If you are facing problems with Windows Security and seeing a message that says Windows Security Service or SecurityHealthService.exe started and then stopped working, then this post is sure to help you.
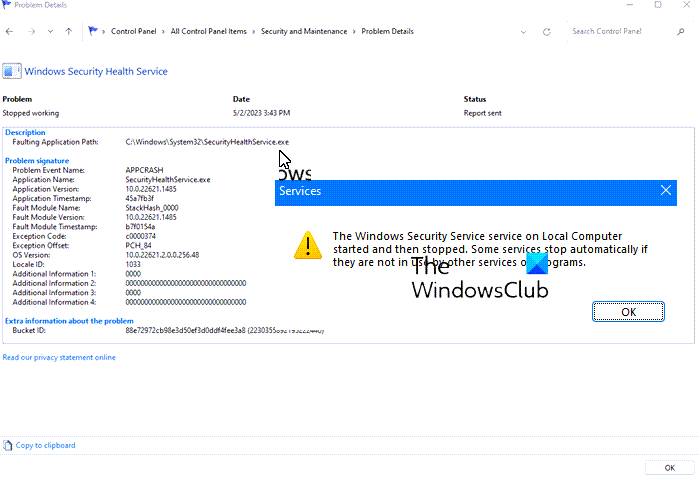
Why does securityhealthservice.exe crash in Windows 11?
The reason why securityhealthservice.exe is crashing quite often probably has a lot to do with corruption or missing system files. Sometimes, your Windows 11 computer may require an update to get things back on track.
If you have encountered a problem with SecurityHealthService.exe crashing, then the suggestions here should help a great deal.
- Restart Windows Security Service via Services Manager
- Reset the Security Health Service
- Reinstall Windows Security using the Powershell command
- Run SFC and DISM
1] Restart Windows Security Service via Services Manager
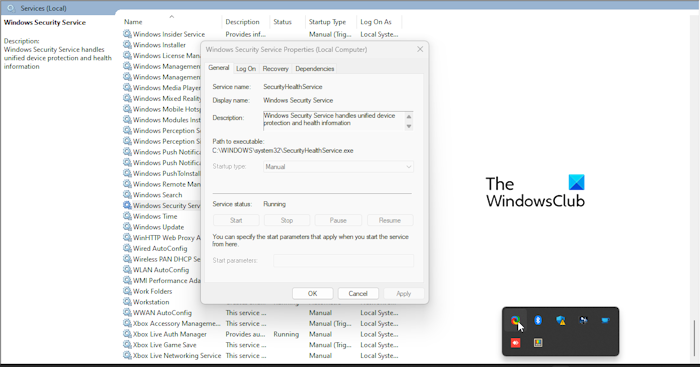
Restarting the Windows Security Service is the first thing we should do here, and it must be done via the Service Manager. So, with that in mind, let us explain what needs to be done.
- To begin, you must right-click on the Windows key, then select Run from the context menu.
- After that, type services.msc, then hit the Enter key.
- Doing the above should open the Services Manager window.
- Go ahead and scroll down to the bottom until you come across Windows Security Service.
- Double-click on it to open the Properties window.
- From this window, please click on the Stop button, then select Apply > OK.
Restart your computer and Windows Security Service should automatically restart. If that doesn’t happen, then follow the steps above and return to the Properties window where you can simply click on the Start button.
READ: Security Intelligence Update not installing automatically
2] Reset the Security Health Service
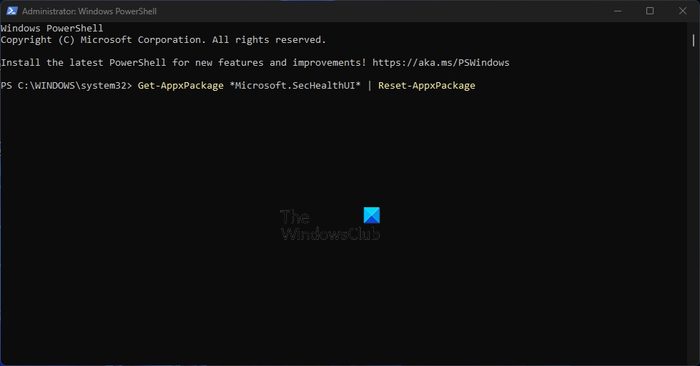
We must now move to reset the Security Health Service in hopes things will return to normal.
To do this, you must open PowerShell.
Please run it as an administrator.
From there, please copy and paste the following command directly into PowerShell:
Get-AppxPackage *Microsoft.SecHealthUI* | Reset-AppxPackage
After that, hit the Enter key on your keyboard.
When the process has run its course, go ahead, and restart the computer.
See this post for additional ways to reset the Windows Security app. Resetting Windows Security will also reset this Service and all other related components.
Similar: Reset Windows Security Settings to default values
3] Reinstall Windows Security using the Powershell command
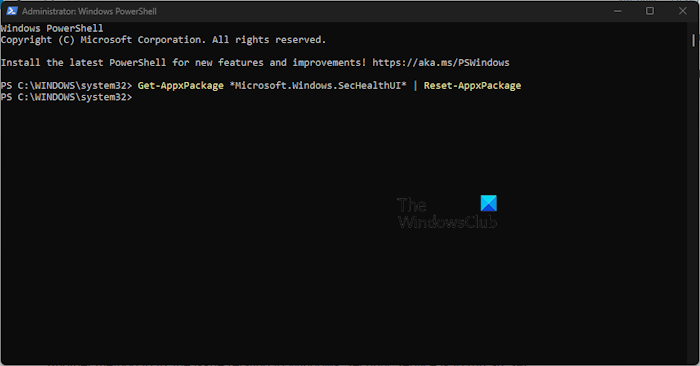
Another way to set things right where Windows Security Service is concerned is to reinstall it via PowerShell. How do we get this done? well, let us explain.
First, you must open PowerShell by clicking on the Windows key, then search for PowerShell.
Once done, please open the tool as an Admin.
Next, you must type the following command:
Get-AppxPackage *Microsoft.Windows.SecHealthUI* | Reset-AppxPackage
Hit the Enter key on your keyboard to execute the command. All you have to do now is wait a few seconds, then close PowerShell to complete the process.
4] Run SFC and DISM
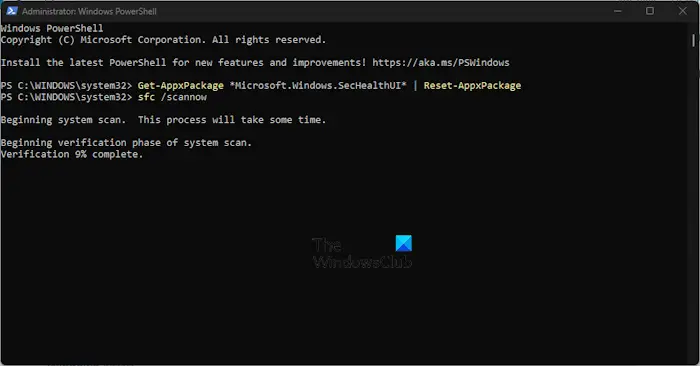
Another method to fix the issue relating to Windows Security Service is to run an SFC scan. Not only that, but we also suggest running a DISM scan as well, so let us explain how to accomplish these tasks.
To run an SFC scan, you must open the PowerShell application.
From there, type the following command:
sfc /scannow
Hit the Enter key on your keyboard, then wait.
In terms of running DISM in a bid to fix the Windows 11/10 system image, we suggest running DISM to repair Windows System Image along with Windows Component Store.
READ: Windows Security Service missing after malware attack
How do I fix Windows Security?
The best way to fix issues relating to Windows Security is to repair and reset the service. To repair it, please press the Windows key + I to open the Settings menu. From there, select App, then go to Installed Apps.
- Press the Windows key +I to open the Settings app.
- From the left side, click on App Settings.
- Search for Windows Security under Installed Apps.
- Select Advanced Options after clicking the three-dotted button.
- On the next page, click on the Repair button in Settings. Next, click on the Repair button, then select Repair again to confirm your choice.
If that doesn’t work, then go ahead and reset Windows Security, and that should complete the job.
SecurityHealthService.exe file information

The process known as Windows Security Health Service or BOINC client or load belongs to software Microsoft Windows Operating System or BOINC Client Software by (www.microsoft.com) or Space Sciences Laboratory (www.ssl.berkeley.edu).
Description: The original SecurityHealthService.exe from Microsoft is an important part of Windows, but often causes problems. The SecurityHealthService.exe file is located in the C:\Windows\System32 folder.
Known file sizes on Windows 10/11/7 are 336,320 bytes (12% of all occurrences), 800,056 bytes and 6 more variants.
The process runs as service SecurityHealthService.
SecurityHealthService.exe is a Windows core system file. The program has no visible window. The SecurityHealthService.exe file is certified by a trustworthy company. It is a trustworthy file from Microsoft.
Therefore the technical security rating is 0% dangerous; however you should also read the user reviews.
Uninstalling this variant:
You could uninstall the software Microsoft Windows using the Uninstall a Program function of Windows Control Panel (Windows: Start, Settings, Control Panel, Uninstall a Program) or ask Customer Support to assist you.
Recommended: Identify SecurityHealthService.exe related errors
Viruses with the same file name
Is SecurityHealthService.exe a virus? No, it is not. The true SecurityHealthService.exe file is a safe Microsoft Windows system process, called «Windows Security Health Service».
However, writers of malware programs, such as viruses, worms, and Trojans deliberately give their processes the same file name to escape detection. Viruses with the same file name are for instance Trojan.Gen.MBT or Trojan.Gen.2 (detected by Symantec), and TROJ_FRS.VSNTGL23 (detected by TrendMicro).
To ensure that no rogue SecurityHealthService.exe is running on your PC, click here to run a Free Malware Scan.
How to recognize suspicious variants?
- If SecurityHealthService.exe is located in a subfolder of «C:\Program Files», the security rating is 40% dangerous. The file size is 5,900,128 bytes (50% of all occurrences) or 56,368 bytes.
The SecurityHealthService.exe file is not a Windows system file. The SecurityHealthService.exe file is digitally signed.Uninstalling this variant:
You could uninstall the software aspnet_compiler.exe or BOINC Client Software using the Uninstall a Program function of Windows Control Panel (Windows: Start, Settings, Control Panel, Uninstall a Program) or search for help on the company [1][2]‘s website. - If SecurityHealthService.exe is located in a subfolder of C:\, the security rating is 98% dangerous. The file size is 8,091,288 bytes.
There is no description of the program. The program is not visible. The file is not a Windows core file. The software listens for or sends data on open ports to a LAN or the Internet.
SecurityHealthService.exe appears to be a compressed file. - If SecurityHealthService.exe is located in a subfolder of Windows folder for temporary files, the security rating is 96% dangerous. The file size is 3,769,856 bytes.
Important: Some malware disguises itself as SecurityHealthService.exe, particularly when not located in the C:\Windows\System32 folder. Therefore, you should check the SecurityHealthService.exe process on your PC to see if it is a threat. We recommend Security Task Manager for verifying your computer’s security. This was one of the Top Download Picks of The Washington Post and PC World.
Best practices for resolving SecurityHealthService issues
A clean and tidy computer is the key requirement for avoiding problems with SecurityHealthService. This means running a scan for malware, cleaning your hard drive using 1cleanmgr and 2sfc /scannow, 3uninstalling programs that you no longer need, checking for Autostart programs (using 4msconfig) and enabling Windows’ 5Automatic Update. Always remember to perform periodic backups, or at least to set restore points.
Should you experience an actual problem, try to recall the last thing you did, or the last thing you installed before the problem appeared for the first time. Use the 6resmon command to identify the processes that are causing your problem. Even for serious problems, rather than reinstalling Windows, you are better off repairing of your installation or, for Windows 8 and later versions, executing the 7DISM.exe /Online /Cleanup-image /Restorehealth command. This allows you to repair the operating system without losing data.
To help you analyze the SecurityHealthService.exe process on your computer, the following programs have proven to be helpful: ASecurity Task Manager displays all running Windows tasks, including embedded hidden processes, such as keyboard and browser monitoring or Autostart entries. A unique security risk rating indicates the likelihood of the process being potential spyware, malware or a Trojan. BMalwarebytes Anti-Malware detects and removes sleeping spyware, adware, Trojans, keyloggers, malware and trackers from your hard drive.
Other processes
hmpalert.dll ccd.exe aact.exe SecurityHealthService.exe raregistry.exe secupdutilsvc.exe rzsurroundvadstreamingservice.exe browserdefender.dll x10nets.exe opvapp.exe steelseriesengine3.exe [all]
Windows Security Health Service High CPU is a common issue that many computer users encounter. It can be frustrating when your computer’s performance is affected by this issue, causing slowdowns and delays in your work. But what exactly is causing this high CPU usage? Let’s take a closer look.
The Windows Security Health Service is a built-in feature in Windows operating systems that monitors the security status of your computer. Its primary function is to ensure that your system is protected against various threats such as malware, viruses, and other security risks. However, in some cases, this service can consume a significant amount of CPU resources, leading to high CPU usage. This can happen due to multiple factors, including outdated software, conflicting applications, or even malware infections. Resolving this issue involves troubleshooting and optimizing your system’s security settings to minimize the impact on CPU performance.
If you’re experiencing high CPU usage due to the Windows Security Health Service, here’s what you can do. First, open the Task Manager by pressing Ctrl+Shift+Esc. Then, go to the «Processes» tab and locate the «SecurityHealthService.exe» process. Right-click on it and select «End Task» to stop it temporarily. If the issue persists, you may need to disable the Windows Security Health Service permanently. To do this, go to «Services» in the Task Manager, find «wscsvc» (Windows Security Center Service), right-click on it, and choose «Properties.» Change the Startup type to «Disabled» and click «OK.» This will prevent the Windows Security Health Service from starting and consuming excessive CPU resources.

Introduction
Windows Security Health Service is a critical component of Windows operating systems that monitors the overall health and security of your system. However, in some cases, users may encounter a common issue where the Windows Security Health Service consumes a high amount of CPU resources. This can lead to decreased system performance and a slower overall user experience.
Understanding Windows Security Health Service
Windows Security Health Service, also known as «SecurityHealthService.exe,» is responsible for multiple security-related tasks on your Windows system. It actively monitors and maintains the health of your security features, including Windows Defender Antivirus, Windows Defender Firewall, and Windows Update. The service constantly checks for security vulnerabilities, updates, and scans for malware to ensure your system remains protected.
Windows Security Health Service integrates with the Windows Security app, which provides users with a centralized location to manage their system’s security settings. It offers real-time protection and regularly scans your system for potential threats. The service operates in the background, ensuring that your system remains secure without causing interruptions to your normal workflow.
However, in certain scenarios, the Windows Security Health Service may encounter issues that result in high CPU usage. This can be a temporary issue due to an ongoing security scan or an underlying problem that requires troubleshooting.
Common Causes of High CPU Usage
- Security Scan: The Windows Security Health Service might consume high CPU resources when performing a scheduled or manual security scan. Scans require significant system resources to analyze files for potential threats.
- Real-time Protection: Real-time protection constantly monitors files, applications, and activities on your system to detect and block potential threats. This process can occasionally result in increased CPU usage, especially when scanning newly downloaded or accessed files.
- Software Conflicts: Some third-party security software can conflict with the Windows Security Health Service, resulting in high CPU usage. It’s essential to ensure that only one antivirus program is running on your system to prevent conflicts.
- Incompatible Drivers: Outdated or incompatible device drivers can cause the Windows Security Health Service to use excessive CPU resources. It’s crucial to keep your drivers up to date to maintain system stability and performance.
Impact of High CPU Usage
When the Windows Security Health Service consumes a significant amount of CPU resources, it can lead to several negative consequences:
- Sluggish Performance: High CPU usage can cause your system to become slow and unresponsive. Applications may take longer to open, and multitasking can become challenging.
- Increased Heat: As the CPU works harder to process the tasks of the Windows Security Health Service, it generates more heat. Over time, excessive heat can affect your system’s overall performance and potentially damage hardware components.
- Reduced Battery Life: Laptops and other portable devices might experience significantly reduced battery life due to the increased power consumption caused by high CPU usage.
- Limited System Resources: When the Windows Security Health Service utilizes a substantial portion of CPU resources, other processes and applications may not have sufficient resources to operate efficiently, leading to further performance degradation.
Resolving High CPU Usage
If you are facing high CPU usage due to the Windows Security Health Service, here are some steps you can take to resolve the issue:
- Perform a Full System Scan: Initiate a full system scan using Windows Security to ensure that your system is free from malware. Allow the scan to complete, as it might temporarily increase CPU usage during the process.
- Update Windows: Make sure that your Windows operating system is up to date. Microsoft regularly releases security updates and bug fixes that can address underlying issues with the Windows Security Health Service.
- Check for Software Conflicts: If you have third-party antivirus or security software installed, disable or uninstall it temporarily to check if it is conflicting with the Windows Security Health Service. Remember to only have one antivirus program actively running on your system.
- Update Device Drivers: Visit your device manufacturer’s website or use an automated driver updater tool to check for and install any available driver updates. Outdated or incompatible drivers can sometimes cause high CPU usage.
- Restart the Security Health Service: Open the Services application (press Win + R, type «services.msc,» and press Enter), locate the «SecurityHealthService» entry, right-click on it, and select «Restart.» This action can help refresh the service and troubleshoot any temporary issues causing high CPU usage.
Monitoring and Preventing High CPU Usage
To monitor and prevent high CPU usage caused by the Windows Security Health Service, consider the following:
Performance Adjustments
If you frequently experience high CPU usage due to the Windows Security Health Service, you can adjust some settings to manage its impact:
- Scan Scheduling: Configure the Windows Security app to perform scheduled scans during periods of low system activity. This can help minimize the impact on your system’s performance during your regular usage hours.
- Exclusion List: Add specific files, folders, or applications to the exclusion list in Windows Security to prevent them from being scanned. Be cautious when using this feature, as it may reduce the overall security of your system.
Regular Maintenance
Consistently maintaining your system can help prevent high CPU usage caused by the Windows Security Health Service:
- Keep Windows Updated: Regularly check for and install Windows updates to ensure your system has the latest security patches and bug fixes.
- Update Security Software: If you are using third-party security software, always keep it up to date to benefit from the latest features and performance improvements.
- Perform Regular Disk Cleanup: Use the built-in Disk Cleanup utility to remove temporary files, unnecessary system files, and other clutter that can impact system performance.
Alternative Solutions for High CPU Usage
If you’ve tried the above steps and are still experiencing high CPU usage caused by the Windows Security Health Service, consider the following alternative solutions:
Contacting Microsoft Support
If you are unable to resolve the issue on your own, reaching out to Microsoft Support for further assistance is recommended. They can provide guidance specific to your system configuration and help identify and address any underlying issues causing high CPU usage.
Seeking Professional Help
If you are not comfortable troubleshooting the issue yourself or prefer to have an expert handle the problem, consider contacting a professional computer technician or IT support service. They have the knowledge and experience to diagnose and resolve complex system issues, including high CPU usage caused by the Windows Security Health Service.
Consider Using Alternative Security Software
If the high CPU usage persists and significantly affects your system’s performance, you may want to explore alternative security software that provides similar functionality while consuming fewer system resources. There are many reputable antivirus programs available that offer robust protection without compromising your system’s performance.
However, before switching to a different security software, thoroughly research and ensure that the alternative program meets your security requirements and is compatible with your operating system.
Overall, dealing with high CPU usage caused by the Windows Security Health Service requires a systematic approach. By following the troubleshooting steps outlined above and considering alternative solutions if needed, you can effectively address the issue and ensure that your system remains secure while maintaining optimal performance.

Windows Security Health Service High CPU
In the world of operating systems, Windows Security Health Service plays a critical role in ensuring the safety and security of user data. However, it is not uncommon for users to experience high CPU usage due to this service. This issue can arise for various reasons, such as outdated security definitions or corrupted system files.
To resolve this issue, there are a few troubleshooting steps that can be followed:
- Update Windows Defender: Ensure that you have the latest updates installed for Windows Defender, which includes security definitions and system bug fixes.
- Reset Windows Security Health Service: Sometimes, resetting the service can help resolve the high CPU usage issue. This can be done by navigating to the Services menu, locating the Windows Security Health Service, and selecting the «Restart» option.
- Perform System File Check: Running the System File Checker (SFC) scan can help identify and repair any corrupted system files that may be causing the high CPU usage. This can be done by opening the Command Prompt as an administrator and running the command «sfc /scannow».
- Check for Malware: Ensure that your system is free from any malware or viruses by running a reliable antivirus scan. It is recommended to use a trusted antivirus software and regularly update it.
Key Takeaways
- Windows Security Health Service can sometimes consume high CPU resources.
- High CPU usage by Windows Security Health Service can slow down your computer.
- One possible cause of high CPU usage is the scanning process for malware and security threats.
- Disabling or reducing the scanning frequency can help reduce CPU usage.
- Updating antivirus software and performing regular system scans can also help prevent high CPU usage by Windows Security Health Service.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are some common questions related to Windows Security Health Service causing high CPU usage.
1. What is Windows Security Health Service?
Windows Security Health Service is a component of the Windows operating system that continuously monitors the health and security of your computer. It helps protect your system by scanning for malware, checking for the latest updates, and ensuring the security settings are properly configured.
However, sometimes the Windows Security Health Service can consume high CPU resources, causing your computer to slow down. This could be due to various factors, such as conflicts with other software or outdated system files.
2. Why does the Windows Security Health Service cause high CPU usage?
The Windows Security Health Service may cause high CPU usage due to several reasons:
1. Real-time scanning: The service continuously scans your system for malware and other threats in real-time, which can consume CPU resources.
2. Resource conflicts: The Windows Security Health Service may conflict with other security software or applications installed on your computer, causing high CPU usage.
3. Outdated system files: If the service encounters outdated system files or settings, it may consume more CPU resources to perform its tasks.
3. How can I reduce the CPU usage of Windows Security Health Service?
To reduce the CPU usage of Windows Security Health Service, you can try the following solutions:
1. Update your system: Ensure that your Windows operating system and all security-related software are up to date. This can help resolve any compatibility issues and optimize the performance of the service.
2. Exclude certain files or folders from scanning: If you have files or folders that you know are safe, you can exclude them from being scanned by the Windows Security Health Service. This can help reduce CPU usage.
3. Adjust the scanning settings: You can modify the scanning frequency or the types of files being scanned by the service. This can help reduce the CPU usage without compromising the overall security of your system.
4. Can I disable Windows Security Health Service?
It is not recommended to disable the Windows Security Health Service completely, as it plays an important role in protecting your system from malware and ensuring its overall health and security.
However, if you are experiencing persistent high CPU usage caused by the service, you can temporarily disable it for troubleshooting purposes. Keep in mind that disabling the service will leave your system vulnerable to security threats, so it should only be done temporarily and with caution.
5. Should I seek professional help if I encounter high CPU usage from Windows Security Health Service?
If you have tried the suggested solutions and are still experiencing high CPU usage from the Windows Security Health Service, it is recommended to seek professional help. A professional can diagnose the issue and provide advanced troubleshooting techniques to resolve the problem.
It is important to ensure the security and performance of your computer, and professionals have the expertise to address complex issues related to the Windows Security Health Service.
So, to wrap things up, the Windows Security Health Service High CPU issue can be quite a headache for users. It involves the Windows Security app consuming excessive CPU resources, leading to system slowdowns and decreased performance.
However, there are a few steps you can take to address this problem. You can try updating Windows and the Windows Security app to the latest versions, as these updates often include bug fixes and performance improvements. Additionally, you can disable certain Windows Security features temporarily, such as the Cloud-delivered Protection and Automatic Sample Submission. If the issue persists, you may need to seek further assistance from Microsoft support or consider a professional IT service.
-
Home
-
News
- 4 Fixes for SecurityHealthService.exe Crashing or Stopped Working
4 Fixes for SecurityHealthService.exe Crashing or Stopped Working
By Amy | Follow |
Last Updated
This post tells you how to fix the “SecurityHealthService.exe crashing or stopped working” issue. When SecurityHealthService.exe keeps crashing on your computer, try the methods offered by Partition Magic in this post immediately.
Windows Security Health Service crashing is one of SecurityHealthService.exe problems. It confuses plenty of users. If you are one of them, you come to the right place. This post offers you 4 available methods to fix the Windows Security Health Service crashing issue.
Tips:
To avoid data loss due to unexpected errors, you can clone the hard drive regularly by using MiniTool Partition Wizard. As PC cloning software, it also helps you make a Windows backup to safeguard your computer.
MiniTool Partition Wizard DemoClick to Download100%Clean & Safe
Method 1: Restart Windows Security Service
The first thing you should try is to restart Windows Security Service when the “SecurityHealthService.exe crashing or stopped working” issue occurs. To do that, please refer to the steps below.
Step 1: Hold the Windows and R keys to open the Run dialog window.
Step 2: Type services.msc in the Run window and click OK to open Services.
Step 3: In the Services window, scroll down the content to find Windows Security Service. Right-click on the Windows Security Service and click Properties.
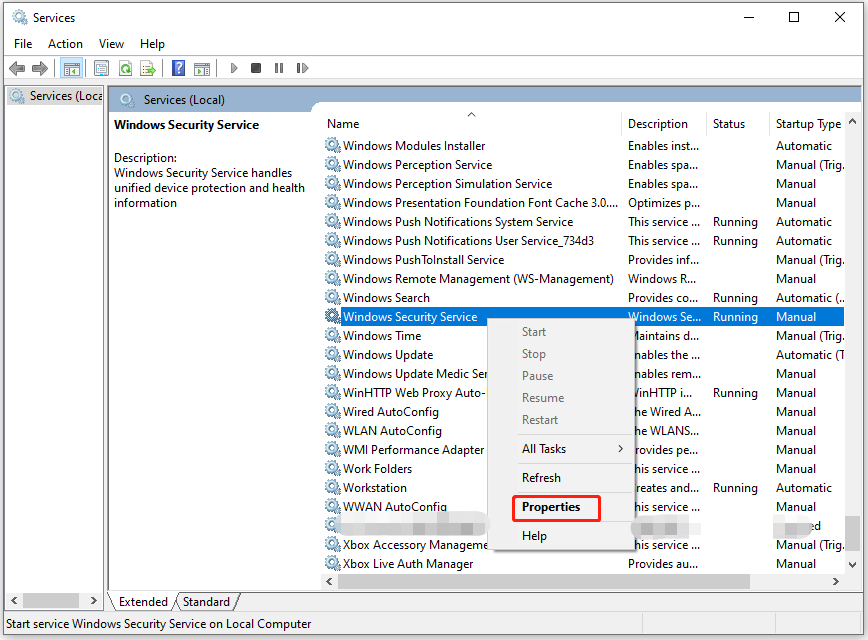
Step 4: Click on the Stop button and hit Apply > OK.
Step 5: The Windows Security Service should automatically restart after you restart the computer. If it doesn’t work, follow the above steps to start the service manually.
Method 2: Run SFC or DISM
The Windows Security Health Service crashing issue can be caused by corrupted or missing system files. So, one solution to the SecurityHealthService.exe crashing or stopped working issue is to run SFC or DISM scans.
Step 1: Hold the Windows + R key to open the Run window.
Step 2: Type cmd in the Run window and press Ctrl + Shift + Enter to run Command Prompt as administrator.
Step 3: In the Command Prompt window, type sfc /scannow and hit Enter to execute the command. As the picture below indicates, you need to restart the computer to complete the process as this is a system repair task.
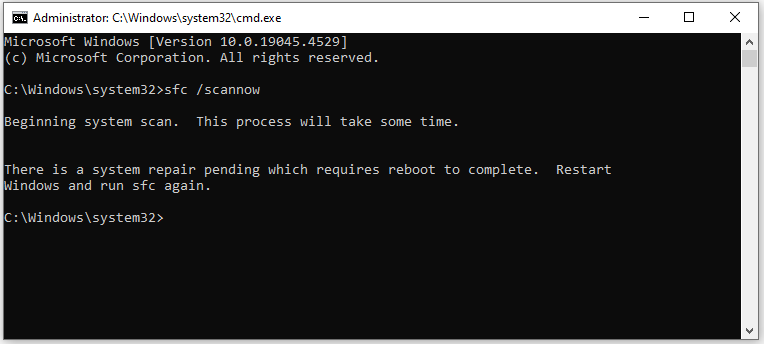
Step 4: Restart the computer and run SFC again.
Step 5: After the process ends, check if SecurityHealthService.exe keeps crashing. If the issue persists, run DISM commands.
- Run Command Prompt as administrator.
- Type the following commands and hit Enter after each.
- dism /online /cleanup-image /scanhealth
- dism /online /cleanup-image /checkhealth
- dism /online /cleanup-image /restorehealth
Method 3: Reset the Security Health Service
You can reset the Security Health Service to get rid of the SecurityHealthService.exe crashing issue. Additionally, this method also works for other SecurityHealthService.exe problems.
Step 1: Right-click on the Windows icon to open the Start menu.
Step 2: Click on Windows PowerShell (Admin) and click Yes in the prompted User Account Control window.
Step 3: In the Windows PowerShell window, type the command below and hit Enter to execute the command.
Get-AppxPackage *Microsoft.SecHealthUI* | Reset-AppxPackage
Step 4: After the process ends, restart the computer.
Method 4: Reinstall Windows Security via PowerShell
The last resort to the “SecurityHealthService.exe crashing or stopped working” issue is to reinstall Windows Security. Like Security Health Service reset, Windows Security uninstallation is also useful for solving other SecurityHealthService.exe problems.
Step 1: Run Windows PowerShell as administrator.
Step 2: In the elevated window, type the following command and hit the Enter key to execute it.
add-appxpackage -disabledevelopmentmode -register ((Get-AppxPackage Microsoft.SecHealthUI -allusers).InstallLocation + ‘\AppxManifest.xml’)
If the above command fails, follow the instructions below.
- Download Farbar Recovery Scan Tool (FRST64.exe).
- Rename FRST64.exe to EnglighFRST64.exe and then run the file. Don’t check or uncheck any updates.
- Upload the two logs (FRST.txt and Addition.txt) to your OneDrive and share the link here.
- Download defender_diag.bat.
- Right-click on the bat file and click Properties > Unlock > OK.
- Run the batch file as administrator.
Conclusion
Four available methods for the “SecurityHealthService.exe crashing or stopped working” issue have been shown to you. If SecurityHealthService.exe keeps crashing on your PC, apply these methods to troubleshoot it.
About The Author
Position: Columnist
Having writing articles about computer tech for a long time, I am rather experienced especially on the aspect of computer optimization, PC enhancement, as well as tech terms explanation. The habit of looking through tech forums makes me a great computer issues collector. And then, many articles related to these issues are released, which benefit plenty of users. Professional, effective, and innovative are always the pursuit of an editing worker.
When you open the Task Manager on your Windows computer, you may come across a process called “SecurityHealthService” running in the background. This process might raise some questions and concerns about its purpose and whether it is a legitimate component of your system. In this article, we will delve into the details of the SecurityHealthService process, its functions, and why it is running in Task Manager.

Understanding the SecurityHealthService Process
The SecurityHealthService process is a part of the Windows Defender Security Center, which is a built-in security feature in Windows 10. It is responsible for monitoring and maintaining the security of your system by performing various tasks related to antivirus protection, firewall management, and system health checks.
Windows Defender Security Center combines multiple security features into a single interface, providing users with a centralized location to manage their security settings and monitor the overall health of their system. The SecurityHealthService process plays a crucial role in ensuring the effectiveness of these security features.
Functions of the SecurityHealthService Process
The SecurityHealthService process performs several important functions to keep your system secure:
- Real-time Protection: The process continuously monitors your system for any suspicious or malicious activities. It scans files, programs, and network connections in real-time to detect and block potential threats.
- Virus and Malware Scanning: It regularly scans your system for viruses, malware, and other malicious software. This helps in identifying and removing any existing threats.
- Windows Defender Firewall Management: The process also manages the Windows Defender Firewall, which acts as a barrier between your computer and the external network. It controls incoming and outgoing network traffic to protect your system from unauthorized access.
- System Health Checks: SecurityHealthService performs periodic system health checks to ensure that your system is up to date with the latest security patches and updates. It also checks for any potential vulnerabilities that could be exploited by attackers.
Why Is SecurityHealthService Running in Task Manager?
The presence of the SecurityHealthService process in Task Manager indicates that Windows Defender Security Center is actively protecting your system. It is a legitimate component of Windows 10 and is essential for maintaining the security and integrity of your computer.
However, it is worth noting that the process may consume system resources, especially during virus scans or when performing intensive security checks. This can temporarily slow down your system, but it is a necessary trade-off for ensuring the security of your computer.
Should You Be Concerned?
If you see the SecurityHealthService process running in Task Manager, there is generally no need to be concerned. It is a legitimate process that is designed to protect your system from various security threats.
However, if you notice any unusual behavior or suspect that your system might be infected with malware, it is always recommended to perform a thorough scan using reliable antivirus software. Malwarebytes Free is a popular choice for scanning and removing malware.
Conclusion
The SecurityHealthService process running in Task Manager is an integral part of the Windows Defender Security Center. It performs essential functions such as real-time protection, virus scanning, firewall management, and system health checks to ensure the security of your system.
While the process may consume system resources, it is a necessary trade-off for maintaining a secure computer environment. If you encounter any concerns or suspect malware infection, it is always recommended to perform a thorough scan using reliable antivirus software like Malwarebytes Free.
By understanding the role and importance of the SecurityHealthService process, you can have peace of mind knowing that your system is being actively protected against security threats.
How to Stay Safe Online
Here are 10 basic security tips to help you avoid malware and protect your device:
-
Use a good antivirus and keep it up-to-date.
It’s essential to use a good quality antivirus and keep it up-to-date to stay ahead of the latest cyber threats. We are huge fans of Malwarebytes Premium and use it on all of our devices, including Windows and Mac computers as well as our mobile devices. Malwarebytes sits beside your traditional antivirus, filling in any gaps in its defenses, and providing extra protection against sneakier security threats.
-
Keep software and operating systems up-to-date.
Keep your operating system and apps up to date. Whenever an update is released for your device, download and install it right away. These updates often include security fixes, vulnerability patches, and other necessary maintenance.
-
Be careful when installing programs and apps.
Pay close attention to installation screens and license agreements when installing software. Custom or advanced installation options will often disclose any third-party software that is also being installed. Take great care in every stage of the process and make sure you know what it is you’re agreeing to before you click «Next.»
-
Install an ad blocker.
Use a browser-based content blocker, like AdGuard. Content blockers help stop malicious ads, Trojans, phishing, and other undesirable content that an antivirus product alone may not stop.
-
Be careful what you download.
A top goal of cybercriminals is to trick you into downloading malware—programs or apps that carry malware or try to steal information. This malware can be disguised as an app: anything from a popular game to something that checks traffic or the weather.
-
Be alert for people trying to trick you.
Whether it’s your email, phone, messenger, or other applications, always be alert and on guard for someone trying to trick you into clicking on links or replying to messages. Remember that it’s easy to spoof phone numbers, so a familiar name or number doesn’t make messages more trustworthy.
-
Back up your data.
Back up your data frequently and check that your backup data can be restored. You can do this manually on an external HDD/USB stick, or automatically using backup software. This is also the best way to counter ransomware. Never connect the backup drive to a computer if you suspect that the computer is infected with malware.
-
Choose strong passwords.
Use strong and unique passwords for each of your accounts. Avoid using personal information or easily guessable words in your passwords. Enable two-factor authentication (2FA) on your accounts whenever possible.
-
Be careful where you click.
Be cautious when clicking on links or downloading attachments from unknown sources. These could potentially contain malware or phishing scams.
-
Don’t use pirated software.
Avoid using Peer-to-Peer (P2P) file-sharing programs, keygens, cracks, and other pirated software that can often compromise your data, privacy, or both.
To avoid potential dangers on the internet, it’s important to follow these 10 basic safety rules. By doing so, you can protect yourself from many of the unpleasant surprises that can arise when using the web.
