SID (Security IDentifier) – это уникальный идентификатор, который присваивается пользователям, группам, компьютерам или другим объектам безопасности при их создании в Windows или Active Directory. Windows использует SID, а не имя пользователя для контроля доступа к различным ресурсам: сетевым папкам, ключам реестра, объектам файловой системы (NTFS разрешения), принтерам и т.д. В этой статье мы покажем несколько простых способов получить SID пользователя, группы или компьютера, и обратную процедуру – получить объект по известному SID.
Содержание:
- Что такое SID объекта в Windows?
- Как получить SID локального пользователя?
- Узнать SID пользователя или группы в домене Active Directory
- Получить SID компьютера
- Как узнать имя пользователя или группы по известному SID?
- Поиск объектов в Active Directory по SID
Что такое SID объекта в Windows?
Как мы уже сказали, SID (security identifier) позволяет уникально идентифицировать пользовали, группу или компьютер в пределах определенной области (домена или локального компьютера). SID представляет собой строку вида:
S-1-5-21-2927053466-1818515551-2824591131—1103.
В данном примере:
- 2927053466-1818515551-2824591131 – это уникальный идентификатор домена, выдавшего SID (у всего объекта в одном домене эта часть будет одинакова)
- 1103 – относительный идентификатор безопасности объекта (RID). Начинается с 1000 и увеличивается на 1 для каждого нового объекта. Выдается контроллером домена с FSMO ролью RID Master)
SIDы объектов Active Directory хранятся в базе ntds.dit, а SIDы локальных пользователей и групп в локальной базе диспетчера учетных записей Windows (SAM, Security Account Manager в ветке реестра HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SAM\SAM).
В Windows есть так называемые известные идентификаторы безопасности (Well-known SID). Это SID встроенных (BuiltIn) пользователей и групп, которые есть на любых компьютерах Windows. Например:
-
S-1-5-32-544
– встроенная группу Administrators -
S-1-5-32-545
– локальные пользователи -
S-1-5-32-555
– группа Remote Desktop Users, которым разрешен вход по RDP -
S-1-5-domainID-500
– учетная запись встроенного администратора Windows - И т.д.
В Windows можно использовать различные средства для преобразования SID -> Name и Username -> SID: утилиту whoami, wmic, WMI, классы PowerShell или сторонние утилиты.
Как получить SID локального пользователя?
Чтобы получить SID локальной учетной записи, можно воспользоваться утилитой wmic, которая позволяет обратится к пространству имен WMI (Windows Management Instrumentation) компьютера.
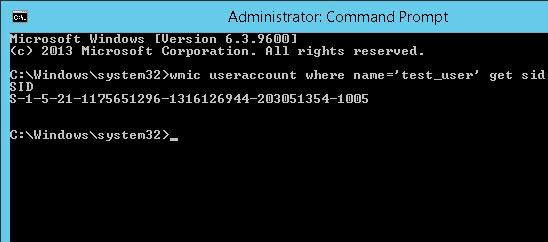
wmic useraccount where name='test_user' get sid
Команда может вернуть ошибку, если репозиторий WMI поврежден. Воспользуйтесь этой инструкцией для восстановления WMI репозитория.
Команда вернула SID указанного пользователя —
S-1-5-21-1175651296-1316126944-203051354-1005
.
Чтобы вывести список SID всех локальных пользователей Windows, выполните:
wmic useraccount get name,sid.
Если нужно узнать SID текущего пользователя (под которым выполняется команда), используйте такую команду:
wmic useraccount where name='%username%' get sid
Можно обратится к WMI напрямую из PowerShell:
(Get-CimInstance -Class win32_userAccount -Filter "name='test_user' and domain='$env:computername'").SID
В новых версиях PowerShell Core 7.x вместо команды Get-WmiObject нужно использовать Get-CimInstance.
Но еще проще получить SID локального пользователя с помощью встроенного PowerShell модуля управления локальными пользователями и группами (Microsoft.PowerShell.LocalAccounts).
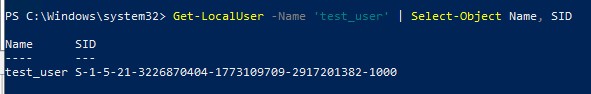
Get-LocalUser -Name 'test_user' | Select-Object Name, SID
По аналогии можно получить SID локальной группы:
Get-LocalGroup -Name tstGroup1 | Select-Object Name, SID
Также вы можете использовать.NET классы System.Security.Principal.SecurityIdentifier и System.Security.Principal.NTAccount для получения SID пользователя с помощью PowerShell:
$objUser = New-Object System.Security.Principal.NTAccount("LOCAL_USER_NAME")
$strSID = $objUser.Translate([System.Security.Principal.SecurityIdentifier])
$strSID.Value
Узнать SID пользователя или группы в домене Active Directory
Вы можете узнать SID своей доменной учетной записи командой:
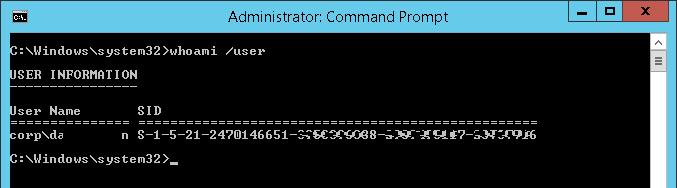
whoami /user
Получить SID пользователя домена Active Directory можно с помощью WMIC. В этом случае в команде нужно указать имя домена:
wmic useraccount where (name='jjsmith' and domain=′corp.winitpro.ru′) get sid
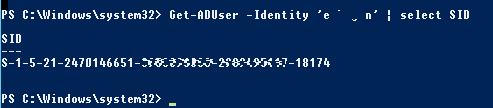
Для получения SID доменного пользователя можно воспользоваться командлетом Get-ADUser, входящего в состав модуля Active Directory Module для Windows PowerShell. Получим SID для доменного пользователя jjsmith:
Get-ADUser -Identity 'jjsmith' | select SID
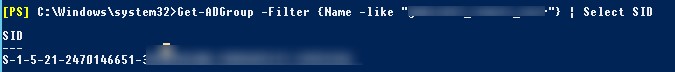
Вы можете получить SID группы AD с помощью командлета Get-ADGroup:
Get-ADGroup -Filter {Name -like "msk-admin*"} | Select SID
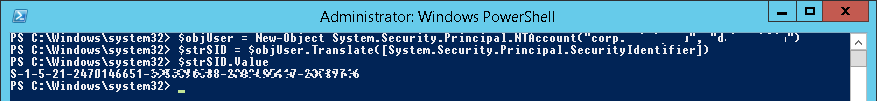
Если на вашем компьютере не установлен модуль AD для PowerShell, вы можете получить SID пользователя с помощью классов .Net:
$objUser = New-Object System.Security.Principal.NTAccount("corp.wintpro.ru","jjsmith")
$strSID = $objUser.Translate([System.Security.Principal.SecurityIdentifier])
$strSID.Value
Эта же команда PowerShell в одну строку:
(new-object security.principal.ntaccount “jjsmith").translate([security.principal.securityidentifier])
Получить SID компьютера
Если компьютер с Windows добавлен в домен Active Directory, у него будет два разных SID. Первый SID – идентификатор локального компьютера (Machine SID), а второе – уникальный идентификатор компьютера в AD.
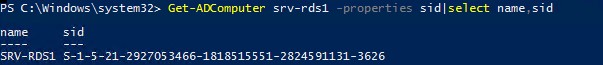
SID компьютера в домене Active Directory можно получить с помощью команды:
Get-ADComputer srv-rds1 -properties sid|select name,sid
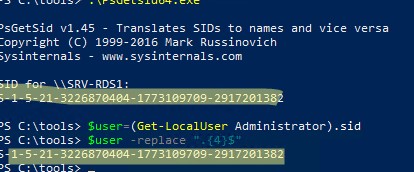
SID локального компьютера (Machine SID) можно получить с помощью бесплатной утилиты PsGetsid (https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/sysinternals/downloads/psgetsid): Но ее придется скачивать и устанавливать на каждый компьютер вручную.
.\PsGetsid64.exe
Или просто, обрезав последние 4 символа RID и SID любого локального пользователя:
$user=(Get-LocalUser Administrator).sid
$user -replace ".{4}$"
Важно, чтобы у каждого компьютера в домене был уникальный локальный SID. Если вы клонируете компьютеры или виртуальные машины, или создаете их из одного шаблона, то перед тем как добавить их в домен нужно выполнить команду sysprep. Эта утилита сбрасывает локальный Machine SID. Это избавит вас от частых ошибок “Не удалось восстановить доверительные отношения между рабочей станцией и доменом”.
Как узнать имя пользователя или группы по известному SID?
Чтобы узнать имя учетной записи пользователя по SID (обратная процедура), можно воспользоваться одной из следующих команд:
wmic useraccount where sid='S-1-3-12-12452343106-3544442455-30354867-1434' get name
Для поиска имени доменного пользователя по SID используйте командлеты из модуля
RSAT-AD-PowerShell
:
Get-ADUser -Identity S-1-5-21-247647651-3952524288-2944781117-23711116
Чтобы определить имя группы по известному SID, используйте команду:
Get-ADGroup -Identity S-1-5-21-247647651-3952524288-2944781117-23711116
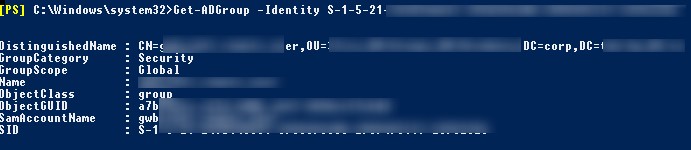
Также можно узнать получить SID группы и пользователя с помощью встроенных классов PowerShell (без использования дополнительных модулей):
$objSID = New-Object System.Security.Principal.SecurityIdentifier ("S-1-5-21-2470456651-3958312488-29145117-23345716")
$objUser = $objSID.Translate( [System.Security.Principal.NTAccount])
$objUser.Value
Поиск объектов в Active Directory по SID
Если вы не знаете к какому типу объекта AD относится SID и какой точно командлет нужно использовать для его поиска (Get-AdUser, Get-ADComputer или Get-ADGroup), вы можете использовать универсальный метод поиска объектов в Active Directory по SID с помощью командлета Get-ADObject
$sid = ‘S-1-5-21-2470146651-3951111111-2989411117-11119501’
Get-ADObject –IncludeDeletedObjects -Filter "objectSid -eq '$sid'" | Select-Object name, objectClass
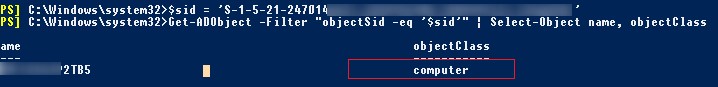
В нашем случае объект AD, который имеет данный SID, является компьютером (objectClass=computer).
on October 24, 2011
In Windows environment, each user is assigned a unique identifier called Security ID or SID, which is used to control access to various resources like Files, Registry keys, network shares etc. We can obtain SID of a user through WMIC USERACCOUNT command. Below you can find syntax and examples for the same.
Get SID of a local user
wmic useraccount where name='username' get sid
For example, to get the SID for a local user with the login name ‘John’, the command would be as below
wmic useraccount where name='John' get sid
Get SID for current logged in user
To retrieve the SID for current logged in user we can run the below command. This does not require you to specify the user name in the command. This can be used in batch files which may be executed from different user accounts.
wmic useraccount where name='%username%' get sid
Get SID for current logged in domain user
Run the command ‘whoami /user’ from command line to get the SID for the logged in user.
Example:
c:\>whoami /user USER INFORMATION ---------------- User Name SID ============== ============================================== mydomain\wincmd S-1-5-21-7375663-6890924511-1272660413-2944159 c:\>
Get SID for the local administrator of the computer
wmic useraccount where (name='administrator' and domain='%computername%') get name,sid
Get SID for the domain administrator
wmic useraccount where (name='administrator' and domain='%userdomain%') get name,sid
Find username from a SID
Now this is tip is to find the user account when you have a SID. One of the readers of this post had this usecase and he figured out the command himself with the help of the commands given above. Adding the same here.
wmic useraccount where sid='S-1-3-12-1234525106-3567804255-30012867-1437' get name
183
183 people found this article helpful
Find a user’s SID with WMIC or in the registry
Updated on January 15, 2022
What to Know
- In Command Prompt, type wmic useraccount get name,sid and press Enter.
- You can also determine a user’s SID by looking through the ProfileImagePath values in each S-1-5-21 prefixed SID listed under:
- HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows NT\CurrentVersion\ProfileList
A common reason why you might want to find the security identifier (SID) for a user’s account in Windows is to determine which key under HKEY_USERS in the Windows Registry to look for user-specific registry data. Matching SIDs to usernames is easy with the wmic command—available from the Command Prompt in most versions of Windows.
How to Find a User’s SID With WMIC
Follow these easy steps to display a table of usernames and their corresponding SIDs. It’ll probably only take a minute, maybe less, to find a user’s SID in Windows via WMIC:
See How to Find a User’s SID in the Registry further down the page for instructions on matching a username to an SID via information in the Windows Registry, an alternative method to using WMIC. The wmic command didn’t exist before Windows XP, so you’ll have to use the registry method in those older versions of Windows.
-
Open Terminal (Windows 11), or open Command Prompt in older Windows versions.
If you’re using a keyboard and mouse in Windows 11/10/8, the fastest way is through the Power User Menu, accessible with the WIN+X shortcut.
If you don’t see Command Prompt there, type cmd into the search bar in the Start menu, and select Command Prompt when you see it.
You don’t have to open an elevated Command Prompt for this to work. Some Windows commands require it, but in the WMIC command example below, you can open a regular, non-administrative Command Prompt.
-
Type the following command into Command Prompt exactly as it’s shown here, including spaces or lack thereof:
wmic useraccount get name,sid…and then press Enter.
If you know the username and would like to grab only that one user’s SID, enter this command but replace USER with the username (keep the quotes):
wmic useraccount where name="USER" get sidIf you get an error that the wmic command isn’t recognized, change the working directory to be C:\Windows\System32\wbem\ and try again. You can do that with the cd (change directory) command.
-
You should see a table displayed in Command Prompt. This is a list of each user account in Windows, listed by username, followed by the account’s corresponding SID.
Now that you’re confident a particular user name corresponds to a particular SID, you can make whatever changes you need to in the registry or do whatever else you needed this information for.
Lifewire / Emily Mendoza
Finding the Username Using the SID
If you happen to have a case where you need to find the user name but all you have is the security identifier, you can «reverse» the command like this (just replace this SID with the one in question):
wmic useraccount where sid="S-1-5-21-992878714-4041223874-2616370337-1001" get name
…to get a result like this:
Namejonfi
How to Find a User’s SID in the Registry
You can also determine a user’s SID by looking through the ProfileImagePath values in each S-1-5-21 prefixed SID listed under this key:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows NT\CurrentVersion\ProfileList
The ProfileImagePath value within each SID-named registry key lists the profile directory, which includes the username.
For example, the value under the S-1-5-21-992878714-4041223874-2616370337-1001 key on the computer you see above is C:\Users\jonfi, so we know that’s the SID for that user.
This method of matching users to SIDs will only show those users who are logged in or have logged in and switched users. To continue to use the registry method for determining other user’s SIDs, you’ll need to log in as each user on the system and repeat these steps. This is a big drawback; assuming you’re able, you’re much better off using the wmic command method above.
FAQ
-
Open the Command Prompt by pressing Windows key+R. Then, enter the following command and press Enter: whoami /user.
-
To create a new user account in Windows, go to Start > Settings > Accounts > Family & others users. Under Other users > Add other user, select Add account. Enter the user’s information and follow the prompts.
Thanks for letting us know!
Get the Latest Tech News Delivered Every Day
Subscribe
A SID or a Security Identifier is a unique code that helps identify any user or group and computer accounts across Windows Operating Systems. They are created as soon as a user account is created and being the unique identifiers, no two SIDs are the same on a common computer, ever. It is also referred to as a Security ID. This unique identification is used internally in the operating system instead of displaying names that we set like, Personal, Dad or anything else. This also means that, even if you change your display name, it will not affect anything pre-configured for that account as every configuration is tied up to the SID, which remains constant even when you change your display name or even your username.
SIDs are crucial to systems because every user account is associated with an unchangeable alphanumeric character string. Any changes to the username will not affect the user’s access to the system resources, and in case if you delete a username and later someone tries to create an account with your old username, it’s impossible to regain access to the resources as the SIDs are always unique to every username and in this case it isn’t the same.
Let us see how to find the Security Identifier (SID) of any User in Windows 11/10.
1] Using WMIC
Finding a user’s SID or Security Identifier is really easy. We must use the Windows Management Instrumentation Command Line (WMIC) to do this.
So first of all, start by, opening the Command Prompt. You can do this by searching for Command Prompt in the Cortana Search Box. Or if you are using Windows 8 or newer, hit the WINKEY + X button combination to launch a context menu on the Start Button and click on Command Prompt (Admin).
Now, type in the following command,
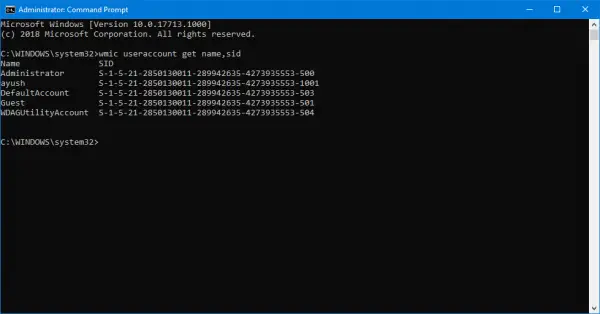
wmic useraccount get name,sid
And then hit the Enter key.
Now you will get results like in the screen snippet below. You will get the User Account with the SID of the same.
Filtering out SID for your desired user
Readers who are used to be using SQL queries might relate to this. But this command helps the user to get SID of a particular user and ignore all the hassle. This is most useful when a large system (like a server) is logged in and used simultaneously by multiple users, this command will save a lot of your time. But will only work if you know the username of the user.
Now, the command you are gonna use is-
wmic useraccount where name="USER" get sid
Now, you have to replace USER with the actual username of the user inside the quotes in the command above.
For example, it should be like-
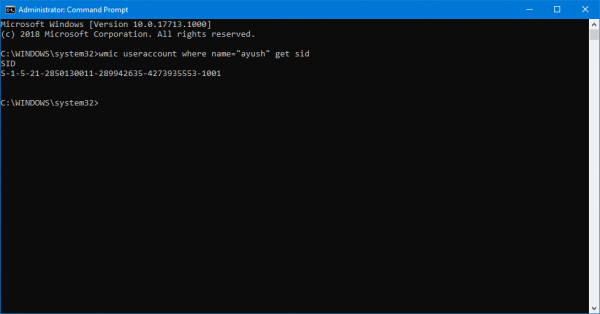
wmic useraccount where name="Ayush" get sid
In case, you get an error while using the command above, try changing the path to C:\Windows|System32|wbem instead of C:\Windows\System32\
The result of the above command would look something like this,
2] Using Whoami
Find SID of Current User using Command Prompt or PowerShell
Open a PowerShell/CMD window and type the following command:
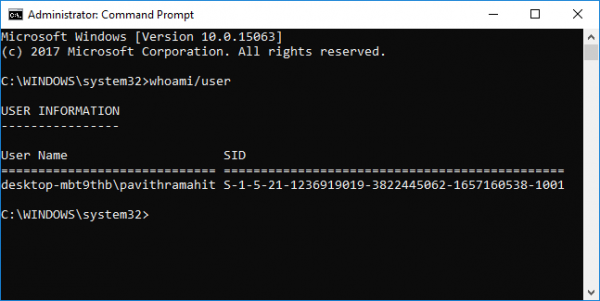
whoami/user
Press Enter.
Another way to find SID of a Current user is using the command wmic useraccount as below
Open a PowerShell/CMD window and type the following command:
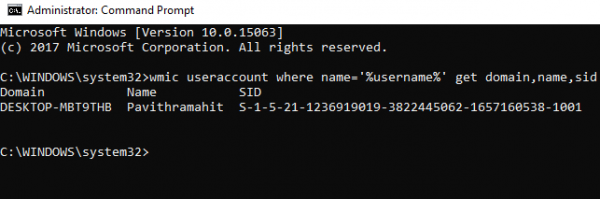
wmic useraccount where name='%username%' get domain,name,sid
Press Enter.
Find SID of All Users using Command Prompt or PowerShell
Open a Command Prompt/PowerShell window and type the following command:
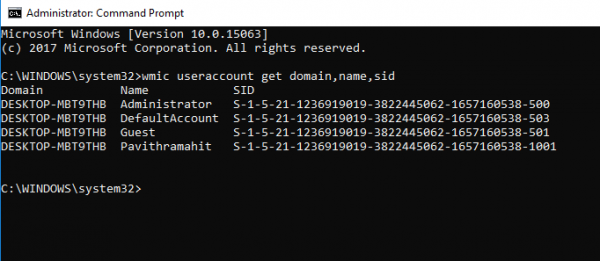
wmic useraccount get domain,name,sid
Press Enter.
Find SID of a Specific User using CommandPrompt or PowerShell
Open a Command Prompt/PowerShell and type the following command:
wmic useraccount where name='username' get sid
Give the actual name of the user in place of username in the above command.
Press Enter.
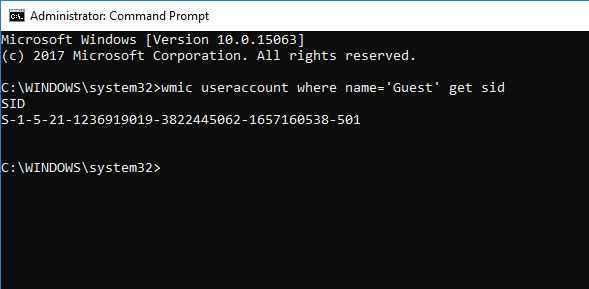
Find Username of SID using Command Prompt or PowerShell
Open a Command Prompt/PowerShell and type the following command
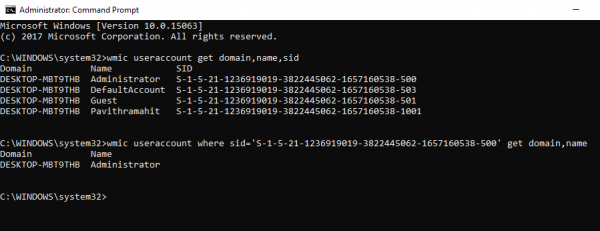
wmic useraccount where sid='<sid>' get domain,name
Give the actual SID value in place of <sid> in the above command.
Press Enter.
3] Use PowerShell
Another way to find SID of all user is using the command Get-WmiObject in the PowerShell.
Open PowerShell and type the following command:
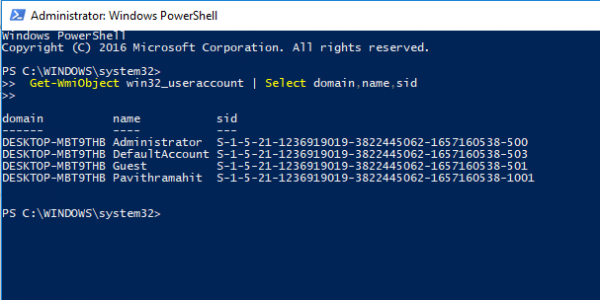
Get-WmiObject win32_useraccount | Select domain,name,sid
Press Enter.
4] Using the Registry Editor
Here, start by opening the Registry Editor. You can do it by searching for it in the Cortana Search box or just hit WINKEY + R combination to launch start and type in regedit and then hit Enter.
Once you have opened the Registry Editor, navigate to the following path,
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows NT\CurrentVersion\ProfileList
Now, inside the ProfileImagePath values for each SID under the folder of ProfileList, you can find the desired SIDs and other details like Usernames. The page would look similar to this screen snippet below.
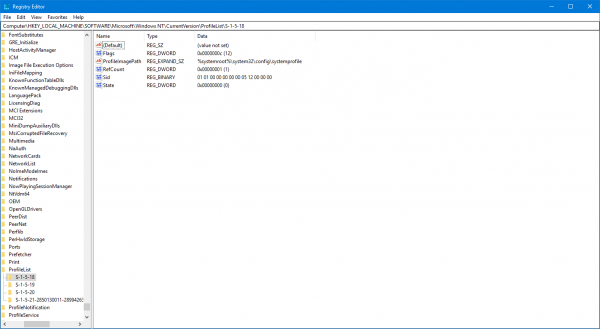
It is worth noting that you can find the SIDs for the users who are already logged in to the computer. Either they should be accessing their account remotely or their account should be logged in and then switched to another user on whose account this activity is being done. This is the only drawback of this method but the Method 1 of using WMIC, it is not an issue at all.
Identifying SIDs
A SID in the format of S-1-0-0 is called as a Null SID. It is assigned to a SID when its value is unknown or it is assigned to a group without any members.
Also, a SID in the format of S-1-1-0 is a World SID. It is assigned to a group of every user.
Finally, a SID in the format of S-1-2-0 is called as a Local SID. It is assigned to a user who is supposed to be logged in from a local terminal.
You can learn more about these System Identifiers here on Microsoft Developer Network.
With inputs from Pavithra Bhat
-
This opens the Windows “power user” menu at the bottom-left corner of the screen.
-
A confirmation message will appear.
Advertisement
-
Now you’ll see a terminal window displaying the command prompt.
-
This is the command to display the SIDs of all user accounts on the system.
- If you know the person’s username, use this command instead: wmic useraccount where name="USER" get sid (but replace USER with the username).[1]
- If you know the person’s username, use this command instead: wmic useraccount where name="USER" get sid (but replace USER with the username).[1]
-
The SID is the long number that appears after each username.
Advertisement
Add New Question
-
Question
What is a Windows SID?
An SID, or «security identifier,» is a unique number used to identify users, groups, and computer accounts in Windows. SIDs are generated when an account is created, ensuring that no two SIDs on a computer are identical. The term «security ID» is sometimes used interchangeably with SID.
Ask a Question
200 characters left
Include your email address to get a message when this question is answered.
Submit
Advertisement
Thanks for submitting a tip for review!
References
About This Article
Thanks to all authors for creating a page that has been read 294,718 times.
Is this article up to date?
wikiHow Tech Help:
Tech troubles got you down? We’ve got the tips you need
Subscribe
You’re all set!
—
—





