В Microsoft Security Baseline содержатся рекомендованные настройки, которые Microsoft предлагает использовать на рабочих станциях и серверах Windows для обеспечения безопасной конфигурации для защиты контролеров домена, рядовых серверов, компьютеров и пользователей. На основе Microsoft Security Baseline разработаны эталонные групповые политики (GPO), которые администраторы могут использовать в своих доменах AD. Настройки безопасности в групповых политиках Microsoft Security Baseline позволяют администраторам обеспечить уровень защиты корпоративной инфраструктуры Windows, соответствующий актуальным мировым стандартам. В этой статье мы покажем, как внедрить групповые политики на основе Microsoft Security Baseline в вашем домене.
Эталонные политики Microsoft Security Baseline входят в состав продукта Microsoft Security Compliance Manager (SCM). SCM это бесплатный продукт, в который входит несколько инструментов для анализа, тестирование и применения лучших и актуальных рекомендаций безопасности для Windows и других продуктов Microsoft.
Microsoft Security Compliance Toolkit доступен по ссылке https://www.microsoft.com/en-us/download/details.aspx?id=55319. На данный момент в Security Compliance Toolkit доступны Baseline для следующих продуктов:
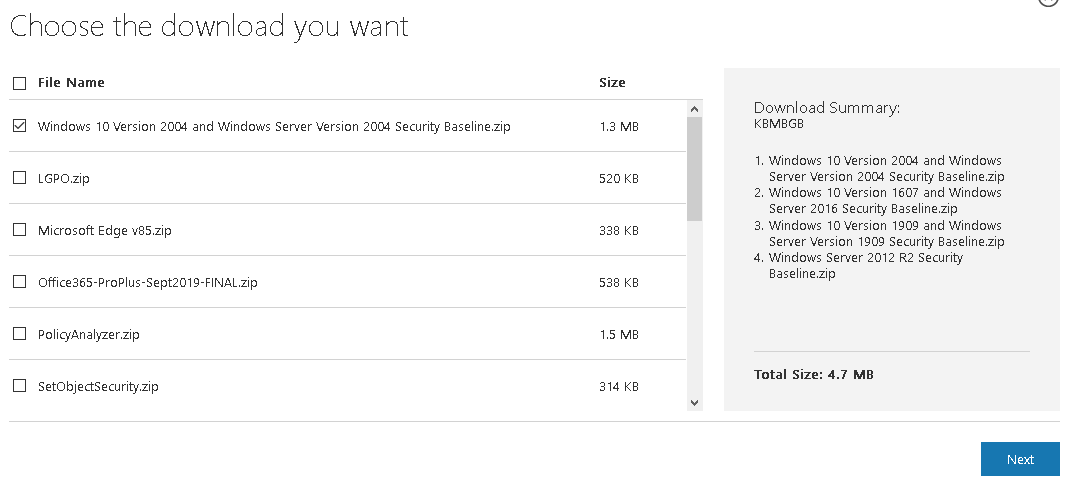
- Windows 10 Version 2004 and Windows Server Version 2004;
- Windows 10 Version 1909 and Windows Server Version 1909;
- Windows 10 Version 1903 and Windows Server Version 1903;
- Windows 10 Version 1809 and Windows Server 2019;
- Microsoft Edge v85;
- Office365 ProPlus;
- Windows Server 2012 R2.
Также можно скачать утилиты:
- LGPO – используется для управления настройками локальной политики;
- PolicyAnalyzer – инструмент для анализа имеющихся групповых политик и сравнения их с эталонными политиками в Security Baseline;
- SetObjectSecurity.
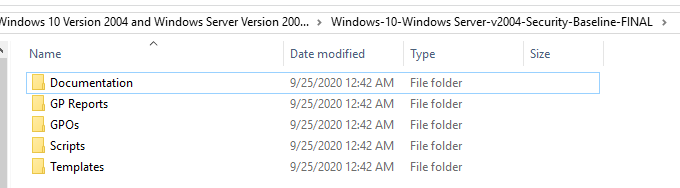
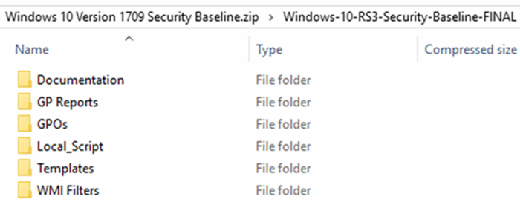
Архив с Security Baseline для каждой версии Windows содержит несколько папок:
- Documentation – xlsx и docx файлы с подробным описанием настроек, которые применяются в данном Security Baseline;
- GP Reports – html отчеты с настройками GPO, которые будут применены;
- GPOs – каталог с готовыми объектами GPO для различных сценариев. Данные политики можно импортировать в Group Policy Management console;
- Scripts – PowerShell скрипты для упрощения импорта настроек GPO в доменные или локальные политики): Baseline-ADImport.ps1, Baseline-LocalInstall.ps1, Remove-EPBaselineSettings.ps1, MapGuidsToGpoNames.ps1;
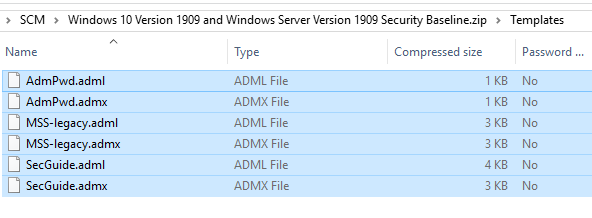
- Templates – дополнительные admx/adml шаблоны GPO (например, AdmPwd.admx – настройки управления локальными паролями для LAPS, MSS-legacy.admx, SecGuide.admx).
В доменной среде Active Directory проще всего внедрить Security Baseline через групповые политики (в рабочей группе можно применять рекомендованные настройки безопасности через локальную политику с помощью утилиты LGPO.exe) .
Есть шаблоны GPO Security Baseline для различных элементов инфраструктуры Windows: политики для компьютеров, пользователей, доменных серверов, контроллеров домена (есть отдельная политика для виртуальных DC), настройки Internet Explorer, BitLocker, Credential Guard, Windows Defender Antivirus. В папке GPOs хранятся готовые GPO политики для различных сценариев использования Windows (далее перечислен список GPO для Windows Server 2019 и Windows 10 1909):
- MSFT Internet Explorer 11 — Computer
- MSFT Internet Explorer 11 — User
- MSFT Windows 10 1909 — BitLocker
- MSFT Windows 10 1909 — Computer
- MSFT Windows 10 1909 — User
- MSFT Windows 10 1909 and Server 1909 — Defender Antivirus
- MSFT Windows 10 1909 and Server 1909 — Domain Security
- MSFT Windows 10 1909 and Server 1909 Member Server — Credential Guard
- MSFT Windows Server 1909 — Domain Controller Virtualization Based Security
- MSFT Windows Server 1909 — Domain Controller
- MSFT Windows Server 1909 — Member Server
Обратите внимание, что для каждой версии Windows Server или билда Windows 10 есть собственный набор Security Baseline.
Распакуйте архив с версией Security Baseline для нужной версии Windows и запустите консоль управления доменными групповыми политиками Group Policy Management (gpmc.msc).
- Скопируйте ADMX шаблоны в центральное хранилище GPO (Central Store) PolicyDefinitions на DC;
- Создайте новую политику с названием Windows 10 2004 Security Baseline;
- Щелкните по новой GPO правой кнопкой и выберите Import Settings;
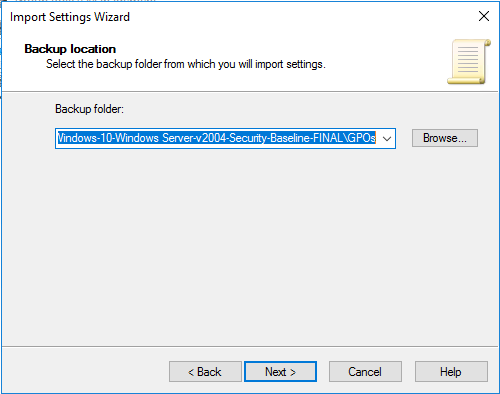
- В качестве Backup Location укажите путь к файлу с Security Baseline для нужной версии Windows (например, C:\distr\SCM\Windows 10 Version 2004 and Windows Server Version 2004 Security Baseline\Windows-10-Windows Server-v2004-Security-Baseline-FINAL\GPOs);
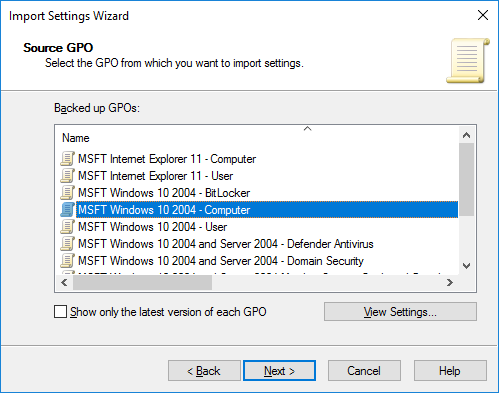
- Перед вами появится список шаблонов политик. В нашем случае я импортирую политику с настройками компьютера. Выберите политику MSFT Windows 10 2004 – Computer (с помощью кнопки View Settings можно посмотреть настройки политики в виде отчета gpresult);
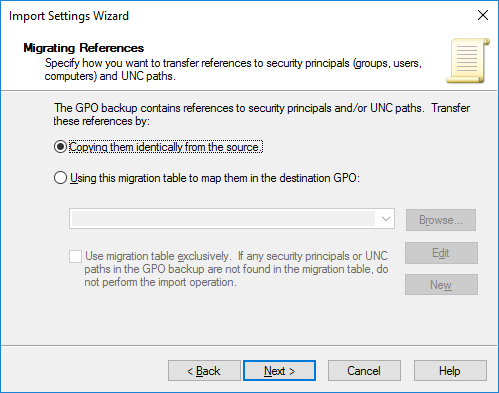
- Далее предлагается указать как нужно переносить ссылки на объекты безопасности и UNC пути. Т.к. политика у нас чистая, выберите пункт Copying them identically from the source;
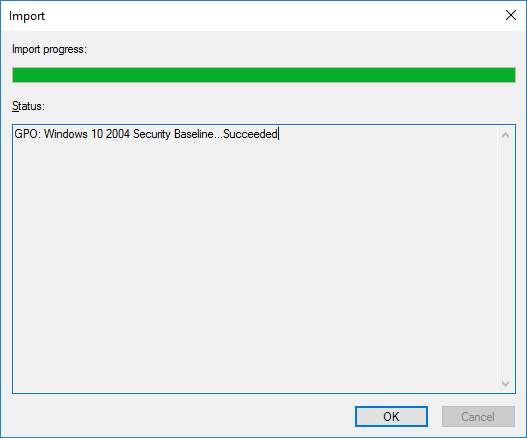
- После этого настройки эталонной политики Security Baseline для компьютеров с Windows 10 2004 будут импортированы в новую GPO.
Чтобы применить данную политику только для компьютеров с нужной версией Windows, нужно использовать WMI фильтры GPO. Например, для Windows 10 2004 можно использовать такой WMI фильтр:
Select Version,ProductType from Win32_OperatingSystem WHERE Version LIKE "10.0.19041%" and ProductType = "1"
Примените данный фильтр к вашей политике.
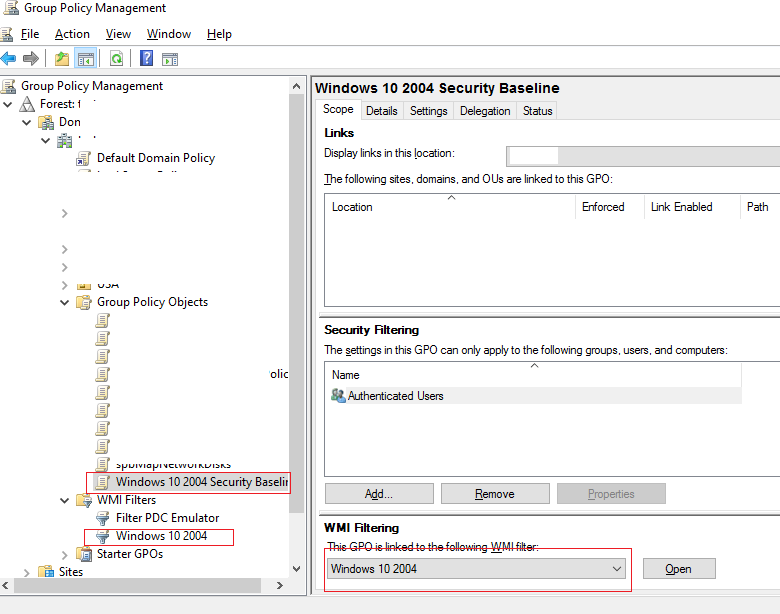
Аналогично можно импортировать Security Baseline для пользователей, контроллеров домена, рядовых серверов и т.д.
Перед применением Security Baseline на компьютеры пользователей, нужно внимательно проверить предлагаемые настройки и сначала применить на OU с тестовыми пользователями или компьютерами. При необходимости, вы можете в политике отключить некоторые настройки, которые предлагаются в Security Baseline.Только после успешного испытания настроек Security Baseline на тестовых компьютерах можно применять настройки для всех компьютеров/серверов в домене.
В Security Baseline содержаться десятки и сотни настроек. Рассмотреть их все в рамках одной статье довольно сложно. Рассмотрим настройки безопасности, которые так или иначе мы рассматривали в рамках других статей сайта:
- Управление правилами запуска и установки программ: AppLocker (SRP), UAC и Windows Installer
- Политики паролей и блокировки учетных записей
- Ограничения административных аккаунтов
- Ограничение анонимного доступа
- Настройки политик аудита для получения информации о всех событиях и входов пользователей
- Защита памяти LSA (для
- Доступ к периферийным устройствам (в том числе политики установки принтеров и USB)
- Отключение NetBIOS и NTLM
- Настройки Remote Assistance, теневых подключений, таймаутов RDS, параметров CredSSP Oracle Remediation
- Политика запуска скриптов PowerShell
- Настройка Windows Error Reporting
- Управление правилами Windows Firewall
- Настройки WinRM
- Отключение встроенного администратора
- Политика Hardened UNC paths
- Отключение SMBv1
Если вы хотите защитить более надежно защитить свой домашний компьютер с Windows 10, вы можете применить на нем политики Security Baseline с помощью готового PowerShell скрипта.
Разрешите запуск неподписанных скриптов:
Set-ExecutionPolicy -ExecutionPolicy
Примените политику:
Baseline-LocalInstall.ps1 -Win10NonDomainJoined.
Политики Security Baseline позволяет существенно повысить защищенность инфраструктуры Windows и гарантировать, что одинаковые настройки применяются на всех (в том числе новых) компьютерах в сети.
Many organizations lack security standards across their desktop deployments, and across all Microsoft products and platforms for that matter.
If IT professionals really want to shore up the gaps and weaknesses in their security standards, they must check out and integrate Microsoft’s Security Compliance Toolkit and its Windows 10 security baselines. The baselines go beyond common endpoint security controls, such as malware protection, and they are a gold mine for security guidance in Windows 10.
What are the Windows 10 security baselines?
Based on expert feedback from both inside and outside Microsoft, the Windows 10 security baselines are effectively a set of best practices IT pros can use to further lock down their Windows desktops and create and support security policies and standards in their organizations.
The security baselines can also help save IT time and effort and help it focus on the security of the thousands of Group Policy Objects (GPOs) and settings built into Windows 10. In addition, the existence and implementation of Windows 10 security best practices can help demonstrate to third parties, such as business partners and customers, that a company is following an industry standard that serves to minimize network security-related risks.
Not only is this Microsoft guidance free, it’s coming from the very creator of the software, so it’s well-researched and properly vetted.
How does it work?
Once IT pros download the Security Compliance Toolkit for their particular version of Windows 10, they can peruse the accompanying spreadsheet — as shown in Figure A — to see which areas of security they might want to address on an ad hoc basis.
IT pros can use the analysis and testing capabilities in the Security Compliance Toolkit to establish the Windows 10 security best practices for their organizations.
Selecting the download option for the Windows 10 Version 1709 Security Baseline.zip file provides IT with the spreadsheet above, as well as the necessary GPOs, templates and client install script it needs to get rolling.
On the Security Compliance Toolkit download page, IT also has the option to download Microsoft’s policy analyzer tools, as well as the Local Group Policy Object Utility for managing local Windows policies.
When establishing Windows 10 security baselines, IT pros should proceed with the goal of balancing Microsoft’s recommendations with what they actually need — based on the results of their vulnerability and penetration testing — and how it will best work in their deployment.
ASD’s Blueprint for Secure Cloud
Microsoft Windows Security Baseline
Basics
| Item | Value |
|---|---|
| Name | Microsoft Windows Security Baseline |
| Description | |
| Platform | Windows 10 and later |
Assignments
| Item | Value |
|---|---|
| Included groups | grp-windows10-users |
| Excluded groups |
Configuration settings
Above Lock
| Item | Value |
|---|---|
| Voice activate apps from locked screen | Disabled |
| Block display of toast notification | Yes |
App Runtime
| Item | Value |
|---|---|
| Microsoft accounts optional for Windows Store apps | Enabled |
Application management
| Item | Value |
|---|---|
| Block app installations with elevated privileges | Yes |
| Block user control over installations | Yes |
| Block game DVR (desktop only) | Yes |
Audit
| Item | Value |
|---|---|
| Account Logon Audit Credential Validation (Device) | Success and Failure |
| Account Logon Audit Kerberos Authentication Service (Device) | None |
| Account Logon Logoff Audit Account Lockout (Device) | Failure |
| Account Logon Logoff Audit Group Membership (Device) | Success |
| Account Logon Logoff Audit Logon (Device) | Success and Failure |
| Audit Other Logon Logoff Events (Device) | Success and Failure |
| Audit Special Logon (Device) | None |
| Audit Security Group Management (Device) | None |
| Audit User Account Management (Device) | Success and Failure |
| Detailed Tracking Audit PNP Activity (Device) | Success |
| Detailed Tracking Audit Process Creation (Device) | Success |
| Object Access Audit Detailed File Share (Device) | Failure |
| Audit File Share Access (Device) | Success and Failure |
| Object Access Audit Other Object Access Events (Device) | Success and Failure |
| Object Access Audit Removable Storage (Device) | Success and Failure |
| Audit Authentication Policy Change (Device) | Success |
| Policy Change Audit MPSSVC Rule Level Policy Change (Device) | Success and Failure |
| Policy Change Audit Other Policy Change Events (Device) | None |
| Audit Changes to Audit Policy (Device) | None |
| Privilege Use Audit Sensitive Privilege Use (Device) | Success and Failure |
| System Audit Other System Events (Device) | Success and Failure |
| System Audit Security State Change (Device) | Success |
| Audit Security System Extension (Device) | Success |
| System Audit System Integrity (Device) | Success and Failure |
Auto Play
| Item | Value |
|---|---|
| Auto play default auto run behavior | Not configured |
| Auto play mode | Not configured |
| Block auto play for non-volume devices | Not configured |
BitLocker
| Item | Value |
|---|---|
| BitLocker removable drive policy | Configure |
| — Block write access to removable data-drives not protected by BitLocker | Yes |
Browser
| Item | Value |
|---|---|
| Block Password Manager | Not configured |
| Require SmartScreen for Microsoft Edge Legacy | Yes |
| Block malicious site access | Yes |
| Block unverified file download | Yes |
| Prevent user from overriding certificate errors | Yes |
Connectivity
| Item | Value |
|---|---|
| Configure secure access to UNC paths | Not configured |
| Block downloading of print drivers over HTTP | Enabled |
| Block Internet download for web publishing and online ordering wizards | Enabled |
Credentials Delegation
| Item | Value |
|---|---|
| Remote host delegation of non-exportable credentials | Not configured |
Credentials UI
| Item | Value |
|---|---|
| Enumerate administrators | Not configured |
Data Protection
| Item | Value |
|---|---|
| Block direct memory access | Enabled |
Device Guard
| Item | Value |
|---|---|
| Virtualization based security | Not configured |
| Enable virtualization based security | Not configured |
| Launch system guard | Enabled |
| Turn on Credential Guard | Enable with UEFI lock |
Device Installation
| Item | Value |
|---|---|
| Block hardware device installation by setup classes | Yes |
| — Remove matching hardware devices | Yes |
| Block list | {d48179be-ec20-11d1-b6b8-00c04fa372a7} |
Device Lock
| Item | Value |
|---|---|
| Require password | Yes |
| — Required password | Alphanumeric |
| — Password expiration (days) | 60 |
| — Password minimum character set count | 3 |
| — Prevent reuse of previous passwords | 24 |
| — Minimum password length | 8 |
| — Number of sign-in failures before wiping device | 10 |
| — Block simple passwords | Yes |
| Password minimum age in days | 1 |
| Prevent use of camera | Not configured |
| Prevent slide show | Not configured |
DMA Guard
| Item | Value |
|---|---|
| Enumeration of external devices incompatible with Kernel DMA Protection | Block all |
Event Log Service
| Item | Value |
|---|---|
| Application log maximum file size in KB | |
| System log maximum file size in KB | |
| Security log maximum file size in KB |
Experience
| Item | Value |
|---|---|
| Block Windows Spotlight | Not configured |
| — Block third-party suggestions in Windows Spotlight | Not configured |
| — Block consumer specific features | Not configured |
File Explorer
| Item | Value |
|---|---|
| Block data execution prevention | Not configured |
| Block heap termination on corruption | Not configured |
Firewall
| Item | Value |
|---|---|
| Firewall profile domain | Configure |
| — Inbound connections blocked | Yes |
| — Outbound connections required | Yes |
| — Inbound notifications blocked | Yes |
| — Firewall enabled | Allowed |
| Firewall profile private | Configure |
| — Inbound connections blocked | Yes |
| — Outbound connections required | Yes |
| — Inbound notifications blocked | Yes |
| — Firewall enabled | Allowed |
| Firewall profile public | Configure |
| — Inbound connections blocked | Yes |
| — Outbound connections required | Yes |
| — Inbound notifications blocked | Yes |
| — Firewall enabled | Allowed |
| — Connection security rules from group policy not merged | Yes |
| — Policy rules from group policy not merged | Yes |
Internet Explorer
| Item | Value |
|---|---|
| Internet Explorer encryption support | TLS v1.1 TLS v1.2 |
| Internet Explorer prevent managing smart screen filter | Enable |
| Internet Explorer restricted zone script Active X controls marked safe for scripting | Disable |
| Internet Explorer restricted zone file downloads | Disable |
| Internet Explorer certificate address mismatch warning | Enabled |
| Internet Explorer enhanced protected mode | Enabled |
| Internet Explorer fallback to SSL3 | No sites |
| Internet Explorer software when signature is invalid | Disabled |
| Internet Explorer check server certificate revocation | Enabled |
| Internet Explorer check signatures on downloaded programs | Enabled |
| Internet Explorer processes consistent MIME handling | Enabled |
| Internet Explorer bypass smart screen warnings | Disabled |
| Internet Explorer bypass smart screen warnings about uncommon files | Disabled |
| Internet Explorer crash detection | Disabled |
| Internet Explorer download enclosures | Not configured |
| Internet Explorer ignore certificate errors | Disabled |
| Internet Explorer disable processes in enhanced protected mode | Enabled |
| Internet Explorer security settings check | Enabled |
| Internet Explorer Active X controls in protected mode | Disabled |
| Internet Explorer users adding sites | Disabled |
| Internet Explorer users changing policies | Disabled |
| Internet Explorer block outdated Active X controls | Enabled |
| Internet Explorer include all network paths | Disabled |
| Internet Explorer internet zone access to data sources | Disable |
| Internet Explorer internet zone automatic prompt for file downloads | Disabled |
| Internet Explorer internet zone copy and paste via script | Disable |
| Internet Explorer internet zone drag and drop or copy and paste files | Disable |
| Internet Explorer internet zone less privileged sites | Disable |
| Internet Explorer internet zone loading of XAML files | Disable |
| Internet Explorer internet zone .NET Framework reliant components | Disable |
| Internet Explorer internet zone allow only approved domains to use ActiveX controls | Enabled |
| Internet Explorer internet zone allow only approved domains to use tdc ActiveX controls | Enabled |
| Internet Explorer internet zone scripting of web browser controls | Disabled |
| Internet Explorer internet zone script initiated windows | Disabled |
| Internet Explorer internet zone scriptlets | Disable |
| Internet Explorer internet zone smart screen | Enabled |
| Internet Explorer internet zone updates to status bar via script | Disabled |
| Internet Explorer internet zone user data persistence | Disabled |
| Internet Explorer internet zone allow VBscript to run | Disable |
| Internet Explorer internet zone do not run antimalware against ActiveX controls | Disabled |
| Internet Explorer internet zone download signed ActiveX controls | Disable |
| Internet Explorer internet zone download unsigned ActiveX controls | Disable |
| Internet Explorer internet zone cross site scripting filter | Enabled |
| Internet Explorer internet zone drag content from different domains across windows | Disabled |
| Internet Explorer internet zone drag content from different domains within windows | Disabled |
| Internet Explorer internet zone protected mode | Enable |
| Internet Explorer internet zone include local path when uploading files to server | Disabled |
| Internet Explorer internet zone initialize and script Active X controls not marked as safe | Disable |
| Internet Explorer internet zone java permissions | Disable java |
| Internet Explorer internet zone launch applications and files in an iframe | Disable |
| Internet Explorer internet zone logon options | Prompt |
| Internet Explorer internet zone navigate windows and frames across different domains | Disable |
| Internet Explorer internet zone run .NET Framework reliant components signed with Authenticode | Disable |
| Internet Explorer internet zone security warning for potentially unsafe files | Prompt |
| Internet Explorer internet zone popup blocker | Enable |
| Internet Explorer intranet zone do not run antimalware against Active X controls | Disabled |
| Internet Explorer intranet zone initialize and script Active X controls not marked as safe | Disable |
| Internet Explorer intranet zone java permissions | High safety |
| Internet Explorer local machine zone do not run antimalware against Active X controls | Disabled |
| Internet Explorer local machine zone java permissions | Disable java |
| Internet Explorer locked down internet zone smart screen | Enabled |
| Internet Explorer locked down intranet zone java permissions | Disable java |
| Internet Explorer locked down local machine zone java permissions | Disable java |
| Internet Explorer locked down restricted zone smart screen | Enabled |
| Internet Explorer locked down restricted zone java permissions | Disable java |
| Internet Explorer locked down trusted zone java permissions | Disable java |
| Internet Explorer processes MIME sniffing safety feature | Enabled |
| Internet Explorer processes MK protocol security restriction | Enabled |
| Internet Explorer processes notification bar | Enabled |
| Internet Explorer prevent per user installation of Active X controls | Enabled |
| Internet Explorer processes protection from zone elevation | Enabled |
| Internet Explorer remove run this time button for outdated Active X controls | Enabled |
| Internet Explorer processes restrict Active X install | Enabled |
| Internet Explorer restricted zone access to data sources | Disable |
| Internet Explorer restricted zone active scripting | Disable |
| Internet Explorer restricted zone automatic prompt for file downloads | Disabled |
| Internet Explorer restricted zone binary and script behaviors | Disable |
| Internet Explorer restricted zone copy and paste via script | Disable |
| Internet Explorer restricted zone drag and drop or copy and paste files | Disable |
| Internet Explorer restricted zone less privileged sites | Disable |
| Internet Explorer restricted zone loading of XAML files | Disable |
| Internet Explorer restricted zone meta refresh | Disabled |
| Internet Explorer restricted zone .NET Framework reliant components | Disable |
| Internet Explorer restricted zone allow only approved domains to use Active X controls | Enabled |
| Internet Explorer restricted zone allow only approved domains to use tdc Active X controls | Enabled |
| Internet Explorer restricted zone scripting of web browser controls | Disabled |
| Internet Explorer restricted zone script initiated windows | Disabled |
| Internet Explorer restricted zone scriptlets | Disabled |
| Internet Explorer restricted zone smart screen | Enabled |
| Internet Explorer restricted zone updates to status bar via script | Disabled |
| Internet Explorer restricted zone user data persistence | Disabled |
| Internet Explorer restricted zone allow vbscript to run | Disable |
| Internet Explorer restricted zone do not run antimalware against Active X controls | Disabled |
| Internet Explorer restricted zone download signed Active X controls | Disable |
| Internet Explorer restricted zone download unsigned Active X controls | Disable |
| Internet Explorer restricted zone cross site scripting filter | Enabled |
| Internet Explorer restricted zone drag content from different domains across windows | Disabled |
| Internet Explorer restricted zone drag content from different domains within windows | Disabled |
| Internet Explorer restricted zone include local path when uploading files to server | Disabled |
| Internet Explorer restricted zone initialize and script Active X controls not marked as safe | Disable |
| Internet Explorer restricted zone java permissions | Disable java |
| Internet Explorer restricted zone launch applications and files in an iFrame | Disable |
| Internet Explorer restricted zone logon options | Anonymous |
| Internet Explorer restricted zone navigate windows and frames across different domains | Disable |
| Internet Explorer restricted zone run Active X controls and plugins | Disable |
| Internet Explorer restricted zone run .NET Framework reliant components signed with Authenticode | Disable |
| Internet Explorer restricted zone scripting of java applets | Disable |
| Internet Explorer restricted zone security warning for potentially unsafe files | Disable |
| Internet Explorer restricted zone protected mode | Enable |
| Internet Explorer restricted zone popup blocker | Enable |
| Internet Explorer processes restrict file download | Enabled |
| Internet Explorer processes scripted window security restrictions | Enabled |
| Internet Explorer security zones use only machine settings | Enabled |
| Internet Explorer use Active X installer service | Enabled |
| Internet Explorer trusted zone do not run antimalware against Active X controls | Disabled |
| Internet Explorer trusted zone initialize and script Active X controls not marked as safe | Disable |
| Internet Explorer trusted zone java permissions | High safety |
| Internet Explorer auto complete | Disabled |
Local Policies Security Options
| Item | Value |
|---|---|
| Block remote logon with blank password | Yes |
| Minutes of lock screen inactivity until screen saver activates | 15 |
| Smart card removal behavior | Lock workstation |
| Require client to always digitally sign communications | Yes |
| Prevent clients from sending unencrypted passwords to third party SMB servers | Yes |
| Require server digitally signing communications always | Yes |
| Prevent anonymous enumeration of SAM accounts | Yes |
| Block anonymous enumeration of SAM accounts and shares | Yes |
| Restrict anonymous access to named pipes and shares | Yes |
| Allow remote calls to security accounts manager | |
| Prevent storing LAN manager hash value on next password change | Yes |
| Authentication level | Send NTLMv2 response only. Refuse LM and NTLM |
| Minimum session security for NTLM SSP based clients | Require NTLM V2 and 128 bit encryption |
| Minimum session security for NTLM SSP based servers | Require NTLM V2 and 128 bit encryption |
| Administrator elevation prompt behavior | Not configured |
| Standard user elevation prompt behavior | Automatically deny elevation requests |
| Detect application installations and prompt for elevation | Yes |
| Only allow UI access applications for secure locations | Yes |
| Require admin approval mode for administrators | Yes |
| Use admin approval mode | Not configured |
| Virtualize file and registry write failures to per user locations | Yes |
Microsoft Defender
| Item | Value |
|---|---|
| Block Adobe Reader from creating child processes | Enable |
| Block Office communication apps from creating child processes | Enable |
| Enter how often (0-24 hours) to check for security intelligence updates | 4 |
| Scan type | Quick scan |
| Defender schedule scan day | Everyday |
| Scheduled scan start time | Not configured |
| Cloud-delivered protection level | Not configured |
| Scan network files | Yes |
| Turn on real-time protection | Yes |
| Scan scripts that are used in Microsoft browsers | Yes |
| Scan archive files | Yes |
| Turn on behavior monitoring | Yes |
| Turn on cloud-delivered protection | Yes |
| Scan incoming email messages | Yes |
| Scan removable drives during full scan | Yes |
| Block Office applications from injecting code into other processes | Block |
| Block Office applications from creating executable content | Block |
| Block all Office applications from creating child processes | Block |
| Block Win32 API calls from Office macro | Block |
| Block execution of potentially obfuscated scripts (js/vbs/ps) | Block |
| Block JavaScript or VBScript from launching downloaded executable content | Block |
| Block executable content download from email and webmail clients | Block |
| Block credential stealing from the Windows local security authority subsystem (lsass.exe) | Enable |
| Defender potentially unwanted app action | Block |
| Block untrusted and unsigned processes that run from USB | Block |
| Enable network protection | Enable |
| Defender sample submission consent | Send safe samples automatically |
MS Security Guide
| Item | Value |
|---|---|
| SMB v1 client driver start configuration | Not configured |
| Apply UAC restrictions to local accounts on network logon | Not configured |
| Structured exception handling overwrite protection | Not configured |
| SMB v1 server | Not configured |
| Digest authentication | Not configured |
MSS Legacy
| Item | Value |
|---|---|
| Network IPv6 source routing protection level | Not configured |
| Network IP source routing protection level | Not configured |
| Network ignore NetBIOS name release requests except from WINS servers | Not configured |
| Network ICMP redirects override OSPF generated routes | Not configured |
Power
| Item | Value |
|---|---|
| Require password on wake while on battery | Not configured |
| Require password on wake while plugged in | Not configured |
| Standby states when sleeping while on battery | Not configured |
| Standby states when sleeping while plugged in | Not configured |
Remote Assistance
| Item | Value |
|---|---|
| Remote Assistance solicited | Not configured |
Remote Desktop Services
| Item | Value |
|---|---|
| Remote desktop services client connection encryption level | Not configured |
| Block drive redirection | Not configured |
| Block password saving | Not configured |
| Prompt for password upon connection | Not configured |
| Secure RPC communication | Not configured |
Remote Management
| Item | Value |
|---|---|
| Block client digest authentication | Not configured |
| Block storing run as credentials | Not configured |
| Client basic authentication | Not configured |
| Basic authentication | Not configured |
| Client unencrypted traffic | Not configured |
| Unencrypted traffic | Not configured |
Remote Procedure Call
| Item | Value |
|---|---|
| RPC unauthenticated client options | Not configured |
Search
| Item | Value |
|---|---|
| Disable indexing encrypted items | Yes |
Smart Screen
| Item | Value |
|---|---|
| Turn on Windows SmartScreen | Yes |
| Block users from ignoring SmartScreen warnings | Yes |
System
| Item | Value |
|---|---|
| System boot start driver initialization | Not configured |
Wi-Fi
| Item | Value |
|---|---|
| Block Automatically connecting to Wi-Fi hotspots | Not configured |
| Block Internet sharing | Yes |
Windows Connection Manager
| Item | Value |
|---|---|
| Block connection to non-domain networks | Not configured |
Windows Ink Workspace
| Item | Value |
|---|---|
| Ink Workspace | Enabled |
Windows PowerShell
| Item | Value |
|---|---|
| PowerShell script block logging | Not configured |
Security & Governance
- Authentication Hardening
- Enterprise Mobility
- Essential Eight: Restrict Microsoft Office Macros
Design
- None identified
Configuration
- None identified
References
- None identified
Create Security Baselines to improve security of devices and protect users. Security baselines are sets of recommended settings which created and maintained by Microsoft. In the beginning of 2019 Security baselines became available in Intune (1901 service release). In this blogpost I will show how to create Security Baselines using Intune. More information and news about Security baselines can be found on the Microsoft Security Baselines Techcommunity site.

At the moment there are four security baselines available in Intune:
- Windows 10 Security Baseline
- Microsoft Defender ATP Baseline
- Microsoft Edge Baseline
- Security baseline for Office*
*Security baseline for Office is available, but is not deployed via the Security baselines blade. To apply the security baseline for Office you need to create a policy for Office apps. The baseline settings are preconfigured as a security recommendation. So when you create an policy for Office apps without applying any settings you are basically implementing a Security Baseline for Office apps.

Picture 2: Example of a security recommendation for Office apps
Profiles and Versions
Security baselines consist out of Profiles and Versions. Microsoft maintains and updates the versions of security baselines these contain the recommended settings. To deploy a baseline you need to create a profile based on a baseline. The profile only contains the setting of the version you want to deploy. You do not need to use all the settings which are in the baseline. Some settings you may not want to use because it can block functionality used within your organization. The created profile will be assigned to users and devices. You can create multiple profiles of a Security Baseline version.
Versions
In the Versions screen you see the versions which are available and used within your organization. To deploy a version of As you can see in the following screenshot of the versions screen of Microsoft Edge baseline, there are currently two versions within the organization. As you can see in the overview only the “April 2020” version is assigned using a profile (Number of Profiles). In the description of this version you can read “This baseline version is deprecated.” to remind you there is a newer version.

Picture 3: Microsoft Edge baseline versions
Profiles
As mentioned before to deploy a security baseline you will need to create a profile. The profile is based on a version of the security baseline. In Picture 2 you can see two profiles, in the column “Current Baseline” you can see on which version baseline it was created. The yellow notification in the top indicates that one of the profiles is using a deprecated version baseline. In my next blog I will show how to upgrade a profile to a newer baseline.

Picture 4: Microsoft Edge baseline Profiles
Create Security Baseline
In this tutorial I will demonstrate how to create Security Baseline by creating a new Microsoft Edge Baseline. The same steps can be used to create the Windows 10 or Microsoft Defender baselines.
1. Go to “Endpoint security” -> “Security baselines” -> “Microsoft Edge baseline” or press here. Select “+ Create profile” to setup a Microsoft Edge baseline.

2. Enter a name for the baseline and description (optional). Press “Next” to continue.

3. Select the configuration settings you want to assign. By default all the baseline settings are configured, but you may want to change a settings because it’s needed for a program to function. Also you need to check if the settings in the baseline are not configured in a different configuration policy. This could cause conflicts when the settings are applied to a device. Press “Next” to continue.

4. Add additional scope tags (optional) and press “Next”.

5. Assign the Security baseline to a group. The baseline can be assigned to User groups and device groups for guidance click here. Press “Next” to continue.

6. Review the settings and press “Create” to create and apply the settings to the configured assignment group.

7. Monitor the status of the deployment and test the settings to resolve any policy conflicts.

This is how you create security baselines. Hope you liked this blog.
Microsoft Security Baseline contains recommended settings Microsoft suggests for Windows workstations and servers to provide secure configuration and protect domain controllers, servers, computers, and users.
Microsoft has developed reference Group Policy Objects and templates based on the Security Baselines. Administrators can apply them in their AD domains. The security settings in the Microsoft Security Baseline GPO enable administrators to protect Windows infrastructure in accordance with the latest global security best practices.
Here at Ibmi Media, as part of our Server Management Services, we regularly help our Customers to perform related Windows queries.
In this context, we shall look into how to harden Windows Using Microsoft Security Baseline.
Hardening Windows Using Microsoft Security Baseline
Today, let us see how to implement Microsoft Security Baseline GPOs in our domain.
We can use security baselines to:
1. Firstly, ensure that user and device configuration settings are compliant with the baseline.
2. Secondly, set configuration settings. For example, we can use Group Policy, Microsoft Endpoint Configuration Manager or Microsoft Intune to configure a device with the setting values specified in the baseline.
Reference Microsoft Security Baseline Group Policies are a part of Microsoft Security Compliance Manager (SCM). SCM is a free product that contains multiple tools to analyze, test and apply the best practices and current security recommendations for Windows and other Microsoft products.
Microsoft Security Compliance Toolkit is available following this link: https://www.microsoft.com/en-us/download/details.aspx?id=55319
We can download these tools:
i. LGPO is used to manage local GPO settings.
ii. PolicyAnalyzer is a tool to analyze existing Group Policies and compare them with the reference policies in the Security Baseline.
iii. SetObjectSecurity
The Security Baseline archive for each Windows version contains several folders:
i. Documentation contains XLSX and PDF files with the detailed description of the settings applied in the Security Baseline.
ii. GP Reports has HTML reports with the GPO settings to be applied.
iii. GPOs – contains GPO objects for different scenarios. We can import the policies to our Group Policy Management (GPMC) console.
iv. Scripts contains PowerShell scripts to easily import GPO settings to domain or local policies: Baseline-ADImport.ps1, Baseline-LocalInstall.ps1, Remove-EPBaselineSettings.ps1, MapGuidsToGpoNames.ps1.
v. Templates – additional ADMX/ADML GPO templates (for example, AdmPwd.admx contains local password management settings for LAPS, MSS-legacy.admx, SecGuide.admx).
There are GPO Security Baseline templates for different Windows infrastructure elements:
Policies for computers, users, domain servers, domain controllers (there is a separate policy for virtual DCs), as well as Internet Explorer, BitLocker, Credential Guard and Windows Defender Antivirus settings. Configured Group Policies for various scenarios are located in the GPOs folder.
Note that there is a separate Security Baseline set for each Windows Server version or Windows 10 build.
In order to, extract the archive with the Security Baseline version matching our Windows version and open the Group Policy Management (gpmc.msc) console.
1. Firstly, copy ADMX templates to the SYSVOL PolicyDefinitions folder (GPO Central Store) on our DC.
2. Then, create a new GPO with the name Windows 10 2004 Security Baseline.
3. Next, right-click the GPO and select Import Settings.
4. Then, specify a path to the Security Baseline file for our Windows version as a Backup Location.
5. Next, import a policy with the computer settings. Select MSFT Windows 10 2004 – Computer (using the View Settings button, we can view the policy settings in the form of a gpresult report).
6. Then, we are prompted to select how to migrate reference links to security objects and UNC paths. Since the policy is new, select Copying them identically from the source.
7. Then, the reference Security Baseline policy settings for computers running Windows 10 2004 will be imported to our GPO.
To apply the Group Policy object only to computers running the specific Windows build, use GPO WMI filters. For example, for Windows 10 2004, we can use the following WMI filter:
Select Version,ProductType from Win32_OperatingSystem WHERE Version LIKE “10.0.19041%” and ProductType = “1”
Then, apply the filter to our policy and link the policy to the Organizational Unit we need.
In the same way, we can import Security Baselines for users, domain controllers, domain member servers, etc.
Security Baseline contains dozens or even hundreds of settings. Let us see a few security settings:
i. Firstly, managing the program start and installation rules: AppLocker (Software Restriction Policies), UAC and Windows Installer
ii. Then, domain password and account lockout policies
iii. Next, privileged account restrictions
iv. Next, snonymous access restrictions
v. Then, audit policy settings to get information about all events and user logon history
vi. LSA memory protection
vii. Access to peripherals (including printer and USB installation policies)
viii. Disabling NetBIOS and NTLM protocols
ix. Settings of Remote Assistance, shadow connections, RDS timeouts, CredSSP Oracle Remediation
x. PowerShell Execution Policy
xi. Then, configuration of Windows Error Reporting
xii. Management of Windows Firewall rules
xiii. WinRM settings
xiv. Disabling the built-in administrator account
xv. Hardened UNC paths policy
xvi. Finally, disabling SMBv1
If we want to protect our home computer running Windows 10, we can apply Security Baseline settings on it using a ready PowerShell script.
Allow unsigned scripts to run:
Set-ExecutionPolicy -Scope Process Unrestricted
Apply the policy:
Baseline-LocalInstall.ps1 -Win10NonDomainJoined
Usually, microsoft Security Baseline settings can enhance the security of our Windows infrastructure and help to make sure that the same settings are applied to all computers (including new ones) on our network.