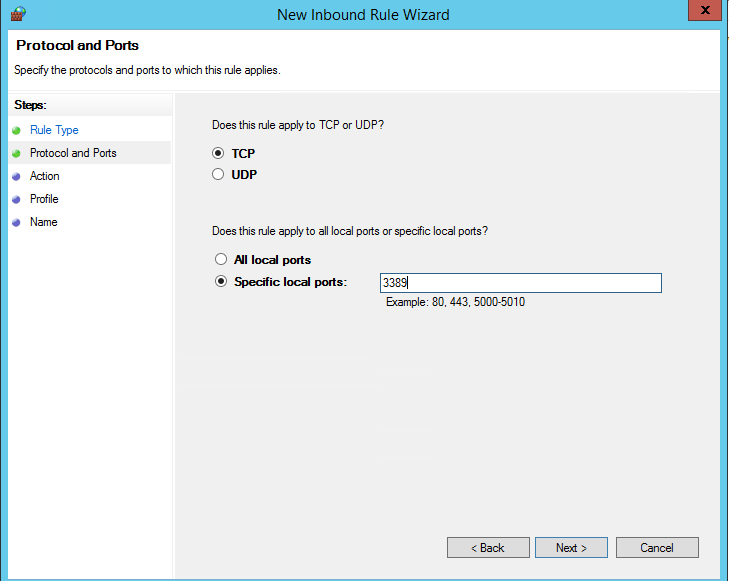
В нашем случае мы выберем правило Port. В качестве протокола укажем TCP, в качестве порта – Specific local ports -> 3389.
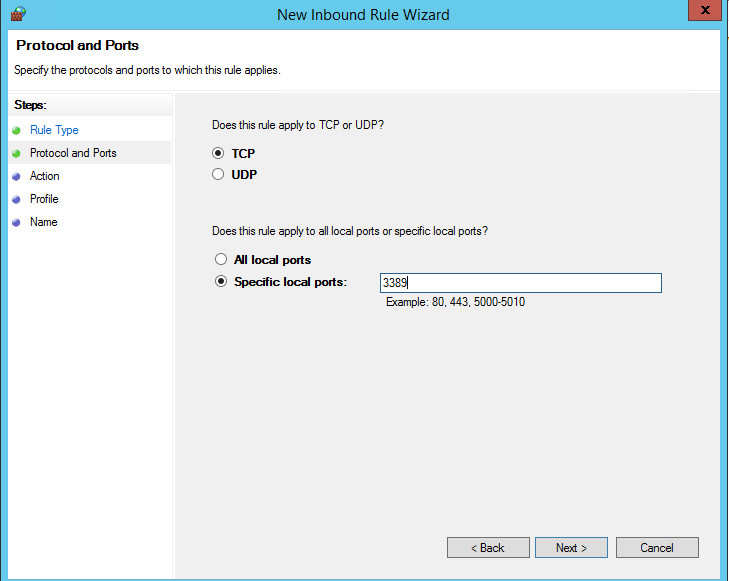
Далее нужно выбрать что нужно сделать с таким сетевым подключением: разрешить (Allow the connection), разрешить если оно безопасное или заблокировать (Block the connection).
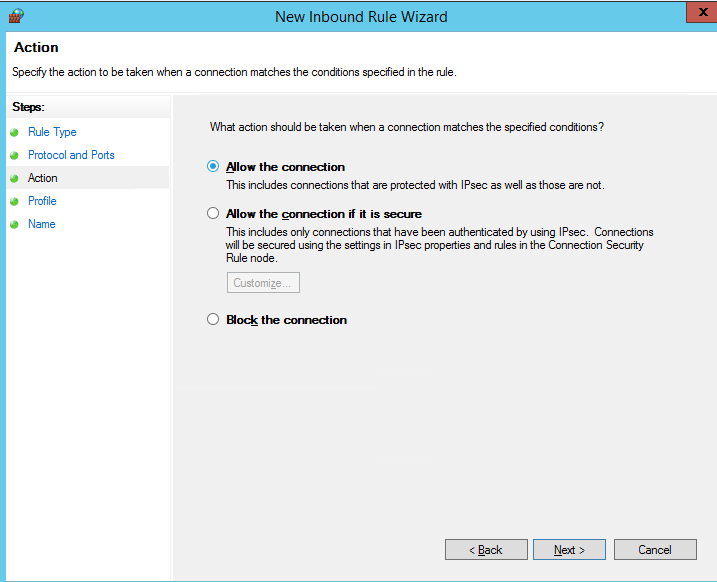
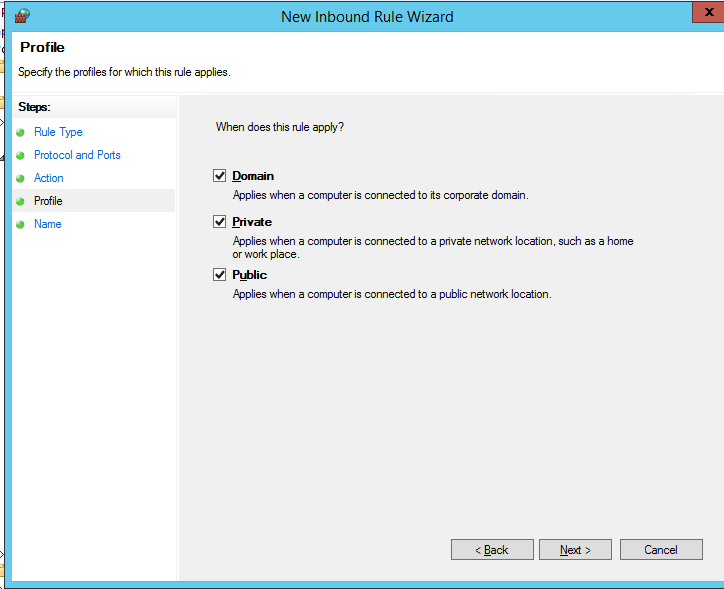
Осталось выбрать профили сети, для которых нужно применить это правило. Можно оставить все профили (Domain, Private и Public).
На последнем шаге нужно указать имя правило и его описание. Нажмите кнопку Finish и оно появится в списке правил брандмауэра.
В современных версиях Windows для трафика удаленного рабочего стола RDP также используется порт UDP 3389. Поэтому создайте второе правила Microsoft Defender и для этого порта.
Аналогичным образом вы можете настроить другие правила для входящего трафика, которые должны применятся к вашим клиентам Windows.
Вы можете создать правила как для входящего и исходящего трафика.
Выше мы рассмотрели, как использовать графический мастер для создания правил Windows Defender Firewall. Также вы можете сформировать список правил в простом текстовой форме и быстро создать правила для групповой политики Defender.
Перейдите в раздел Computer Configuration -> Policies -> Administrative Templates -> Network -> Network Connections -> Windows Defender Profile -> Domain Profile и откройте параметр Windows Defender Firewall: Define inbound port exceptions. Здесь вы можете создать список правил с помощью простых текстовых строчек.
Ниже представлен список правил, который я хочу добавить в групповую политику
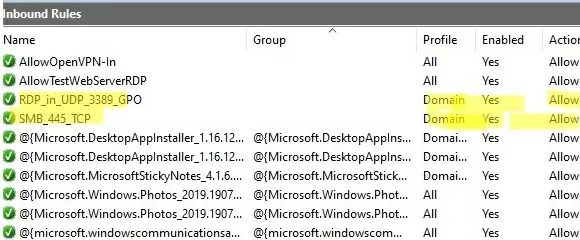
3389:UDP:localsubnet:enabled:RDP_in_UDP_3389_GPO 445:TCP:localsubnet:enabled:SMB_445_TCP 443:TCP:192.168.100.10:enabled:HTTP_in_445_TCP
Нажмите кнопку Show и построчно скопируйте ваши правила в окно Define port exceptions.
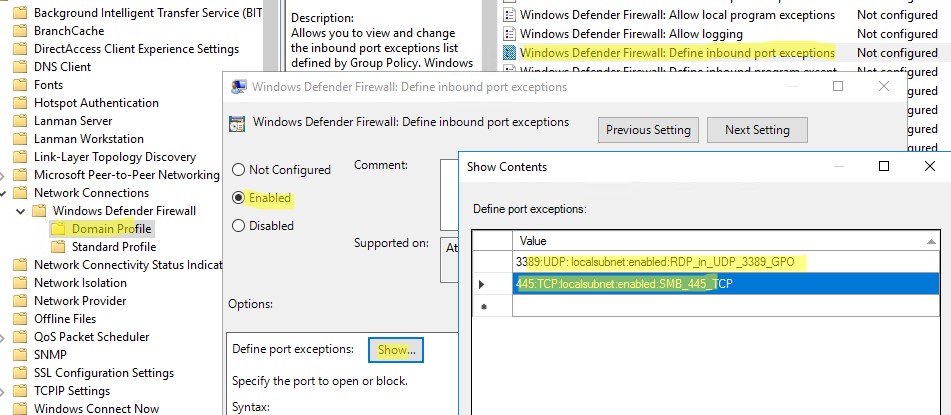
Этот способ позволяет вам быстро создать большое количество входящих правил для файервола Windows.
Применить политики брандмауэра Microsoft Defender к компьютерам Windows
Теперь осталось назначить политику Firewall-Policy на OU (Organizational Unit) с компьютерами пользователей. Найдите в консоли Group Policy Management нужный OU, щелкните по нему правой кнопкой и выберите Link an Existing GPO. Выберите в списке вашу политику.
Важно. Прежде, чем применять политику файервола к OU с продуктивными компьютерами, настоятельно рекомендуется проверить ее на тестовых компьютерах. Из-за некорректной настройки брандмауэра вы можете полностью заблокировать сетевой доступ компьютерам. Для диагностики применения групповых политик используйте утилиту gpresult.exe.
Обновите настройки групповых политик на клиентах (
gpupdate /force
). Проверьте, что указанные вами порты открыты на компьютерах пользователей (можно использовать командлет Test-NetConnection или утилиту Portqry).
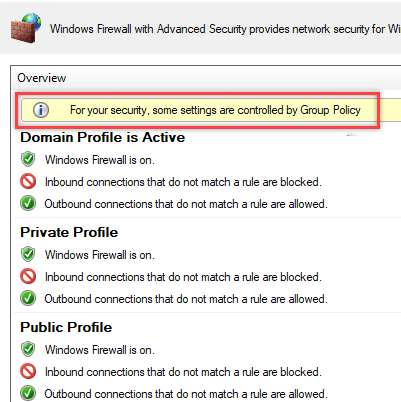
На компьютере пользователя откройте Панель управления\Система и безопасность\Брандмауэр Защитника Windows и убедитесь, что появилась надпись: Для обеспечения безопасности, некоторые параметры управляются групповой политикой (For your security, some settings are controlled by Group Policy), и используются заданные вами настройки брандмаэера.
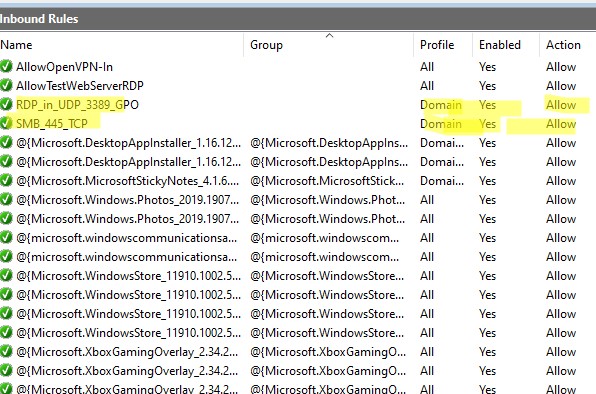
Пользователь теперь не может изменить настройки брандмауэра, а в списке Inbound Rules должны быть указаны все созданные вами правила. Обратите внимание, что по умолчанию новые правила из GPO добавляются к уже существующим локальным правилам файервола.
Также вы можете вывести текущие настройки Windows Defender с помощью команды:
netsh firewall show state
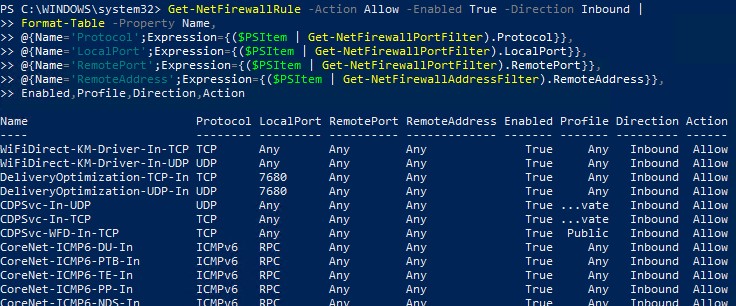
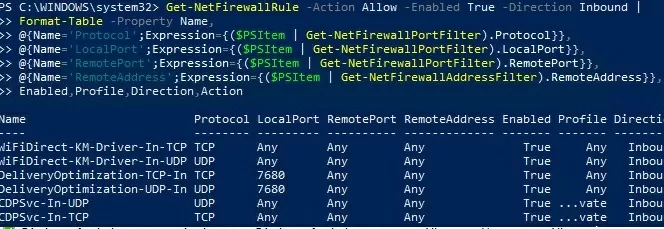
Или можно представить список правил в табличной форме с помощью скрипта PowerShell:
Get-NetFirewallRule -Action Allow -Enabled True -Direction Inbound |
Format-Table -Property Name,
@{Name='Protocol';Expression={($PSItem | Get-NetFirewallPortFilter).Protocol}},
@{Name='LocalPort';Expression={($PSItem | Get-NetFirewallPortFilter).LocalPort}},
@{Name='RemotePort';Expression={($PSItem | Get-NetFirewallPortFilter).RemotePort}},
@{Name='RemoteAddress';Expression={($PSItem | Get-NetFirewallAddressFilter).RemoteAddress}},
Enabled,Profile,Direction,Action
Импорт и экспорт правил брандмауэра Windows в GPO
Консоль Windows Defender Firewall позволяет экспортировать и импортировать текущие настройки файервола в текстовый файл. Вы можете настроить правила брандмауэра на эталонном компьютере и экспортировать их в консоль групповых политики.
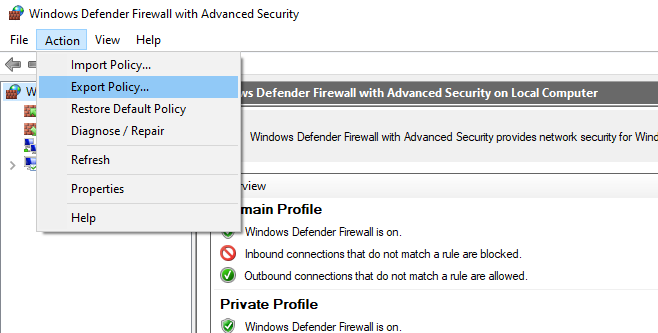
Настройте нужные правила, замет встаньте на корень оснастки брандмауэра (Монитор Брандмауэра Защитника Windows в режиме повышенной безопасности) и выберите пункт Действие -> Экспорт политики
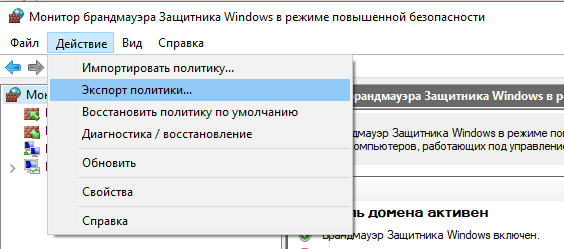
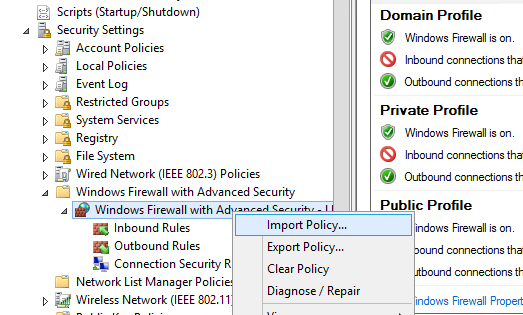
Политика выгружается в WFW файл, который можно импортировать в редакторе Group Policy Management Editor, выбрав пункт Import Policy и указав путь к файлу wfw (текущие настройки будут перезаписаны).
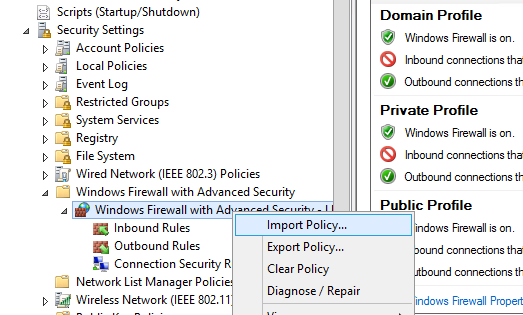
Доменные и локальные правила Microsoft Defender
В GPO вы можете настроить, хотите ли вы разрешить локальным администраторам создавать на своих компьютерах собственные правила брандмауэра и как эти правила должны объединяться с правилами, назначенными через GPO.
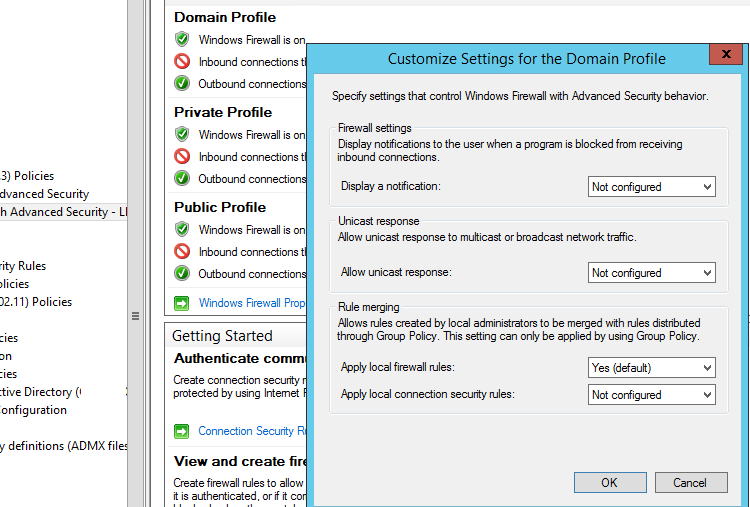
Откройте в GPO свойства политики (Windows Firewall Properties), выберите вкладку с профилем (Domain) и нажмите кнопку Customize.
Обратите внимание на настройки в разделе Rule merging. По умолчанию режим объединения правил включен. Вы можете принудительно указать, что локальный администратор может создавать собственные правила брандмауэра: в параметре Apply local firewall rules выберите Yes (default).
Совет. Блокирующие правила файервола имеют приоритет над разрешающими. Т.е. пользователь не сможет создать собственное разрешающее правило доступа, противоречащее запрещающему правилу, настроенному администратором через GPO. Однако пользователь может создать локальное запрещающее правило, даже если этот доступ разрешен администратором в политике.
Несколько советов об управлении брандмауэром Windows через GPO
- Создавайте отдельные политики с правилами брандмауэра для серверов и рабочих станций (для каждой группы одинаковых серверов возможно придется создать собственные политики в зависимости от их роли). Т.е. правила файервола для контроллера домена, почтового Exchange сервера, сервера с ролью Remote Desktop Services Host (RDSH) или Microsoft SQL Server будут отличаться;
- Для более точного нацеливания политики на клиентов можно использовать WMI фильтры GPO (например, вы можете привязать политику к хостам определенной IP подсети)
- Какие порты нужно открыть для той или иной службы нужно искать в документации на сайте разработчика. Процесс довольно кропотливый и на первый взгляд сложный. Но постепенно вполне реальной прийти к работоспособной конфигурации Windows файервола, который разрешает только одобренные подключения и блокирует все остальное. По опыту хочу отметить, что на ПО Microsoft можно довольно быстро найти список используемых TCP/UDP портов.
The Microsoft Defender Firewall is built into all modern versions of Windows and Windows Server and allows you to configure rules for filtering incoming and/or outgoing network traffic on your computer. Windows Firewall rules can be configured locally on the user’s computer (using the wf.msc console, the netsh command, or the built-in NetSecurity PowerShell module). On Windows computers joined to an Active Directory domain, you can centrally manage Microsoft Defender Firewall rules and settings using Group Policies.
In enterprise networks, the port filtering rules are usually set at the level of routers, L3 switches, or dedicated firewall devices. However, nothing prevents you from deploying your Windows Firewall network access rules to workstations or Windows servers.
Contents:
- Enable Microsoft Defender Firewall via GPO
- How to Create Windows Firewall Rule with GPO?
- Applying Microsoft Defender Firewall Rules to Windows Computers
- How to Export and Import Firewall Rules on Windows?
- Merging Domain and Local Microsoft Defender Firewall Rules
Enable Microsoft Defender Firewall via GPO
Open the domain Group Policy Management console (gpmc.msc), create a new GPO object (policy) with the name gpoFirewallDefault, and switch to Edit mode.
In order to prevent users (even having local admin permissions) to stop the firewall service, it is recommended to configure the automatic startup of the Windows Firewall using GPO. To do it, go to Computer Configuration- > Windows Settings -> Security Settings -> System Services. Find Windows Firewall in the list of services and change the startup type to automatic (Define this policy setting -> Service startup mode Automatic). Make sure that your users don’t have the permission to stop the service.
Then go to Computer Configuration -> Policies -> Administrative Templates -> Network -> Network Connections -> Windows Defender -> Firewall -> Domain Profile and enable the policy Windows Defender Firewall: Protect all network connections.
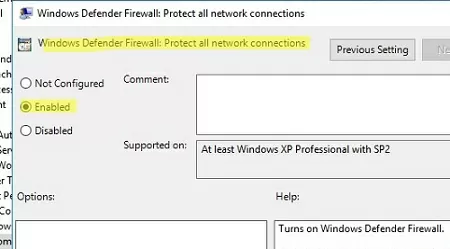
Go to the Computer Configuration -> Windows Settings -> Security Settings section in the GPO console. Right-click Windows Firewall with Advanced Security and open the properties.
Change the Firewall state to On (recommended) in all three tabs: Domain Profile, Private Profile, and Public Profile (What are network profiles (locations) in Windows?). Depending on the security policies in your company, you can specify that all inbound connections are blocked by default (Inbound connections -> Block), and outbound connections are allowed (Outbound connections -> Allow). Save the changes.
You can debug your Windows Defender Firewall rules on clients’ computers by enabling logging in %systemroot%\system32\logfiles\firewall\pfirewall.log. By default, network connection logging is disabled in Windows. You can log only rejected packets (Log dropped packets) or packets that were allowed by firewall rules (Log successful connections).
How to Create Windows Firewall Rule with GPO?
Now let’s look at how to create Microsoft Defender firewall rules via Group Policy. To configure your rules, go to Computer Configuration -> Windows Settings -> Security Settings -> Windows Firewall with Advanced Security.
The following sections are available in Firewall GPO:
- Inbound rules
- Outbound rules
- Connection security rules
Let’s try to create an allowing inbound firewall rule. For example, we want to allow the incoming RDP connection on Windows (the default RDP port is TCP 3389). Right-click the Inbound Rules section and select New Rule. The New Firewall Rule Wizard starts.
The firewall rule wizard has an interface similar to that of the local Windows Firewall on the user’s desktop computer.
Select the rule type. You can allow access to:
- Program – you can select a program executable (.exe);
- Port – you can select a TCP/UDP port or a port range;
- Predefined – select one of the standard Windows rules, which already contain access rules (both executable files and ports are described) to typical services (e. g., AD, HTTP(s), DFS, BranchCache, Remote restart, SNMP, KMS, WinRM, etc.);
- Custom – here you can specify a program, a protocol (protocols other than TCP or UDP, like ICMP, GRE, L2TP, IGMP, etc.), client IP addresses, or an entire IP network (subnet).
In our case, we’ll select the Port rule. Let’s specify TCP as the protocol, and 3389 as the local port number.
Then you must select what to do with such a network connection: Allow the connection, Allow the connection if it is secure, or Block the connection.
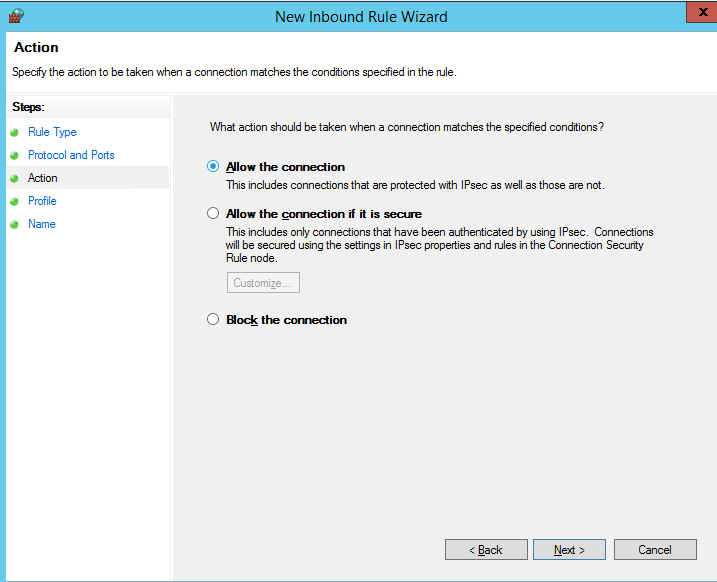
Then select the network profiles to apply the firewall rule. You can leave all profiles enabled (Domain, Private and Public).
In the last step, specify the name and description of the rule. Click Finish, and it will appear in the list of firewall rules.
Modern versions of Windows also use UDP port 3389 for Remote Desktop (RDP) traffic. Therefore, create a second Microsoft Defender rule for that port as well.
In the same way, you can configure other inbound firewall rules to apply to your Windows clients. You can create rules for both inbound and outbound traffic.
Above, we looked at how to use the graphical wizard to create Windows Defender Firewall rules. You can also create a list of rules in plain text form and quickly add a large number of exceptions to Defender Firewall GPO.
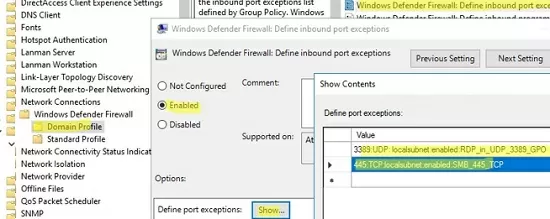
Go to Computer Configuration -> Policies -> Administrative Templates -> Network -> Network Connections -> Windows Defender Profile -> Domain Profile and open the Windows Defender Firewall: Define inbound port exceptions policy. Here you can create a list of firewall rules with simple text strings.
Below is the list of inbound firewall rules that I want to add to the Group Policy:
3389:UDP:localsubnet:enabled:In_RDP_UDP_3389 445:TCP:localsubnet:enabled:In_SMB_TCP_443 443:TCP:192.168.110.11:enabled:In_HTTP_TCP_445
Click the Show button and copy your rules line by line into the Define Port Exceptions form.
This method allows you to quickly create a large number of inbound rules for the Windows firewall.
Applying Microsoft Defender Firewall Rules to Windows Computers
Now it remains to assign the Firewall-Policy policy to the OU (Organizational Unit) with the user’s computers. Locate the desired OU in the Group Policy Management console, right-click on it, and select Link an Existing GPO. Select your firewall policy from the list.
Important. Before applying a firewall policy to OU with production computers, it is strongly recommended to try it out on some test computers. Otherwise, due to wrong firewall settings, you can completely block network access on computers. To diagnose how your Group Policy is applied, use the gpresult tool.
Update the Group Policy settings on your clients (gpupdate /force). Verify that the ports you specified are open on users’ computers (you can use Test-NetConnection cmdlet or Portqry tool to check for open ports).
On a user’s computer, open the Control Panel -> System and Security -> Windows Defender Firewall and make sure that there is the message For your security, some settings are controlled by Group Policy and your firewall settings are used.
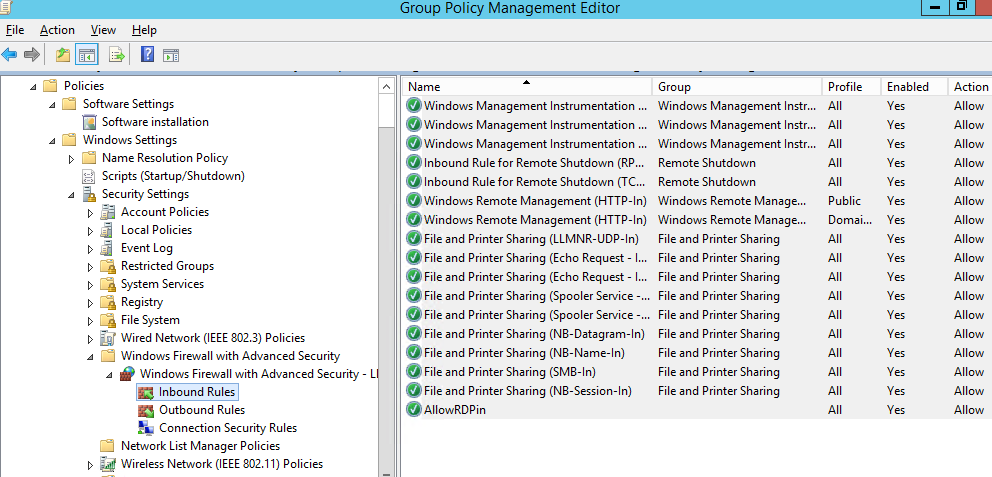
Now a user cannot change the firewall settings, and all rules that you have created must appear in the Inbound Rules list. Note that by default, new rules from the GPO are added to existing local firewall rules.
You can also display the current Windows Defender settings with the command:
netsh firewall show state
Or you can get the list of inbound rules in a table form using a PowerShell script:
Get-NetFirewallRule -Action Allow -Enabled True -Direction Inbound |
Format-Table -Property Name,
@{Name='Protocol';Expression={($PSItem | Get-NetFirewallPortFilter).Protocol}},
@{Name='LocalPort';Expression={($PSItem | Get-NetFirewallPortFilter).LocalPort}},
@{Name='RemotePort';Expression={($PSItem | Get-NetFirewallPortFilter).RemotePort}},
@{Name='RemoteAddress';Expression={($PSItem | Get-NetFirewallAddressFilter).RemoteAddress}},
Enabled,Profile,Direction,Action
How to Export and Import Firewall Rules on Windows?
The Windows Defender Firewall Console allows you to export and import the current firewall settings to a text file. You can configure firewall rules on the reference computer and export them to the Group Policy console.
Configure the rules you need, then go to the root of the firewall snap-in (Windows Defender Firewall Monitor with Advanced Security) and select Action -> Export Policy
Your firewall rules will be exported into a WFW file, which can be imported to the Group Policy Management Editor by selecting the Import Policy option and specifying the path to the .wfw file (the current policy settings will be overwritten).
Merging Domain and Local Microsoft Defender Firewall Rules
In the GPO, you can specify whether you want to allow local administrators to create their own firewall rules on their computers, and how these rules should be merged with the rules assigned through the GPO.
Open the Windows Firewall policy properties in the GPO, select the tab with the profile (Domain) and click the Customize button. Check the settings in the Rule merging section. By default, rule merging is enabled. You can force a local administrator can create their own firewall rules: select Yes (default) in the Apply local firewall rules option.
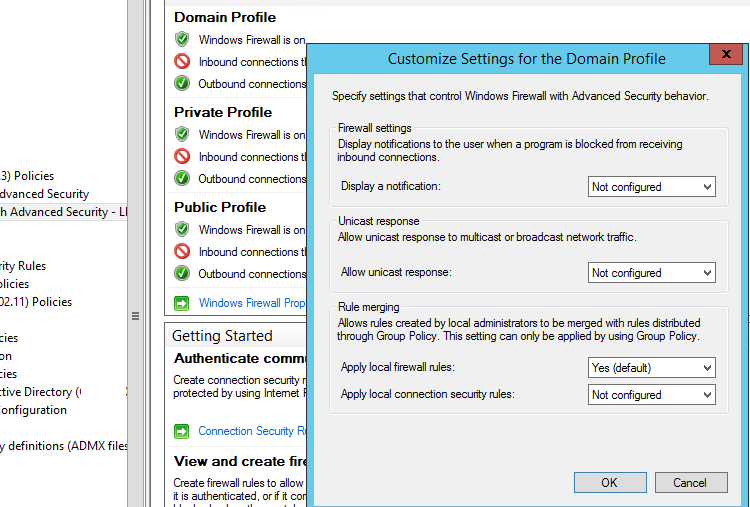
Tip. Blocking firewall rules have a higher priority than allowing ones. It means that a user cannot create an allowing access rule if it contradicts the deny rule configured by an administrator using GPO. However, a user will be able to create a local blocking rule, even if the access is allowed in the policy by the administrator.
Some tips on managing the Windows Firewall using a GPO:
- Create separate GPOs with firewall rules for servers and workstations (you may need to create your own policies for each group of similar servers depending on their role. This means that the firewall rules for a domain controller, an Exchange server, a server with the Remote Desktop Services Host (RDSH) role, or Microsoft SQL Server will differ;
- You can use WMI GPO filters to target policies more precisely to clients (for example, you can apply the policy to hosts on a specific IP subnet);
- You can find out which ports must be opened for each service in the documentation on the vendor’s website. The process is quite painstaking and complicated at the first glance. However, you can finally get a working Windows Firewall configuration that allows only approved network connections and blocks the rest. From my experience, I’d like to note that you can quickly find the list of used TCP/UDP ports for most Microsoft services.
How to enable Windows firewall rules with Group Policy
In this post, we will show you how to enable Windows firewall rules with Group Policy. With a Group Policy Object (GPO) configuration, we could either manually add each firewall rule or we can import the firewall rules from a reference computer.
Following our earlier post on how to enable the WMI firewall rules for client accessibility in MPA Tools, we will demonstrate the option to import the WMI firewall rules from a reference computer.
What is Group Policy?
Group Policy is a feature of Microsoft’s Active Directory infrastructure that allows you to implement managed configurations for users and computers in a Windows environment. Group Policy provides centralized management and configuration of Windows operating systems, applications, and end-user settings. For more information, see Group Policy Overview | Microsoft Learn.
Exporting the firewall rule policy
On a reference Windows 10 or Windows 11 computer, open the Windows Defender Firewall with Advanced Security management console. Right-click the top-level Windows Defender Firewall with Advanced Security node and select Export Policy.

Specify a file name and then save the file in a location that is accessible to the computer where the Group Policy Management console can be used.

This will generate a policy file with a .wfw extension. Click OK.
Creating the Group Policy Object (GPO)
Next, to create the GPO, we will need to determine the relevant OU where the GPO will be assigned. In this example, we will link the GPO to the CLIENT DEVICES Organizational Unit (OU).

In the Group Policy Management console, navigate to the chosen OU and right-click and select Create a GPO in this domain, and Link it here…

Specify the GPO name and then click OK.

Important: Since this GPO is now actively linked, any changes we make to the GPO at this point will effectively start applying to the devices in the selected OU. So, to be careful, we will disable all settings in the GPO status, until the GPO is fully configured. Alternatively, we could have first created the GPO and link it to the OU later. Both methods are acceptably safe.

Filtering the assignment to a global group
If you would like to assign the GPO to a subset of devices in the OU (for example, test or pilot devices) then create a domain global group that contains only these test or pilot devices. Then under the Scope tab, in the Security Filtering pane, remove Authenticated Users and then add the global group.
Note: Since this GPO will be using the Computer Configuration, the membership of the global group should only contain computers (and not users).

Importing the firewall rule policy
Next, right-click on the new GPO link and then select Edit.

In the Group Policy Management Editor window, navigate to Computer Configuration\Policies\Windows Settings\Security Settings\Windows Defender Firewall with Advanced Security. Right-click and select Import Policy.

Since we do not have any firewall rules defined in this new GPO yet, we can ignore this message. Click Yes.
Note: If we imported the policy to an existing GPO, then the imported firewall rules would overwrite any existing firewall rules in the GPO.

Navigate to the policy file (.wfw) that was previously exported on the reference device. Select the file and then click Open.

Click OK.

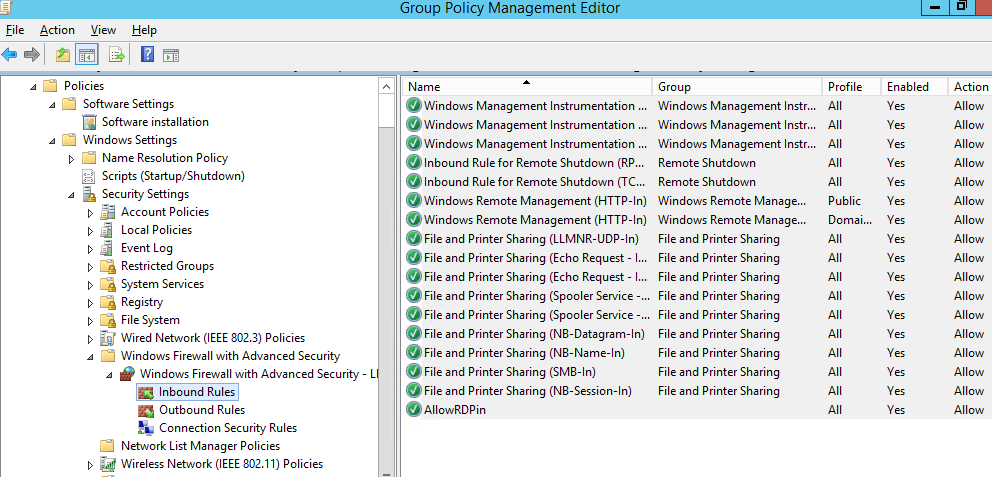
On the left-hand navigation pane, select Inbound Rules. Select all the firewall rules except the rules within the group “Windows Management Instrumentation (WMI)”, right-click and then select Delete.

Click Yes.

This should leave just the 6x inbound WMI firewall rules. Ensure that the firewall rules are enabled, otherwise select all the rules and then right-click and select Enable Rule.

On the left-hand navigation pane, select Outbound Rules. Select all the firewall rules, right-click and then select Delete.

Click Yes.

There should be no outbound firewall rules configured. The Group Policy Management Editor window can now be closed, and the settings will be saved.

Select the GPO link, right-click and select Refresh to refresh the settings.

Then select the Settings tab, scroll through, and confirm that all 6x inbound rules are configured and are enabled.

Enabling the GPO
Now we can re-enable the GPO in the GPO status on the Details tab.

Click OK.

Testing the GPO
The GPO should now begin applying to all devices in the linked OU at the next group policy refresh interval. To accelerate the process on a test or pilot device, you can execute the group policy update command in an Administrator CMD window.

Then on the applicable clients, you can confirm in the Windows Defender Firewall with Advanced Security management console, that all the firewall rules within the group “Windows Management Instrumentation (WMI)” are enabled and have a green check icon next to them.
Note: This GPO method will cause a duplication of the WMI firewall rules, however, the domain GPO defined firewall rules will override the locally configured ones.

Finally, we can confirm that MPA Tools should now be able to retrieve all management data from the client and all the client fields will now be populated with the relevant data and the status icon for the client accessibility should now be green (as shown below).

This concludes the comprehensive series for enabling the WMI firewall rules for client accessibility in MPA Tools. Remember if you encounter any issues, please reach out to us for support.
As a system administrator, finding relatively low-effort ways to improve your organization’s security posture is always a win.
When using Windows-based workstations, one way you can easily implement added protection to your environment is by enabling and deploying Windows Firewall.
What is Windows Firewall?
Windows Firewall — which Microsoft rebranded to Windows Defender Firewall with the release of Windows 10 — is a stateful host firewall within the Windows OS that helps secure your device by creating rules to manage inbound and outbound network connections. Windows Defender Firewall with Advanced Security is the tool that enables admins to deploy rules to Windows Defender Firewall — essentially a more robust version of the control panel.
Enabling Windows Defender Firewall is an important step to achieving a layered security model. It will help reduce the risk of network security threats, safeguard your sensitive data and intellectual property, and extend the value of your existing investments.
Windows Defender Firewall is available on Windows Vista, 7, 8, 10 and 11 for workstations and Windows 2008, 2008 R2, 2012, 2016, 2019 and 2022 for servers.
What is Group Policy?
In a Windows-based environment, Group Policy is the infrastructure that allows you to specify managed configurations for users and computers through Group Policy settings and Group Policy Preferences.
Group Policy is every systems administrator’s dream. It helps deploy and manage anything in their environment and helps control certain security elements, like firewall settings, DNS, remote desktop rules, domain profiles, file and folder permissions, and countless others.
To use and implement Group Policy Objects (GPOs), you will need to have an Active Directory setup on a server (most likely a Domain Controller) and then install Group Policy Management Console (GPMC). There are even ways to help automate and deploy GPOs using Windows PowerShell, which will get installed with GPMC or Remote Server Administration Tools (RSAT).
Watch our webinar on GPO settings that expose your environment>
Benefits of Group Policy
Besides helping to control security settings, Group Policy has a variety of benefits:
- Ease of Management – Managing any size organization can be time consuming for any system administrator. To make things simpler, deploying Group Policy can help manage every user and workstation in your environment to have the same rules and settings by deploying from the central location.
- Security – Using Group Policy can help institute some of the best security practices at any organization. Firewall rules, password rules and remote computer access are some examples of security practices that all organizations should establish and implement.
- Cost and Time – The ability to manage large amounts of endpoints with one centralized management system eliminates the overhead of hiring a larger staff of system administrators. It can scale for any organization, but Group Policy severely cuts down the time to manage the endpoints and the amount of staff required.
Configuring Windows Firewall via Group Policy
Managing Windows Firewall with Group Policy can save time, making it an ideal option for smaller or resource-strapped IT teams. Here’s a step-by-step tutorial of how to configure Windows Firewall with Group Policy.
1. Open your domain’s Group Policy Management Console (gpmc.msc).

2. Navigate to the Domain and the Group Policy Object folder. Create a new GPO (following your company’s naming convention).

3. Right-click the new GPO and select Edit.

4. You’ll need to set the firewall for autostartup. To do it, go to Computer Configuration > Policies > Windows Settings > Security Settings > System Services. Find Windows Firewall in the list of services and change the startup type to Automatic (Define this policy setting -> Service startup mode Automatic).

5. Then, we will want to enable the firewall to protect all connections. Go to Computer Configuration > Policies > Administrative Templates > Network > Network Connections > Windows Defender > Firewall > Domain Profile and enable the policy Windows Defender Firewall: Protect all network connections.

6. Within the GPO console, navigate to the Computer Configuration > Windows Settings > Security Settings section. Right-click Windows Firewall with Advanced Security and open the properties. Make sure to enable the Firewall State to On(Recommended) on each of the profiles you will be using (enabling on all is best practice).

Logging for Windows Firewall and Windows Defender Firewall are disabled by default. If you are running Blumira Advanced Edition (now replaced by SIEM + Endpoint Visibility and XDR Platform editions), you can ensure you are getting all the necessary logs by deploying Poshim, an automated script by Blumira that will not only enable those logs, but will enable Sysmon and NXLog to capture all necessary logs and send to your Blumira Sensor to ingest, parse and trigger detections.
Configure Firewall Rules via Group Policy
1. Using the same GPO as implemented — or creating a new one if you feel it’s necessary in your environment — we can create firewall rules. To configure your rules, go to Computer Configuration > Policies > Windows Settings > Security Settings > Windows Firewall with Advanced Security.

2. Select the rule type. You can allow access to:

-
- Program – you can select a program executable (.exe);
- Port – you can select a TCP/UDP port or a port range;
- Predefined – select one of the standard Windows rules, which already contain access rules (both executable files and ports are described) to typical services (e. g., AD, HTTP(s), DFS, BranchCache, Remote restart, SNMP, KMS, WinRM, etc.);
- Custom – here you can specify a program, a protocol (protocols other than TCP or UDP, like ICMP, GRE, L2TP, IGMP, etc.), client IP addresses, or an entire IP network (subnet).
3. For this example, we will look to allow Port 8080 on TCP:

4. There are three options: Allow the connection, Allow the connection if it is secure, and Block the Connection. In this case, we will select Allow the Connection:

5. You will then select which Profiles to deploy the rule for:

6. Give the rule a name and then select Finish:

Learn best practices for configuring firewall rules>
Blumira: Going Beyond Windows Firewall Security
Enabling Windows Firewall is a great way to get started with Microsoft security, but it’s just the tip of the iceberg. For more complete visibility, you’ll need to centralize those firewall logs, as well as receive alerting around them.
Blumira is a cloud-based SIEM with threat detection and response that integrates with Windows Firewall, along with a variety of other security tools, to give you enhanced visibility over your entire environment.
Blumira is dedicated to helping small teams achieve easy-to-use, effective security that meets compliance and protects them against breaches and ransomware. We do things differently by providing more value for better security outcomes, including:
- Automate Tasks For You – We do all the heavy lifting for your team to save them time, including parsing, creating native third-party integrations, and testing and tuning detection rules to reduce noisy alerts.
- Faster Time to Security – Our unique approach to detections notifies you of threats other security tools may miss, sending you real-time alerts in under a minute of initial detection to help you respond to threats faster than ever.
- Easily Meet Compliance – With a year of data retention and deployment that takes minutes to hours, we help you meet cyber insurance and compliance easily and quickly with the team you have today.
Blumira’s free edition integrates directly with your Microsoft 365 tenant to detect suspicious activity in your environment — at no cost. Get your free account and see the value of Blumira today.
GPO – Configure the Windows firewall
GPO – Configure the Windows firewall
Would you like to learn how to use a group policy to enable and configure the Firewall of a computer running Windows? In this tutorial, we will show you how to enable the Firewall service and create network rules on all computers in the domain using a GPO.
• Windows 2012 R2
• Windows 2016
• Windows 2019
• Windows 10
• Windows 7
Hardware List:
The following section presents the list of equipment used to create this tutorial.
Every piece of hardware listed above can be found at Amazon website.
Windows Related Tutorial:
On this page, we offer quick access to a list of tutorials related to Windows.
Tutorial GPO – Configure the Windows firewall
On the domain controller, open the group policy management tool.
Create a new group policy.
Enter a name for the new group policy.
In our example, the new GPO was named: MY-GPO.
On the Group Policy Management screen, expand the folder named Group Policy Objects.
Right-click your new Group Policy Object and select the Edit option.
On the group policy editor screen, expand the Computer configuration folder and locate the following item.
Select the option named Windows Firewall with Advanced Security
Access the option named Windows firewall properties.
Select the desired network profile and perform the following configuration:
• Firewall state – On.
• Inbound connections – Block.
• Outbound connections – Allow.
Click on the OK button.
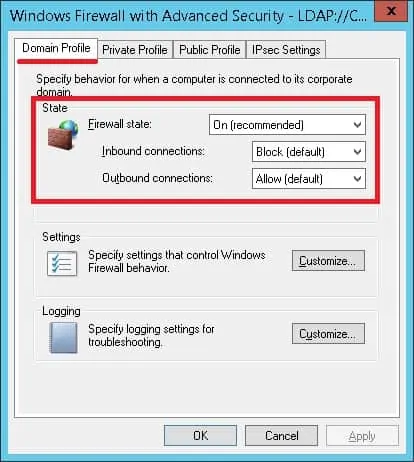
In our example, we are going to enable the Windows firewall when the computer is connected to the Domain network.
In our example, we are going to allow outbound connections.
In our example, we are going to block inbound connections.
The computer will be allowed to start a communication with any device.
Other devices will not be allowed to start communication with the computer.
Optionally, enable the log of blocked packets.
Enable the option named Log dropped packets.
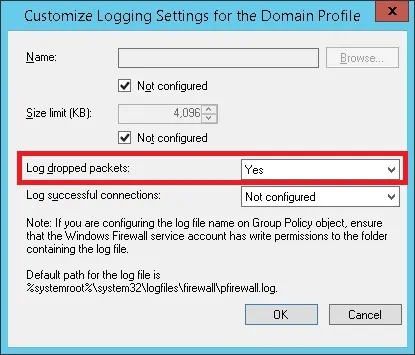
This is the default path for the Windows firewall log.
To save the group policy configuration, you need to close the Group Policy editor.
Congratulations! You have finished the GPO creation.
Tutorial GPO – Create a firewall rule
As an example, we are going to create a white list.
This rule will contain a list of IP addresses that are allowed to start a network connection to the computer.
On the group policy editor, select the option named Windows Firewall with Advanced Security.
Create a new Inbound rule.
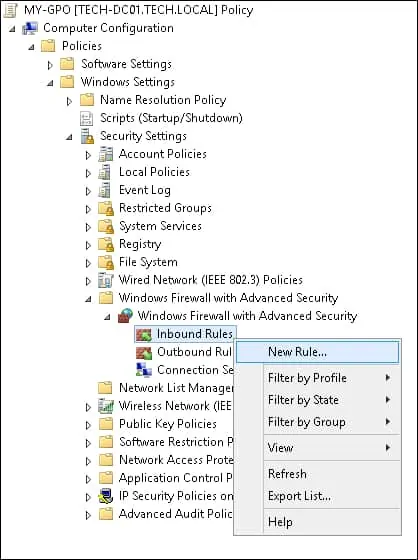
Select the Custom option.
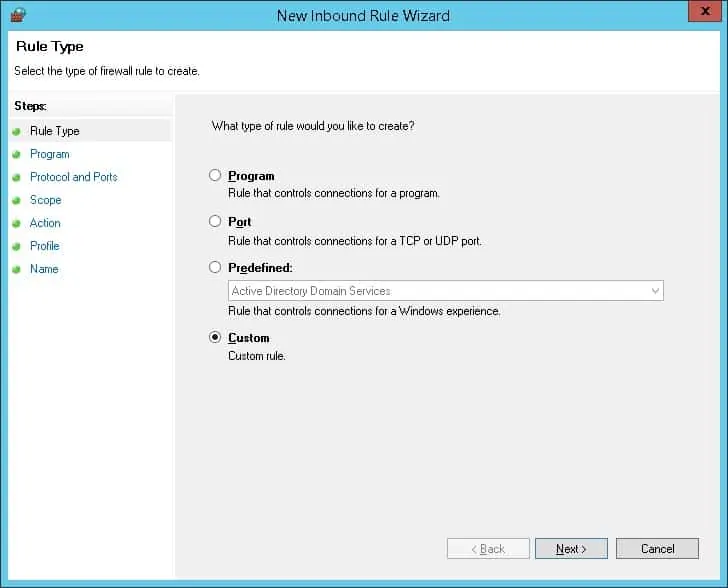
Select the All Programs option and click on the Next button.
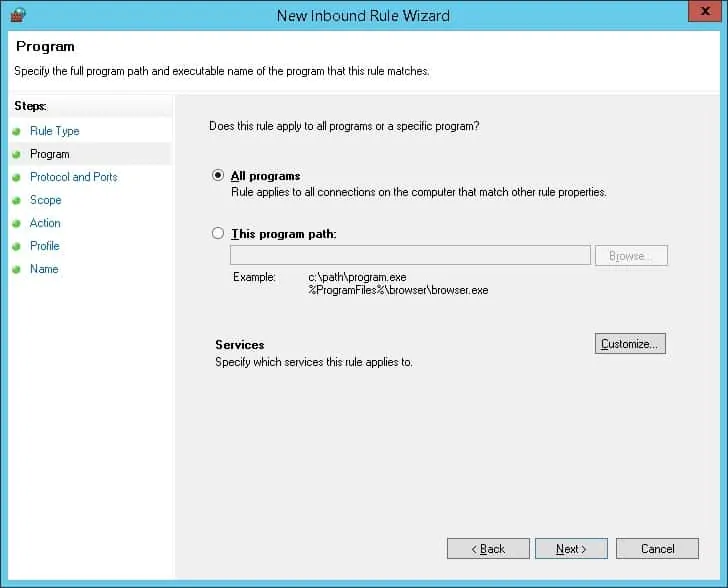
Click on the Next button.
Enter a list of authorized IP addresses and click on the Next button.
The IP addresses included in the list will be authorized to start communication without restrictions.
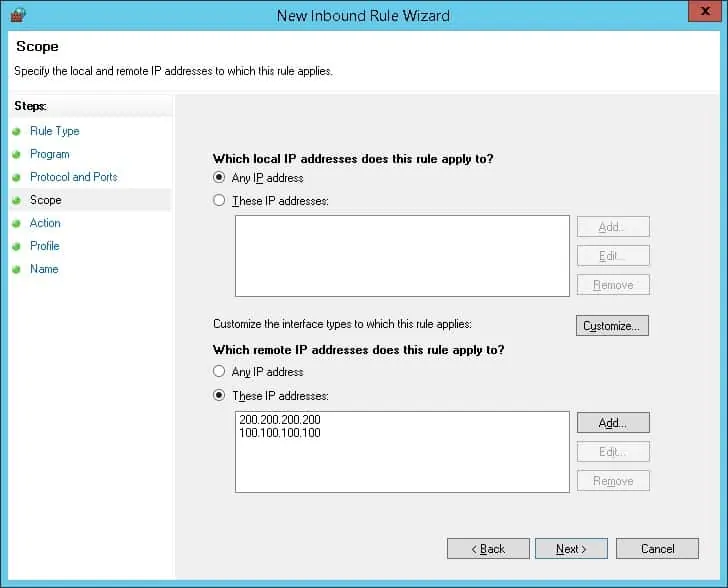
Select the option to allow the connection.
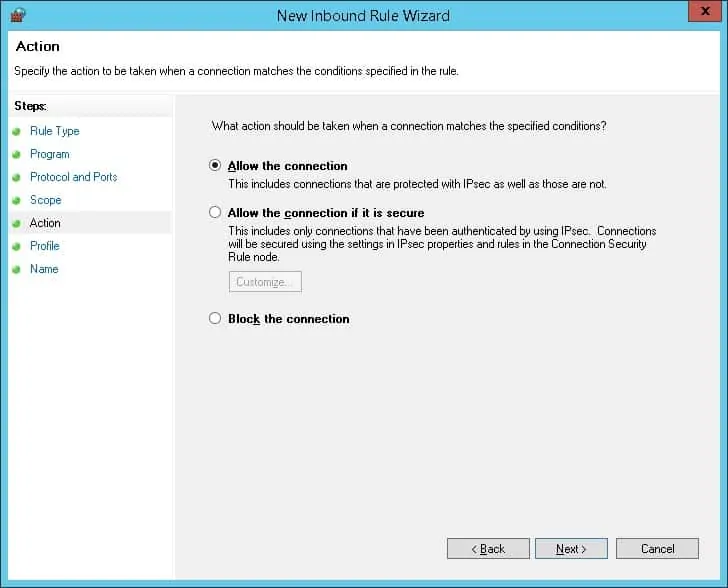
Select the desired network profile and click on the Next button.
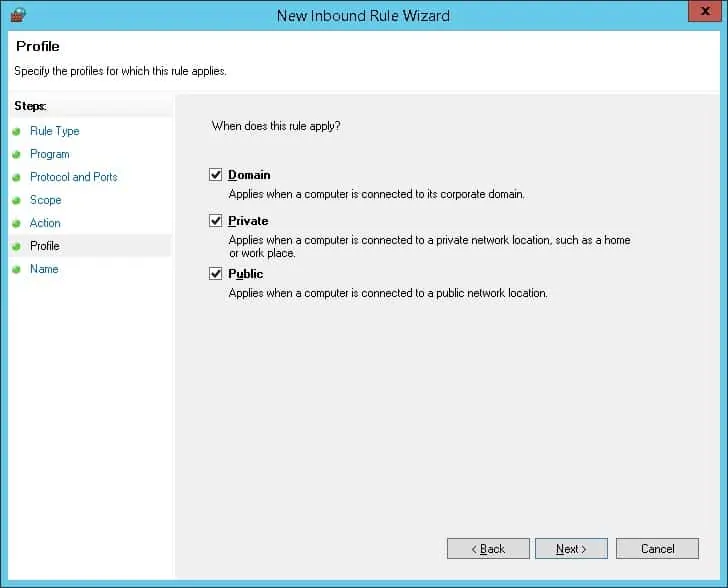
Enter a name to identify the new inbound rule.
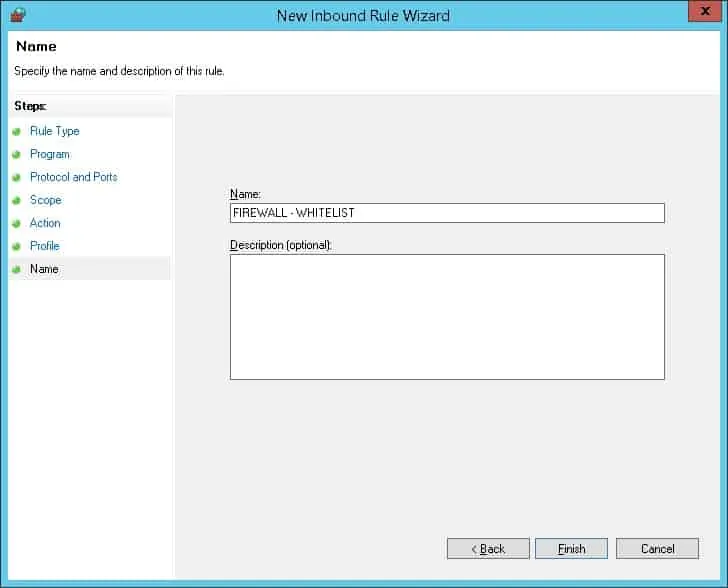
Click on the Finish button.
To save the group policy configuration, you need to close the Group Policy editor.
Congratulations! You have finished the creation of an Inbound rule using a GPO.
Tutorial GPO – Enable the Windows firewall
On the Group policy management screen, you need to right-click the Organizational Unit desired and select the option to link an existent GPO.
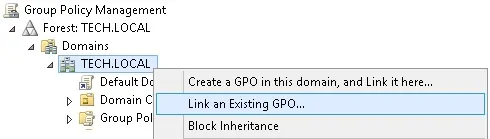
In our example, we are going to link the group policy named MY-GPO to the root of the domain.
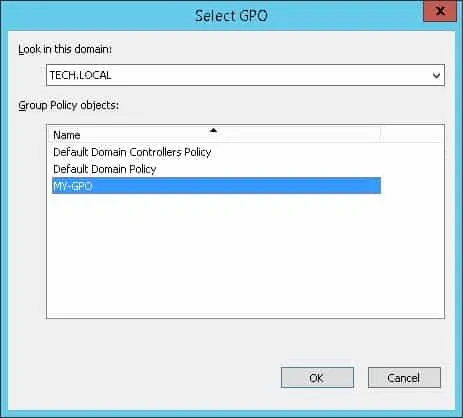
After applying the GPO you need to wait for 10 or 20 minutes.
During this time the GPO will be replicated to other domain controllers.
In our example, we used a GPO to enable and configure the Windows firewall.
VirtualCoin CISSP, PMP, CCNP, MCSE, LPIC22020-12-22T13:50:48-03:00
Related Posts
Page load link
