Windows Fundamentals 3 is the third room in the ‘Windows Fundamentals’ series on TryHackMe.
It introduces a number of security-related tools including Windows Update, Microsoft Defender antivirus, firewall and SmartScreen, Trusted Platform Module (TPM), BitLocker, and Volume Shadow Copy Service (VSS).
About This Walkthrough:
In my walkthroughs I try to provide a unique perspective into the topics covered by the room. Sometimes I will also review a topic that isn’t covered in the TryHackMe room because I feel it may be a useful supplement.
I try to prevent spoilers by making finding the solutions a manual action, similar to how you might watch a video of a walkthrough; they can be found in the walkthrough but require an intentional action to obtain. Always try to work as hard as you can through every problem and only use the solutions as a last resort.
This room can be found at: https://tryhackme.com/room/windowsfundamentals3xzx
Walkthrough
Task 1 – Introduction
This room is the third part in the Windows Fundamentals series.
Use the green ‘Start Machine’ button to launch the Windows VM for this room.
Question 1
Read above and start the virtual machine.
Answer:
No answer needed
Task 2 – Windows Updates
Have you ever been in the middle of something important when Windows barged in, forcing you to update? Updates might occasionally be inconvenient but they’re also super important.
Microsoft provides Windows updates on the 2nd Tuesday of the month, called ‘Patch Tuesday‘. But if an update is urgent, they might not wait for the next Patch Tuesday before rolling it out.
There is also a utility called Windows Update, which has options for scheduling updates and viewing update history among others.
If you push off updates for long enough, Windows may force you to restart your computer.
Question 1
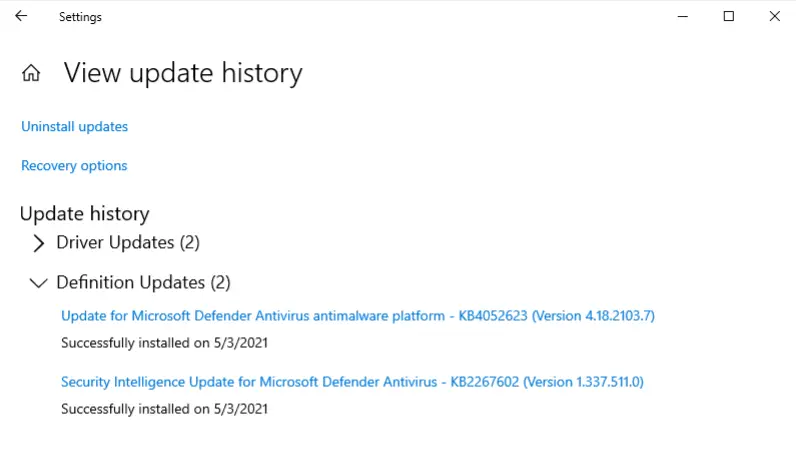
There were two definition updates installed in the attached VM. On what date were these updates installed?
Walkthrough:
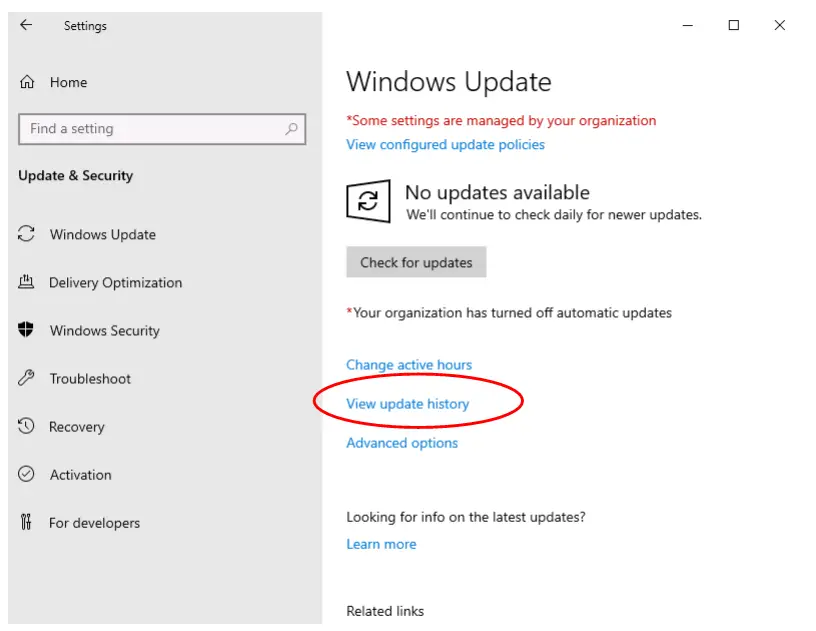
Access Windows Updates on the VM using Settings or the Start Menu search box.
Click on ‘View update history’:
Under the ‘Definition Updates’ category, you should see two updates that were successfully started on the same day.
Answer:
(Highlight below to see the answer):
5/3/2021
Task 3 – Windows Security
Windows includes a utility for managing security, aptly named Windows Security.
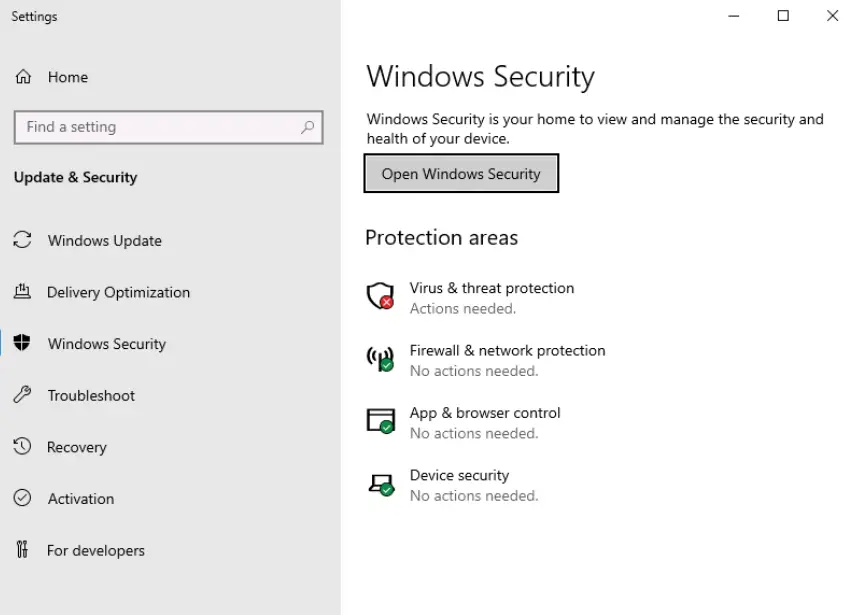
This utility gives you a dashboard where you can quickly review any outstanding issues and assess how critical they are using the green, yellow, and red color coding.
There are links allowing you to access many different security features including virus and threat protection and the Defender firewall.
Question 1
In the above image, which area needs immediate attention?
Walkthrough:
The need for attention is signaled via color-coding.
Answer:
Virus & threat protection
Task 4 – Virus & Threat Protection
Windows has a built-in Virus scanner called Microsoft Defender. Microsoft Defender can be managed via the virus and threat protection utility.
The current threats area allows you to see the results of the latest scan, if there are any current threats that need to be resolved, and options for scanning.
Scanning options include quick, full, custom, and offline. Quick scan is a great starting point, as it will generally tell you if a full scan is needed. The offline scan can also be useful if you’re concerned about infection with a virus or malware.
There are lots of settings, which are located under ‘Manage Settings’. Real-time protection prevents viruses or malware from executing. It only works when it’s turned on. Cloud-delivered protection allows Microsoft to query a database in the cloud to quickly assess any suspect code found on your system. This improves speed and robustness.
To learn more, I recommend reading Microsoft’s support page.
Question 1
Specifically, what is turned off that Windows is notifying you to turn on?
Walkthrough:
In the last task, we saw on the Windows Security dashboard that action is needed in the category of Virus & Threat Protection.
You can find more details on the dashboard in Virus & Threat Protection:
Answer:
Real-time protection
Task 5 – Firewall & Network Protection
Windows has a built-in firewall to help protect networks and devices. The firewall operates using three network profiles: domain, private network, and public network.
The firewall is very simple to use: options including turning each profile firewall on or off, blocking all incoming connections, and using custom rules to allow specific connections.
Question 1
If you were connected to airport Wi-Fi, what most likely will be the active firewall profile?
Walkthrough:
This question is used to demonstrate the reason for having different firewall profiles.
Of the three options (domain, private, public), which one best describes airport Wi-Fi?
Answer:
(Highlight below to see the answer):
Public network
Task 6 – App & Browser Control
The App & Browser Control utility helps to supplement the Virus scanner in protecting against malware. The two main categories are check apps and files (or reputation-based protection), and exploit protection.
The ‘check apps and files’ feature uses Microsoft Defender SmartScreen to check unrecognized apps and files. It produces a warning anytime you may be downloading or running potential malware.
Exploit protection prevents a number of attacks, providing an extra defense against specific exploits.
Question 1
Read the above.
Answer:
No answer needed
Task 7 – Device Security
Device Security is used to manage security options to protect the device against malicious software. There are only a few options available in Device Security, and these are rarely touched.
Core isolation is used to isolate processes from the OS. The main option for core isolation is memory integrity. This allows Windows to use Hyper-V hardware virtualization to essentially create a virtual machine (VM) that remains isolated in computer memory, protecting it against attacks.
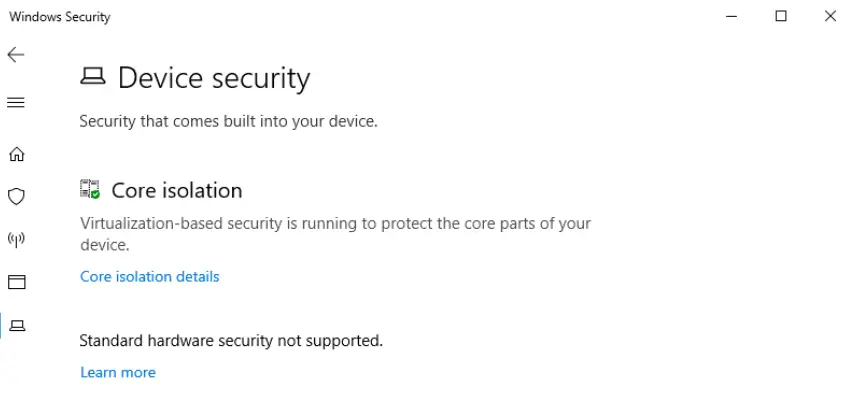
Some computers have a chip called a security processor, or, more specifically, a Trusted Platform Module (TPM).
A TPM is a computer chip used to perform cryptographic operations. Systems with a TPM will also see details about their security processor in the Device Security tool.
Question 1
What is the TPM?
Answer:
Trusted Platform Module
Task 8 – BitLocker
BitLocker is used to prevent data exposure on lost or stolen computers. It is best used with a TPM (security processor).
You can use BitLocker on a system without a TPM, but this requires inserting a USB key on startup or when resuming from hibernation.
Question 1
What must a user insert on computers that DO NOT have a TPM version 1.2 or later?
Answer:
USB startup key
Task 9 – Volume Shadow Copy Service
In order to ensure a successful backup and/or restore operations, coordination has to take place between different entities: the application performing the backup, the applications being backed up, and the storage processes.
Microsoft created the Volume Shadow Copy Service (VSS) to handle this coordination. VSS was introduced with Windows Server 2003, and can backup application data without taking the application offline.
Malware writers are often aware of VSS and have ways of getting around it. For this reason, it’s important to have offline backups available.
Question 1
What is VSS?
Answer:
Volume Shadow Copy Service
Task 10 – Conclusion
This room tackled a number of security tools that come packaged with the Windows OS.
Question 1
Read the above.
Answer:
No answer needed
Conclusion
The is the third of the Windows Fundamentals series, and does a good job of introducing Windows security options at a very high level. Personally this is not my favorite THM room, as it has no real interactivity and introduces the topics at about the same level as you would get by simply navigating to the tools and reading the options. But it does a good job of providing an overview.
Overall, I thought this room was a useful addition. A huge thanks to heavenraiza for putting this room together!
Provide feedback
Saved searches
Use saved searches to filter your results more quickly
Sign up
Appearance settings
In this walk through, we will be going through the Windows Fundamentals 3 from Tryhackme. In this room we will explore about the built-in Microsoft tools that help keep us to keep the device secure, such as Windows Updates, Windows Security, BitLocker, and much more. So, let’s get started without any delay.
Table of Contents
Task 1 – Introduction
Question 1 – Read the above and start the virtual machine.
DoneTask 2 – Windows Updates
Question 1 – There were two definition updates installed in the attached VM. On what date were these updates installed?
5/3/2021Task 3 – Windows Security
Question 1 – In the above image, which area needs immediate attention?
Virus & threat protectionTask 4 – Virus & threat protection
Question 1 – Specifically, what is turned off that Windows is notifying you to turn on?
Real-time protectionTask 5 – Firewall & network protection
Question 1 – If you were connected to airport Wi-Fi, what most likely will be the active firewall profile?
Public NetworkTask 6 – App & browser control
Question 1 – Read the above.
DoneTask 7 – Device security
Question 1 – What is the TPM?
Trusted Platform ModuleTask 8 – BitLocker
Question 1 – What must a user insert on computers that DO NOT have a TPM version 1.2 or later?
Link: https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/windows/security/information-protection/bitlocker/bitlocker-overview
USB startup keyTask 9 – Volume Shadow Copy Service
Question 1 – What is VSS?
Volume Shadow Copy ServiceTask 10 – Conclusion
Also Read: Tryhackme – Windows Fundamentals 1
So that was “Windows Fundamentals 3” for you. We have learned about Windows Updates, Windows Security and Virus & Threat Protection. Further, we looked into Firewall and network protection, App & Browser control and Device Security. At last, took a dive into Bitlocker and Volume shadow copy service. This was the final part of a three parts series on Tryhackme and we have completed all of them. On that note, i will take your leave and will see you in next one, Till then “Hack the Planet”.
概要
TryHackMe「Windows Fundamentals 3」のWalkthroughです。
Task2
Q1.There were two definition updates installed in the attached VM. On what date were these updates installed?
Settings->Windows UpdateからWindowsアップデート画面を開きます。

View update history->Definition Updatesを確認します。

A.5/3/2021
Task3
Q1.Checking the Security section on your VM, which area needs immediate attention?
Settings->Windows Securityを確認します。

A.Virus & threat protection
Task4
Q1.Specifically, what is turned off that Windows is notifying you to turn on?
Windows Security->Virus & threat protection settings->Manage settingsへ進みます。

Real-time protectionのアラートが付いていると分かります。

A.Real-time protection
Task5
Q1.If you were connected to airport Wi-Fi, what most likely will be the active firewall profile?
Hint.xyz network
空港のWi-FiはPublic networkに分類されます。

A.Public network
Task7
Q1.What is the TPM?
A.Trusted Platform Module
Task8
Q1.We should use a removable drive on systems without a TPM version 1.2 or later. What does this removable drive contain?
Hint.Refer to the Microsoft documentation on BitLocker.
BitLockerの公式ドキュメントから確認できます。

A.startup key
Task9
Q1.What is VSS?
A.Volume Shadow Copy Service
Windows is in Notification Mode: How to Turn it Off
Windows operating systems have integrated various notification features to make the user experience more interactive and intuitive. While these notifications can be helpful, they can also become overwhelming or intrusive. One feature that signifies this often-encountered annoyance is when Windows is in «Notification Mode.»
This article delves into what Notification Mode is, why you might want to turn it off, and provides step-by-step instructions on how to do so. In addition, we will explore alternative solutions for managing notifications to create a customized user experience that fits your needs.
Understanding Notification Mode
What Is Notification Mode?
Notification Mode in Windows is part of the Action Center feature, which allows the operating system to relay important information via notifications. These notifications can include updates from the system, alerts from applications, reminders, and messages from social media platforms. Though the intent is to keep users informed, many find the constant interruptions distracting.
When your system is in Notification Mode, it often means your notifications are temporarily silenced or displayed in a way that reduces their impact on your workflow. This can manifest as visual cues on your screen, sound alerts, or both.
Why Does Windows Enter Notification Mode?
There are several reasons why Windows might enter a state of heightened notification alert:
-
DND Mode: When you enable «Do Not Disturb» (DND) mode, it silences all notifications for a set period or until you turn it off. This is particularly useful during presentations or when you need uninterrupted focus time.
-
Focus Assist: This feature helps you manage notifications during certain times, such as when you’re gaming, working, or presenting. It aims to minimize distractions by filtering which notifications show up based on your activity.
-
System or Application Updates: Occasionally, during system updates or when an application is actively trying to communicate with you, Windows can be set to display notifications prominently.
The Downsides of Notification Mode
While notifications aim to be helpful, they can often become a hindrance. Here are some common complaints from users regarding notifications:
-
Distraction: Constant notifications can interrupt your workflow, making it difficult to concentrate on tasks.
-
Information Overload: An excess of notifications can lead to missed important alerts, as users may start to ignore all notifications.
-
Privacy Concerns: Notifications may display information that you don’t want to be publicly visible when you have guests around or are on a shared computer.
-
Battery Drain: On laptops and tablets, excessive notifications can lead to unnecessary background processes, consuming battery life.
Understanding these downsides often leads users to explore options to turn off or manage their notifications more effectively.
Turning Off Windows Notification Mode
If you decide that you want to turn off Notification Mode or manage notifications in a way that best suits your needs, follow these steps:
Step 1: Open Settings
- Click the Start menu in the bottom left corner of your screen.
- Select the Settings icon (it looks like a gear).
Step 2: Navigate to System Options
- In the Settings menu, choose System.
- Select Notifications & actions from the left sidebar.
Step 3: Managing Notifications
Here, you’ll find several options to manage notifications:
-
Turn Off Notifications: If you prefer to disable all notifications, toggle off the switch under Get notifications from apps and other senders. This will silence all notifications.
-
Customizing Notification Settings: If you want to keep some notifications but silence others, scroll down to the Get notifications from these senders section. Here you can turn off notifications for specific applications by toggling them off.
-
Focus Assist: If you wish to engage Focus Assist to minimize interruptions actively, use the Focus Assist feature. You can set it to automatically turn on during certain hours or when duplicating displays.
-
Priority Notifications: You may also wish to configure priority notifications by choosing which apps have the ability to bypass Focus Assist. Click the Focus Assist dropdown to customize your priorities.
Step 4: Advanced Notification Settings
For users who seek finer control over how notifications behave, explore the advanced settings:
-
Show notifications on the lock screen: This option can be toggled if privacy is a concern.
-
Show reminders: You can opt to display reminders, which can be helpful in some contexts but bothersome in others.
-
Allow notifications to play a sound: Disabling this feature can help silence alerts, turning notification prompts into silent visual cues.
Alternative Methods to Disable Notifications
In addition to managing notifications system-wide through Windows settings, there are several application-specific methods to stop notifications or minimize their impact.
Disable Notifications from Specific Applications
-
From within the Application: Many applications have built-in notification settings. For example, social media platforms such as Facebook, Twitter, or messaging apps like Slack often have notifications settings you can customize.
-
Browser Notifications: If your browser sends notifications, you can disable them by following these steps:
- Open your browser (e.g., Chrome, Firefox).
- Go to Settings > Privacy and security > Site Settings.
- Select Notifications and adjust as necessary.
Use Third-Party Tools
If you find Windows’ built-in settings inadequate, consider third-party applications that specialize in managing notifications. For example, apps like FocusWriter or StayFocusd help create a distraction-free environment, minimizing the potential for interruptions from other apps or notifications.
The Benefits of Managing Your Notifications
Choosing to turn off or manage notifications effectively can lead to a much more streamlined experience using your Windows operating system. Here are some benefits of having a tailored notification system:
-
Increased Productivity: With fewer notifications, you can focus more on tasks at hand, improving your overall productivity.
-
Reduced Stress: Keeping notifications to a minimum can contribute to lower stress levels, especially for users who are sensitive to constant alerts and disturbances.
-
Enhanced Privacy: You’ll gain control over what information is displayed on your screen or lock screen, keeping sensitive data private.
-
Better Battery Life: For portable devices, managing background notifications can save battery life and extend usability between charges.
Conclusion
While notifications are intended to enhance user interaction and ensure crucial information is conveyed, they can often overshadow productivity and privacy. Understanding how to turn off or finely tune Notification Mode on Windows can help create a more conducive working environment that caters to your needs.
Whether you opt to disable notifications entirely or engage with them selectively, you are empowered to create a user experience that fosters focus and efficiency. Follow the outlined steps, explore your options, and make the most of your time spent using Windows. In a world bursting with distractions, taking charge of how you receive information may be one of the most significant productivity hacks you can adopt.
