Время на прочтение2 мин
Количество просмотров76K

Исследователи портала Bleeping Computer обнаружили, что компания Microsoft в составе обновления Windows 10 October 2018 Update без информирования пользователей добавила в ОС незаметную программу для диагностики сети и мониторинга пакетов под названием pktmon (Packet Monitor). Ее можно найти по этому пути: C:\Windows\system32\pktmon.exe.
Причем, информации об этой программе на сайте Microsoft нигде нет. Есть только описание в самой программе, там написано, что это «Monitor internal packet propagation and packet drop reports». Специалисты Bleeping Computer смогли научиться использовать pktmon, тем более у программы есть встроенный справочник. Также они опубликовали в своем исследовании несколько примеров активации разных возможностей pktmon для системных администраторов. Пользователи без административных прав не могут запускать эту программу.
Фактически, в Windows 10 появился встроенный аналог tcpdump, мощного и популярного инструмента для перехвата и анализа сетевых пакетов. Правда pktmon в настоящее время имеет ограниченный производителем функционал, который еще дорабатывается специалистами Microsoft. Причем полученные и сохраненные данные из pktmon уже сейчас можно использовать и в более функциональных приложениях, например, Microsoft Network Monitor или Wireshark. Вдобавок встроенная справочная документация приложения pktmon достаточно подробная, и лучше с ней ознакомиться, перед тем как начать экспериментировать с возможностями этой программы.
При использовании pktmon для мониторинга сетевого трафика необходимо настроить в программе фильтры пакетов на нужных портах, например, использовать команду «pktmon filter add -p 20». Для просмотра фильтров пакетов нужно использовать команду «pktmon filter list». Для удаления фильтров есть команда «pktmon filter remove».
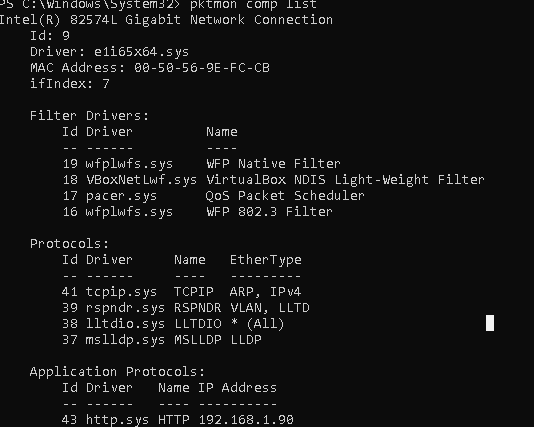
Чтобы отслеживать пакеты на конкретных устройствах необходимо определить ID сетевого адаптера с помощью команды «pktmon comp list». Далее можно начинать перехватывать нужные пакеты: pktmon start —etw -p 0 -c 13, где «-p 0» — аргумент для захвата всего пакета, а «-c 13» — захват только с адаптера с ID 13. Данные будут записываться в файл pktMon.etl:

Для остановки работы процедуры захвата нужно ввести команду «pktmon stop». Далее можно преобразовать полученный файл в текстовый формат: pktmon PktMon.etl -o ftp.txt. Там будет записана в краткой форме информация о сетевом трафике:

Полностью файл pktMon.etl можно открыть и анализировать, например, с помощью Microsoft Network Monitor.

Оказывается, что в новом обновлении Windows 10 May 2020 Update (Windows 10 версии 2004) Microsoft также обновила инструмент pktmon. Теперь с его помощью можно будет перехватывать пакеты в режиме реального времени и даже конвертировать файлы с расширением ETL в формат PCAPNG, которые можно исследовать в программе для захвата и анализа сетевого трафика Wireshark.

Ранее в начале мая 2020 года Microsoft перенесла на конец мая 2020 начало развертывания большого майского обновления Windows 10 May 2020 Update (версия 2004) для обычных пользователей. Компания планировала выпустить это обновление 12 мая 2020 года. Теперь этот срок сдвинут по соображениям безопасности еще на две недели из-за необходимости исправить выявленную в последний момент уязвимость нулевого дня в Windows 10.
Встроенный анализатор (сниффер) сетевого трафика Packet Monitor (PktMon.exe) появился еще в Windows 10 1809 и Windows Server 2019. В последнем билде Windows 10 2004 (May 2020 Update), функционал анализатора пакета был существенно расширен (появилась поддержка захвата пакетов в реальном времени, и поддержка формата PCAPNG для простого импорта в анализатор сетевого трафика Wireshark). Таким образом в Windows появился функционал захвата сетевого трафика, аналогичный tcpdump, и его можно смело использовать системными и сетевыми администраторам для диагностики работы сети.
Packet Monitor позволяет получить всю сетевую активность, проходящую через сетевой интерфейс компьютера на уровне каждого пакета.
Ранее для захвата сетевого трафика и инспектирования пакетов в Windows использовалась команда netsh trace.
Справку по использованию параметров
pktmon.exe
можно получить, набрав команду в командной строке.
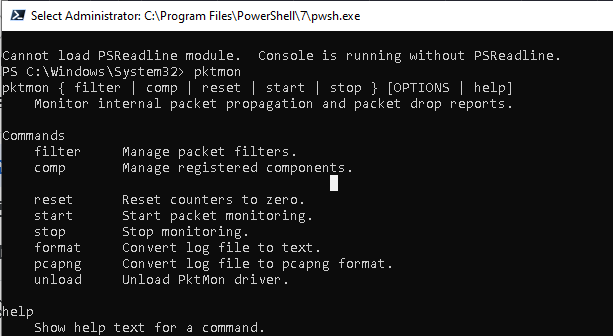
Основные команды утилиты Packet Monitor:
- filter — управление фильтрами пакетов
- comp – управление зарегистрированными компонентами;
- reset — сброс счетчиков;
- start – запустить мониторинг пакетов;
- stop— остановить сбор пакетов;
- format – конвертировать лог файл трафика в текстовый формат;
- pcapng – конвертация в формат pcapng;
- unload – выгрузить драйвер PktMon.
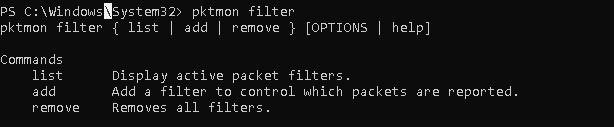
Чтобы получить справку по субкоманде, укажите ее имя:
pktmon filter
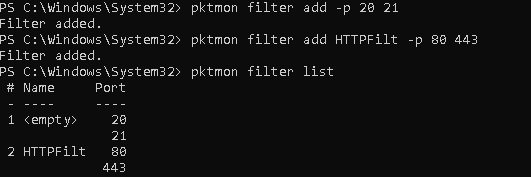
Попробуем собрать дамп трафика, который приходит на некоторые запущенные службы компьютера. Допустим, нам нужно проанализировать трафик FTP (TCP порты 20, 21) и HTTP (порты 80 и 443).
Создадим фильтр пакетов для 4 TCP портов (также можно мониторить UDP и ICMP трафик):
pktmon filter add -p 20 21
pktmon filter add HTTPFilt –p 80 443
Выведем список имеющихся фильтров:
pktmon filter list
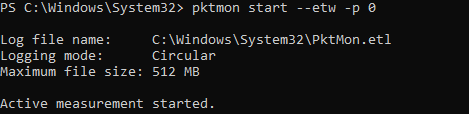
Чтобы запустить фоновый сбор трафика, выполните команду:
pktmon start –etw
Log file name: C:\Windows\System32\PktMon.etl Logging mode: Circular Maximum file size: 512 MB Active measurement started.
В таком режиме pktmon собирает данные со всех сетевых интерфейсов, но в журнал попадают только первые 128 байтов пакета. Чтобы захватить пакеты целиком и только на определенном интерфейсе компьютера, используется команда:
pktmon start --etw -p 0 -c 9
где значение аргумента c – номер (ID) нужного сетевого интерфейса, полученного с помощью:
pktmon comp list
Фильтр пакетов начнет запись всего трафика, соответствующего заданным фильтрам в файл C:\Windows\System32\PktMon.etl (максимальный размер 512 Мб). Чтобы остановить запись дампа, выполните команду:
pktmon stop
Также сбор сетевых пакетов прекращается после перезегрузки Windows.
Теперь вы можете сконвертировать файл с дампом трафика из формата ETL в обычный текст:
pktmon format PktMon.etl -o c:\ps\packetsniffer.txt
или
pktmon PCAPNG PktMon.etl -o c:\ps\packetsniffer.pcapng
Полученный дамп трафика можно анализировать в текстовом виде, загрузить ETL файл в установленный на компьютере администратора Microsoft Network Monitor или WireShark (в форматер PCAPNG).
Чтобы удалить все созданные фильтры Packet Monitor, выполните:
pktmon filter remove
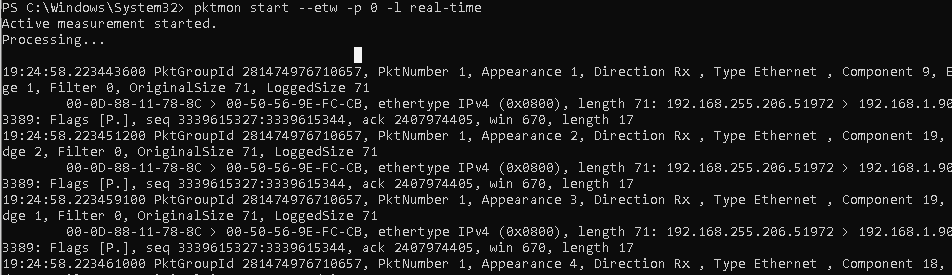
Вы можете использовать PktMon для мониторинга сетевого трафика в реальном времени. Для этого используется параметр
-l real-time
. В этом режиме захваченные сетевые пакеты отображаются в консоли, и не пишутся в фоновом режиме в лог файл.
pktmon start --etw -p 0 -l real-time
Чтобы остановить сбор трафика, используйте комбинацию клавиш Ctrl+C.
Если у вас наблюдается drop пакетов на сетевом интерфейсе, PacketMon может показать причину дропов (например, некорректный MTU или VLAN).
Также вы можете использовать PktMon в Windows Admin Center через расширения. Собранные данные с компьютеров и серверов при диагностике сетевых проблем можно использовать для анализа в более мощных программах анализа сетевого трафика, таких как Microsoft Network Monitor или Wireshark.
СКАЧАТЬ
Описание
Отзывы
Выберите вариант загрузки:
- скачать с сервера SoftPortal (для Windows 32-bit, zip-файл)
- скачать с сервера SoftPortal (для Windows 64-bit, zip-файл)
- скачать с официального сайта (для Windows 64-bit, zip-файл)
- скачать с официального сайта (для Windows 32-bit, zip-файл)
- скачать с официального сайта (русификатор)
SmartSniff — небольшая бесплатная утилита для перехвата и просмотра Вашего сетевого трафика. Сниффер захватывает пакеты, которые проходят через Ваш сетевой адаптер и просматривает захваченные данные как последовательность общения между клиентом и сервером (полное описание…)

Рекомендуем популярное
Advanced IP Scanner 2.5.4594.1
Advanced IP Scanner — Это быстрый, надежный и простой в использовании сканер локальных сетей (LAN) для…
Nmap 7.97
Nmap — Самый популярный сканер портов. Использовался в фильме «Матрица: Перезагрузка» при реальном взломе компьютера…
Wireshark 4.4.0
Wireshark — утилита для детального анализа сетевых пакетов локальных сетей в реальном времени,…
LANScope 2.9.1
LANScope — бесплатная утилита, с помощью которой можно легко и быстро определить доступность…
Serial Port Monitor 1.7
Программа-сниффер, которая позволяет отслеживать трафик COM-порта вашего ПК. Также…
MAC spoofer 2.1.0.9
Небольшая бесплатная утилита, которая предназначена для изменения MAC адреса сетевой…
We are reader supported and may earn a commission when you buy through links on our site. Read Disclosure
Packet sniffing is a deep type of network analysis in which details of the network traffic are decoded to be analyzed. It is one of the most important troubleshooting skills any network administrator should possess. Analyzing network traffic is a complicated task. In order to cope with unreliable networks, data is not sent in one continuous stream. Instead, it is chopped up in fragments sent individually. Analyzing network traffic involves being able to collect these packets of data and reassemble them into something meaningful. This is not something that you can do manually so packet sniffers and network analyzers were created. Today, we’re having a look at seven of the best packet sniffers and network analyzers.
We’re starting off today’s journey by giving you some background information on what packet sniffers are. We’ll try to figure what the difference is–or if there is a difference–between a packet sniffer and a network analyzer. We’ll then proceed to the core of our subject and not only list but also briefly review each of our seven picks. What we have for you is a combination of GUI tools and command-line utilities that run on various operating systems.
A Few Words About Packet Sniffers and Network Analyzers
Let’s begin by settling something. For the sake of this article, we’ll assume that packet sniffers and network analyzers are one and the same. Some will argue that they are different and they may be right. But in the context of this article, we’ll look at them together, mainly because even though they might operate differently–but do they really?–they serve the same purpose.
Packet Sniffers usually do three things. First, they capture all data packets as they enter or exit a network interface. Secondly, they optionally apply filters to ignore some of the packets and save others to disk. They then perform some form of analysis of the captured data. It is in that last function of packet sniffers that they differ the most.
For the actual capture of the data packets, most tools use an external module. The most common are libpcap on Unix/Linux systems and Winpcap on Windows. You typically won’t have to install these tools as they are usually installed by the different tools installers.
Another important thing to know is that Packet Sniffers–even the best one–won’t do everything for you. They are just tools. It’s just like a hammer that won’t drive any nail by itself. So, you need to make sure you learn how to best use each tool. The packet sniffer will just let you see the traffic but it is up to you to use that information to find issues. There have been whole books on using packet capture tools. I, myself, once took a three-day course on the subject. I’m not trying to discourage you. I’m only trying to set your expectations straight.
How To Use A Packet Sniffer
As we’ve explained, a packet sniffer will capture and analyze traffic. So, if you’re trying to troubleshoot a specific issue–which is typically why you’d use such a tool–you first need to make sure that the traffic your capturing is the right traffic. Imagine a situation where all users are complaining that a particular application is slow. In that type of situation, your best bet would probably be to capture traffic at the application server’s network interface. You might then realize that requests arrive at the server normally but that the server takes a long time to send out responses. That would indicate a server problem.
If, on the other hand, you see the server responding in a timely manner, it possibly means that the issue is somewhere on the network between the client and the server. You would then move your packet sniffer one hop closer to the client and see if responses are delayed. If it’s not, you move more hop closer to the client, and so on and so forth. You’ll eventually get to the spot where delays occur. And once you’ve identified the location of the problem, you are one big step closer to solving it.
Now you may be wondering how we manage to capture packets at a specific point. It’s pretty simple, we take advantage of a feature of most network switches called port mirroring or replication. This is a configuration option that will replicate all traffic in and out of a specific switch port to another port on the same switch. Let’s say your server is connected to port 15 of a switch and that port 23 of that same switch is available. You connect your packet sniffer to port 23 and configure the switch to replicate all traffic from port 15 to port 23. What you get as a result on port 23 is a mirror image–hence the port mirroring name–of what’s going through port 15.
Now that you better understand what packet sniffers and network analyzers are, let’s see what are the seven best we could find. We’ve tried to include a mix of command-line and GUI tools as well as include tools running on various operating systems. After all, not all network administrators are running Windows.
1. SolarWinds Deep Packet Inspection and Analysis tool (FREE TRIAL)
SolarWinds is well-known for its many useful free tools and its state of the art network management software. One of its tools is called the Deep Packet Inspection and Analysis Tool. It comes as a component of SolarWinds’ flagship product, the Network Performance Monitor. Its operation is quite different from more “traditional” packet sniffers although it serves a similar purpose.
To summarize the tool’s functionality: it will help you find and resolve the cause of network latencies, identify impacted applications, and determine if slowness is caused by the network or an application. The software will also use deep packet inspection techniques to calculate response time for over twelve hundred applications. It will also classify network traffic by category, business vs. social, and risk level, helping you identify non-business traffic that may need to be filtered or otherwise eliminated.
And don’t forget that the SolarWinds Deep Packet Inspection and Analysis Tool comes as part of the Network Performace Monitor. NPM, as it is often called is an impressive piece of software with so many components that a whole article could be dedicated to it. At its core, it is a complete network monitoring solution that combines the best technologies such as SNMP and deep packet inspection to provide as much information about the state of your network as possible. The tool, which is reasonably priced comes with a 30-day free trial so you can make sure it really fits your needs before committing to purchasing it.
2. tcpdump
Tcpdump is probably THE original packet sniffer. It was created back in 1987. Since then, it has been maintained and improved but remains essentially unchanged, at least it the way it is used. It is pre-installed in virtually every Unix-like operating system and has become the de-facto standard when one needs a quick tool to capture packets. Tcpdump uses the libpcap library for the actual packet capture.
By default. tcpdump captures all traffic on the specified interface and “dumps” it–hence its name–on the screen. The dump can also be piped to a capture file and analyzed later using one–or a combination–of several available tools. A key to tcpdump’s strength and usefulness is the possibility to apply all sorts of filters and to pipe its output to grep–another common Unix command-line utility–for further filtering. Someone with a good knowledge of tcpdump, grep and the command shell can get it to capture precisely the right traffic for any debugging task.
3. Windump
Windump is essentially just a port of tcpdump to the Windows platform. As such, it behaves in much the same way. It is not uncommon to see such ports of successful utility programs from one platform to another. Windump is a Windows application but don’t expect a fancy GUI. This is a command-line only utility. Using Windump, therefore, is basically the same as using its Unix counterpart. The command-line options are the same and the results are also almost identical. The output from Windump can also be saved to a file for later analysis with a third-party tool.
One major difference with tcpdump is that Windump is not built into Windows. You’ll have to download it from the Windump website. The software is delivered as an executable file and requires no installation. However, just like tcpdump uses the libpcap library, Windump uses Winpcap which, like most Windows libraries, needs to be separately downloaded and installed.
4. Wireshark
Wireshark is the reference in packet sniffers. It has become the de-facto standard and most other tools tend to emulate it. This tool will not only capture traffic, it also has quite powerful analysis capabilities. So powerful that many administrators will use tcpdump or Windump to capture traffic to a file then load the file into Wireshark for analysis. This is such a common way of using Wireshark that upon startup, you’re prompted to either open an existing pcap file or start capturing traffic. Another strength of Wireshark is all the filters it incorporates which allow you to zero in on precisely the data you’re interested in.
To be perfectly honest, this tool has a steep learning curve but it is well-worth learning. It will prove invaluable time and time again. And once you’ve learned it, you’ll be able to use it everywhere as it has been ported to almost every operating system and it is free and open-source.
5. tshark
Tshark is sort of like a cross between tcpdump and Wireshark. This is a great thing as they are some of the best packet sniffers out there. Tshark is like tcpdump in that it is a command-line only tool. But it is also like Wireshark in that it not only captures but also analyzes traffic. Tshark is from the same developers as Wireshark. It is, more or less, the command-line version of Wireshark. It uses the same type of filtering as Wireshark and can therefore quickly isolate just the traffic you need to analyze.
But why, you may ask, would anyone want a command-line version of Wireshark? Why not just use Wireshark; with its graphical interface, it’s got to be simpler to use and to learn? The main reason is that it would allow you to use it on a non-GUI server.
6. Network Miner
Network Miner is more of a forensic tool more than a true packet sniffer. Network Miner will follow a TCP stream and reconstruct an entire conversation. It is truly one powerful tool. It can work in offline mode where you’d import some capture file to let Network Miner work its magic. This is a useful feature as the software runs only on Windows. You could use tcpdump on Linux to capture some traffic and Network Miner on Windows to analyze it.
Network Miner is available in a free version but, for the more advanced features such as IP-based geolocation and scripting, you’ll need to purchase a Profesional license. Another advanced function of the professional version is the possibility to decode and playback VoIP calls.
7. Fiddler (HTTP)
Some of our more knowledgeable readers might argue that Fiddler is not a packet sniffer nor is it a network analyzer. They are probably right but we felt we should include this tool on our list as it is very useful in many situations. Fiddler will actually capture traffic but not any traffic. It only works with HTTTP traffic. You can imagine how valuable it can be despite its limitation when you consider that so many applications today are web-based or use the HTTP protocol in the background. And since Fiddler will capture not only browser traffic but just about any HTTP, it’s very useful in troubleshooting
The advantage of a tool like Fiddler over a bona fide packet sniffer like, for example, Wireshark, is that Fiddler was built to “understand” HTTP traffic. It will, for instance, discover cookies and certificates. It will also find actual data coming from HTTP-based applications. Fiddler is free and it’s available for Windows only although beta builds for OS X and Linux (using the Mono framework) can be downloaded.
Conclusion
When we publish lists like this one, we’re often asked which one is the best. In this particular situation, if I were asked that question, I’d have to answer “all of them”. They are all free tools and all have their value. Why not have them all at hand and familiarize yourself with each one. When you get to a situation where you need to use them, it will be much easier and efficient. Even command-line tools have a tremendous value. For instance, they can be scripted and scheduled. Imagine you have an issue that happens at 2:00 am daily. You could schedule a job to run tcpdump of Windump between 1:50 and 2:10 and analyze the capture file the next morning. No need to stay up all night.
Readers help support Windows Report. We may get a commission if you buy through our links.
Read our disclosure page to find out how can you help Windows Report sustain the editorial team. Read more
A packet sniffer, also known as a network analyzer or a protocol analyzer, is a program that can intercept and log traffic that passes over a digital network.
Packet sniffers are diagnostic tools that allow network technicians to analyze the network and diagnose network problems.
In order to work, the packet sniffer must have access to the wireless or wired network interface on its host computer. The tool can analyze traffic from the entire network or only a small part.
Then the sniffer converts the analysis into a readable format, helping the network technicians to pinpoint network faults.
What is a network packet sniffer?
If you’re wondering what a packet sniffer is, it can be explained in a few words: A network traffic analysis tool.
The utility of this software relies on the support for analyzing great amounts of network data, such as passwords and log-in credentials or users’ online activity.
Most of the network packet sniffers gather data from your network using two systems, Unix-like systems or Windows systems. In case you require a network sniffer for Windows, you can easily find them on the market.
You should also know that it’s possible to use software or hardware network sniffers. The hardware sniffers will best help you troubleshoot network issues.
Nevertheless, software network sniffing tools are more reliable and don’t need plugging support to detect network insights.
To discover the best packet or free network sniffers for Windows 10 and 11, dive deep into this article and find the one you need.
- NetFlow Analyzer – Effective Bandwidth monitoring
- PRTG Network Monitor – Professional network analyzer
- Wireshark – Live capturing and offline analysis
- Free Network Analyzer – Real-time protocol analyzer
- Solarwinds Network Packet Sniffer – Easy to use
- Capsa Free Network Analyzer – Customizable reports
NetFlow Analyzer

Packet sniffers need to be a complete package that allows network management and control and provides in-depth statistics regarding the traffic analytics of a given network.
NetFlow Analyzer is one such tool, and it is one of the best packet sniffers on the market today, providing hundreds of companies with much-needed intel regarding their network status, and how they could improve it.
The software is built around the idea that things need to be easy to understand and as transparent as possible, and that’s exactly how the data is displayed for any Network administrator using it.
Here are some of the features of this program:
- Network forensics and troubleshooting
- Efficient bandwidth monitoring
- App-centric monitoring
- In-depth traffic analysis
- Security analysis
NetFlow Analyzer
If you’re looking for an efficient packet sniffer, both in terms of costs and performance, then you need to try out NetFlow Analyzer.
PRTG Network Monitor

PRTG Network Monitor is an advanced, professional tool for analyzing and monitoring local networks. The tool captures the data passing through your network, analyzes it, and then presents it in a readable format.
It has a special Packet Sniffing Sensor that will let you know if any network packets are suspicious.
Be careful, as such a sensor could use many of your PC’s resources, and you will need to manage your processes carefully when you want to scan for dangerous data packets.
PRTG Network Monitor detects all network data activity and application usage of the system’s ports.
The tool offers a flexible system of configurable filters and reports that users can use to capture specific traffic patterns and network data.
Also, it supports many selections of events, methods, and properties.
PRTG Network Monitor comes in two variants: a completely free, basic edition and a paid version with full features. You can test the tool for free for 30 days and continue on a free basis with limited features or buy the full version with user support.
PRTG Network Monitor
Manage the way your PC uses your bandwidth with one of the best network monitoring tools on the market today!
Wireshark
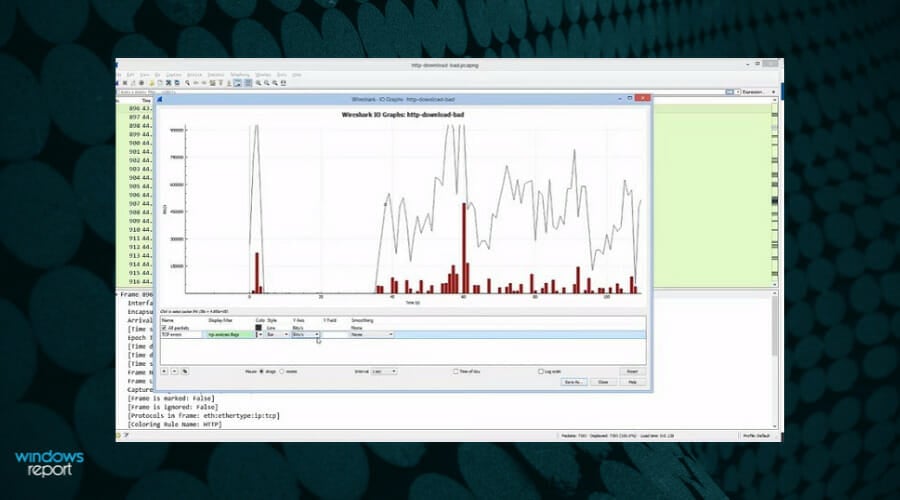
Wireshark is one of the most popular packet sniffers in the world, allowing you to see what’s happening on your network at a microscopic level. This free tool is used by industries and educational institutions.
Wireshark has powerful display filters that can read and write a huge number of capture file formats, such as:
tcpdump (libpcap), Pcap NG, Catapult DCT2000, Cisco Secure IDS iplog, Microsoft Network Monitor, Network General Sniffer, Sniffer Pro, and NetXray, Network Instruments Observer, NetScreen snoop, Novell LANalyzer, RADCOM WAN/LAN Analyzer, Shomiti/Finisar Surveyor, Tektronix K12xx, and more.
Other features include:
- Deep inspection of hundreds of protocols, with more being added all the time
- Live capture and offline analysis
- Standard three-pane packet browser
- Captured network data can be browsed via a GUI, or via the TTY-mode TShark utility
- Rich VoIP analysis
- Live data can be read from Ethernet, IEEE 802.11, PPP/HDLC, ATM, Bluetooth, USB, Token Ring, Frame Relay, FDDI, and others
- Decryption support for many protocols, including IPsec, ISAKMP, Kerberos, SNMPv3, SSL/TLS, WEP, and WPA/WPA2
- Coloring rules can be applied to the packet list for quick, intuitive analysis
- Output can be exported to XML, PostScript®, CSV, or plain text/
⇒ Get Wireshark
Free Network Analyzer

Free Network Analyzer is another excellent free network monitoring software that can analyze the wired or wireless connections of your computer. The tool can capture, filter, and display all traffic data and decode the network packet raw data.
Packets are then parsed, extracted, and presented in a readable form, offering you a throughout analysis of the data transferred via your PC network interfaces.
Key features include:
- Real-time protocol analysis and effective dataflow processing even under high traffic load on high data rate communications
- Data filtered by specific protocol
- Search for data patterns with RegEx (Regular Expressions) support
- Importing log files from third party protocol analyzers
- More than 70 different data encodings supported.
⇒ Get Free Network Analyzer
Solarwinds Network Packet Sniffer

This network traffic platform offers an exhaustive solution for valuable insights regarding your network connection.
In the first place, the tool will measure your network performance from every side and isolate the cause of potential connection issues on your network.
There are so numerous traffic analysis tools that can capture packets but are not actually able to present information clearly and accurately.
For this reason, SolarWinds offers detailed reports from over 1.200 applications or networks that impact the end-user experience.
Ultimately, you have included a Wi-fi packet capture that gives valuable information for your wireless networks, such as connection performance, traffic, or configuration details.
⇒ Get Solarwinds Network Packet Sniffer
Capsa Free Network Analyzer
This tool is the right choice for regular users, such as students, teachers, or computer geeks. Capsa Free allows you to monitor network traffic, troubleshoot network issues and analyze packets.
It supports over 300 network protocols, MSN and Yahoo Messenger filters, email monitor and auto-save, as well as customizable reports and dashboards.
The main advantage of this tool is that it allows you to learn how to monitor network activities, pinpoint network problems, and improve network security.
⇒ Get Capsa Free
How do packet sniffers work?
The packet network sniffing tools will efficiently work by intercepting network traffic using the software or hardware interface on the user’s PC.
With the network sniffing process you have the necessary method to capture the packets that pass through your network and analyze detailed network data or connectivity issues.
A network sniffer for Windows will monitor and offer connection insights for the whole network or only a certain section, depending on the network configuration, not matter if you are looking for home network monitoring software or enterprise grade one.
On the other hand, using the packet sniffer for a wireless network, you will be able to monitor and analyze only one channel at a time. However, if your PC supports multiple wireless interfaces, you can do it for multiple channels.
There are valuable free network sniffers for Windows 10 and 11 on the market, so employ the ones we covered for you in this article and easily catch traffic data.
Madalina Dinita
Networking & Security Specialist
Madalina has been a Windows fan ever since she got her hands on her first Windows XP computer.
She is interested in all things technology, especially emerging technologies — AI and DNA computing in particular.
Prior to joining the WindowsReport team, she worked in the corporate world for a number of years.
