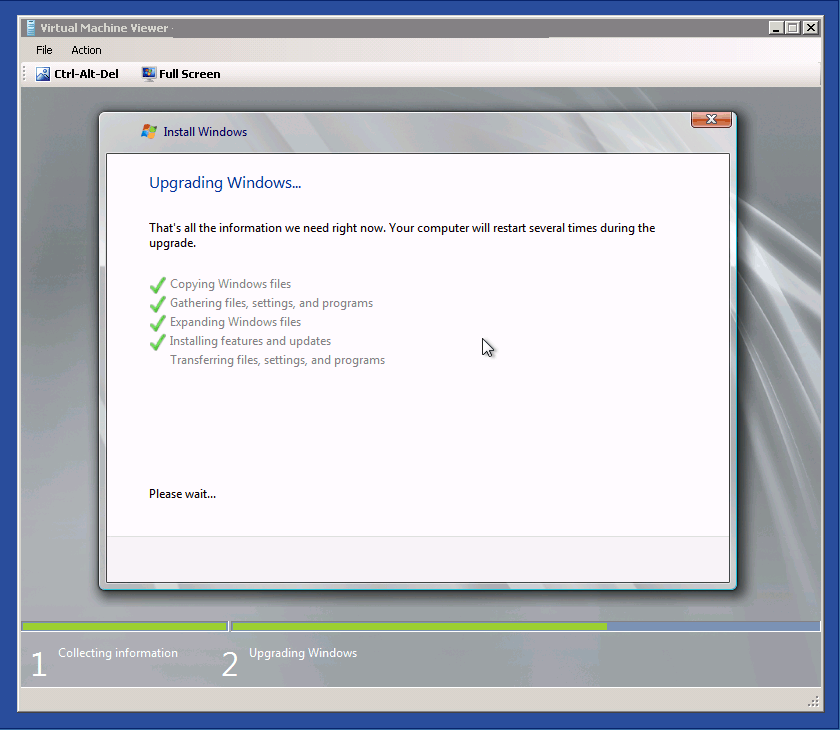
I’m not a big fan of In-place Windows Upgrades, especially in the server environment. But we had some servers with a small application running on Windows Server 2008, so we decided to in-place upgrade this server to Windows Server 2008 R2. Now guess what, it worked. If the hardware and all applications are compatible with Windows Server 2008 R2, you can try to upgrade.
You can also check out the Windows Server Upgrade Center, which helps you to find different upgrade scenarios.
- Start Windows Server 2008 R2 DVD or attached ISO file.
- Choose Operation System
- Now choose Upgrade
- Check the compatibly report
- Upgrading Windows
- After that Windows reboot and if everything worked, you have now a Windows Server 2008 R2
I hope this gives you a quick look at how you can in-place upgrade Windows Server 2008 to Windows Server 2008 R2. If you have any questions, feel free to leave a comment.
Tags: In-place, In-place upgrade, Microsoft, Upgrade, Upgrade 2008 to 2008 R2, Windows, Windows Server, windows server 2008, Windows Server 2008 R2 Last modified: July 8, 2019
About the Author / Thomas Maurer
Thomas works as a Principal Program Manager & Chief Evangelist Azure Hybrid at Microsoft (Cloud + AI). He engages with the community and customers around the world to share his knowledge and collect feedback to improve the Azure hybrid cloud and edge platform. Prior to joining the Azure engineering team (Cloud + AI), Thomas was a Lead Architect and Microsoft MVP, to help architect, implement and promote Microsoft cloud technology.
If you want to know more about Thomas, check out his blog: www.thomasmaurer.ch and Twitter: www.twitter.com/thomasmaurer
The Big Bang approach to migrate from Windows Server
2008 to Windows Server 2008 R2 is the most straightforward approach to
migration. An upgrade simply takes any and all settings on the domain
controllers and upgrades them to Windows Server 2008 R2. If a Windows
Server 2008 server handles Windows Internet Naming Service (WINS),
domain name system (DNS), and Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol
(DHCP), the upgrade process will upgrade all WINS, DNS, and DHCP
components, as well as the base operating system. This makes this type
of migration very tempting, and it can be extremely effective, as long
as all prerequisites described in the following sections are satisfied.
The prerequisites are as
follows:
-
The operating system on
the domain controllers is Windows Server 2003 SP2 or higher. -
The domain controller
hardware exceeds the Windows Server 2008 R2 requirements and all
software is compatible with Windows Server 2008 R2, including antivirus
software and drivers. -
There is enough disk space free to perform the operating
system and Active Directory upgrade. Specifically, verify that your free
space is at least twice the size of your Active Directory database plus
the minimum 32GB needed to install the operating system. -
The current domain functional
level is Windows 2000 Native or Windows Server 2003. You cannot upgrade
directly from Windows NT 4.0, Windows 2000 Mixed, or Windows Server 2003
interim domain functional levels.
Often, upgrading any given server can be a project
in itself. The standalone member servers in an environment are often the
workhorses of the network, loaded with a myriad of different
applications and critical tools. Performing an upgrade on these servers
would be simple if they were used only for file or print duties and if
their hardware systems were all up to date. Because this is not always
the case, it is important to detail the specifics of each server that is
marked for migration.
Verifying Hardware
Compatibility
It is critical to test the
hardware compatibility of any server that will be directly upgraded to
Windows Server 2008 R2. The middle of the installation process is not
the most ideal time to be notified of problems with compatibility
between older system components and the drivers required for Windows
Server 2008 R2. Subsequently, the hardware in a server should be
verified for Windows Server 2008 R2 on the manufacturer’s website or on
Microsoft’s Hardware Compatibility List (HCL), currently located at http://www.microsoft.com/whdc/hcl/default.mspx.
Microsoft suggests minimum
hardware levels on which Windows Server 2008 R2 will run, but it is
highly recommended that you install the OS on systems of a much higher
caliber because these recommendations do not take into account any
application loads, domain controller duties, and so on. The following is
a list of Microsoft’s minimum hardware levels for Windows Server 2008
R2:
-
1.4GHz 64-bit processor
-
512MB of RAM
-
32GB free
disk space
That said, it cannot be stressed
enough that it is almost always recommended that you exceed these levels
to provide for a robust computing environment.
Note
One of the most
important features that mission-critical servers can have is redundancy.
Putting the operating system on a mirrored array of disks, for example,
is a simple yet effective way of increasing redundancy in an
environment.
Verifying Application
Readiness
Nothing ruins a
migration process like discovering a mission-critical application that
is installed on the current Windows Server 2003 server will not work in
the new environment. Subsequently, it is very important to identify and
list all applications on a server that will be required in the new
environment. Applications that will not be used or whose functionality
is replaced in Windows Server 2008 R2 can be retired and removed from
consideration. Likewise, applications that have been verified for
Windows Server 2008 R2 can be designated as safe for upgrade. For any
other applications that might not be compatible but are necessary, you
either need to move them to another Windows Server 2003 server or delay
the upgrade of that specific server.
In addition to the
applications, the version of the operating system that will be upgraded
is an important consideration in the process. A Windows Server 2003 SP2
or R2, Standard Edition domain controller can be upgraded to either
Windows Server 2008 R2, Standard Edition or Windows Server 2008 R2,
Enterprise Edition. However, a Windows Server 2003 SP2 or R2, Enterprise
Edition installation can only be upgraded to Windows Server 2008 R2,
Enterprise Edition.
Backing Up and Creating
a Recovery Process
It is critical that a
migration does not cause more harm than good to an environment.
Subsequently, we cannot stress enough that a good backup system is
essential for quick recovery in the event of upgrade failure. Often,
especially with the in-place upgrade scenario, a full system backup
might be the only way to recover; consequently, it is very important to
detail fallback steps in the event of problems. The backup should
include the boot and system partitions as well as the System State.
Virtual Domain
Controller Rollback Option
It is always good to
have several fallback options, in case one of the options is
unsuccessful. Another option to consider, in addition to a full backup,
is to create a virtual domain controller. Using a virtual server
platform such as Hyper-V or VMware Server, you can create a domain
controller for little or no cost.
A virtual machine is created
on the host, which can be an existing installation or even on a desktop
with Virtual PC or VMware Workstation. This virtual machine is then
joined to the domain and promoted to be a domain controller.
Prior to the upgrade,
the virtual domain controller is shut down. Backup copies of the virtual
domain controller files can even be made for safekeeping.
In the event of a major failure
in the upgrade process, the virtual domain controller can be used to
rebuild the domain from scratch. If the upgrade is successful, the
virtual domain controller can either be turned back on and demoted, or
simply be deleted and cleaned from the domain.
Performing an Upgrade
on a Single Domain Controller Server
After all various
considerations regarding applications and hardware compatibility have
been thoroughly validated, a standalone server can be upgraded.
The health of the domain
controllers should be verified prior to upgrading the domain
controllers. In particular, the Domain Controller Diagnostics (DCDIAG)
utility should be run and any errors fixed before the upgrade. The
Windows Server 2003 DCDIAG utility is part of the Support
Tools, which can be found on the installation media under
\support\tools\. The Support Tools are installed via an MSI package
named SUPTOOLS.MSI in Windows Server 2003. After installing the tools,
the DCDIAG utility can be run. The same utility is included in Windows
Server 2008 with no additional installs required. Execute the tool and
verify that all tests passed.
The Active Directory
Domain Services forest and the domain need to be prepared prior to the
upgrade. This installs the schema updates that are new to Windows Server
2008 R2 Active Directory. The following steps should be run on the
Flexible Single Master Operations (FSMO) role holder(s), specifically
the schema master for forestprep and the infrastructure master for
domainprep. In a small environment or a single domain, all these roles
are typically on the same domain controller. To prepare the forest and
domain, execute the following steps on the domain controller with the
roles:
|
1. |
Insert Note When preparing the forest, be |
|
2. |
Select |
|
3. |
Enter d:\support\adprep\adprep.exe |
|
4. |
A warning appears to verify that all Windows 2000 |
|
5. |
Enter d:\support\adprep\adprep.exe /domainprep |
|
6. |
Enter d:\support\adprep\adprep.exe /rodcprep |
Now that the schema updates
have been installed and the domain preparation is done, the domain is
ready to be upgraded. The FSMO role holder should be the first Windows
Server 2003/2008 domain controller to be upgraded. Follow these steps to
upgrade:
|
1. |
Insert |
|
2. |
The |
|
3. |
Click |
|
4. |
Click the |
|
5. |
Enter your product key and click Next. |
|
6. |
Select the I Accept the License Terms option on the |
|
7. |
Click the large Upgrade button. |
|
8. |
Review the compatibility report and verify that all |
|
9. |
The system then copies files and reboots as a Windows Figure 1. Big Bang upgrade.

|
|
10. |
After the Figure 2. Server Manager console after
|
The upgrade process shown in
steps 1 through 10 is then repeated for each of the remaining Windows
Server 2003/2008 domain controllers.
<google>BUY_WINSERV_2008R2</google>
In the previous chapter of Windows Server 2008 R2 Essentials we looked at performing a clean installation of Windows Server 2008 R2. Whilst this approach is acceptable in some instances, it is probably more common that Windows Server 2008 R2 will be installed as an upgrade to a previously installed version of Windows.
In this chapter the steps involved in performing an upgrade to Windows Server 2008 R2, together with supported upgrade paths will be covered in detail.
Contents
Contents
|
||
Windows Server 2008 R2 Upgrade Paths
Before performing an upgrade to Windows Server 2008 R2 the key prerequisite is that the currently installed operating system provides an upgrade path to the chosen edition of Windows Server 2008 R2. Whilst it was possible to upgrade to the original version of Windows Server 2008 from a somewhat wide range of older operating systems, the upgrade options provided by the R2 version are considerably more limited. In fact, Windows Server 2008 R2 may not be upgraded from any of the following operating systems:
Windows® 95, Windows 98, Windows Millennium Edition, Windows XP, Windows Vista®, Windows Vista Starter, or Windows 7, Windows NT® Server 4.0, Windows 2000 Server, Windows Server 2003 RTM, Windows Server 2003 with SP1, Windows Server 2003 Web, Windows Server 2008 R2 M3, or Windows Server 2008 R2 Beta, Windows Server 2003 for Itanium-based Systems, Windows Server 2003 x64, Windows Server 2008 for Itanium-based Systems, Windows Server 2008 R2 for Itanium-based Systems
In fact, it is only possible to upgrade from Windows Server 2008 to Windows Server 2008 R2 and even then with the following restrictions:
- Only 64-bit Windows Server 2008 based systems may be upgraded to Windows Server 2008 R2
- The upgrade can only be performed to the same or higher level edition of the operating system.
For example, it is possible to upgrade from a 64-bit Windows Server 2008 Standard to Windows Server 2008 R2 Standard, Enterprise or Datacenter editions. It is not, however, possible to upgrade from Windows Server 2008 Enterprise to Windows Server 2008 R2 Standard (since this constitutes a downgrade in functionality).
How an Upgrade to Windows Server 2008 R2 Works
During the Windows Server 2008 R2 upgrade process the files, folders and applications associated with the previously installed Windows version are relocated to a windows.old folder and all user settings stored. Once this task is complete, a clean installation of the new operating system is performed and the saved user settings migrated to the new environment. Upon completion of a successful upgrade the Windows Server 2008 R2 system will include all applications, settings and user files from the previous operating system installation.
Performing the Upgrade
<google>WIN28BOX</google>
An upgrade to Windows Server 2008 R2 can only be performed by launching the installation process from within the currently installed operating system. In other words, it is not possible to perform an upgrade by booting from the installation media. To initiate the upgrade process, therefore, boot the existing Windows installation (if not already running), log into an account with administrative privileges and insert the installation DVD. If the system is configured to do so, the setup process on the DVD will autorun once it is mounted displaying the Windows Server 2008 R2 installation screen:

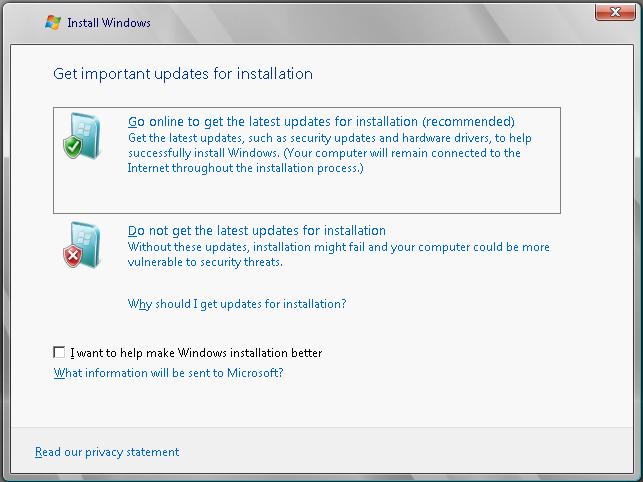
From this screen the installation may be started by clicking on the Install now button. Alternatively, the What To Know Before Installing Windows link will provide information of system requirements and advice about issues such as application and driver compatibility. Clicking on Install now proceeds to the next screen. If the setup program detects an internet connection on the host operating system the next screen displayed will provide the option to have the installation process download any available updates and incorporate them into the installation. The recommended course of action at this point is to accept the default here and install the latest updates:
After Setup has searched for, and downloaded any available updates operating system selection screen will appear as follows:
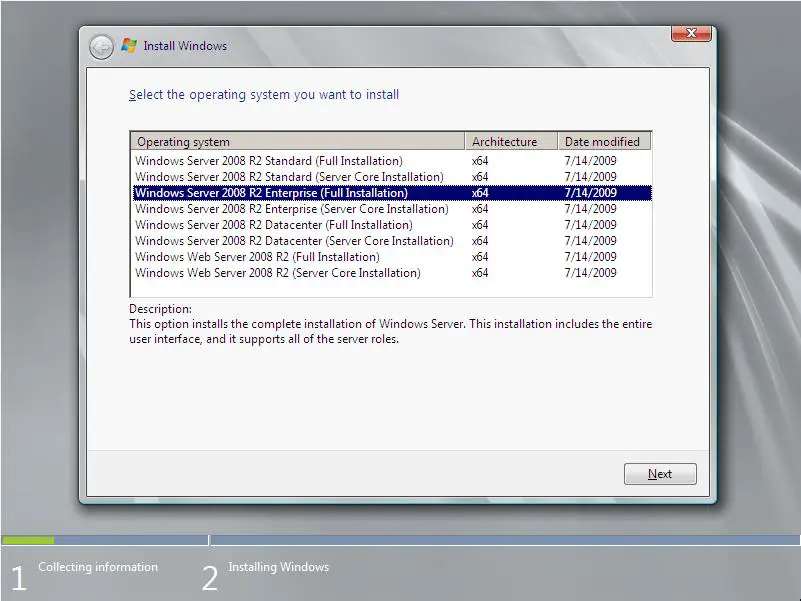
Select the desired edition and click Next to proceed.
Read and agree to the license terms and proceed to the next screen where the options to upgrade or perform a clean installation are provided. If the installer was invoked by booting from the DVD, or the host operating system is not suitable for upgrade only the clean installation option will be provided.
Windows Server 2008 R2 Compatibility Report
Assuming that the installation was launched from within a compatible operating system, the Upgrade option will be provided. Click on this option to proceed and carefully read the Compatibility Report to get information about any potential problems that may be encountered after the upgrade. Having read the report click Next to proceed.
At this point the installation will begin and continue until completed.
Accessing the Command Prompt during Installation
At any point during the setup process (except when the installation is actually being performed) Shift+F10 may be pressed to gain access to the command-prompt. From within this command prompt window most of the standard Windows Server 2008 R2 command-line tools are available allowing tasks to be performed that might otherwise not be possible from within the setup interface. A full list of available commands and respective descriptions can be found in the chapter entitled Windows Server 2008 R2 Command-line Tools.
<google>BUY_WINSERV_2008R2_BOTTOM</google>
Выполнение асинхронных задач в Python с asyncio
py-thonny 12.05.2025
Современный мир программирования похож на оживлённый мегаполис – тысячи процессов одновременно требуют внимания, ресурсов и времени. В этих джунглях операций возникают ситуации, когда программа. . .
Работа с gRPC сервисами на C#
UnmanagedCoder 12.05.2025
gRPC (Google Remote Procedure Call) — открытый высокопроизводительный RPC-фреймворк, изначально разработанный компанией Google. Он отличается от традиционых REST-сервисов как минимум тем, что. . .
CQRS (Command Query Responsibility Segregation) на Java
Javaican 12.05.2025
CQRS — Command Query Responsibility Segregation, или разделение ответственности команд и запросов. Суть этого архитектурного паттерна проста: операции чтения данных (запросы) отделяются от операций. . .
Шаблоны и приёмы реализации DDD на C#
stackOverflow 12.05.2025
Когда я впервые погрузился в мир Domain-Driven Design, мне показалось, что это очередная модная методология, которая скоро канет в лету. Однако годы практики убедили меня в обратном. DDD — не просто. . .
Исследование рантаймов контейнеров Docker, containerd и rkt
Mr. Docker 11.05.2025
Когда мы говорим о контейнерных рантаймах, мы обсуждаем программные компоненты, отвечающие за исполнение контейнеризованных приложений. Это тот слой, который берет образ контейнера и превращает его в. . .
Micronaut и GraalVM — будущее микросервисов на Java?
Javaican 11.05.2025
Облачные вычисления безжалостно обнажили ахиллесову пяту Java — прожорливость к ресурсам и медлительный старт приложений. Традиционные фреймворки, годами радовавшие корпоративных разработчиков своей. . .
Инфраструктура как код на C#
stackOverflow 11.05.2025
IaC — это управление и развертывание инфраструктуры через машиночитаемые файлы определений, а не через физическую настройку оборудования или интерактивные инструменты. Представьте: все ваши серверы,. . .
Инъекция зависимостей в ASP.NET Core — Практический подход
UnmanagedCoder 11.05.2025
Инъекция зависимостей (Dependency Injection, DI) — это техника программирования, которая кардинально меняет подход к управлению зависимостями в приложениях. Представьте модульный дом, где каждая. . .
Битва за скорость: может ли Java догнать Rust и C++?
Javaican 11.05.2025
Java, с её мантрой «напиши один раз, запускай где угодно», десятилетиями остаётся в тени своих «быстрых» собратьев, когда речь заходит о сырой вычислительной мощи. Rust и C++ традиционно занимают. . .
Упрощение разработки облачной инфраструктуры с Golang
golander 11.05.2025
Причины популярности Go в облачной инфраструктуре просты и одновременно глубоки. Прежде всего — поразительная конкурентность, реализованная через горутины, которые дешевле традиционных потоков в. . .
How to Upgrade to Windows Server 2008 R2
Our mission is to undertake an in-place upgrade from Windows Server 2008 to R2.
Topics Upgrade to Windows Server 2008 R2
- Install Phase One
- Install Phase Two
- Three tasks in the ICT manager
- Troubleshooting Windows Server 2008 Installation
♦
Upgrade to Windows Server 2008 R2
In a nutshell it was easy. One day Gung-ho Guy will come unstuck, but not on this job. I say upgrading to R2 was easy because I followed my usual path of ignoring all instructions, just clicking on setup and following my nose, and it worked. I have done this for every Microsoft operating system since Windows 2. Say what you will about Microsoft, their installs are the best of any software that I have ever seen. If it worked for me, then it will be even smoother for an organized person who reads the release notes, checks the pre-requisites.
One thing to note about Microsoft installs, the past never equals the future, each operating system setup has its idiosyncrasies, menus that I have never seen before.
What get’s me through is a belief that this setup will work. So if it stalls, then you do have to go back and read and re-read the menu to see what it wants you to do. I confess to sometimes doing silly things just to see if the install can cope. This time I tried to print out the product key while install was collecting data. This was particularly stupid as:
A) You don’t need the product key until AFTER the upgrade.
B) Printing seemed to upset the install. Intelligently, it asked for a reboot then carried on without trouble.
With Windows Server installs you always get options, such as do you want Core (headless server) or Web server. Ah yes, it has to be on 64-bit hardware, phew I was OK. These day’s always take the time for install to see if it has any updates, presumably late breaking corrections in the light of customer feedback.
I saw install reboot automatically at least once, but then I left it to get on with install, it did not need me to do anything at all. I had stuff in the startup folder, no worries, it handled that easily. I also had AutoAdminLogon set to 1, so I don’t know if install would normally require a physical name / password logon.
In passing I noticed it stuck on 18% Expanded for about half an hour, but eventually it finished that aspect and proceeded.
I cannot say how relieved I was to see the install transfer 97% of my old settings. This saved me hours of work, and of course all the apps like Word for Windows were there and did not need re-installing. I almost forgot, all the old server services such as DNS were there just as I left them in W2K8.
The only two imperfections that I could vaguely blame Microsoft for were I had to a new version of IE8, even though the old Server 2008 had IE8. Also I had to find PowerShell in the ‘Turn on Windows features’ (Control Panel), it was expecting a bit much for it to detect the CTP version of PowerShell and upgrade that.
The IE8 for W2K8 R2 (Windows 7) opens up a whole can of worms, add-ons flash, silverlight. Could not find a Adobe Flash add-on.
Guy Recommends: A Free Trial of the Network Performance Monitor (NPM) v12
SolarWinds’ Network Performance Monitor will help you discover what’s happening on your network. This utility will also guide you through troubleshooting; the dashboard will indicate whether the root cause is a broken link, faulty equipment or resource overload.
Perhaps the NPM’s best feature is the way it suggests solutions to network problems. Its second best feature is the ability to monitor the health of individual VMware virtual machines. If you are interested in troubleshooting, and creating network maps, then I recommend that you give this Network Performance Monitor a try.
Download your free trial of SolarWinds Network Performance Monitor.
Other Minor Irritations
In-place upgrades have different challenges from fresh installations. One plus is all the apps and hardware are there, at least 80% will give no trouble and work just as before. With the other 20%, how can put this, at least you know they are there, you can remember where to find them on your system, its just you have a challenge finding a driver, or re-installing them. What I am trying to say is that with a fresh installation, you get hassle when you want a program but you have forgotten where you filed the DVD, or you have lost the product key.
I had to Enable the Sound, which I did in the Control Panel, Hardware, Sound.
I then had to Disable Windows sounds! I like music, but I don’t like my speaker squawking when I click in Explorer, I tweaked this setting via Change system sounds, and adjusted ‘No sounds modified’ to plain: ‘No sounds’.
Like many other Windows 7 / W2K8 R2 aficionados, my web camera gave up the ghost after the upgrade. I phoned Logitech, they took all my details, made me read-out product codes on the camera’s lead, but could not find me a driver. In a fit of pique I then punched these same numbers into Logitech’s download section, and low-and-behold, there was a recommended driver of about 50 MB, even more impressively, it worked my web camera burst into life. A classic case where a germ of an idea leads to a solution, I would never have written down those numbers left to my own devices.
Skype needed re-installing, I guess if I had done any sort of compatibility check, then I would have found this out ahead of the Windows Server 2008 R2 upgrade. (You WILL have the same problem, but with different program.)
Taskbar is new. Very much in the style of Windows 7. The downside is no shortcuts are no longer allowed in this area. You have to create a new toolbar with Quick Launch attributes to get that feature back.
Your upgrade is bound to have similar wrinkles. So my bet is your upgrade will provide you a good working platform with all your old important Windows Server 2008 stuff just as before, however, I guarantee there will be minor glitches with peripheral hardware, or moody software may not work. Your salvation is a little research on the software site, or from the superuser forum.
Follow-up
The strange case of the silent Microsoft Product Key. Did I miss it? Did I dismiss it? Anyway I found in the usual place, Control Panel System and Internet, System (Again), bottom of the screen click on: ‘Change product key’, naturally you need a genuine 24 digit number.
Features – Hybrid Windows Server 2008 and Windows 7.
Library
Windows Desktop Experience
What’s in the Desktop Experience Feature? The Desktop Experience feature includes the following Windows Vista components and features: Windows Calendar Windows Mail Windows Media Player Windows Aero and other desktop themes Video for Windows (AVI support) Windows Photo Gallery Windows SideShow Windows Defender Disk Cleanup Sync Center Sound Recorder Character Map
Requirements
Minimum Recommend Optimal
Processor: 1 Ghz 2 Ghz 3 Ghz
RAM Mem: 512 Gb 2 Gb Depends on the edition
Disk Space: 8 Gb 40 Gb 80 Gb
Also common sense actions, disable UPS, remove any anti-virus software, realize once get the GUI, the firewall is active by default.
»
Troubleshooting Windows Server 2008 Installation
- Disconnect the UPS
- Run the Windows memory diagnostic tool
- Get updated mass storage drivers
- In Phase Two – disable the firewall to connect to other servers
- Disable Virus Protection (If you are upgrading)
- If all else fails, check ‘Help and Support’ on the first menu of the Windows Server 2008 setup.
If you like this page then please share it with your friends
Microsoft Windows Server 2008 Topics:
• Server 2008 Home • Overview • What’s New? • Migration Advice • Editions
• Features •Resource Manager • Add Aero Themes • GP Preferences
• Network Performance Monitor • Upgrade W2k8 R2 • Windows Server 2012