Для завершения процессов в Windows можно использовать команду (программу) taskkill, через командирую строку CMD, используя ключи f im. Команда taskkill позволяет закрывать одно или несколько программ как по имени образа, так и по идентификатору процесса (PID) в Windows системах.
На обычных рабочих станциях данная команда не особо востребована, так как можно завершить процесс через диспетчер задач. Хотя, не всегда это получается и в данной ситуации команда Taskkill пригодится, но, это скорее исключение из правил.
В каких ситуациях пригодится программа Taskkill?
В основном, данная команда используется системными администраторами и лично я сталкивался со следующими ситуациями:
- Обновление программ на терминальном сервере – при администрировании терминального сервера большое количество людей может запустить одно и тоже приложение. Но, в большинстве случаев, при обновлении программы её необходимо сначала закрыть, т.е. завершить её процесс. Если клиентов не много, то, можно воспользоваться диспетчером задач, а если их порядка 100, то это уже проблематично. А команда Taskkill позволяет убить все процессы для определенного приложения.
- Автоматический перезапуск программы – как вы знаете не все программы работают идеально и бывает, что они подвисают. А если данная программа должна работать 24 часа в сутки и 7 дней в неделю, то приходится периодически проверять её работоспособность.
Лично я сталкивался со следующей ситуацией: есть интернет магазин, в который данные о товарах выгружаются из 1С-ки. Но, обработчик написан как-то криво, в результате чего обмен подвисает раз в сутки, а то и через каждые 2-3 часа. По этому, появилась необходимость каждый час принудительно перезапускать обработчик, не зависимо от того, подвисла программа или нет.
И так, перейдем к практике.
Синтаксис команды Taskkill
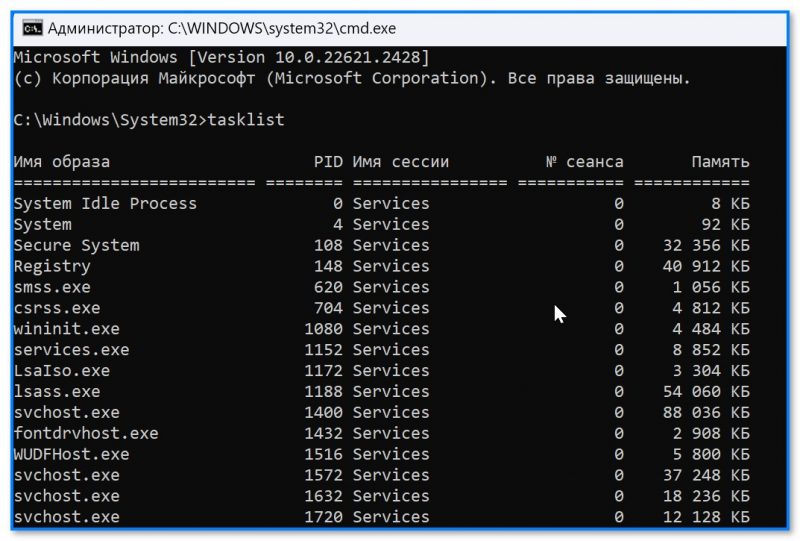
Запустим браузер Google Chrome и попробуем завершить его процесс (Пуск \ Стандартные \ Выполнить \ cmd \ taskkill /? — чтобы посмотреть синтаксис команды)
- /s КОМПЬЮТЕР, где КОМПЬЮТЕР — это IP или адрес удаленного компьютера. По умолчанию, операция выполняется в локальной системе. Если именно это вас и интересует, данную опцию можно не использовать.
- /u ДОМЕН\ПОЛЬЗОВАТЕЛЬ, где ДОМЕН — это имя домена, а ПОЛЬЗОВАТЕЛЬ — имя пользователя, для которого нужно выполнить команду. Данная опция позволяет запускать taskkill с правами определенной учетной записи или домена.
- /p — обязательно используется в сочетании с опцией /u для указания пароля к учетной записи пользователя.
- /fi — позволяет выполнять команду taskkill с определенными фильтрами.
- /f — принудительно завершает выполнение команды.
- /IM — позволяет использовать имя приложения вместо идентификатора процесса.
- /T — завершение дерева процессов.

Теперь нам нужно узнать имя приложения, которое использует данный процесс. Это можно сделать через диспетчер задач (Ctrl+Alt+Del \ Запустить диспетчер задач \ Процессы \ chrome.exe).
Если у вас нет возможности запустить диспетчер задач, допустим, вы подключились к компьютеру удаленно через командную строку, то можно воспользоваться командой tasklist, она так же отображает все процессы.
Завершение процесса через Taskkill /f /im
Taskkill /f /im chrome.exe – принудительно завершить приложение с именем chrome.exe

Chrome завершил работу, однако, возможно появление ошибки «Не удалось завершить процесс, ни один из экземпляров задания не запущен». Данное сообщение появляется из-за того, что эти процессы были связанными и когда завершил работу основной, остальные автоматически завершились.
Теперь запустим Chrome под разными пользователями, чтобы сымитировать работу терминального сервера, для этого запустим под обычным пользователем и под пользователем XP (Chrome \ Shift \ ПКМ \ Запустить от имени другого пользователя \ ОК). Теперь мы видим, что одно и тоже приложение запущено под разными пользователями, повторим команду Taskkill /f /im chrome.exe, чтобы проверить, для всех ли пользователей будет завершен процесс.
Автоматическое завершение процесса через Taskkill
Теперь попробуем сделать автоматический перезапуск приложения, в этом нам поможет планировщик задач (Пуск \ Все программы \ Стандартные \ Служебные \ Планировщик заданий \ Библиотека планировщика \ ПКМ \ Создать папку \ Перезапуск Chrome – в зависимости от вашей цели)
Создаем задачу на запуск (Создать новую задачу \ Запуск \ Выполнять с наивысшими правами \ Триггер: по расписанию, ежедневно, начиная с 11:00, повторять каждый час бесконечно, включено \ Действия: запуск программы, chrome \ ОК)
Создадим задачу на завершение процесса (Создать новую задачу \ Завершение \ Выполнять с наивысшими правами \ Триггер: по расписанию, ежедневно, начиная с 10:59:50, повторять каждый час бесконечно, включено \ Действия: запуск программы, Taskkill, дополнительные аргументы: /f /im chrome.exe \ ОК)

Теперь запустим Chrome и подведем часы к более близкому времени, чтобы увидеть, как Хром завершит работу, а потом запустится заново.
Однако, порой требуется запретить только процесс запущенный под определенным пользователем. Именно такая ситуация у меня возникла с обработчиком 1С, который выгружал данные о товарах на сайт.
Дело в том, что, можно каждый час перезапускать зависшую 1С-ку, но, если завершать все процессы 1С, то все удаленные пользователи будут из неё вылетать, а этого нельзя допустить. По этому, нужно завершать процесс, запущенный из под определенной учетной записи.
Завершение процесса для определенного пользователя
Для этого в дополнительные аргументы добавим следующую строчку /fi “username eq station-4-7” данная команда фильтрует по имени пользователя и завершает процесс только того, чье имя совпадает с указанным в фильтре.
Запустим Chrome под другим пользователем и посмотрим, сработал ли фильтр.
Содержание статьи:
- Способы завершить процесс
- Вариант 1: через диспетчер задач
- Вариант 2: с помощью командной строки
- Вариант 3: с помощью спец. приложений
- Вопросы и ответы: 0
Всем здравия!
Время от времени некоторые приложения в Windows могут подвисать, закрываться с ошибками, давать сбои (иногда и вовсе при закрытии окна приложения — сам процесс не завершается и остается в памяти. У меня, например, регулярно такое происходит с uTorrent на домашнем ПК: процесс «utorrent.exe» висит в памяти, а самого окна нет!).
Разумеется, если «такой сбойный» процесс остался в памяти — он может мешать норм. работе: из-за него, возможно, вы не сможете запустить приложение снова; он может загружать ЦП до 50-99%; копирование и открытие файлов может тормозить, идти рывками, и т.п.
В общем, в рамках этой заметки рассмотрим несколько способов, как можно завершать такие процессы (иногда опытные пользовали используют другую аббревиатуру: «Убить процесс»).
*
📌 Важно!
Простая перезагрузка компьютера позволяет «убивать» все текущие процессы… (правда, если есть зависший процесс — то, возможно, понадобиться принудительное завершение работы через кнопку «reset»).
*
Способы завершить процесс
Вариант 1: через диспетчер задач
Клавиши для вызова диспетчера задач: Ctrl+Alt+Del или Ctrl+Shift+Esc
Встроенный в Windows 📌диспетчер задач позволяет просмотреть все запущенные программы (процессы). Чтобы закрыть один из них — во вкладке «Процессы» найдите нужный, сделайте по нему правый клик мыши и в появившемся меню нажмите «Снять задачу».
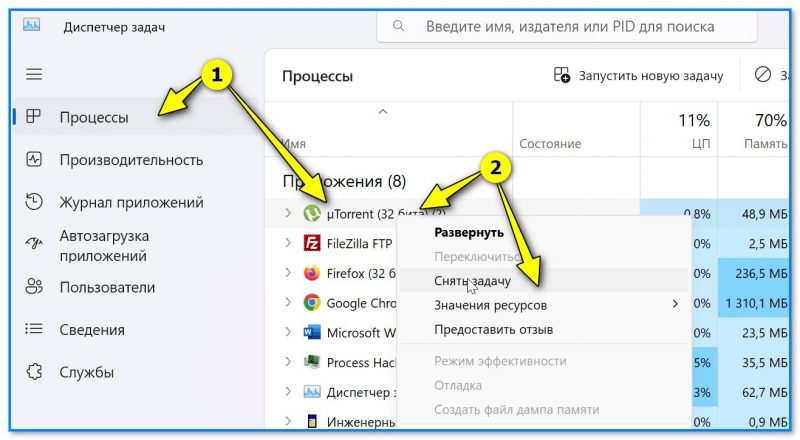
Диспетчер задач — снять задачу — Windows 11
Кстати, также просмотреть все процессы и закрыть их позволяет вкладка «Пользователи». См. скрин ниже. 👇
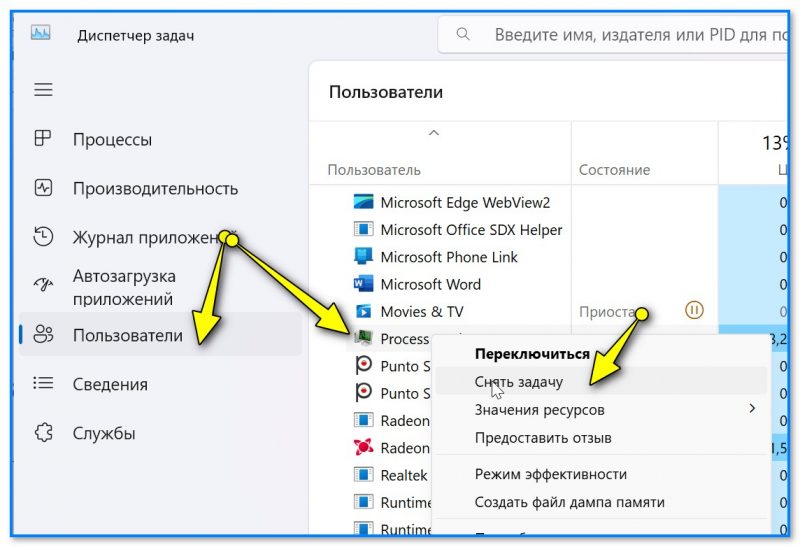
Пользователи — снять задачу // Скрин из Windows 11
*
Что делать, если процесс не завершается
- перезагрузить ПК, если это возможно;
- откл. диски, приводы, и др. оборудование, с которым может быть связан процесс (например, тот же uTorrent может подвисать, если вы загружаете информацию на внешний накопитель… И если этот диск переподключить — процесс тут же будет завершен);
- возможно, у вас нет 📌администраторских прав (попробуйте запустить диспетчер задач так: нажать Win+R, ввести команду taskmgr и нажать Ctrl+Shift+Enter);
- воспользуйтесь нижеприведенными вариантами принудительного завершения процессов.
*
Вариант 2: с помощью командной строки
- для начала нужно запустить 📌командную строку от имени администратора (Win+R, команда CMD, и затем нажать Ctrl+Shift+Enter);
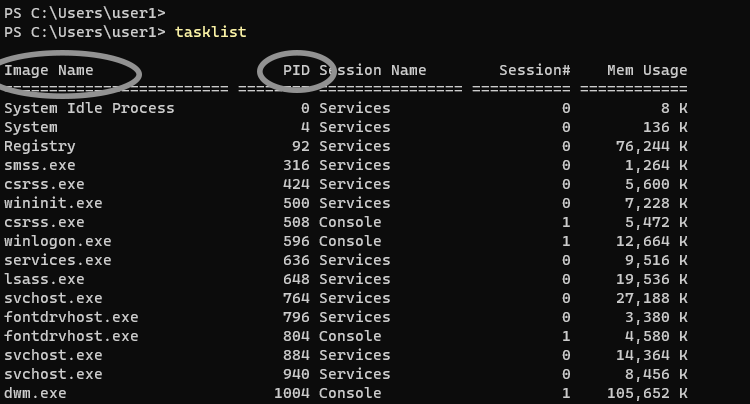
- затем рекомендуется ввести команду tasklist для просмотра всех процессов;
tasklist — просмотр всех процессов
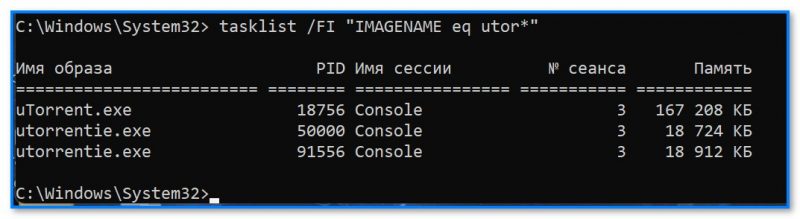
- обычно список всех процессов достаточно длинный и работать с ним не очень удобно — поэтому, чтобы найти конкретный процесс я бы порекомендовал попробовать такую команду: tasklist /FI «IMAGENAME eq utor*» (разумеется, вместо «utor*» — укажите часть своего имени процесса. Звездочка тут помогает не указывать полное имя процесса «utorrent.exe», т.к. возможно вы его и не знаете);
tasklist — как просмотреть только процессы с нужным именем
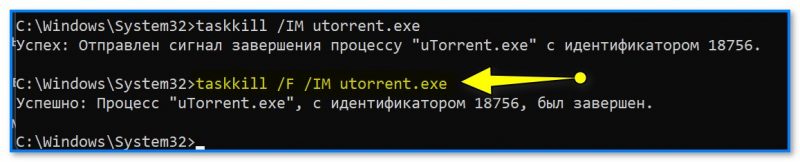
- теперь для принудительного завершения процесса нужно ввести эту команду (например): taskkill /F /IM utorrent.exe (Разумеется, имя процесса у вас будет свое. Кстати, обратите внимание на ключ «/F» — он указывает на принудительное завершение процесса);
Процесс был успешно завершен!
- дополню вышесказанное: завершить процесс можно не только по имени, но и по PID (идентификатору). Например, так: taskkill /F /PID 18756
📌 Важно!
Завершая процесс принудительно — очень вероятно вы не позволите сохраниться данным, кэшу (у того же uTorrent потом придется ждать пере-хеширования всех торрентов в списке). Поэтому делать это лучше тогда, когда другие варианты не сработали…
*
Вариант 3: с помощью спец. приложений
Есть одно довольно удобно приложение, позволяющее просмотреть все процессы в Windows — речь 📌о Process Explorer (обратите внимание, что оно выложено на сайте Microsoft, в установке не нуждается — достаточно просто запустить).
Так вот, сразу же в главном окне можно найти весь список процессов, отсортировать его по имени, нагрузке на ЦП, память и т.п. Чтобы завершить один из процессов — просто сделайте по нему правый клик мышкой, а затем выберите в меню «Kill Process» (см. скрин ниже). 👇
Удобно?! 👌
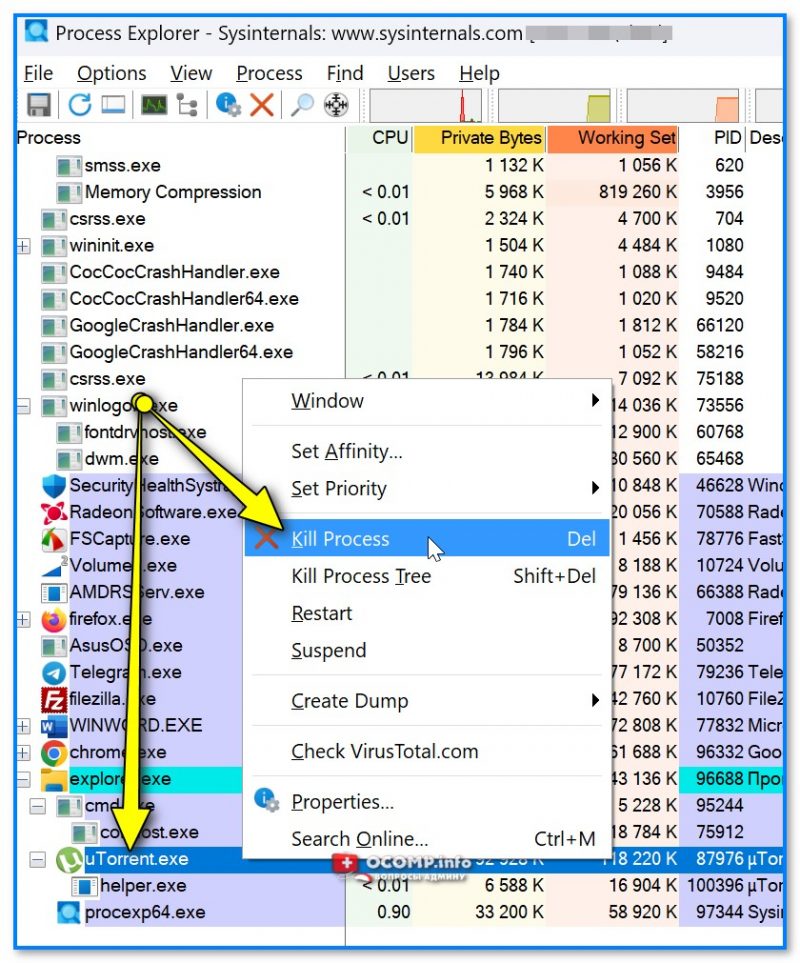
Kill Process (убить процесс) — утилита Process Explorer
Кстати, у Process Explorer есть аналог — утилита Process Hacker 2 (не смотрите не название, для текущей нашей задачи она ничем не отличается от Process Explorer. Правда, давненько не обновлялась, но работает в Windows 11 до сих пор).
*
Дополнения по теме — можно оставить ниже, с помощью формы комментирования.
Всего доброго!
👋
We use the taskkill command to terminate applications and processes in the Windows command prompt. Running taskkill is the same as using the End task button in the Windows Task Manager.
With taskkill, we kill one or more processes based on the process ID (PID) or name (image name). The syntax of this command is as follows:
taskkill /pid PID
taskkill /im nameYou can use the tasklist command to find the PID or image name of a Windows process.
The /F option tells Windows to force kill the process:
taskkill /f /im notepad.exeKill a Process by PID
In the following example, we run the taskkill command to terminate a process with a PID of 1000:
taskkill /f /pid 3688The multiple processes can be terminated at once, as shown in the following example:
taskkill /pid 3688 /pid 4248 /pid 4258Kill a Process by Name
To kill a process by its name, we use the /IM option. In the following example, we run the taskkill command to terminate the notepad.exe process:
taskkill /im notepad.exeThe /t option tells Windows to terminate the specified process and all child processes. In the following example, we force kill Microsoft Edge and its child processes:
taskkill /f /t /im msedge.exeCommand Options
| /S | Specifies the IP Address or name of the remote system to connect to. |
| /U | Specifies the name of the Windows user under which the command should execute. |
| /P | Password for the user. Prompts for input if omitted. |
| /FI | This option is to apply filters (see examples below). |
| /PID | Specifies the PID of the process to be terminated. |
| /IM | Specifies the image name of the process to be terminated. |
| /T | Terminates the specified process and its child processes (end all tasks). |
| /F | Forcefully kill a process. |
Examples
Terminate a process with a PID of 4000:
taskkill /pid 4000Terminate spoolsv.exe (which is the Print Spooler service on Windows):
taskkill /im spoolsv.exeUsing /f and /t options to forcefully terminate the entire process tree of the Microsoft Edge browser:
taskkill /f /t /im msedge.exe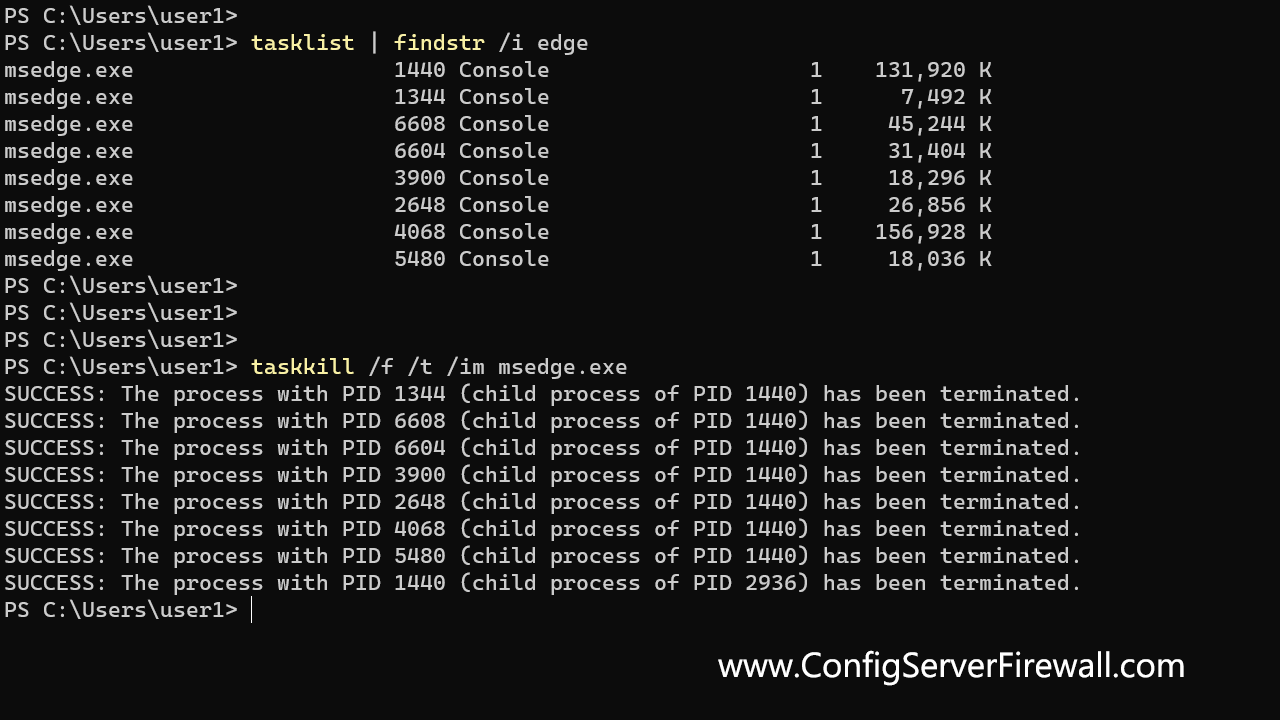
Force kill any process that starts with the name note:
taskkill /f /t /im note*In the following example, we terminate all processes that are not responding by using a filter:
taskkill /f /fi "status eq not responding"In the above example, eq stands for equal. You can use the following filters with the /fi option.
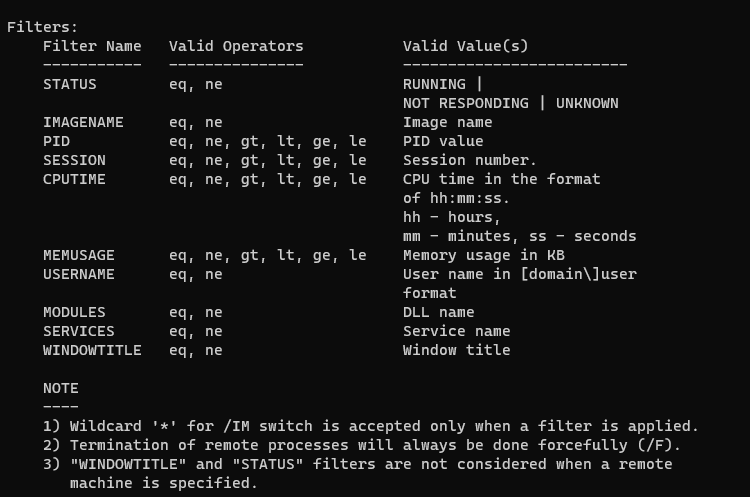
Run taskkill command on a remote computer:
taskkill /s 192.168.1.100 /u robst /pid 5936In the above example, the process with PID 5936 will be terminated on a remote computer with an IP address of 192.168.1.100.
Note that the Windows Firewall must be configured on the remote computer to allow the taskkill command. Click the link below for instructions on how to do it.
How to allow tasklist and taskkill commands from Windows Firewall
All right, here’s the end of this tutorial. While working on the CMD, you can run taskkill /? to display the help page, command options, and filters of the tasklist command.
The PowerShell equivalent to the taskkill is the Stop-Process cmdlet. But you can always use taskkill in PowerShell as well.
Перейти к содержимому
Управлять процессами в Windows можно не только через UI («Менеджер задач»), но и через командную строку. К тому же командная строка предоставляет больше контроля над данными действиями.
Для вывода списка запущенных процессов нужно ввести команду:
tasklist
Image Name PID Session Name Session# Mem Usage ========================= ======== ================ =========== ============ System Idle Process 0 Services 0 4 K System 4 Services 0 4 124 K smss.exe 348 Services 0 336 K csrss.exe 480 Services 0 2 780 K wininit.exe 552 Services 0 572 K csrss.exe 568 Console 1 9 260 K winlogon.exe 616 Console 1 2 736 K services.exe 640 Services 0 9 284 K lsass.exe 660 Services 0 16 464 K explorer.exe 27736 Console 1 125 660 K
«Убить» процесс можно как по его имени, так и по PID:
>Taskkill /IM explorer.exe /F
>Taskkill /PID 27736 /F
Флаг /F указывает, что завершить процесс нужно принудительно. Без данного флага, в некоторых случаях, процесс может не «убиться» (к примеру, это актуально как раз для процесса explorer.exe).
Multitasking with many apps and programs in the background can become difficult to manage and kill the processes running in the background using just the Task Manager or even with tools like Microsoft Process Explorer. However, another way to kill tasks and processes is from the command line in Windows.
However, you can open the Task Manager, right-click the process, and then click “End Task” to kill off the process. You can also terminate a specific process from the Details tab in the Task Manager. Sometimes you encounter issues with the Task Manager itself. For times like these, you may need to kill a process using the command line, which includes both the Command Prompt and Windows PowerShell.
In this article, we show you multiple ways to kill a process in Windows using Command Line.
Table of Contents
Why use the command line to terminate a process?
Although a normal user will not require killing processes using the command line, there are several use cases where command line tools are much better than their visual counterparts like the task manager. The following command line tools can be used in the following scenarios:
- Troubleshooting: Some processes are simply stubborn. They just stop responding and refuse to die. In such a condition, killing them forcefully using the command line is an easier and safer option.
- System administration: If you are a sysadmin, you should be a fan of command line utilities. These tools save a lot of work and time. You can run these commands remotely throughout your network to troubleshoot systems remotely.
- Script Automation: If you are a developer and need to start or stop processes in Windows, you will need these command line tools for automation.
- Virus prevention: If your system gets infected with viruses, it will simply not let you kill the compromised processes, as they will respawn upon kill. In this case, you can automate a monitoring process where the process is killed as soon as it starts.
There are several other use cases, but these are the most common ones.
How to Kill a Process from Command Prompt
You can kill the process in cmd using the taskkill command. However, you must either know its Process Identifier (PID) or the name of the process before you can end it.
To view and list the tasks and processes currently running on your computer, run the following command in an elevated Command Prompt:
Tasklist
Note either the name under the Image name column or the PID number of the task you want to kill. These will be used in the cmdlets to kill the respective process.
Once you have either the name or the PID of the task, use either of the following cmdlets to kill the process:
-
Kill task using process name in Command Prompt:
Replace [ProcessName] with the name of the process.
taskkill /IM "[ProcessName]" /FKill process from Command Prompt using process name -
Kill task using PID in Command Prompt:
Replace [PID] with the Process ID.
taskkill /F /PID [PID]Kill process from Command Prompt using a process ID
If you are using earlier versions of Windows, like Windows 7, Windows Vista or even Windows XP, you can use tskill command, which is similar to taskkill but limited in functionality. You just need to provide the process ID to kill a task using tskill command:
tskill process-idReplace process-id with the actual process ID. For example,
tskill 1234How to Kill a Process from Windows PowerShell
Similar to the Command Prompt, you can also kill processes using PowerShell. But first, we must get the name or the process ID for the process to kill.
To obtain a list of the running processes in PowerShell, run the following command in PowerShell with elevated privileges:
Get-Process
From here, note down the process name or the PID (in the ID column) of the process that you want to kill, and then use it in the following commands:
Note: Unlike the Command Prompt, Windows PowerShell shows no output once a process is killed.
-
Kill task using process name in PowerShell:
Replace [ProcessName] with the name of the process.
Stop-Process -Name "[ProcessName]" -ForceKill process from PowerShell using process name -
Kill task using PID in PowerShell:
Replace [PID] with the Process ID.
Stop-Process -ID [PID] -ForceKill process from PowerShell using a process ID
How to Kill a Process using WMIC
Windows Management Instrumentation Command-Line (WMIC) is a useful command line tool to perform administrative tasks especially for sysadmins and power users. You can terminate the process using wmic command.
Please note all the below mentioned commands will only work if you open Command Prompt, PowerShell or Terminal as an administrator.
wmic process where "ProcessId='process-id'" deleteReplace process-id with the actual process ID. For example,
wmic process where "ProcessId='1234'" deleteYou can also terminate the process using its name:
wmic process where "name='process-name'" deleteReplace process-name with the actual process name. For example,
wmic process where "name='Skype.exe'" deleteIf there are multiple processes by the same name, this command will kill all of them. For example, the above mentioned command will delete all instances with the name Skype.exe.

How to Kill a Process using SysInternals PsKills
PsKill is a tiny tool that comes with the PsTools Suite by SysInternals. This is a command-line tool used to kill processes, both locally and remotely on other computers on the network.
Although it was designed for WindowsNT and Windows 2000 that did not include the other command-line tools (Killtask and Stop-Process), PsKill can still be used to end processes.
Learn how to manage processes and services on remote computers.
Use the following steps to download and use PsKill to kill tasks using the command line on a Windows computer:
-
Start by downloading PsTools.
Download PSTools -
Extract the contents of the PsTool file.
Extract PsTools -
Launch an elevated Command Prompt and then use the
CDcmdlet to change your directory to the extracted PsTools folder.CD [PathToPsTools]Change directory to PsTools folder -
Run the following command to list all the running processes:
PsListList all running processes using PsList Note down the name of the process that you want to kill.
-
Now use the following command to kill a process using its name:
PsKill.exe [ProcessName]Kill process using PsKill
As you can see from the image above, the respective process will be killed, and the associated service or program will be terminated.
Ending Thoughts
Even without the use of the Task Manager, there are multiple ways of killing a task or a process directly from the command line. You can even use these commands in scripts to end a Windows process.
On top of that, you can choose whether to kill a process using its name or its PID. Either way, Command Prompt and Windows PowerShell can be used with both native and external commands for this purpose. Not only that, but you can also use these commands in Windows Terminal for the same purpose.
If you are a sysadmin who wants quick and convenient methods to kill running processes, the given command line methods just might be the most convenient way of accomplishing it.