on August 15, 2010
We normally use Services.msc to start or stop or disable or enable any service. We can do the same from windows command line also using net and sc utilities. Below are commands for controlling the operation of a service.
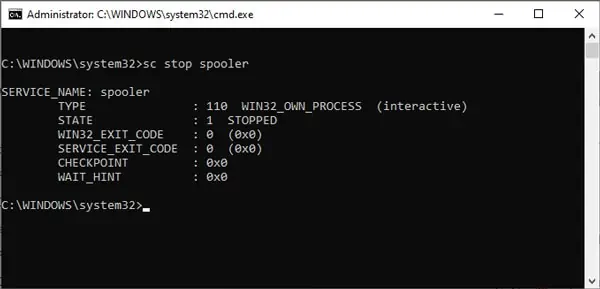
Command to stop a service:
net stop servicename
To start a service:
net start servicename
You need to have administrator privileges to run net start/stop commands. If you are just a normal user on the computer, you would get an error like below.
C:\>net start webclient System error 5 has occurred. Access is denied. C:\>
To disable a service:
sc config servicename start= disabled
To enable a service:
sc config servicename start= demand
To make a service start automatically with system boot:
sc config servicename start= auto
Note: Space is mandatory after ‘=’ in the above sc commands.
This SC command works on a Windows 7 machine and also on the down-level editions of Windows i.e Windows XP/2003 and Windows Vista. Again, if you do not have administrator previliges you would get the below error.
C:\>sc config webclient start= auto [SC] OpenService FAILED 5: Access is denied.
Note that the service name is not the display name of a service. Each service is given a unique identification name which can be used with net or sc commands. For example, Remote procedure call (RPC) is the display name of the service. But the service name we need to use in the above commands is RpcSs.
So to start Remote procedure call service the command is:
net start RpcSsTo stop Remote procedure call service
net stop RpcSs
These service names are listed below for each service. The first column shows the display name of a service and the second column shows the service name that should be used in net start or net stop or sc config commands.
| Display Name of the service | ServiceName which should be used with ‘net’ and ‘sc config’ commands. |
| Alerter | Alerter |
| Application Layer Gateway Service | ALG |
| Application Management | AppMgmt |
| ASP.NET State Service | aspnet_state |
| Windows Audio | AudioSrv |
| Background Intelligent Transfer Service | BITS |
| Computer Browser | Browser |
| Bluetooth Support Service | BthServ |
| Bluetooth Service | btwdins |
| SMS Agent Host | CcmExec |
| Indexing Service | CiSvc |
| ClipBook | ClipSrv |
| .NET Runtime Optimization Service v2.0.50727_X86 | clr_optimization_v2.0.50727_32 |
| COM+ System Application | COMSysApp |
| Cryptographic Services | CryptSvc |
| Cisco Systems, Inc. VPN Service | CVPND |
| DCOM Server Process Launcher | DcomLaunch |
| DHCP Client | Dhcp |
| Logical Disk Manager Administrative Service | dmadmin |
| Logical Disk Manager | dmserver |
| DNS Client | Dnscache |
| Lenovo Doze Mode Service | DozeSvc |
| Error Reporting Service | ERSvc |
| Event Log | Eventlog |
| COM+ Event System | EventSystem |
| Intel(R) PROSet/Wireless Event Log | EvtEng |
| Fast User Switching Compatibility | FastUserSwitchingCompatibility |
| Windows Presentation Foundation Font Cache 3.0.0.0 | FontCache3.0.0.0 |
| Group Policy Monitor | GPMON_SRV |
| Help and Support | helpsvc |
| HID Input Service | HidServ |
| HTTP SSL | HTTPFilter |
| ThinkPad PM Service | IBMPMSVC |
| Windows CardSpace | idsvc |
| IMAPI CD-Burning COM Service | ImapiService |
| iPassConnectEngine | iPassConnectEngine |
| iPassPeriodicUpdateApp | iPassPeriodicUpdateApp |
| iPassPeriodicUpdateService | iPassPeriodicUpdateService |
| IviRegMgr | IviRegMgr |
| Server | lanmanserver |
| Workstation | lanmanworkstation |
| Lenovo Camera Mute | LENOVO.CAMMUTE |
| Lenovo Microphone Mute | Lenovo.micmute |
| TCP/IP NetBIOS Helper | LmHosts |
| Intel(R) Management and Security Application Local Management Service | LMS |
| McAfee Framework Service | McAfeeFramework |
| McAfee McShield | McShield |
| McAfee Task Manager | McTaskManager |
| Machine Debug Manager | MDM |
| Messenger | Messenger |
| NetMeeting Remote Desktop Sharing | mnmsrvc |
| Distributed Transaction Coordinator | MSDTC |
| Windows Installer | MSIServer |
| Net Driver HPZ12 | Net Driver HPZ12 |
| Network DDE | NetDDE |
| Network DDE DSDM | NetDDEdsdm |
| Net Logon | Netlogon |
| Network Connections | Netman |
| Net.Tcp Port Sharing Service | NetTcpPortSharing |
| Network Location Awareness (NLA) | Nla |
| NT LM Security Support Provider | NtLmSsp |
| Removable Storage | NtmsSvc |
| Microsoft Office Diagnostics Service | odserv |
| Office Source Engine | ose |
| Plug and Play | PlugPlay |
| Pml Driver HPZ12 | Pml Driver HPZ12 |
| IPSEC Services | PolicyAgent |
| Power Manager DBC Service | Power Manager DBC Service |
| Protected Storage | ProtectedStorage |
| Remote Access Auto Connection Manager | RasAuto |
| Remote Access Connection Manager | RasMan |
| Remote Desktop Help Session Manager | RDSessMgr |
| Intel(R) PROSet/Wireless Registry Service | RegSrvc |
| Routing and Remote Access | RemoteAccess |
| Remote Registry | RemoteRegistry |
| Remote Procedure Call (RPC) Locator | RpcLocator |
| Remote Procedure Call (RPC) | RpcSs |
| QoS RSVP | RSVP |
| Intel(R) PROSet/Wireless WiFi Service | S24EventMonitor |
| Security Accounts Manager | SamSs |
| Smart Card | SCardSvr |
| Task Scheduler | Schedule |
| Secondary Logon | seclogon |
| System Event Notification | SENS |
| Windows Firewall/Internet Connection Sharing (ICS) | SharedAccess |
| Shell Hardware Detection | ShellHWDetection |
| Print Spooler | Spooler |
| System Restore Service | srservice |
| SSDP Discovery Service | SSDPSRV |
| Windows Image Acquisition (WIA) | stisvc |
| System Update | SUService |
| MS Software Shadow Copy Provider | SwPrv |
| Performance Logs and Alerts | SysmonLog |
| Telephony | TapiSrv |
| Terminal Services | TermService |
| Themes | Themes |
| ThinkVantage Registry Monitor Service | ThinkVantage Registry Monitor Service |
| Telnet | TlntSvr |
| On Screen Display | TPHKSVC |
| Distributed Link Tracking Client | TrkWks |
| TVT Scheduler | TVT Scheduler |
| Windows User Mode Driver Framework | UMWdf |
| Intel(R) Management & Security Application User Notification Service | UNS |
| Universal Plug and Play Device Host | upnphost |
| Uninterruptible Power Supply | UPS |
| Volume Shadow Copy | VSS |
| Windows Time | W32Time |
| WebClient | WebClient |
| Windows Management Instrumentation | winmgmt |
| Portable Media Serial Number Service | WmdmPmSN |
| Windows Management Instrumentation Driver Extensions | Wmi |
| WMI Performance Adapter | WmiApSrv |
| Security Center | wscsvc |
| Automatic Updates | wuauserv |
| SMS Remote Control Agent | Wuser32 |
| Wireless Zero Configuration | WZCSVC |
| Network Provisioning Service | xmlprov |
(Image credit: Future)
On Windows 10, services are programs that run in the background without a user interface and enable system features (such as printing, networking, remote access, File Explorer, Windows Search, updates, etc.) and apps to operate as intended.
Although the system does a pretty good job managing background services, you may sometimes need to control them manually when a feature or app isn’t working correctly or requires you to manage its services manually.
Whatever the case might be, Windows 10 includes at least four methods to stop, start, disable, or enable services using the Services console, Task Manager, Command Prompt, and PowerShell.
This guide will walk you through the steps to manage system and app services on Windows 10.
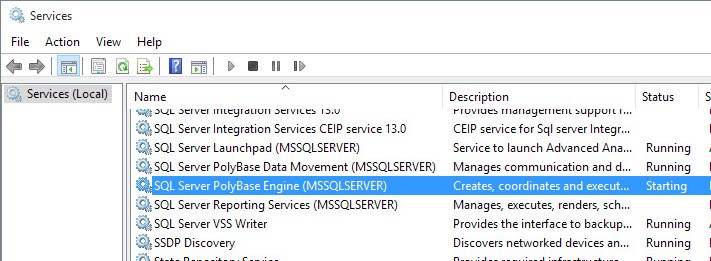
How to manage services from Services console
Using the Services consoles is perhaps the simplest method to stop, start, disable, or enable one or multiple services on Windows 10.
Stop service
To stop a running service using Services, use these steps:
All the latest news, reviews, and guides for Windows and Xbox diehards.
- Open Start.
- Search for Services and click the top result to open the console.
- Double-click the service that you intend to stop.
- Click the Stop button.
- Quick tip: You can also manage the state by right-clicking the service and selecting the option. Or you can select the service and then use the controls at the top to start, stop, pause, or restart.
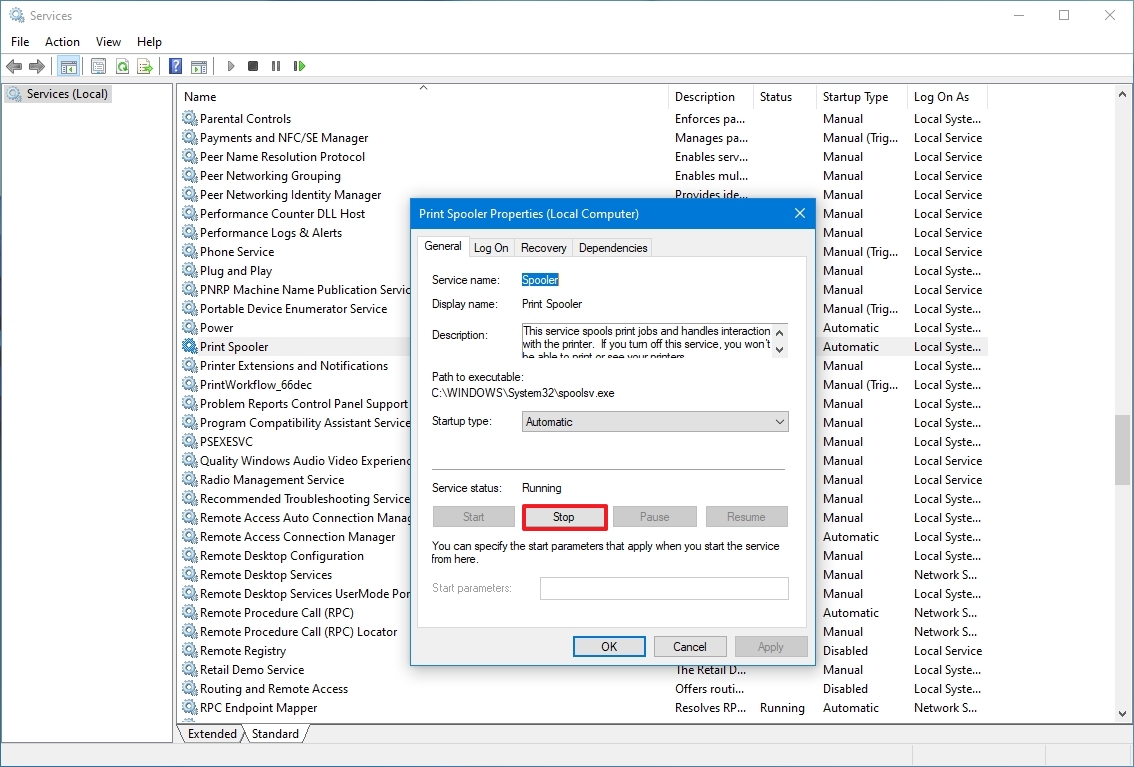
- Click the Apply button.
- Click the OK button.
Once you complete the steps, the service will stop running on the device.
If you’re unable to stop a system service, consider that some services are required for the operation of Windows 10, and they can’t be stopped.
Start service
To start a service on Windows 10, use these steps:
- Open Start.
- Search for Services and click the top result to open the console.
- Double-click the service that you intend to stop.
- Click the Start button.
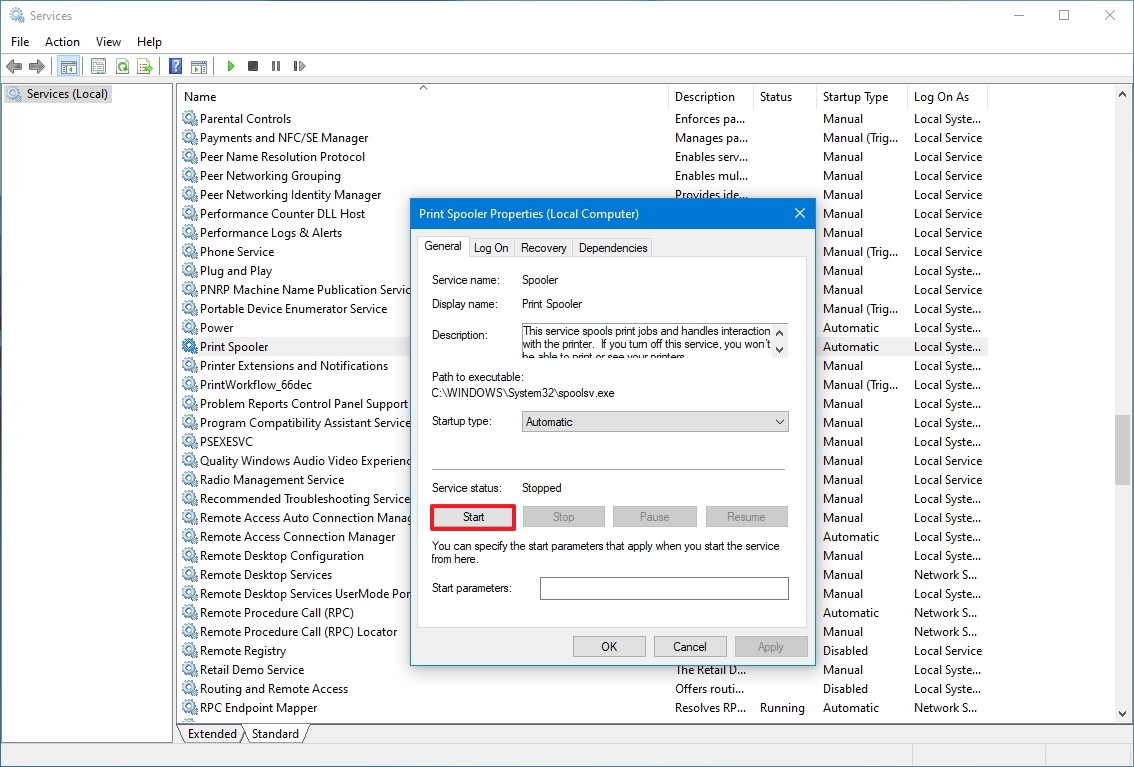
- Click the Apply button.
- Click the OK button.
After you complete the steps, the service you specified will start for the current session.
Disable service
To set a service a disabled, use these steps:
- Open Start.
- Search for Services and click the top result to open the console.
- Double-click the service that you intend to stop.
- Click the Stop button.
- Use the «Start type» drop-down menu and select the Disabled option.
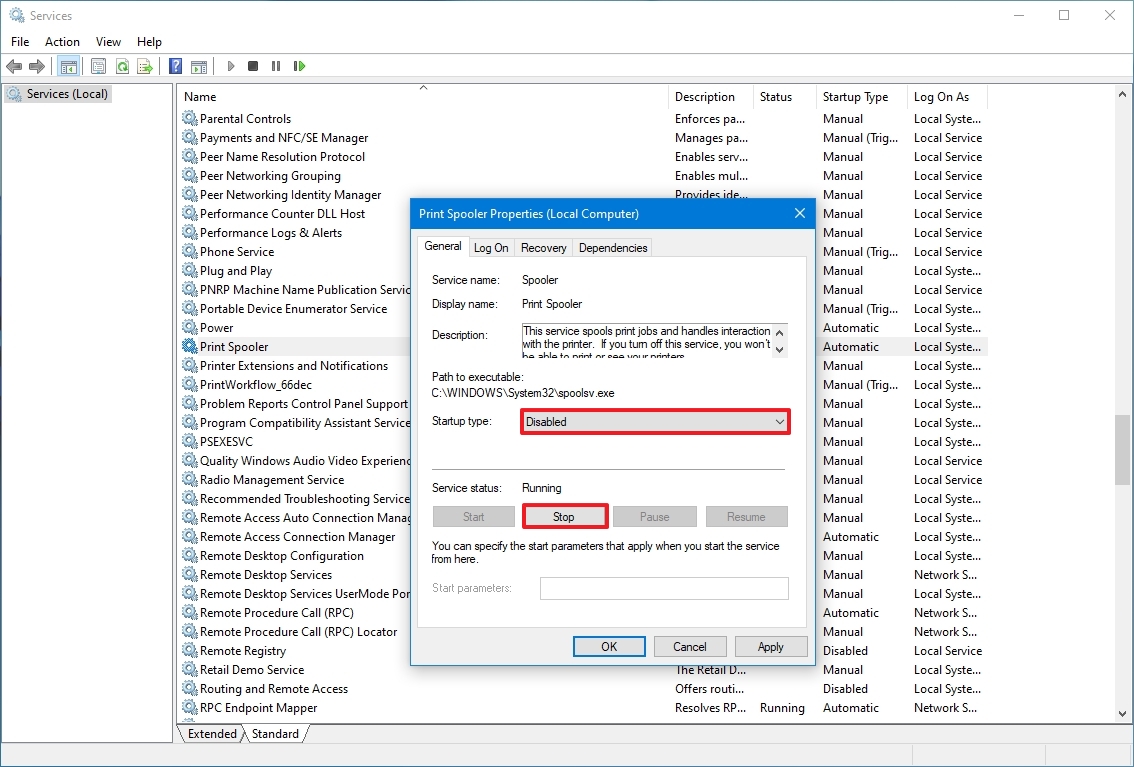
- Click the Apply button.
- Click the OK button.
Once you complete the steps, the service will no longer start automatically after restarting your device.
Enable service
To enable a specific service, use these steps:
- Open Start.
- Search for Services and click the top result to open the console.
- Double-click the service that you intend to stop.
- Click the Start button.
- Use the «Start type» drop-down menu and select the Automatic option. These are the Startup types on Windows 10:
- Automatic – service starts at boot.
- Automatic (Delayed Start) – service start after boot.
- Manual – starts service manually as needed.
- Disabled – stops service from running.
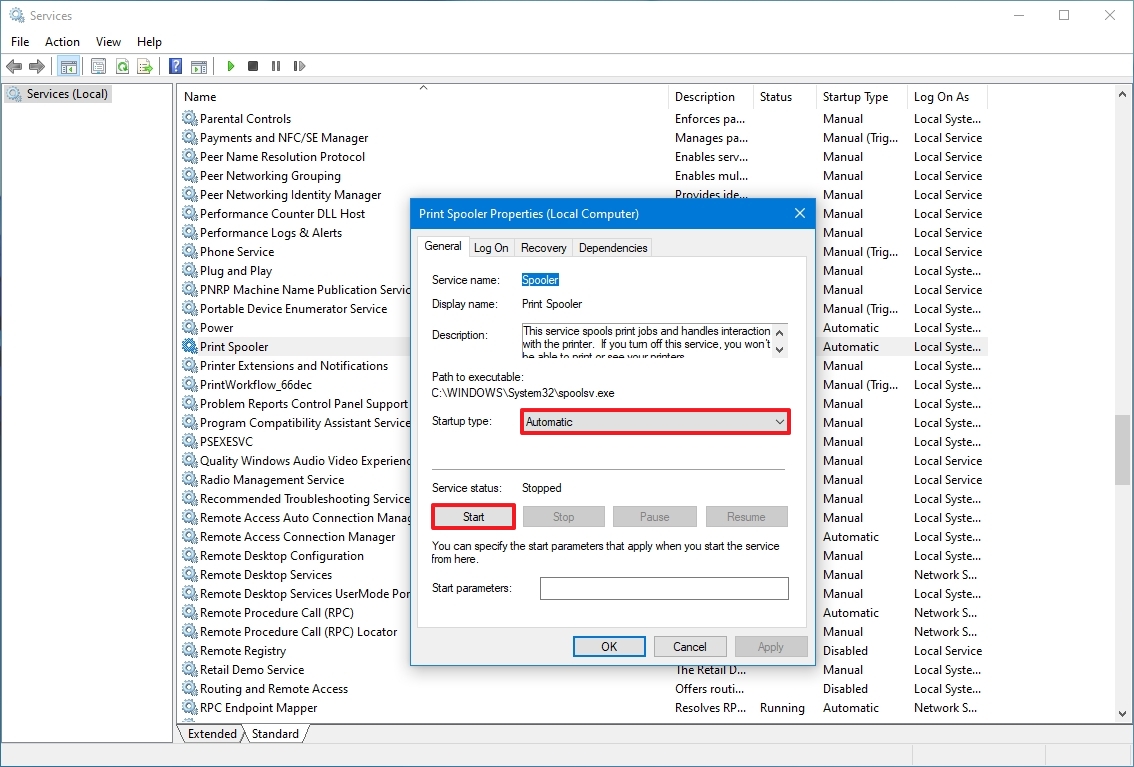
- Click the Apply button.
- Click the OK button.
After you complete the steps, the Windows 10 or app service will enable, but if it was in a stopped state, you’d need to start it manually or restart the device for the service to run.
How to manage services from Task Manager
Task Manager also includes a section to manage services for Windows 10 and apps quickly.
To stop, start, or restart a service using Task Manager, use these steps:
- Open Start.
- Search for Task Manager and click the top result to open the app.
- Quick tip: Windows 10 includes many other ways to open the experience, including right-clicking the taskbar and selecting the Task Manager option, and using the «Ctrl + Shift + ESC» keyboard shortcut.
- Click the Services tab.
- Right-click the service name and select one of the options:
- Stop.
- Start.
- Restart.
- Quick note: Task Manager only displays the service name, not the display name. For example, if you’re using this method, you’ll the «Print Spooler» defined as «Spooler.»
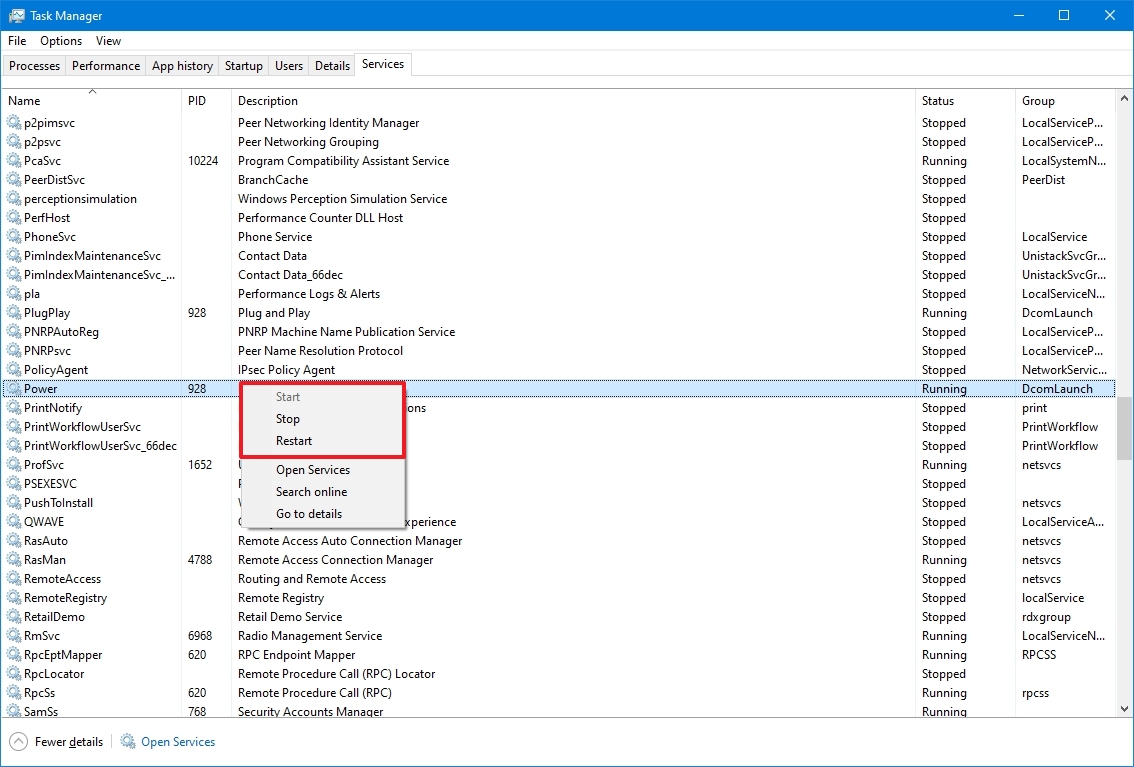
Once you complete the steps, the service will respond to the option you selected.
How to manage services from PowerShell
You can also use PowerShell commands to manage background services for Windows 10 and apps.
Stop service
To stop a specific service with PowerShell, use these steps:
- Open Start.
- Search for PowerShell, right-click the top result, and select the Run as administrator option.
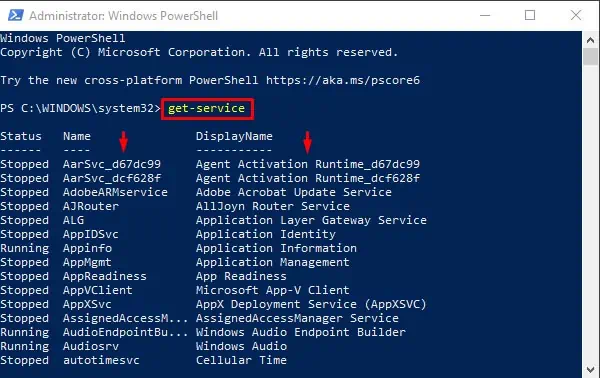
- (Optional) Type the following command to view a list of all the services and press Enter: Get-Service
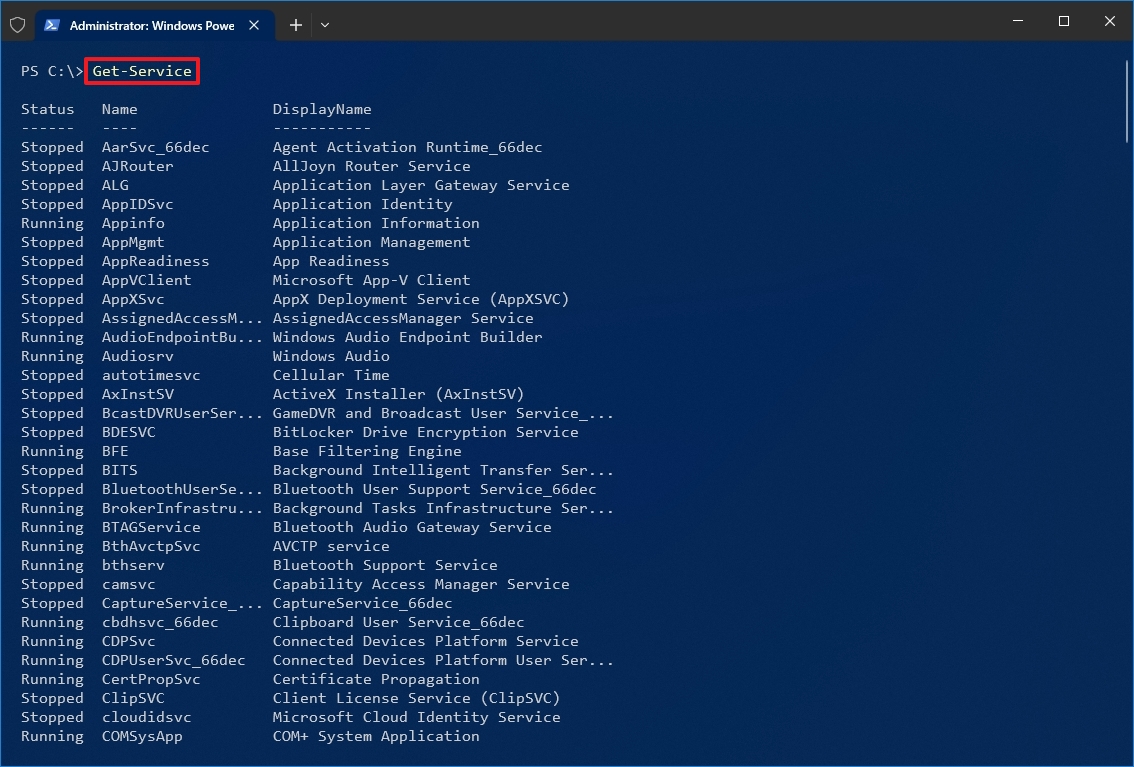
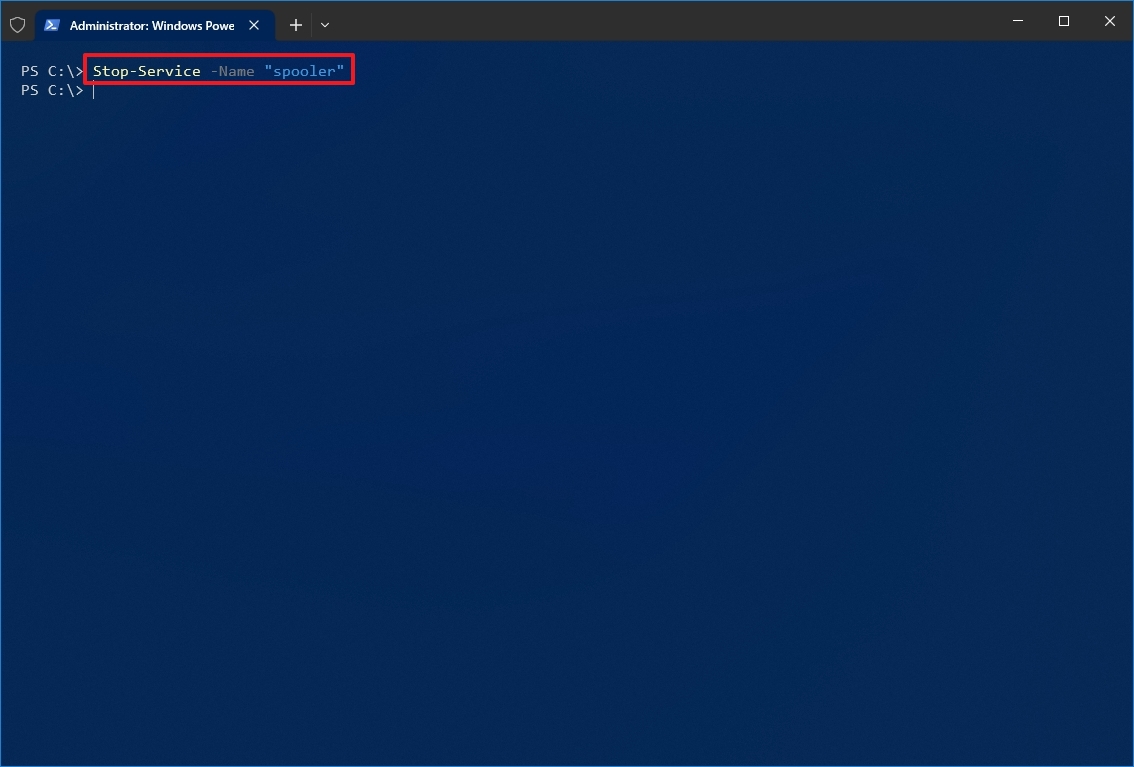
- Type the following command to stop a service and press Enter: Stop-Service -Name «SERVICE-NAME»
For example, this command stops the printer spooler service on Windows 10: Stop-Service -Name «spooler»
In the command, replace «SERVICE-NAME» with the name of the service you intend to stop. If you want to use the display name, replace -Name with -DisplayName and then specify the service’s display name.
Alternatively, you can also use this variant of the command to stop the service: Set-Service -Name «SERVICE-NAME» -Status stopped
In the command, replace «SERVICE-NAME» with the name of the service you intend to stop. If you want to use the display name, replace -Name with -DisplayName and then specify the service’s display name. You only need quotation marks if there’s a space within the name.
- Quick tip: If you’re getting a dependency error, you can append the -force option in either of the commands to stop the service. For example, Stop-Service -Name «SERVICE-NAME» -Force.
After you complete the steps, the PowerShell command will stop the service on your device.
Start service
To start a Windows 10 or app service with PowerShell, use these steps:
- Open Start.
- Search for PowerShell, right-click the top result, and select the Run as administrator option.
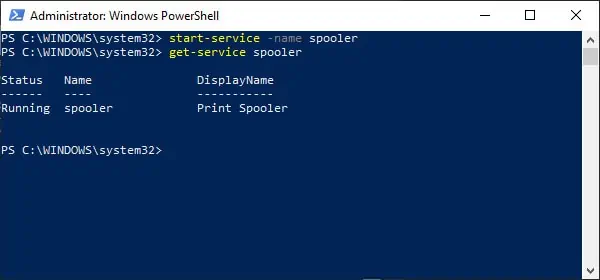
- Type the following command to start a service and press Enter: Start-Service -Name «SERVICE-NAME»
For example, this command starts the printer spooler service on Windows 10: Start-Service -Name «spooler»
In the command, replace «SERVICE-NAME» with the name of the service. Using the display name is supported, replacing -Name with -DisplayName and specifying the service’s display name.
Alternatively, you can also use this variant of the command to start a service: Set-Service -Name «SERVICE-NAME» -Status running
In the command, replace «SERVICE-NAME» with the name of the service. If you want to use the display name, replace -Name with -DisplayName and then specify the service’s display name.
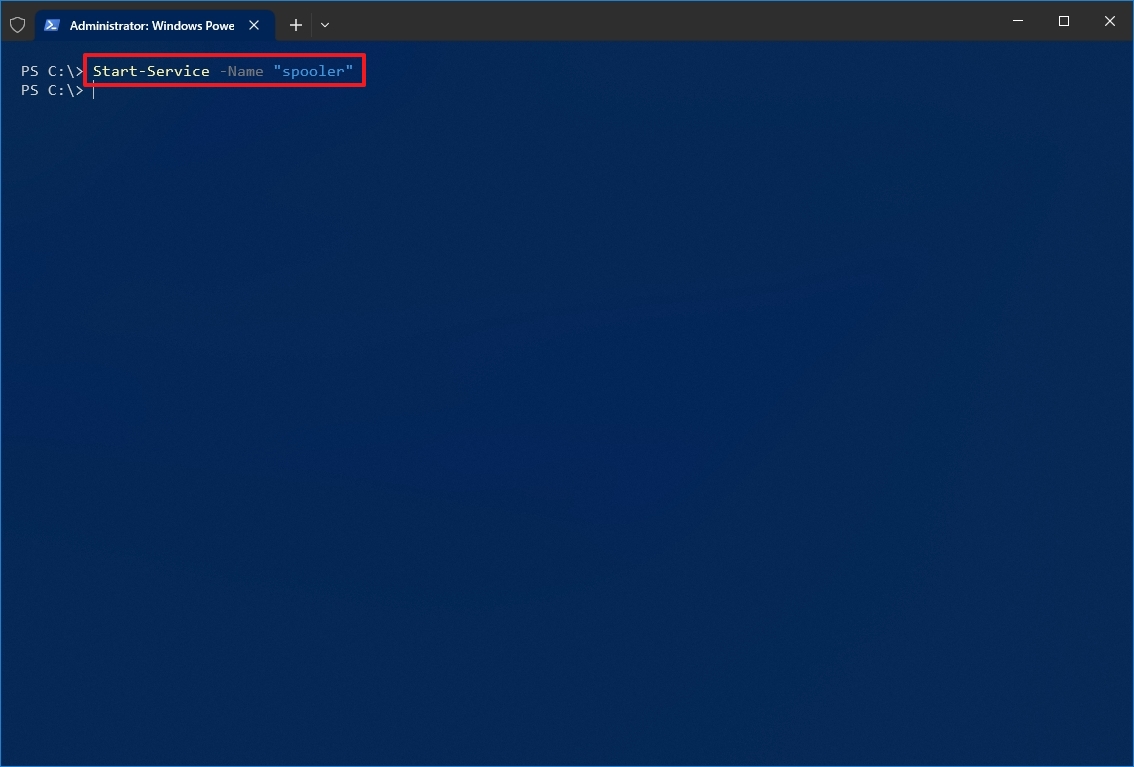
Once you complete the steps, the service will start on your computer.
Disable service
To disable a service using a PowerShell command, use these steps:
- Open Start.
- Search for PowerShell, right-click the top result, and select the Run as administrator option.
- Type the following command to disable a service and press Enter: Set-Service -Name «SERVICE-NAME» -Status stopped -StartupType disabled
In the command, update «SERVICE-NAME» for the name of the service. If you want to use the service’s display name, replace -Name with -DisplayName and specify the service name. If you want to disable the service without stopping it immediately, you can remove the -Status stopped portion of the command.
For example, this command disables the printer spooler service on Windows 10: Set-Service -Name «spooler» -Status stopped -StartupType disabled
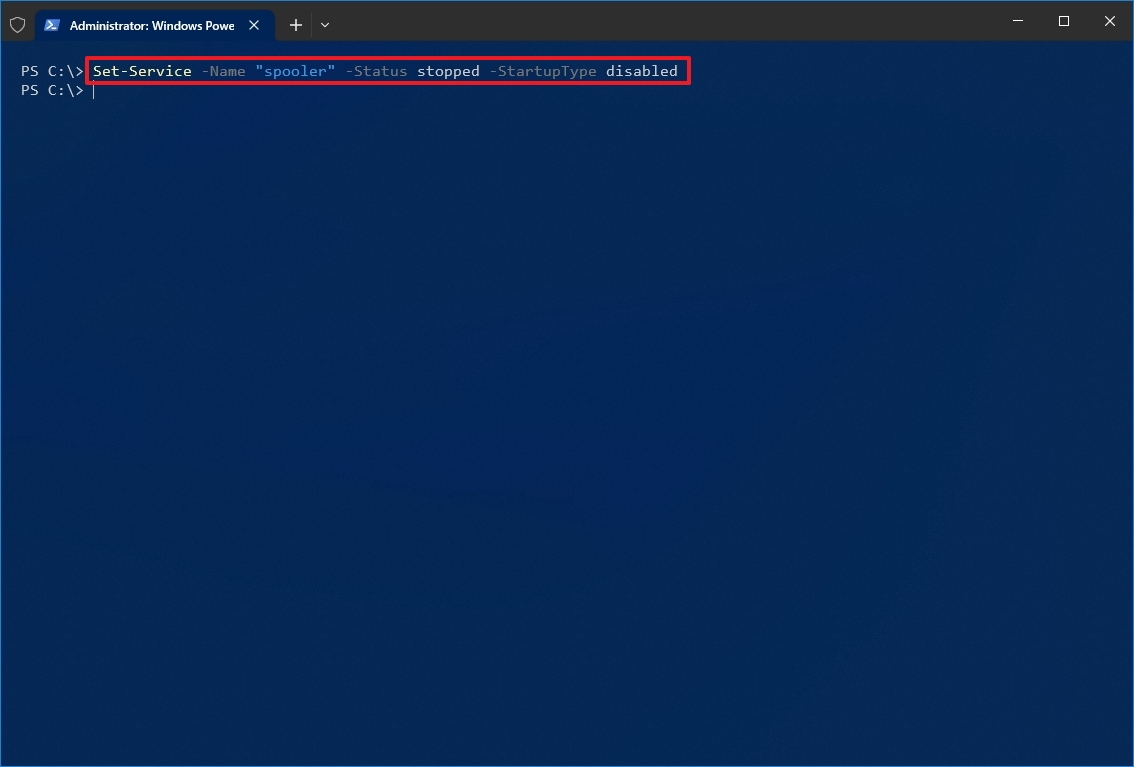
After you complete the steps, the PowerShell command will disable the specified service.
Enable service
To enable a specific background service with PowerShell, use these steps:
- Open Start.
- Search for PowerShell, right-click the top result, and select the Run as administrator option.
- Type the following command to enable a service and press Enter: Set-Service -Name «SERVICE-NAME» -Status running -StartupType automatic
For example, this command enables the printer spooler service using PowerShell: Set-Service -Name «spooler» -Status running -StartupType automatic
- Quick note: You may able to use the display -DisplayName option, but the command may also prompt you to supply the name of the service, adding an extra step to the process. If you want to enable the service without starting it immediately, you can remove the -Status running portion of the command.
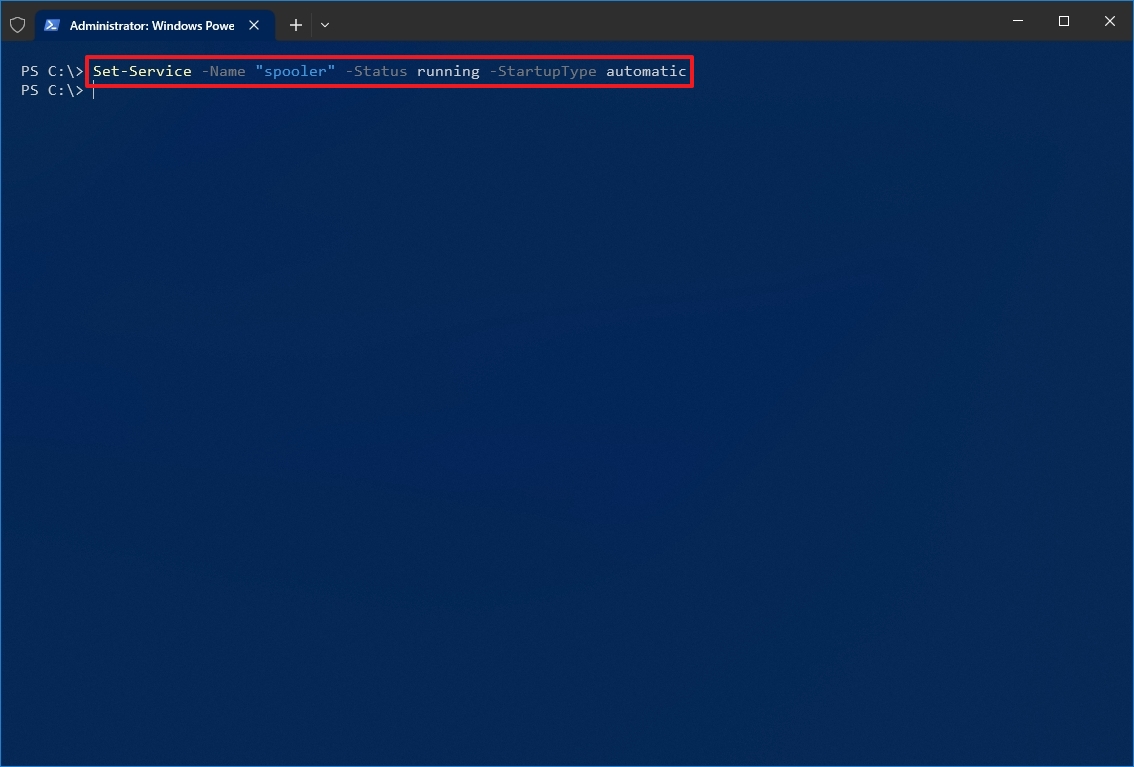
Once you complete the steps, PowerShell will enable the service specified with the command.
How to manage services from Command Prompt
If you’re comfortable using the command line, Command Prompt offers the «net» command (older) to stop or start or the «sc» command (newer) to stop, start, disable, or enable services on Windows 10.
Stop service
To stop a Windows 10 or app service with Command Prompt, use these steps:
- Open Start.
- Search for Command Prompt, right-click the top result, and select the Run as administrator option.
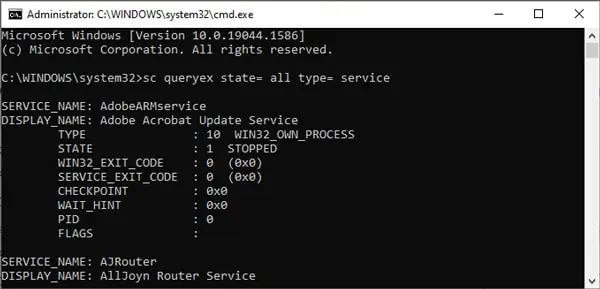
- (Optional) Type the following command to view a list of all the services and press Enter: sc queryex state=all type=service
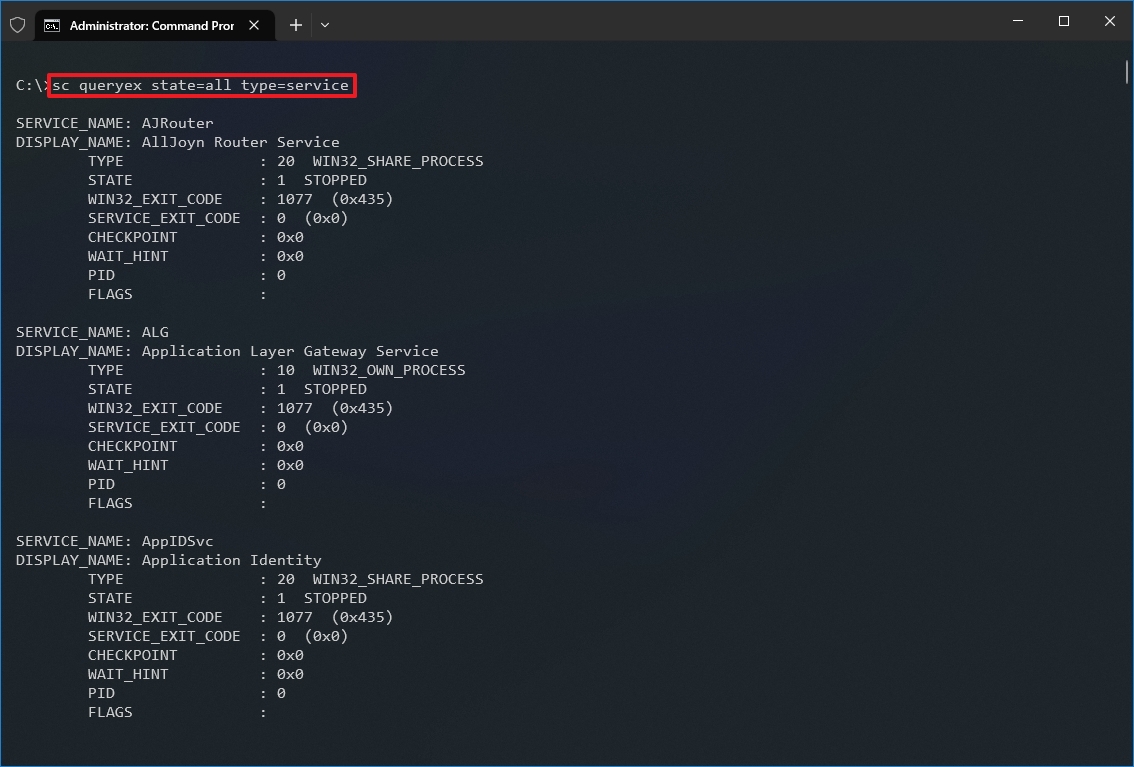
- Type the following command to stop a service and press Enter: net stop «SERVICE-NAME»
In the command, replace «SERVICE-NAME» with the name or display the name of the service. You only need quotation marks if there’s a space within the name. For example, this command stops the printer spooler using the service name: net stop «spooler»
Alternatively, you can also use the more advanced «sc» command: sc stop «SERVICE-NAME»
For example, this command stops the printer spooler using the service name: sc stop «spooler»
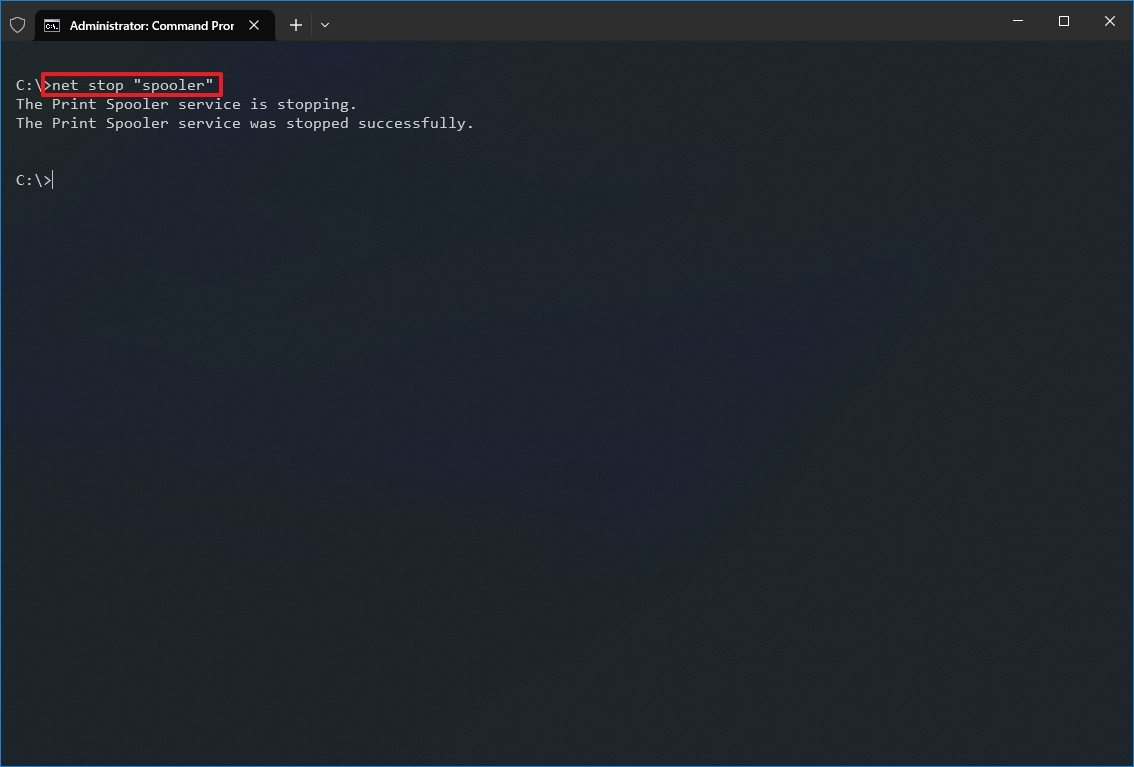
After you complete the steps, the command will stop the specified service on Windows 10.
Start service
To start a service with the command line, use these steps:
- Open Start.
- Search for Command Prompt, right-click the top result, and select the Run as administrator option.
- Type the following command to start a service and press Enter:
net start «SERVICE-NAME»
In the command, replace «SERVICE-NAME» with the name or display the name of the service. You only need quotation marks if there’s a space within the name. For example, this command starts the printer spooler using the service name: net start «spooler»
Alternatively, you can also use the «sc» command: sc start «SERVICE-NAME»
For example, this command starts the printer spooler using the service name: sc start «spooler»
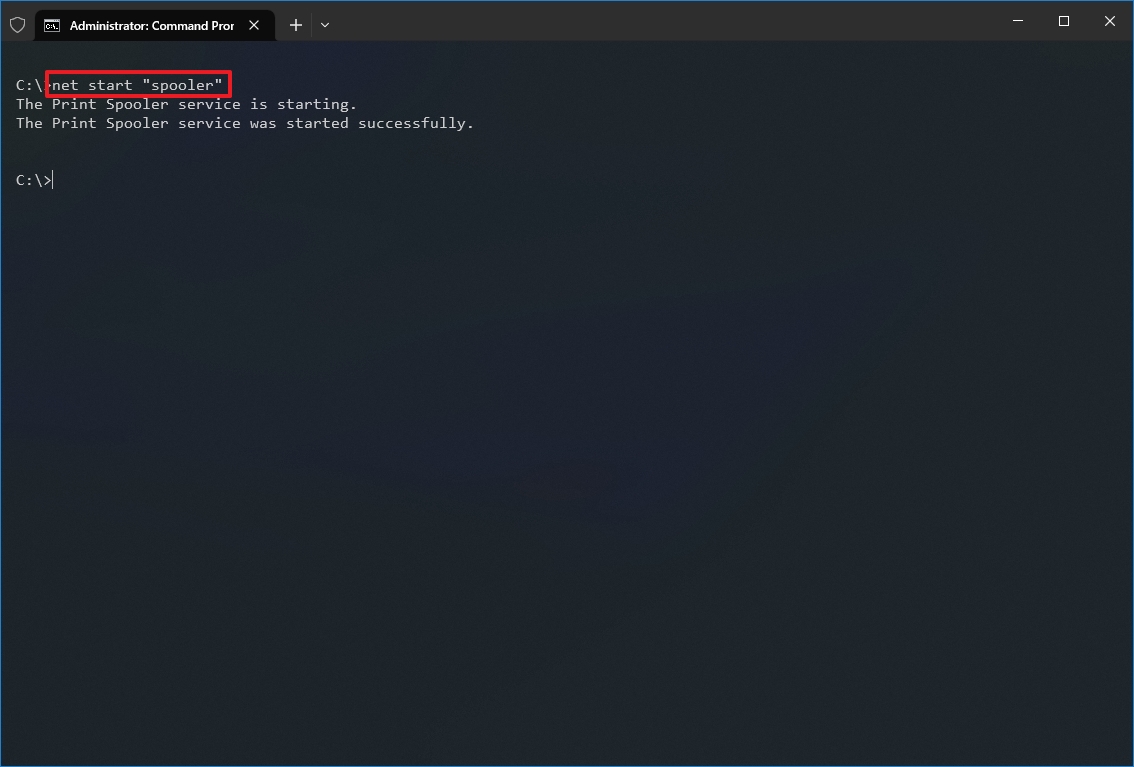
Once you complete the steps, the command will execute and start the service you specified.
Disable service
To disable a service with Command Prompt, use these steps:
- Open Start.
- Search for Command Prompt, right-click the top result, and select the Run as administrator option.
- Type the following command to disable a service and press Enter: sc config «SERVICE-NAME» start=disabled
In the command, replace «SERVICE-NAME» with the name of the service that you want to disable.
For example, this command disables the printer spooler using the service name: sc config «spooler» start=disabled
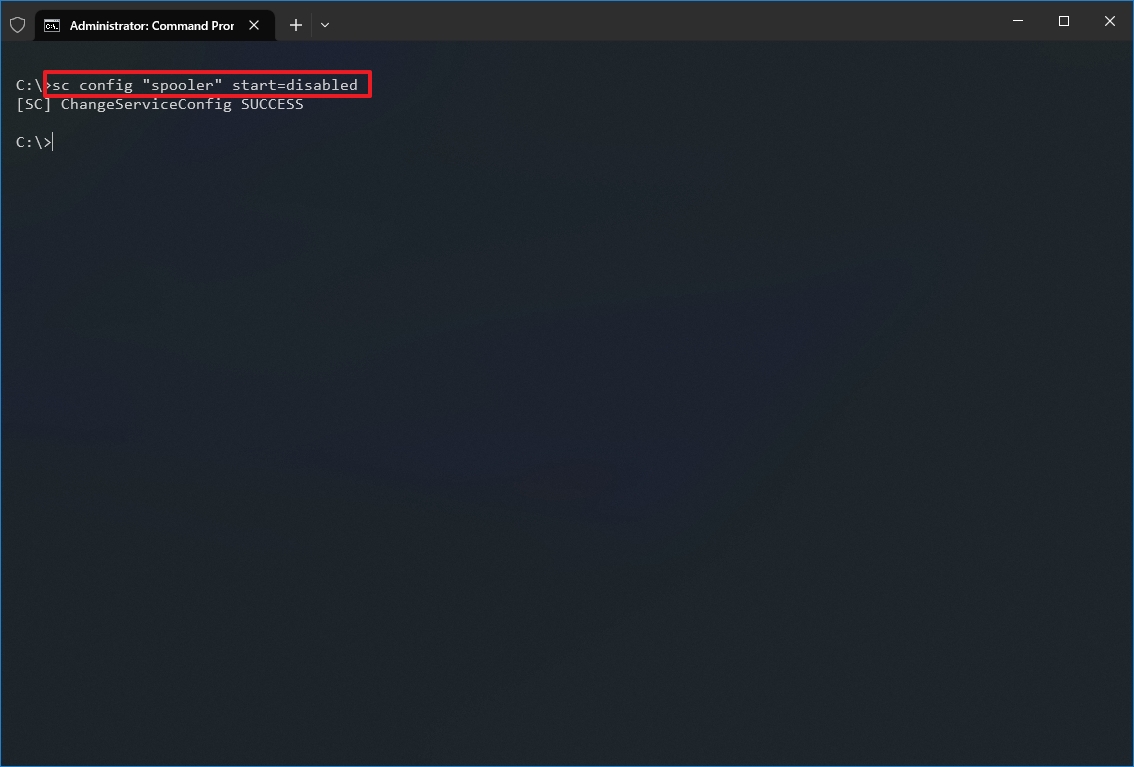
- (Optional) Type the following command to stop the service and press Enter: sc stop «SERVICE-NAME»
- Quick note: When you disable a service, it doesn’t stop the current state of the service. You can either restart your computer or stop the service using the above command.
After you complete the steps, the sc command will run disabling the Windows 10 or app service you specified.
Enable service
To enable a service with a command, use these steps:
- Open Start.
- Search for Command Prompt, right-click the top result, and select the Run as administrator option.
- Type the following command to enable a particular service and press Enter:
sc config «SERVICE-NAME» start=auto
In the command, replace «SERVICE-NAME» with the name of the service that you want to enable. For example, this command enables the printer spooler automatically using the service name: sc config «spooler» start=auto
These are alternative commands to enable a particular service:
- Manual: sc config «SERVICE-NAME» start=demand
- Automatic Delayed: sc config «SERVICE-NAME» start=delayed-auto
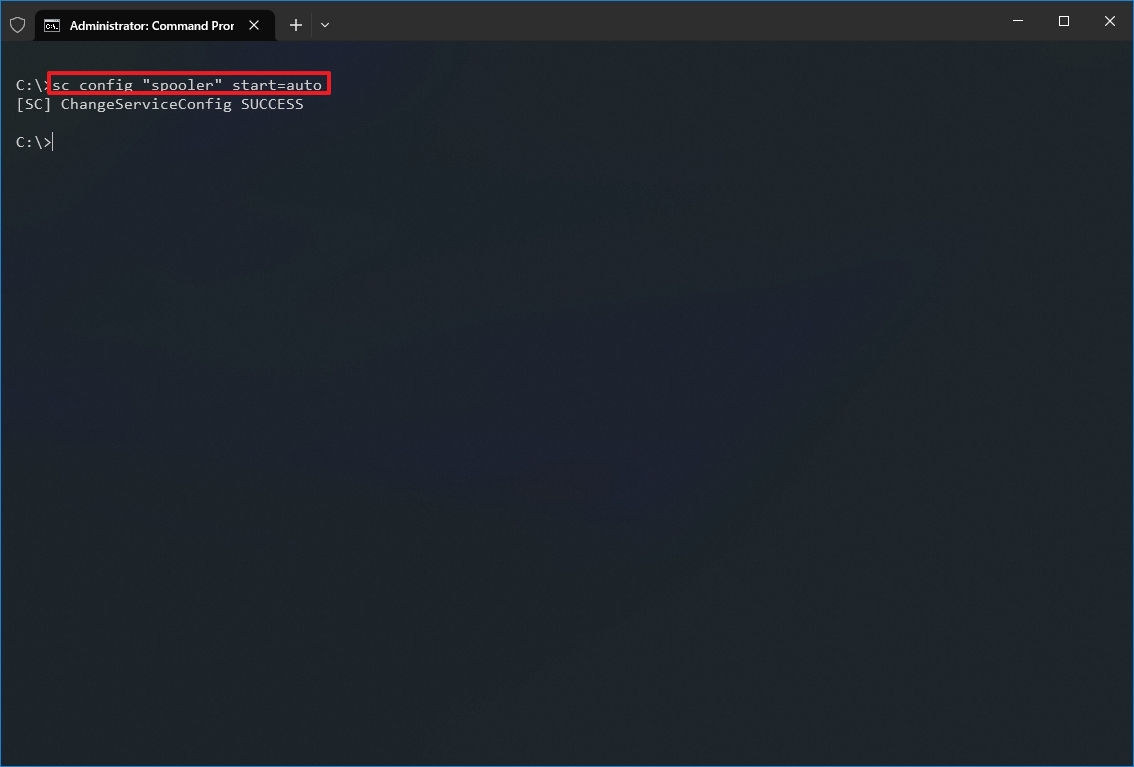
- (Optional) Type the following command to start the service and press Enter: sc start «SERVICE-NAME»
Once you complete the steps, the service will enable and start automatically on reboot according to the command you used.
You can only use the «net» command to start or stop services. The «sc» command allows you to perform more tasks, including start, stop, enable, or disable services, among other options. If you’re choosing to manage services with command lines, then, in either case, it’s best to use the service name instead of the display name.
Also, when using any of the methods outlined above, consider that making modifications to the default settings can alter the operation of one or more features that depend on that service, negatively affecting the experience. Furthermore, if you restart a service, you might be required to start its dependencies manually as well to make the app or feature operational again.
We’re focusing this guide on Windows 10, but the ability to manage services has been available for several years, which means that you can refer to this guide if you’re still running Windows 8.1, Windows 7, and older versions.
More resources
For more helpful articles, coverage, and answers to common questions about Windows 10 and Windows 11, visit the following resources:
- Windows 11 on Windows Central — All you need to know
- Windows 10 on Windows Central — All you need to know
Cutting-edge operating system
A refreshed design in Windows 11 enables you to do what you want effortlessly and safely, with biometric logins for encrypted authentication and advanced antivirus defenses.
Mauro Huculak has been a Windows How-To Expert contributor for WindowsCentral.com for nearly a decade and has over 15 years of experience writing comprehensive guides. He also has an IT background and has achieved different professional certifications from Microsoft, Cisco, VMware, and CompTIA. He has been recognized as a Microsoft MVP for many years.
GUI is very popular due to its simplicity and ease of access. But when it comes to managing or automating Windows services, CLI is simply superior and more efficient if you are used to using it.
To stop a Windows service through Command-Line, you can use the Stop-Service cmdlet in PowerShell or the Net stop command in CMD.
We’ve provided step-by-step guidelines on how to do so below.
How to Stop a Windows Service From Command Line
In addition to the commands mentioned above, you can also use the Set-Service cmdlet in Powershell or theSc stop command in CMD to stop a Windows Service.
Using PowerShell
Before going to the actual process, here’s what the commands do.
Get-Servicedisplays a list of all services on the computer.Stop-Serviceis used to stop one or more running services.Set-Servicecan change the properties of a service, including the Status and StartupType.
- Press Windows + X and then press A to open Windows PowerShell (Admin).
- Type and enter
Get-Serviceto get a list of all services. - Type either of the following commands:
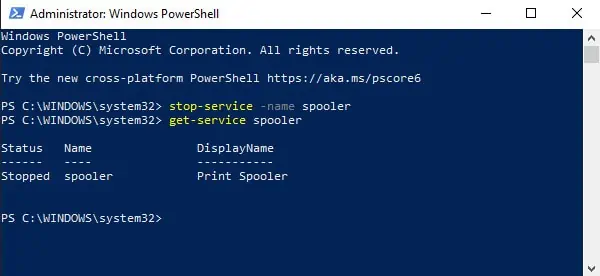
Stop-Service -Name “service-name-here”Set-Service -Name “service-name-here” -Status stopped
Replace “service-name-here” with the Name or DisplayName from Step 2 and press Enter.
For e.g.Stop-Service -Name AJRouter
- Type
get-service “service-name-here“to check if the service is stopped.
Note: If you’re unable to stop the service because of a dependency error, add -Force at the end as such:
Stop-Service -Name “service-name-here” -ForceSet-Service -Name “service-name-here” -Status stopped -Force
Using Command Prompt
Sc queryex obtains and displays detailed information about all active services by default. With the use of certain parameters, it can also show info on drivers, their state, and more.
Both Net stop and sc stop can stop a service. But Net only works locally while sc can be used over a network.
- Press Windows + R to launch Run.
- Type cmd and press CTRL + Shift + Enter to launch Elevated Command Prompt.
- Type
sc queryex state= all type= serviceand press Enter to get a list of all the services. - Note the SERVICE_NAME and DISPLAY_NAME of the service you want to stop. You can replace “service-name-here” with either of these values in Step 5.
For Step 6, replace it with SERVICE_NAME specifically, as DISPLAY_NAME won’t work with thesc stopcommand. - Type and enter
net stop “service-name-here”. - Alternatively, type
sc stop “service-name-here”and press Enter.
For e.g.sc stop spooler
Start/Restart Windows Service from Command Line
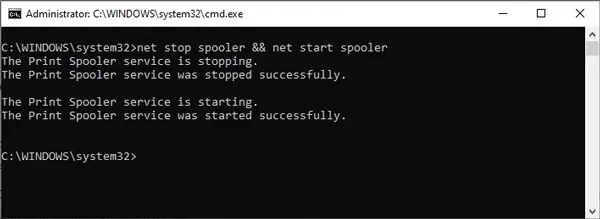
In Powershell, you can use the start-service or restart-service cmdlets as appropriate. As CMD doesn’t have a command to restart a service directly, we’ll combine the net stop and net start commands instead.
Powershell
Start-Servicestarts one or more stopped services.Restart-Servicestops, then starts one or more services.
- Press Windows + X and press A to launch Windows PowerShell (Admin).
- Type
Get-Serviceand press Enter to get a list of all services. - Note the Name and DisplayName of the service you want to start. Replace “service-name-here” with either of these values in the next step. Also, note the status.
- If the status is stopped, type the following command and press Enter:
Start-Service -Name “service-name-here” - If the status is running, type the following command and press Enter:
Restart-Service -Name “service-name-here” - Check the status of the service with the following command:
get-service “service-name-here”
Command Prompt
In CMD, you’ll have to stop the service first and restart it afterward. Otherwise, you’ll get a The requested Service has already been started error.
- Press Windows + R to launch Run.
- Type cmd and press CTRL + Shift + Enter to launch Elevated Command Prompt.
- Type
sc queryex state= all type= serviceand press Enter to get a list of all the services. - Note the SERVICE_NAME and DISPLAY_NAME of the service you want to stop. You can replace “service-name-here” with either of these values in Step 5.
For Step 6, replace it with SERVICE_NAME specifically as DISPLAY_NAME won’t work with thesc startcommand. - Type
net stop “service-name-here” && net start “service-name-here”and press Enter. - Check the status of the service with the following command:
sc queryex “service-name-here”
Change Windows Service Startup Type from Command Line
You can use the Set-Service cmdlet to change the startup type in Powershell. In Command Prompt, you can instead use the sc config command.
Powershell
The acceptable values for the StartupType parameter are as follows:
- Automatic – The service starts automatically at system startup.
- AutomaticDelayedStart – The service starts automatically, slightly after other automatic services start.
- Manual – The service needs to be started manually by a user or program.
- Disabled – The service cannot be started.
- Press Windows + X to open the quick link menu.
- Press A and accept the prompt to launch Windows PowerShell (Admin).
- Type
Get-Serviceand press Enter to get a list of all services. - Note the Name and DisplayName of the service you want to start. Replace “service-name-here” with either of these values in the next step.
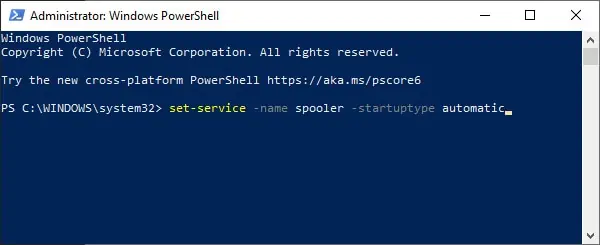
- Type the following command, replace Automatic with the appropriate startup type, and press Enter:
Set-Service -Name “service-name-here” -StartupType Automatic
Command Prompt
The acceptable values for the start parameter are as follows:
- auto – The service starts automatically at system startup.
- delayed-auto – The service starts automatically at boot, but with a slight delay.
- demand – The service needs to be started manually by a user or program.
- boot – The boot loader loads the device driver.
- system – The device driver starts during kernel initialization.
- disabled – The service is disabled and won’t start.
- Press Windows + R to launch Run.
- Type cmd and press CTRL + Shift + Enter to launch Elevated Command Prompt.
- Type
sc queryex state= all type= serviceand press Enter to get a list of all the services. - Note the SERVICE_NAME and DISPLAY_NAME of the service you want to stop. Replace “service-name-here” with either of these values in the next step.
- Type the following command, replace auto with the appropriate start option, and press Enter:
sc config “service-name-here” start=auto
How to Fix Can’t Stop Windows Service Because Of Access Denied System Error?
If you launch CMD/PowerShell without admin privileges and try to stop a Windows Service, you will encounter this error. To fix this, launch them in elevated mode, and you’ll be able to stop the service.
To stop a service in cmd, use the following command replacing `ServiceName` with the actual name of the service you want to stop:
sc stop ServiceName
What is a Windows Service?
A Windows service is a background process that performs tasks without requiring user intervention. These services are essential for a wide range of system functionalities, such as networking, security, and application support. Common examples of Windows services include:
- Print Spooler: Manages print jobs sent to the printer.
- SQL Server: Manages SQL database processes.
- Windows Update: Handles updates for the operating system.
Knowing how to stop a service is crucial when troubleshooting system issues or optimizing performance. Sometimes, you may need to stop unresponsive services or prevent them from running during specific tasks.

How to Send a Message in Cmd: A Simple Guide
Preparing to Use CMD
Accessing Command Prompt
To manage services through CMD, you must first open the Command Prompt:
- Press `Windows + R` to open the Run dialog.
- Type `cmd` and press Enter.
- For administrative tasks, right-click and select Run as Administrator. This is essential as many service management commands require higher privileges.
Checking Current Services
Before stopping a service, you might want to view the list of currently running services. You can achieve this in CMD by using the following command:
sc query
This command lists all services and their statuses, allowing you to identify the service you wish to stop. Look for the `RUNNING` state next to the service name to ensure it’s currently active.

How to Open Services from Cmd in a Flash
Stopping a Service Using CMD
The Basic Stop Command
Once you’ve identified the service you want to stop, you can use the following command:
sc stop <ServiceName>
For example, to stop the Print Spooler service, the command would be:
sc stop Spooler
This command instructs Windows to halt the specified service. The `<ServiceName>` must match the service name exactly as it appears in the `sc query` command output.
Force Stop a Service in CMD
If a service is unresponsive and does not stop with the basic command, you may need to force stop it. Here is the process:
-
First, find the PID (Process ID) of the service using:
sc queryex <ServiceName>The output will contain the PID, which you’ll use next.
-
Now, use the following command to forcefully terminate the service:
taskkill /F /PID <PID>
This method ensures that you can stop a service that isn’t responding to conventional commands.

How to Run a EXE in Cmd: A Quick Guide
Handling Common Errors
Service Not Responding
Sometimes, when you attempt to stop a service, you may encounter errors indicating that the service is unresponsive. It can be due to:
- System resource issues.
- Dependencies that prevent the service from stopping.
In such cases, checking the service’s dependencies may help. Ensure no other services are reliant on the service you wish to stop.
Access Denied Errors
If you receive an access denied error when trying to stop a service, it’s likely that you have not run Command Prompt with administrative rights. Ensure that you have elevated permissions by right-clicking CMD and selecting Run as Administrator.

Start a Service Cmd: Quick Guide to Command Mastery
Stopping Services with Additional Options
Stop a Specific Type of Service
To filter services by type before stopping them, you can use the command:
sc query state= all
This command allows you to see the state of all services—running, stopped, or paused—enabling you to make more informed decisions about which services to stop.
Using PowerShell as an Alternative
While CMD is powerful, you may also consider using PowerShell as an alternative for service management. PowerShell provides more capabilities and syntax that may be more intuitive for some users. For instance, to stop a service, you can use:
Stop-Service <ServiceName>
This command performs a similar function but can be more flexible.

Open Services in Cmd: A Quick Guide to Command Mastery
Tips for Managing Services via CMD
Creating a Batch File to Stop Services
If you frequently need to stop certain services, you can automate the process by creating a batch file. Here’s an example batch script to stop multiple services:
@echo off
sc stop Spooler
sc stop SQLServer
Save it with a `.bat` extension, and run it as an administrator to stop all specified services at once.
Scheduling Service Stops with Task Scheduler
You can automate stopping services using Task Scheduler. This enables you to set a specific time or condition to stop a service without manual intervention. Create a new task, specify the actions needed (run your batch file or CMD command), and set your triggers according to your preferences.

How to Copy Files in Cmd: A Simple Guide
Conclusion
Understanding how to stop a service in CMD is a powerful skill that can significantly enhance your ability to manage your Windows environment. This knowledge allows you to optimize system performance, resolve issues, and maintain control over the services running on your machine. Regular practice of these commands will increase your confidence and efficiency in managing system resources effectively.
Mastering Windows Services Cmd: A Quick Guide
Further Reading
For further exploration, consider diving deeper into related CMD commands or advanced service management techniques to broaden your command-line skills. Familiarizing yourself with additional resources will strengthen your ability to navigate and troubleshoot Windows operating systems effectively.

Uninstall Service Cmd: A Quick Guide to Mastery
FAQs
What is the difference between sc stop and taskkill?
The `sc stop` command is used to properly stop a Windows service, allowing it to complete any running processes and release resources without immediate termination. On the other hand, `taskkill` is used to forcefully end processes based on their PID, which may lead to data loss or corruption if the process is abruptly terminated.
Can I stop a service without administrative privileges?
No, stopping a service generally requires administrative privileges. Running CMD without administrator access will limit your ability to manage critical system services.
What should I do if a service won’t stop?
If a service fails to stop, consider the following steps:
- Verify if there are dependent services running.
- Check for any system resource issues.
- Restart the computer to ensure all services reset properly.
With this comprehensive guide, you’re now equipped with the essential knowledge and commands necessary to manage Windows services effectively through CMD.
Как завершить процесс службы Windows, которая зависла в статусе stopping (остановка) или starting (запуск)? Большинство администраторов Windows встречалось с ситуациями, когда при попытке остановить (перезапустить) службу из графического интерфейса консоли управления службами (
Services.msc
), служба зависает намертво и висит в статусе Stopping (или Starting). При этом все кнопки управления службой в консоли (Start, Stop, Restart) становятся недоступными (серыми). Самый простой способ – перезагрузить сервер, но это не всегда допустимо. Рассмотрим альтернативные способы, позволяющие принудительно завершить зависшую службу или процесс без необходимости перезагрузки Windows.
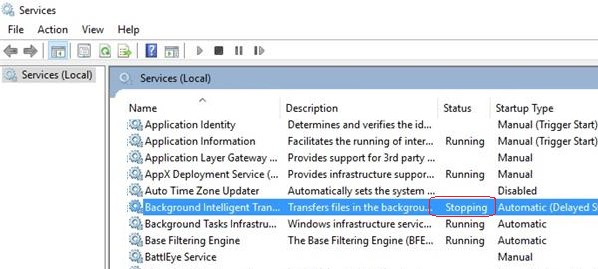
Если в течении 30 секунд после попытки остановки службы, она не останавливается, Windows выводит сообщение:
Не удалось остановить службу xxxxxxx Windows на локальном компьютере. Ошибка 1053. Служба не ответила на запрос своевременно.
Windows Could not stop the xxxxxx service on Local Computer Error 1053: The service did not respond in a timely fashion.
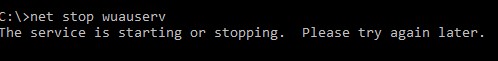
При попытке остановить такую службу командой:
net stop wuauserv
, появляется сообщение:
The service is starting or stopping. Please try again later.
Или:
[SC] ControlService: ошибка: 1061: Служба в настоящее время не может принимать команды.
Windows could not stop the Service on Local Computer. Error 1061: The service cannot accept control messages at this time.
Содержание:
- Как остановить зависшую службу Windows из командной строки?
- Принудительное завершение зависшей службы в PowerShell
- Анализ цепочки ожидания зависшего приложения с помощью ResMon
- Process Explorer: Завершение зависшего процесса из-под SYSTEM
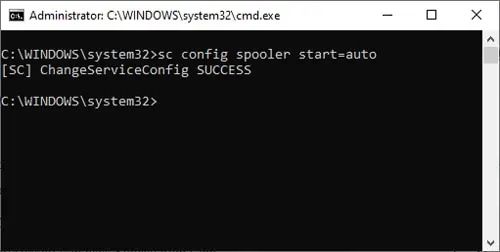
Как остановить зависшую службу Windows из командной строки?
Самый простой способ завершить зависшую служу – воспользоваться утилитой taskkill. В первую очередь нужно определить PID (идентификатор процесса) нашей службы. В качестве примера возьмем службу Windows Update. Ее системное имя wuauserv (имя можно посмотреть в свойствах службы в консоли
services.msc
).
Важно. Будьте внимательными. Принудительная отставка процесса критичной службы Windows может привести к BSOD или перезагрузке операционной системы.
Отройте командную строку с правами правами администратора (иначе будет ошибка access denied) и выполите команду:
sc queryex wuauserv
В данном случае PID процесса —
9186
.
Чтобы принудительно завершить зависший процесс с PID 9186 воспользуйтесь утилитой taskkill:
taskkill /PID 9168 /F
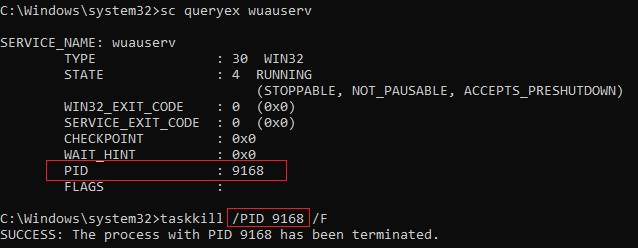
SUCCESS: The process with PID 9168 has been terminated.
Данная команда принудительно завершит процесс службы. Теперь вы можете запустите службу командой sc start servicename или через консоль управления службами (или совсем удалить эту службу, если она не нужна).
«Выстрел в голову» зависшей службы можно выполнить и более элегантно, не выполняя ручное определение PID процесса. У утилиты taskkill есть параметр /FI, позволяющий использовать фильтр для выбора необходимых служб или процессов. Вы можете остановить конкретную службу командой:
TASKKILL /F /FI “SERVICES eq wuauserv”
Или можно вообще не указывать имя, службы, завершив все сервисы в зависшем состоянии с помощью команды:
taskkill /F /FI “status eq not responding”
После этого служба, зависшая в статусе Stopping должна остановиться.
Также вы можете использовать утилиту taskkill для принудительной остановки зависших служб на удаленном компьютере:
TASKKILL /S CORPFS01 /F /FI “SERVICES eq wuauserv”
Принудительное завершение зависшей службы в PowerShell
Также вы можете использовать PowerShell для принудительной остановки службы. С помощью следующей команды можно получить список служб, находящихся в состоянии Stopping:
Get-WmiObject -Class win32_service | Where-Object {$_.state -eq 'stop pending'}
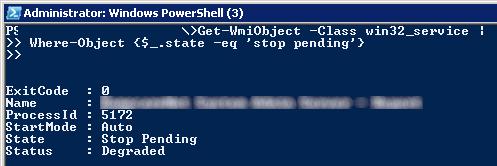
Завершить процесс для всех найденных служб поможет командлет Stop-Process. Следующий PowerShell скрипт завершит все процессы зависших служб в Windows:
$Services = Get-WmiObject -Class win32_service -Filter "state = 'stop pending'"
if ($Services) {
foreach ($service in $Services) {
try {
Stop-Process -Id $service.processid -Force -PassThru -ErrorAction Stop
}
catch {
Write-Warning -Message " Error. Error details: $_.Exception.Message"
}
}
}
else {
Write-Output "No services with 'Stopping'.status"
}
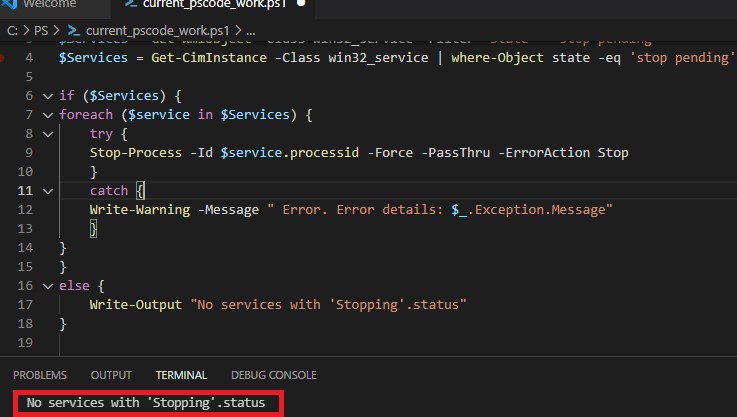
В новом PowerShell Core 6.x/7.x вместо командлета Get-WmiObject нужно использовать Get-CimInstance. Замените первую команду скрипта на:
$Services = Get-CimInstance -Class win32_service | where-Object state -eq 'stop pending'
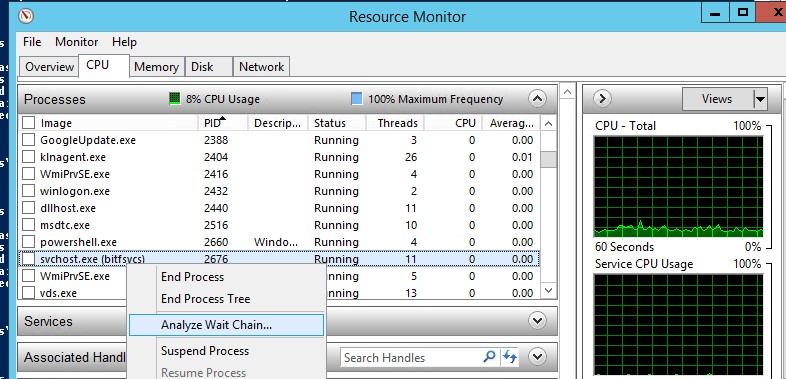
Анализ цепочки ожидания зависшего приложения с помощью ResMon
Вы можете определить процесс, из-за которого зависла служба с помощью монитора ресурсов (
resmon.exe
).
- В окне Монитора ресурсов перейдите на вкладку ЦП (CPU) и найдите процесс зависшей службы;
- Выберите пункт Анализ цепочки ожидания (Analyze Wait Chain);
- В новом окне скорее всего вы увидите, что вам процесс ожидает другой процесс. Завершите его. Если выполняется ожидание системного процесса svchost.exe, завершать его не нужно. Попробуйте проанализировать цепочку ожидания для этого процесса. Найдите PID процесса, которого ожидает ваш svchost.exe и завершите его
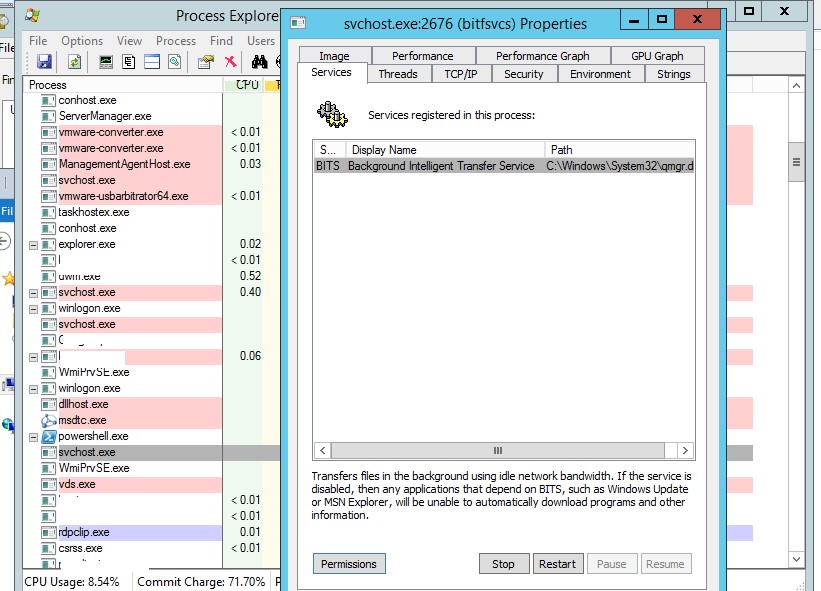
Process Explorer: Завершение зависшего процесса из-под SYSTEM
Некоторые процессы, запущенные из-под SYSTEM, не может завершить даже локальный администратора сервера. Дело в том, что у него просто может не быть прав на некоторые процессы или службы. Чтобы завершить такие процесс (службы), вам необходимо предоставить локальной группе Administrators права на службу (процесс), а потом завершить их. Для этого нам понадобятся две утилиты: psexec.exe и ProcessExplorer (доступны на сайте Microsoft).
- Чтобы запустить утилиту ProcessExplorer с правами системы (SYSTEM), выполните команду:
PSExec -s -i ProcExp.exe - В списке процессов Process Explorer найдите процесс зависшей службы и откройте ее свойства;
- Перейдите на вкладку Services, найдите свою службу и нажмите кнопку Permissions;
- В разрешения службы предоставьте права Full Control для группы администраторов (Administrators). Сохраните изменения;
- Теперь попробуйте завершить процесс службы.
Обратите внимание, что права на службу и ее процесс выдались временно, до ее перезапуска. Для предоставления постоянных прав на службы познакомьтесь со статьей Права на службы в Windows.
Таймаут, в течении которого Service Control Manager ждет ожидания запуска или остановки службы можно изменить через параметр реестра ServicesPipeTimeout. Если служба не запускается в течении указанного таймаута, Windows записывает ошибку в Event Log (Event ID: 7000, 7009, 7011, A timeout was reached 30000 milliseconds). Вы можете увеличить этот таймаут, например до 60 секунд:
reg add HKLM\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control /v ServicesPipeTimeout /t REG_SZ /d 600000 /f
Это бывает полезным при запуске/остановки тяжелых служб, которые не успевают завершить все процессы быстро (например, MS SQL Server).