Mega Collection of PowerShell Scripts
Contains 500+ free and stand-alone PowerShell scripts for Linux, Mac OS, and Windows. Useful on the command-line (CLI), for remote control via SSH, for automation (on startup/login/logoff/daily/hourly/shutdown or via AutoHotkey/Jenkins/etc.), for context menus, for voice commands (see talk2windows), or simply to learn PowerShell. All scripts are located in the 📂scripts subfolder and support Unicode — a modern console like Windows Terminal is recommended.
Download | PowerShell FAQ | PowerShell Cheat Sheet | PowerShell Documentation
🔊 Scripts for Audio & Voice
| Script | Description |
|---|---|
| list-voices.ps1 | Lists the installed text-to-speech voices. Read more » |
| play-beep-sound.ps1 | Plays a short beep sound. More » |
| play-files.ps1 | Plays the given audio files. More » |
| play-happy-birthday.ps1 | Plays the Happy Birthday song. More » |
| play-imperial-march.ps1 | Plays the Imperial March (Star Wars). More » |
| play-jingle-bells.ps1 | Plays Jingle Bells. More » |
| play-mission-impossible.ps1 | Plays the Mission Impossible theme. More » |
| play-m3u.ps1 | Plays the given M3U playlist. More » |
| play-mp3.ps1 | Plays the given MP3 sound file. More » |
| play-super-mario.ps1 | Plays the Super Mario intro. More » |
| play-tetris-melody.ps1 | Plays the Tetris melody. More » |
| speak-checklist.ps1 | Speaks the given checklist by text-to-speech. More » |
| speak-countdown.ps1 | Speaks a countdown by text-to-speech. More » |
| speak-english.ps1 | Speaks text with an English text-to-speech voice. More » |
| speak-epub.ps1 | Speaks the content of the given Epub file by text-to-speech. More » |
| speak-file.ps1 | Speaks the content of the given text file by text-to-speech. More » |
| speak-french.ps1 | Speaks text with a French text-to-speech voice. More » |
| speak-german.ps1 | Speaks text with a German text-to-speech voice. More » |
| speak-italian.ps1 | Speaks text with an Italian text-to-speech voice. More » |
| speak-spanish.ps1 | Speaks text with a Spanish text-to-speech voice. More » |
| speak-test.ps1 | Performs a speak test by text-to-speech. More » |
| speak-text.ps1 | Speaks the given text by text-to-speech. More » |
| spell-word.ps1 | Spells the given word by text-to-speech. More » |
| tell-joke.ps1 | Tells a random joke by text-to-speech. More » |
| tell-quote.ps1 | Tells a random quote by text-to-speech. More » |
| turn-volume-down.ps1 | Turns the audio volume down. More » |
| turn-volume-fully-up.ps1 | Turns the audio fully up. More » |
| turn-volume-off.ps1 | Turns audio off. More » |
| turn-volume-on.ps1 | Turns audio on. More » |
| turn-volume-up.ps1 | Turns the audio volume up. More » |
⚙️ Scripts for Computer Management
| Script | Description |
|---|---|
| add-firewall-rules.ps1 | Adds firewall rules for executables, needs admin rights. Read more » |
| check-cpu.ps1 | Checks the CPU temperature. More » |
| check-dns.ps1 | Checks the DNS resolution. More » |
| check-drive-space.ps1 | Checks a drive for free space left. More » |
| check-file-system.ps1 | Checks the file system of a drive (needs admin rights). More » |
| check-health.ps1 | Checks the system health. More » |
| check-ping.ps1 | Checks the ping latency to the internet. More » |
| check-swap-space.ps1 | Checks the swap space for free space left. More » |
| check-windows-system-files.ps1 | Checks Windows system files (needs admin rights). More » |
| enable-crash-dumps.ps1 | Enables the writing of crash dumps. More » |
| hibernate.ps1 | Hibernates the local computer immediately. More » |
| install-github-cli.ps1 | Installs GitHub CLI. More » |
| install-chrome-browser.ps1 | Installs the Google Chrome browser. More » |
| install-firefox.ps1 | Installs the Firefox browser. More » |
| install-knot-resolver.ps1 | Installs the Knot Resolver (needs admin rights). More » |
| install-salesforce-cli.ps1 | Installs the Salesforce CLI (sfdx). More » |
| install-ssh-client.ps1 | Installs a SSH client (needs admin rights). More » |
| install-ssh-server.ps1 | Installs a SSH server (needs admin rights). More » |
| install-signal-cli.ps1 | Installs the CLI edition of the Signal messenger. More » |
| install-updates.ps1 | Installs updates (need admin rights). More » |
| install-wsl.ps1 | Installs Windows Subsystem for Linux (WSL), needs admin rights. More » |
| list-apps.ps1 | Lists the installed applications. More » |
| list-cli-tools.ps1 | Lists installed command-line interface (CLI) tools. More » |
| list-dns-servers.ps1 | Lists public DNS servers. More » |
| list-drives.ps1 | Lists all drives. More » |
| list-network-shares.ps1 | Lists all network shares of the local computer. More » |
| list-installed-software.ps1 | Lists the installed software. More » |
| list-printers.ps1 | Lists all printer known to the computer. More » |
| list-print-jobs.ps1 | Lists all jobs of all printers. More » |
| list-processes.ps1 | Lists the local computer processes. More » |
| list-services.ps1 | Lists the services on the local computer. More » |
| list-system-info.ps1 | Lists system information on the local computer. More » |
| list-tasks.ps1 | Lists all Windows scheduler tasks. More » |
| list-timezone.ps1 | Lists the current time zone details. More » |
| list-timezones.ps1 | Lists all time zones available. More » |
| list-user-groups.ps1 | Lists the user groups on the local computer. More » |
| new-power-plan.ps1 | Creates a custom power plan based on the active one. More » |
| poweroff.ps1 | Halts the local computer (needs admin rights). More » |
| query-smart-data.ps1 | Queries the S.M.A.R.T. data of your HDD/SSD’s. More » |
| reboot.ps1 | Reboots the local computer (needs admin rights). More » |
| remove-print-jobs.ps1 | Removes all jobs from all printers. More » |
| restart-network-adapters.ps1 | Restarts all local network adapters. More » |
| upgrade-ubuntu.ps1 | Upgrades Ubuntu Linux to the latest (LTS) release. More » |
| wake-up-host.ps1 | Wakes up a computer using Wake-on-LAN. More » |
| windefender.ps1 | Turn Windows Defender on/off/check real time monitoring. More » |
💻 Scripts for the Desktop
| Script | Description |
|---|---|
| close-calculator.ps1 | Closes the calculator application. Read more » |
| close-cortana.ps1 | Closes Cortana. More » |
| close-chrome.ps1 | Closes the Google Chrome browser. More » |
| close-program.ps1 | Closes the given program gracefully. More » |
| close-edge.ps1 | Closes the Edge browser. More » |
| close-file-explorer.ps1 | Closes Microsoft File Explorer. More » |
| close-firefox.ps1 | Closes the Firefox browser. More » |
| close-microsoft-store.ps1 | Closes the Microsoft Store app. More » |
| close-netflix.ps1 | Closes the Netflix app. More » |
| close-onedrive.ps1 | Closes Microsoft OneDrive. More » |
| close-serenade.ps1 | Closes the Serenade application. More » |
| close-snipping-tool.ps1 | Closes the Snipping Tool application. More » |
| close-spotify.ps1 | Closes Spotify. More » |
| close-system-settings.ps1 | Closes the System Settings window. More » |
| close-task-manager.ps1 | Closes the Task Manager. More » |
| close-thunderbird.ps1 | Closes Mozilla Thunderbird. More » |
| close-vlc.ps1 | Closes the VLC media player application. More » |
| close-windows-terminal.ps1 | Closes the Windows Terminal application. More » |
| enable-god-mode.ps1 | Enables the god mode (adds a new icon to the desktop). More » |
| install-chrome.ps1 | Installs the Google Chrome browser. Read more… |
| install-firefox.ps1 | Installs the Firefox browser. Read more… |
| list-clipboard.ps1 | Lists the contents of the clipboard. Read more… |
| new-email.ps1 | Starts the default email client to write a new email. Read more… |
| open-amazon-website.ps1 | Opens Amazon’s website. Read more… |
| open-default-browser.ps1 | Launches the default Web browser. Read more… |
| open-calculator.ps1 | Starts the calculator program. Read more… |
| open-c-drive.ps1 | Opens the C: drive folder. Read more… |
| open-downloads-folders.ps1 | Opens the user’s downloads folder. Read more… |
| open-dropbox-folder.ps1 | Opens the user’s Dropbox folder. Read more… |
| open-edge.ps1 | Launches the Edge browser. Read more… |
| open-email-client.ps1 | Starts the default email client. Read more… |
| open-facebook-website.ps1 | Opens Facebook’s website. Read more… |
| open-file-explorer.ps1 | Opens the File Explorer. Read more… |
| open-firefox.ps1 | Launches the Firefox browser. Read more… |
| open-fritz-box.ps1 | Opens FRITZ!Box’s web interface. Read more… |
| open-github.ps1 | Opens GitHub’s website. Read more… |
| open-google-contacts.ps1 | Opens Google Contacts. Read more… |
| open-google-earth.ps1 | Opens Google Earth. Read more… |
| open-google-mail.ps1 | Opens Google Mail. Read more… |
| open-google-maps.ps1 | Opens Google Maps. Read more… |
| open-google-news.ps1 | Opens Google News. Read more… |
| open-google-play.ps1 | Opens Google Play. Read more… |
| open-google-search.ps1 | Opens Google Search. Read more… |
| open-google-translate.ps1 | Opens Google Translate. Read more… |
| open-home-folder.ps1 | Opens the user’s home folder. Read more… |
| open-music-folder.ps1 | Opens the user’s music folder. Read more… |
| open-netflix.ps1 | Starts the Netflix app. Read more… |
| open-microsoft-store.ps1 | Launches the Microsoft Store app. Read more… |
| open-notepad.ps1 | Starts the Notepad app. Read more… |
| open-onedrive-folder.ps1 | Opens the user’s OneDrive folder. Read more… |
| open-pictures-folder.ps1 | Opens the user’s pictures folder. Read more… |
| open-recycle-bin.ps1 | Opens the user’s recycle bin folder. Read more… |
| open-repos-folder.ps1 | Opens the user’s Git repositories folder. Read more… |
| open-snipping-tool.ps1 | Starts the Snipping Tool. Read more… |
| open-speed-test.ps1 | Opens Cloudflare’s speed test. Read more… |
| open-spotify.ps1 | Opens Spotify. Read more… |
| open-system-settings.ps1 | Opens the system settings of Windows. Read more… |
| open-task-manager.ps1 | Starts the Task Manager. Read more… |
| open-videos-folder.ps1 | Opens the user’s videos folder. Read more… |
| open-windows-terminal.ps1 | Launches Windows Terminal. Read more… |
| open-wikipedia-website.ps1 | Opens Wikipedia’s website. Read more… |
| open-youtube-website.ps1 | Opens YouTube’s website. Read more… |
| remind-me.ps1 | Creates a scheduled task that will display a popup message. Read more… |
| save-screenshot.ps1 | Saves a single screenshot. Read more… |
| set-wallpaper.ps1 | Sets the given image as wallpaper. Read more… |
📁 Scripts for Files & Folders
| Script | Description |
|---|---|
| cd-autostart.ps1 | Set the working directory to the user’s autostart folder. Read more » |
| cd-desktop.ps1 | Set the working directory to the user’s desktop folder. More » |
| cd-docs.ps1 | Set the working directory to the user’s documents folder. More » |
| cd-downloads.ps1 | Set the working directory to the user’s downloads folder. More » |
| cd-dropbox.ps1 | Set the working directory to the user’s Dropbox folder. More » |
| cd-home.ps1 | Set the working directory to the user’s home folder. More » |
| cd-music.ps1 | Set the working directory to the user’s music folder. Read more… |
| cd-onedrive.ps1 | Set the working directory to the user’s OneDrive folder. Read more… |
| cd-pics.ps1 | Set the working directory to the user’s pictures folder. Read more… |
| cd-recycle-bin.ps1 | Set the working directory to the user’s recycle bin folder. Read more… |
| cd-repos.ps1 | Change the working directory to the user’s Git repositories folder. Read more… |
| cd-repo.ps1 | Change the working directory to the given Git repository folder. Read more… |
| cd-root.ps1 | Set the working directory to the root directory. Read more… |
| cd-scripts.ps1 | Set the working directory to the PowerShell Scripts folder. Read more… |
| cd-ssh.ps1 | Set the working directory to the user’s SSH folder. Read more… |
| cd-up.ps1 | Set the working directory to one directory level up. Read more… |
| cd-up2.ps1 | Set the working directory to two directory levels up. Read more… |
| cd-up3.ps1 | Set the working directory to three directory levels up. Read more… |
| cd-up4.ps1 | Set the working directory to four directory levels up. Read more… |
| cd-videos.ps1 | Set the working directory to the user’s videos folder. Read more… |
| check-symlinks.ps1 | Checks every symlink in a directory tree. Read more… |
| check-xml-file.ps1 | Checks the given XML file for validity. Read more… |
| clear-recycle-bin.ps1 | Removes the content of the recycle bin folder (can not be undo!). Read more… |
| copy-photos-sorted.ps1 | Copy image files sorted by year and month. Read more… |
| decrypt-file.ps1 | Decrypts the given file. Read more… |
| download-dir.ps1 | Downloads a directory tree from the given URL. Read more… |
| download-file.ps1 | Downloads a file from the given URL. Read more… |
| edit.ps1 | Edits the given file with the built-in text editor. Read more… |
| encrypt-file.ps1 | Encrypts the given file. Read more… |
| get-md5.ps1 | Prints the MD5 checksum of the given file. Read more… |
| get-sha1.ps1 | Prints the SHA1 checksum of the given file. Read more… |
| get-sha256.ps1 | Prints the SHA256 checksum of the given file. Read more… |
| inspect-exe.ps1 | Prints basic information of the given executable file. Read more… |
| install-fonts.ps1 | installs fonts and updates the registry. Read more… |
| list-dir-tree.ps1 | Lists the directory tree content. Read more… |
| list-empty-dirs.ps1 | Lists empty subfolders within the given directory tree. Read more… |
| list-empty-files.ps1 | Lists empty files within the given directory tree. Read more… |
| list-files.ps1 | Lists all files in the given folder and also in every subfolder. Read more… |
| list-folder.ps1 | Lists the folder content. Read more… |
| list-hidden-files.ps1 | Lists hidden files within the given directory tree. Read more… |
| list-recycle-bin.ps1 | Lists the content of the recycle bin folder. Read more… |
| list-unused-files.ps1 | Lists unused files in a directory tree. Read more… |
| list-workdir.ps1 | Lists the current working directory. Read more… |
| make-install.ps1 | Installs built executables and libs to the installation directory. Read more… |
| new-shortcut.ps1 | Creates a new shortcut file. Read more… |
| new-symlink.ps1 | Creates a new symbolic link file. Read more… |
| new-zipfile.ps1 | Creates a new .zip file from a directory. Read more… |
| publish-to-ipfs.ps1 | Publishes the given files or directory to IPFS. Read more… |
| remove-empty-dirs.ps1 | Removes empty subfolders within the given directory tree. Read more… |
| replace-in-files.ps1 | Search and replace a pattern in the given files by the replacement. Read more… |
| search-filename.ps1 | Searches the directory tree for filenames by given pattern. Read more… |
| search-files.ps1 | Searches the given pattern in the given files. Read more… |
| upload-file.ps1 | Uploads the local file to the given FTP server. Read more… |
♻️ Scripts to Convert Files
| Script | Description |
|---|---|
| convert-csv2txt.ps1 | Converts a .CSV file to a text file. Read more » |
| convert-dir27z.ps1 | Converts a directory tree to a compressed .7z file. Read more » |
| convert-dir2zip.ps1 | Converts a directory tree to a compressed .ZIP file. Read more » |
| convert-history2ps1.ps1 | Converts your command history to a PowerShell script. Read more » |
| convert-image2ascii.ps1 | Converts images to ASCII art. Read more » |
| convert-images2webp.ps1 | Converts images in a directory or a single image file to WebP format in parallel. More » |
| convert-mysql2csv.ps1 | Converts a MySQL database table to a .CSV file. More » |
| convert-ps2bat.ps1 | Converts a PowerShell script to a Batch script. More » |
| convert-ps2md.ps1 | Converts the comment-based help of a PowerShell script to Markdown. More » |
| convert-md2docx.ps1 | Converts Markdown file(s) to .DOCX format. Read more » |
| convert-md2html.ps1 | Converts Markdown file(s) to HTML format. Read more » |
| convert-md2pdf.ps1 | Converts Markdown file(s) to PDF format. Read more » |
| convert-sql2csv.ps1 | Converts a SQL database table to a .CSV file. More » |
| convert-txt2wav.ps1 | Converts text to a .WAV audio file. More » |
| export-to-manuals.ps1 | Exports all scripts as manuals. More » |
📝 Scripts for Git
| Script | Description |
|---|---|
| build-repo.ps1 | Builds a Git repository. Read more » |
| build-repos.ps1 | Builds all Git repositories in a folder. More » |
| check-repo.ps1 | Checks a Git repository. More » |
| clean-repo.ps1 | Cleans a Git repository from untracked files. More » |
| clean-repos.ps1 | Cleans all Git repositories in a folder from untracked files. More » |
| clone-repos.ps1 | Clones well-known Git repositories. More » |
| configure-git.ps1 | Sets up the Git user configuration. More » |
| fetch-repo.ps1 | Fetches updates for a Git repository. More » |
| fetch-repos.ps1 | Fetches updates for all Git repositories in a folder. More » |
| list-branches.ps1 | Lists all branches in a Git repository. More » |
| list-commit-stats.ps1 | Lists a Git commit statistics. More » |
| list-commits.ps1 | Lists all commits in a Git repository. More » |
| list-latest-tag.ps1 | Lists the latest tag on the current branch in a Git repository. More » |
| list-latest-tags.ps1 | Lists the latests tags in all Git repositories under a directory. More » |
| list-repos.ps1 | Lists all Git repositories in a folder. More » |
| list-submodules.ps1 | Lists all submodules in a Git repository. More » |
| list-tags.ps1 | Lists all tags in a Git repository. More » |
| new-branch.ps1 | Creates a new branch in a Git repository. More » |
| new-tag.ps1 | Creates a new tag in a Git repository. More » |
| pick-commit.ps1 | Cherry-picks a Git commit into multiple branches. More » |
| pull-repo.ps1 | Pulls updates into a Git repository. More » |
| pull-repos.ps1 | Pulls updates into all Git repositories in a folder. More » |
| remove-tag.ps1 | Removes a tag in a Git repository. More » |
| switch-branch.ps1 | Switches the branch in a Git repository. More » |
| sync-repo.ps1 | Synchronizes a Git repository by pull & push. More » |
| write-changelog.ps1 | Writes a changelog from Git commits. More » |
🔎 Scripts for PowerShell
| Script | Description |
|---|---|
| daily-tasks.sh | Execute PowerShell scripts automatically as daily tasks (Linux only). Read more » |
| introduce-powershell.ps1 | Introduces PowerShell to new users. More » |
| list-aliases.ps1 | Lists all PowerShell aliases. More » |
| list-automatic-variables.ps1 | Lists the automatic variables of PowerShell. More » |
| list-cheat-sheet.ps1 | Lists the PowerShell cheat sheet. More » |
| list-cmdlets.ps1 | Lists the PowerShell cmdlets. More » |
| list-console-colors.ps1 | Lists all console colors. More » |
| list-modules.ps1 | Lists the PowerShell modules. More » |
| list-profiles.ps1 | Lists your PowerShell profiles. More » |
| list-scripts.ps1 | Lists all PowerShell scripts in this repository. More » |
| new-script.ps1 | Creates a new PowerShell script. More » |
| set-profile.ps1 | Updates your PowerShell user profile. More » |
🛒 Various PowerShell Scripts
| Script | Description |
|---|---|
| add-memo.ps1 | Adds the given memo text to $HOME/Memos.csv. Read more » |
| check-ipv4-address.ps1 | Checks the given IPv4 address for validity. More » |
| check-ipv6-address.ps1 | Checks the given IPv6 address for validity. More » |
| check-mac-address.ps1 | Checks the given MAC address for validity. More » |
| check-subnet-mask.ps1 | Checks the given subnet mask for validity. More » |
| check-weather.ps1 | Checks the current weather for critical values. More » |
| display-time.ps1 | Displays the current time for 10 seconds by default. Read more… |
| list-anagrams.ps1 | Lists all anagrams of the given word. Read more… |
| list-city-weather.ps1 | Lists the current weather of cities worldwide (west to east). Read more… |
| list-countries.ps1 | Lists details of all countries. Read more… |
| list-credits.ps1 | Shows the credits. Read more… |
| list-crypto-rates.ps1 | Lists the current crypto exchange rates. Read more… |
| list-environment-variables.ps1 | Lists all environment variables. Read more… |
| list-emojis.ps1 | Lists the emojis of Unicode 13.0. Read more… |
| list-fritzbox-calls.ps1 | Lists the FRITZ!Box calls. Read more… |
| list-fritzbox-devices.ps1 | Lists FRITZ!Box’s known devices. Read more… |
| list-earthquakes.ps1 | Lists earthquakes with magnitude >= 6.0 for the last 30 days. Read more… |
| list-exchange-rates.ps1 | Lists the current exchange rates for the given currency. Read more… |
| list-memos.ps1 | Lists the memos at $HOME/Memos.csv. Read more… |
| list-mysql-tables.ps1 | Lists the MySQL server tables. Read more… |
| list-news.ps1 | Lists the latest news. Read more… |
| list-os-releases.ps1 | Lists operating system releases and download URL. Read more… |
| list-os-updates.ps1 | Lists operating system updates. Read more… |
| list-passwords.ps1 | Prints a list of random passwords. Read more… |
| list-pins.ps1 | Prints a list of random PIN’s. Read more… |
| list-sql-tables.ps1 | Lists the SQL server tables. Read more… |
| list-tiobe-index.ps1 | Lists the TIOBE index of top programming languages. Read more… |
| list-weather.ps1 | Lists the hourly weather. Read more… |
| locate-city.ps1 | Prints the geographic location of the given city. Read more… |
| locate-ipaddress.ps1 | Prints the geographic location of the given IP address. Read more… |
| locate-zip-code.ps1 | Prints the geographic location of the given zip-code. Read more… |
| moon.ps1 | Prints the current moon phase. Read more… |
| new-qrcode.ps1 | Generates a new QR code image file. Read more… |
| reboot-fritzbox.ps1 | Reboots the FRITZ!box device. Read more… |
| scan-ports.ps1 | Scans the network for open/closed ports. Read more… |
| send-email.ps1 | Sends an email message. Read more… |
| send-tcp.ps1 | Sends a TCP message to the given IP address and port. Read more… |
| send-udp.ps1 | Sends a UDP datagram message to the given IP address and port. Read more… |
| set-timer.ps1 | Sets a timer for a countdown. Read more… |
| simulate-presence.ps1 | Simulates the human presence against burglars. Read more… |
| start-calibre-server.ps1 | Starts a local Calibre server. Read more… |
| start-ipfs-server.ps1 | Starts a local IPFS server. Read more… |
| switch-shelly1.ps1 | Switches a Shelly1 device in the local network. Read more… |
| translate-file.ps1 | Translates the given text file into other languages. Read more… |
| translate-files.ps1 | Translates the given text files into any supported language. Read more… |
| translate-text.ps1 | Translates the given text in English into other languages. Read more… |
| weather.ps1 | Prints the current weather forecast. Read more… |
| weather-report.ps1 | Prints the local weather report. Read more… |
| what-is.ps1 | Prints a description of the given abbreviation. Read more… |
| write-animated.ps1 | Writes animated text. Read more… |
| write-big.ps1 | Writes the given text in big letters. Read more… |
| write-blue.ps1 | Writes the given text in a blue foreground color. Read more… |
| write-braille.ps1 | Writes the given text in Braille. Read more… |
| write-calendar.ps1 | Writes the calendar (month of year). Read more… |
| write-green.ps1 | Writes the given text in a green foreground color. Read more… |
| write-joke.ps1 | Writes a random Juck Norris joke. Read more… |
| write-lowercase.ps1 | Writes the given text in lowercase letters. Read more… |
| write-marquee.ps1 | Writes the given text as marquee. Read more… |
| write-morse-code.ps1 | Writes the given text in Morse code. Read more… |
| write-motd.ps1 | Writes the message of the day (MOTD). Read more… |
| write-quote.ps1 | Writes a random quote. Read more… |
| write-red.ps1 | Writes the given text in a red foreground color. Read more… |
| write-rot13.ps1 | Encodes or decodes the given text with ROT13. Read more… |
| write-typewriter.ps1 | Writes the given text with the typewriter effect. More » |
| write-uppercase.ps1 | Writes the given text in uppercase letters. More » |
| write-vertical.ps1 | Writes the given text in vertical direction. More » |
| show-notification-motivation-quote.ps1 | Show notification with random cat picture and motivation quote. More » |
📧 Feedback
Send your email feedback to: markus.fleschutz [at] gmail.com
🤝 License & Copyright
This open source project is licensed under the CC0-1.0 license. All trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
Навигация по странице
- Как сделать и запустить скрипт PowerShell?
- Как запустить скрипт в PowerShell?
- Как разрешить выполнение неподписанного скрипта PowerShell?
- Как запустить скрипт PowerShell в фоновом режиме?
- Как запустить скрипт через PowerShell с параметрами?
- Как запустить скрипт PowerShell с помощью ярлыка?
- Полезные сценарии для Windows
- Что такое командные скрипты Windows?
- Что такое Bat-скрипты Windows?
- Что такое исполняемые скрипты Windows?
- Какое расширение имеют файлы скриптов PowerShell?
- Какие скрипты PowerShell используются администраторами?
Выполнение скриптов в PowerShell
PowerShell представляет собой новую командную оболочку для операционной системы Windows, созданную Microsoft с целью полного замещения и улучшения cmd. Эта оболочка уже включена в состав операционных систем Windows 7 и выше. Если у вас старая версия операционной системы или вы хотите загрузить более новую версию PowerShell. Windows — операционная система, пользующаяся огромной популярностью среди миллионов пользователей по всему миру. В ее арсенале множество функций и возможностей, однако некоторые из них остаются недостаточно известными обычным пользователям. В данной статье мы расскажем о нескольких полезных сценариях, способных сделать вашу работу с Windows более эффективной и удобной.
Политика исполнения PowerShell-скриптов представляет собой механизм безопасности, управляющий условиями загрузки конфигурационных файлов и запуска сценариев в данной среде. Её основное предназначение — предотвращение выполнения потенциально вредоносных сценариев.

Как сделать и запустить скрипт PowerShell
Создать скрипт PowerShell довольно просто. Вот шаги, которые вы можете выполнить, чтобы создать свой первый скрипт:
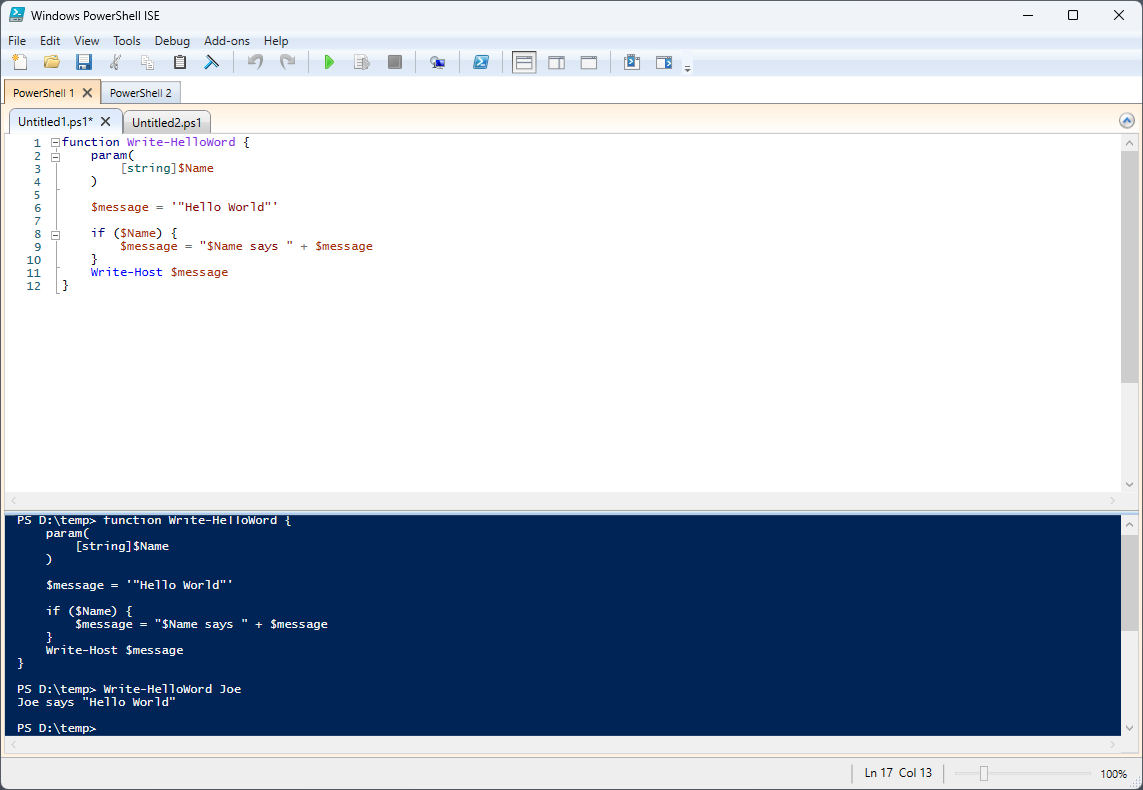
1. Откройте редактор PowerShell ISE:
PowerShell ISE (Integrated Scripting Environment) предоставляет удобную среду для написания и отладки скриптов. Вы можете его найти в меню «Пуск» (Start) под разделом «Стандартные» (Standard) или выполнить команду `PowerShell_ise` в командной строке.
2. Напишите свой скрипт:
В окне редактора PowerShell ISE напишите свой скрипт. Ниже приведен пример простого скрипта, который выводит «Hello, World!» в консоль:
Write-Host «Hello, World!»
3. Сохраните скрипт:
- Нажмите `Ctrl + S` или выберите «Файл» (File) -> «Сохранить» (Save).
- Укажите имя файла и добавьте расширение `.ps1` (например, `MyScript.ps1`).
4. Запустите скрипт:
- Выберите весь текст скрипта.
- Нажмите `F5` или выберите «Запустить сценарий» (Run Script) в PowerShell ISE.
Примеры более сложных скриптов:
#Скрипт, создающий новую папку:
$folderPath = «C:\Path\To\NewFolder»
New-Item -ItemType Directory -Path $folderPath
#Скрипт, удаляющий все файлы старше 7 дней в папке:
$folderPath = «C:\Path\To\Folder»
$limitDate = (Get-Date).AddDays(-7)
Get-ChildItem $folderPath | Where-Object { $_.LastWriteTime -lt $limitDate } | Remove-Item
#Скрипт, проверяющий статус службы:
$serviceName = «wuauserv»
$serviceStatus = Get-Service -Name $serviceName | Select-Object Status
Write-Host «The status of service $serviceName is: $($serviceStatus.Status)»
Ваши скрипты могут включать более сложные команды, использовать условия, циклы и вызывать функции. Как только вы освоите основы, вы сможете создавать более мощные и гибкие скрипты PowerShell.

Скрипты для Windows — не просто строки кода, а волшебные ключи, открывающие дверь в мир автоматизации. В руках умелого пользователя они становятся инструментом, способным не только сэкономить время, но и превратить рутинные задачи в захватывающее путешествие по потокам байтов и командам.
Как запустить скрипт в PowerShell?
Существует несколько способов запуска скрипта, вот основные из них:
- Запустить оболочку PowerShell и выполнить в ней скрипт, указав путь к файлу и его имя (например, C:\Scripts\test.ps1) или перейдя в каталог скрипта командой cd C:\Scripts и выполнить его с помощью команды .\test.ps1.
- Оболочку можно найти и запустить разными способами. Один из них — через меню «Пуск». Для Windows 7 пройдите по следующему пути: «Все программы» — «Стандартные» — «Windows PowerShell» и запустите оболочку «Windows PowerShell». Для Windows 10 найдите группу по букве «W» и в ней выберите «Windows PowerShell».
- Запустить «Интегрированную среду сценариев Windows PowerShell ISE», которая представляет собой среду разработки, позволяющую редактировать и отлаживать скрипты PowerShell. Откройте программу, выберите «Открыть» или в меню Файл выберите «Открыть» и укажите нужный скрипт, затем нажмите F5 или кнопку «Выполнить скрипт». Поиск Windows PowerShell ISE можно осуществить так же, как и оболочки PowerShell, через меню «Пуск».
- Запустить стандартный командный интерфейс и ввести следующую команду:
PowerShell -file <имя_скрипта> (например: PowerShell -file myscript.ps1)
Если вы ранее не запускали скрипты PowerShell, возможно, вы получите сообщение о том, что файл <имя_скрипта> не может быть загружен, так как выполнение скриптов запрещено для данной системы. В этом случае введите «get-help about_signing» для получения дополнительной информации. Это связано с безопасностью и предотвращением случайного выполнения вредоносного кода, поэтому все скрипты должны быть подписаны цифровой подписью.
Как разрешить выполнение неподписанного скрипта PowerShell?
- В оболочке PowerShell перед запуском скрипта выполните следующую команду для разрешения выполнения неподписанных скриптов в текущем сеансе оболочки:
Set-ExecutionPolicy RemoteSigned -Scope Process
- При запуске из стандартного командного интерфейса используйте параметр -executionpolicy, например:
PowerShell -executionpolicy RemoteSigned -file <имя_скрипта>
Оба способа устанавливают политику только для текущего сеанса, при этом политика безопасности выполнения скриптов PowerShell, установленная в реестре, остается неизменной. Если вы хотите изменить политику безопасности выполнения скриптов «навсегда», используйте следующий способ:
- Разрешить выполнение навсегда: запустите оболочку PowerShell от имени «Администратора» и выполните команду:
Set-ExecutionPolicy RemoteSigned
Однако рекомендуется избегать этого способа, чтобы не подвергать ваш компьютер возможным угрозам, поскольку это разрешает выполнение всех скриптов всегда.
Примечание: Если скрипт был загружен из интернета, чтобы избежать запроса на подтверждение выполнения, используйте параметр Bypass вместо RemoteSigned — это полное отключение любых запросов и предупреждений.

Как запустить скрипт PowerShell в фоновом режиме?
Для этого используйте параметр -WindowStyle, который может принимать значения: Normal, Minimized, Maximized и Hidden. Чтобы запустить неподписанный скрипт в фоновом режиме, выполните команду:
PowerShell -executionpolicy RemoteSigned -WindowStyle Hidden -file <имя_скрипта>
Также при желании вы можете добавить -NonInteractive, чтобы скрипт не задавал никаких вопросов. Таким образом, скрипт выполнится незаметно для пользователя. Однако будьте внимательны, используя этот способ.

Как запустить скрипт через PowerShell с параметрами?
Запуск осуществляется аналогично запуску обычной программы или bat-файла с параметрами. Например, чтобы запустить скрипт с параметрами из командной строки, используйте следующую команду:
PowerShell -executionpolicy RemoteSigned -file <имя_скрипта> param1 param2 «еще один текстовый параметр«
В самом скрипте параметры могут быть получены так:
param ($var1, $var2, $var3)
echo $var1, $var2, $var3
В интегрированной среде PowerShell ISE скрипт с параметрами можно запустить аналогично, используя область команд.

Как запустить скрипт PowerShell с помощью ярлыка?
Это можно сделать двумя способами:
- Создать файл bat/cmd, в котором прописать команду для запуска скрипта (с параметрами, как описано выше).
- Создать ярлык на PowerShell, который находится в папке c:\Windows\System32\WindowsPowerShell\v<версия>\. В свойствах ярлыка в поле «Объект» добавьте необходимые параметры.
Таким образом, например, чтобы запустить скрипт PowerShell при входе пользователя, просто создайте ярлык, как описано во втором пункте, и поместите его в автозагрузку. Также создание ярлыка с использованием одного из вышеописанных методов позволяет легко запускать скрипт от имени администратора или от имени любого другого пользователя, как обычную программу.
Скриптовый язык PowerShell — мощный инструмент для решения различных задач. Однако следует использовать его с осторожностью, поскольку он может быть использован не только для полезных, но и для вредоносных целей. Будьте внимательны при работе с ним.
Полезные сценарии для Windows
1. Скрипт выключения Windows (или перезагрузки):
Простейшая операция выключения компьютера. Откройте блокнот и введите:
shutdown -s -t 0
Сохраните файл с расширением *.cmd* (например, *shutdown.cmd*). При запуске этого файла компьютер выключится. Замените «-s» на «-r» для перезагрузки. Параметр «-t» устанавливает таймер; в данном случае, он равен 0 секунд, но можно установить, например, на 60 для выключения через 60 секунд.
2. Удаление ненужных приложений:
С помощью следующего скрипта можно удалить предустановленные приложения:
get-appxpackage -name *APPNAME* | remove-appxpackage
Замените *APPNAME* на название ненужного приложения. Хотя удаление можно выполнить стандартным способом или через программы, этот скрипт делает процесс более удобным.
3. Управление процессами:
Воспользуйтесь PowerShell для борьбы с медленными процессами. Выведите все службы:
Get-Service
Или получите информацию о конкретной службе с кодовым именем *NAME*:
Get-Service *NAME*
Создайте файл, который закрывает процессы с повышенным потреблением ресурсов:
Stop-Service -Name *ANTIVIRUS*
Stop-Service -Name *BROWSER*
Замените *ANTIVIRUS* и *BROWSER* на соответствующие названия.
4. Переименование группы файлов:
Решите проблему однотипных файлов с помощью скрипта группового переименования:
$path = «$comp\desktop\journey\russia»
$filter = ‘*.jpg’
get-childitem -path $path -filter $filter | rename-item -newname {$_.name -replace ‘HGNMD’,’RUSSIA’}
Укажите путь, расширение и выполните замены в строке.
5. Поиск файлов:
Используйте PowerShell для поиска файлов в директории:
Get-Childitem C:\Windows\*.log
Для более сложного поиска в подпапках:
Get-ChildItem C:\Windows\* -Include *.log -Recurse -Force
6. Справка:
Пользуйтесь командой *Get-Help* для получения информации:
Get-Help Services
Для более подробной справки по конкретной команде:
Get-Help —Name *CMDLET*
7. Получение информации о системе:
Используйте PowerShell для получения данных о системе, например, уровне заряда аккумулятора:
Add-Type -AssemblyName System.Windows.Forms
[Windows.Forms.PowerStatus].GetConstructor(‘NonPublic, Instance’, $null, [Type[]]@(), $null ).Invoke($null)
Информация об архитектуре процессора удаленного компьютера:
[PSObject].Assembly.GetType(‘System.Management.Automation.PsUtils’).GetMethod(‘GetProcessorArchitecture’, [Reflection.BindingFlags]40).Invoke($null, @())
Проверка прав администратора текущего пользователя:
[PSObject].Assembly.GetType(‘System.Management.Automation.Utils’).GetMethod(‘IsAdministrator’, [Reflection.BindingFlags]40).Invoke($null, @())
Эти простые и полезные сценарии помогут вам эффективнее управлять вашей системой Windows.
Командные скрипты Windows
Это общий термин, который включает в себя различные типы скриптов и командных файлов, используемых в операционной системе Windows для автоматизации задач. Включают в себя как скрипты на языке командной строки (например, скрипты CMD), так и на более современных языках, таких как PowerShell. Например, Bat-скрипты (*.bat), PowerShell-скрипты (*.ps1), а также другие сценарии, созданные для автоматизации определенных задач.
Bat-скрипты Windows
Bat-скрипты, или файлы пакетных команд (Batch-файлы), представляют собой текстовые файлы, содержащие команды и инструкции для выполнения в командной строке Windows. Основаны на языке пакетных команд (Batch scripting language). Расширение файла: *.bat* (например, *myscript.bat*).
Пример простого bat-скрипта:
«`batch
@echo off
echo Hello, World!
pause
Выполняемые скрипты Windows
Это скрипты, которые могут быть выполнены в среде операционной системы Windows и обычно предназначены для автоматизации различных задач. Включают в себя bat-скрипты (командные файлы), PowerShell-скрипты, а также другие типы скриптов, которые можно выполнять в Windows. Общее отличие между bat-скриптами и PowerShell-скриптами заключается в языке программирования, используемом для написания команд и инструкций. Bat-скрипты используют язык пакетных команд, который является устаревшим и имеет ограниченные возможности по сравнению с PowerShell, который представляет более современный и мощный язык с разнообразными функциональными возможностями для автоматизации задач в Windows.
Какое расширение имеют файлы скриптов PowerShell
PowerShell-скрипты имеют расширение *.ps1*, и для их выполнения часто требуется предварительная настройка политики выполнения скриптов (Execution Policy), чтобы разрешить запуск скрипта через PowerShell в системе.
Скрипты PowerShell для администратора
PowerShell — мощный инструмент для сисадминов Windows, предоставляя широкий набор команд и сценариев для автоматизации и управления системой. Ниже приведены несколько примеров PowerShell-скриптов, которые могут быть полезны администраторам:
1. Создание резервной копии файлов:
$sourcePath = «C:\Path\To\Source»
$destinationPath = «D:\Backup»
$timestamp = Get-Date -Format «yyyyMMddHHmmss»
$backupFolder = «$destinationPath\Backup_$timestamp»
Copy-Item -Path $sourcePath -Destination $backupFolder -Recurse
2. Мониторинг дискового пространства:
$threshold = 80
$disks = Get-WmiObject Win32_LogicalDisk | Where-Object { $_.DriveType -eq 3 }
foreach ($disk in $disks) {
$freeSpacePercentage = [math]::Round(($disk.FreeSpace / $disk.Size) * 100, 2)
$diskLetter = $disk.DeviceID
if ($freeSpacePercentage -lt $threshold) {
Write-Host «Warning: Disk $diskLetter is running low on free space ($freeSpacePercentage%)»
# Можно добавить уведомление администратора
}
}
3. Создание нового пользователя:
$username = «NewUser»
$password = ConvertTo-SecureString «SecurePassword123» -AsPlainText -Force
$fullname = «New User»
$description = «Description of the new user»
$ou = «OU=Users,DC=Domain,DC=com»
New-ADUser -SamAccountName $username -UserPrincipalName «$username@domain.com» -Name $fullname -GivenName $fullname -Surname $username -Description $description -AccountPassword $password -Enabled $true -PassThru -Path $ou
4. Мониторинг событий в журнале событий:
$logName = «System»
$events = Get-WinEvent -LogName $logName -MaxEvents 10
foreach ($event in $events) {
Write-Host «Event ID $($event.Id): $($event.Message)»
}
5. Обновление всех установленных модулей PowerShell:
Get-Module -ListAvailable | ForEach-Object {
Update-Module -Name $_.Name -Force
}
6. Удаление временных файлов в системной директории:
$tempPath = [System.IO.Path]::GetTempPath()
Remove-Item «$tempPath\*» -Force
7. Создание отчета о состоянии служб:
$services = Get-Service | Select-Object DisplayName, Status, StartType
$services | Export-Csv -Path «C:\Path\To\ServiceReport.csv» -NoTypeInformation
8. Настройка правил брандмауэра:
New-NetFirewallRule -DisplayName «Allow-SSH» -Direction Inbound -Protocol TCP -LocalPort 22 -Action Allow
9. Удаление неиспользуемых профилей пользователей:
$inactiveDays = 90
$userProfiles = Get-WmiObject Win32_UserProfile | Where-Object { $_.Special -eq $false }
foreach ($profile in $userProfiles) {
$lastUseDate = $profile.LastUseTime
$difference = (Get-Date) — $lastUseDate
if ($difference.Days -ge $inactiveDays) {
Remove-WmiObject -InputObject $profile -Confirm:$false
Write-Host «User profile $($profile.LocalPath) deleted.»
}
}
Эти примеры предоставляют общее представление о том, как PowerShell может использоваться администраторами для автоматизации различных задач в Windows-среде. Помните, что некоторые команды могут потребовать выполнения от имени администратора.
Для вызова скриптов PowerShell, вы можете использовать команду `Invoke-Expression` или просто указать путь к файлу скрипта. Предположим, у вас есть следующие скрипты: `ClearDisk.ps1`, `InstallPrograms.ps1`, `BackupScript.ps1`, и `UpdateSystem.ps1`.
1. Скрипт очистки диска (ClearDisk.ps1):
# ClearDisk.ps1
# Ваш код для очистки диска
# Пример: удаление временных файлов
Remove-Item -Path «$env:TEMP\*» -Recurse -Force
Как вызвать:
# Используйте Invoke-Expression
Invoke-Expression -Command «.\ClearDisk.ps1»
# Или просто указывайте путь к файлу скрипта
.\ClearDisk.ps1
2. Скрипт автоматической установки программ (InstallPrograms.ps1):
# InstallPrograms.ps1
# Ваш код для автоматической установки программ
# Пример: установка программы Chocolatey и установка пакетов
Set-ExecutionPolicy Bypass -Scope Process -Force; iex ((New-Object System.Net.WebClient).DownloadString(‘https://chocolatey.org/install.ps1’))
choco install packageName -y
Как вызвать:
# Используйте Invoke-Expression
Invoke-Expression -Command «.\InstallPrograms.ps1»
# Или просто указывайте путь к файлу скрипта
.\InstallPrograms.ps1
3. Скрипт резервного копирования (BackupScript.ps1):
# BackupScript.ps1
# Ваш код для создания резервной копии
# Пример: копирование файлов в другую директорию
$sourcePath = «C:\Path\To\Source»
$destinationPath = «D:\Backup»
Copy-Item -Path $sourcePath -Destination $destinationPath -Recurse
Как вызвать:
# Используйте Invoke-Expression
Invoke-Expression -Command «.\BackupScript.ps1»
# Или просто указывайте путь к файлу скрипта
.\BackupScript.ps1
4. Скрипт автоматического обновления системы (UpdateSystem.ps1):
# UpdateSystem.ps1
# Ваш код для автоматического обновления системы
# Пример: обновление всех установленных модулей PowerShell
Get-Module -ListAvailable | ForEach-Object {
Update-Module -Name $_.Name -Force
}
Как вызвать:
# Используйте Invoke-Expression
Invoke-Expression -Command «.\UpdateSystem.ps1»
# Или просто указывайте путь к файлу скрипта
.\UpdateSystem.ps1
Убедитесь, что вы находитесь в той же директории, что и ваши скрипты, или укажите полный путь к файлу скрипта.
В этой статье мы коснулись всех аспектов создания, запуска и использования скриптов в Windows. Надеемся, что эти советы и примеры помогут вам освоить этот увлекательный мир автоматизации и сделают вашу работу более эффективной и приятной.
В статье рассказывается:
В статье рассказывается:
- Выключение и перезапуск
- Удаляем ненужное
- Управляем процессами
- Переименовываем группу файлов
- Ищем файлы
- Справка
- Находим данные
-
Пройди тест и узнай, какая сфера тебе подходит:
айти, дизайн или маркетинг.Бесплатно от Geekbrains
Если вы только недавно встали на путь программирования и ещё даже не пробовали поиграться с установленной операционной системой, то манипулирование с помощью скриптов может вызвать резонные вопросы необходимости и удобства. Однако, даже если опустить тот простой факт, что они помогают лучше понять, как функционирует ОС, в будущем при создании приложений, исполнение сценариев может оказаться крайне полезным навыком.
Для исполнения следующих скриптов мы обратимся к PowerShell. Любой системный администратор (по профессии или в душе) знает его возможности и периодически пользуется, для всех остальных это просто интерфейс командной строки или иностранное слово. На популярных ресурсах вы можете найти уйму идей, как использовать PowerShell для развлечения и дела, здесь же мы рассмотрим лишь простые скрипты, которые помогут войти в курс дела.
Выключение и перезапуск
Итак, самая простая операция выключения вашего компьютера. Открываем ;блокнот, прописываем:
shutdown -s -t 0
Сохраняем файл, как *.cmd (*- имя вашего файла, например shutdown.cmd) и не забудьте в типе выбрать “все файлы”. Всё, исполняемый файл по запуску выключит ваш компьютер. “-s”, в данном случае означает выключение, замените на “-r” — получите перезагрузку. “-t” — таймер, у нас он установлен на 0 секунд, но если установить на 60 — получите выключение через 60 секунд.
Удаляем ненужное
В различных сборках, предустановленных на компьютер или ноутбук, вы можете наткнуться на массу абсолютно ненужных пакетов приложений. Удалить их с помощью скрипта проще простого:
get-appxpackage -name *APPNAME* | remove-appxpackage
Как вы понимаете, *APPNAME* — название неинтересующей надстройки. Да, удалять эти пакеты можно стандартным путём или через специальные программы, но вы можете создать скрипт, который удалит их все одним двойным кликом.
Топ-30 самых востребованных и высокооплачиваемых профессий 2023
Поможет разобраться в актуальной ситуации на рынке труда
Подборка 50+ бесплатных нейросетей для упрощения работы и увеличения заработка
Только проверенные нейросети с доступом из России и свободным использованием
ТОП-100 площадок для поиска работы от GeekBrains
Список проверенных ресурсов реальных вакансий с доходом от 210 000 ₽
Уже скачали 34166
Управляем процессами
Есть в PowerShell две полезные команды, которые позволят бороться с ветряными мельницами (процессами, снижающими быстродействие). Вывести их на экран можно просто прописав:
Get-Service
Или информацию о конкретном сервисе под кодовым названием *NAME* (на этом месте должно быть название интересующего сервиса):
Get-Service *NAME*
Но это можно сделать в диспетчере задач, а вот действительно полезным может оказаться создание файла, который по клику закрывал бы все процессы с повышенным потреблением ресурсов (браузеры, антивирусы и пр.). Для этого воспользуйтесь командой Stop-Service:
Stop-Service -Name *ANTIVIRUS*
Stop-Service -Name *BROWSER*
Названия для замены указаны в * *.
Переименовываем группу файлов
Ещё одна назойливая проблема: вы скопировали с фотоаппарата или телефона изображения. Огромная куча фотографий, которые называются однотипно вроде HGNMD034, где HGNMD — название общей директории, объединяющей файлы, например, отснятые за один день.
Для того, чтобы сделать название этих файлов приятнее или иметь возможность объединить несколько папок, не получив при этом хронологическую путаницу из-за имен, можно использовать скрипт группового переименования:
$path = «$comp\desktop\journey\russia»
$filter = ‘*.jpg’
get-childitem -path $path -filter $filter |
rename-item -newname {$_.name -replace ‘HGNMD’,’RUSSIA’}
В первой строке в кавычках укажите точный путь к файлам. Во второй строке — расширение файлов, подлежащих изменению. В последней строке вместо “HGNMD” — общее в названиях файлов, подлежащее замене, на что-то, вместо “RUSSIA” — имя, которое вы хотите присвоить. Если данный скрипт опять сохранить в качестве исполняемого файла, то подобные однотипные операции будут отнимать у вас всего несколько секунд времени.
Скачать
файл
Ищем файлы
Ещё одна простая задача, реализуемая на PowerShell — поиск файлов в директории. В данном случае рассмотрим поиск log-файлов:
Get-Childitem C:\Windows\*.log
Или чуть более сложный пример, когда поиск будет производиться ещё и в подпапках:
Get-ChildItem C:\Windows\* -Include *.log -Recurse -Force
Это чуть более правильная и полная запись, где “Include” — указывает на искомую часть, “Recurse” — на поиск во вложенных каталогах, “Force” — поиск включает в себя системные и скрытые файлы.
Дарим скидку от 60%
на курсы от GeekBrains до 11 мая
Уже через 9 месяцев сможете устроиться на работу с доходом от 150 000 рублей
Забронировать скидку
Справка
Итак, с общими принципами функционирования PowerShell мы более-менее разобрались. Если что-то непонятно — обратитесь к справочной информации следующим образом:
Get-Help Services
Это команда, которая выведет на экран все доступные команды с кратким описанием. Хотите подробнее? Нет ничего проще:
Get-Help -Name *CMDLET*
Где вместо *CMDLET* вставьте любую интересующую команду.
Только до 8.05
Скачай подборку материалов, чтобы гарантированно найти работу в IT за 14 дней
Список документов:
ТОП-100 площадок для поиска работы от GeekBrains
20 профессий 2023 года, с доходом от 150 000 рублей
Чек-лист «Как успешно пройти собеседование»
Чтобы получить файл, укажите e-mail:
Введите e-mail, чтобы получить доступ к документам
Подтвердите, что вы не робот,
указав номер телефона:
Введите телефон, чтобы получить доступ к документам
Уже скачали 52300
Находим данные
Теперь перейдём к простым скриптам, описанным чуть более сложными командами. Например, с помощью PowerShell вы можете выудить почти всю информацию о железе и комплектующих. Как вариант, вот скрипт для оценки уровня заряда аккумулятора:
Add-Type -AssemblyName System.Windows.Forms
[Windows.Forms.PowerStatus].GetConstructor(‘NonPublic, Instance’, $null, [Type[]]@(), $null ).Invoke($null)
Архитектура процессора удалённого компьютера:
[PSObject].Assembly.GetType( ‘System.Management.Automation.PsUtils’
).GetMethod(‘GetProcessorArchitecture’, [Reflection.BindingFlags]40
).Invoke($null, @())
Иногда важной задачей бывает проверка прав администратора у текущего пользователя. Вот простой способ на PowerShell:
[PSObject].Assembly.GetType(‘System.Management.Automation.Utils’).GetMethod(
‘IsAdministrator’, [Reflection.BindingFlags]40).Invoke($null, @())
Читайте также!
Что такое браузер и как он работает

На этом пока остановимся. Как вы наверное убедились, PowerShell не самый сложный, но очень полезный инструмент, который способен выполнять, как простейшие операции, так и достаточно сложные. Однако PowerShell не единственный инструмент для создания скриптов для Windows. Но об этом в следующий раз.
Начало карьеры: интенсив «Основы веб-разработки».

What’s AutoHotkey
AHK is an open-source scripting software for Windows that is used to automate repetitive tasks, remap keys, build small utility tools, etc. You create scripts that would do the tasks for you. It’s an extremely lightweight app (~ 2MB RAM) and works on old and newer versions of windows.

How to set up and run
- Download and install main program (one-time step) https://www.autohotkey.com
- Download a script (
.ahk) or copy-paste script content in a text file and then rename it with.ahkextension, e.g.,my-script.ahk - To run the script: Right-click ->
Run script.
You can also run scripts by double-click or do right-click ->Open with->AutoHotkey - Bonus: you can right-click and
Compile scriptto make it a standalone.exeprogram that would run without installing AutoHotkey software on a computer.
Autorun script at startup
Method 1:
- Open startup folder: open
Runwindow byWin+Rand then writeshell:startupand enter. - It’ll open explorer at something like this path:
C:\Users\{username}\AppData\Roaming\Microsoft\Windows\Start Menu\Programs\Startup - Copy a script (
.ahk) -> go to thatStartupfolder -> right-click and selectPaste shortcut.
OR
Method 2:
- Put
script_autorun_startup.vbsat startup folder. Make sure to put the correct path of your ahk scripts in that file first.
AHK communities to get help
- https://www.reddit.com/r/AutoHotkey/
- https://www.autohotkey.com/boards/
Useful Scripts
You can see all scripts here: https://github.com/GorvGoyl/Autohotkey-Scripts-Windows
Look up selected text
script: look_up.ahk
use alt+g to open selected text in the browser and do a google search or visit the site (if it’s url). It’s one of the most frequent scripts I use on a regular basis. Especially to quickly google some error from the terminal when programming. Works everywhere.
Assign a different shortcut:
To assign a different shortcut, replace !g (here ! means Alt so !g = Alt+G) in the script with your desired key combo and run again. All running scripts can be found in the Windows tray menu.
To use a different browser instead of Microsoft Edge, Add its path instead of C:\\Program Files (x86)\\Microsoft\\Edge\\Application\\msedge.exe in the script.
Use Win key as mouse left-click
script: mouseless.ahk
This little script has been a game-changer for me. I don’t like to carry a mouse around, and my HP laptop touchpad isn’t much responsive, so I needed a better alternative to performing left-click. I realized I don’t use the left Win key as much, so I modified its action to do left-click instead (using left-thumb). Once you get the hang of it, I assure you you’ll do clicks with godspeed.
I still needed the Win key, so I replaced the rarely used right Ctrl key as Win key.
To sum-up:
Win → Mouse Left-click
Right-Ctrl → Win
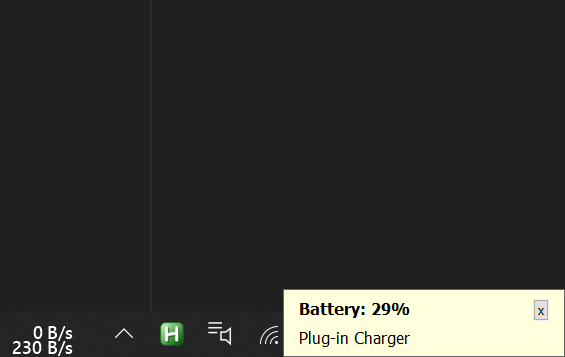
Show notification on low battery or when fully charged
script: battery_alert.ahk
Keeping your laptop constantly plugged in shortens the battery life!
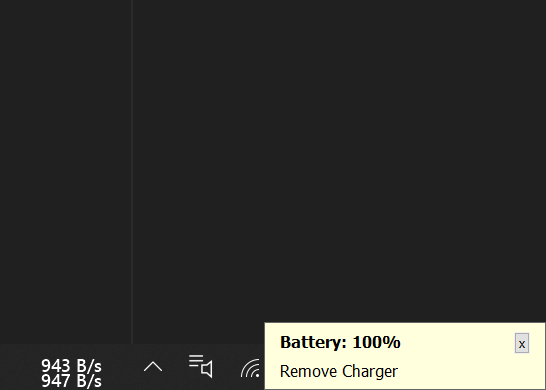
If the battery is below 30% and the charger is not plugged in, it’ll show a silent notification on the bottom-right corner to plug in the charger. Notification will pop up every few minutes until you take action.
And, if the laptop is charged and the charger is still plugged in, it’ll show a silent notification on the bottom-right corner to remove the charger. Notification will pop up every few minutes until you take action.
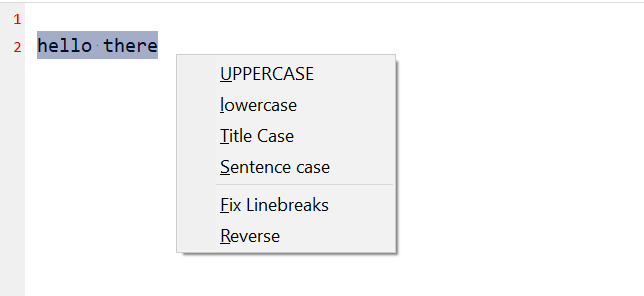
script: ctrl_caps_as_case_change.ahk
Use ctrl+capslock to invoke a handy transform text menu on selected text e.g., convert text to UPPERCASE/lowercase/Title Case etc. Press esc to close the menu.
Show Windows switcher with capslock key
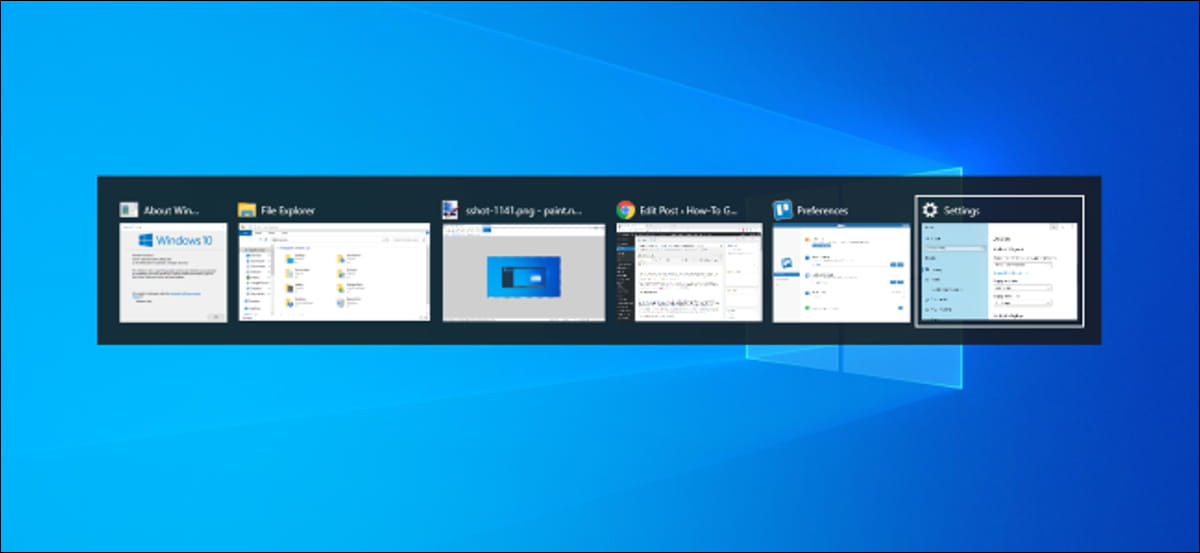
script: caps_as_window_switcher.ahk
If you don’t use capslock key much, you could replace it to show Windows switcher (e.g., Alt + Tab) instead. You’d still be able to turn on/off capslock with shift+capslock combo.
To sum-up:
Capslock → Alt+Tab
Shift+Capslock → Capslock
Create new text file here
script: create_file_here.ahk
Windows has a shortcut (ctrl+shft+n) to create an empty folder at the current location but not for creating a new file. So, I made a script to do exactly that. Use ctrl+shift+m to create an empty text file (NewFile.txt) at the current folder location in file explorer.
Open PowerShell here
script: open_shell_here.ahk
Use ctrl+shift+p to open PowerShell with the current folder path in file explorer.
In-line calculator
script: in-line calculator.ahk
Activate the calculator by = then write your equation and finally type = again to get the calculation result. Works everywhere.
Use # key at the end instead of = to keep the equation and the result (output: 7*5+5 = 40).
See more info in README file.
Drag window without activating it
script: MoveInactiveWin.ahk
Hold alt+right-click to move a window without activating it.
Disable zoom when ctrl+scroll in the browser
script: disable_scroll_zoom_edge.ahk
Disable zoom when doing ctrl+scroll in Edge browser. To use different application, replace Microsoft Edge with other application title in the ahk script.
Hot corner
script: left_edge_as_window_switcher.ahk
Trigger Alt+Tab (Window switcher) when the mouse is on the left edge of the screen. Keep the mouse there to tab through the other windows.
Pin window at the top
script: pin_window.ahk
Use ctrl+alt+p to pin/unpin current window at top. Super handy.
Win key to show taskbar
script: win_key_to_show_taskbar.ahk
It shows the taskbar only when the Win key is pressed; otherwise, it stays hidden.
Contribute
👋 Got some sick ahk script you’d like to add to the list? Please submit here https://github.com/GorvGoyl/Autohotkey-Scripts-Windows
💬 Discuss on Github
Scripts by others
- Learn AutoHotKey by stealing my scripts (hillelwayne.com) | hwayne/autohotkey-scripts: Some of my AutoHotKey scripts (github.com)
That’s all, folks!
Hiring React Devs (in IST timezone) for my
AI Startup.
Whether you’re an IT analyst or a regular computer user, there are a lot of tasks you may need to do frequently on your PC. VB Scripts are scaled down Visual Basic programs that serve as Windows scripts that can do anything from pull up important information about your computer hardware, to stopping and starting services or resetting your network card.
It’s possible to learn how to do all of those individual things the normal way, or do them using batch files. But VB scripts are better than batch scripts because they’re more flexible. If you store the following scripts in a common place that’s quick to get to when you need it, you can accomplish these tasks in a fraction of the time. You just double-click the script, answer a prompt, and the task is done.
Take a look at the following VB Windows scripts and if you see any you’d like to use, just copy and paste the script into Notepad or other coding notes tool and save it as a WSF file.
Prepare Your Windows Scripts
Each of the scripts detailed below will run with just a double click so long as you’ve named the file with the .WSF extension, and you’ve also enclosed the code at the beginning with:
<job>
<script language="VBScript">
And close out the code with:
WScript.Quit
</script>
</job>
This ensures that Windows will recognize the language your script is written in, and process it properly.
1. Use Windows Scripts for Computer Information
Windows offers something called WMI, or Windows Management Instrumentation, which provides your script with an interface to access components of the operating system. You can actually run queries against WMI to get current live information about your system. Microsoft offers a full list of all of the categories of queries you can make against the system.
We’ve covered how to use VBA to pull computer information into Excel, but you can do this same thing using a simple VB script outside of Excel.
In this example we’re going to query the system for processor information (family, manufacturer, and number of cores), battery information (description and status), and logical disk information (name, free space remaining, and overall size). Then we’ll output all of this information to a CSV file for easy viewing.
The first step is to set up the FileSystemObject you’ll use to output to the CSV file, and create the file:
Set oFSO = CreateObject("Scripting.FileSystemObject")
sFile1 = "MyComputerInfo.csv"
Set oFile1 = oFSO.CreateTextFile(sFile1, 1)
The next step is to set up the WMI query and execute it:
strQuery = "SELECT Family,Manufacturer,NumberOfCores FROM Win32_Processor"
Set colResults = GetObject("winmgmts://./root/cimv2").ExecQuery( strQuery )
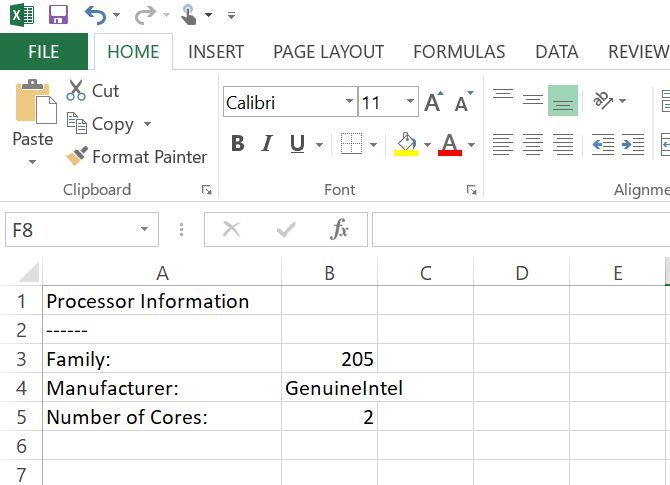
Finally, sort through the results and output the information to the CSV file. If you want to be fancy, preface this with a couple of lines to help make your output file look better:
oFile1.WriteLine "Processor Information"
oFile1.WriteLine "------"
For Each objResult In colResults
strResults = "Family:,"+CStr(objResult.Family)
oFile1.WriteLine strResults
strResults = "Manufacturer:,"+CStr(objResult.Manufacturer)
oFile1.WriteLine strResults
strResults = "Number of Cores:,"+CStr(objResult.NumberOfCores)
oFile1.WriteLine strResults
Next
If you run your code now, this is what your output will look like:
For the next two sections of your code, you’re just going to repeat and change the query to look for the additional information. Here’s the battery info query:
oFile1.WriteLine ""
strQuery = "SELECT Description,Status FROM Win32_Battery"
Set colResults = GetObject("winmgmts://./root/cimv2").ExecQuery( strQuery )
oFile1.WriteLine "Battery Information"
oFile1.WriteLine "------"
For Each objResult In colResults
strResults = "Status:,"+CStr(objResult.Description)
oFile1.WriteLine strResults
strResults = "Description:,"+CStr(objResult.Status)
oFile1.WriteLine strResults
Next
And here’s the next section for the logical disk query:
oFile1.WriteLine ""
strQuery = "Select Name, FreeSpace, Size from Win32_LogicalDisk"
Set colResults = GetObject("winmgmts://./root/cimv2").ExecQuery( strQuery )
oFile1.WriteLine "Disk Information"
oFile1.WriteLine "------"
'Identify the Logical Disk Space
For Each objResult In colResults
strResults = "Name:,"+CStr(objResult.Name)
oFile1.WriteLine strResults
strResults = "Free Space:,"+CStr(objResult.FreeSpace)
oFile1.WriteLine strResults
strResults = "Disk Size:,"+CStr(objResult.Size)
oFile1.WriteLine strResults
Next
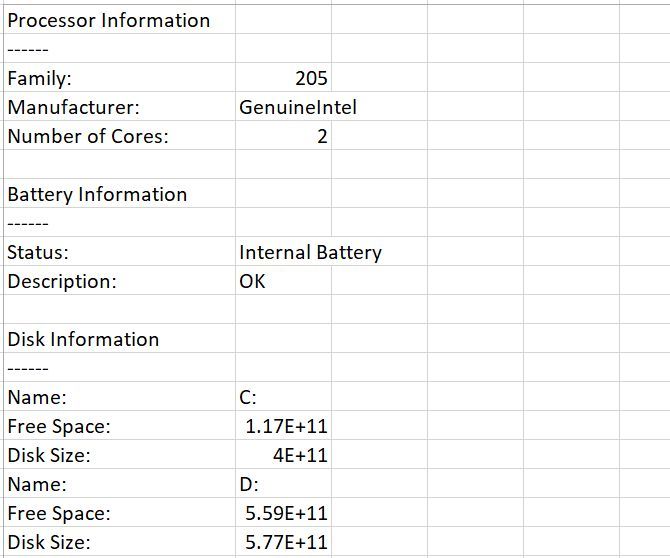
Finally, remember to close out the code by closing the file and setting the objects to «Nothing»:
oFile1.Close
Set oFile1 = Nothing
set colResults = Nothing
strResults = ""
Put all that code into your new .WSF file, run it, and here’s what your output will look like:
Just swap up the queries above for any other computer devices or software you want to get information about, and you can get a full system report any time you like with just a click of the mouse.
2. Stop and Start Services
There will be times when certain services have issues, and require just a quick restart to get running properly again. This is especially true in IT when you’re forced to run server software that is sometimes a little bit buggy.
If you want to shave a minute or so off of the service restart process, just store the following script some place convenient. It’ll prompt you to type in the name of the service you want to restart, and then it’ll do exactly that.
Since stopping and starting services requires administrative privileges, you need to place the following code at the start of your script to give your script elevated privileges:
If Not WScript.Arguments.Named.Exists("elevate") Then
CreateObject("Shell.Application").ShellExecute WScript.FullName _
, """" & WScript.ScriptFullName & """ /elevate", "", "runas", 1
WScript.Quit
End If
Once this is done, add the rest of the code to run the input box for user input, launch the command window, and send it the «net stop» and «net start commands»:
Set cmdShell = CreateObject("WScript.Shell")
strServiceName=Inputbox("Inter Service to Stop","Input Required")
cmdShell.Run "cmd.exe"
WScript.Sleep 1000
cmdShell.SendKeys "net stop "+strServiceName
cmdShell.SendKeys "{Enter}"
WScript.Sleep 1000
cmdShell.SendKeys "net start "+strServiceName
cmdShell.SendKeys "{Enter}"
WScript.Sleep 1000
cmdShell.SendKeys "Exit"
cmdShell.SendKeys "{Enter}"
That’s all there is to it. No need to hunt around for the services tool. Just run this script and stop and start any service in seconds.
3. Change Registry Settings, Default Admin Password
With the following script, we’re going to kill two birds with one stone. This script will show you how to edit the registry with a VB script. It’ll also give you a script that’ll let you set the default Windows username and password by editing those registry settings.
Here’s how it works. First, since editing the registry requires admin rights, you’ll need to set up elevated privileges for your script:
If Not WScript.Arguments.Named.Exists("elevate") Then
CreateObject("Shell.Application").ShellExecute WScript.FullName _
, """" & WScript.ScriptFullName & """ /elevate", "", "runas", 1
WScript.Quit
End If
First run two input boxes to ask the user what user name and password to use:
strUserName=Inputbox("Enter the default User Name","Input Required")
strPassword=Inputbox("Enter the default Password","Input Required")
Next, set up the shell object, and write those values to the appropriate registry keys:
Set wshShell = CreateObject( "WScript.Shell" )
wshShell.RegWrite "HKLM\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows NT\CurrentVersion\Winlogon\DefaultUserName", strUserName, "REG_SZ"
wshShell.RegWrite "HKLM\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows NT\CurrentVersion\Winlogon\DefaultPassword", strPassword, "REG_SZ"
Set wshShell = Nothing
And that’s all there is to it. The «RegWrite» method lets you write any value to any registry key using a VB Windows script. All you have to know is the appropriate path.
Run the script and answer the prompts.
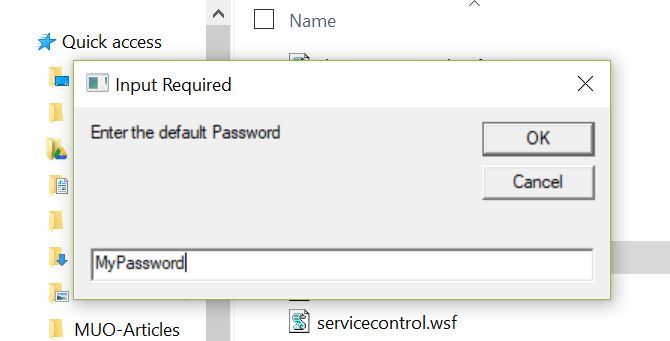
The values you enter will get inserted right into the registry settings you’ve set up in the script.

Play around with the script and tweak it to your liking. You can edit any registry keys you like, so be creative!
4. Reset Your Network Connection
Resetting your network connection using VB scripting is something we’ve covered before here at MakeUseOf. The following version of this is actually scaled down and much simpler to implement. Instead of prompting for individual network cards, it resets all of your active connections which would hopefully resolve any network issues you may be having.
As with other scripts that need admin rights, you’ll need to add the section at the start for elevated privileges. Copy that code from the script above.
Next, create the WMI object and query it for a list of enabled network adapters on your system:
strComputer = "."
Set objWMIService = GetObject("winmgmts:\\" & strComputer & "\root\CIMV2")
Set colItems = objWMIService.ExecQuery( _
"SELECT * FROM Win32_NetworkAdapter Where NetEnabled = 'True'")
Finally, loop through all of the enabled adapters and reset them:
For Each objItem in colItems
objItem.Disable
WScript.Sleep 1000
objItem.Enable
Next
This will reset all of your active network adapters, which is often the fastest way to resolve annoying network issues. Keep this script handy and try it first any time you have a slow network or other weird network problems.
5. Ping Devices or Websites
I’ve saved my favorite VB windows script for last. This is one that I actually set up as a scheduled task on my home computer and have it run several times a day just to check if my website is active. I have the script email me if the site is down. You can use this same script to monitor important servers or computers on your network and email yourself any time your script can’t ping the device.
First, set up the script for the target you want to ping, create the shell object, and then run the ping command.
strTarget = "topsecretwriters.com"
Set WshShell = WScript.CreateObject("WScript.Shell")
Ping = WshShell.Run("ping -n 1 " & strTarget, 0, True)
Use a Select Case statement to run through the Ping results and respond accordingly. If results come back as zero, then you know the site (or server) is online and you don’t have to do anything. If it returns a «1» then the ping failed and you need to do something. In my case, I send an email using the Windows CDO object:
Select Case Ping
Case 0
Case 1
Set objMessage = CreateObject("CDO.Message")
Set objConfig = CreateObject("CDO.Configuration")
objConfig.Load -1
Set Flds = objConfig.Fields
With Flds
.Item ("http://schemas.microsoft.com/cdo/configuration/smtpusessl") = True
.Item ("http://schemas.microsoft.com/cdo/configuration/smtpauthenticate")=1
.Item ("http://schemas.microsoft.com/cdo/configuration/sendusername")="xxxxxx@gmail.com"
.Item ("http://schemas.microsoft.com/cdo/configuration/sendpassword")="xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx"
.Item ("http://schemas.microsoft.com/cdo/configuration/smtpserver")="smtp.gmail.com"
.Item ("http://schemas.microsoft.com/cdo/configuration/sendusing")=2
.Item ("http://schemas.microsoft.com/cdo/configuration/smtpserverport")=465
.Update
End With
With objMessage
Set .Configuration = objConfig
.Subject = "Your site is offline"
.From = "me@mycomputer.com"
.To = "xxxxxx@gmail.com"
.TextBody = "Hey, your website is offline."
.Send
End With
End Select
Once the script runs and can’t ping the device or website, you get an instant message.
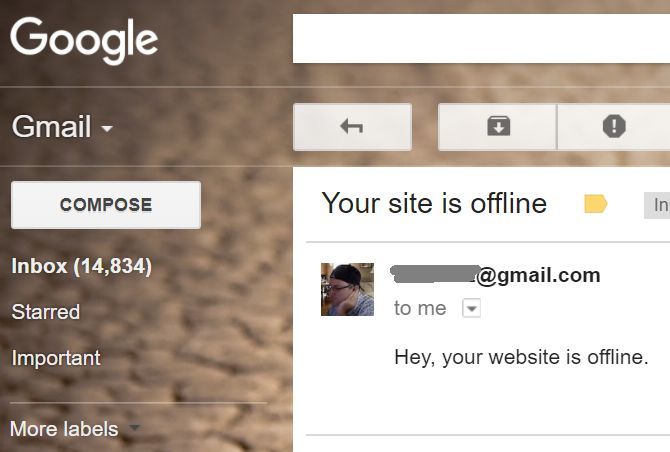
It’s quick and easy, and every efficient!
Using VB Windows Scripts to Control Your Computer
These are just a few examples of some of the cool things you can do with VB scripting to streamline your computer use. There are lots of other things you can do like automated backups with VB and Synctoy, automating telnet commands, or even open and control application windows.
What are some of the things you’ve automated on your computer with a Windows script? Do you write yours using VB, or use some other tool like PowerShell?
