Updated May 2025: Stop error messages and fix your computer problem with this tool. Get it now at this link
- Download and install the software.
- It will scan your computer for problems.
- The tool will then fix the issues that were found.
The System Idle Process is one of those things we don’t really think about, but it plays such an integral role in our computers’ operation that it’s worth taking some time to understand what it does and why it exists.
When you start up your computer, there are many processes running in the background. Some are necessary to make sure everything works properly; others are just there to help speed up the booting process. For example, the System Idle Process is responsible for cleaning up files left behind by applications like Chrome and Internet Explorer.
But while the System Idle Process is doing its job, it consumes quite a lot of resources. In fact, it takes up almost 20% of the total CPU usage during normal operations. If you’re having trouble getting your PC to run smoothly, chances are good that the System Idle Process is hogging most of the processor power.
To see how much resource the System Idle Process is consuming, open Task Manager and look under the Performance tab. You’ll notice that the percentage of CPU used by the System Idle Process is listed next to “Idle.”
If you want to find out exactly what program is causing the problem, use the Processes tab to sort by CPU consumption. Look for a program called “system” and you’ll likely find the culprit.
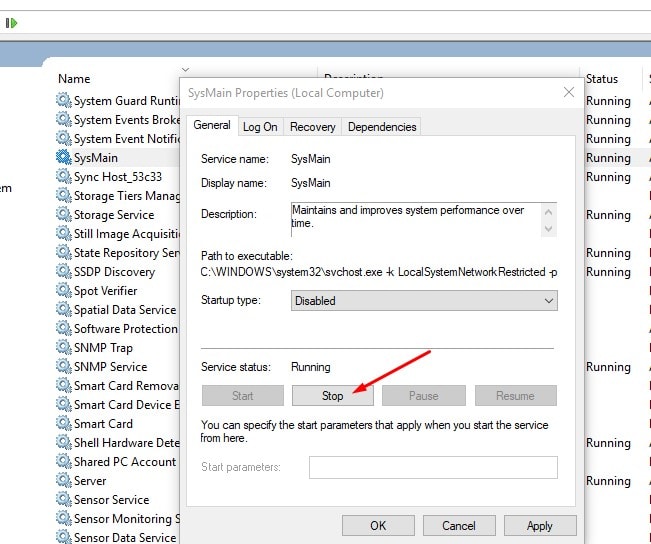
Then uncheck the box labeled “Turn off display screen after”. Click Apply and OK.
What does “System Idle Process” mean?
System Idle Process is a background process that monitors the performance of your system. This process helps you identify issues that could cause your computer to slow down over time.
If your PC seems sluggish, it might be because the System Idle Process is running too often. You can see how much time your computer spends doing nothing by opening Task Manager. In the Performance tab, under the Services section, look at the “Idle Time” column.
The System Idle Process uses up resources like memory and processor cycles. When the System Idle Process runs constantly, it makes your computer run slower.
To fix System Idle Process High Memory Usage, follow our steps.
What’s the point of Windows’s System Idle Process?
Without an IDLE process, it would take ages for your computer to start up again. You might think that the system idle process is just something that keeps the CPU occupied while waiting for programs to finish loading. But what happens when no program needs to load anymore? In fact, without an IDLE process, Windows wouldn’t even boot. Microsoft has always been very careful about how much work it puts into the operating systems it releases. And this one is no exception.
The IDLE process is responsible for keeping the CPU active. If you’re running low on memory, the OS will use the IDLE process to free some RAM. It’s also used to make sure that processes don’t hog too many resources. For example, the IDLE process is used to prevent programs such as Chrome or Firefox from taking over the whole machine.
In short, the IDLE process does everything that makes sure that your computer doesn’t become unresponsive. And it does it well.
Updated: May 2025
We highly recommend that you use this tool for your error. Furthermore, this tool detects and removes common computer errors, protects you from loss of files, malware, and hardware failures, and optimizes your device for maximum performance. This software will help you fix your PC problems and prevent others from happening again:
- Step 1 : Install PC Repair & Optimizer Tool (Windows 11, 10, 8, 7, XP, Vista).
- Step 2 : Click Start Scan to find out what issues are causing PC problems.
- Step 3 : Click on Repair All to correct all issues.
Why is so much CPU being used?
CPU stands for central processing unit. It’s what makes computers work. You might think that since your computer isn’t doing much, it shouldn’t use up too much of your processor power. But sometimes, your computer needs to do something quickly — like load a program or play a game. When it does, it takes over the CPU so that everything else can run smoothly.
But why does it take over the CPU? Well, it’s because the hardware inside your PC is designed to make sure that the CPU gets enough resources to complete whatever task it’s working on. In some cases, the CPU can become overloaded and slow down. To prevent this, the operating system puts limits on how many processes are allowed to run simultaneously.
When you’re watching videos online, playing games, or browsing the web, your browser opens multiple windows and tabs. Each window or tab consumes memory, which slows down the performance of your computer. Because browsers open so many different things at once, they often cause problems for the OS.
So when you see your computer running slowly, check out your browser settings. Make sure that you don’t have too many windows and tabs open. And if you want to speed up your computer again, try closing those extra programs.
Fix-1 Clean Boot your computer-
This article will help you fix the problem of “Your Computer Takes Too Long To Boot”. In fact it will solve the problem permanently. You might think that this article is just another scam, but trust me, it works. I’ve been using it myself and my friends are now using it successfully.
The reason for slow booting is because there is something wrong with the registry. If you don’t know what the registry is, then you’ll find out soon enough. But if you do know what the registry is then read this article.
If you want to learn how to clean up your registry, then you’re reading the right article.
You see, every time you start your computer, it goes through some steps to load programs into memory. These steps include loading drivers, opening files, and starting processes. All of these things take time. And since we use our computers everyday, they tend to run slower over time.
Fix- 2 Disable Startup processes-
Disabling startup programs can help you save some RAM and CPU usage. In Windows 10, there are several startup applications that consume a lot of system resources. So it is recommended to disable those apps. Here we are sharing few steps to disable those apps.
1. Open Settings app.
2. 3. Scroll down and find Startup tab.
4. Select each application one by one and uncheck “Startup”.
5. Restart your computer.
6. Now open Start menu and check whether the startup program is disabled. If yes, then great job done. 🙂
Fix- 3 Run .bat file
The Fix-3 run.bat file is used to fix some common problems in Windows 7/8/10. This batch script is very helpful for beginners because it contains simple commands to solve most of the issues. If you are facing any problem related to Windows 10, follow these steps to resolve such errors.
#1 – Error Code 0x80070002
If you are getting error code 0x80070002 while installing Windows 10, then try to update your system. You can download the latest version of Windows 10 ISO image from Microsoft site. Make sure that you select English language during installation process. After updating your OS, restart your computer. Now open Command Prompt window and type “wusa /updatenow”. Then press Enter key. Your Windows 10 will start downloading the required files. Wait till it completes the process. Once done, reboot your PC.
#2 – Error Code 0x8024401c
If you are unable to install Windows 10 due to error code 0x8024401C, then try to repair your system. Select the option called Erase everything and hit OK button. When prompted, choose Yes to confirm. Now clean up your disk space. Restart your PC and try again.
#3 – Error Code 0x80004005
Error code 0x80004005 occurs when you don’t have enough free space on your hard drive. So, make sure that there is sufficient amount of space left on your hard drive. Also, check whether your partition is damaged or corrupted. In case, format the entire drive and reinstall Windows 10.
Fix-4 Clean the disk with Disk Cleanup-
Running Disk Cleanup cleans out the junk files from your hard drive. If you are running Windows 7, 8, 10, or Server 2008/2012/2016, you can use it to free up space on your hard drive. You can run Disk Cleanup manually or schedule it to clean out the junk automatically.
To find out how much memory the system idle process consumes, open Task Manager and check under the Performance tab. This will show you the amount of RAM being used by each application and the total amount of RAM being used.
The System Idle Process takes up about 2% of the processor resources, so if you notice that the percentage of CPU usage is high, try cleaning out some of the junk files with Disk Cleanup.
Fix-5 Run Disk Fragmentation-
Disk fragmentation happens when files are scattered across different parts of the disk. This makes it difficult for the operating system to find the file quickly. In turn, this slows down the computer. To fix this problem, follow these steps:
1. 2. Click on Tools tab.
3. Select “Check Now”.
4. If you want to check whether the drive is fragmented, go to File Explorer window.
5. Open folder where you store important data.
6. Press CTRL+A keys together to open All Files option.
Fix-6 Update USB drivers on your computer-
Updating the USB drivers on your computer may solve your problem.-Check whether System Idle Process is taking too much CPU usage -or not after updating the USB driver.
Fix-7 Run Driver Verifier on your computer-
Driver Verifier is an application which checks whether your driver is working properly or not. This tool works like a virtual machine and simulates different scenarios on your system. After running the tool, it gives you information about the errors found on your system. If there are no errors, then it says everything is fine. But if there are some problems, then you can fix those problems easily.
You can use this tool to check your driver version, compatibility, performance, etc. You can even run this tool on multiple computers simultaneously. So you don’t need to install the software on each device separately.
RECOMMENATION: Click here for help with Windows errors.
Frequently Asked Questions
Does the WMI Provider Host (WiPrvSE.EXE) use a lot of CPU?
The WMI Provider Host process is part of Windows and helps organizations monitor and troubleshoot a large number of systems. This process runs under the LocalSystem account and is responsible for managing the WMI provider host interface. While this process isn’t normally something that administrators worry about, there are times when it can cause problems. For example, if the system is experiencing a lot of errors, the WMI Provider Host might be consuming too much memory and causing the computer to slow down. In addition, if the WMI Provider Host becomes unresponsive, it could mean that the machine is having trouble communicating with one of its devices.
You can check whether this is happening on your system by opening the Task Manager and looking for the WMI Prvse.exe process. If its CPU usage is high, and you aren’t running any programs that would impact it, the WMI Provider host is probably malfunctioning. To fix this issue, you’ll want to restart the machine.
Are there too many processes running in the background?
A background process is a program running on your PC, whether it’s open or closed. For example, your email client might be downloading messages as you read them, or your browser could be refreshing webpages while you’re reading an article online. These tasks aren’t visible to you—you don’t see them in the taskbar or notice them in your system tray—but they still use up resources.
Windows uses multiple background processes to keep everything running smoothly, but too many can slow down your PC. When you start seeing issues like freezing, lag, or crashing, there’s probably something wrong with one of those apps.
The easiest way to check is to look at the Processes tab in Task Manager. This displays information about every single process running on your machine, including how much memory it’s taking up, what percentage of your processor power it’s consuming, and how long it’s been running. If you find a problem app, close it and see if things improve.
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
System Idle Process
|
Windows Task Manager in Windows XP showing System Idle Process usage at 99%, indicating that no other process is using significant CPU time. |
|
| Operating system | Microsoft Windows |
|---|---|
| Type | Kernel |
In Windows NT operating systems, the System Idle Process contains one or more kernel threads which run when no other runnable thread can be scheduled on a CPU. In a multiprocessor system, there is one idle thread associated with each CPU core. For a system with hyperthreading enabled, there is an idle thread for each logical processor.
The primary purpose of the idle process and its threads is to eliminate what would otherwise be a special case in the scheduler. Without the idle threads, there could be cases when no threads were runnable (or «Ready» in terms of Windows scheduling states). Since the idle threads are always in a Ready state (if not already Running), this can never happen. Thus whenever the scheduler is called due to the current thread leaving its CPU, another thread can always be found to run on that CPU, even if it is only the CPU’s idle thread. The CPU time attributed to the idle process is therefore indicative of the amount of CPU time that is not needed or wanted by any other threads in the system.
The scheduler treats the idle threads as special cases in terms of thread scheduling priority. The idle threads are scheduled as if they each had a priority lower than can be set for any ordinary thread.
Because of the idle process’s function, its CPU time measurement (visible through, for example, Windows Task Manager) may make it appear to users that the idle process is monopolizing the CPU. However, the idle process does not use up computer resources (even when stated to be running at a high percent). Its CPU time «usage» is a measure of how much CPU time is not being used by other threads.
In Windows 2000 and later the threads in the System Idle Process are also used to implement CPU power saving. The exact power saving scheme depends on the operating system version and on the hardware and firmware capabilities of the system in question. For instance, on x86 processors under Windows 2000, the idle thread will run a loop of halt instructions, which causes the CPU to turn off many internal components until an interrupt request arrives. Later versions of Windows implement more complex CPU power saving methods. On these systems the idle thread will call routines in the Hardware Abstraction Layer to reduce CPU clock speed or to implement other power-saving mechanisms.
There are more detailed sources of such information available through Windows’ performance monitoring system (accessible with the perfmon program), which includes more finely grained categorization of CPU usage. A limited subset of the CPU time categorization is also accessible through the Task Manager, which can display CPU usage by CPU, and categorized by time spent in user vs. kernel code.
- List of Microsoft Windows components
- Idle (CPU)
- Microsoft Windows
- HLT (x86 instruction)
- Process Explorer
- Russinovich, Mark; David A. Solomon (2005). «Chapter 2: System Architecture». Microsoft Windows Internals (4th ed.). Microsoft Press. pp. 75–76. ISBN 0-7356-1917-4.
- «What Is «System Idle Process,» and Why Is It Using So Much CPU?». How-To Geek. 25 April 2019. Retrieved 2022-01-13.
- «system idle process — What is system idle process?». www.processlibrary.com. Retrieved 2022-01-13.
Windows Task Manager is a brilliant way to see what’s going on with your computer, but it’s also a little scary to see what’s eating up your system resources. In particular, you may notice that there’s a task called System Idle Process that may be high, taking anything up to 99% of your CPU’s time.
So, what’s going on, is your computer affected by malware, or is it just burning itself out for no reason?
The simple answer is, none of the above. The System Idle Process is simply a visual measure of how much free CPU capacity your system currently has, rather than an actual process taking up resources. That means if you’re reading a 99% System Idle Process in your Task Manager, that means only 1% of your system is in use.

(Image credit: Getty Images)
You may be wondering why Windows tracks this metric at all. Well, there are two main reasons.
The first is that it helps the Task Scheduler keep everything running – it uses the System Idle Process to help inform what CPU cores are currently free and can be assigned new functions.
The second reason is all about power efficiency. The System Idle Process tracker informs the system when certain areas of a CPU can be safely shut down to reduce overall power consumption. These are then turned back on when an actual task is created.
The System Idle Process has also evolved alongside new advances in CPU technology. These days the process is able to further optimise the system by doing things like reducing a processor’s clock speed on the fly when appropriate.
Sign up today and you will receive a free copy of our Future Focus 2025 report — the leading guidance on AI, cybersecurity and other IT challenges as per 700+ senior executives
How to check System Idle Process on Windows 10 and 11
(Image: © Future)
- Start the Task Manager by pressing CTRL-SHIFT-ESC
- Click on the Details tab
- Sort by CPU when your PC isn’t doing much
- The System Idle Process should be displayed at the top
How to check System Idle Process on Windows 7 and 8
- Start the Task manager by pressing CTRL-SHIFT-ESC
- Tick the ‘Show processes from all users’ box
- Click the CPU header to sort the list
- When your system is not very busy, the System Idle Process should appear at the top
Dale Walker is a contributor specializing in cybersecurity, data protection, and IT regulations. He was the former managing editor at ITPro, as well as its sibling sites CloudPro and ChannelPro. He spent a number of years reporting for ITPro from numerous domestic and international events, including IBM, Red Hat, Google, and has been a regular reporter for Microsoft’s various yearly showcases, including Ignite.
Download Windows Speedup Tool to fix errors and make PC run faster
The System Idle Process is an important aspect of Windows 11/10 operating system, but what’s interesting about it is the fact that from time to time, it tends to use a lot of system resources. We suspect that many users who have launched the Task Manager might have wondered why is this the case.
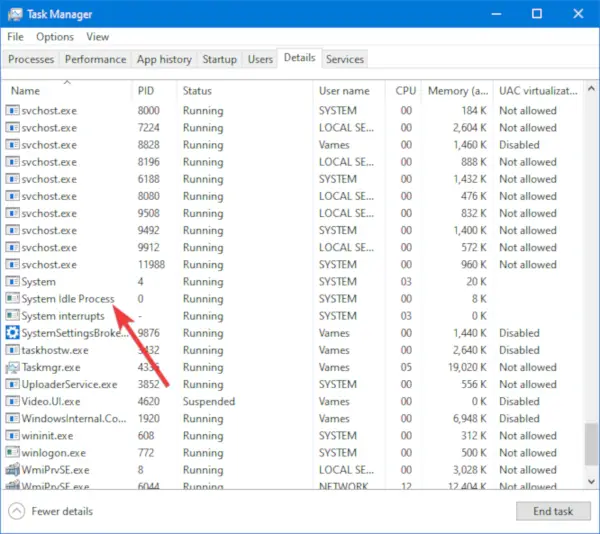
The System Idle Process is a measure of how much free processor time your computer currently has. If System Idle Process is taking up 98 percent of your CPU’s time, this means that your CPU is only using 2 percent of its processing capability to run actual tasks.
Contrary to what many might believe, it’s not a bad thing if the System Idle Process is using up a lot of CPU resources. Microsoft created the System Idle Process to give your computer something to do whenever it’s in idle mode. The System Idle Process is nothing but an idle process. Its purpose is to keep the CPU busy doing something. It contains kernel threads that execute when there are no running tasks. If you try to stop it, the OS could freeze.
As it stands, then, the high resources used by the System Idle Process is the resources not being used by the CPU. It might sound crazy, but trust us when we say that it makes a lot of sense if you think about it. It’s basically a placeholder, but according to the Task Manager, it’s the “percentage of time the processor is idle.” Now, the folks at Microsoft chose to hide the System Idle Process in Windows 11/10, but clicking on the details tab should bring it before your eyes.
We should point out that this feature dates back to 1993 with the launch of Windows NT. Not to mention, the same feature can be found in a Linux-based operating system, though it works a bit differently there. Clearly, this is a normal aspect of most operating systems; therefore, the user should have nothing to fear at all.
There’s not much you need to do in this case, but you may do the following if you see System Idle Process regularly using high CPU usage:
- Disable Startup programs
- Uninstall programs you do not need
- Run System File Checker to replace potentially corrupted OS files with good ones
- Run your antivirus scan to check for malware.
If your computer is suffering from slowdowns, the first step is usually to check the Task Manager to see what is running in the background. You might come across the System Idle Process and wonder if it is the cause, but that’s not the case.
You see, as we’ve stated above, the high CPU usage by this system process is merely a placeholder. That means, if your computer is running poorly, then chances are it has everything to do with low memory than anything else.
Surely, it has almost nothing to do with the System Idle Process so you can remove such thoughts from your mind right now.
I hope this bit helped.
Want to know about these processes, files or file types?
Browser_Broker.exe | SettingSyncHost.exe | Sppsvc.exe | mDNSResponder.exe | winlogon.exe | atieclxx.exe | Conhost.exe | Taskhostw.exe | AppVShNotify.exe.
Vamien has studied Computer Information Services and Web Design. He has over 10 years of experience in building desktop computers, fixing problems relating to Windows, and Python coding.
Have you ever opened up Task Manager and noticed the System Idle Process is using 90% or more of your CPU? Contrary to what you might think, that’s not a bad thing. Here’s what that process actually does.
This article is part of our ongoing series explaining various processes found in Task Manager, like Runtime Broker, svchost.exe, dwm.exe, ctfmon.exe, rundll32.exe, Adobe_Updater.exe, and many others. Don’t know what those services are? Better start reading!
What Is the System Idle Process?
If you’ve ever poked around in the Task Manager—Windows 10 users have to look under the «Details» tab—you’ll see that the System Idle Process is using most, if not all, of your CPU. But the System Idle Process is just that; an idling process made by the operating system. Without this process constantly keeping your processor occupied with something to do, your system could potentially freeze.
In other words, the CPU resources used by the System Idle Process are just the CPU resources that aren’t being used. If programs are using 5% of your CPU, the System Idle Process will be using 95% of your CPU. You can think of it as a simple placeholder. That’s why the Task Manager describes this process as the «percentage of time the processor is idle.» It has a PID (process identifier) of 0.
Windows hides the System Idle Process information from the normal Processes tab in Windows 10’s Task Manager to keep things simple, but it’s still shown on the Details tab.
Why Does Windows Need a System Idle Process?
Without this process always keeping your processor occupied with something to do, your system could potentially freeze. Windows runs this process as part of the SYSTEM user account, so it’s always active in the background while Windows is running.
System Idle Processes are native to Windows NT operating systems, dating back to 1993—they also appear in Unix-like operating systems such as Linux but operate a bit differently. A System Idle Process is a normal part of your OS that runs a single thread on each CPU core for a multiprocessor system, while systems that use hyperthreading have one idle thread per logical processor.
The System Idle Process’ sole purpose is to keep the CPU busy doing something—literally anything—while it waits for the next computation or process fed into it. The reason this all works is that the idle threads use a zero priority, which is lower than ordinary threads have, allowing for them to be pushed out of the queue when the OS has legitimate processes to be run. Then, once the CPU finishes with that job, it’s ready to handle the System Idle Process all over again. Having idle threads always in a Ready state—if they’re not already running—keeps the CPU running and waiting for anything the OS throws at it.
Why Is It Using So Much CPU?
Like mentioned earlier, this process appears to use a lot of CPU, which is something you’ll spot if you open the Task Manager, looking for resource hungry processes. That’s normal because it’s a special task run by the OS scheduler only when your CPU is idle, which—unless you’re doing something that demands a lot of processing power—will look to be quite high.
To understand the number next to the process in Task Manager, you have to think the opposite of what you normally understand it to mean. It represents the percent of CPU that’s available, not how much it’s using. If programs are using 5% of the CPU, then the SIP will show to be using 95% of the CPU, or 95% of the CPU is unused, or unwanted by other threads in the system.
But My Computer Is Slow!
If your computer is slow and you notice high usage by the System Idle Process—well, that’s not the System Idle Process’s fault. This process’s behavior is perfectly normal and suggests the problem isn’t due to high CPU usage. It may be caused by a lack of memory, slow storage, or something else using up your computer’s resources. As always, it’s a good idea to run a scan with an antivirus program if you’re experiencing problems and you’re not running anything that might be slowing your PC down.
If that yields nothing and you’re still experiencing slower than usual performance, try uninstalling unused programs, disabling programs that launch when you start up your computer, reduce system animations, free up disk space, or defrag your HDD.
The System Idle Process is an integral part of the Windows operating system and, while it may look like it’s hogging upwards of 90%, that’s just showing you available resources and that your CPU isn’t doing anything with at the moment.
