OpenCV Bootcamp
Before you begin your journey into the exciting world of Computer Vision, Deep Learning, and AI, you need to become an expert at using the world’s largest resource of Computer Vision, the OpenCV library. This free OpenCV course will teach you how to manipulate images and videos, and detect objects and faces, among other exciting topics in just about 3 hours.
Enroll for Free
Get Started With OpenCV in Just 3 Hours!
Join 100K+ learners who trust OpenCV.
Dive into the world of Computer Vision, Deep Learning, and AI with OpenCV – the most powerful library for image and video processing. In just 3 hours, this free course will teach you how to transform images, detect faces and objects, and unlock new possibilities in tech.
Get Instant Access.
No spam. Unsubscribe anytime.
Installation
Select your preferences and run the install command.
Language:
Python
C++
Java
Android
iOS
JavaScript
Run this Command:
Default Result: pip3 install opencv-python
Verification
To ensure that OpenCV is installed correctly, we can run the following example to show how to read and display image
Python
Change path/to/image to a real path of an image, then run this demo
import cv2 as cv
img = cv.imread("path/to/image")
cv.imshow("Display window", img)
k = cv.waitKey(0) # Wait for a keystroke in the window
C++
Change path/to/image to a real path of an image, then build this demo with OpenCV package and run it
#include
#include
using namespace cv;
int main()
{
std::string image_path = "path/to/image";
Mat img = imread(image_path, IMREAD_COLOR);
imshow("Display window", img);
int k = waitKey(0); // Wait for a keystroke in the window
return 0;
}
JavaScript
Copy this code into an html file and open it in your web browser
Hello OpenCV.js
Hello OpenCV.js
OpenCV.js is loading...
imageSrc
canvasOutput
let imgElement = document.getElementById('imageSrc');
let inputElement = document.getElementById('fileInput');
inputElement.addEventListener('change', (e) => {
imgElement.src = URL.createObjectURL(e.target.files[0]);
}, false);
imgElement.onload = function () {
let mat = cv.imread(imgElement);
cv.imshow('canvasOutput', mat);
mat.delete();
};
var Module = {
// https://emscripten.org/docs/api_reference/module.html#Module.onRuntimeInitialized
onRuntimeInitialized() {
document.getElementById('status').innerHTML = 'OpenCV.js is ready.';
}
};
Last Updated :
07 Aug, 2024
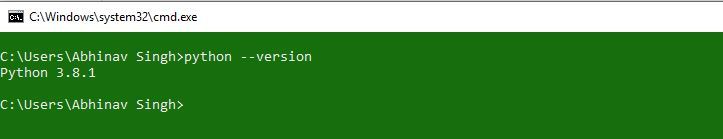
Prerequisite: Python Language Introduction OpenCV is the huge open-source library for computer vision, machine learning, and image processing and now it plays a major role in real-time operation which is very important in today’s systems. By using it, one can process images and videos to identify objects, faces, or even the handwriting of a human. When it integrated with various libraries, such as Numpy, python is capable of processing the OpenCV array structure for analysis. To Identify image patterns and its various features we use vector space and perform mathematical operations on these features. To install OpenCV, one must have Python and PIP, preinstalled on their system. To check if your system already contains Python, go through the following instructions: Open the Command line(search for cmd in the Run dialog( + R). Now run the following command:
python --version
If Python is already installed, it will generate a message with the Python version available.
If Python is not present, go through How to install Python on Windows? and follow the instructions provided. PIP is a package management system used to install and manage software packages/libraries written in Python. These files are stored in a large “on-line repository” termed as Python Package Index (PyPI). To check if PIP is already installed on your system, just go to the command line and execute the following command:
pip -V
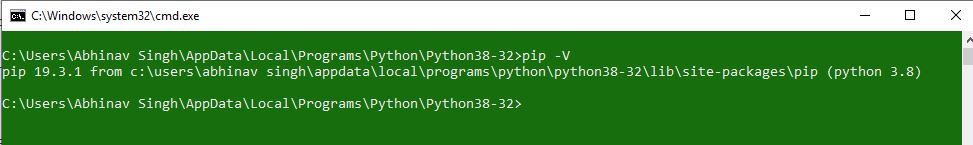
If PIP is not present, go through How to install PIP on Windows? and follow the instructions provided.
Downloading and Installing OpenCV:
OpenCV can be directly downloaded and installed with the use of pip (package manager). To install OpenCV, just go to the command-line and type the following command:
pip install opencv-python
Beginning with the installation:
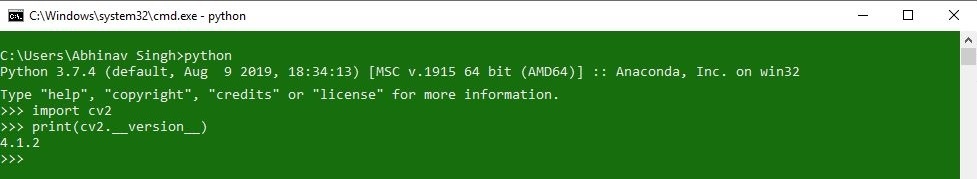
To check if OpenCV is correctly installed, just run the following commands to perform a version check:
python
>>>import cv2
>>>print(cv2.__version__)
В статье разберем, как установить библиотеку OpenCV на компьютеры с операционной системой Windows и MacOS.
Установка OpenCV на компьютер с ОС Windows
- Установить Python со встроенными библиотеками.
- После установки Python нажимаем на комбинацию кнопок Win+R. В открывшемся окне нужно прописать:
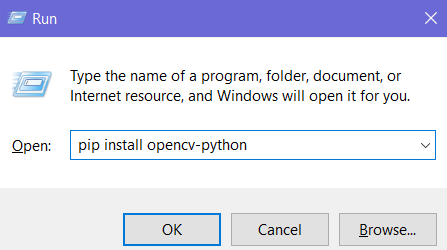
Начнётся скачивание и установка:
Готово! Библиотека OpenCV установлена на ваш Windows-компьютер.
Для установки OpenCV на компьютер с ОС Linux вводим такую же команду.
Установка OpenCV на MacOS
- Установить Python со встроенными библиотеками для своей операционной системы.
Если у Вас уже установлен Python, рекомендуем переустановить и обязательно поставить галочку у пункта «добавить в PATH».
2. Открываем терминал и пишем туда несколько команд:
pip install --upgrade pip
pip install opencv-pythonПосле ввода произойдёт скачивание и установка.
Проверка установки
Для проверки откроем Python и напишем:
Если ошибок нет, значит, OpenCV установился.
Курсы Робикс, в которых изучается этот материал.
- Duckietown: робот с системой Автопилота
Keep OpenCV Free
OpenCV is raising funds to keep the library free for everyone, and we need the support of the entire community to do it. Donate to OpenCV on Github to show your support.
- OpenCV on Wheels
- Installation and Usage
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Documentation for opencv-python
- CI build process
- Manual builds
- Manual debug builds
- Source distributions
- Licensing
- Versioning
- Releases
- Development builds
- Manylinux wheels
- Supported Python versions
- Backward compatibility
OpenCV on Wheels
Pre-built CPU-only OpenCV packages for Python.
Check the manual build section if you wish to compile the bindings from source to enable additional modules such as CUDA.
Installation and Usage
-
If you have previous/other manually installed (= not installed via
pip) version of OpenCV installed (e.g. cv2 module in the root of Python’s site-packages), remove it before installation to avoid conflicts. -
Make sure that your
pipversion is up-to-date (19.3 is the minimum supported version):pip install --upgrade pip. Check version withpip -V. For example Linux distributions ship usually with very oldpipversions which cause a lot of unexpected problems especially with themanylinuxformat. -
Select the correct package for your environment:
There are four different packages (see options 1, 2, 3 and 4 below) and you should SELECT ONLY ONE OF THEM. Do not install multiple different packages in the same environment. There is no plugin architecture: all the packages use the same namespace (
cv2). If you installed multiple different packages in the same environment, uninstall them all withpip uninstalland reinstall only one package.a. Packages for standard desktop environments (Windows, macOS, almost any GNU/Linux distribution)
- Option 1 — Main modules package:
pip install opencv-python - Option 2 — Full package (contains both main modules and contrib/extra modules):
pip install opencv-contrib-python(check contrib/extra modules listing from OpenCV documentation)
b. Packages for server (headless) environments (such as Docker, cloud environments etc.), no GUI library dependencies
These packages are smaller than the two other packages above because they do not contain any GUI functionality (not compiled with Qt / other GUI components). This means that the packages avoid a heavy dependency chain to X11 libraries and you will have for example smaller Docker images as a result. You should always use these packages if you do not use
cv2.imshowet al. or you are using some other package (such as PyQt) than OpenCV to create your GUI.- Option 3 — Headless main modules package:
pip install opencv-python-headless - Option 4 — Headless full package (contains both main modules and contrib/extra modules):
pip install opencv-contrib-python-headless(check contrib/extra modules listing from OpenCV documentation)
- Option 1 — Main modules package:
-
Import the package:
import cv2All packages contain Haar cascade files.
cv2.data.haarcascadescan be used as a shortcut to the data folder. For example:cv2.CascadeClassifier(cv2.data.haarcascades + "haarcascade_frontalface_default.xml") -
Read OpenCV documentation
-
Before opening a new issue, read the FAQ below and have a look at the other issues which are already open.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: Do I need to install also OpenCV separately?
A: No, the packages are special wheel binary packages and they already contain statically built OpenCV binaries.
Q: Pip install fails with ModuleNotFoundError: No module named 'skbuild'?
Since opencv-python version 4.3.0.*, manylinux1 wheels were replaced by manylinux2014 wheels. If your pip is too old, it will try to use the new source distribution introduced in 4.3.0.38 to manually build OpenCV because it does not know how to install manylinux2014 wheels. However, source build will also fail because of too old pip because it does not understand build dependencies in pyproject.toml. To use the new manylinux2014 pre-built wheels (or to build from source), your pip version must be >= 19.3. Please upgrade pip with pip install --upgrade pip.
Q: Import fails on Windows: ImportError: DLL load failed: The specified module could not be found.?
A: If the import fails on Windows, make sure you have Visual C++ redistributable 2015 installed. If you are using older Windows version than Windows 10 and latest system updates are not installed, Universal C Runtime might be also required.
Windows N and KN editions do not include Media Feature Pack which is required by OpenCV. If you are using Windows N or KN edition, please install also Windows Media Feature Pack.
If you have Windows Server 2012+, media DLLs are probably missing too; please install the Feature called «Media Foundation» in the Server Manager. Beware, some posts advise to install «Windows Server Essentials Media Pack», but this one requires the «Windows Server Essentials Experience» role, and this role will deeply affect your Windows Server configuration (by enforcing active directory integration etc.); so just installing the «Media Foundation» should be a safer choice.
If the above does not help, check if you are using Anaconda. Old Anaconda versions have a bug which causes the error, see this issue for a manual fix.
If you still encounter the error after you have checked all the previous solutions, download Dependencies and open the cv2.pyd (located usually at C:\Users\username\AppData\Local\Programs\Python\PythonXX\Lib\site-packages\cv2) file with it to debug missing DLL issues.
Q: I have some other import errors?
A: Make sure you have removed old manual installations of OpenCV Python bindings (cv2.so or cv2.pyd in site-packages).
Q: Function foo() or method bar() returns wrong result, throws exception or crashes interpreter. What should I do?
A: The repository contains only OpenCV-Python package build scripts, but not OpenCV itself. Python bindings for OpenCV are developed in official OpenCV repository and it’s the best place to report issues. Also please check OpenCV wiki and the official OpenCV forum before file new bugs.
Q: Why the packages do not include non-free algorithms?
A: Non-free algorithms such as SURF are not included in these packages because they are patented / non-free and therefore cannot be distributed as built binaries. Note that SIFT is included in the builds due to patent expiration since OpenCV versions 4.3.0 and 3.4.10. See this issue for more info: https://github.com/skvark/opencv-python/issues/126
Q: Why the package and import are different (opencv-python vs. cv2)?
A: It’s easier for users to understand opencv-python than cv2 and it makes it easier to find the package with search engines. cv2 (old interface in old OpenCV versions was named as cv) is the name that OpenCV developers chose when they created the binding generators. This is kept as the import name to be consistent with different kind of tutorials around the internet. Changing the import name or behaviour would be also confusing to experienced users who are accustomed to the import cv2.
Documentation for opencv-python
The aim of this repository is to provide means to package each new OpenCV release for the most used Python versions and platforms.
CI build process
The project is structured like a normal Python package with a standard setup.py file.
The build process for a single entry in the build matrices is as follows (see for example .github/workflows/build_wheels_linux.yml file):
-
In Linux and MacOS build: get OpenCV’s optional C dependencies that we compile against
-
Checkout repository and submodules
- OpenCV is included as submodule and the version is updated
manually by maintainers when a new OpenCV release has been made - Contrib modules are also included as a submodule
- OpenCV is included as submodule and the version is updated
-
Find OpenCV version from the sources
-
Build OpenCV
- tests are disabled, otherwise build time increases too much
- there are 4 build matrix entries for each build combination: with and without contrib modules, with and without GUI (headless)
- Linux builds run in manylinux Docker containers (CentOS 5)
- source distributions are separate entries in the build matrix
-
Rearrange OpenCV’s build result, add our custom files and generate wheel
-
Linux and macOS wheels are transformed with auditwheel and delocate, correspondingly
-
Install the generated wheel
-
Test that Python can import the library and run some sanity checks
-
Use twine to upload the generated wheel to PyPI (only in release builds)
Steps 1—4 are handled by pip wheel.
The build can be customized with environment variables. In addition to any variables that OpenCV’s build accepts, we recognize:
CI_BUILD. Set to1to emulate the CI environment build behaviour. Used only in CI builds to force certain build flags on insetup.py. Do not use this unless you know what you are doing.ENABLE_CONTRIBandENABLE_HEADLESS. Set to1to build the contrib and/or headless versionENABLE_JAVA, Set to1to enable the Java client build. This is disabled by default.CMAKE_ARGS. Additional arguments for OpenCV’s CMake invocation. You can use this to make a custom build.
See the next section for more info about manual builds outside the CI environment.
Manual builds
If some dependency is not enabled in the pre-built wheels, you can also run the build locally to create a custom wheel.
- Clone this repository:
git clone --recursive https://github.com/opencv/opencv-python.git cd opencv-python- you can use
gitto checkout some other version of OpenCV in theopencvandopencv_contribsubmodules if needed
- you can use
- Add custom Cmake flags if needed, for example:
export CMAKE_ARGS="-DSOME_FLAG=ON -DSOME_OTHER_FLAG=OFF"(in Windows you need to set environment variables differently depending on Command Line or PowerShell) - Select the package flavor which you wish to build with
ENABLE_CONTRIBandENABLE_HEADLESS: i.e.export ENABLE_CONTRIB=1if you wish to buildopencv-contrib-python - Run
pip wheel . --verbose. NOTE: make sure you have the latestpipversion, thepip wheelcommand replaces the oldpython setup.py bdist_wheelcommand which does not supportpyproject.toml.- this might take anything from 5 minutes to over 2 hours depending on your hardware
- Pip will print fresh wheel location at the end of build procedure. If you use old approach with
setup.pyfile wheel package will be placed indistfolder. Package is ready and you can do with that whatever you wish.- Optional: on Linux use some of the
manylinuximages as a build hosts if maximum portability is needed and runauditwheelfor the wheel after build - Optional: on macOS use
delocate(same asauditwheelbut for macOS) for better portability
- Optional: on Linux use some of the
Manual debug builds
In order to build opencv-python in an unoptimized debug build, you need to side-step the normal process a bit.
- Install the packages
scikit-buildandnumpyvia pip. - Run the command
python setup.py bdist_wheel --build-type=Debug. - Install the generated wheel file in the
dist/folder withpip install dist/wheelname.whl.
If you would like the build produce all compiler commands, then the following combination of flags and environment variables has been tested to work on Linux:
export CMAKE_ARGS='-DCMAKE_VERBOSE_MAKEFILE=ON'
export VERBOSE=1
python3 setup.py bdist_wheel --build-type=Debug
See this issue for more discussion: https://github.com/opencv/opencv-python/issues/424
Source distributions
Since OpenCV version 4.3.0, also source distributions are provided in PyPI. This means that if your system is not compatible with any of the wheels in PyPI, pip will attempt to build OpenCV from sources. If you need a OpenCV version which is not available in PyPI as a source distribution, please follow the manual build guidance above instead of this one.
You can also force pip to build the wheels from the source distribution. Some examples:
pip install --no-binary opencv-python opencv-pythonpip install --no-binary :all: opencv-python
If you need contrib modules or headless version, just change the package name (step 4 in the previous section is not needed). However, any additional CMake flags can be provided via environment variables as described in step 3 of the manual build section. If none are provided, OpenCV’s CMake scripts will attempt to find and enable any suitable dependencies. Headless distributions have hard coded CMake flags which disable all possible GUI dependencies.
On slow systems such as Raspberry Pi the full build may take several hours. On a 8-core Ryzen 7 3700X the build takes about 6 minutes.
Licensing
Opencv-python package (scripts in this repository) is available under MIT license.
OpenCV itself is available under Apache 2 license.
Third party package licenses are at LICENSE-3RD-PARTY.txt.
All wheels ship with FFmpeg licensed under the LGPLv2.1.
Non-headless Linux wheels ship with Qt 5 licensed under the LGPLv3.
The packages include also other binaries. Full list of licenses can be found from LICENSE-3RD-PARTY.txt.
Versioning
find_version.py script searches for the version information from OpenCV sources and appends also a revision number specific to this repository to the version string. It saves the version information to version.py file under cv2 in addition to some other flags.
Releases
A release is made and uploaded to PyPI when a new tag is pushed to master branch. These tags differentiate packages (this repo might have modifications but OpenCV version stays same) and should be incremented sequentially. In practice, release version numbers look like this:
cv_major.cv_minor.cv_revision.package_revision e.g. 3.1.0.0
The master branch follows OpenCV master branch releases. 3.4 branch follows OpenCV 3.4 bugfix releases.
Development builds
Every commit to the master branch of this repo will be built. Possible build artifacts use local version identifiers:
cv_major.cv_minor.cv_revision+git_hash_of_this_repo e.g. 3.1.0+14a8d39
These artifacts can’t be and will not be uploaded to PyPI.
Manylinux wheels
Linux wheels are built using manylinux2014. These wheels should work out of the box for most of the distros (which use GNU C standard library) out there since they are built against an old version of glibc.
The default manylinux2014 images have been extended with some OpenCV dependencies. See Docker folder for more info.
Supported Python versions
Python 3.x compatible pre-built wheels are provided for the officially supported Python versions (not in EOL):
- 3.7
- 3.8
- 3.9
- 3.10
- 3.11
- 3.12
Backward compatibility
Starting from 4.2.0 and 3.4.9 builds the macOS Travis build environment was updated to XCode 9.4. The change effectively dropped support for older than 10.13 macOS versions.
Starting from 4.3.0 and 3.4.10 builds the Linux build environment was updated from manylinux1 to manylinux2014. This dropped support for old Linux distributions.
Starting from version 4.7.0 the Mac OS GitHub Actions build environment was update to version 11. Mac OS 10.x support deprecated. See https://github.com/actions/runner-images/issues/5583
Starting from version 4.9.0 the Mac OS GitHub Actions build environment was update to version 12. Mac OS 10.x support deprecated by Brew and most of used packages.
Goals¶
- In this tutorial
-
- We will learn to setup OpenCV-Python in your Windows system.
Below steps are tested in a Windows 7-64 bit machine with Visual Studio 2010 and Visual Studio 2012. The screenshots shows VS2012.
Installing OpenCV from prebuilt binaries¶
-
Below Python packages are to be downloaded and installed to their default locations.
-
Install all packages into their default locations. Python will be installed to C:/Python27/.
-
After installation, open Python IDLE. Enter
import numpyand make sure Numpy is working fine. -
Download latest OpenCV release from sourceforge site and double-click to extract it.
-
Goto opencv/build/python/2.7 folder.
-
Copy cv2.pyd to C:/Python27/lib/site-packeges.
-
Open Python IDLE and type following codes in Python terminal.
>>> import cv2 >>> print cv2.__version__
If the results are printed out without any errors, congratulations !!! You have installed OpenCV-Python successfully.
Building OpenCV from source¶
-
Download and install Visual Studio and CMake.
-
Download and install necessary Python packages to their default locations
Note
In this case, we are using 32-bit binaries of Python packages. But if you want to use OpenCV for x64, 64-bit binaries of Python packages are to be installed. Problem is that, there is no official 64-bit binaries of Numpy. You have to build it on your own. For that, you have to use the same compiler used to build Python. When you start Python IDLE, it shows the compiler details. You can get more information here. So your system must have the same Visual Studio version and build Numpy from source.
Note
Another method to have 64-bit Python packages is to use ready-made Python distributions from third-parties like Anaconda, Enthought etc. It will be bigger in size, but will have everything you need. Everything in a single shell. You can also download 32-bit versions also.
-
Make sure Python and Numpy are working fine.
-
Download OpenCV source. It can be from Sourceforge (for official release version) or from Github (for latest source).
-
Extract it to a folder,
opencvand create a new folderbuildin it. -
Open CMake-gui (Start > All Programs > CMake-gui)
-
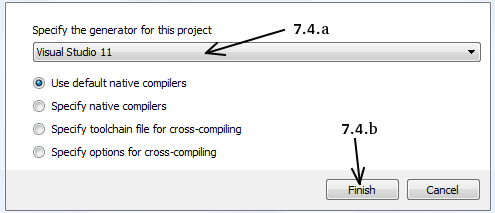
Fill the fields as follows (see the image below):
7.1. Click on Browse Source… and locate the
opencvfolder.7.2. Click on Browse Build… and locate the
buildfolder we created.7.3. Click on Configure.
7.4. It will open a new window to select the compiler. Choose appropriate compiler (here, Visual Studio 11) and click Finish.
7.5. Wait until analysis is finished.
-
You will see all the fields are marked in red. Click on the WITH field to expand it. It decides what extra features you need. So mark appropriate fields. See the below image:
-
Now click on BUILD field to expand it. First few fields configure the build method. See the below image:
-
Remaining fields specify what modules are to be built. Since GPU modules are not yet supported by OpenCV-Python, you can completely avoid it to save time (But if you work with them, keep it there). See the image below:
-
Now click on ENABLE field to expand it. Make sure ENABLE_SOLUTION_FOLDERS is unchecked (Solution folders are not supported by Visual Studio Express edition). See the image below:
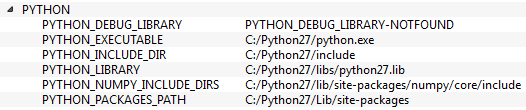
-
Also make sure that in the PYTHON field, everything is filled. (Ignore PYTHON_DEBUG_LIBRARY). See image below:
-
Finally click the Generate button.
-
Now go to our opencv/build folder. There you will find OpenCV.sln file. Open it with Visual Studio.
-
Check build mode as Release instead of Debug.
-
In the solution explorer, right-click on the Solution (or ALL_BUILD) and build it. It will take some time to finish.
-
Again, right-click on INSTALL and build it. Now OpenCV-Python will be installed.
-
Open Python IDLE and enter
import cv2. If no error, it is installed correctly.
Note
We have installed with no other support like TBB, Eigen, Qt, Documentation etc. It would be difficult to explain it here. A more detailed video will be added soon or you can just hack around.
Additional Resources¶
Exercises¶
- If you have a windows machine, compile the OpenCV from source. Do all kinds of hacks. If you meet any problem, visit OpenCV forum and explain your problem.