Environment variables are special settings that store information about the system and the programs installed on it. They can be used to customize the behavior of applications, scripts, and commands. But can environment variables be deleted? The answer is yes, and that’s a good thing, as sometimes, you may need to modify or remove an environment variable. For example, to change a configuration option or to fix a problem. In this article, I’ll show you how to edit or delete environment variables, as well as how to unset environment variables in Windows using different methods and tools, including Command Prompt and PowerShell.
NOTE: The instructions in this guide apply to both Windows 11 and Windows 10, as everything related to handling environment variables is the same in both operating systems.
Open the Environment Variables window
To make many of the edits shown in this article, you first need to open the Environment Variables window. This guide explains how to do that and shows you the basics about working with environment variables: What are environment variables in Windows?.
The Environment Variables window in Windows
If you want to skip reading it, one path that works the same in Windows 11 and Windows 10 is to open the Run window (Win + R) and execute the command:
rundll32.exe sysdm.cpl,EditEnvironmentVariables
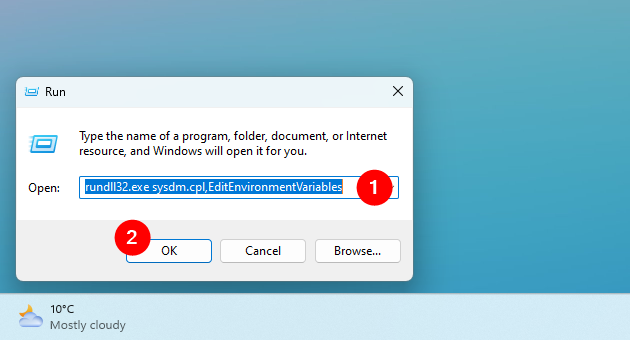
How to open the Environment Variables in Windows
TIP: You can run the command in Command Prompt, PowerShell, or Windows Terminal to the same end, too.
How to edit an environment variable in Windows
If you want to change the value of an existing environment variable, first select it in the Environment Variables window. Then, click or tap Edit.
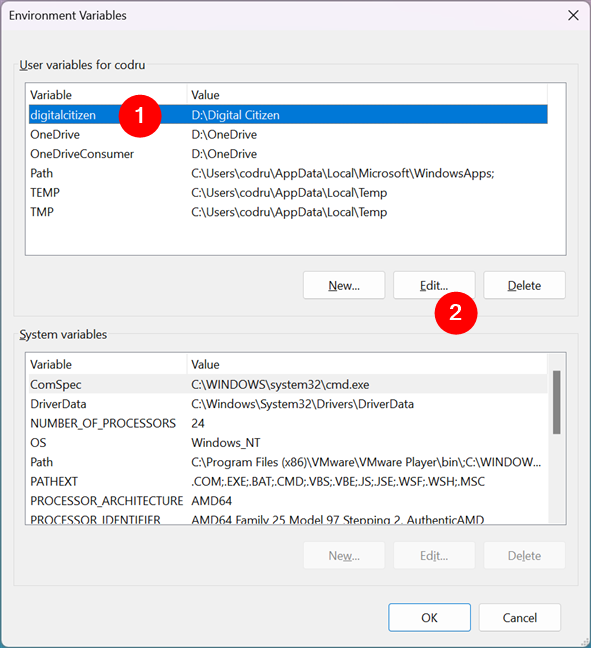
How to edit an environment variable in Windows
You are shown a window where you can edit both the name and the value of the variable. Make the modifications you want and press OK. Then, press OK one more time in the Environment Variables window.
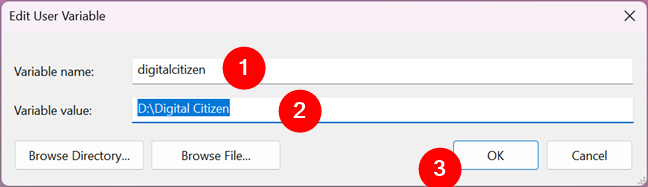
Editing an environment variable
How to edit an environment variable from Command Prompt
You can create a new environment variable or edit the value of an existing environment variable (but not its name) from the Command Prompt too. If you want to create a user environment variable, enter this command:
setx variable_name “value”
If you want to create a system environment variable, add the m argument to the command like this:
setx variable_name “value” /m
For example, I wanted to create a user variable named TEST with the value C:\digitalcitizen. To that end, I had to run this command:
setx TEST “C:\digitalcitizen”
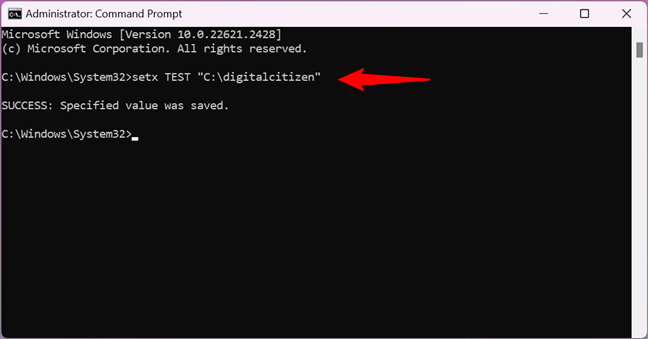
How to set an environment variable using Command Prompt
To change the value of an environment variable, run the same setx command but specify a new value for the variable. For instance, to change the value of my TEST environment variable to C:\DC, I have to execute this command:
setx TEST “C:\DC”
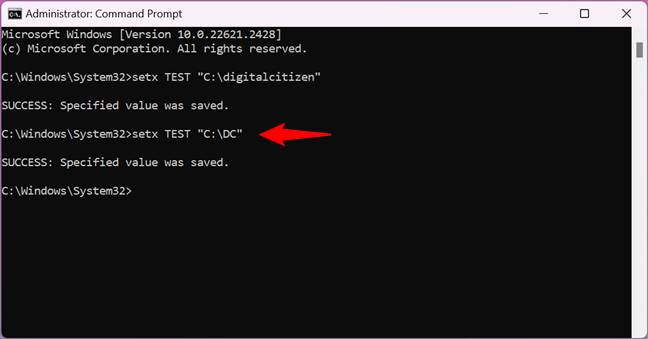
How to change the value of an environment variable in Command Prompt
That works because the setx command rewrites the existing value with the last one you type. Therefore, if you use this command multiple times on the same variable, the variable will keep the last value you typed.
If you want a variable to have multiple paths in its value, you must specify them all in a single setx command, like in the next screenshot. Make sure that each value you enter is separated from the previous one by a semicolon, without spaces.
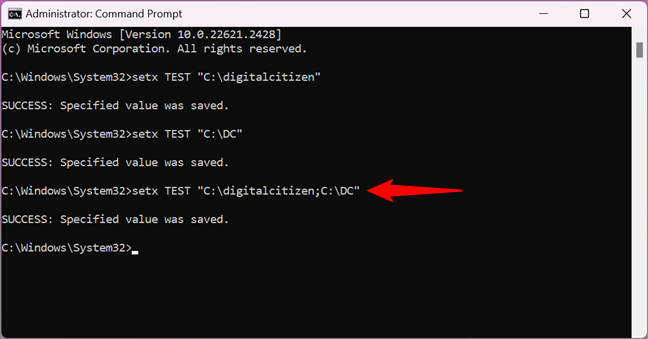
Add multiple values to an environment variable using CMD
TIP: You can get a list of all the environment variables available by running the command:
set
Note that the command is set, not setx, and there aren’t any parameters added to it. Moreover, if you just created or edited an environment variable, you must close and reopen Command Prompt for the changes to show up.
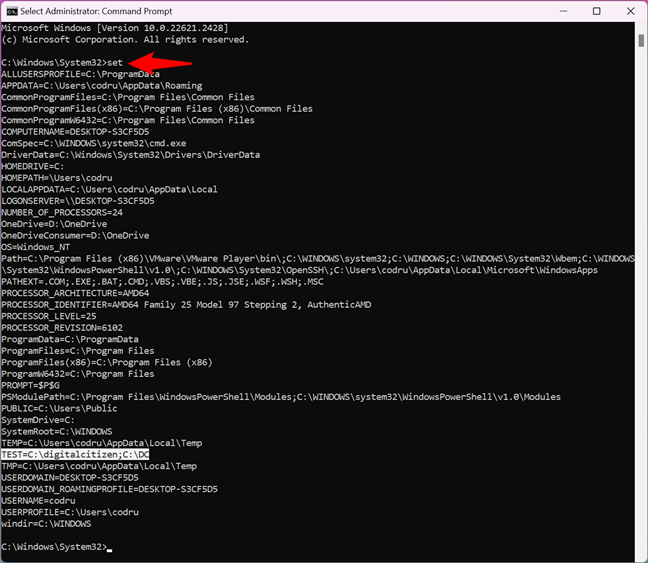
How to see all the environment variables in Command Prompt
How to edit an environment variable from PowerShell
You can also create or edit the value of an existing environment variable from PowerShell. If you want to create a user environment variable, the PowerShell command is:
[Environment]::SetEnvironmentVariable(«variable_name»,»variable_value»,»User»)
If you want to create a system environment variable, the command is this one:
[Environment]::SetEnvironmentVariable(«variable_name»,»variable_value»,»Machine»)
For instance, in order to create a user environment variable called TEST with the value digitalcitizen.life, I ran the command:
[Environment]::SetEnvironmentVariable(«TEST»,»digitalcitizen.life»,»User»)
To change the value of the variable later, you can run the same command using a different value. Just like setx in Command Prompt, this command rewrites the value of the specified variable each time you run it.
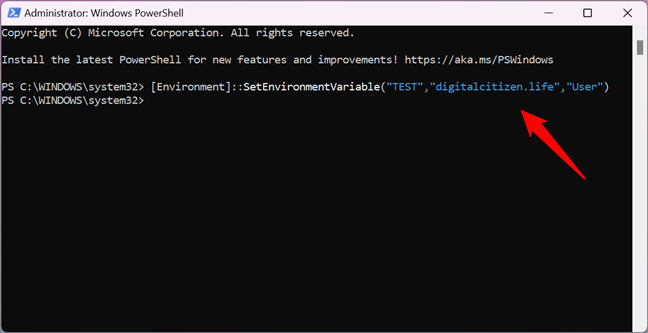
How to set an environment variable with PowerShell
If you want to assign multiple values to a variable, type all of them in the command, with semicolons between each value, as illustrated below.
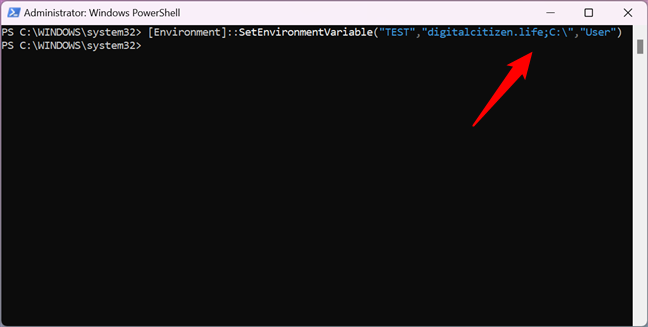
How to add multiple values to an environment variable in PowerShell
TIP: In PowerShell, you can get a list of all the environment variables by running the command:
Get-ChildItem Env:
However, if you just created or edited an environment variable, you must close and reopen PowerShell for the changes to show up.
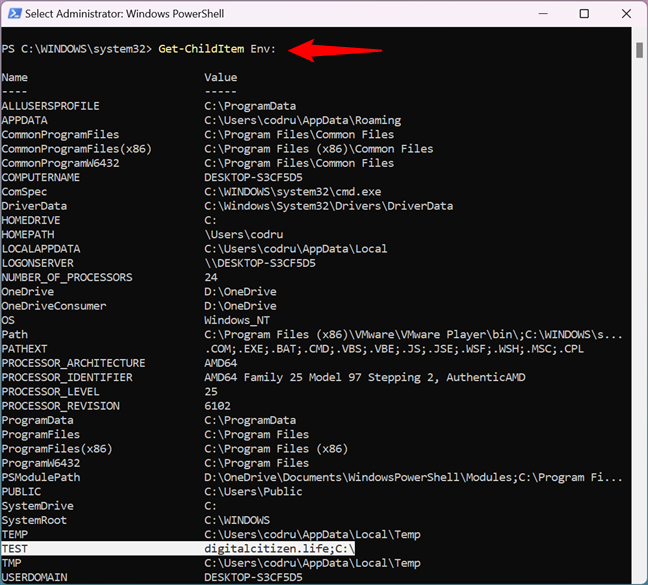
How to see all the environment variables in PowerShell
How to clear the value of an environment variable in Windows (from Command Prompt)
If you want to remove the value of an environment variable (while keeping its name), you can’t do it with the mouse and keyboard from the Environment Variables window. If you select a variable and press Edit, you can delete the value, but you cannot press OK, as this button gets grayed out. Therefore, you can’t save your changes.
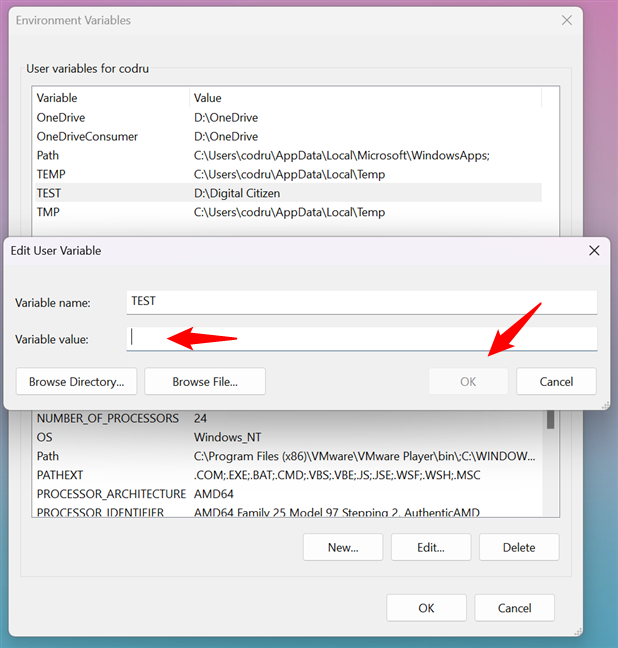
Attempt to clear an environment variable in Windows
However, you can clear the value of an environment variable using Command Prompt. To unset an environment variable from Command Prompt, type the command:
setx variable_name “”
For example, because I wanted to unset my TEST variable and give it an empty value, I ran this command:
setx TEST “”
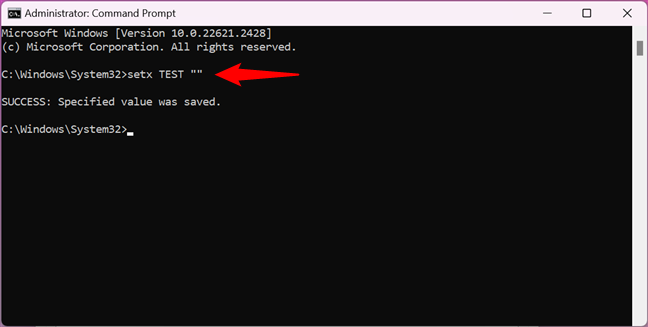
How to clear an environment variable with Command Prompt
Next, let’s see how to remove an environment variable.
How to delete an environment variable in Windows
If you no longer want to use a particular environment variable, select it in the Environment Variables window. Then, press Delete. Windows does not ask for any confirmation of this action.
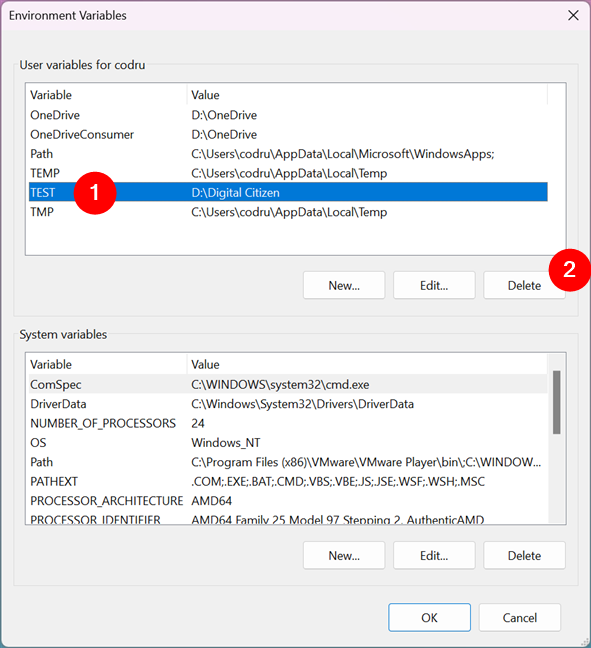
How to delete an environment variable in Windows
Therefore, if you’ve changed your mind, you must press Cancel to NOT apply the removal. If you want to proceed with the deletion, press OK.
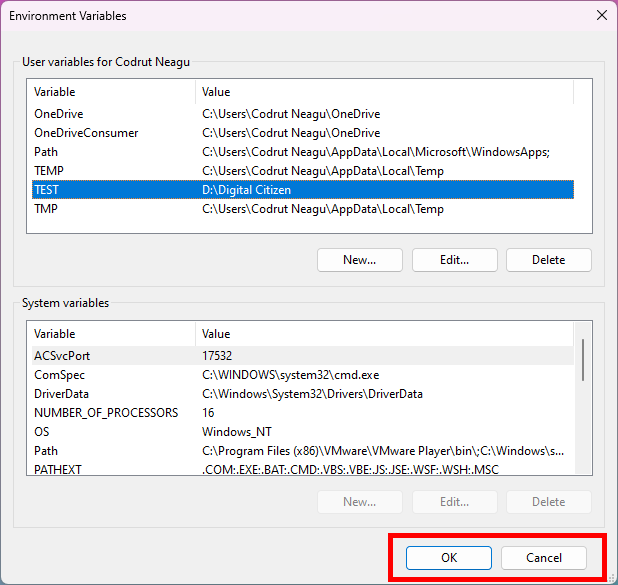
Press OK to delete the variable, or Cancel to keep it
How to use Command Prompt (CMD) to delete an environment variable
To delete an environment variable from Command Prompt, run this command:
REG delete “HKCU\Environment” /F /V “variable_name”
… if it’s a user environment variable, or run this command if it’s a system environment variable:
REG delete “HKLM\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\Session Manager\Environment” /F /V “variable_name”
For example, to remove my TEST environment variable from my user’s profile, I ran:
REG delete “HKCU\Environment” /F /V “TEST”
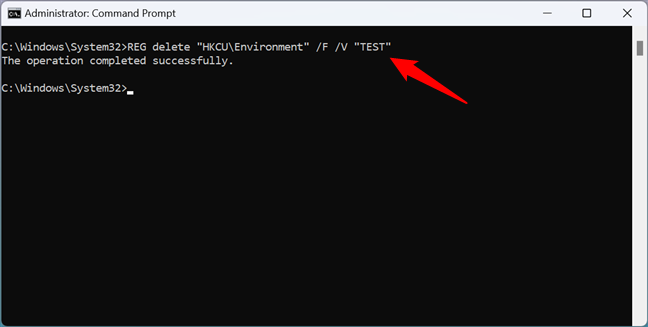
How to unset an environment variable in Windows using Command Prompt
How to use PowerShell to delete an environment variable
To unset and remove an environment variable with PowerShell, type the command:
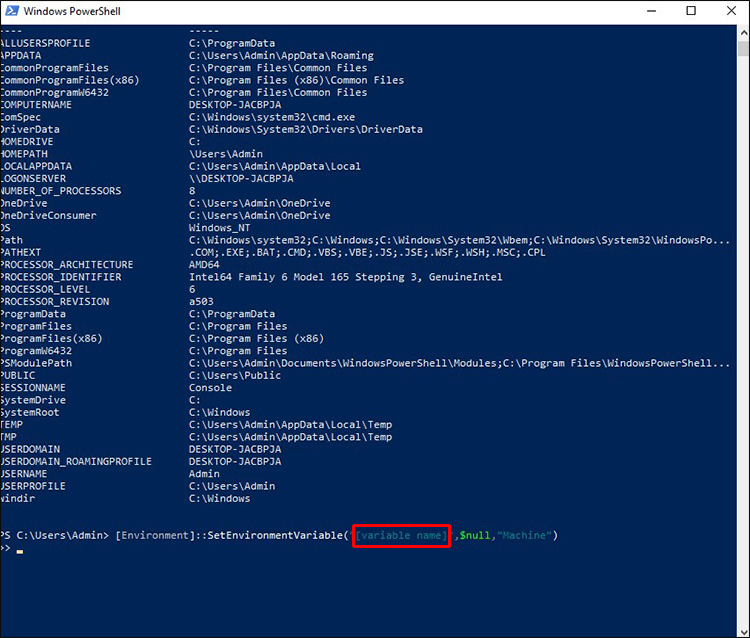
[Environment]::SetEnvironmentVariable(«variable_name», $null, «User»)
…if it’s a user profile variable, or run this command if it’s a system-wide variable:
[Environment]::SetEnvironmentVariable(«variable_name», $null, «Machine»)
For example, to have PowerShell remove my TEST environment variable from my user profile, I had to run this command:
[Environment]::SetEnvironmentVariable(«TEST», $null, «User»)
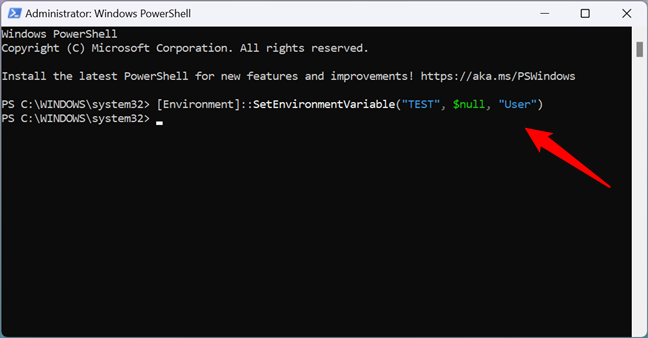
How to delete an environment variable from PowerShell
That’s it!
Why did you need to edit or delete environment variables in Windows?
You now know that Windows can unset environment variables. You’ve seen how to use PowerShell to delete environment variable values and how to use PowerShell to remove environment variables completely. Moreover, you also know how to use CMD to delete any environment variable. But why did you want to change or edit environment variables? Was it because there were leftover variables on your system from certain apps that you no longer used? Or was it because you have a special setup and you need to work with environment variables? Let me know in the comments section below.
Environment variables may be helpful to programmers, system administrators, and other advanced users. They provide us with details about the environment wherein an application is running. In some instances, you can delete an environment variable. In other cases, you can change only its value.
Sometimes you might need to clear the environment variable on your Windows. But how can you do this? Keep reading to find out all the methods you can use to remove and change environment variables.
How to Unset Env Variable in Windows
The operating system’s environment makes use of data stored in environment variables. There is a lot of information we can learn from them about how the software works. Environment variables can be divided into two categories:
- When a program is installed, the OS or driver sets these environment variables, which include information about system resources. These are called System Environment Variables. For instance, the windir variable will hold the location of Windows.
- Information specific to a given user account is stored in User Environment Variables. Setting the PATH variable in order for the commands to run without having to provide the file path every time is an example of this.
There are ways to unset both types of Env Variables. You can do so by using the Environment Variables window, Power Shell, and Registry Editor.
Environment Variables Window
You can use Command Prompt to clear System and User Env Variables on your Windows PC. Here is how to clear System Env Variables:
- Launch Control Panel and select the System symbol.
- Select the “Advanced system settings” link on the left side, and if desired, shut the System control panel window.
- Select the Env Variables icon with your mouse or tapping device.
- Press “Delete” next to the variable you wish to delete at the bottom of the System variables section.
- Once you’re finished eliminating system variables, click “OK” to confirm.
To clear the User Env Variables, follow these steps:
- Click on the “User Accounts” button in the Control Panel.
- On the left, click or tap the “Change my environment variables” link, and if you wish, shut the User Accounts control panel window.
- Pick a variable you would like to remove outlined at the top of the User variables for <current user name> section, and press the “Delete” option.
- When you’re finished eliminating user variables from your account, select “OK” to confirm the deletion.
Power Shell
Power Shell can also be used to clear both types of Env Variables effectively. Here is how to clear System Env Variables:
- Launch a Windows PowerShell session in the elevated mode.
- Paste the following command into the elevated PowerShell:
Get-ChildItem Env: - Hit “Enter” and make a note of the name of the system variable you wish to unset.
- Enter the command below into the elevated PowerShell:
[Environment]::SetEnvironmentVariable("[variable name]",$null,"Machine") - Substitute [variable name] with the variable name you wish to remove in the command above.
- You may now exit the elevated Windows PowerShell.
If you want to delete User Env Variable, follow these steps:
- Run Windows PowerShell in elevated mode.
- In the elevated PowerShell prompt, paste the following command:
Get-ChildItem Env: - Press “Enter.”
- Now type or paste the command below:
[Environment]::SetEnvironmentVariable("[variable name]",$null,"User") - Hit “Enter” again and close PowerShell.
Registry Editor
Here’s how to clear System Env Variables using Registry Editor:
- To launch Registry Editor, press Win + R to open Run, input “
regedit” into Run, then click on “OK.” - On the left side of Registry Editor, navigate to the key shown below.
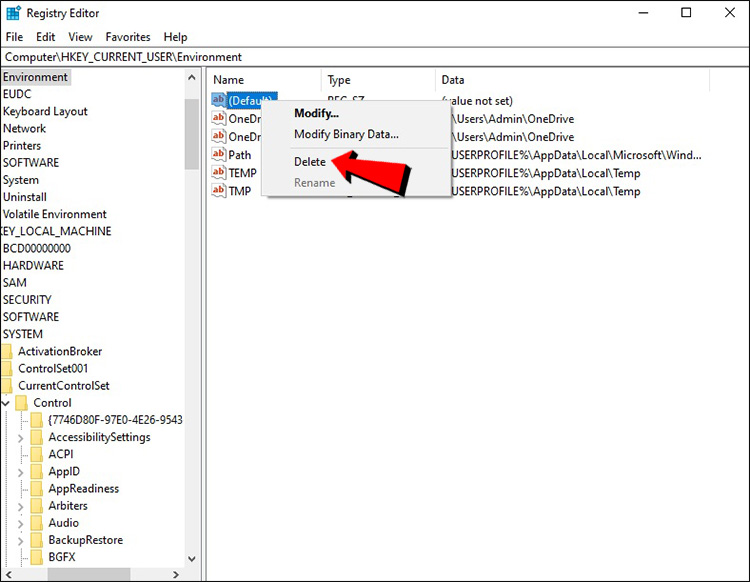
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\Session Manager\Environment - Click or press and hold on the value name of the variable you wish to delete on the right side of the Environment key in Registry Editor. Then click or tap on “Delete.”
- Confirm by clicking on “Yes.”
- Close the Registry Editor.
And to clear user Env Variable, the steps are:
- To open Registry Editor, use Win + R to bring up Run, type “
regedit” into Run, and then click “OK.” - In the Registry Editor’s left pane, go to the key indicated below.
HKEY CURRENT USER\Environment - On Registry Editor, click or press and hold the value name of the variable you intend to remove on the right side of the Environment key. After that, select “Delete.”
- Confirm your selection by selecting “Yes.”
- Ensure that the Registry Editor is closed.
Additional FAQs
Why are Env Variables important?
The answer to the question, “What are environment variables?” is a relatively difficult one. As you can observe from this guide, dealing with Windows programs makes it tough to locate and observe environment variables.
Their management is handled in the background by the OS and the numerous apps and drivers you run on your computer. The OS and your existing programs, on the other hand, rely on them. Your system could malfunction if you mess about with the values of critical system variables without understanding what you’re doing.
What are the default Windows Environment Variables?
Each Windows PC has a vast array of variables. Variables such as OS, TEMP, and PATH are often utilized. You may find default values for Windows environment variables on websites like Wikipedia.
Have Control Over Your Env Variables
The same software used for clearing Env Variables can be used to edit or create new ones as well. However, if you’re not sure about it, it’s better to leave it to a professional. Since the variables are the backbone of your Operating System and software, messing with them can result in a system crash. This can be more expensive than asking a professional to deal with them in the first place.
Have you ever tried to clear Env Variables? Have you tried editing or creating new ones? Did you find it difficult? Let us know in the comment section below!
Environment variables are key-value pairs a system uses to set up a software environment. The environment variables also play a crucial role in certain installations, such as installing Java on your PC or Raspberry Pi.
In this tutorial, we will cover different ways you can set, list, and unset environment variables in Windows 10.
Prerequisites
- A system running Windows 10
- User account with admin privileges
- Access to the Command Prompt or Windows PowerShell
Check Current Environment Variables
The method for checking current environment variables depends on whether you are using the Command Prompt or Windows PowerShell:
List All Environment Variables
In the Command Prompt, use the following command to list all environment variables:
set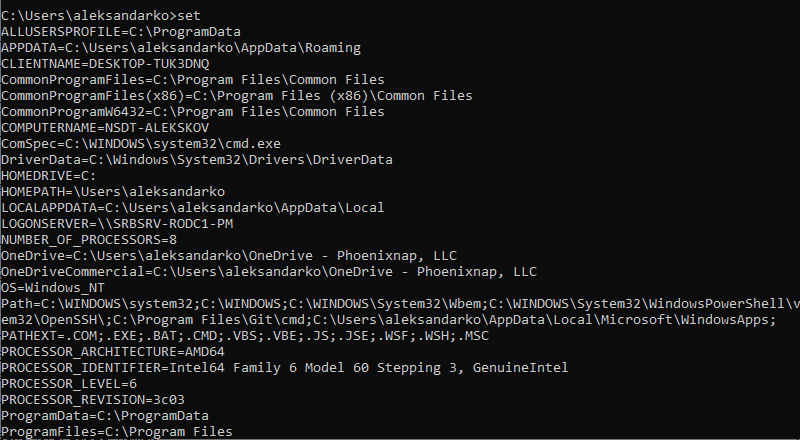
If you are using Windows PowerShell, list all the environment variables with:
Get-ChildItem Env: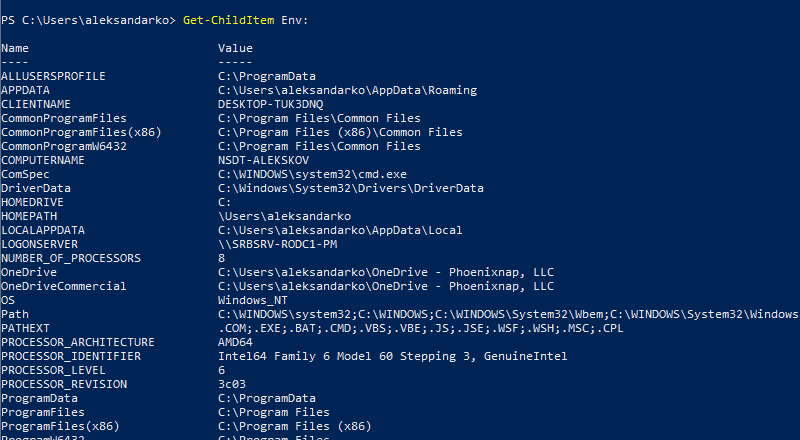
Check A Specific Environment Variable
Both the Command Prompt and PowerShell use the echo command to list specific environment variables.
The Command prompt uses the following syntax:
echo %[variable_name]%
In Windows PowerShell, use:
echo $Env:[variable_name]
Here, [variable_name] is the name of the environment variable you want to check.
Set Environment Variable in Windows via GUI
Follow the steps to set environment variables using the Windows GUI:
1. Press Windows + R to open the Windows Run prompt.
2. Type in sysdm.cpl and click OK.
3. Open the Advanced tab and click on the Environment Variables button in the System Properties window.
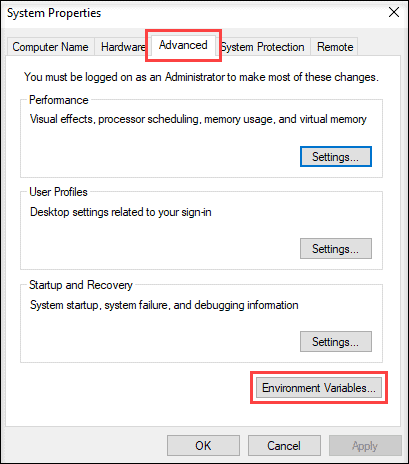
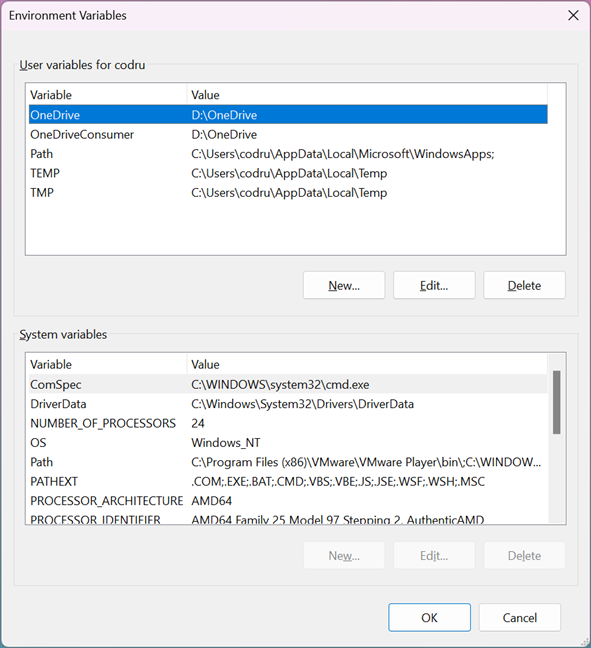
4. The Environment Variables window is divided into two sections. The sections display user-specific and system-wide environment variables. To add a variable, click the New… button under the appropriate section.
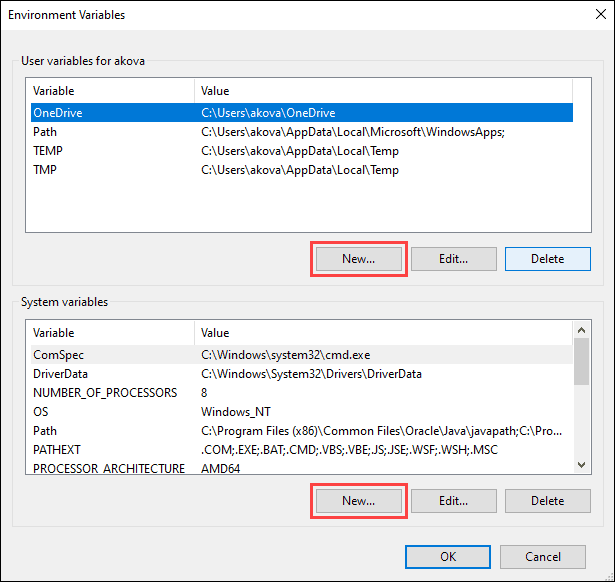
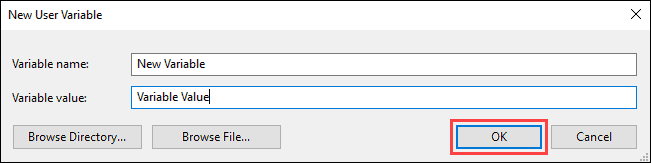
5. Enter the variable name and value in the New User Variable prompt and click OK.
Set Environment Variable in Windows via Command Prompt
Use the setx command to set a new user-specific environment variable via the Command Prompt:
setx [variable_name] "[variable_value]"Where:
[variable_name]: The name of the environment variable you want to set.[variable_value]: The value you want to assign to the new environment variable.
For instance:
setx Test_variable "Variable value"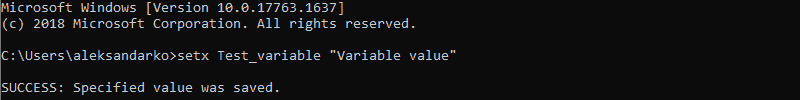
Note: You need to restart the Command Prompt for the changes to take effect.
To add a system-wide environment variable, open the Command Prompt as administrator and use:
setx [variable_name] "[variable_value]" /M
Unset Environment Variables
There are two ways to unset environment variables in Windows:
Unset Environment Variables in Windows via GUI
To unset an environment variable using the GUI, follow the steps in the section on setting environment variables via GUI to reach the Environment Variables window.
In this window:
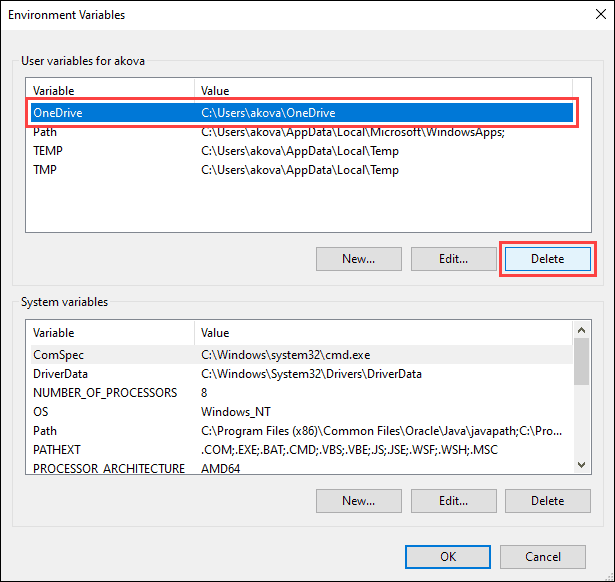
1. Locate the variable you want to unset in the appropriate section.
2. Click the variable to highlight it.
3. Click the Delete button to unset it.
Unset Environment Variables in Windows via Registry
When you add an environment variable in Windows, the key-value pair is saved in the registry. The default registry folders for environment variables are:
- user-specific variables: HKEY_CURRENT_USEREnvironment
- system-wide variables: HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESYSTEMCurrentControlSetControlSession ManagerEnvironment
Using the reg command allows you to review and unset environment variables directly in the registry.
Note: The reg command works the same in the Command Prompt and Windows PowerShell.
Use the following command to list all user-specific environment variables:
reg query HKEY_CURRENT_USEREnvironment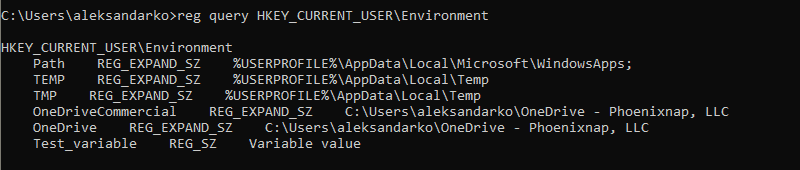
List all the system environment variables with:
reg query "HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESYSTEMCurrentControlSetControlSession ManagerEnvironment"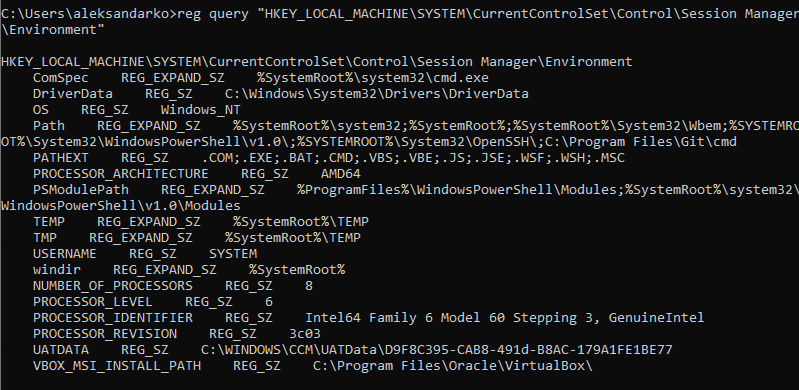
If you want to list a specific variable, use:
reg query HKEY_CURRENT_USEREnvironment /v [variable_name]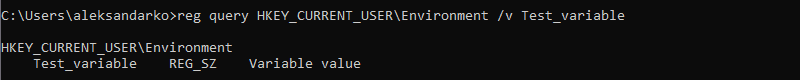
or
reg query "HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESYSTEMCurrentControlSetControlSession ManagerEnvironment" /v [variable_name]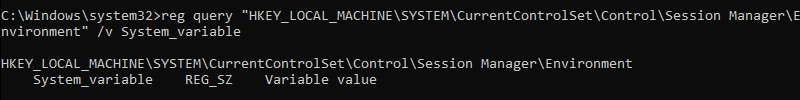
Where:
/v: Declares the intent to list a specific variable.[variable_name]: The name of the environment variable you want to list.
Use the following command to unset an environment variable in the registry:
reg delete HKEY_CURRENT_USEREnvironment /v [variable_name] /f
or
reg delete "HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESYSTEMCurrentControlSetControlSession ManagerEnvironment" /v [variable_name] /f
Note: The /f parameter is used to confirm the reg delete command. Without it, entering the command triggers the Delete the registry value EXAMPLE (Yes/No)? prompt.
Run the setx command again to propagate the environment variables and confirm the changes to the registry.
Note: If you don’t have any other variables to add with the setx command, set a throwaway variable. For example:
setx [variable_name] trash
Conclusion
After following this guide, you should know how to set user-specific and system-wide environment variables in Windows 10.
Looking for this tutorial for a different OS? Check out our guides on How to Set Environment Variables in Linux, How to Set Environment Variables in ZSH, and How to Set Environment Variables in MacOS.
Was this article helpful?
YesNo
Introduction
In Windows, you sometimes need to modify environment variables.
There are environment variables like %APPDATA% and %PROGRAMFILES%
which contain useful paths, and others that contain things like
your username (%USERNAME%). An important one that you may
want to modify is %PATH%. In this guide we will look at
how to set, check, update, and unset environment variables
using the GUI and the command prompt.
Note that environment variables are case-insentive and that
there are system-wide environment variables
and user-specific environment variables.
Using GUI
You can edit the environment through the Windows settings
You can get to the GUI a few ways:
- Press Windows key and search for «environment» and click
Edit the system environment variablesfrom the Control Panel. - Press Windows key+R to directly run:
SystemPropertiesAdvanced.exe
Once in the System Properties panel, click the «Environment Variables…» button in the bottom-right.
From the GUI, you can edit the user variables on the top and the system variables on the bottom.
After setting an environment variable using this GUI method,
you will need to restart your applications for it to take effect.
Using command prompt
Use set and setx to manipulate environment variables from the command line.
Get help with set /? and setx /?. Let’s look at what each one does.
Check an environment variable
Check all environment variables with set:
set
Check a specific variable like this:
set X
You can print out an environment variable like this:
echo %X%
Set environment variable for a single session
To set an environment variable just for the current command prompt, use set.
set X=something
Permanently set environment variable
To permanently set an environment variable that will persist across
command prompts and through restart, use setx. Get help with setx /?.
setx X 123
By default, this is a user environment variable, not a system one.
To set a system environment variable, add the /M flag (will require admin prompt).
A common scenario is the need to update your PATH.
In this situation you want to add to the existing variable.
You can do that by referencing the original value like this:
setx PATH "%PATH%;C:\opt\bin\"
Unset environment variable
To unset an environment variable, set to to an empty string.
set X=
or
setx X ""
Conclusion
After reading this, you should know how to set environment variables in Windows
permanently or for a single session using the GUI or the command prompt.
Published: Apr 7, 2021
Updated: Jun 7, 2021
Table of Contents
List All Environment Variables
#
set
Get an Environment Variable
#
Syntax:
echo %<VAR_NAME>%
Usage:
Let’s pretend that your Windows account is named foo. On a traditional Windows machine, here’s what you’d see:
echo %USERNAME% will output foo
echo %USERPROFILE% will output C:\Users\foo
Set an Environment Variable (Only for Current Session)
#
Syntax:
set <VAR_NAME>="<VAR_VALUE>"
Usage:
set MY_NAME="Jane Doe"
Set an Environment Variable (Persist)
#
Syntax:
setx <VAR_NAME> "<VAR_VALUE>"
Usage:
setx MY_NAME "Jane Doe"
Note: Changes made by setx will only be picked up in new instances of Command Prompt. So, restart Command Prompt to pick up the change.
Unset an Environment Variable (Only for Current Session)
#
Syntax:
set <VAR_NAME>=
Usage:
set MY_NAME=
Unset an Environment Variable (Persist)
#
Syntax:
reg delete "HKCU\Environment" /v <VAR_NAME> /f
Usage:
reg delete "HKCU\Environment" /v MY_NAME /f
Note: Changes made by reg will only be picked up in new instances of Command Prompt. So, restart Command Prompt to pick up the change.
Docs
#
- set
- setx
- reg delete
- List, Get, Set, and Unset Mac and Linux Environment Variables in Terminal