In this guide, you will learn how to share a folder between Windows guest, running under a Linux host – such as Fedora, Ubuntu or Linux Mint using KVM.
The virt-manager application (with libvirt) and packages provide a flexible set of tools to manage virtual machines in Linux. It is free and open-source and used for KVM virtual machines and other hypervisors.
In the prior article, I explained how to share folders between a Linux guest and a Linux host. However, when you are trying to create a shared folder using Windows Guest and Linux host, it’s a little difficult and complex process. Because both the operating system works differently and a lot of configuration is needed.
Follow the below instructions as mentioned to share the folder between Windows guest and Linux host.
A note about virtiofs
The sharing files and folders are powered by the libvirt shared file system called virtiofs. It provides all the features and parameters to access the directory tree on the host machine. Since most of the virt-manager virtual machine configurations are translated to XML, the share files/folders can also be specified by the XML file.
Note: If you are looking for file sharing using KVM between two Linux machines (guest and host), read this article.
The following instructions assume that you have installed Windows in virt-manager in any Linux host. If not, you can read this complete guide on how to install Windows in Linux.
Set up a mount tag in virt-manager
- First, make sure your guest virtual machine is powered off. From the virt-manager GUI, select the virtual machine and click on Open to pull up the console settings.
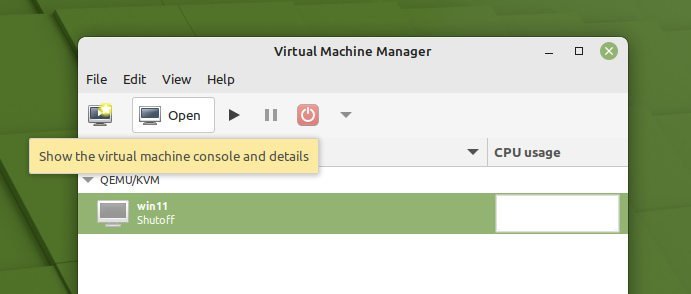
- Click on the icon which says show virtual hardware details in the toolbar. And then click on Memory on the left panel.
- Select the option “Enable shared memory“. Click Apply.
- Make sure the XML shows “access mode=shared” as below in the XML tab.
<memoryBacking>
<source type="memfd"/>
<access mode="shared"/>
</memoryBacking>

- Click “Add hardware” at the bottom.
- Select File system from the left panel in the add new hardware window.
- Then select Driver=virtiofs in the details tab. Click on
browse > browse localand select the host path from your Linux system. - In the target path, mention any name you want. It’s just a file tag which will be used during mount. This name in the target path will be mounted as Drive in Windows – My PC in Explorer.
- I have added “linux_pictures” as the target mount tag.
- So, if I want to access the Pictures folder (
/home/debugpoint/Pictures), sample settings could be the following: - Click Finish.

The XML settings are below for the above configuration. You can find it in the XML tab.
<filesystem type="mount" accessmode="passthrough"> <driver type="virtiofs"/> <source dir="/home/debugpoint/Pictures"/> <target dir="linux_pictures"/> <address type="pci" domain="0x0000" bus="0x05" slot="0x00" function="0x0"/> </filesystem>
In the main virt-manager window, right-click on the Windows virtual machine and click Run to start the virtual machine. Make sure to click on the “show the graphical console” (monitor icon in the toolbar) – if the VM is not showing.
Set up WinFSP – FUSE for Windows
Make sure Windows virtual machine (guest) is running.
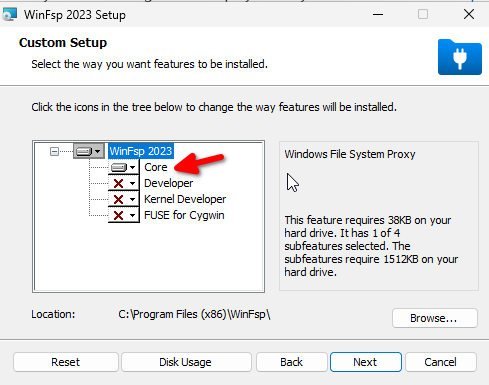
- First, we need to set up the WinFSP or Windows File System Proxy – FUSE for Windows. This enables you to mount any UNIX-like filesystem without any difficulties.
- Open the below page in the WinFSP GitHub from the guest Windows machine.
- Download the WinFSP .msi installer.
- Install the package on Windows virtual machine. Make sure to select “Core” while installing the package. Finish the installation.
Create VirtIO-FS as a service
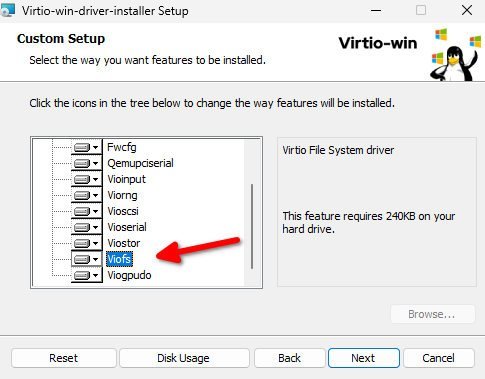
- Download the virtio-win-guest-tools.exe from the below path by going inside stable-virtio folder.

- Install the package on Windows virtual machine.
- After installation is complete, reboot Windows virtual machine.
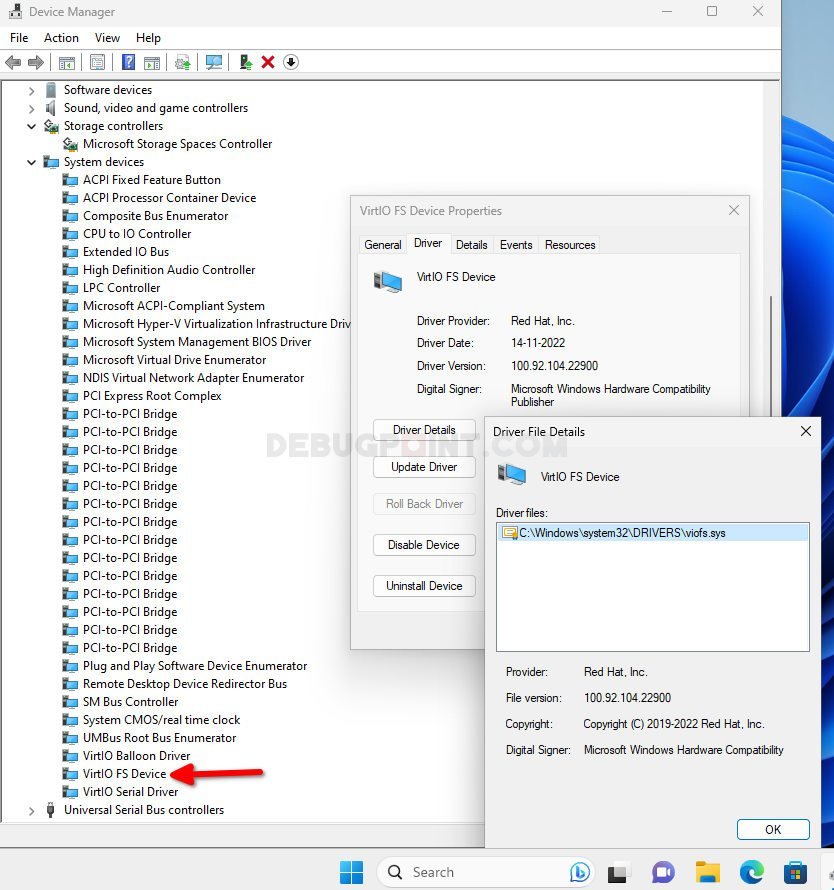
- After reboot, open the “Device Manager” by searching in the start menu.
- Navigate to System devices and look for “VirtIO FS Device”. It should be recognized and driver should be signed by Red Hat.
- Note: (optional) If you see an exclamation mark i.e. driver is not detected, then follow the instructions here on how to download ISO file, mount it and manually detect the driver.
- Open the start menu and search for “Services”.
- Scroll down to find out the “VirtIO-FS Service”. Right-click and hit Start to start the service.
- (Optional) If you want to start the service each time you boot Windows guest, then set VirtIO-Sevice-FS > Properties > Startup type > Manual to Automatic
- Alternatively, you can run the below command from PowerShell/command prompt as admin to start the service.
sc create VirtioFsSvc binpath="C:\Program Files\Virtio-Win\VioFS\virtiofs.exe" start=auto depend="WinFsp.Launcher/VirtioFsDrv" DisplayName="Virtio FS Service"
sc start VirtioFsSvc

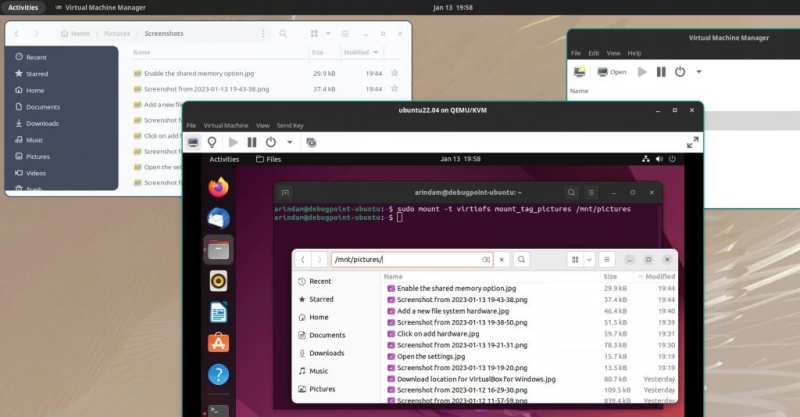
- After the service start, open Explorer, and you should see the mount tag which you have created in the first step above, which should be mapped as Z drive. See below.
- You can now access the entire Linux folder with modified permission as per your need.

Here is a side-by-side comparison of the same folder accessed in Linux Mint and Windows guest.

Conclusion
I hope you can now able to share a folder between Windows guest and Linux host system. The above method is tested in Linux Mint for this article. It should work for Ubuntu, Fedora as well.
If the above method works, drop a comment below for the benefit of others.
References
- https://virtio-fs.gitlab.io/howto-windows.html
- https://docs.fedoraproject.org/en-US/quick-docs/creating-windows-virtual-machines-using-virtio-drivers/
- https://github.com/virtio-win/virtio-win-pkg-scripts/blob/master/README.md
- https://github.com/virtio-win/kvm-guest-drivers-windows/issues/473
Приложение или пакет virt-manager использует библиотеку libvirt для предоставления услуг управления виртуальными машинами. Оно имеет интерфейс рабочего стола, который помогает создавать, удалять и управлять несколькими виртуальными машинами.
Интерфейс рабочего стола virt-manager и его компоненты предоставляют гибкое управление виртуальными машинами для различных случаев использования. Это бесплатное приложение с открытым исходным кодом, используемое в основном для виртуальных машин KVM. Однако оно может поддерживать и другие гипервизоры, такие как Xen и LXC.
Замечание о virtiofs
Общий доступ к файлам и папкам обеспечивается общей файловой системой libvirt под названием virtiofs. Она предоставляет все возможности и параметры для доступа к дереву каталогов на хост-машине. Поскольку большинство конфигураций виртуальных машин virt-manager переведены в XML, общие файлы/папки также могут быть заданы XML-файлом.
Интересно: Релиз Incus 6.2 Container — менеджера виртуальных машин
Общая папка в virt-manager
<filesystem type="mount" accessmode="passthrough"> <driver type="virtiofs"/> <binary path="/usr/libexec/virtiofsd"/> <source dir="/home/debugpoint/Pictures/Screenshots"/> <target dir="mount_tag_pictures"/> <alias name="fs1"/> <address type="pci" domain="0x0000" bus="0x08" slot="0x00" function="0x0"/> </filesystem>
Нажмите кнопку Готово. В главном окне virt-manager щелкните правой кнопкой мыши на виртуальной машине и нажмите Run, чтобы запустить виртуальную машину. Не забудьте нажать на «показать графическую консоль» (значок монитора на панели инструментов – если ВМ не отображается.
В гостевой машине создайте папку, в которую вы хотите смонтировать папку хоста. Для этого примера я использовал /mnt/pictures.
sudo mkdir /mnt/pictures
И, наконец, смонтируйте папку хоста с помощью метки, созданной в предыдущем шаге, в эту новую папку. Используйте следующую команду для этого. Убедитесь, что имя тега и папки в приведенной ниже команде соответствует вашей системе.
sudo mount -t virtiofs mount_tag_pictures /mnt/pictures
Теперь вы можете просматривать папки и добавлять/удалять элементы без проблем в virt-manager между хостом и гостем.
Подведение итогов
Надеюсь, это решение поможет вам получить доступ к файлам и папкам хоста с гостевой машины. Помните, что ваш идентификатор пользователя, который используется для запуска приложения virt-manager, должен иметь такой же доступ к папке хоста.
Skip to content
Sharing data between guest and host system is necessary in many scenarios. If the guest is a Linux system, you can simply add a shared folder that will be automatically mounted. However, this does not work if the guest is Windows. Sometimes, you can simply workaround it by using Samba shares, but in some scenarios network configuration makes it difficult. For example, when using usermode networking, the host machine can’t communicate easily via the network with the guest.
However, there is another way to share folders in virt-manager that actually works for Windows guest – SPICE . The first step is to configure the sharing in virt-manager. In the VM details view, click on “Add Hardware” and select a “Channel” device. Set the new device name to org.spice-space.webdav.0 and leave the other fields as-is.
Now start the guest machine and install spice-webdav on the guest machine. After installing spice-webdav make sure the “Spice webdav proxy” service is actually running (via services.msc).
Now running C:\Program File\SPICE webdavd\map-drive.bat will map the shared folder, which is by default ~/Public. If you encounter the following error
System error 67 has occurred.
the network name cannot be foundIt means that the Spice webdav proxy service is not running.
If you want to change the shared folder, you will have to use virt-viewer instead of virt-manager, and configure it under File->Preferences.
Provide feedback
Saved searches
Use saved searches to filter your results more quickly
Sign up
Virt-Manager Shared Folders for Windows Guests
Virt-Manager is a powerful tool for managing virtual machines (VMs). It allows you to create, start, stop, and delete VMs, as well as manage their resources, such as CPU, memory, and storage. One of the most useful features of Virt-Manager is the ability to share folders between a host machine and a VM. This can be a great way to access files on the host machine from within the VM, or to share files between multiple VMs.
In this article, we will show you how to share a folder between a host machine running Linux and a Windows guest VM using Virt-Manager. We will also provide some tips on how to troubleshoot common problems.
Prerequisites
To follow along with this tutorial, you will need the following:
- A Linux host machine with Virt-Manager installed
- A Windows guest VM
- A shared folder on the host machine that you want to access from the VM
Step 1: Create a Shared Folder on the Host Machine
The first step is to create a shared folder on the host machine. To do this, open a terminal window and run the following command:
sudo mkdir /mnt/shared
This will create a new folder called `/mnt/shared` on the host machine. You can use any name you want for the folder.
Step 2: Enable Shared Folders in Virt-Manager
Once you have created the shared folder on the host machine, you need to enable shared folders in Virt-Manager. To do this, open Virt-Manager and select the VM you want to share folders with. Then, click the Edit button and select the Options tab.
In the Options tab, click the Shared Folders button. This will open the Shared Folders dialog box.
In the Shared Folders dialog box, click the Add button. This will open the Add Shared Folder dialog box.
In the Add Shared Folder dialog box, enter the following information:
- Name: The name of the shared folder. This will be the name that you use to access the shared folder from within the VM.
- Path: The path to the shared folder on the host machine.
- Mode: The mode of the shared folder. You can choose between Read-only and Read-write.
Once you have entered all of the information, click the OK button. The shared folder will be added to the list of shared folders.
Step 3: Connect to the Shared Folder from the VM
Once you have enabled shared folders in Virt-Manager, you can connect to the shared folder from the VM. To do this, open a terminal window in the VM and run the following command:
mount -t cifs /// /mnt/shared -o username=,password=
Replace « with the IP address of the host machine, and replace « with the name of the shared folder. You will also need to provide the username and password for the user account that you used to create the shared folder.
Once you have run this command, the shared folder will be mounted on the VM. You can access the shared folder by using the `/mnt/shared` path.
| Column 1 | Column 2 | Column 3 |
|---|---|---|
| Title | Description | Link |
| How to share a folder with a Windows guest in Virt-Manager | This article explains how to share a folder from your host machine with a Windows guest virtual machine in Virt-Manager. | How to share a folder with a Windows guest in Virt-Manager |
| Troubleshooting shared folders in Virt-Manager | This article provides troubleshooting tips for shared folders in Virt-Manager. | Troubleshooting shared folders in Virt-Manager |
Overview of virt-manager shared folders
Virt-manager is a graphical user interface (GUI) for managing virtual machines (VMs) on Linux. It allows you to create, start, stop, and delete VMs, as well as manage their resources, such as memory, CPU, and storage.
Shared folders allow you to share files and folders between a host machine and a guest machine. This can be useful for transferring files between the two machines, or for providing access to shared resources, such as a printer or a database.
To create a shared folder in virt-manager, you must first create a VM. Then, open the VM’s settings and click on the “Shared Folders” tab. Click on the “Add” button and select the folder that you want to share. You can then choose whether to make the folder read-only or read-write, and whether to allow the guest machine to create new files in the folder.
To access a shared folder from a Windows guest, you must first mount the folder. To do this, open the File Explorer and click on the “This PC” icon. Then, click on the “Map network drive” button and select the shared folder. You will be prompted to enter the username and password of the user account that you are using on the host machine.
Once the folder is mounted, you can access it like any other folder on your computer. You can open files, create new files, and delete files.
Prerequisites for shared folders
In order to use shared folders with virt-manager, the following prerequisites must be met:
- The host machine must be running Linux.
- The guest machine must be running Windows.
- The host machine and the guest machine must be on the same network.
Creating a shared folder in virt-manager
To create a shared folder in virt-manager, follow these steps:
1. Open virt-manager.
2. Click on the “File” menu and select “New Virtual Machine”.
3. Follow the instructions to create a new VM.
4. Open the VM’s settings and click on the “Shared Folders” tab.
5. Click on the “Add” button and select the folder that you want to share.
6. Choose whether to make the folder read-only or read-write, and whether to allow the guest machine to create new files in the folder.
7. Click on the “OK” button.
The shared folder will now be available to the guest machine.
Accessing a shared folder from a Windows guest
To access a shared folder from a Windows guest, follow these steps:
1. Open the File Explorer.
2. Click on the “This PC” icon.
3. Click on the “Map network drive” button.
4. Enter the following information:
- Drive letter: The drive letter that you want to use for the shared folder.
- Folder path: The path to the shared folder on the host machine.
- Username: The username of the user account that you are using on the host machine.
- Password: The password for the user account that you are using on the host machine.
5. Click on the “OK” button.
The shared folder will now be mounted on the guest machine. You can access it like any other folder on your computer.
Shared folders can be a useful way to share files and folders between a host machine and a guest machine. By following the steps in this guide, you can easily create and access shared folders in virt-manager.
Steps to create a shared folder
To create a shared folder, follow these steps:
1. Open the Virt-Manager application.
2. Click the File menu and select New.
3. In the New VM window, select Install from ISO image.
4. Click the Browse button and select the ISO image of the operating system you want to install.
5. Click the Next button.
6. In the Name field, enter a name for the virtual machine.
7. In the Memory field, enter the amount of RAM you want to allocate to the virtual machine.
8. In the CPU field, enter the number of CPUs you want to allocate to the virtual machine.
9. Click the Next button.
10. In the Storage section, click the Add button.
11. In the Storage Device window, select Disk.
12. Click the Next button.
13. In the Disk Type field, select IDE.
14. In the Disk Device field, select VirtIO Disk.
15. Click the Next button.
16. In the Storage Location field, select the location where you want to store the virtual machine’s disk image.
17. Click the Next button.
18. In the Format section, select the Format you want to use for the virtual machine’s disk image.
19. Click the Next button.
20. In the Provisioning section, select the Provisioning method you want to use for the virtual machine’s disk image.
21. Click the Next button.
22. In the Networking section, click the Add button.
23. In the Network Device window, select Bridged Network.
24. Click the Next button.
25. In the Options section, you can configure additional settings for the virtual machine.
26. Click the Finish button.
The virtual machine will now be created and started. You can access the shared folder by opening the File menu in the virtual machine and selecting Shared Folders.
To open virt-manager, follow these steps:
1. Open the Activities overview.
2. Type virt-manager in the search bar.
3. Click the virt-manager icon to open the application.
Q: How do I share a folder from my host machine to a Windows guest in Virt-Manager?
A: To share a folder from your host machine to a Windows guest in Virt-Manager, follow these steps:
1. Open Virt-Manager and select the Windows guest machine.
2. Click the Edit button in the toolbar.
3. Click the Storage tab.
4. Click the Add button and select Folder.
5. In the Source field, select the folder on your host machine that you want to share.
6. In the Target field, enter the path to the folder on the Windows guest where you want to share the folder.
7. Click the OK button.
The folder will now be shared from your host machine to the Windows guest. You can access the shared folder from the Windows guest by opening the File Explorer and navigating to the Network location.
Q: How do I mount a shared folder from a Windows host to a Linux guest in Virt-Manager?
A: To mount a shared folder from a Windows host to a Linux guest in Virt-Manager, follow these steps:
1. Open Virt-Manager and select the Linux guest machine.
2. Click the Edit button in the toolbar.
3. Click the Storage tab.
4. Click the Add button and select Disk.
5. In the Source field, select the VirtIO SCSI device.
6. In the Target field, enter the path to the shared folder on the Windows host.
7. Click the OK button.
The shared folder will now be mounted as a disk device on the Linux guest. You can access the shared folder by opening the File Manager and navigating to the /mnt/ directory.
Q: How do I change the permissions on a shared folder in Virt-Manager?
A: To change the permissions on a shared folder in Virt-Manager, follow these steps:
1. Open Virt-Manager and select the Windows guest machine.
2. Click the Edit button in the toolbar.
3. Click the Storage tab.
4. Click the Shared Folders tab.
5. Select the shared folder that you want to change the permissions on.
6. Click the Permissions button.
7. Change the permissions as desired.
8. Click the OK button.
The permissions on the shared folder will be changed.
Q: How do I delete a shared folder in Virt-Manager?
A: To delete a shared folder in Virt-Manager, follow these steps:
1. Open Virt-Manager and select the Windows guest machine.
2. Click the Edit button in the toolbar.
3. Click the Storage tab.
4. Click the Shared Folders tab.
5. Select the shared folder that you want to delete.
6. Click the Delete button.
The shared folder will be deleted.
In this blog post, we discussed how to set up a shared folder between a Virt-Manager host and a Windows guest. We covered the steps involved in creating the shared folder on the host, adding the guest to the shared folder, and mounting the shared folder on the guest. We also provided some troubleshooting tips in case you encounter any problems.
We hope that this blog post has been helpful. If you have any questions or feedback, please feel free to leave a comment below.
Here are some key takeaways from this blog post:
- To create a shared folder on the host, you need to create a directory and give it the appropriate permissions.
- To add the guest to the shared folder, you need to add the guest’s IP address to the list of allowed hosts.
- To mount the shared folder on the guest, you need to use the \\\ path.
- If you encounter any problems, you can try troubleshooting the following:
- Make sure that the host and guest are on the same network.
- Make sure that the shared folder is accessible from the host.
- Make sure that the guest’s IP address is correct.
Author Profile
-
Hatch, established in 2011 by Marcus Greenwood, has evolved significantly over the years. Marcus, a seasoned developer, brought a rich background in developing both B2B and consumer software for a diverse range of organizations, including hedge funds and web agencies.
Originally, Hatch was designed to seamlessly merge content management with social networking. We observed that social functionalities were often an afterthought in CMS-driven websites and set out to change that. Hatch was built to be inherently social, ensuring a fully integrated experience for users.
Now, Hatch embarks on a new chapter. While our past was rooted in bridging technical gaps and fostering open-source collaboration, our present and future are focused on unraveling mysteries and answering a myriad of questions. We have expanded our horizons to cover an extensive array of topics and inquiries, delving into the unknown and the unexplored.
