Удаление резервных копий, которые делает Windows Server Backup, в момент когда вы сталкиваетесь с проблемой заполненого жесткого диска, в то время когда по ряду причин система архивации данных Windows Server не видит отсутствие свободного места и не перезаписывает старые версии. Или когда на диске избыток точек резервного копирования.
Через Powershell:
Get-WBSummary
В результате выполнения команды будет видно количество резервных копий, строка NumberOfVersions.

Чтобы удалить резервные копии, необходимо использовать команду Remove-WBBackupSet, в моем примере я хочу оставить 20 последних копий.
Remove-WBBackupSet -KeepVersions 20

В результате выполнения команды, удалилось 3, осталось 20 резервных копий.
Удаление через командную строку CMD:
WBADMIN DELETE BACKUP -keepVersions:30

Описанные выше команды всегда можно использовать по расписанию, через планировщик заданий. Например, можно создать *.bat файл со следующим содержимым:

Windows
1 Minute
Windows Server Backup is the built-in tool in Windows Server 2008/R2 that allows you to backup and restore files, folders, and critical system data such as the System State, entire volumes and even the full server itself.
After using it, Windows Server Backup will begin to display a log of recent backup and restore operations. This log allows the administrator to keep track of what backup and restore operations were taken on that server, and may be quite useful especially when having many people dealing with your servers.
While useful, sometimes one might want to delete or clear that list of log entries. Strangely, there’s no obvious place, button, command or checkbox you can use to clear that log.
After some digging, we found a workaround.
Clearing Windows Server Event Log
To clear the event log:
- Open Event Viewer from the Administrative Tools folder.
-
Go to Applications and Services Logs.
-
Expand Microsoft > Windows > Backup.
-
Right click on the Operational Channel log and choose Save and Clear or just Clear in case you don’t want to save the existing log (we suggest you save the logs before clearing for any future reference).


Now, if you open Windows Server Backup, you’ll see that the log is empty.

Clearing Windows Server Backup Status Catalog
Use this below command in PowerShell.
wbadmin delete catalog
Deletes the backup catalog on the local computer. Use this subcommand only if the backup catalog on this computer is corrupted and you have no backups stored at another location that you can use to restore the catalog.
Published
A client uses Windows Server Backup to back up a small Hyper-V server running Windows Server 2008 R2. Today free space on the backup drive F: dropped below 100GB of 698GB, triggering a 15% monitoring threshold. Some quick notes on what I did.
Research
Review this Microsoft blog post:
Backup Version and Space Management in Windows Server Backup
List shadow copies:
wbadmin get versions -backupTarget:f:
vssadmin list shadows /for=f:
Delete Old Shadow Copies
Delete 5 oldest shadow copies on the target volume:
diskshadow
delete shadows oldest f:
delete shadows oldest f:
delete shadows oldest f:
delete shadows oldest f:
delete shadows oldest f:
That freed up about 4.5GB per shadow copy, so now 122GB free (17%), 175GB in shadow copies. I could delete more—there must be 20 left.
No System State Backups to Delete
Tried this command to delete system state backups:
wbadmin delete systemstatebackup -deleteOldest
Got this message:
Enumerating system state backups...
ERROR - No system state backups were found.
This command can be used to delete backups that only contain the system state.
So apparently that’s only needed if you’re doing separate system state backups. I do system state backups together with other backups.
Update November 17, 2012
About three hours after I did the above, free disk space fell under 15% again. By the next morning, it was 97.7GB free and 199GB in shadow copies. What? How did I drop from 122GB free to 97.7GB free in a matter of hours? I did delete the shadows while a backup was running, but should that matter? Does Windows Server Backup just use as much space as possible? I just deleted another five shadow copies, this time with no backup running, and I’m back to 126GB free and 171GB in shadow copies. We’ll see what happens.
Update November 19, 2012
Two days and two backups later, the F: drive is showing 115GB (16.5%) free and 187GB in shadow copies. Better.
Update January 17, 2013
2012 Essentials Issues and References
I’m having similar issues with Windows Server Backup (WSB) on Server Essentials 2012. I had a backup fail for lack of disk space, even though 61 backups were available. I had to manually delete old shadow copies to get the backup running again. More research and forum posts have turned up some additional information.
The Windows Server Backup Overview on TechNet says, “Windows Server Backup does not require user intervention to periodically delete older backups to free up disk space for newer backups—older backups are deleted automatically.” Unfortunately, that is not always the case.
Windows Server Backup automatic disk usage management, also on TechNet, explains how the auto-delete works, why it sometimes doesn’t delete enough, and why backups fail. Basically WSB always leaves 1/8 of the backup volume allocated to shadow copies, which is how it stores previous backups. If that doesn’t leave enough space for the backup (which, I’ve discovered, is not compressed), the backup fails.
Update February 26, 2013
Configure Shadow Copies
I’m trying a different approach for maintaining free space on a dedicated backup volume: Configure Shadow Copies.
- In Disk Management, assign a drive letter to the backup drive. You probably did this already if you’ve been using wbadmin or vssadmin as described above.
- In Windows Explorer, right-click on the drive and select Configure Shadow Copies.
- In the Shadow Copies dialog, make sure the drive is highlighted. The Next Run Time should show Disabled. Click on Settings.
- Change Maximum Size from No limit to Use limit and set the value to leave about 15% of the drive free. For example, if a 100GB drive has become full using 40GB of shadow copy space, reduce the shadow copy space to a fixed 25GB to leave 15GB free.
I’ve had that set for a few days and it does seem to be maintaining 15% free space without my having to manually delete backups.
Caution I have not seen this method recommended anywhere so I can’t promise that it’s a safe approach to managing backup space. Use at your own risk!
Update April 14, 2016
To configure shadow copies on a desktop computer, you can select Control Panel > System, open System Protection, select the target drive, then click the Configure button. You’ll want to leave Restore Settings off for the backup target, but you can still adjust maximum Disk Space Usage for shadow copies on that drive.
This article mentions a couple more helpful vssadmin commands for doing the same thing. This should work on a desktop (if it’s a Pro version of Windows) or a server.
List shadow storage in use on all drives:
vssadmin list shadowstorage
Change shadow storage on one drive:
vssadmin resize shadowstorage /on=F: /for=F: /maxsize=25%
Для удаление старых копий воспользуемся программой wbadmin
Полный список команд можно получиться с помощью запроса
wbadmin /?
Мы же будем использовать удаление и нам понадобиться команда delete backup
Параметры:
-keepVersions Число более новых версий резервных копий, которые нужно хранить. Значение должно быть целым положительным числом. Значение -keepVersions:0 указывает, что все резервные копии будут удалены.
-version Идентификатор версии резервной копии в формате «ДД.ММ.ГГГГ-ЧЧ:ММ» Если вы не знаете идентификатор версии, введите в командной строке команду «WBADMIN GET VERSIONS». С ее помощью можно удалить версии, которые являются только резервными копиями. Чтобы просмотреть тип версии, используйте команду «WBADMIN GET ITEMS».
-deleteOldest Удаляет самую старую резервную копию.
-backupTarget Задает место хранения резервной копии, которую нужно удалить. Это значение может быть буквой диска, точкой подключения или путем к тому на основе GUID. Его нужно указывать только для резервных копий, которые находятся не на локальном компьютере. Узнать, какие резервные копии находятся на локальном компьютере, можно по каталогу архивации на нем.
-machine Компьютер, резервную копию которого вы хотите удалить. Этот параметр удобно использовать, если в одном расположении были созданы резервные копии для нескольких компьютеров. Его необходимо использовать, если задан параметр -backupTarget.
-quiet Подавляет вывод запросов при выполнении.
Рассмотрим несколько вариантов
1. Удаление всех копий, кроме одной самой «свежей»
wbadmin delete backup -keepVersions:1 -quiet (параметр quiet применяется для отключения подтверждения об удаление у пользователя, если его убрать система спросит — действительно ли вы ходите удалить все копии кроме одной)
2. Удаление определенной копии
wbadmin delete backup -version: 01.01.2017-23:30 -quiet ( данная команда удалить копию за 1 января 2017 года, созданная в 23:30)
3. Удаление самой старой резервной копии
wbadmin delete backup -deleteOldest -quiet
4. Удаление копии с одного из дисков для резервного копирования
wbadmin delete backup -backupTarget:f: -deleteOldest -quiet (удалит самую старую копию с резервного диска с букой F)
После того как вы определились какой вариант вам больше подходит, создадим файл с расширение .bat
В моем случае это будет
wbadmin delete backup -backupTarget:f: -deleteOldest -quiet
Сохраняем и добавляем в Планировщик заданий в удобное вам время (не должно совпадать с временем, когда идет процесс резервного копирования)
Так же можно добавить команду напрямую в планировщик заданий

Windows Server Backup (WSB) is a built-in backup and recovery solution for Windows Server environments. Some users report that they meet the “Windows Server Backup not deleting old backups” issue. This post from MiniTool helps you fix it.
In Windows Server Backup, there is a feature called Automatic Disk Usage Management, which was first introduced in Windows Server 2008 and later inherited in new versions. It can manage disk space for scheduled backups. It shrinks the storage space allocated for the snapshot to create space for new backups. Once the differential area is reduced, the old snapshots and corresponding backup versions are deleted.
But after running scheduled backup a few times, you will get more backups and less disk space. Some Windows Server users report that they encounter the “Windows Server Backup not deleting old backups” issue. Here, we introduce how to fix the issue.
Way 1: Via Command Prompt
How to delete old backups on Windows Server Backup? You can try to manually overwrite the old backup using Wbadmin. The methods to delete them are different and it is based on the items you want to delete. It is divided into system state backup and non-system state backup. Here is how to do that:
Situation 1: Delete System State Backup
If your backup is the system state, you can try the following steps to fix the “Windows Server Backup not deleting old backups” issue.
1. Type cmd in the Search box and choose Run as administrator.
2. Wbadmin provides 3 different parameters to help you specify the way to delete backups. You should execute it based on your needs.
- -version: to delete specific version(s).
- -keepVersions: to delete all backups but the specified ones.
- -deleteOldest: to delete the oldest backup.
For example, to delete the system backup that was taken at a specific time, just run the following command:
wbadmin delete systemstatebackup -version:02/07/2024-12:00 -backupTarget:D
Tips:
The parameter “BackupTarget” refers to deleting the system state backup stored on a specific volume.
Situation 2: Delete Non-System State Backup
If your backup is a non-system state, follow the instructions below to delete that:
1. Type cmd in the Search box and choose Run as administrator.
2. For example, to delete all backups except the latest three versions, run the command below:
wbadmin delete backup -keepVersions:3 -backupTarget: D: machine: WIN-1234ETYFH20
Tips:
The parameter “machine” is only needed when you have backed up many computers to the same location.
Way 2: Via Windows Server Backup Alternative
It’s difficult to use Command Prompt for some users. There is an easier way for you to fix the “can’t delete Windows Server Backup old backups” issue. You can use another tool to replace Windows Server Backup.
Here, MiniTool ShadowMaker is worth trying. As a piece of professional Server backup software, it is useful to back up files, back up systems, clone SSD to larger SSD, etc. This program is compatible with Windows Server 2022/2019/2016/2012/2012 R2.
Now, click the following button to get MiniTool ShadowMaker Trial Edition and have a try.
MiniTool ShadowMaker TrialClick to Download100%Clean & Safe
1. Launch MiniTool ShadowMaker and click Keep Trial to start a backup.
2. In the main function interface, click Backup.
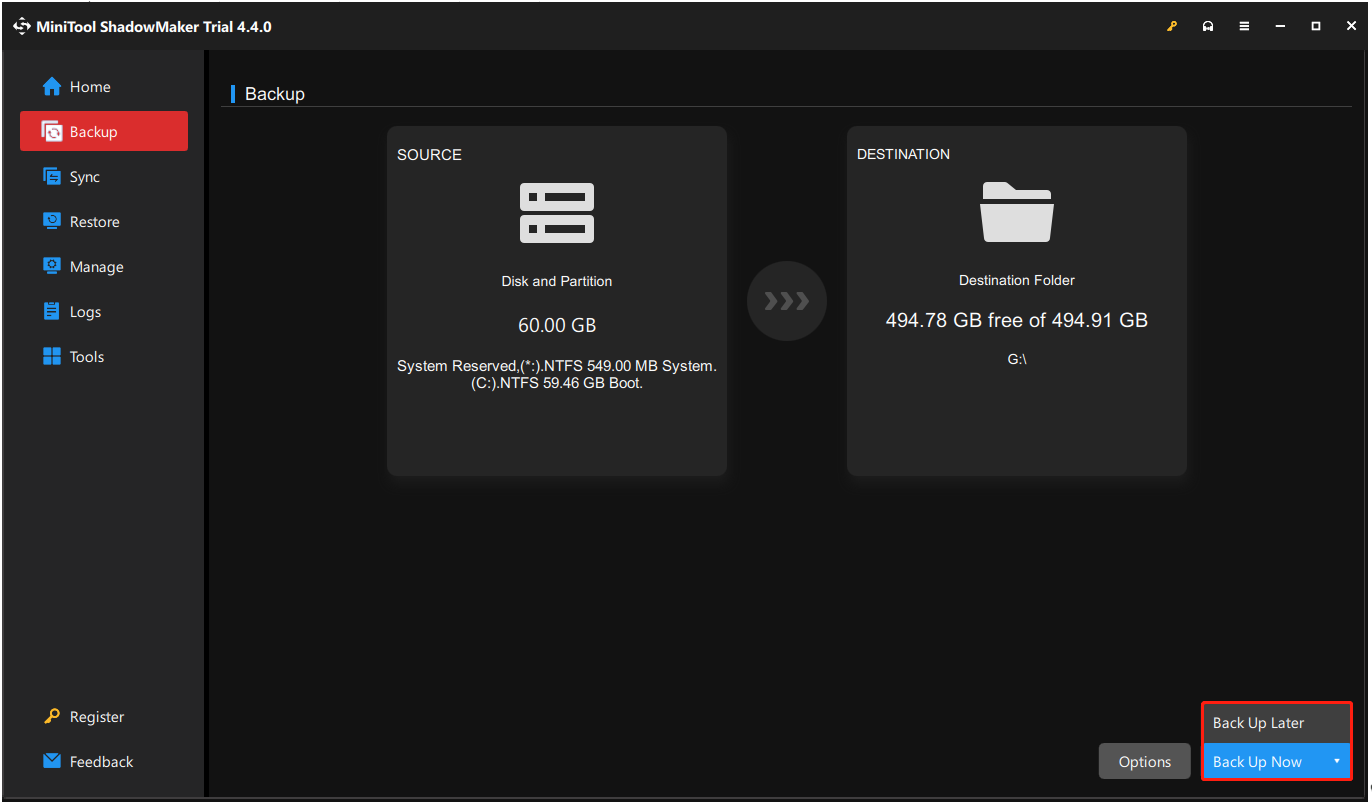
3. As you can see, system C and system reserved partition in SOURCE are chosen by default. Then, you need to select a destination path by clicking DESTINATION to store the system image. You can choose the external drive, USB flash drive, NAS, etc.
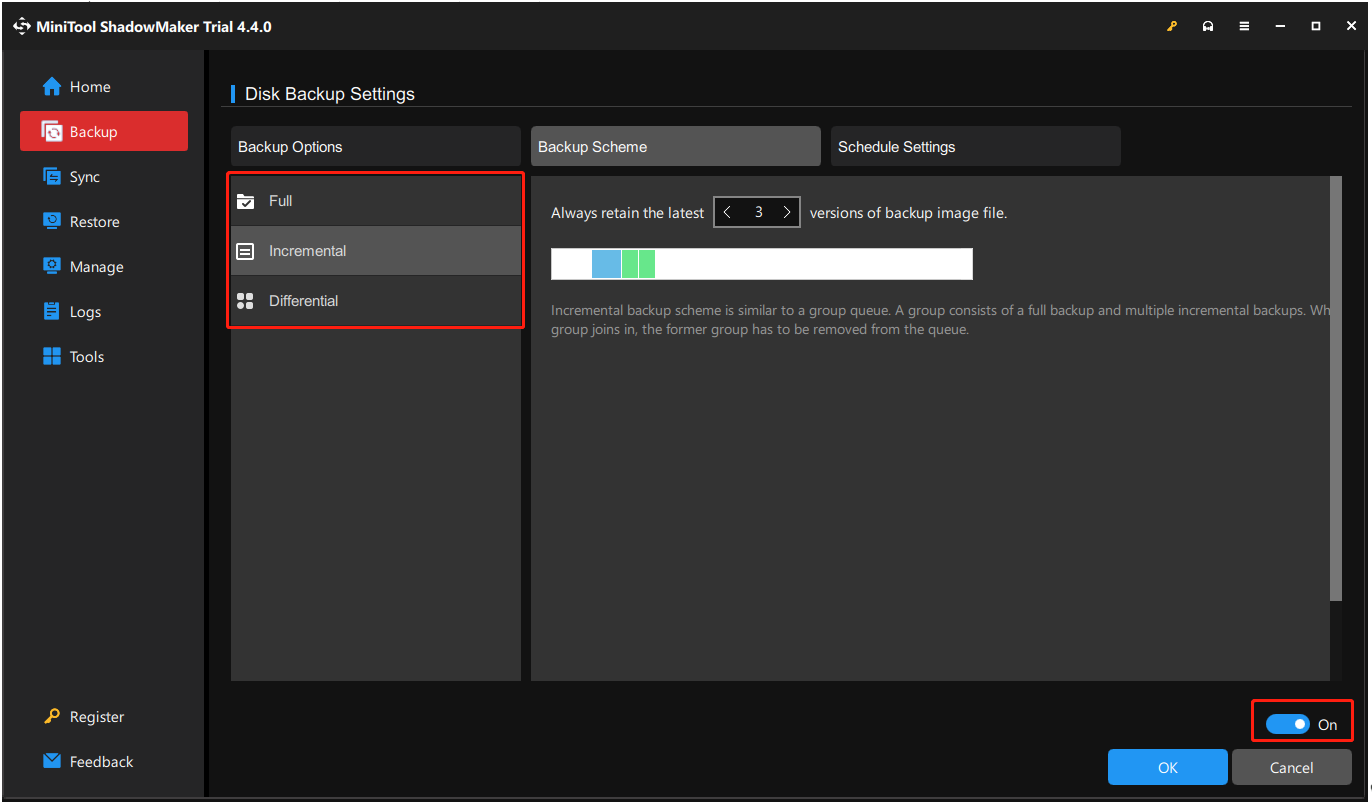
4. To set to delete the old backups, you need to go to Options and click Backup Scheme. By default, the Backup Scheme button is disabled and you need to turn it on. Here, you can choose incremental backup or differential backup.
Incremental backup: Back up the changed contents since the very last backup, such as the newly added items and the changed items. When a later group joins in, the former group has to be removed from the queue.
Example:
Always retain the latest 3 versions of the backup image file.
FULL1→INC1→INC2→FULL2→INC3→INC4(delete FULL1, INC1, INC2)→FULL3→INC5→INC6 (delete FULL2, INC3, INC4)
Differential backup: Only backs up the newly added or changed items since the first full backup. When the queue is full and a new member joins in, one of the old members will be deleted from the queue.
Example:
Always retain the latest 3 versions of the backup image file.
FULL1→DIFF1→DIFF2→FULL2 (delete DIFF1)→DIFF3 (delete DIFF2)→DIFF4 (delete FULL1)
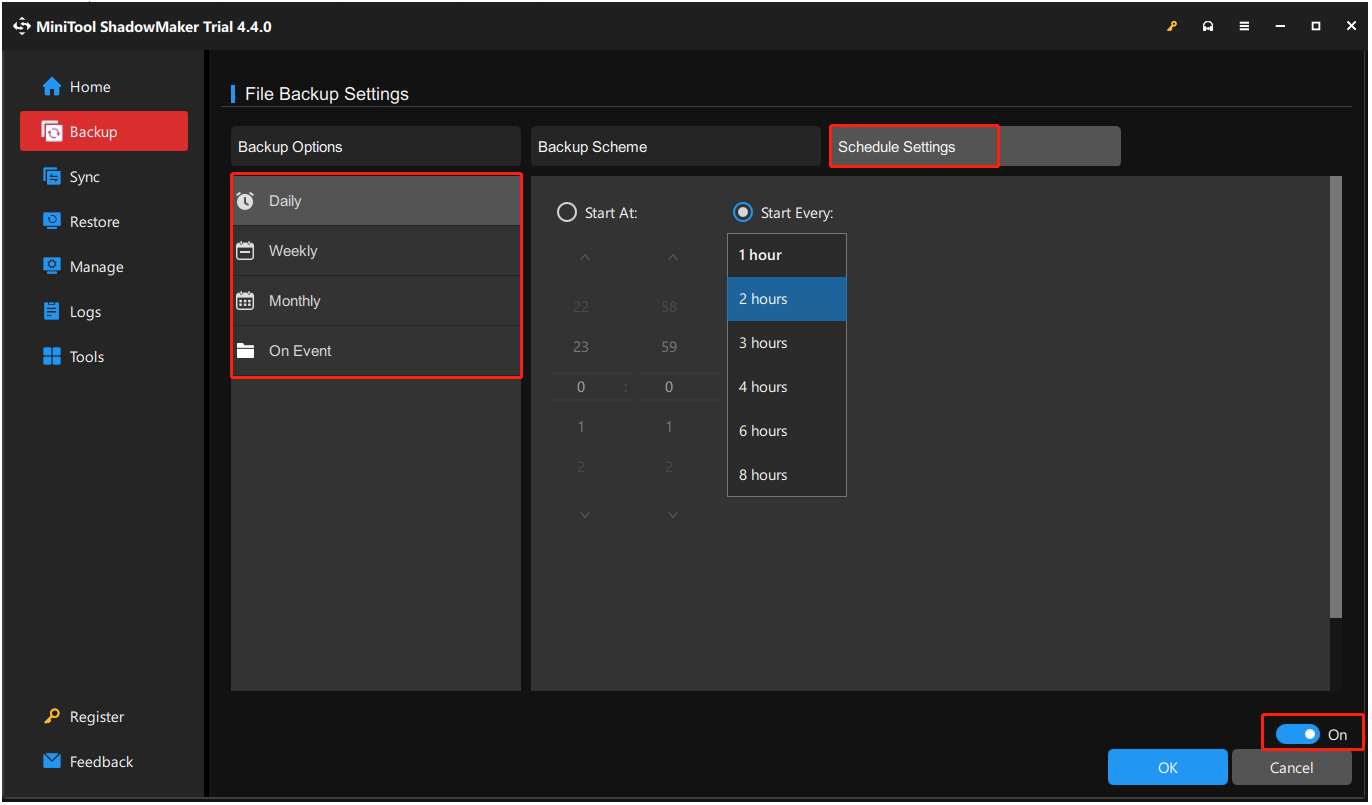
Schedule Setting is useful to make a backup regularly. You can click Options > Schedule Settings, you see this feature is disabled by default. Just enable it by switching the button to On. Then you can set it.
5. At last, click Back Up Now or Back Up Later.
Restore the backup:
Incremental: Do not manually delete backups that are scheduled for incremental backups. If you delete the backups in the last backup, the backups will be invalid since the scheduled incremental backups require the last full backup, including the last full backup and the later incremental backups.
Differential: To restore the differential backup, you should keep both the last full backup and the last differential backup.
Final Words
Have you encountered the “Windows Server Backup not deleting old backups” error? Take it easy and you can get many solutions to get rid of this error. Also, any questions on MiniTool software are appreciated and you can contact us via [email protected].
