Looking for a way to get the user’s home directory in Java? You’re in luck! If you are new to the Java programming language and want to know how how to get a user home directory in Java then, this article is just for you. 🙂
There are several different ways to get the user’s home directory in Java, depending on your specific needs and the environment in which your Java code is running.
Before illustrating the methods of getting the user’s home directory in Java, we should have basic concepts of the user’s home directory and how we can check the current directory in the Windows command prompt. So without wasting time, let’s start the topic.
Table of Contents
- What is User Home Directory?
- How to Check the User’s Home Directory in Windows?
- 6 Ways to Get the User Home Directory in Java
- Method 1: Using File Object
- Method 2: Using Path.gets()
- Method 3: Using System.getProperty()
- Method 4: Using System.getenv()
- Method 5: Using FileSystemView.getFileSystemView().getHomeDirectory()
- Method 6: Using the Paths Class
What is User Home Directory?
A user home directory is a directory or folder commonly given to a user on an operating system. The home directory allows users to store all their personal information, data files, and user information. In the case of the Windows operating system, the user home Directory is also known as the current working directory. Most commonly Java root directory is boot drive:\Users\PC Name, for example:
C:\Users\pc
How to Check the User’s Home Directory in Windows?
Follow these steps to check the User home directory in Windows:
- Open a command prompt window (Windows button + R, type cmd and press Enter).
- Enter the command echo %homedrive% to check the drive name
- Enter the command echo %homepath% to check the drive name
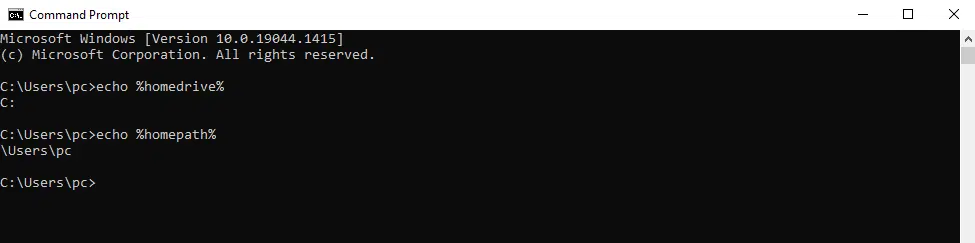
This command will return the path of the user’s home directory; in my case, this command returns:
We have the following four different ways to get the user home directory in Java:
- Using File object.
- Using Paths.get().
- Using System.getProperty().
- Using System.getenv().
- Using FileSystemView.getFileSystemView().getHomeDirectory().
- Using the Paths class.
Now explore these ways in detail one by one.
Method 1: Using File Object
File and directory names have different formats on different operating systems, so a simple string is not sufficient to name them. Here we need a File class to handle the situation. The File class contains useful methods for working with the path, renaming, creating, and deleting files. The File object represents the actual file or directory on the disk drive.
Hierarchy of File Class
java.lang.Object java.io.File
We can create an object of File Class by importing the java.io.File package first. After importing the package, we can create a File object by passing a string representing a file’s name. The general syntax of creating a File object is as follows.
File a = new File(String filepath);
To get the user home directory, we have to pass an empty string to the File object, resulting in an empty abstract pathname that always returns the current user directory. Now understand this concept with the help of an example:
Code
import java.io.File;
public class Main {
public static void main( String args[] ) {
// Create File obj with empty string
File fileObj = new File("");
// In case of an empty absolute path curDir got the Home Directory path
String curDir = fileObj.getAbsolutePath();
System.out.println("User home directory is:");
System.out.println(curDir);
}
}
Output
User home directory is: C:\Users\pc\IdeaProjects\userhomedirectory
Method 2: Using Path.gets()
Gets() is a method of the Path interface that contains static methods that return a Path by converting a path string or URI. If we pass an empty string to this method, it will return the path of the user’s home directory.
To use this method, we have to import java.nio.file.Path and java.nio.file.Paths. We use the toAbsolutePath() method to get a complete path starting from the root and show all subdirectories with file separator (/). Let’s see how it works with the help of an example:
Code
import java.io.IOException;
import java.nio.file.Path;
import java.nio.file.Paths;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
// Pass an empty string so have the user's current directory
Path mypath = Paths.get("");
// Use toabsolutepath method to get a complete path
Path currentdir = mypath.toAbsolutePath();
System.out.println("User Current Directory is: " + currentdir);
}
}
Output
User Current Directory is: C:\Users\pc\IdeaProjects\userhomedirectory
Method 3: Using System.getProperty()
This method is my favorite; it is easy and to the point. getProperty is the method of System Class if we pass the user.dir key to this method, we will get the user’s home directory. The System class provides access to system-level functions and variables, and the getProperty() method allows you to get the value of a specific system property. Here’s an example of how to use the System class and the getProperty() method to get the user’s home directory:
Code
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// calling getproperty method with user.dir key will return the current directory
String currentdir = System.getProperty("user.dir");;
System.out.println("User Current Directory is: " + currentdir);
}
}
Output
User Current Directory is: C:\Users\pc\IdeaProjects\userhomedirectory
This code uses the System.getProperty() method to get the value of the user.dir system property, which represents the user’s home directory. The currentdir variable is then used to store the value of the user.dir property.
Method 4: Using System.getenv()
One way to get the user’s home directory in a more reliable way is to use the System.getenv() method to get the value of the HOME environment variable. The HOME environment variable is usually set to the user’s home directory, and it is available on most operating systems.
We can get the user’s home directory with the help of System.getenv(). In this method, we must pass the string USERPROFILE, which will return the user’s home directory. Now understand this method with the help of an example:
Code
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// calling the getenv method with the string USERPROFILE will return the home directory
String homedir = System.getenv("USERPROFILE");
System.out.println("User Home Directory is: " + homedir);
}
}
Output
User Home Directory is: C:\Users\pc
This code uses the System.getenv() method to get the value of the USERPROFILE environment variable, and stores it in the homeDir variable.
By using the System.getProperty() method, the FileSystemView.getHomeDirectory() method, or the System.getenv() method, you can get the user’s home directory in Java. Which method you choose will depend on your specific needs and the environment in which your Java code is running. Regardless of which method you choose, you should now have a better understanding of how to get the user’s home directory in Java.
Method 5: Using FileSystemView.getFileSystemView().getHomeDirectory()
Another way to get the user’s home directory in Java is to use the FileSystemView class and the getHomeDirectory() method. The FileSystemView class provides information about the file system and its components, and the getHomeDirectory() method allows you to get the user’s home directory as a File object. Here’s an example of how to use the FileSystemView class and the getHomeDirectory() method to get the user’s home directory:
File homeDir = FileSystemView.getFileSystemView().getHomeDirectory();
This code uses the FileSystemView.getFileSystemView() method to get an instance of the ‘FileSystemView’ class, and then calls the getHomeDirectory() method on that instance to get the user’s home directory as a File object.
It’s worth noting that the getProperty() method of the System class and the getHomeDirectory() method of the FileSystemView class may not work in all environments. For example, they may not work correctly in certain types of containers, such as Docker containers, or in certain types of environments, such as Google App Engine. In these cases, you may need to use a different approach to get the user’s home directory.
Method 6: Using the Paths Class
It’s also worth noting that you can use the Paths class and the get() method to get the user’s home directory in Java. The Paths class provides utility methods for working with Path objects, and the get() method allows you to get a Path object by providing a string representation of a file or directory. Here’s an example of how to use the Paths class and the get() method to get the user’s home directory:
Path homeDir = Paths.get(System.getProperty("user.home"));
This code uses the System.getProperty() method to get the value of the user.home system property, which represents the user’s home directory, and then passes that value to the Paths.get() method to get a Path object for the user’s home directory. The homeDir variable is then used to store the Path object.
By using the Paths class and the get() method, you can get the user’s home directory as a Path object, which can be useful if you need to perform operations on the directory, such as reading or writing files.
Conclusion
To summarize the article on how to check a user home directory in Java, In this article, we have discussed four different methods to get the user home directory in Java, including File object, Path.gets(), System.getproperty(), System.getenv,FileSystemView.getFileSystemView().getHomeDirectory(), and the Paths class.
Among all these different methods the System.getProperty (user.dir) works best; no doubt other methods are also useful and used in scenarios, but getProperty() is a simple and easy way to get the job done.
In conclusion, there are several different ways to get the user’s home directory in Java, depending on your specific needs and the environment in which your Java code is running.
Let’s have a quick review of the topics discussed in this article.
- What is User Home Directory?
- How to check the user’s home directory?
- Ways to get user home directory
- How to get the user’s current directory using a File object?
- How to get the user’s current directory using Path.gets()?
- How to get the user’s current directory using System.getProperty()?
- How to get the user’s current directory using System.getenv()?
- How to get the user’s current directory using FileSystemView.getFileSystemView().getHomeDirectory()?
- How to get the user’s current directory using Paths Class?
If you’ve found this article helpful, don’t forget to share it with your coding mates, also comment below 👇 which solution has worked in your case.
Happy coding!🥳
Пройдите тест, узнайте какой профессии подходите
При разработке приложений на Java, особенно кросс-платформенных, часто возникает необходимость обнаружить домашний каталог пользователя. Причем, обнаружение
При разработке приложений на Java, особенно кросс-платформенных, часто возникает необходимость обнаружить домашний каталог пользователя. Причем, обнаружение должно работать на различных операционных системах: Windows (2000, XP, Vista), OS X, Linux и других Unix-подобных. В качестве примера можно привести приложение, которое сохраняет пользовательские настройки в домашнем каталоге пользователя.
Однако, возникает сложность. Системное свойство user.home в Java, которое обычно используется для обнаружения домашнего каталога пользователя, не работает корректно на некоторых платформах (например, на Windows XP). Это значит, что использование этого системного свойства не является универсальным решением.
Но не стоит отчаиваться, есть другой способ решения этой задачи. Для обнаружения домашнего каталога пользователя на всех платформах можно использовать следующий код:
String home = System.getProperty("user.home");
if (home == null) {
home = System.getenv("HOME");
}
В этом коде сначала пытаемся получить домашний каталог пользователя из системного свойства user.home. Если это свойство пустое (что может случиться на некоторых платформах), то в качестве «запасного» варианта используется переменная окружения HOME.
Такой подход обеспечивает кросс-платформенность и позволяет надежно обнаружить домашний каталог пользователя на большинстве платформ.
-
Get the User’s Home Directory Using the
System.getProperty()Method in Java -
Get the User’s Home Directory Using the Apache Commons IO Library in Java
-
Get the User’s Home Directory Using the
System.getenv()Method in Java -
Conclusion

In Java, obtaining the user’s home directory is a common task, especially when working with file and directory operations. There are several methods to achieve this, each with its advantages and considerations.
For a multi-user operating system, there exists a file system directory for every user; this directory is known as the user’s home directory. There are different ways to find the user home directory in Java.
In this article, we’ll explore different methods to get the user’s home directory in Java, providing detailed examples for each.
Get the User’s Home Directory Using the System.getProperty() Method in Java
The System.getProperty() method is part of the java.lang.System class, which provides access to system-specific properties.
It takes a system property name as an argument and returns the value associated with that property. In the case of the user’s home directory, the property name is "user.home".
The System.getProperty() method in Java is used to retrieve system properties. It allows you to access information about the system, such as file separator, user’s home directory, Java version, and more.
The syntax of System.getProperty() is as follows:
public static String getProperty(String key)
Here’s what each part of the syntax means:
public: This method is accessible by any class.static: ThegetProperty()method belongs to theSystemclass itself rather than an instance of the class.String: This is the return type of the method. It returns the value of the system property as a string.getProperty: This is the name of the method.(String key): This is the parameter that the method takes.keyis a string representing the name of the system property you want to retrieve.
Here’s an example of how you might use System.getProperty() to retrieve the user’s home directory in Java:
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String userHomeDir = System.getProperty("user.home");
System.out.printf("The User Home Directory is %s", userHomeDir);
}
}
In this example, System.getProperty("user.home") is called to retrieve the user’s home directory, and the result is stored in the variable userHomeDir. The value is then printed to the console.
Output:
The User Home Directory is C:\Users\Admin
If you’re curious and want to view all the system properties, you can use the getProperties() method. The code for the getProperties() method is shown below.
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Properties;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Properties props = System.getProperties();
for (Map.Entry<Object, Object> prop : props.entrySet())
System.out.println("Property: +" + prop.getKey() + "\tValue: " + prop.getValue());
}
}
The above code is designed to retrieve and print out system properties using the System.getProperties() method. It uses a Properties object to store the system properties and then iterates over the entries to display them on the console.
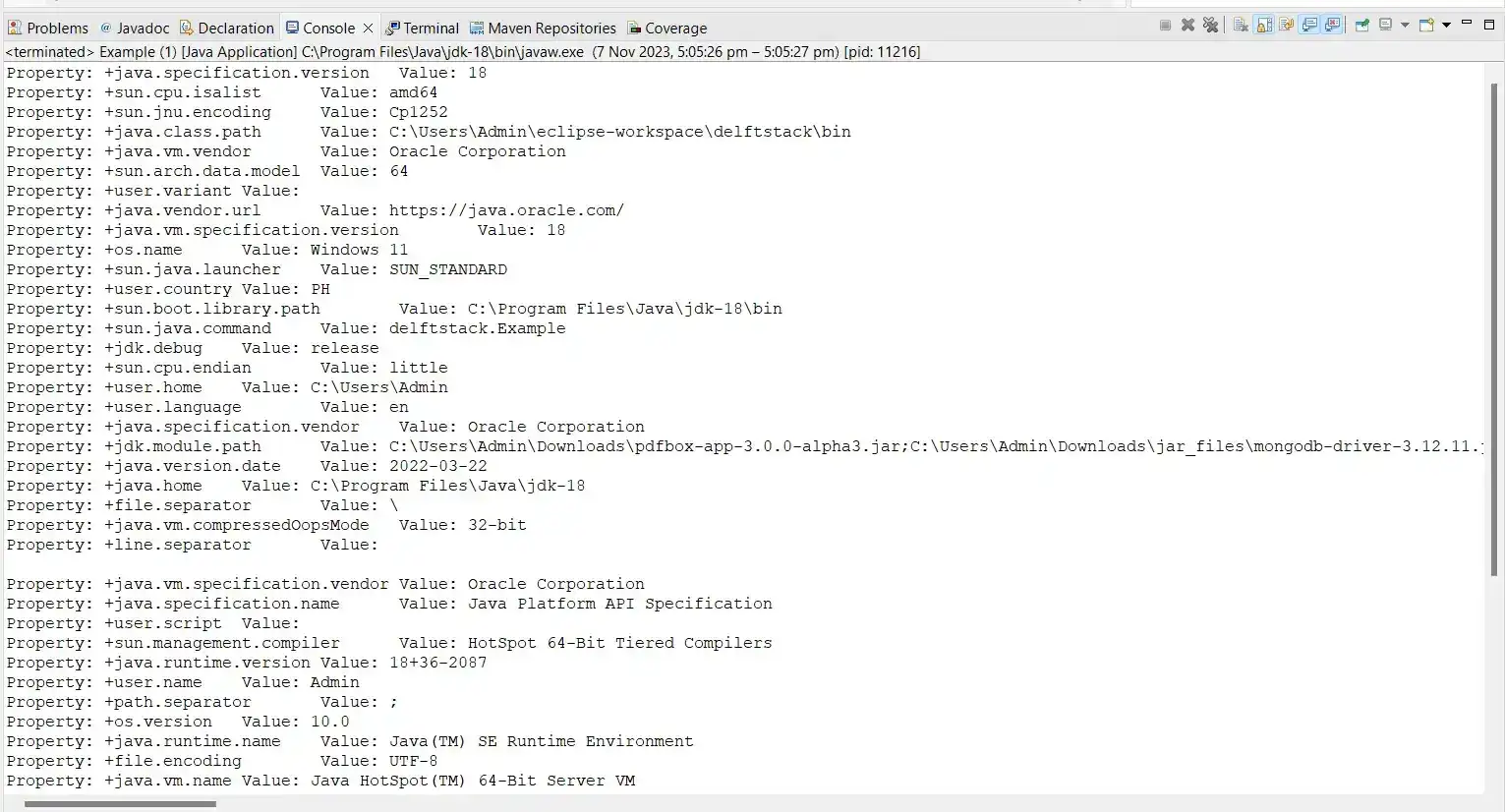
Overall, this program fetches the system properties, iterates over them, and prints out each property name along with its corresponding value. This can be useful for obtaining information about the environment in which the Java program is running.
Using Paths.get() From java.nio.file With the System.getProperty() Method
The Paths.get() method from the java.nio.file package provides a convenient way to obtain the user’s home directory.
import java.nio.file.*;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Path userHome = Paths.get(System.getProperty("user.home"));
System.out.println("User's Home Directory: " + userHome);
}
}
Here, we first use System.getProperty("user.home") to get the user’s home directory as a string. Then, we use Paths.get() to convert it into a Path object.
Output:
User's Home Directory: C:\Users\Admin
This method is particularly useful when performing file operations, as it provides a powerful API for working with file paths.
Using the File Class With the System.getProperty() Method
The File class in Java can be used to represent both directories and files. It also provides a method to obtain the user’s home directory.
import java.io.File;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
File userHome = new File(System.getProperty("user.home"));
System.out.println("User's Home Directory: " + userHome);
}
}
In this example, we create a new File object using the user’s home directory path obtained from System.getProperty("user.home"). The File object represents the directory, and we can use it for various file and directory operations.
Output:
User's Home Directory: C:\Users\Admin
Using Paths and FileSystems With the System.getProperty() Method for Flexibility
For added flexibility, you can use Paths in combination with FileSystems to obtain the user’s home directory.
import java.nio.file.*;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
FileSystem fs = FileSystems.getDefault();
Path userHome = fs.getPath(System.getProperty("user.home"));
System.out.println("User's Home Directory: " + userHome);
}
}
Here, we obtain the default FileSystem using FileSystems.getDefault(). Then, we use fs.getPath() to get a Path object representing the user’s home directory.
Output:
User's Home Directory: C:\Users\Admin
This method provides additional flexibility if you need to work with different file systems.
Get the User’s Home Directory Using the Apache Commons IO Library in Java
The Apache Commons IO library is a popular set of utility classes for common I/O operations in Java. It provides a convenient way to perform various tasks related to file handling, including accessing the user’s home directory.
Apache Commons is a very powerful library, and the FileUtils class of the CommonsIO library can be used to fetch the home directory.
Installing Apache Commons IO
To use the Apache Commons IO library in your Java project, you’ll need to add the library’s JAR file to your project’s classpath. You can download the JAR file from the official Apache Commons website.
Once you have the JAR file, you can add it to your project using your preferred build tool (e.g., Maven, Gradle) or by manually adding it to your project’s libraries.
Using Apache Commons IO to Get the User’s Home Directory
We can simply use the getUserDirectory() method of this class to view the user’s home directory. It returns a File object that represents the home directory.
We can also get a String path of the home directory by using the getUserDirectoryPath() method.
The code and output for these methods are shown below.
import java.io.File;
import org.apache.commons.io.FileUtils;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
File homeDir = FileUtils.getUserDirectory();
String homeDirPath = FileUtils.getUserDirectoryPath();
System.out.printf("The User Home Directory is %s\n", homeDir);
System.out.printf("The path of User Home Directory is %s", homeDirPath);
}
}
This program uses the Apache Commons IO library to retrieve and display information about the user’s home directory. It imports necessary classes, including File and FileUtils from the Apache Commons IO library.
The getUserDirectory() method gets the user’s home directory as a File object, while getUserDirectoryPath() returns its path as a string. The program then prints out the user’s home directory and its path to the console.
Output:
The User Home Directory is C:\Users\Admin
The path of User Home Directory is C:\Users\Admin
Overall, the code demonstrates how to use Apache Commons IO for file-related operations, specifically accessing the user’s home directory.
Why Use Apache Commons IO?
While Java provides the System.getProperty("user.home") method to retrieve the user’s home directory, Apache Commons IO offers additional benefits:
- Cross-Platform Compatibility: Commons IO ensures consistent behavior across different operating systems, making it a reliable choice for applications targeting multiple platforms.
- Simplified Code: The library provides a straightforward and concise way to perform file-related tasks, reducing the need for boilerplate code.
- Robust Error Handling: Commons IO includes exception classes that make error handling more robust, enhancing the reliability of file operations.
Get the User’s Home Directory Using the System.getenv() Method in Java
The System.getenv() method is part of the java.lang.System class in Java. It allows you to access environment variables, which are system-specific values that programs can use.
In the case of the user’s home directory, the environment variable name is typically "HOME" on Unix-based systems and "USERPROFILE" on Windows.
The syntax of getenv() is as follows:
public static String getenv(String name)
Here’s what each part of the syntax means:
public: This method is accessible by any class.static: Thegetenv()method belongs to theSystemclass itself rather than an instance of the class.String: This is the return type of the method. It returns the value of the environment variable as a string.getenv: This is the name of the method.(String name): This is the parameter that the method takes.nameis a string representing the name of the environment variable you want to retrieve.
Here’s an overview of the steps we’ll take to get the user’s home directory using System.getenv():
-
Call
System.getenv("HOME")orSystem.getenv("USERPROFILE"), depending on the operating system. -
Handle the obtained value, which represents the user’s home directory.
public class GetUserHomeDirectory {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String os = System.getProperty("os.name").toLowerCase();
String userHome;
if (os.contains("win")) {
userHome = System.getenv("USERPROFILE");
} else {
userHome = System.getenv("HOME");
}
System.out.println("User's Home Directory: " + userHome);
}
}
In this example code, we first declare a Java class named GetUserHomeDirectory. We include a main method, which serves as the entry point of the Java program.
We then retrieve the name of the operating system using the System.getProperty("os.name"). The result is converted to lowercase using toLowerCase() for case-insensitive comparison.
Next, we declare the userHome variable that will store the user’s home directory.
An if-else condition is then included in the main function. It checks if the operating system name contains "win" (indicating a Windows system).
If the result of the if-else condition is true, the System.getenv("USERPROFILE") is used to get the user’s home directory on Windows. Otherwise, the System.getenv("Home") is used to get the user’s home directory on Unix-based systems.
Finally, System.out.println("User's Home Directory: " + userHome); prints out the user’s home directory to the console.
Output:
User's Home Directory: C:\Users\Admin
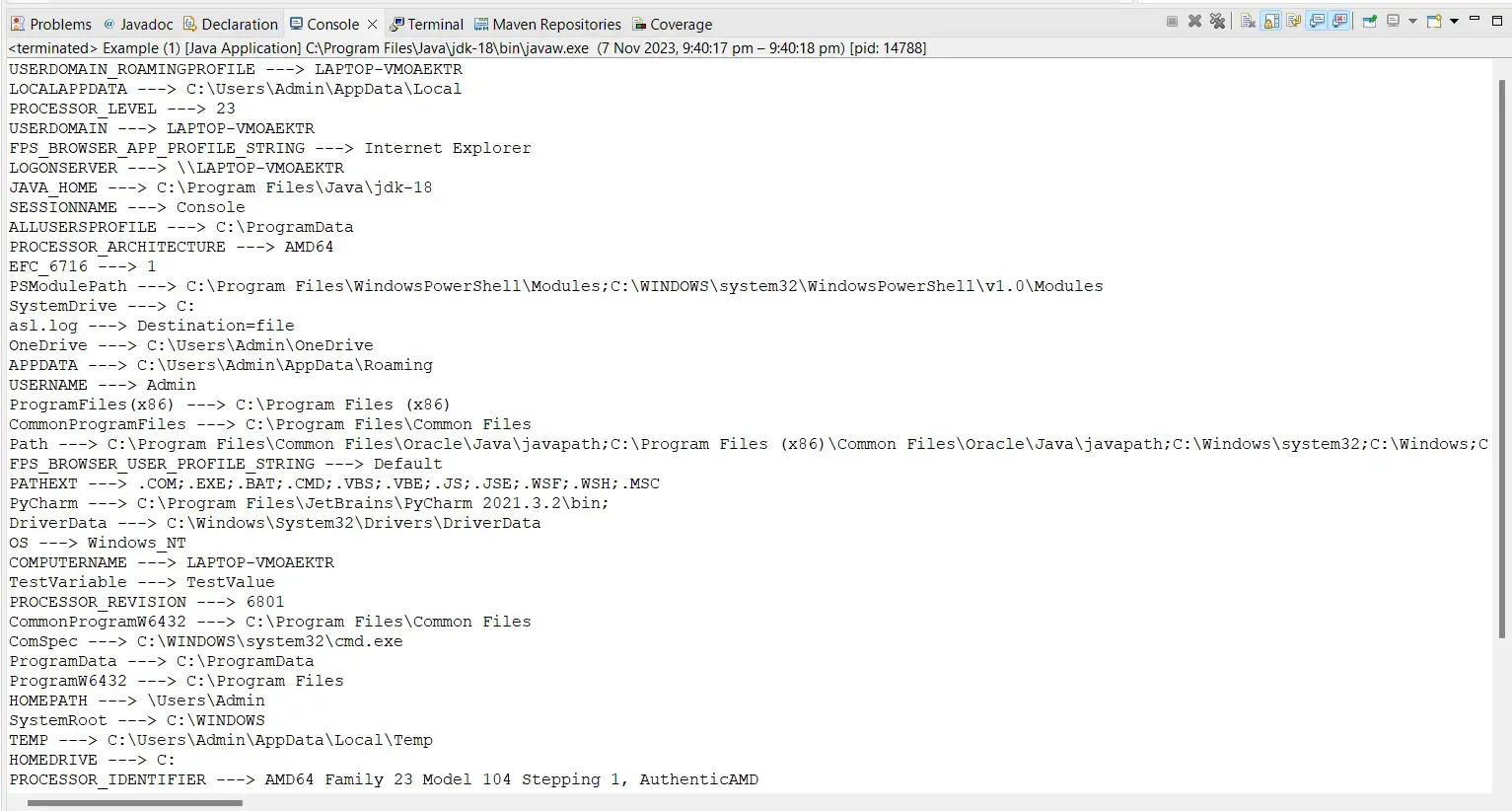
You can also use this method to view all the environment variables. Run the following program if you are curious to know more about your system’s environment variables.
import java.util.Map;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Map<String, String> envVars = System.getenv();
for (Map.Entry<String, String> var : envVars.entrySet())
System.out.println(var.getKey() + " ---> " + var.getValue());
}
}
This program retrieves and prints out all environment variables present in the current system. It imports the Map interface to handle key-value pairs and utilizes the System.getenv() method to fetch the environment variables.
The program then iterates through the entries, displaying each variable name along with its corresponding value. This code provides a way to inspect the system’s configuration and environment settings.
Output:
Conclusion
This article comprehensively covers various methods to retrieve the user’s home directory in Java. It discusses six different approaches with code examples and explanations for each:
- Using
System.getProperty("user.home")to directly access the user’s home directory. - Employing
Paths.get()from thejava.nio.filepackage for easy retrieval of the user’s home directory as aPathobject. - Utilizing the
Fileclass to represent directories and obtain the user’s home directory. - Combining
PathsandFileSystemswithSystem.getProperty()for added flexibility, especially across different file systems. - Leveraging the Apache Commons IO library, specifically the
FileUtilsclass, for simplified file-related operations, including accessing the user’s home directory. - Using the
System.getenv()method to retrieve environment variables, such as the user’s home directory.
Each method is described in detail, highlighting its advantages and use cases. This comprehensive guide equips Java developers with a range of options for effectively interacting with the file system and utilizing the user’s home directory in their applications.
Enjoying our tutorials? Subscribe to DelftStack on YouTube to support us in creating more high-quality video guides. Subscribe
How to get user home directory in java is the common question arises while creating Java/Swing GUI applications. You can get home directory of user using System.getProperty("user.home") function.
Below java code shows you how to get User home directory. This code will work on Java 1.8 for all OS.
/****************************************************************************************
* Created on 09-2017 Copyright(c) https://kodehelp.com All Rights Reserved.
****************************************************************************************/
package com.kodehelp.java8.util;
/**
* Created by https://kodehelp.com
* Date: 09-2017
*/
public class GetUserHomeDirectory {
public static void main(String [] args){
String userHomeDirectory = System.getProperty("user.home");
System.out.println("User Home Directory is ==> "+userHomeDirectory);
}
}Output:
Home Directory is ==> C:\Users\kodehelp
There is a bug#JDK-6519127 which don’t let you use above approach on Windows in Java 1.6 and 1.7. If you are using Java 1.6 or Java 1.7 and would like to get home directory of user on windows OS then you can use below approach
/****************************************************************************************
* Created on 09-2017 Copyright(c) https://kodehelp.com All Rights Reserved.
****************************************************************************************/
package com.kodehelp.java8.util;
/**
* Created by https://kodehelp.com
* Date: 09-2017
*/
public class GetUserHomeDirectory {
public static void main(String [] args){
String userHomeDirectory = System.getenv("USERPROFILE");
System.out.println("User Home Directory is ==> "+userHomeDirectory);
}
}
Output:
Home Directory is ==> C:\Users\kodehelp
In this post, we will see how to get user profile’s home directory in java. It is quite simple, we can use System.getProperty(“user.home”) to get it.
Java program:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 |
package org.arpit.java2blog; /* * @Author Arpit Mandliya */ public class getHomeDirectoryMain { public static void main(String[] args) { System.out.println(«—————«); String homeDirectory=«»; homeDirectory = System.getProperty(«user.home»); System.out.println(«Home directory is : «+homeDirectory); System.out.println(«—————«); } } |
When I ran above program, I got below output:
|
——————— Home directory is : /Users/Arpit ——————— |
