Skip to content
При попытке установить любой пакет через NuGet в Visual Studio 2013 (VS 2013) получаю сообщение об ошибке:
Install failed. Rolling back…
Failed to initialize the PowerShell host. If your PowerShell execution policy setting is set to AllSigned, open the Package Manager Console to initialize the host first.
При попытке вызвать консоль в VS 2013 — View — Other Windows — Package Manager Console так же получаю сообщение об ошибке:
Windows PowerShell updated your execution policy successfully, but the setting is overridden by a policy defined at a more specific scope. Due to the override, your shell will retain its current effective execution policy of Unrestricted. Type «Get-ExecutionPolicy -List» to view your execution policy settings. For more information please see «Get-Help Set-ExecutionPolicy».
В групповой политике (gpedit.msc) выставлены настройки



И всё равно, при попытке в Power Shell Console выставить нужные политики, с помощью Set-ExecutionPolicy AllSigned — получаю сообщение об ошибке:
Set-ExecutionPolicy : Оболочка Windows PowerShell успешно обновила вашу политику выполнения, но данный параметр переопределяется политикой, определенной в более конкретной области. В связи с переопределением оболочка сохранит текущую политику выполнения «Unrestricted». Для просмотра параметров политики выполнения введите «Get-ExecutionPolicy -List». Для получения дополнительных сведений введите «Get-Help Set-ExecutionPolicy».
строка:1 знак:1
+ Set-ExecutionPolicy AllSigned
+ ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
+ CategoryInfo : PermissionDenied: (:) [Set-ExecutionPolicy], SecurityException
+ FullyQualifiedErrorId : ExecutionPolicyOverride,Microsoft.PowerShell.Commands.SetExecutionPolicyCommand

РЕШЕНИЕ: Мне помогло, установка параметра реестра ExecutionPolicy = Bypass в разделе HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Policies\Microsoft\Windows\PowerShell
на всякий случай установил такое же значение еще и здесь
HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Software\Policies\Microsoft\Windows\PowerShell
После этого консоль в Visual Studio и NuGet заработали.
А политики стали такими:

По-умолчанию настройки Windows запрещают запуск скриптов PowerShell. Это необходимо для предотвращения запуска вредоносного кода на PowerShell. Настройки политик запуска PowerShell скриптов определяются в Execution Policy. В этой статье мы рассмотрим доступные политики запуска PS скриптов, как изменить Execution Policy и настроить политики использования PowerShell скриптов на компьютерах в домене.
Содержание:
- Выполнение PowerShell скриптов запрещено для данной системы
- Как разрешить запуск скриптов PowerShell с помощью Execution Policy?
- Настройка PowerShell Execution Policy с помощью групповых политик
- Способы обхода политики PowerShell Execution
Выполнение PowerShell скриптов запрещено для данной системы
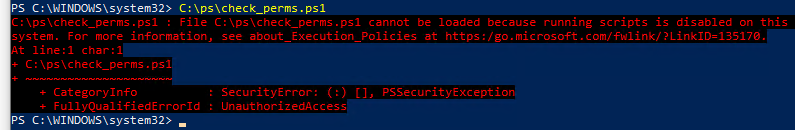
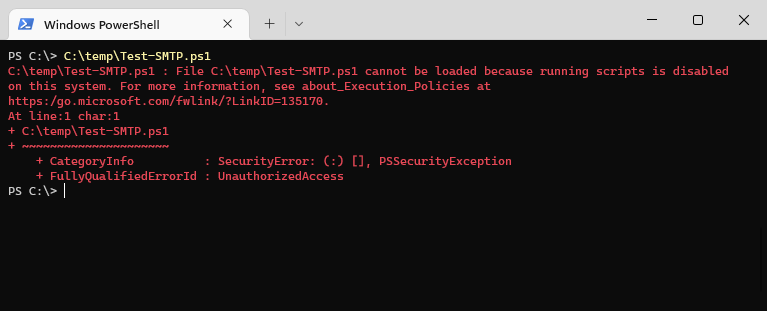
При попытке выполнить PowerShell скрипт (файл с расширением PS1) на чистой Windows 10, появляется ошибка:
File C:\ps\.ps1 cannot be loaded because running scripts is disabled on this system. For more information, see about_Execution_Policies at https:/go.microsoft.com/fwlink/?LinkID=135170. + CategoryInfo : SecurityError: (:) [], PSSecurityException + FullyQualifiedErrorId : UnauthorizedAccess
Не удается загрузить файл.ps1, так как выполнение скриптов запрещено для данной системы.
Текущее значение политики выполнения скриптов PowerShell на компьютере можно получить командой:
Get-ExecutionPolicy
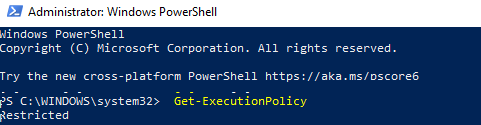
Доступны следующие значения PowerShell Execution Policy:
- Restricted – запрещен запуск скриптов PowerShell, можно выполнять только интерактивные команды в консоли;
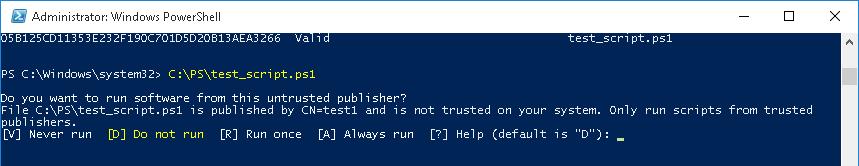
- AllSigned – разрешено выполнять только подписанные PS скрипты с цифровой подписью от доверенного издателя (можно подписать скрипт самоподписанным сертификатом и добавить его в доверенные). При запуске недоверенных скриптов появляется предупреждение:
Do you want to run software from this untrusted publisher? File .ps1 is published by CN=test1 and is not trusted on your system. Only run scripts from trusted publishers
- RemoteSigned – можно запускать локальные PowerShell скрипты без ограничения. Можно запускать удаленные PS файлы с цифровой подписью (нельзя запустить PS1 файлы, скачанные из Интернета, запущенные из сетевой папки по UNC пути и т.д.);
- Unrestricted – разрешен запуск всех PowerShell скриптов;
При запуске сторонних PowerShell скриптов может появляется предупреждение с подтверждением запуска, см. ниже.
- Bypass – разрешён запуск любых PS файлов (предупреждения не выводятся) – эта политика обычно используется для автоматического запуска PS скриптов без вывода каких-либо уведомлений (например при запуске через GPO, SCCM, планировщик и т.д.) и не рекомендуется для постоянного использования;
- Default – сброс настроек выполнения скриптов на стандартную;
В Windows 10 значение политики выполнения PowerShell по-умолчанию Restricted, а в Windows Server 2016 — RemoteSigned.
- Undefined – не задано. Применяется политика Restricted для десктопных ОС и RemoteSigned для серверных.
Как разрешить запуск скриптов PowerShell с помощью Execution Policy?
Чтобы изменить текущее значение политики запуска PowerShell скриптов, используется командлет Set-ExecutionPolicy.
Например, разрешим запуск локальных скриптов:
Set-ExecutionPolicy RemoteSigned
Подтвердите изменение политики запуска PS1 скриптов, нажав Y или A.
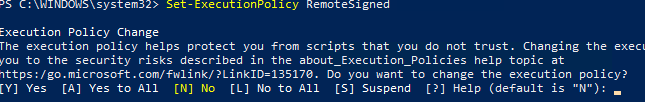
Чтобы запрос не появлялся, можно использовать параметр Force.
Set-ExecutionPolicy RemoteSigned –Force
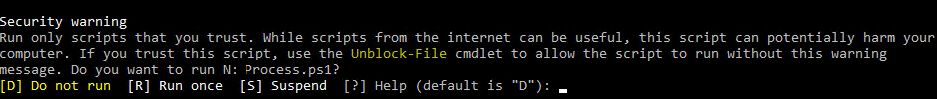
Если вы установили значение политики PowerShell Execution Policy в Unrestricted, то при запуске удаленных скриптов из сетевых каталогов по UNC пути, скачанных из интернета файлов, все равно будет появляться предупреждение:
Security warning Run only scripts that you trust. While scripts from the internet can be useful, this script can potentially harm your computer. If you trust this script, use the Unblock-File cmdlet to allow the script to run without this warning message. Do you want to run? [D] Do not run [R] Run once [S] Suspend [?] Help (default is "D")
Как PowerShell различает локальные и удаленные скрипты? Все дело в идентификаторе зоны ZoneId, которую выставляет браузер в альтернативном потоке при загрузке файла (см. статью “Как Windows определяет, что файл скачан из Интернета?”). Вы можете разблокировать такой файл, поставив галку “Разблокирвать” в его свойствах или очиститься метку зоны с помощью комадлета Unblock-File.
Также следует различать различные области действия политик выполнения скриптов PowerShell (scopes):
- MachinePolicy – действует для всех пользователей компьютера, настраивается через GPO;
- UserPolicy – действует на пользователей компьютера, также настраивается через GPO;
- Process — настройки ExecutionPolicy действует только для текущего сеанса PowerShell.exe (сбрасываются при закрытии процесса);
- CurrentUser – политика ExecutionPolicy применяется только к текущему пользователю (параметр из ветки реестра HKEY_CURRENT_USER);
- LocalMachine – политика для всех пользователей компьютера (параметр из ветки реестра HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE);
Область применения политики можно указать с помощью параметр Scope командлета Set-ExecutionPolicy. Например:
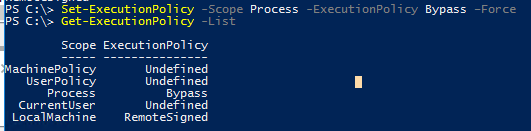
Set-ExecutionPolicy -Scope Process -ExecutionPolicy Bypass –Force
Проверим текущие настройки ExecutionPolicy для всех областей:
Get-ExecutionPolicy -List
Scope ExecutionPolicy ----- --------------- MachinePolicy Undefined UserPolicy Undefined Process Bypass CurrentUser Undefined LocalMachine RemoteSigned
Значение политики выполнения, которые вы задаете с помощью командлета Set-ExecutionPolicy для областей CurrentUser и LocalMachine, хранятся в реестре. Например, выполните командлет:
Set-ExecutionPolicy -Scope LocalMachine -ExecutionPolicy Restricted –Force
Откройте ветку реестра HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\PowerShell\1\ShellIds\Microsoft.PowerShell и проверьте значение REG_SZ параметра ExecutionPolicy. Оно изменилось на Restricted (допустимые значения параметра Restricted, AllSigned, RemoteSigned, Bypass, Unrestricted и Undefined).
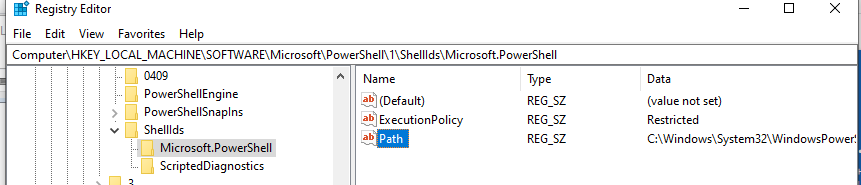
Аналогичные настройки для области CurrentUser находятся в разделе реестра пользователя HKEY_CURRENT_USER\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\PowerShell\1\ShellIds\Microsoft.PowerShell.
Отметим, что чаще всего в корпоративной среде используется ExecutionPolicy со значением AllSigned на уровне LocalMachine. Это обеспечивает максимальный баланс между безопасностью и удобством. Для личного пользования на компьютере можно использовать RemoteSigned. Ну а Bypass политику лучше использовать только для запуска отдельных задач (например для запуска скриптов через GPO или заданий планировщика).
Настройка PowerShell Execution Policy с помощью групповых политик
Вы можете настроить политику выполнения PowerShel скриптов на серверах или компьютерах домена с помощью групповых политик.
- С помощью редактора доменных GPO (gpmc.msc) создайте новую GPO (или отредактируйте) существующую и назначьте ее на OU с компьютерами, к которым нужно применить политику запуска PowerShell скриптов;
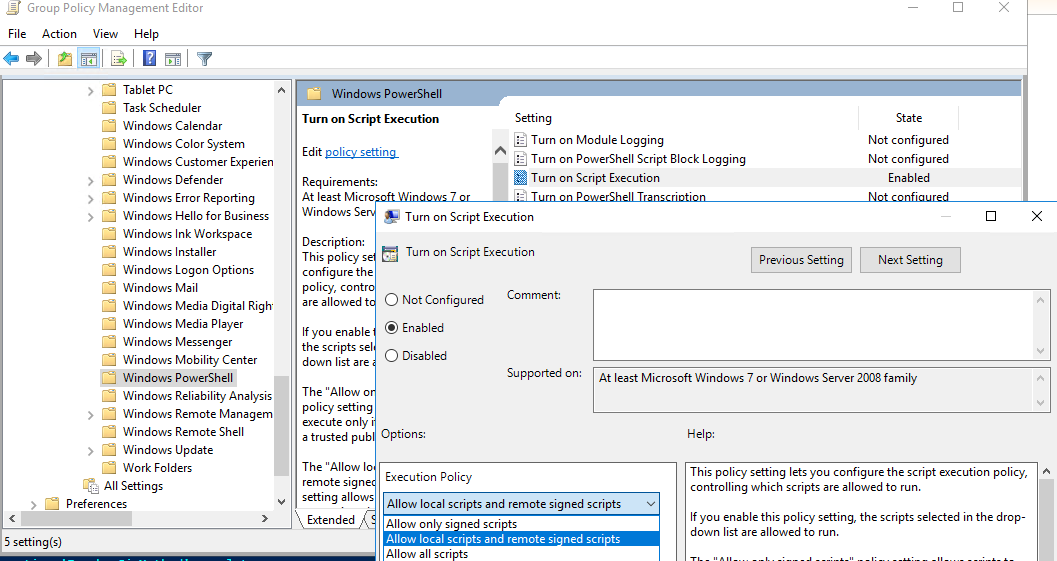
- В редакторе политики перейдите в раздел Computer Configuration -> Policies -> Administrative Templates -> Windows Components -> Windows PowerShell и найдите политику Turn on Script Execution (Включить выполнение сценариев);
Аналогичная политика есть в пользовательском разделе GPO — User Configuration, но политика компьютера имеет приоритет.
- Для политики доступны три значения:
- Allow only signed scripts (Разрешать только подписанные сценарии) — соответствует политике AllSigned;
- Allow local scripts and remote signed scripts (Разрешать локальные и удаленные подписанные сценарии) — соответствует политике PS RemoteSigned;
- Allow all scripts (Разрешать все сценарии) — политика Unrestricted.
- Выберите необходимое значение политики, сохраните GPO и обновите политики на компьютере.
- Проверьте, что для области MachinePolicy теперь действуют новые настройки выполнения.
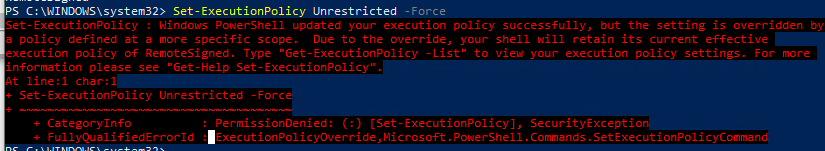
После настройки политики выполнения через GPO вы не сможете изменить настройки политики выполнения скриптов вручную. При попытке изменить настройки Execution Policy на компьютере, на который применяется такая GPO, появится ошибка:
Set-ExecutionPolicy : Windows PowerShell updated your execution policy successfully, but the setting is overridden by a policy defined at a more specific scope. Due to the override, your shell will retain its current effective execution policy of RemoteSigned. Type "Get-ExecutionPolicy -List" to view your execution policy settings.
Способы обхода политики PowerShell Execution
Есть несколько трюков, которые могут помочь вам, когда нужно запустить на компьютере PowerShell скрипт, не изменяя настройки политики выполнения. Например, я хочу запустить простой PS1 скрипт, который поверяет, что запущен с правами администратора.
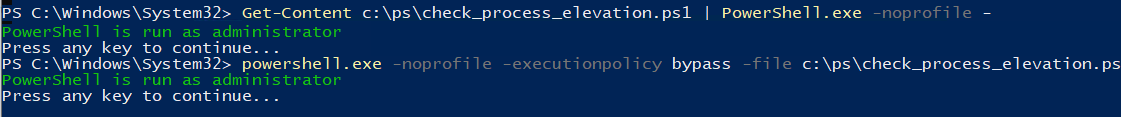
Можно с помощью Get-Content получить содержимое скрипта и перенаправить его в стандартныq поток ввода консоли PS.
Get-Content c:\ps\check_process_elevation.ps1 | PowerShell.exe -noprofile –
Либо можно запустить новый процесс powershell.exe с политикой выполнения Bypass:
powershell.exe -noprofile -executionpolicy bypass -file c:\ps\check_process_elevation.ps1
Trying to run a PowerShell script, and do you get the error “Cannot be loaded because running scripts is disabled on this system”? Then we need to change the execution policy in PowerShell. To protect your computer from malicious scripts, the execution policy of PowerShell is set to restricted by default.
This default setting will prevent you from running any PowerShell script on your computer, even scripts that you have written yourself. Luckily we can easily change the policy with a single command in PowerShell.
In this article
In this article, I will explain how you can quickly fix the error running scripts are disabled on this system, what the different policies are and how to change it on all computers with a Group Policy.
We are going to start with a quick fix. The method below only solves the issue temporarily, so you can run your script and continue. For a more sustainable solution, scroll a bit down to the next chapter.
- Open PowerShell or Windows Terminal
- Enter the command below to run your script
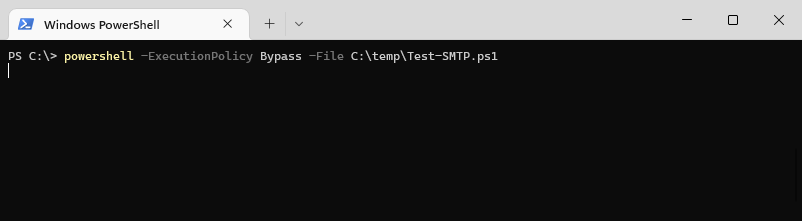
powershell -ExecutionPolicy Bypass -File script.ps1
The method above bypasses the execution policy only temporarily. This works great for a single file, but it requires you to use the command above every time that you want to run the file. A more sustainable solution is to change the execution policy.
Changing the Execution Policy Permanently
When you work a lot with PowerShell scripts then you probably want to change the Execution Policy permanently. But before we look into how to change the policy, let’s first explain its purpose and the different policies that are available.
The execution policy isn’t designed as a security system to restrict users from executing PowerShell scripts. Each user can simply bypass the policy in their current PowerShell session or even copy and paste the content of the script directly into the console. So what is the purpose of the policy then? Well, it’s designed to prevent unintentional execution of PowerShell scripts.
When changing the policy we have five options to choose from:
| Execution Policy | Description |
|---|---|
| Restricted | Default option – Does not allow to run any PowerShell script |
| Unrestricted | Can run any script, shows warning for downloaded scripts |
| RemoteSigned | Requires a digital signature for downloaded scripts. You can run locally written scripts. You can unblock downloaded scripts to run them without signature |
| ByPass | You can run all scripts and no warnings are displayed |
| AllSigned | You can only run signed scripts from trusted publishers |
Most people tend to set the policy to unrestricted, which allows you to run any PowerShell script. But a better option is to use the RemoteSigned policy. This way you can run any locally written scripts, but you will have to unblock all downloaded scripts first. The extra handling prevents users from accidentally downloading and running malicious PowerShell scripts on their system.
All users vs Current user
When changing the policy we can also determine the scope of the change. The following scopes are available for the policy:
| Scope | Description |
|---|---|
| CurrentUser | The policy is only set for the currently logged-in user |
| LocalMachine | Policy is changed for all users on the machine |
| Process | Policy is only changed for the current PowerShell session |
Set Execution Policy for Current user
So the most common scenario is that you want to change the PowerShell Execution policy for the current user. This will solve the error “running scripts is disabled on this system” for the logged-in user. We will set the policy to RemoteSigned, which means that the user still has to perform an extra step for downloaded scripts.
- Open PowerShell
- Enter the command below and press enter
Set-ExecutionPolicy -ExecutionPolicy RemoteSigned -Scope CurrentUser
- Optional – Verify the setting with the command
Get-ExecutionPolicy
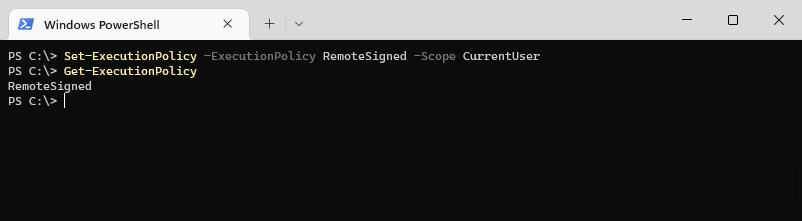
You can now run any locally created PowerShell script without the error running scripts is disabled on this system.
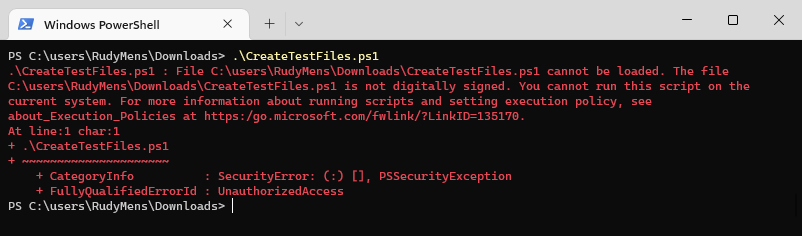
When you try to run a downloaded PowerShell script with the execution policy RemoteSigned, then you get the error that the file cannot be loaded. The PowerShell script is not digitally signed:
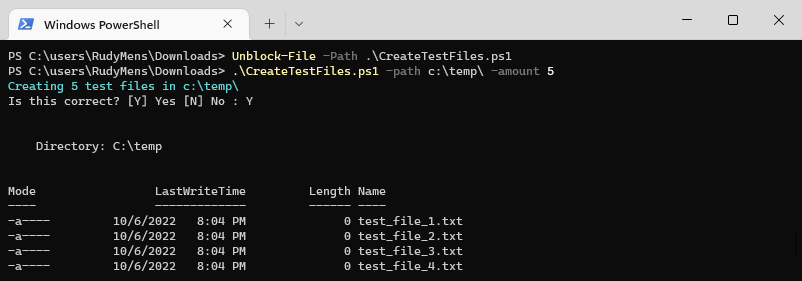
To solve this you will first need to unblock the file. To do this we can of course use a PowerShell cmdlet, Unblock-File. Simply type the cmdlet followed by the filename/path:
Unblock-File -path .\CreateTestFiles.ps1
Set Execution Policy for all Users
We can also change the policy for all users on a computer. To do this, you will need to have elevated permissions (Administrator permission).
- Right-Click on Start or press Windows key + X
- Choose Windows PowerShell (Admin) or Windows Terminal (Admin)
- Type the following command:
Set-ExecutionPolicy -ExecutionPolicy RemoteSigned -Scope LocalMachine
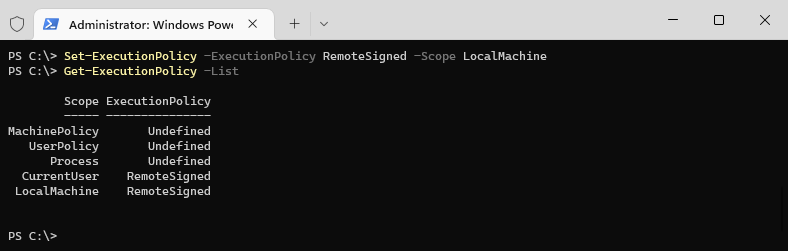
We can verify the results with the cmdlet Get-ExecutionPolicy -List which shows the policy for each scope. Good to know is that the CurrentUser policy takes precedence over the LocalMachine policy. So when you set the CurrentUser policy to restricted and LocalMachine to RemoteSigned, then the user still can’t execute any PowerShell script, because the policy set in the CurrentUser scope overrules the LocalMachine policy.
Change the policy only for the Current Sessions
Another option is to change the policy only for the current PowerShell session. This method is useful when you need to run a couple of PowerShell scripts, but don’t want to change the policy permanently. You could use the Bypass option for each script, but it’s thus also possible to set change the scope for only the current PowerShell session. Use the scope Process for this:
Set-ExecutionPolicy -ExecutionPolicy RemoteSigned -Scope Process
Set Execution policy PowerShell with GPO
When you need to modify the policy on multiple computers, then it’s a good idea to use a Group Policy for this. Group Policies allow you to change Windows settings on multiple computers that are members of a domain. Another advantage of the policy is that the setting can’t be overwritten on the computer.
- Open the Group Policy Management Editor and create a new policy.
- Expand Computer Configuration
- Navigate to Policies > Administrative Templates > Windows Components > Windows PowerShell
- Open the setting Turn on Script Execution
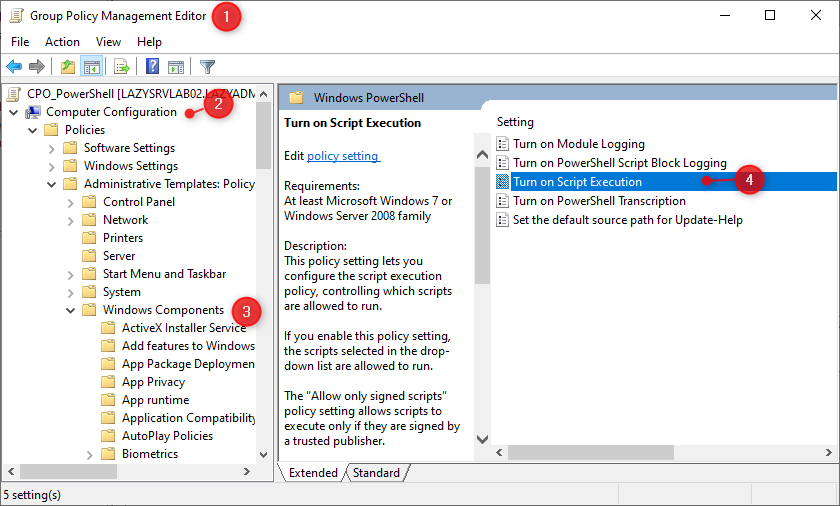
- Change the setting to Enabled
- Select the Execution Policy Allow local scripts and remote signed scripts. This is the same as RemoteSigned that we set earlier.
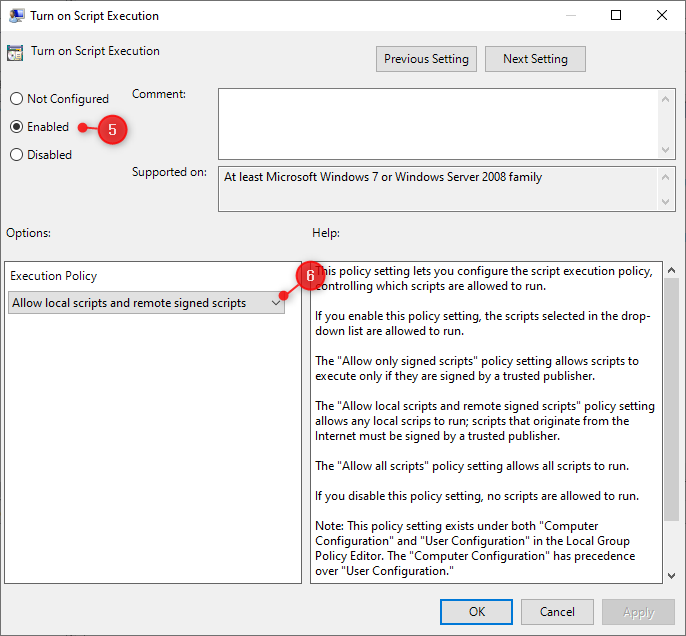
We can verify the setting on one of the clients that are a member of the OU where we just applied the setting. First, make sure that the latest policy is applied on the computer using the GPUpdate command. Optionally you can use the RSOP command to verify the policy, or just check if the execution policy is set with the command:
Get-ExecutionPolicy -list
# Result
Scope ExecutionPolicy
----- ---------------
MachinePolicy RemoteSigned
UserPolicy RemoteSigned
Process Undefined
CurrentUser Undefined
LocalMachine Undefined
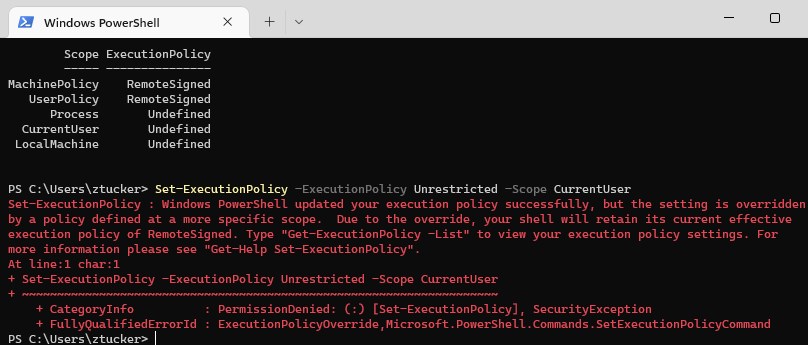
As mentioned, the advantage of the policies is that users can’t change the policy anymore. When you use the cmdlet set-executionpolicy, you will get an error that the policy is changed, but the setting is overridden by a policy defined at a more specific scope:
Wrapping Up
The best way to set the Execution Policy in PowerShell is to use the Group Policy. This way all existing and new machines in your domain can be configured with the correct policy. Of course, you can create a different policy for the IT department.
I hope this article helped you to solve the error “cannot be loaded because running scripts is disabled on this system”, if you have any questions, then just drop a comment below. If you want to learn more about PowerShell, then make sure you read this getting started guide.
There are instance when you execute your PowerShell scripts on server from your command prompt you will end up seeing below mentioned error message.
Error
Message
File cannot be loaded because the execution of scripts is disabled on this system. Please see "get-help about_signing" for more detailsThis article mentions the steps which you need to follow to fix “File cannot be loaded because the execution of scripts is disabled on this system.” error message. Let’s learn how to set executionpolicy in PowerShell.
The primary reason why you end up seeing this error message is because of the PowerShell Execution Policy Security Settings which are built into the Windows PowerShell. It basically decides how PowerShell will execute the scripts.
The Windows PowerShell execution policy is by default set to be RESTRICTED and hence the scripts will not run until the settings are changed.
How
to Verify the Existing PowerShell Execution Policy Setting
Step 1: Open Command Prompt and Enter PowerShell
Step 2: Type Get-ExecutionPolicy and hit enter as shown in the snippet below.
Get-ExecutionPolicy
There are basically Four Different Windows PowerShell Execution Policy behaviours namely:
- Restricted: – It is primarily an interactive mode, wherein no PowerShell scripts can be executed
- Unrestricted: – As the name suggests there is no restriction set and henceforth all the PowerShell scripts can be executed.
- RemoteSigned: – As the name suggests all the downloaded scripts needs to be signed from a trusted published to execute them on the server.
- AllSigned: – It means that the scripts which are signed from a trusted publisher can only be executed
Since in our case we have seen that Windows PowerShell Execution Policy is set to be Restricted on the server. We need to change the behaviour and for that we need to use the PowerShell cmdlet Set-ExecutionPolicy.
about_Execution_Policies
PowerShell’s execution policy is a safety feature that helps to control the conditions in which PowerShell loads configuration files and runs scripts. One of the primary advantages of PowerShell’s execution policy feature is that it helps prevent malicious scripts’ execution.
PowerShell execution policies
The PowerShell execution policies are AllSigned, ByPass, Default, RemoteSigned, Restricted, Undefined, and Unrestricted.
One can set an effective execution policy that is only valid for a particular scope. The available valid values for Scope are MachinePolicy, UserPolicy, Process, CurrentUser, and LocalMachine. When setting an execution policy, the default value is LocalMachine.
Privileges Needed to Execute Set-ExecutionPolicy PowerShell cmdlet | Privileges Needed to Set Executionpolicy PowerShell
One must be having Windows Administrator Privileges to execute Set-ExecutionPolicy PowerShell cmdlet on your windows operating system. If you are an administrator then you can open Command Prompt with Administrator Privileges (Run as Administrator) to execute Set-ExecutionPolicy PowerShell cmdlet. Either of the below options will work fine for you.
How to Change PowerShell Execution Policy Setting to Unrestricted | How to Set ExecutionPolicy Unrestricted
Step 1: Open Command Prompt and Enter PowerShell
Step 2: Type Set-ExecutionPolicy Unrestricted and hit enter as shown in the snippet below.
Set-ExecutionPolicy Unrestricted 
How to Change PowerShell Execution Policy Setting to RemoteSigned | How to Set Executionpolicy RemoteSigned
Step 1: Open Command Prompt and Enter PowerShell
Step 2: Type Set-ExecutionPolicy RemoteSigned and hit enter as shown in the snippet below.
Set-ExecutionPolicy RemoteSigned
How to Get PowerShell
cmdlet Syntax Help to understand information about PowerShell Syntax and
Acceptable Parameters?
If you want to understand the syntax and the parameter acceptable for a PowerShell cmdlet then execute Get-Help followed by PowerShell cmdlet Set-ExecutionPolicy as shown in the snippet below to displays information about PowerShell concepts and commands, including cmdlets, functions, Common Information Model (CIM) commands, workflows, providers, aliases, and scripts.
Get-Help Set-ExecutionPolicy 
Conclusion
In this article we have seen the steps which you need to follow to fix “File cannot be loaded because the execution of scripts is disabled on this system.” error message to run PowerShell scripts in your environment.
Reference
- About Execution Policies
Chetna Bhalla
LESS ME MORE WE
Chetna Bhalla, the founder of MyTechMantra.com, believes that by sharing knowledge and building communities, we can make this world a better place to live in. Chetna is a Graduate in Social Sciences and a Masters in Human Resources and International Business. She is an alumnus of Vignana Jyothi Institute of Management, Hyderabad, India. After graduation, Chetna founded this website, which has since then become quite a favorite in the tech world. Her vision is to make this website the favorite place for seeking information on Databases and other Information Technology areas. She believes that companies which can organize and deploy their data to frame strategies are going to have a competitive edge over others. Her interest areas include Microsoft SQL Server and overall Database Management. Apart from her work, Chetna enjoys spending time with her friends, painting, gardening, playing the violin, and spending time with her son.
When running npm commands in PowerShell, developers might encounter an error message similar to the following:
== PHOTO (Describe issue by photo) ==

== TEXT (Describe issue by text) ==
npm : File C:\Program Files\nodejs\npm.ps1 cannot be loaded because running scripts is disabled on this system. For more information, see about_Execution_Policies at https:/go.microsoft.com/fwlink/?LinkID=135170. At line:1 char:1 + npm run dev + ~~~ + CategoryInfo : SecurityError: (:) [], PSSecurityException + FullyQualifiedErrorId : UnauthorizedAccess
Solution
To resolve this issue, follow these steps:
1. Open PowerShell as Administrator:
Press Win + X and select Windows PowerShell (Admin). This ensures you have the necessary permissions to change the execution policy.
2. Check the Current Execution Policy:
In the PowerShell window, type the following command and press Enter:
powershell
Get-ExecutionPolicy
If the result is Restricted, it means script execution is disabled on your system.
3. Set the Execution Policy to RemoteSigned:
To change the execution policy, type the following command and press Enter:
powershell
Set-ExecutionPolicy RemoteSigned
You might be prompted to confirm the change. Type Y and press Enter to confirm. The RemoteSigned policy allows scripts created on your local computer to run, and scripts downloaded from the internet must be signed by a trusted publisher.
4. Verify the New Execution Policy:
To ensure the new policy is set correctly, type the following command and press Enter:
powershell
Get-ExecutionPolicy
The result should now be RemoteSigned.
5. Run Your npm Command Again:
With the execution policy set to RemoteSigned, you can now run your npm command without encountering the execution policy error:
powershell
npm run dev
_If you encounter an error about execution policies when running npm commands in PowerShell, it is likely because the script execution is disabled. To fix this, follow these steps:
Open PowerShell as Administrator.
Check the Current Execution Policy by typing Get-ExecutionPolicy.
Set the Execution Policy to RemoteSigned by typing Set-ExecutionPolicy RemoteSigned and confirming the change.
Verify the New Execution Policy by typing Get-ExecutionPolicy again.
Run Your npm Command Again without encountering the error._