Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) is a UDP protocol that uses port 161 to monitor and collect detailed information on any network device supporting the SNMP protocol. All Windows servers support SNMP and we’ll show you how to easily install and configure SNMP on your Windows 2016 or 2012 server, including Read Only (RO) or Read Write (RW) SNMP community string.
In our example we will enable the SNMP agent and configure a SNMP community string to allow our Network Monitoring System (NMS) monitor our server resources.
Execution Time: 10 minutes
Step 1 – Install SNMP on Windows Server 2016
Open the Control Panel on your Windows Server and Double-click on the Program and Features icon:
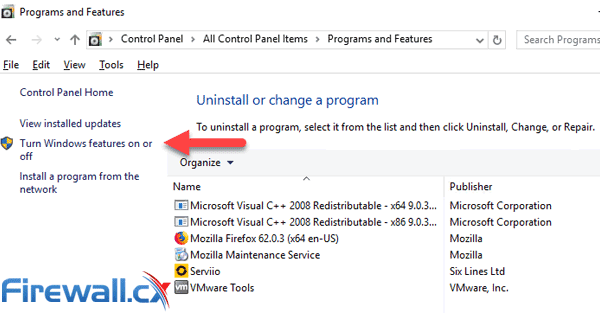
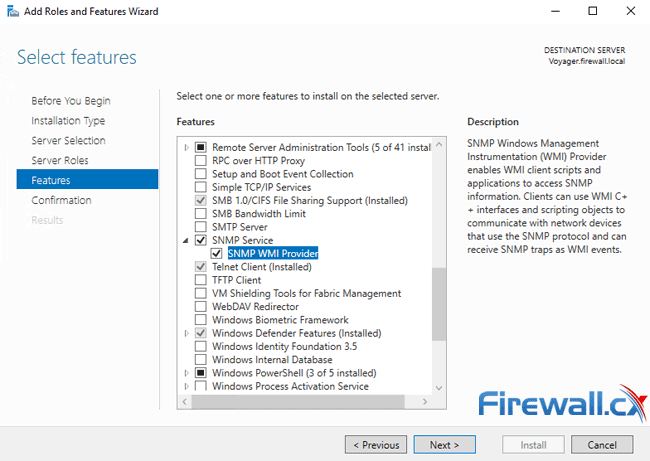
This will open the Add Roles and Features Wizard. Keep clicking on the Next button until you reach the Features section. From there, select the SNMP Service option:
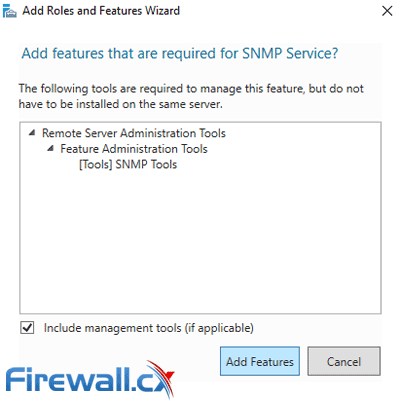
When prompted, click on the Add Features button to include the installation of the Administration SNMP Tools:
Optionally you can include the SNMP WMI Provider option located under the SNMP Service. When ready click on the Next button.
This is the final screen – simply click on the Install button. Ensure the “Restart the destination server automatically if required” option is not selected:
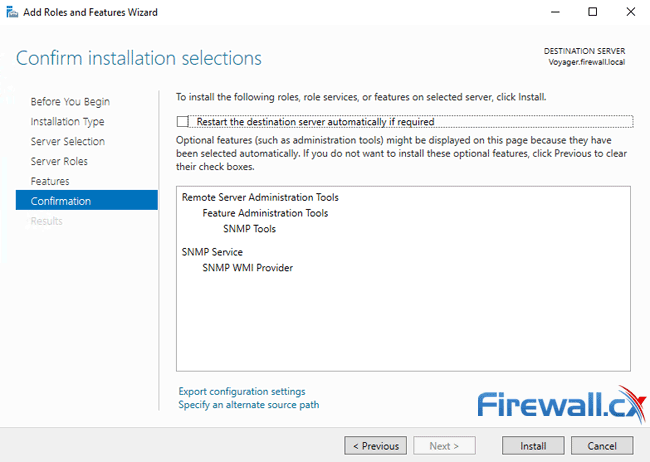
The SNMP Service will now be installed on your Windows 2016 Server. This process will require around 3 minutes to complete. When done, click on the Close button to exit the installation wizard:
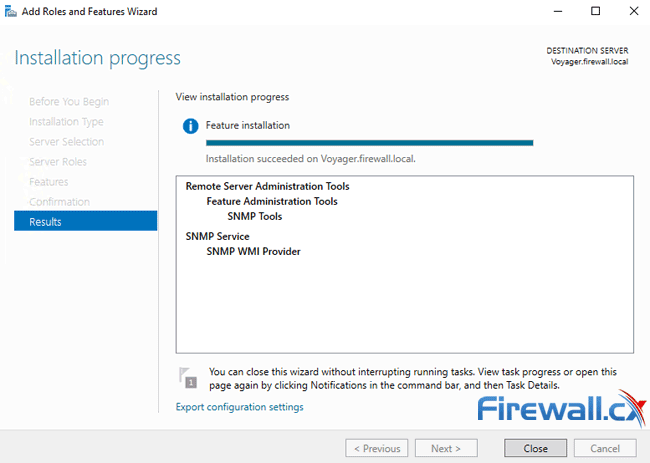
Step 2 – Configure SNMP Service & Read-Only or Read-Write Community String
Configuring the Windows 2016 Server SNMP Service is a simple task. As an administrator, run services.msc or open the Services console from the Administrative Tools. Double-click the SNMP Service and go to the Security tab:
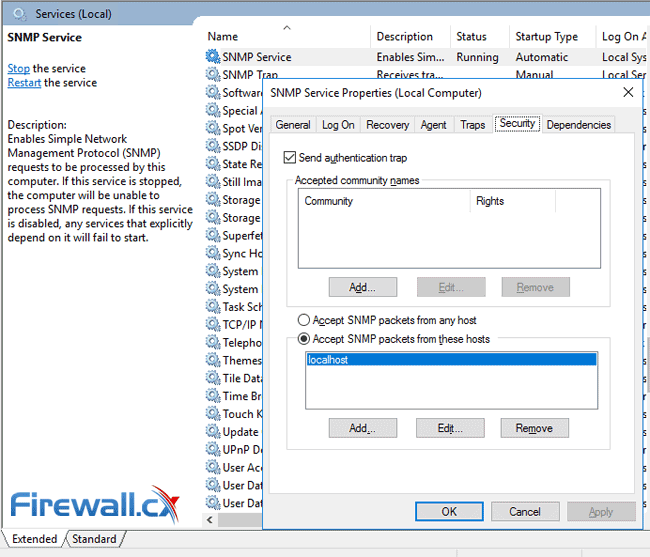
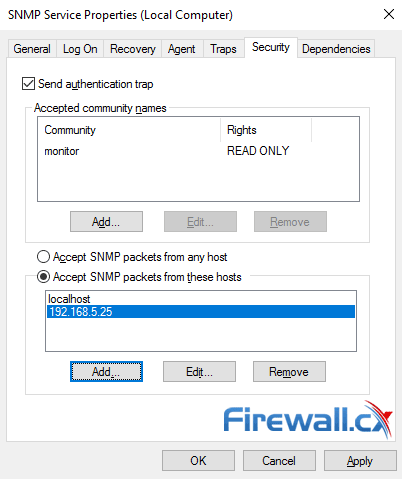
To add a Read-Only community string, click on the Add button under the Accepted community names. Enter the desirable Community Name and set the Community rights to READ ONLY. When done, click on the Add button:
Next, in the lower section of the window, click on the Add button and insert the IP address which will be allowed to poll this server via SNMP. This would be the IP address of your Network Monitoring Service. In our environment our NMS is 192.168.5.25. When done, click on Apply then the OK button:
To confirm SNMP is working correctly, we configured our NMS to query and retrieve information from our server every 5 minutes. After a while we were able to see useful information populating our NMS:
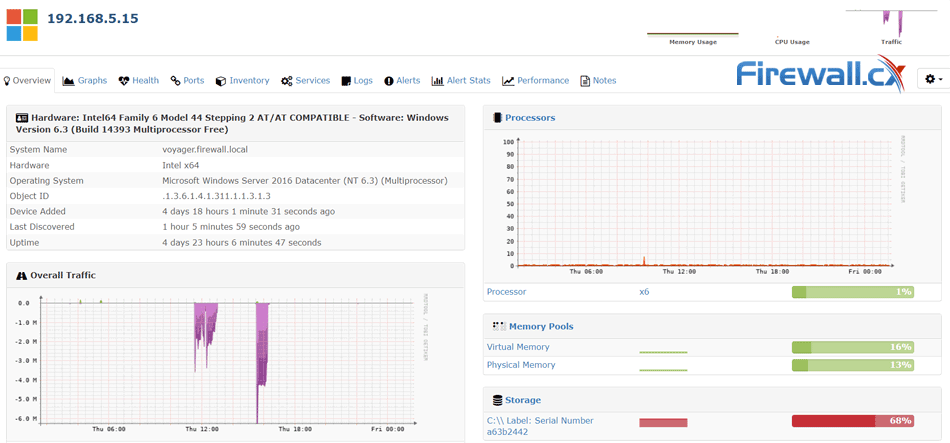
Depending on your Network Monitoring System you’ll be able to obtain detailed information on your server’s status and state of its resources:
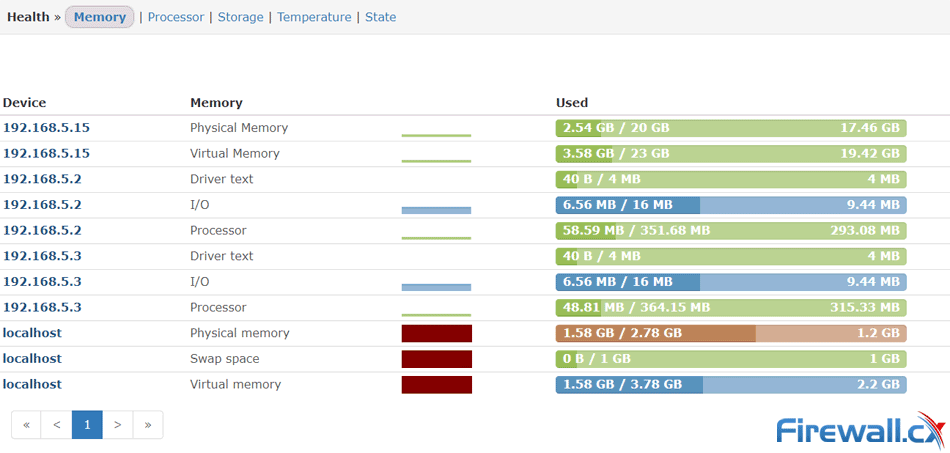
Summary
This article briefly explained the purpose of SNMP and how it can be used to monitor network devices and collect useful information such as CPU, RAM and Disk usage, processes running, host uptime and much more. We also showed how to install and configure the SNMP Service for Windows Server 2016. For more technical Windows articles, please visit our Windows Server section.
When we use a monitoring tool in an enterprise environment, monitoring data of Windows and Windows Server machines is usually done through WMI (Windows Management Instrumentation). However, there may be cases that you may need to use the Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP).
SNMP is already installed in versions prior to Windows 8 and Windows Server 2012. However, in Windows 8, Windows 10, Windows Server 2012, and Windows Server 2016 will need to install it. Note: SNMP Service is deprecated since the Windows Server 2012 R2 version.
Of course, if you are going to install SNMP on multiple endpoints (computers, servers, VMs, etc.), then it would be preferable to do so remotely using PowerShell and/or Group Policy.
Check if SNMP is installed
Before we get started, it’s a good idea to first check if the SNMP service is already installed and running on Windows 10 or Windows Server 2016. This can be done very easily through PowerShell by typing the following command.
If the corresponding service does not appear, then it is not installed. Similarly, on Windows Server, you can type the following command.
Get-WindowsFeature SNMP-Service
Alternatively, you can open the Services or Task Manager window and search for the SNMP Service. If it does not exist then it is not installed.
Install SNMP in Windows 10 and Windows Server 2016
In Windows 10, installing SNMP Service is done through the Add Windows Features window. As shown in the figure below, check Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) and press OK.
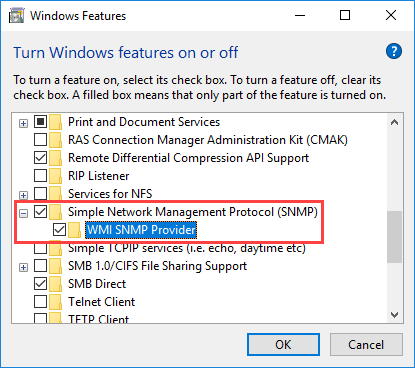
In Windows Server 2016, SNMP is installed through Server Manager. Start the Add Roles and Features wizard, click on Next until you reach the Features section where you will need to check the SNMP Service option. Continue on completing the wizard by pressing Next and Finish.

Installing SNMP is easier with a PowerShell one-liner on Windows Server 2016.
Install-WindowsFeature SNMP-Service -IncludeManagementTools
Configure SNMP on Windows 10 and Windows Server 2016
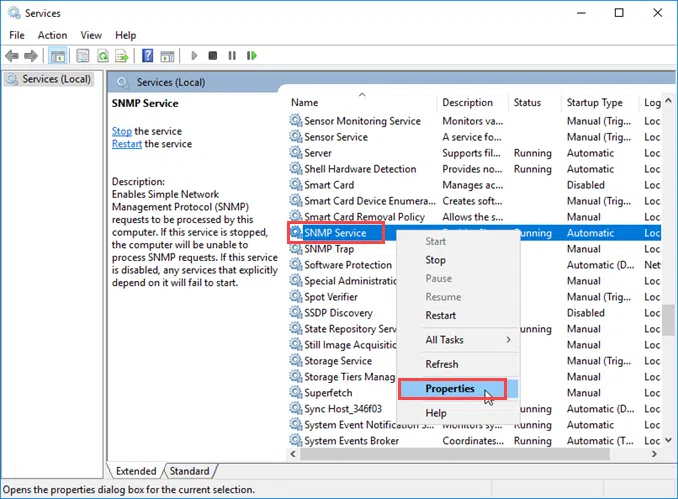
In both Windows 10 and Windows Server 2016, the SNMP setting is configured through the service properties window. So, open the services.msc window, find the SNMP Service, and open Properties.
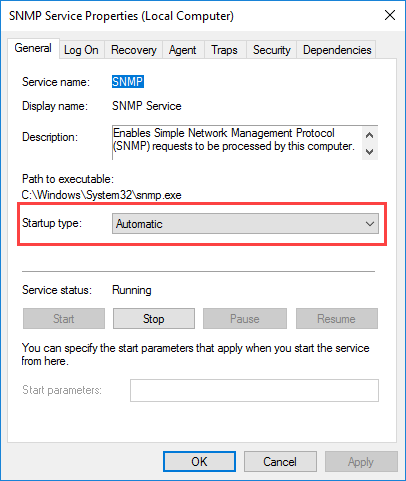
Here, on the General tab, be sure to select Automatic in the Startup Type section so that it is always available even after a restart of the computer or server.
On the Agent tab, be sure to select all the services required by the monitoring tool to collect the data.
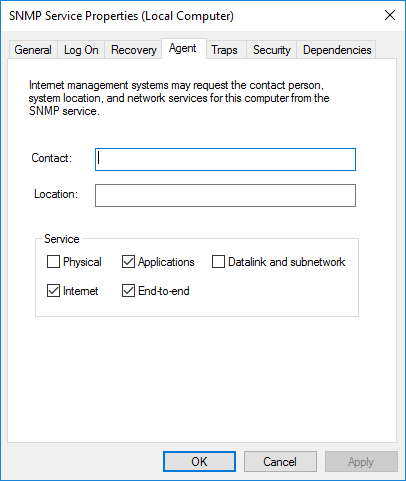
On the Security tab, click the Add button to add the community string, read-only, and the hosts from where SNMP packages will be accepted.
That’s it. Now, the installation and configuration of the SNMP service in Windows 10 and Windows Server 2016 are complete.
SNMP (
Simple Network Management Protocol
) — это классический протокол для мониторинга и сбора информации о сетевых устройствах (сервера, сетевое оборудование, рабочие станции, принтеры и т.д.). Протокол SNMP довольно легкий, быстрый, для передачи данных использует UDP порты 161 и 162. В этой статье мы рассмотрим, как установить и настроить службу SNMP в Windows Server 2022/2019 и Windows 10/11.
Содержание:
- Установка службы SNMP в Windows Server 2022/2019
- Установка SNMP агента в Windows Server Core
- Установка службы SNMP в Windows 10/11
- Настройка службы SNMP в Windows Server и Windows 10/11
Установка службы SNMP в Windows Server 2022/2019
В Windows Server службу SNMP можно установить с помощью Server Manager.
Выберите Add roles and features -> Features. Выберите SNMP Service (если нужно отметьте также SNMP WMI Providers).
Служба SNMP WMI Provider позволяет опрашивать SNMP устройство через WMI.
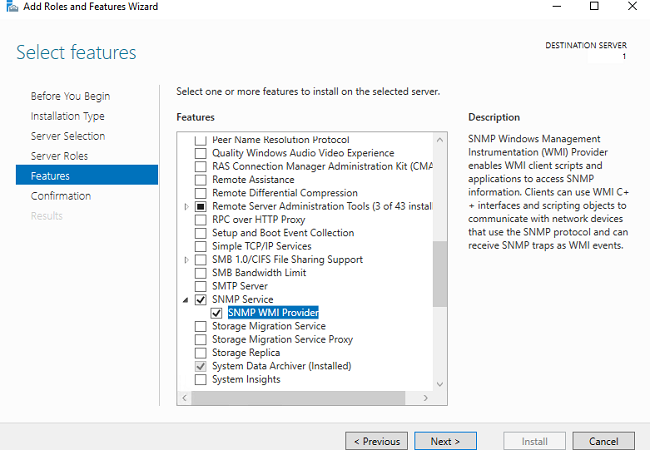
Нажмите Next -> Install и дождитесь окончания установки.
Установка SNMP агента в Windows Server Core
В Windows Server Core можно установить SNMP с помощью веб-интерфеса Windows Admin Center и PowerShell.
Если вы используете Windows Admin Center, подключитесь к хосту Windows Server, выберите Roles and Features -> SNMP Service.
Т.к. в Windows Server Core отсутствует графический интерфейс, а для его управления используется командная строка, вы можете установить службу SNMP из командной строки PowerShell.
Для установки ролей в Windows Server из PowerShell используется командлет Install-WindowsFeature.
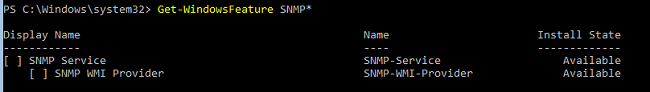
Проверьте, что служба SNMP не установлена:
Get-WindowsFeature SNMP*
Установите роль SNMP и WMI провайдер:
Install-WindowsFeature SNMP-Service,SNMP-WMI-Provider -IncludeManagementTools
Проверьте, что службы SNMP запущены:
Get-Service SNMP*
В нашем примере SNMP служба запущена, а SNMPTRAP остановлена.
Установка службы SNMP в Windows 10/11
Вы можете использовать службу SNMP не только в Windows Server, но и в десктопных редакциях Windows 10 и 11.
В Windows 10/11 служба SNMP, вынесена в отдельный компонент Feature On Demand (как RSAT и OpenSSH).
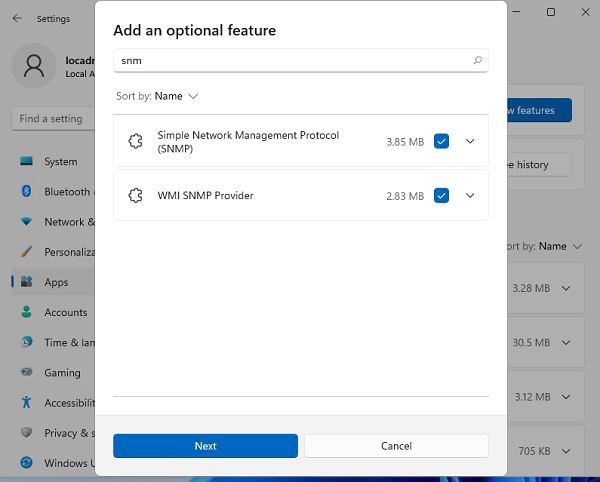
Вы можете установить SNMP через панель Settings. Перейдите в Apps -> Optional features -> Add an optional feature -> View features.
В списке доступных компонентов выберите Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) и WMI SNMP Provider. Для начала установки нажмите Next (понадобится интернет подключение к серверам Microsoft).
Для установки службы SNMP через PowerShell, используйте команду:
Add-WindowsCapability -Online -Name SNMP.Client~~~~0.0.1.0
Для установки службы SNMP без подключения к интернету, вам понадобится скачать ISO образ Windows 10/11 Features on Demand из личного кабинета на сайте лицензирования Volume Licensing Service Center (VLSC).
Для офлайн установки службы SNMP с такого ISO образа используется команда:
Add-WindowsCapability -Online -Name SNMP.Client~~~~0.0.1.0 -LimitAccess -Source \\msk-fs01\Distr\Windows-FOD\Win11\
Настройка службы SNMP в Windows Server и Windows 10/11
Вы можете настроить параметры службы SNMP в консоли services.msc. Найдите службу SNMP Services в списке и откройте ее свойства.
Обратите внимание, что у службы SNMP есть несколько дополнительных вкладок:
- Agent
- Traps
- Security
На вкладке Agent указывается базовая информация об устройстве (контакты администратора, местоположение). Здесь же можно указать тип информации, который может отправлять данное устройство при SNMP опросе.
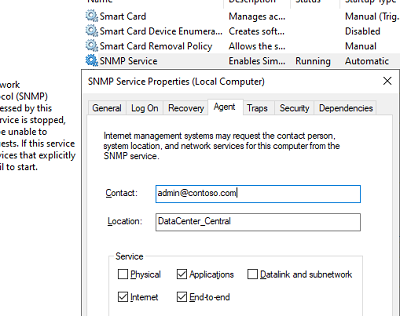
В старых версиях протокола SNMP (SNMP v.1 и SNMP v.2) для авторизации пользователя используется строка сообщества (community string). На вкладке Security можно создать несколько строк подключения.
Можно выбрать один из пяти уровней доступа для сообщества:
- READ ONLY — позволяет получать данные с устройства;
- READ WRITE — позволяет получать данные и изменять конфигурацию устройства;
- NOTIFY — позволяет получать SNMP ловушки;
- READ CREATE – позволяет читать данные, изменять и создавать объекты;
- NONE
Вы можете создать несколько community string. Для этого нужно задать имя и выбрать права/ Для мониторинга состояние сервера достаточно выбрать READ ONLY.
В списке Accept SNMP packets from these hosts можно указать имена/IP адреса серверов, которым разрешено опрашивать данное устройство. Если вы не хотите ограничивать список разрешенных устройств, оставьте здесь Accept SNMP packets from any hosts.
На вкладке Traps указываются адрес серверов, на который SNMP агент должен отправлять SNMP-ловушка (SNMP trap). SNMP Trap это широковещательный USP пакет, используемый для асинхронного уведомления менеджера (например, сообщение о критическом событии).
Не забудьте открыть в Windows Defender Firewall правила, разрешающие входящий и исходящий трафик для SNMP запросов и ловушек (TRAP). Нужные правила фаейрвола можно включить с помощью PowerShell.
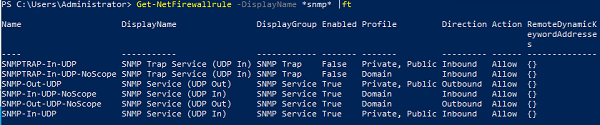
В Windows Firewall есть несколько готовых правил для SNMP трафика:
Get-NetFirewallrule -DisplayName *snmp* |ft
- SNMPTRAP-In-UDP
- SNMPTRAP-In-UDP-NoScope
- SNMP-Out-UDP
- SNMP-In-UDP-NoScope
- SNMP-Out-UDP-NoScope
- SNMP-In-UDP
Можно включить все правила, или только определенное:
Get-NetFirewallrule -DisplayName *snmp* | Enable-NetFirewallRule
Get-NetFirewallrule SNMP-Out-UDP | Disable-NetFirewallRule
В списке служб Windows есть еще одна служба SNMP Trap. Она используется для получения сообщений от других SNMP агентов и пересылки на SNMP сервера (обычно это система мониторинга, опрашивающая устройства по SNMP, например PRTG или Zabbix).
Если вы настраиваете SNMP на Windows Server Core, вы не сможете использовать графический интерфейс службы SNMP для настройки ее параметров. Вместо этого придется вносить изменения в реестр с помощью PowerShell. Настройки службы SNMP хранятся в ветке реестра HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\SNMP\Parameters.
Следующие команды зададут описание агента:
New-ItemProperty -Path "HKLM:\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\services\SNMP\Parameters\RFC1156Agent" -Name "sysContact" -Value "[email protected]" -PropertyType REG_SZ
New-ItemProperty -Path "HKLM:\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\services\SNMP\Parameters\RFC1156Agent" -Name "sysLocation" -Value "MSK_Datacenter1" -PropertyType REG_SZ
Для каждой ловушки SNMP придется создать отдельный ключ в HKLM\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\services\SNMP\Parameters\TrapConfiguration с именем community.
New-Item -Path "HKLM:\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\services\SNMP\Parameters\TrapConfiguration\public1"
Укажите разрешения для community:
New-ItemProperty -Path "HKLM:\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\SNMP\Parameters\ValidCommunities" -Name "public1" -Value 4 -PropertyType DWord
Возможные значения:
- 1 — NONE
- 2 — NOTIFY
- 4 — READ ONLY
- 8 — READ WRITE
- 16 — READ CREATE
Для каждого community можно указать список серверов, с которых разрешено принимать запросы:
New-ItemProperty -Path "HKLM:\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\SNMP\Parameters\PermittedManagers" -Name "1" -Value "server1.winitpro.ru" -PropertyType REG_SZ
Перезапустите службу SNMP для применения новых настроек из реестра:
Get-Service SNMP|Restart Service
Если нужно распространить эти SNMP настройки на множество компьютеров/серверов Windows в домене, используйте возможности внесения изменений в реестр через GPO.
Проверить работу службы SNMP можно с помощью утилиты snmpwalk (доступна в любом Linux дистрибутиве):
# snmpwalk -v 2c -c public1 -O e 192.168.13.122
В этом примере мы опросили наш Windows хост через версию протокола SNMPv2.
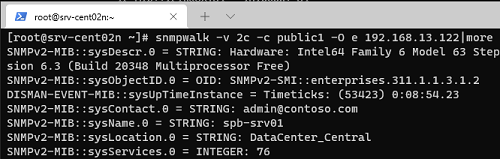
Утилита вернула базовыую информацию о хосте (syscontact, sysname, syslocation) и довольно большое количество информации о состоянии сервера Windows.
If you run Windows Server as Core Installation, like Windows Server 2016 Core or any Microsoft Hyper-V Server edition and you want to use SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol) on that system, you first have to install the SNMP feature on that Core Server. After that you can use the MMC to remotely connect to the services list on the Core Server.
Install SNMP on Windows Server Core
First lets see if the SNMP feature is installed, using PowerShell:
Get-WindowsFeature *SNMP*
By default the SNMP feature is not installed. To install the SNMP feature on Windows Server Core, you can run the following command:
Install-WindowsFeature SNMP-Service -IncludeAllSubFeature -Verbose
Configure SNMP on Windows Server Core
After you have installed the SNMP feature, you and you have enabled Remote Management you can mange and configure smtp via remote MMC.
Simply open up MMC click on File and then on Add/Remove Snap-in. Now you can select the Services snap-in and enter the name or IP address of the Windows Server Core you want to configure the SNMP services.
Important: If you need to configure the SNMP Service on a remote machine using the MMC, you have to install the RSAT-SNMP feature on the local administrative computer. Otherwise, you will not see the SNMP specific tabs. In older versions of Windows and Windows Server, you needed to install the SNMP feature instead of the RSAT-SNMP feature.
Install-WindowsFeature RSAT-SNMP -verbose
I hope this blog post was helpful. And it helps you to install and configure the SNMP feature on Windows Server. Especially you should have a look at the remote management part for the SNMP service. It works with all the latest Windows Server versions like 2008 R2, 2012, 2016 and event Windows Server 2019. If you have any question, feel free to comment on this post.
Tags: Core Server, Hyper-V, Install SNMP, Microsoft, mmc, Monitoring, PowerShell, Remote SNMP, RSAT SNMP, snmp, SNMP Feature, SNMP Trap, Windows Server, Windows Server 2012 R2, Windows Server 2016, Windows Server 2019, Windows Server Core Last modified: March 10, 2021
About the Author / Thomas Maurer
Thomas works as a Principal Program Manager & Chief Evangelist Azure Hybrid at Microsoft (Cloud + AI). He engages with the community and customers around the world to share his knowledge and collect feedback to improve the Azure hybrid cloud and edge platform. Prior to joining the Azure engineering team (Cloud + AI), Thomas was a Lead Architect and Microsoft MVP, to help architect, implement and promote Microsoft cloud technology.
If you want to know more about Thomas, check out his blog: www.thomasmaurer.ch and Twitter: www.twitter.com/thomasmaurer
What is SNMP?
SNMP also known as “Simple Network Management Protocol” is an application-layer protocol used to measure and monitor the performance of the devices within a network. It helps the system administrator to ensure that networks stay up and running. Today, SNMP is one of the most popular networking protocols in the world. All modern manufacturers create SNMP-enabled devices that enterprises can use to obtain performance data from the devices.
How SNMP Works?
SNMP uses the device’s Management Information Database (MIB) to collect the performance data. The MIB is a database that records information about the hardware and contains MIB files. The MIB resides within the SNMP manager designed to collect information and organize it into a hierarchical format. SNMP uses this information from the MIB to interpret messages before sending them onwards to the end-user.
There are different types of queries managers used to poll the information from the SNMP agent including, GET or GET-NEXT commands. The GET command uses the agent’s hostname and Object Identifiers (OID) to obtain the information from the MIB. The GET-NEXT command obtains the data from the next OID.
What is SNMPWALK?
SNMPWALK is a command-line utility used to collect the information from remote SNMP-enabled devices including, routers and switches. It allows you to see all the OID variables available on remote devices. It sends multiple GET-NEXT commands to OIDs then the manager collects the data from all OIDs. SNMPWALK is a command-line utility that can be installed on Linux and Windows operating systems.
In this guide, we will show you how to install SNMPWALK on Windows and Linux. We will also explain how to use it to get the information from the remote devices.
Install SNMP and SNMPWALK on Linux
In this section, we will show you how to install SNMP and SNMPWALK on Debian and RPM-based Linux operating systems.
For RPM-based operating system including, RHEL/CentOS/Fedora, install the SNMP and SNMPWALK using the following command:
yum install net-snmp net-snmp-libs net-snmp-utils -y
For Debian based operating system including, Debian/Ubuntu, install the SNMP and SNMPWALK using the following command:
apt-get install snmpd snmp libsnmp-dev -y
Once the installation has been finished, start the SNMP service and enable it to start at system reboot with the following command:
systemctl start snmpd
systemctl enable snmpd
You can check the status of the SNMP with the following command:
systemctl status snmpd
You should get the following output:
● snmpd.service - Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) Daemon.
Loaded: loaded (/lib/systemd/system/snmpd.service; enabled; vendor preset: enabled)
Active: active (running) since Fri 2021-05-14 06:36:48 UTC; 3min 22s ago
Main PID: 36724 (snmpd)
Tasks: 1 (limit: 4691)
Memory: 8.7M
CGroup: /system.slice/snmpd.service
└─36724 /usr/sbin/snmpd -LOw -u Debian-snmp -g Debian-snmp -I -smux mteTrigger mteTriggerConf -f -p /run/snmpd.pid
May 14 06:36:48 ubuntu2004 systemd[1]: Starting Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) Daemon....
May 14 06:36:48 ubuntu2004 systemd[1]: Started Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) Daemon..By default, SNMP does not allow retrieving all available SNMP information. So you will need to edit the SNMP default configuration file and make some changes so we can retrieve all information using the SNMPWALK command.
nano /etc/snmp/snmpd.conf
Find the following lines:
rocommunity public default -V systemonly
rocommunity6 public default -V systemonly
And, replace them with the following lines:
rocommunity public default
rocommunity6 public default
Save and close the file then restart the SNMP service to apply the changes:
systemctl restart snmpd
Now, open your command-line interface and print help information of SNMPWALK command as shown below:
snmpwalk -h
You should get the following output:
USAGE: snmpwalk [OPTIONS] AGENT [OID]
Version: 5.8
Web: http://www.net-snmp.org/
Email: net-snmp-coders@lists.sourceforge.net
OPTIONS:
-h, --help display this help message
-H display configuration file directives understood
-v 1|2c|3 specifies SNMP version to use
-V, --version display package version number
SNMP Version 1 or 2c specific
-c COMMUNITY set the community string
SNMP Version 3 specific
-a PROTOCOL set authentication protocol (MD5|SHA|SHA-224|SHA-256|SHA-384|SHA-512)
-A PASSPHRASE set authentication protocol pass phrase
-e ENGINE-ID set security engine ID (e.g. 800000020109840301)
-E ENGINE-ID set context engine ID (e.g. 800000020109840301)
-l LEVEL set security level (noAuthNoPriv|authNoPriv|authPriv)
-n CONTEXT set context name (e.g. bridge1)
-u USER-NAME set security name (e.g. bert)
-x PROTOCOL set privacy protocol (DES|AES)
-X PASSPHRASE set privacy protocol pass phrase
-Z BOOTS,TIME set destination engine boots/time
General communication options
-r RETRIES set the number of retries
-t TIMEOUT set the request timeout (in seconds)
Debugging
-d dump input/output packets in hexadecimal
-D[TOKEN[,...]] turn on debugging output for the specified TOKENs
(ALL gives extremely verbose debugging output)
Install SNMP and SNMPWALK on Windows 10 Windows Server 2016 and Windows Server 2019
In this section, we will show you how to install SNMP and SNMPWALK on the Windows operating system.
Follow the below steps to install SNMP on Windows:
Step 1 – Open the Control Panel as shown below:
Step 2 – Click on the Programs and Features you should see in the page below:
Step 3 – Click on the Turn Windows features on or off.
Step 4 – On Windows 10, select Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) and install it.
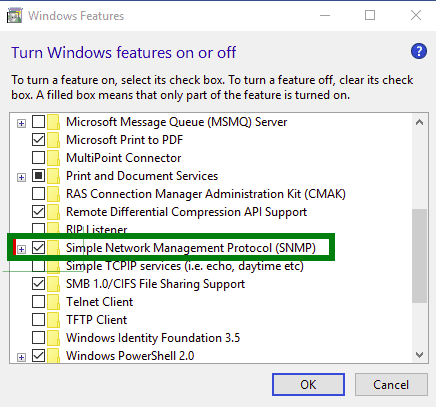
Step 5 – On Windows Server 2016 and 2019, click on the Add Roles and Features Wizard until you reach the Features section then select SNMP service.
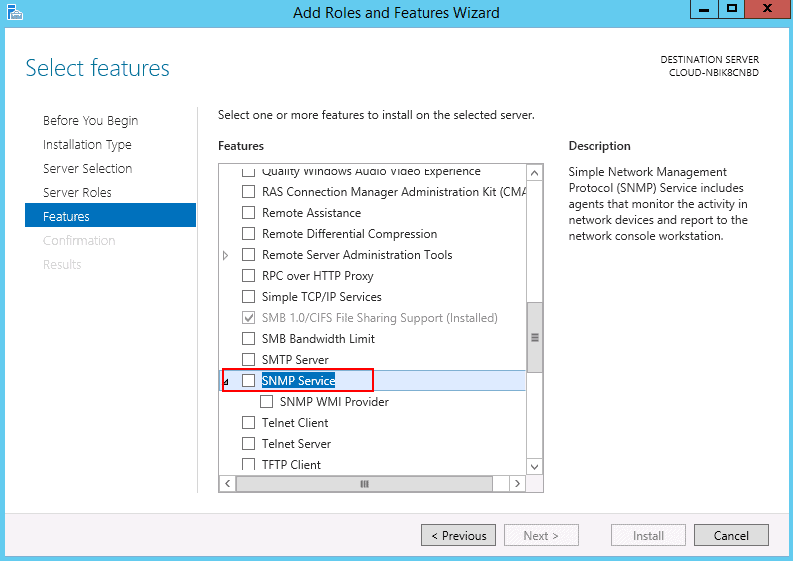
Step 6 – Install SNMP Service.
This will automatically install the SNMP service on your Windows system.
After installing SNMP, you will need to configure it.
Follow the below steps to configure the SNMP service:
Step 1 – Press Windows + R and type services.msc as shown below:
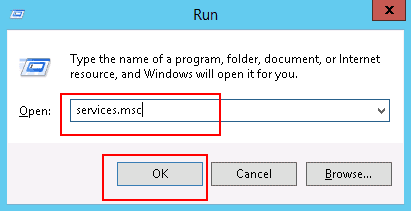
Step 2 – Press OK to open the Windows service configuration wizard.
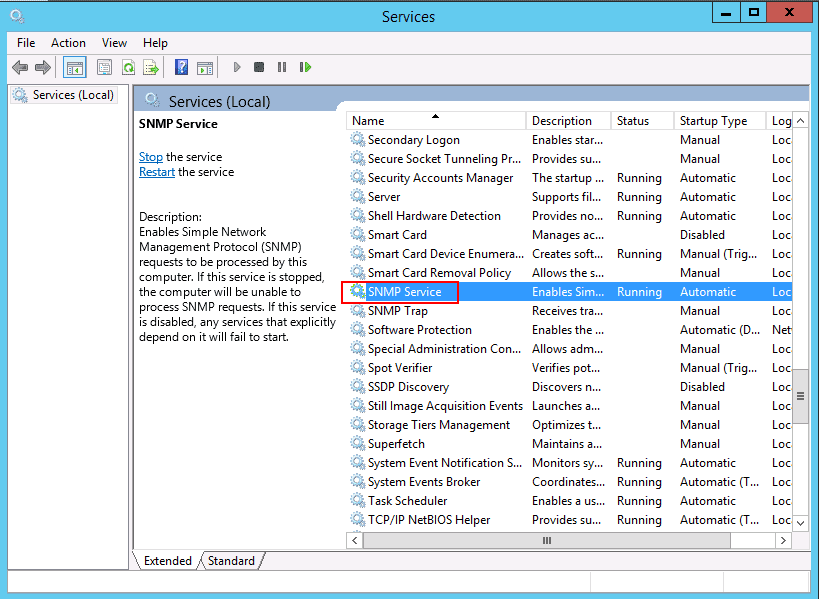
Step 3 – Select the SNMP service, right-click and click on the properties as shown below:
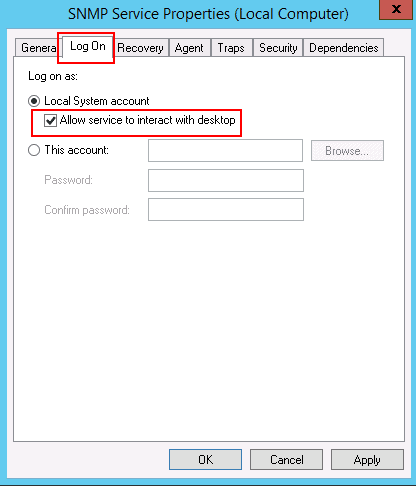
Step 4 – In the Log On tab, select “Allow service to interact with desktop”. Then click on the Agent tab as shown below:
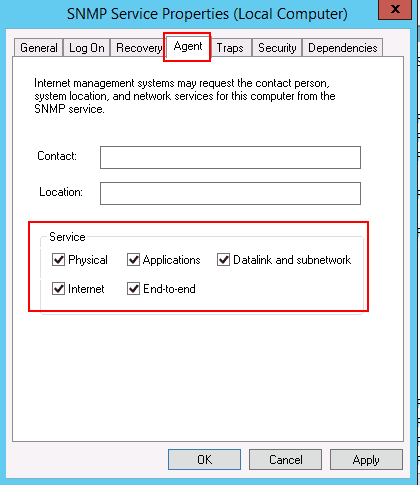
Step 5 – Select all services and click on the Security tab as shown below:
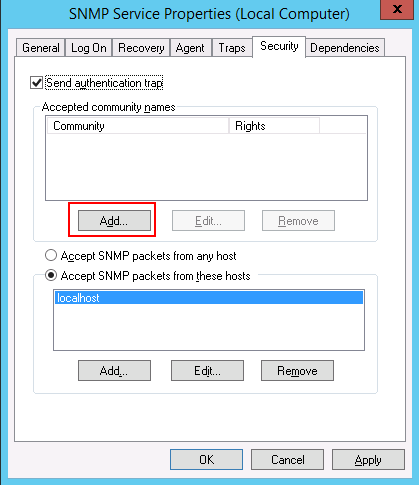
Step 6 – Click on the Add button. You should see the following screen:
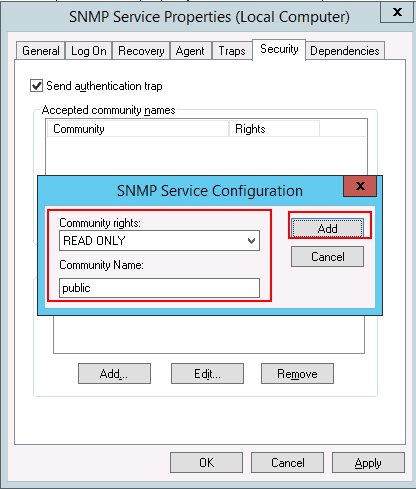
Step 7 – Provide community rights and community name then click on the Add button. You should see the following page:
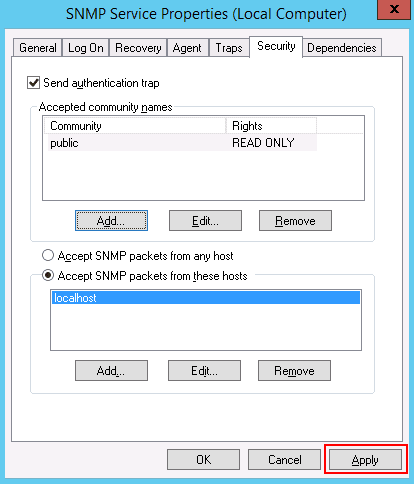
Step 8 – Click on the Apply button to apply the changes.
For full SNMP functionality, you will need to download the SolarWinds MIB Walk module from their Engineer’s Toolset to your windows system. However, you can download the free snmpwalk files from the SourceForge website and follow along with this post.
Once SNMPWALK is downloaded, extract it to the download folder. You can now use snmpwalk.exe to launch and use the SNMPWALK.
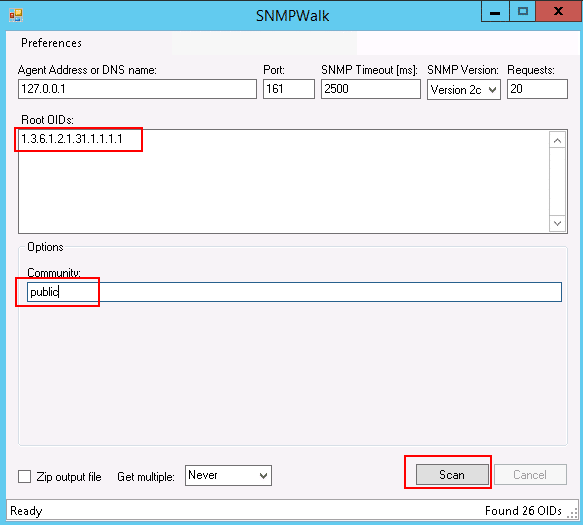
Provide your agent address, OID, community, and click the Scan button. This will generate a complete system information report based on the OID.
How to Use SNMPWALK to Retrieve the System Information
In this section, we will show you how to use the SNMPWALK command in Linux to retrieve the system information.
You can use the following options with the SNMPWALK command to retrieve the system information:
- -v: Specify the SNMP version.
- -c: Specify the community string which you have configured on the SNMP.
- hostname: Specify the hostname or IP address of the system where the SNMP agent is installed.
- OID: Specify the OID to return all SNMP objects.
Now, open your command-line interface and run the following command to list all existing OIDs on the network..
snmpwalk -v 2c -c public localhost
You should get the following output:
iso.3.6.1.2.1.1.1.0 = STRING: "Linux ubuntu2004 5.4.0-29-generic #33-Ubuntu SMP Wed Apr 29 14:32:27 UTC 2020 x86_64"
iso.3.6.1.2.1.1.2.0 = OID: iso.3.6.1.4.1.8072.3.2.10
iso.3.6.1.2.1.1.3.0 = Timeticks: (19907) 0:03:19.07
iso.3.6.1.2.1.1.4.0 = STRING: "Me <me@example.org>"
iso.3.6.1.2.1.1.5.0 = STRING: "ubuntu2004"
iso.3.6.1.2.1.1.6.0 = STRING: "Sitting on the Dock of the Bay"
iso.3.6.1.2.1.1.7.0 = INTEGER: 72
iso.3.6.1.2.1.1.8.0 = Timeticks: (3) 0:00:00.03
iso.3.6.1.2.1.1.9.1.2.1 = OID: iso.3.6.1.6.3.10.3.1.1
iso.3.6.1.2.1.1.9.1.2.2 = OID: iso.3.6.1.6.3.11.3.1.1
iso.3.6.1.2.1.1.9.1.2.3 = OID: iso.3.6.1.6.3.15.2.1.1
iso.3.6.1.2.1.1.9.1.2.4 = OID: iso.3.6.1.6.3.1
iso.3.6.1.2.1.1.9.1.2.5 = OID: iso.3.6.1.6.3.16.2.2.1
iso.3.6.1.2.1.1.9.1.2.6 = OID: iso.3.6.1.2.1.49
iso.3.6.1.2.1.1.9.1.2.7 = OID: iso.3.6.1.2.1.4
iso.3.6.1.2.1.1.9.1.2.8 = OID: iso.3.6.1.2.1.50
iso.3.6.1.2.1.1.9.1.2.9 = OID: iso.3.6.1.6.3.13.3.1.3
iso.3.6.1.2.1.1.9.1.2.10 = OID: iso.3.6.1.2.1.92
iso.3.6.1.2.1.1.9.1.3.1 = STRING: "The SNMP Management Architecture MIB."
iso.3.6.1.2.1.1.9.1.3.2 = STRING: "The MIB for Message Processing and Dispatching."
iso.3.6.1.2.1.1.9.1.3.3 = STRING: "The management information definitions for the SNMP User-based Security Model."
iso.3.6.1.2.1.1.9.1.3.4 = STRING: "The MIB module for SNMPv2 entities"
iso.3.6.1.2.1.1.9.1.3.5 = STRING: "View-based Access Control Model for SNMP."
iso.3.6.1.2.1.1.9.1.3.6 = STRING: "The MIB module for managing TCP implementations"
iso.3.6.1.2.1.1.9.1.3.7 = STRING: "The MIB module for managing IP and ICMP implementations"
iso.3.6.1.2.1.1.9.1.3.8 = STRING: "The MIB module for managing UDP implementations"
iso.3.6.1.2.1.1.9.1.3.9 = STRING: "The MIB modules for managing SNMP Notification, plus filtering."
iso.3.6.1.2.1.1.9.1.3.10 = STRING: "The MIB module for logging SNMP Notifications."
You can see the different OIDs in the above output. The typical format of an OID is shown below:
1.3.6.1.4.1.2021.10.1
A brief explanation of the most commonly used OIDs are shown below:
- 1 – ISO – International Organization for Standardization (ISO)
- 3 – org – Organizations according to ISO/IEC 6523-2
- 6 – dod – US Department of Defense (DOD)
- 1 – Internet protocol
- 4 – Private – Device manufactured by a private company
- 2021 – It is the particular device manufacturer number.
To get the hostname of the system, run the following command:
snmpwalk -v 2c -c public 127.0.0.1 .1.3.6.1.2.1.1.5
You should get the following output:
iso.3.6.1.2.1.1.5.0 = STRING: "ubuntu2004"
To get the hostname and kernel information, run the following command:
snmpwalk -v 2c -c public 127.0.0.1 .1.3.6.1.2.1.1.1
You should get the following output:
iso.3.6.1.2.1.1.1.0 = STRING: "Linux ubuntu2004 5.4.0-29-generic #33-Ubuntu SMP Wed Apr 29 14:32:27 UTC 2020 x86_64"
To get the network interface information, run the following command:
snmpwalk -v 2c 127.0.0.1 -c public .1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2.1.1
You should get the following output:
iso.3.6.1.2.1.2.2.1.1.1 = INTEGER: 1
iso.3.6.1.2.1.2.2.1.1.2 = INTEGER: 2
iso.3.6.1.2.1.2.2.1.1.3 = INTEGER: 3
To get the MAC address information, run the following command:
snmpwalk -v 2c 127.0.0.1 -c public .1.3.6.1.2.1.2.2.1.6
You should get the following output:
iso.3.6.1.2.1.2.2.1.6.1 = ""
iso.3.6.1.2.1.2.2.1.6.2 = Hex-STRING: 00 00 2D 3A 26 A4
iso.3.6.1.2.1.2.2.1.6.3 = Hex-STRING: 00 00 0A 3A 26 A4
To get a list of all network interface, run the following command:
snmpwalk -v 2c -c public 127.0.0.1 .1.3.6.1.2.1.31.1.1.1.1
You should get the following output:
iso.3.6.1.2.1.31.1.1.1.1.1 = STRING: "lo"
iso.3.6.1.2.1.31.1.1.1.1.2 = STRING: "eth0"
iso.3.6.1.2.1.31.1.1.1.1.3 = STRING: "eth1"
To get an IP address of the system, run the following command:
snmpwalk -v 2c -c public 127.0.0.1 .1.3.6.1.2.1.4.20.1.1
You should get the following output:
iso.3.6.1.2.1.4.20.1.1.45.58.38.164 = IpAddress: 45.58.38.164
iso.3.6.1.2.1.4.20.1.1.127.0.0.1 = IpAddress: 127.0.0.1
To get the Subnet Mask of the system, run the following command:
snmpwalk -v 2c -c public 127.0.0.1 .1.3.6.1.2.1.4.20.1.3
You should get the following output:
iso.3.6.1.2.1.4.20.1.3.45.58.38.164 = IpAddress: 255.255.255.0
iso.3.6.1.2.1.4.20.1.3.127.0.0.1 = IpAddress: 255.0.0.0
To get the CPU information, run the following command:
snmpwalk -v 2c -c public 127.0.0.1 .1.3.6.1.2.1.25.3.2.1.3 |grep -i cpu
You should get the following output:
iso.3.6.1.2.1.25.3.2.1.3.196608 = STRING: "GenuineIntel: QEMU Virtual CPU version 2.5+"
iso.3.6.1.2.1.25.3.2.1.3.196609 = STRING: "GenuineIntel: QEMU Virtual CPU version 2.5+"
To get the system load information, run the following command:
snmpwalk -v 2c -c public 127.0.0.1 .1.3.6.1.4.1.2021.10.1
You should get the following output:
iso.3.6.1.4.1.2021.10.1.1.1 = INTEGER: 1
iso.3.6.1.4.1.2021.10.1.1.2 = INTEGER: 2
iso.3.6.1.4.1.2021.10.1.1.3 = INTEGER: 3
iso.3.6.1.4.1.2021.10.1.2.1 = STRING: "Load-1"
iso.3.6.1.4.1.2021.10.1.2.2 = STRING: "Load-5"
iso.3.6.1.4.1.2021.10.1.2.3 = STRING: "Load-15"
iso.3.6.1.4.1.2021.10.1.3.1 = STRING: "0.00"
iso.3.6.1.4.1.2021.10.1.3.2 = STRING: "0.01"
iso.3.6.1.4.1.2021.10.1.3.3 = STRING: "0.00"
iso.3.6.1.4.1.2021.10.1.4.1 = STRING: "12.00"
iso.3.6.1.4.1.2021.10.1.4.2 = STRING: "12.00"
iso.3.6.1.4.1.2021.10.1.4.3 = STRING: "12.00"
iso.3.6.1.4.1.2021.10.1.5.1 = INTEGER: 0
iso.3.6.1.4.1.2021.10.1.5.2 = INTEGER: 1
iso.3.6.1.4.1.2021.10.1.5.3 = INTEGER: 0
iso.3.6.1.4.1.2021.10.1.6.1 = Opaque: Float: 0.000000
iso.3.6.1.4.1.2021.10.1.6.2 = Opaque: Float: 0.010000
iso.3.6.1.4.1.2021.10.1.6.3 = Opaque: Float: 0.000000
iso.3.6.1.4.1.2021.10.1.100.1 = INTEGER: 0
iso.3.6.1.4.1.2021.10.1.100.2 = INTEGER: 0
iso.3.6.1.4.1.2021.10.1.100.3 = INTEGER: 0
iso.3.6.1.4.1.2021.10.1.101.1 = ""
iso.3.6.1.4.1.2021.10.1.101.2 = ""
iso.3.6.1.4.1.2021.10.1.101.3 = ""
To get the system uptime information, run the following command:
snmpwalk -v 2c -c public 127.0.0.1 .1.3.6.1.2.1.1.3.0
You should get the following output:
iso.3.6.1.2.1.1.3.0 = Timeticks: (66282) 0:11:02.82
Conclusion
In the above post, you learned how to install and use SNMP and SNMPWALK on Windows and Linux to get the system information across the connected devices. I hope this will help you to monitor the network devices.
SNMPWALK FAQs
What is a snmpwalk tool?
SNMPWALK is a process of exploring the Management Information Base (MIB) structure of an SNMP report. The MIB has a tree structure that is denoted by a dot-notation number and the “walk” crawls through these numbers, recreating the tree. An SNMPWALK tool can construct a MIB tree by mapping the relationship between the values in a MIB. Each number that identifies a node on the MIB tree will have a label and a value. The OID (Object ID) is a reference code for the label.
Is SNMP v3 TCP or UDP?
All versions of SNMP use the same ports – there are two and they are both UDP. Regular SNMP transactions involve the SNMP Manager sending out a broadcasted request, to which the SNMP device agents reply with a MIB. This communication occurs on UDP port 161. The SNMP agent can send out a warning message without waiting for a request. This is called a Trap and it goes to UDP port 162.
What is OID in Linux?
OID is short for Object ID. It is the level code that identifies a node in a tree structure that is used for reporting in SNMP. An SNMP report is called a Management Information Base (MIB). It has a set number of fields that are identified by OIDs. The OID uses a dot-notation format to indicate the inheritance of a node on the tree.
