PATH is an environment variable that specifies a set of directories, separated with semicolons (;), where executable programs are located.
In this note i am showing how to print the contents of Windows PATH environment variable from the Windows command prompt.
I am also showing how to add a directory to Windows PATH permanently or for the current session only.
Cool Tip: List environment variables in Windows! Read More →
Print the contents of the Windows PATH variable from cmd:
C:\> path
– or –
C:\> echo %PATH%
The above commands return all directories in Windows PATH environment variable on a single line separated with semicolons (;) that is not very readable.
To print each entry of Windows PATH variable on a new line, execute:
C:\> echo %PATH:;=&echo.%
- sample output -
C:\WINDOWS\system32
C:\WINDOWS
C:\WINDOWS\System32\Wbem
C:\WINDOWS\System32\WindowsPowerShell\v1.0\
C:\WINDOWS\System32\OpenSSH\
C:\Program Files\Intel\WiFi\bin\
C:\Program Files\Common Files\Intel\WirelessCommon\
C:\Program Files (x86)\Intel\Intel(R) Management Engine Components\DAL
C:\Program Files\Intel\Intel(R) Management Engine Components\DAL
C:\Program Files\Microsoft VS Code\bin
C:\Users\Admin\AppData\Local\Microsoft\WindowsApps
Cool Tip: Set environment variables in Windows! Read More →
Add To Windows PATH
Warning! This solution may be destructive as Windows truncates PATH to 1024 characters. Make a backup of PATH before any modifications.
Save the contents of the Windows PATH environment variable to C:\path-backup.txt file:
C:\> echo %PATH% > C:\path-backup.txt
Set Windows PATH For The Current Session
Set Windows PATH variable for the current session:
C:\> set PATH="%PATH%;C:\path\to\directory\"
Set Windows PATH Permanently
Run as Administrator: The setx command is only available starting from Windows 7 and requires elevated command prompt.
Permanently add a directory to the user PATH variable:
C:\> setx path "%PATH%;C:\path\to\directory\"
Permanently add a directory to the system PATH variable (for all users):
C:\> setx /M path "%PATH%;C:\path\to\directory\"
Info: To see the changes after running setx – open a new command prompt.
Was it useful? Share this post with the world!
Users can run an executable from windows command prompt either by giving the absolute path of the file or just by the executable file name. In the latter case, Windows searches for the executable in a list of folders which is configured in environment variables. These environment variables are as below.
1. System path
2. User path
The values of these variables can be checked in system properties( Run sysdm.cpl from Run or computer properties). Initially user specific path environment variable will be empty. Users can add paths of the directories having executables to this variable. Administrators can modify the system path environment variable also.
How to set path from command line?
In Vista, Windows 7 and Windows 8 we can set path from command line using ‘setx’ command.
setx path "%path%;c:\directoryPath"
For example, to add c:\dir1\dir2 to the path variable, we can run the below command.
setx path "%path%;c:\dir1\dir2"
Alternative way is to use Windows resource kit tools ‘pathman.exe‘. Using this command we can even remove a directory from path variable. See download windows resource kit tools. This works for Windows 7 also.
Add directory to system path environment variable:
Open administrator command prompt
Run the below command
pathman /as directoryPath
Remove path from system path environment variable:
Run the below command from elevated command prompt
pathman /rs directoryPath
Setting user path environment variable
For user environment varlables, admin privileges are not required. We can run the below command to add a directory to user path environment variable.
pathman /au directoryPath
To remove a directory from user path, you can run the below command.
pathman /ru directoryPath
Default option is not allowed more than ‘2’ time(s)
You get this error if you have not enclosed ‘path’ in double quotes. See the below example for setting the path of firefox.
C:\Users\>setx path %path%;"c:\Program Files (x86)\Mozilla Firefox\" ERROR: Invalid syntax. Default option is not allowed more than '2' time(s). Type "SETX /?" for usage.
Now if you move %path% to be in the double quotes
C:\Users\>setx path "%path%;c:\Program Files (x86)\Mozilla Firefox\" SUCCESS: Specified value was saved. C:\Users\>
To set the PATH environment variable in Windows Command Prompt, you can use the following command to add a directory to your system’s PATH.
set PATH=%PATH%;C:\Your\Directory\Path
Understanding the PATH Variable
What is the PATH Variable?
The PATH variable is an environment variable that tells the operating system where to look for executable files. When you type a command in the Windows CMD interface, the system searches through the directories listed in the PATH variable to find the corresponding executable. Without a properly set PATH, you would need to specify the entire directory path every time you want to run a program, which can be inefficient and cumbersome.
Why You Need to Set the PATH
Setting the PATH has a profound impact on your workflow. This convenience allows you to execute programs from any directory without the need for the full path. For developers, this is especially crucial as it simplifies the execution of scripts and tools, enabling a more efficient workflow. Additionally, it minimizes errors associated with typing long paths, ultimately saving you time and effort.

Repair Cmd Windows 10: Quick Commands to Fix Issues
How to View the Current PATH Variable
Using the CMD Command
To view your current PATH variable, open the Command Prompt and execute the following command:
echo %PATH%
This command will output a list of directories, separated by semicolons. Each directory listed is a location where Windows will look for executable files. Be mindful of how this variable is structured, as it is essential for understanding how to effectively manage it.
Alternative Method: System Properties
Alternatively, you can view the PATH variable through the system properties. Here’s how:
- Right-click on This PC or Computer on your desktop or in File Explorer.
- Select Properties.
- Click on Advanced system settings on the left.
- In the System Properties window, click on the Environment Variables button.
Here, you will find the PATH variable listed under System variables. This method provides additional context and allows you to edit the PATH variable directly, though it is primarily for those who are more comfortable with graphical interfaces.

List Disk Cmd Windows: Quick Guide to Disks Management
Setting the PATH Variable in CMD
Temporary Changes using `set` Command
If you want to make a temporary change to the PATH variable (one that lasts only for the duration of your current CMD session), you can use the `set` command. Here is how you can add a new directory to your existing PATH:
set PATH=%PATH%;C:\NewFolder
This command appends `C:\NewFolder` to the current PATH. However, remember that this change will not persist once you close the Command Prompt window. The original PATH value will be restored in the next session.
Persistent Changes using `setx` Command
For permanent changes to the PATH variable, you will want to utilize the `setx` command. This command enables you to set environment variables permanently in the user or system context. Here’s how to set a new permanent PATH:
setx PATH "%PATH%;C:\PermanentFolder"
It’s crucial to note that `setx` will fail if your PATH exceeds a certain length limitation—generally around 2048 characters. If this occurs, you may need to trim or reorganize your existing PATH entries before continuing.

Mastering Diskpart Cmd Windows 10: Your Quick Guide
Common Issues When Setting the PATH
Overwriting Existing PATH Variables
One of the most common pitfalls when updating the PATH variable is accidentally overwriting existing entries. If you use the `set` or `setx` command without including the existing PATH, you could erase all previously defined paths.
To append a new path without loss, always ensure you are using the `%PATH%` placeholder in your command. This practice preserves the existing entries while adding your changes.
Handling Special Characters and Spaces
When dealing with paths containing spaces, extra caution is required. Commands should be enclosed in quotation marks to ensure correct interpretation. For example, if you want to add a path to a program installed in «Program Files»:
setx PATH "%PATH%;C:\Program Files\MyApp"
Failing to include the quotes may lead to errors, as CMD can misinterpret the path as separate commands.
Checking for Successful Updates
To confirm whether your changes to the PATH variable were successful, use the following command:
echo %PATH%
Re-running this command will allow you to check for the newly included paths. If your addition appears in the echoed list, you have successfully updated your PATH variable.
Reboot Cmd Windows 10: A Quick Guide to Restarting
Best Practices for Managing the PATH Variable
Keeping PATH Entries Organized
For enhanced productivity, maintaining organization within the PATH variable is essential. Regularly clean up entries, especially after uninstalling software, to avoid confusion caused by multiple similar paths. Keeping the paths concise and relevant ensures that Windows can locate executables efficiently.
Regularly Reviewing PATH Entries
It’s good practice to schedule regular reviews of your PATH variable. Over time, software installations accumulate, and changes may lead to redundant or outdated paths. Consider making it a habit to review entries at least once every few months to maintain an efficient environment.

Open a Cmd Window: Your Quick Guide to Command Prompt
Conclusion
Setting the PATH variable in CMD is an essential skill for anyone who frequently uses the Windows command line. By managing this variable effectively, you can streamline your command execution and enhance your overall productivity. Remember, practice makes perfect—so don’t hesitate to experiment with setting and verifying your PATH variable to master it!

Reset Password Windows 11 Cmd: A Quick Guide
Additional Resources
If you’re eager to expand your knowledge of CMD commands, look for related articles or tutorials that delve deeper into managing environment variables and other CMD functionalities. Additionally, various third-party tools can assist with environment variable management, providing even greater ease and efficiency in your workflows.
Do you know, how to set the patch from the command line? The Windows command prompt allows users to run executable files by supplying the absolute path to the file. Regardless of whether it’s just an executable file name. Depending on which environment variable is associated with the executable, Windows will search across a list of folders. The following variables are part of the environment.
![Set Path from Command Line [Add to Path Windows]](https://windowscommand-line.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/04/Set-Path-from-Command-Line.jpg)
A. System path &
B. User path
In the system properties, you can check the values of these variables (run the sysdm.cpl from computer properties or Run). User-specific paths are initially empty in the environment variable. This variable can be used to specify paths to directories containing executables. Administrators can also modify the environment variable indicating the path to the system.
Using the command line, how do you set a path?
Set paths from the command line in Windows 7 and Windows 10 by using the “setx” command.
setx path "%path%;c:\directoryPath"
The following command can be run to add c:/dir1/dir2 to the path variable.
setx path "%path%;c:\dir1\dir2"
It is also possible to use “pathman.exe” from the Windows resource kit. In addition to removing a directory from the path variable, we are also able to use the command described above. The same applies to Windows 7 as well.
Add directory to system path to set environment variable Windows cmd:
Step-1: Open the command prompt from the administrator.
Step-2: Then you need to run the following command below.
pathman /as directoryPath
Environment variable for system path should be removed:
From an elevated command prompt, execute the following command.
pathman /rs directoryPath
An environment variable to set the user path:
Users do not need admin privileges to access user environment variables. Add the following command to the environment variable user path to add a directory.
pathman /au directoryPath
Here is the command you can run to remove the directories from the user path.
pathman /ru directoryPath
As a default, ‘2’ times is the maximum amount of time you can allow each user:
Having no double quotes around ‘path’ results in this error. For an example of setting the Firefox path, see the following.
C:\Users\>setx path %path%;"c:\Program Files (x86)\Mozilla Firefox\" ERROR: Invalid syntax. Default option is not allowed more than '2' time(s). Type "SETX /?" for usage.
When you move %path% inside double quotes it will look like this:
C:\Users\>setx path "%path%;c:\Program Files (x86)\Mozilla Firefox\" SUCCESS: Specified value was saved. C:\Users\>
Read: Stop Windows Update Service CMD
Для быстрого доступа к командам в командной строке без необходимости ввода полного пути к исполняемому файлу можно добавить путь к папке с этими исполняемыми файлами в переменную PATH в Windows, особенно это может быть полезным при работе с adb, pip и python, git, java и другими средствами разработки с отладки.
В этой пошаговой инструкции о том, как добавить нужный путь в системную переменную PATH в Windows 11, Windows 10 или другой версии системы: во всех актуальных версиях ОС действия будут одинаковыми, а сделать это можно как в графическом интерфейсе, так и в командной строке или PowerShell. Отдельная инструкция про переменные среды в целом: Переменные среды Windows 11 и Windows 10.
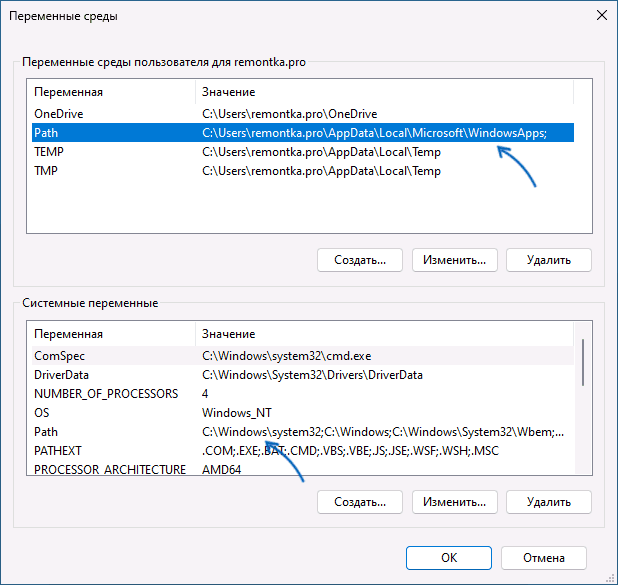
Добавление пути в PATH в Свойствах системы
Для возможности запуска команд простым обращением к исполняемому файлу без указания пути, чтобы это не вызывало ошибок вида «Не является внутренней или внешней командой, исполняемой программой или пакетным файлом», необходимо добавить путь к этому файлу в переменную среды PATH.
Шаги будут следующими:
- Нажмите клавиши Win+R на клавиатуре (в Windows 11 и Windows 10 можно нажать правой кнопкой мыши по кнопке Пуск и выбрать пункт «Выполнить»), введите sysdm.cpl в окно «Выполнить» и нажмите Enter.
- Перейдите на вкладку «Дополнительно» и нажмите кнопку «Переменные среды».
- Вы увидите список переменных среды пользователя (вверху) и системных переменных (внизу). PATH присутствует в обоих расположениях.
- Если вы хотите добавить свой путь в PATH только для текущего пользователя, выберите «Path» в верхней части и нажмите «Изменить» (или дважды нажмите по переменной PATH в списке). Если для всех пользователей — то же самое в нижней части.
- Для добавления нового пути нажмите «Создать», а затем впишите новый путь, который требуется добавить в переменную PATH в новой строке. Вместо нажатия «Создать» можно дважды кликнуть по новой строке для ввода нового пути.
- После ввода всех необходимых путей нажмите «Ок» — ваша папка или папки добавлены в переменную PATH.
Внимание: после добавления пути в переменную PATH потребуется перезапустить командную строку (если она была запущена в момент изменения), чтобы использовать команды без указания полного пути.
Как добавить путь в переменную PATH в командной строке и PowerShell
Вы можете добавить переменную PATH для текущей сессии в консоли: то есть она будет работать до следующего запуска командной строки. Для этого используйте команду:
set PATH=%PATH%;C:\ваш\путь
Есть возможность добавить путь в PATH с помощью командной строки и на постоянной основе (внимание: есть отзывы, что может повредить записи в переменной PATH, а сами изменения производятся для системной переменной PATH), команда будет следующей:
setx /M path "%path%;C:\ваш\путь"

Набор команд для добавления пути в переменную PATH пользователя с помощью PowerShell:
$PATH = [Environment]::GetEnvironmentVariable("PATH")
$my_path = "C:\ваш\путь"
[Environment]::SetEnvironmentVariable("PATH", "$PATH;$my_path", "User")
Если требуется добавить путь в системную переменную PATH для всех пользователей, последнюю команду изменяем на:
[Environment]::SetEnvironmentVariable("PATH", "$PATH;$my_path", "Machine")