For a Microsoft Windows XP version of this article, see 314458.
Summary
This article describes how you can remove the Linux operating system from your computer, and install a Windows operating system. This article also assumes that Linux is already installed on the hard disk using Linux native and Linux swap partitions, which are incompatible with the Windows operating system, and that there is no free space left on the drive.
Windows and Linux can coexist on the same computer. For additional information, refer to your Linux documentation.
More Information
To install Windows on a system that has Linux installed when you want to remove Linux, you must manually delete the partitions used by the Linux operating system. The Windows-compatible partition can be created automatically during the installation of the Windows operating system.
IMPORTANT: Before you follow the steps in this article, verify that you have a bootable disk or bootable CD-ROM for the Linux operating system, because this process completely removes the Linux operating system installed on your computer. If you intend to restore the Linux operating system at a later date, verify that you also have a good backup of all the information stored on your computer. Also, you must have a full release version of the Windows operating system you want to install.
Linux file systems use a «superblock» at the beginning of a disk partition to identify the basic size, shape, and condition of the file system.
The Linux operating system is generally installed on partition type 83 (Linux native) or 82 (Linux swap). The Linux boot manager (LILO) can be configured to start from:
-
The hard disk Master Boot Record (MBR).
-
The root folder of the Linux partition.
The Fdisk tool included with Linux can be used to delete the partitions. (There are other utilities that work just as well, such as Fdisk from MS-DOS 5.0 and later, or you can delete the partitions during the installation process.) To remove Linux from your computer and install Windows:
-
Remove native, swap, and boot partitions used by Linux:
-
Start your computer with the Linux setup floppy disk, type fdisk at the command prompt, and then press ENTER.
NOTE: For help using the Fdisk tool, type m at the command prompt, and then press ENTER.
-
Type p at the command prompt, and then press ENTER to display partition information. The first item listed is hard disk 1, partition 1 information, and the second item listed is hard disk 1, partition 2 information.
-
Type d at the command prompt, and then press ENTER. You are then prompted for the partition number you want to delete. Type 1, and then press ENTER to delete partition number 1. Repeat this step until all the partitions have been deleted.
-
Type w, and then press ENTER to write this information to the partition table. Some error messages may be generated as information is written to the partition table, but they should not be significant at this point because the next step is to restart the computer and then install the new operating system.
-
Type q at the command prompt, and then press ENTER to quit the Fdisk tool.
-
Insert either a bootable floppy disk or a bootable CD-ROM for the Windows operating system on your computer, and then press CTRL+ALT+DELETE to restart your computer.
-
-
Install Windows. Follow the installation instructions for the Windows operating system you want to install on your computer. The installation process assists you with creating the appropriate partitions on your computer.
Examples of Linux Partition Tables
Single SCSI drive
Device Boot Start End Blocks Id System/dev/sda1 * 1 500 4016218 83 Linux native (SCSI hard drive 1, partition 1)/dev/sda2 501 522 176715 82 Linux swap (SCSI hard drive 1, partition 2)
Multiple SCSI drives
Device Boot Start End Blocks Id System/dev/sda1 * 1 500 4016218 83 Linux native (SCSI hard drive 1, partition 1)/dev/sda2 501 522 176715 82 Linux swap (SCSI hard drive 1, partition 2)/dev/sdb1 1 500 4016218 83 Linux native (SCSI hard drive 2, partition 1)
Single IDE drive
Device Boot Start End Blocks Id System/dev/hda1 * 1 500 4016218 83 Linux native (IDE hard drive 1, partition 1)/dev/hda2 501 522 176715 82 Linux swap (IDE hard drive 1, partition 2)
Multiple IDE drives
Device Boot Start End Blocks Id System/dev/hda1 * 1 500 4016218 83 Linux native (IDE hard drive 1, partition 1)/dev/hda2 501 522 176715 82 Linux swap (IDE hard drive 1, partition 2)/dev/hdb1 1 500 4016218 83 Linux native (IDE hard drive 2, partition 1)
Also, Linux recognizes more than forty different partition types, such as:
-
FAT 12 (Type 01)
-
FAT 16 > 32 M Primary (Type 06)
-
FAT 16 Extended (Type 05)
-
FAT 32 w/o LBA Primary (Type 0b)
-
FAT 32 w/LBA Primary (Type 0c)
-
FAT 16 w/LBA (Type 0e)
-
FAT 16 w/LBA Extended (Type 0f)
Note that there are other ways to remove the Linux operating system and install Windows than the one mentioned above. The preceding method is used in this article because the Linux operating system is already functioning and there is no more room on the hard disk. There are methods of changing partition sizes with software. Microsoft does not support Windows installed on partitions manipulated in this manner.
Another method of removing an operating system from the hard disk and installing a different operating system is to use an MS-DOS version 5.0 or later boot disk, a Windows 95 Startup disk, or a Windows 98 Startup disk that contains the Fdisk utility. Run the Fdisk utility. If you have multiple drives, there are 5 choices; use option 5 to select the hard disk that has the partition to be deleted. After that, or if you have only one hard disk, choose option 3 («Delete partition or logical DOS drive»), and then choose option 4 («Delete non-DOS partition»). You should then see the non-DOS partitions you want to delete. Typically, the Linux operating system has two non-DOS partitions, but there may be more. After you delete one partition, use the same steps to delete any other appropriate non-DOS partitions.
After the partitions are deleted, you can create partitions and install the operating system you want. You can only create one primary partition and an extended partition with multiple logical drives by using Fdisk from MS-DOS version 5.0 and later, Windows 95, and Windows 98. The maximum FAT16 primary partition size is 2 gigabytes (GB). The largest FAT16 logical drive size is 2 GB. For additional information, click the article number below to view the article in the Microsoft Knowledge Base:
105074 MS-DOS 6.2 Partitioning Questions and AnswersIf you are installing Windows NT 4.0 or Windows 2000, the Linux partitions can be removed and new partitions created and formatted with the appropriate file system type during the installation process. Windows allows you to create more than one primary partition. The largest partition that Windows NT 4.0 allows you to create during installation is 4 GB because of the limitations of the FAT16 file system during installation. Also, the 4-GB partitions use 64-KB cluster sizes. MS-DOS 6.x and Windows 95 or Windows 98 do not recognize 64-KB cluster file systems, so this file system is usually converted to NTFS during installation. Windows 2000, unlike Windows NT 4.0, recognizes the FAT32 file system. During the installation of Windows 2000, you can create a very large FAT32 drive. The FAT32 drive can be converted to NTFS after the installation has completed if appropriate.
Need more help?
Want more options?
Explore subscription benefits, browse training courses, learn how to secure your device, and more.
To remove Linux from a PC, you first need a bootable disk. You’ll also need to make a backup of your computer’s data. After removing the Linux partition, you should install the Windows operating system. The Linux partition is usually based on a file system called XFS. Its basic file system features include a superblock at the start of each disk partition. If you don’t want to delete it completely, simply press “Y” to confirm the process.
Once your computer is set up to run Windows, you can remove Linux from your PC. To do this, you need to repair your Master Boot Record (MBR). If you try to remove the Linux partition, you will receive a Grub rescue error. Alternatively, you can create a Windows installation media on your Windows 10 computer or a Linux computer. To create the installation media, start by opening the Run dialog box and typing “msconfig.”
If you are considering replacing your existing Windows operating system with a new one, you may be wondering how to remove Linux and install Windows 10 on the same computer. The answer depends on your needs and whether you have a hard drive with enough free space to accommodate both operating systems. If you’re not sure, check the Linux documentation for the specific procedure to follow. Once you’ve followed the directions, reboot your computer and remove the Linux USB flash drive.
To uninstall the previous operating system, navigate to the Control Panel > Disk Management. Right-click or tap the partition you wish to format and click Remove. The deleted partition will be removed from your computer, freeing up space on the hard drive. Next, you’ll need to format the partition in order to reuse it for another OS. Once you’ve done this, you’re ready to install Windows 10.
Can Windows 10 Be Installed After Linux?
You might be wondering if it is possible to install Windows 10 after Linux. After all, most people use Windows 10 on their computer nowadays. While the two can be operated separately, dual-booting is a popular alternative. Dual-booting enables you to choose which operating system to use. You can even install Linux using a USB drive and run it from there. Dual-booting is the most common way to run both Linux and Windows simultaneously.
If you have a backup of your Windows system, you can boot from it. However, do remember that you may lose files, settings, and even the Windows operating system. Therefore, you should backup your data before erasing the disk. Besides, you may end up facing the GNU GRUB screen while booting from the Linux installation media. To fix this issue, simply move the Linux distro higher in the BIOS.
Alternatively, you can install Linux on the block device that Windows is using. The first step is to install GRUB (the boot loader that is built into Linux). Once you’ve installed it, you can then assign it to chainload Windows. This process is relatively simple, but you should follow the instructions carefully. It’s also a good idea to have other boot media, such as USB drives or external hard drives.
How Do I Change From Linux to Windows 10?
Switching from Linux to Windows 10 may seem like a big step, but it’s not. There are several ways to change your operating system, including a dual boot system. Dual boot systems are a great way to run two different operating systems at once. For most people, this is a good option. You can use the Windows backup function to back up your existing Windows 10 installation. You’ll also be able to use your Linux commands on Windows.
In order to switch between operating systems, you’ll need to resize your windows partition. If your computer doesn’t have a large enough partition, you’ll have to resize it to make room for Linux. This will mean that Windows will lose a lot of space, but it will give you a large enough partition to try out Linux. Alternatively, you can use the same partition for both.
How Do I Dual Boot Linux And Install Windows 10?
If you’ve already installed Linux on your computer, follow the instructions below to remove it. Linux uses native and swap partitions, which are incompatible with Windows. You can also install Windows on an existing Linux partition and then overwrite it with the Windows boot loader. To remove Linux and install Windows 10 2 on an existing partition, follow the instructions below. You’ll need to remove the Linux partition first before you can install Windows.
First, ensure that your computer has secure boot enabled. This prevents malware and other attacks from getting into your system while it’s booting. If you’ve installed Linux without disabling secure boot, you’ll probably encounter a few problems during the installation process. Reboot to Windows to make sure the installation process went smoothly. After making sure that your computer has sufficient disk space, prepare the hard drive. The condition of your HDD or SSD will determine the exact amount of space required.
Next, you can choose the version of Windows you’d like to install. If you don’t like the default size, try resizing the partition so it’s smaller. If the partition you’ve created is too large, you can manually resize it using the Ubuntu installer. Using the second method, you can manually resize the Windows partition as well. Once you’re satisfied with the size, you can then click on “Install Now.”
Can I Go Back to Windows After Installing Linux?
Can I Go Back to Windows after installing Linux on my PC? Fortunately, you can. You’ll have to disable Secure Boot first. Windows will try to load from its own partition if you disable Secure Boot. You can also try using a different boot media or boot loader such as GRUB. Make sure you have a GPT block device and an EFI system partition. If this fails, you can reinstall Windows and try again.
If you’ve installed Linux Mint on your PC and are wondering, “Can I go back to Windows after installing Linux?”, follow these simple steps. Backup your system before switching back to Windows. Doing so will ensure that the Linux installation will be preserved and Windows will be ready when you are. In the unlikely event that you want to switch back to Windows, you can always follow the steps described above. It’s worth mentioning that backing up your Linux Mint system is important to maintain the consistency between the two systems.
You can choose to install Linux on one hard drive and Windows on another. Unless you’ve configured a separate partition for each, it’s likely that Windows will remain the default OS. To switch back, you’ll have to resize Windows’ partition to make room for the new OS. To do this, you need enough free space on your PC. After that, you can use the reset function to boot Windows and Linux again.
How Do I Remove a Linux Partition?
You can remove the Linux partition from a Windows computer by first removing the Windows partition. If you have other partitions for Windows, such as a System Reserved partition, you should also remove these. You may also have recovery discs on your machine, so you’ll need to be prepared to use them. Next, you need to resize the Linux partition. To do this, follow the steps outlined above.
To delete the Linux partition, you must repair the Master Boot Record (MBR). Deleting the Linux partition will result in a grub rescue error. To create Windows 10 installation media, you should boot from the Windows 10 computer or a Linux or Mac computer. You can use the Windows key + R to open the Run dialog. In this dialog box, type msconfig in the search box. Choose’remove’ from the list of entries and click OK.
Next, you should launch the Fdisk utility. You should have a Linux setup floppy disk on hand. Once you have it running, run the Fdisk tool. Then, select the partition you want to delete. If you have deleted the Linux partition, the free space will be freed up. If you wish, you can use that space for another partition. It may be useful to have a separate operating system.
How Do I Install Windows 10 And Replace Ubuntu?
If you’re looking for a way to replace Ubuntu with Windows, you can follow these steps. Windows 10 allows you to run Linux operating systems inside of Windows. You need to create a USB drive and format it before installing the new system. Then, use the disk tool to format the USB drive. This tool is available in Windows’s start menu. After you’ve selected the partitioning scheme you want, it takes only a few seconds to format the drive. Once done, your computer is ready to run the new operating system.
To install Windows, you first need to boot into BIOS. This menu can be accessed by pressing F2 or F10. From there, select the option to repair your system. This will allow you to use the newly installed Windows. Once you’ve repaired the system, disconnect the USB drive and reboot the computer. After a reboot, install Windows from the USB. Make sure to install the latest version of your Windows operating system.
Learn More Here:
1.) Windows Help Center
2.) Windows – Wikipedia
3.) Windows Blog
4.) Windows Central
I need help removing my Ubuntu setup from my computer and replacing it with a brand-new installation of Windows 10 on my laptop. How do I uninstall Ubuntu and install Windows 10? I would appreciate any suggestions.
Best Answered by
Jerry· Answered on Dec 04, 2024
To uninstall Ubuntu and install Windows 10, you need to format the hard drive to remove all the installed OS, and do a clean installation of Windows 10. However, this process will erase all data and programs on your PC when installing a fresh copy of Windows 10. Here are the detailed steps you need to follow:
Step 1. Back up your file and data.
Step 2. Create a Windows 10 Bootable media using Windows 10 bootable USB tool, such as EaseUS OS2Go.
Step 3. Connect it to your computer and reboot it.
Step 4. Choose your bootable media by opening the Boot Device options.
Step 5. Choose the partition and the OS version you want to install.
Step 6. A message with something along the lines of «This partition is not NTFS and has an unknown type» will appear.
Step 7. You’ll then have the choice of «unlocated space.»
Step 8. Click on new and enter the values for the new partitions’ sizes in MB. 100000MB for 100GB, for instance.
Step 9. Make the partitions you want, choose one, and then continue with the OS installation.
Step 10. Done.
EaseUS OS2Go is a practical and easy-to-use Windows To Go creator. It can help you run Windows on a Mac computer and put your Windows 10 on another computer. If you want to uninstall Ubuntu and install Windows 10, it can greatly help you!
Remember that if you clean install Windows 10, all of the data on your computer — including any applications and files you may have installed on Ubuntu — will be lost. Therefore, any crucial data should be backed up before installation begins.
🔗Related article: How to Create Windows 10 Live USB
Download the all-compatible Windows To Go creator.
Use EaseUS OS2Go to create portable Windows USB drive, and use your customized Windows serttings on any other PC or Mac .
People Also Ask
Все способы:
- Шаг 1: Очистка дискового пространства
- Шаг 2: Создание загрузочной флешки с Windows 10
- Шаг 3: Восстановление загрузчика Windows 10
- Вопросы и ответы: 0
Шаг 1: Очистка дискового пространства
Сейчас многие пользователи активно устанавливают на один компьютер несколько операционных систем, что иногда вызывает надобность удаления одной из них в будущем. Сегодня мы рассмотрим пример удаления дистрибутива Linux, сохранив при этом текущее состояние Windows 10 и восстановив загрузчик. Начать стоит с очистки дискового пространства, но это действие вполне может следовать после шага с восстановлением загрузчика, поскольку принципиальной важности в последовательности нет.
- Загрузите Windows 10, щелкните правой кнопкой мыши по меню «Пуск» и выберите пункт «Управление дисками».
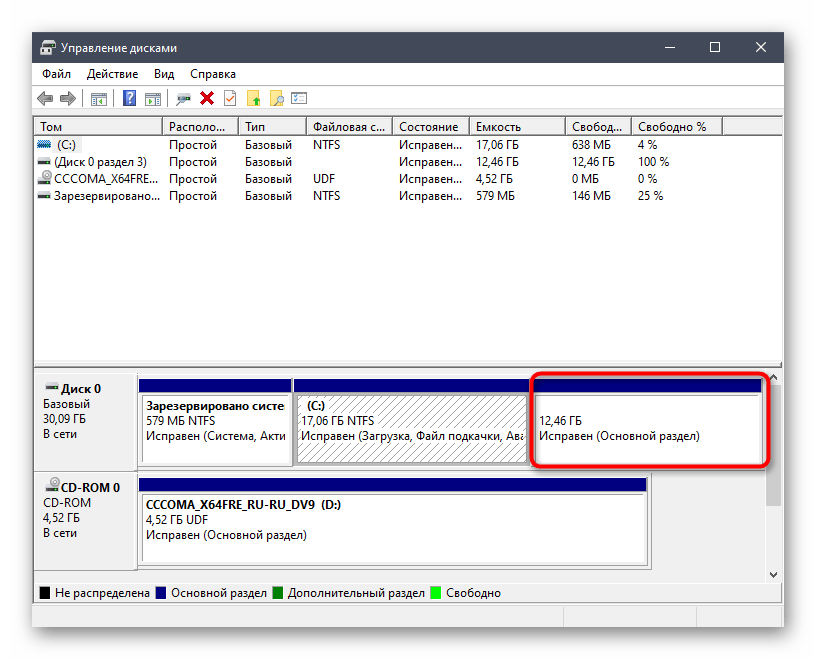
- В открывшемся меню вам следует отыскать все логические тома, связанные именно с Linux. Далее мы расскажем о том, как их определить.
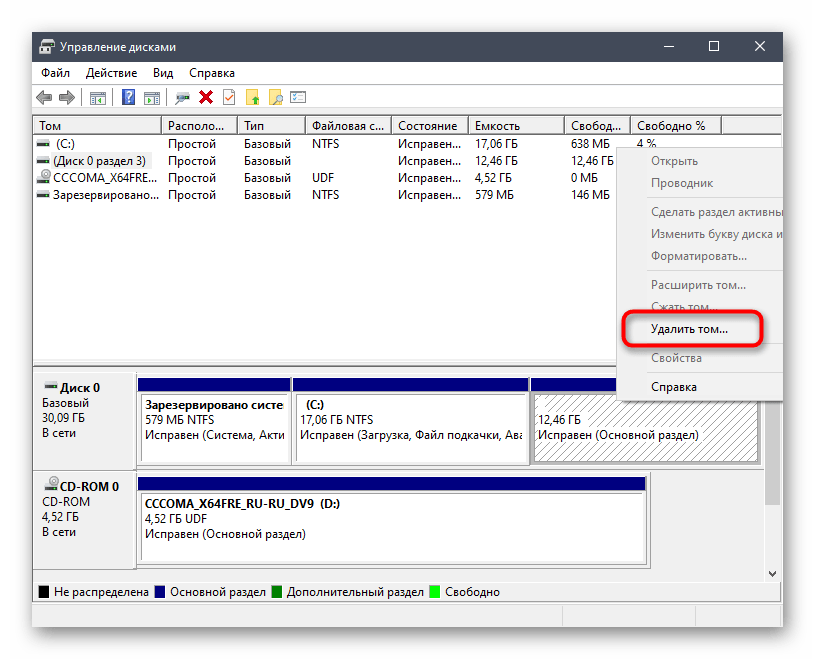
- Нажмите по разделу правой кнопкой мыши и выберите пункт «Удалить том».
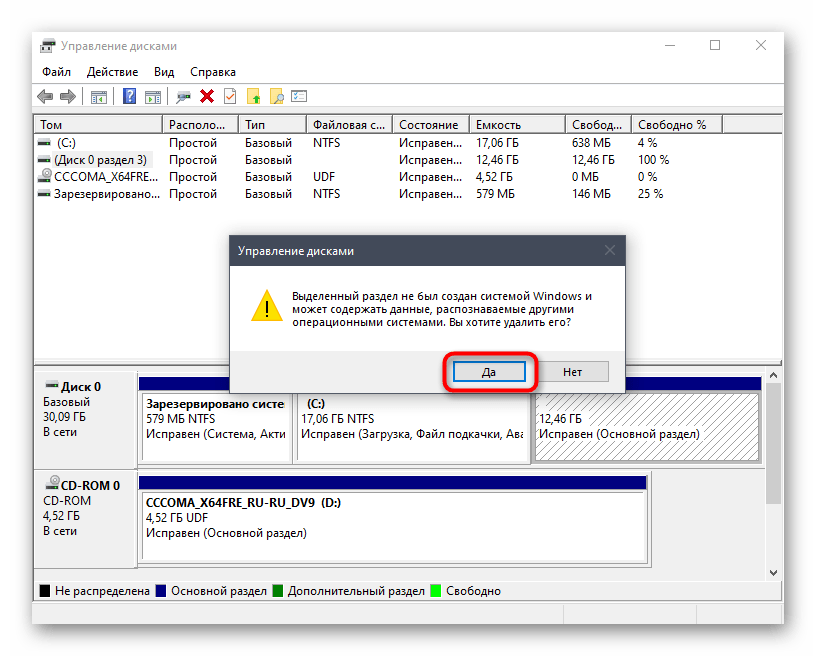
- Как видите, появилось уведомление о том, что данный раздел не был создан Windows, соответственно, принадлежит он файловой системе Linux. Подтвердите удаление и выполните то же самое с оставшимися разделами.
- Пространство обрело атрибут «Свободно». В будущем вы можете расширить уже существующие тома или создать новый, используя именно этот объем, но мы на этом не будем останавливаться, а сразу предлагаем перейти к следующему шагу.
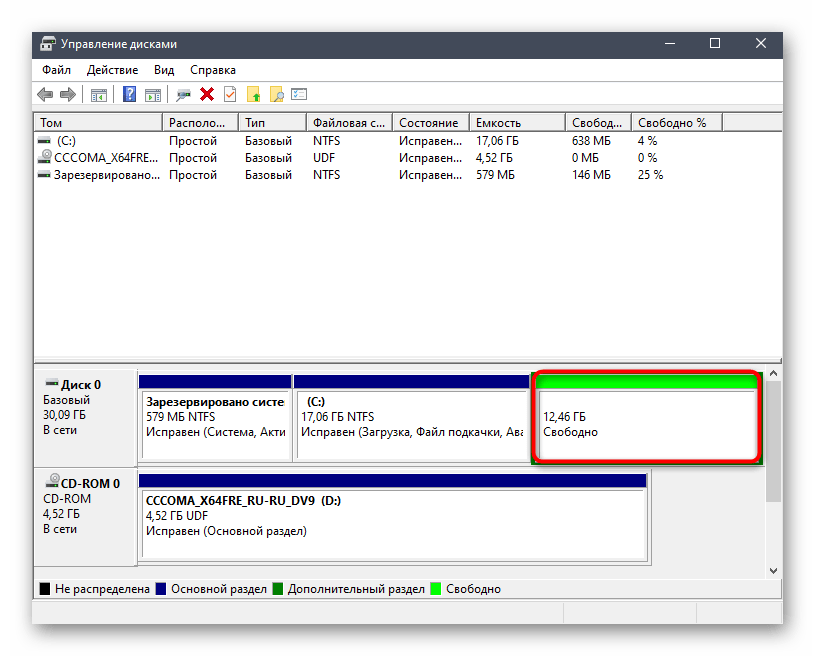
Шаг 2: Создание загрузочной флешки с Windows 10
Этот этап является обязательным, поскольку иначе не получится восстановить загрузчик, необходимый для корректной работы операционной системы. Его суть заключается в скачивании образа с Виндовс 10 и последующей записи его на флешку, создав тем самым загрузочный накопитель. Детальнее об этом процессе читайте в другом материале на нашем сайте, воспользовавшись указанной ниже ссылкой.
Подробнее: Гайд по записи ISO-образа на flash-накопитель
Далее потребуется запустить компьютер с этой флешкой. В большинстве случаев считывание накопителя происходит корректно, однако иногда вероятны сбои, связанные с установкой приоритета носителей информации в BIOS. Исправить это можно простой ручной настройкой, о которой более детально предлагаем прочесть далее.
Подробнее: Настраиваем BIOS для загрузки с флешки
Шаг 3: Восстановление загрузчика Windows 10
Последний и самый важный этап сегодняшнего материала заключается в восстановлении загрузчика необходимой операционной системы, чтобы в будущем не возникло проблем с ее загрузкой. Переходите к выполнению этого шага только после того, как успешно справились с предыдущим.
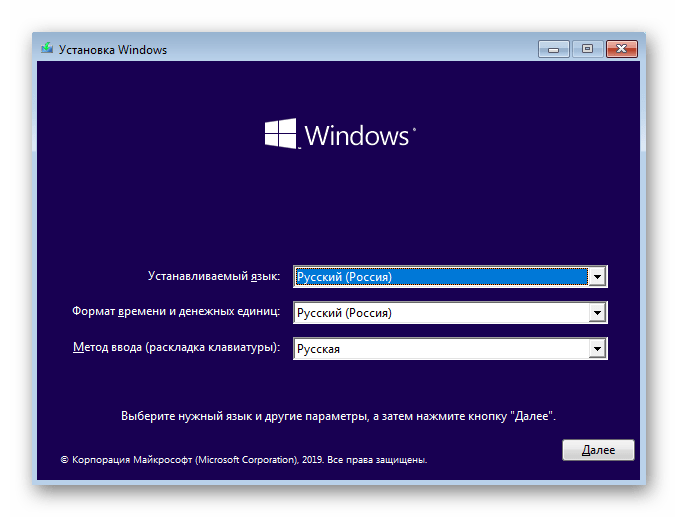
- После запуска ISO-образа с Windows 10 появится основное окно установки языковых параметров. Выберите оптимальный язык и переходите далее.
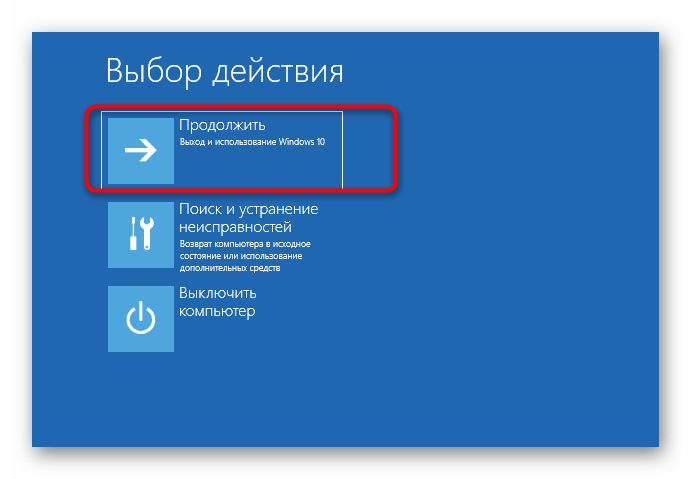
- В следующем окне нас интересует надпись «Восстановление системы». Нажмите на нее, чтобы открыть соответствующее меню.
- Здесь будет всего три кнопки, щелкните на «Поиск и устранение неисправностей».
- В меню «Дополнительные параметры» откройте «Командную строку».
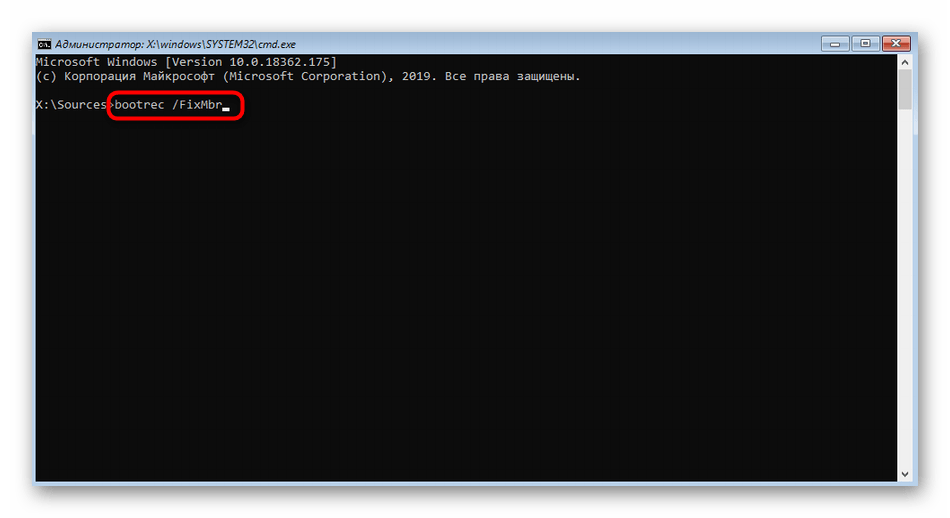
- В строке введите команду
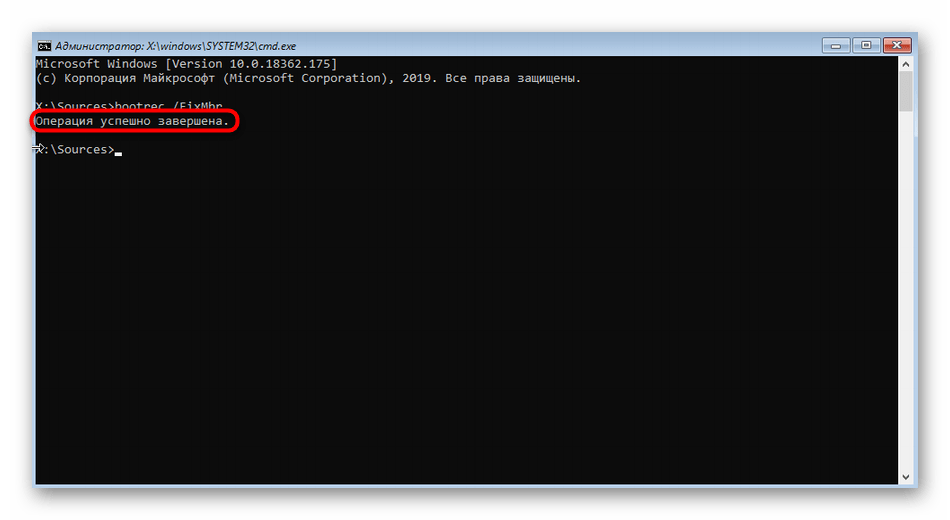
bootrec /FixMbrи нажмите на Enter. - Уведомление «Операция успешно завершена» свидетельствует о корректном внесении изменений в загрузчик. После этого введите похожую команду
bootrec /FixBoot, и можно закрывать консоль. - Продолжите стандартную загрузку ОС, чтобы убедиться в корректности ее функционирования.
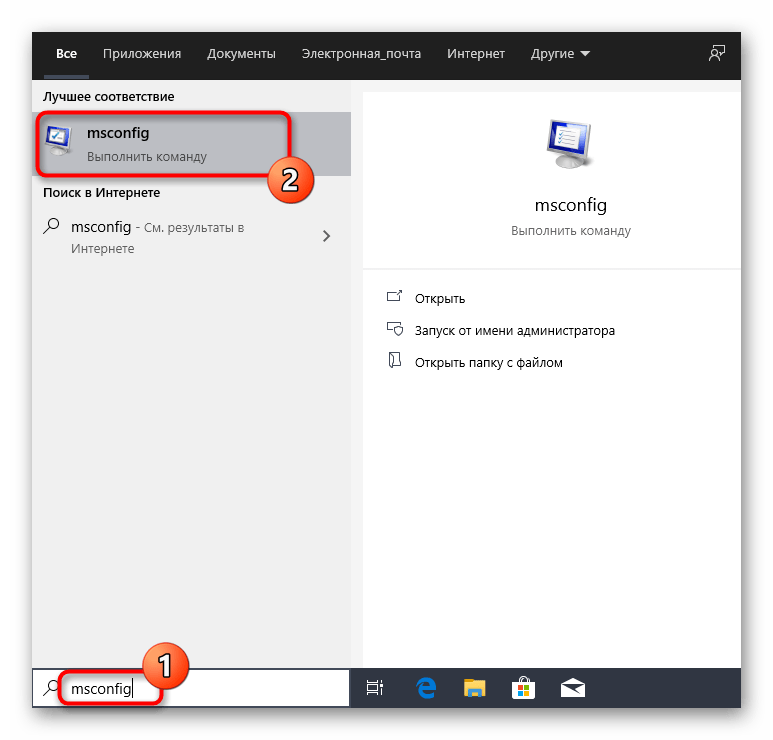
- Дополнительно можно через «Пуск» запустить команду
msconfig. - В открывшемся окне убедитесь, что текущая ОС выбрана в качестве по умолчанию.




В этой статье мы разобрались с удалением Linux, сохранив при этом Windows 10. Приведенные выше инструкции подходят абсолютно для всех существующих дистрибутивов. Важно лишь знать, какие именно логические разделы жестких дисков принадлежат им, чтобы совершить правильное удаление с дальнейшим распределением свободного пространства в своих целях.
Наша группа в TelegramПолезные советы и помощь
Раньше я писал статью о том, как установить Linux после Windows, это довольно простая задача. Но многие пользователи удаляют Windows, ставят Linux, а потом понимают, что им снова нужна Windows. Вот только установить Windows на компьютер, где уже расположился Linux, немного сложнее.
При установке Linux автоматически определяются загрузчики других операционных систем, и добавляются в меню загрузки. Таким образом, вам не надо ничего дополнительно настраивать, чтобы запустить свою Windows. Но если вы устанавливаете Windows поверх Linux, то будет использован загрузчик Windows, и получить доступ к Linux без дополнительных настроек вы не сможете. Однако эта проблема вполне решаемая, и в сегодняшней статье мы поговорим, как правильно инсталлировать Windows после Linux.
Содержание статьи
- Установка Windows после Linux
- Выводы
1. Разметка диска в Linux
Для установки Windows 10 после Linux вам нужно свободное пространство на диске, как минимум 50 гигабайт, а то и больше, если хотите устанавливать туда много игр и программ. Современные версии Windows хотят создавать два раздела:
- Системный;
- Раздел с данными для восстановления;
Но тут надо учитывать один момент, если у вас используется таблица разделов MBR, то основных разделов может быть только четыре. И если у вас уже есть корневой раздел, домашний и swap для Linux, то раздел восстановления получается пятым, а это уже проблема, поэтому нужно создать расширенный раздел и уже там размечать разделы для Windows. Если вы ставите эту ОС на другой жёсткий диск, то никаких проблем нет, но я предполагаю что обе системы устанавливаются именно на один диск.
Во-первых, нам необходимо загрузиться с LiveCD, поскольку надо уменьшить размер либо корневого раздела, либо домашнего, а эти диски примонтированы. Самый простой способ это сделать — загрузиться с Live системы.
Загружаем наш диск, например Ubuntu, и запускаем Gparted:
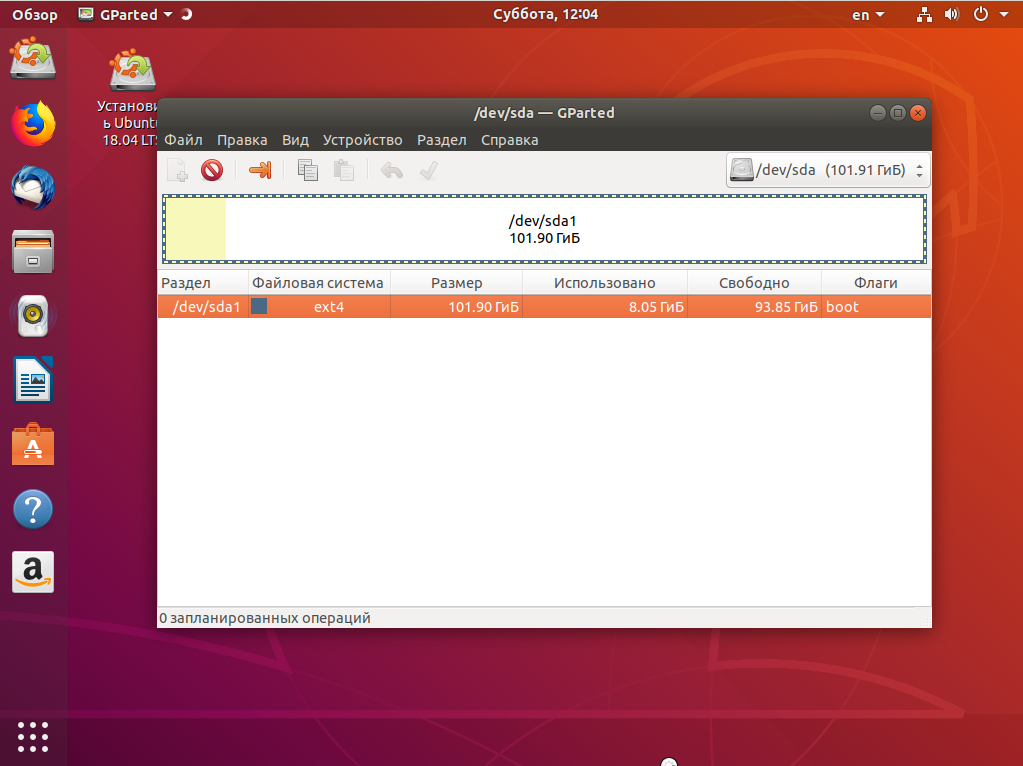
Затем нужно уменьшить раздел. Для этого выберите нужный и кликните Изменить или переместить:
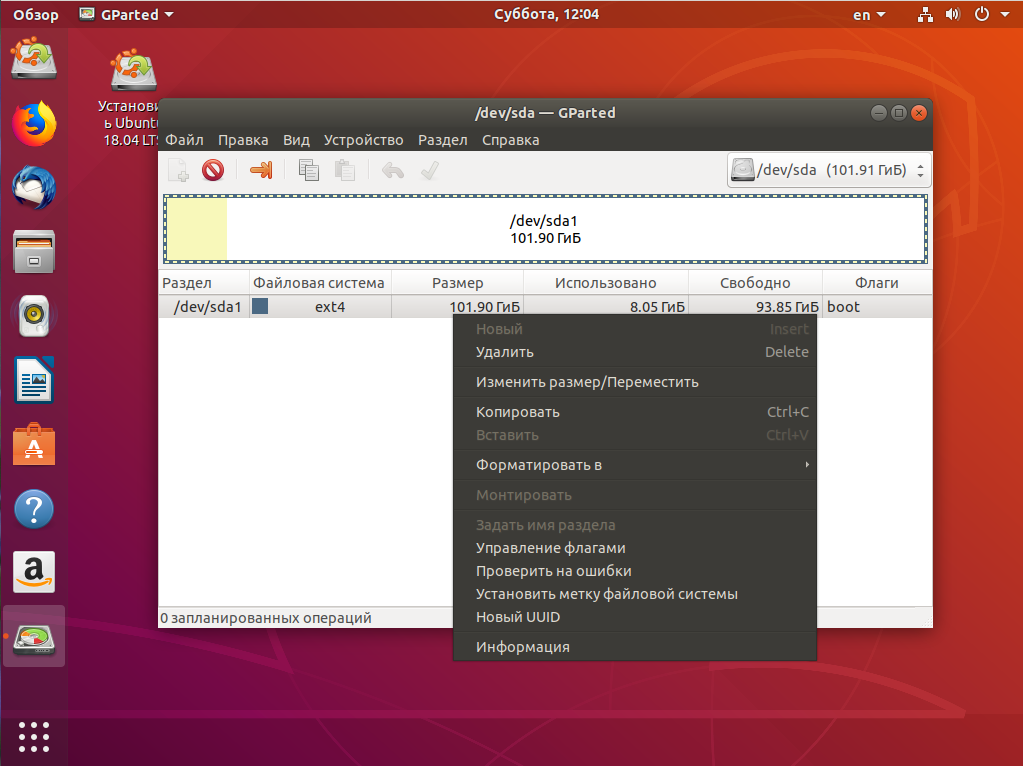
Затем уменьшите раздел так, чтобы после него оставалось 40-50 гигабайт:
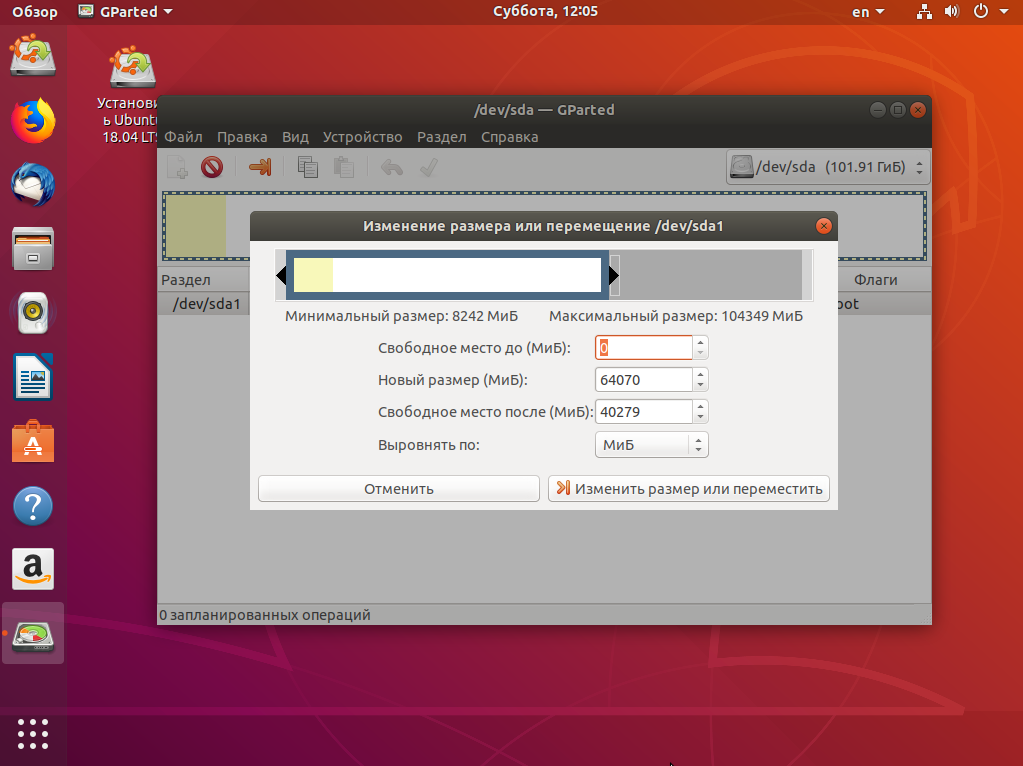
Далее выберите свободное пространство и щёлкните в контекстном меню пункт Новый:
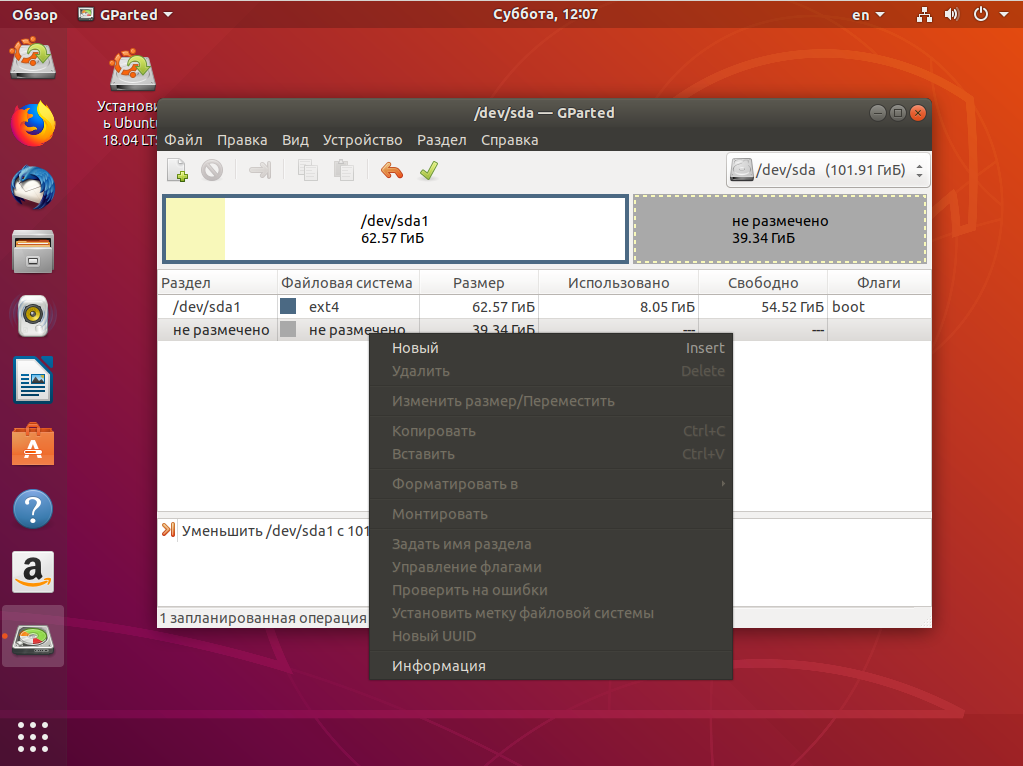
Помните, я выше писал, что с таблицей разделов MBR можно создавать только четыре основных раздела. Поэтому из свободного пространства создаём расширенный раздел. Выберите в поле Создать как -> Расширенный раздел:
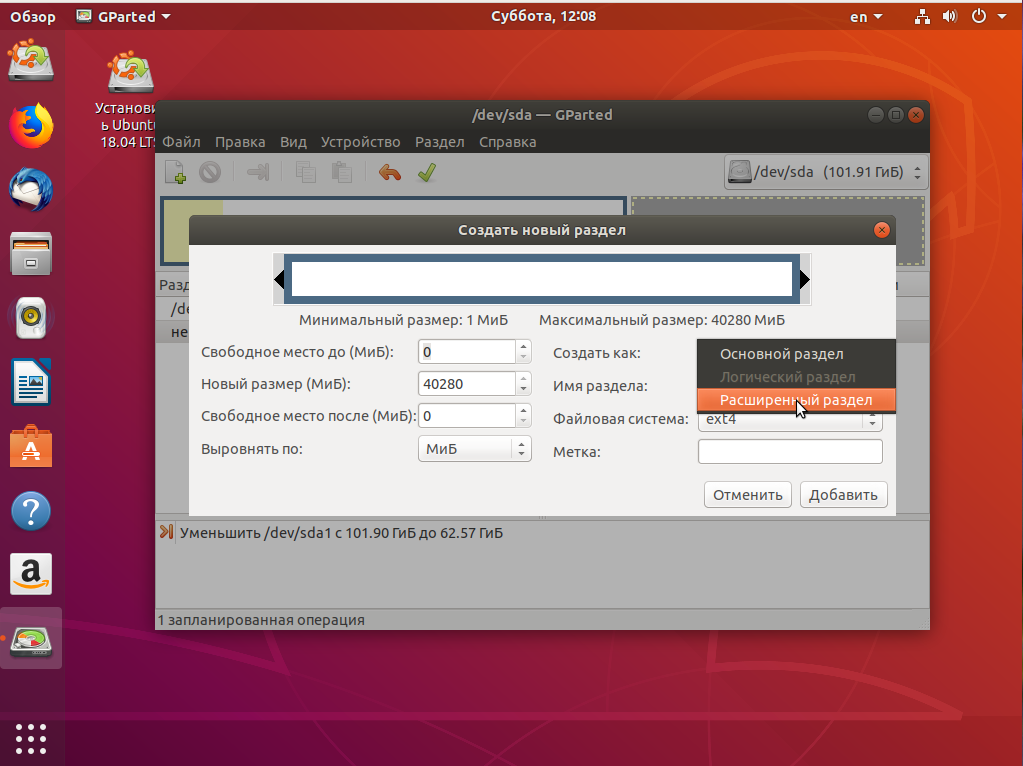
Выберите всё доступное место, а потом нажмите Ок:
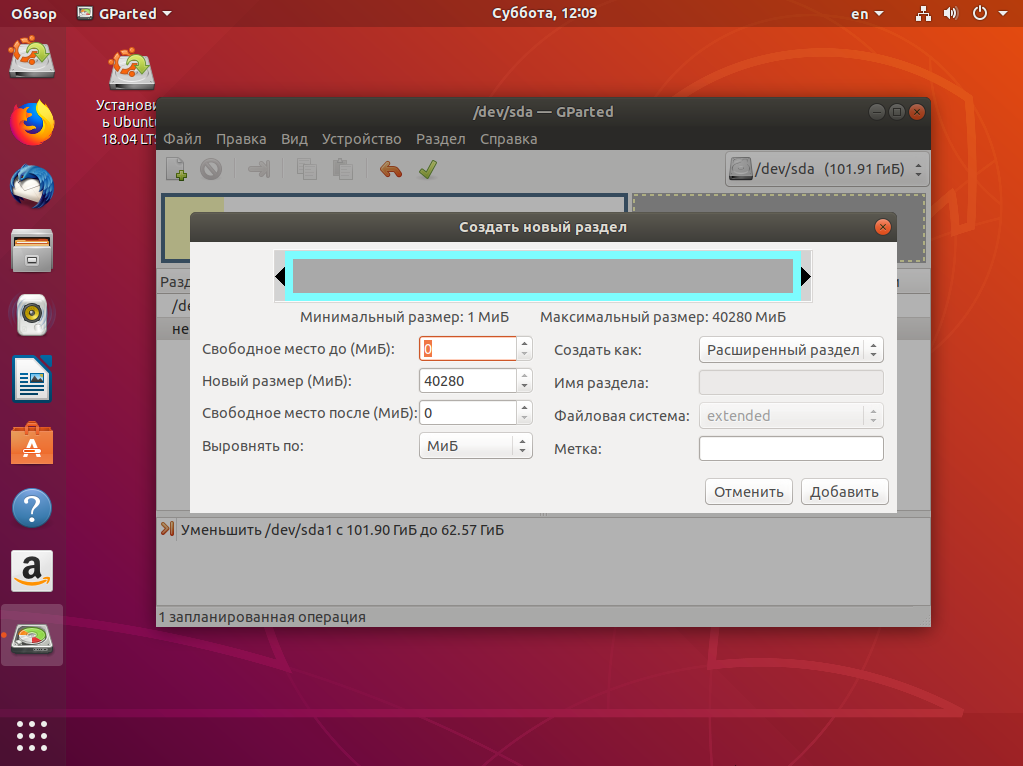
На этом в Gparted всё. Далее нам необходимо нажать зелёную галочку или Правка -> Применить изменения, а потом дождаться завершения всех операций.

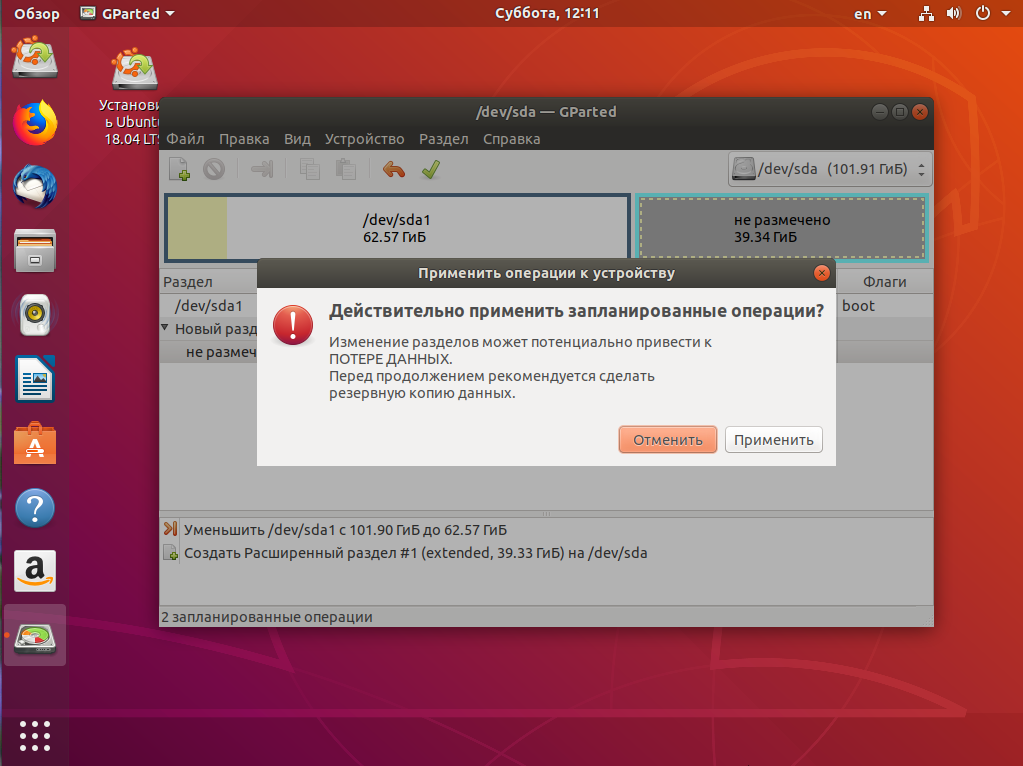
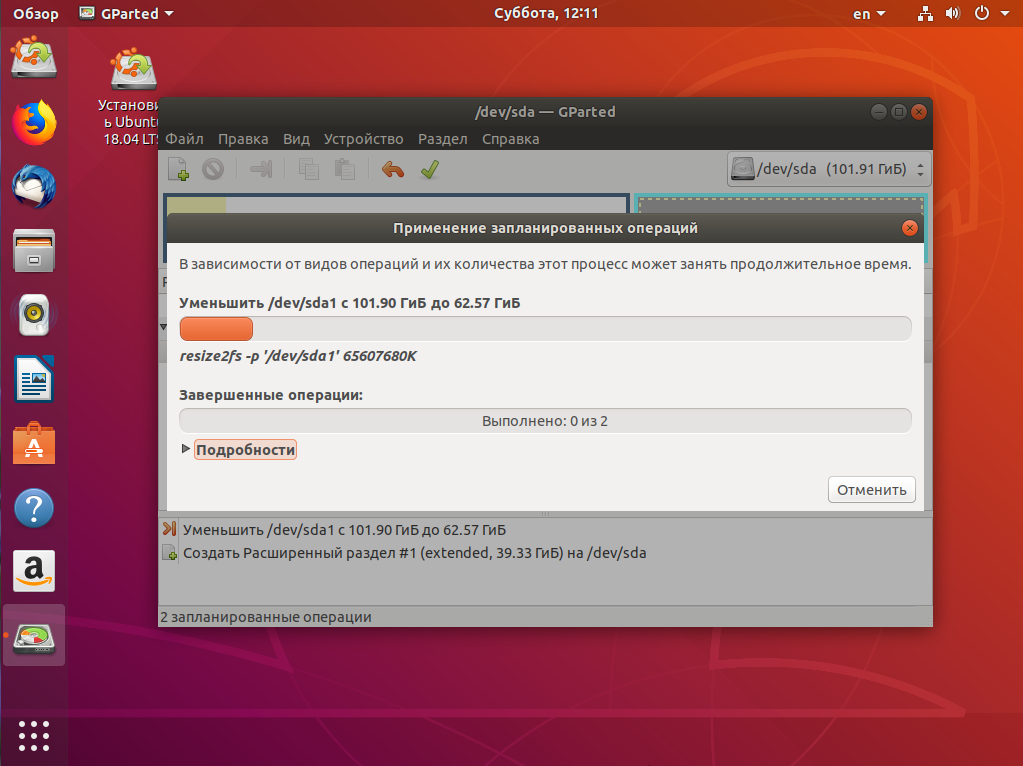
2. Разметка диска в Windows
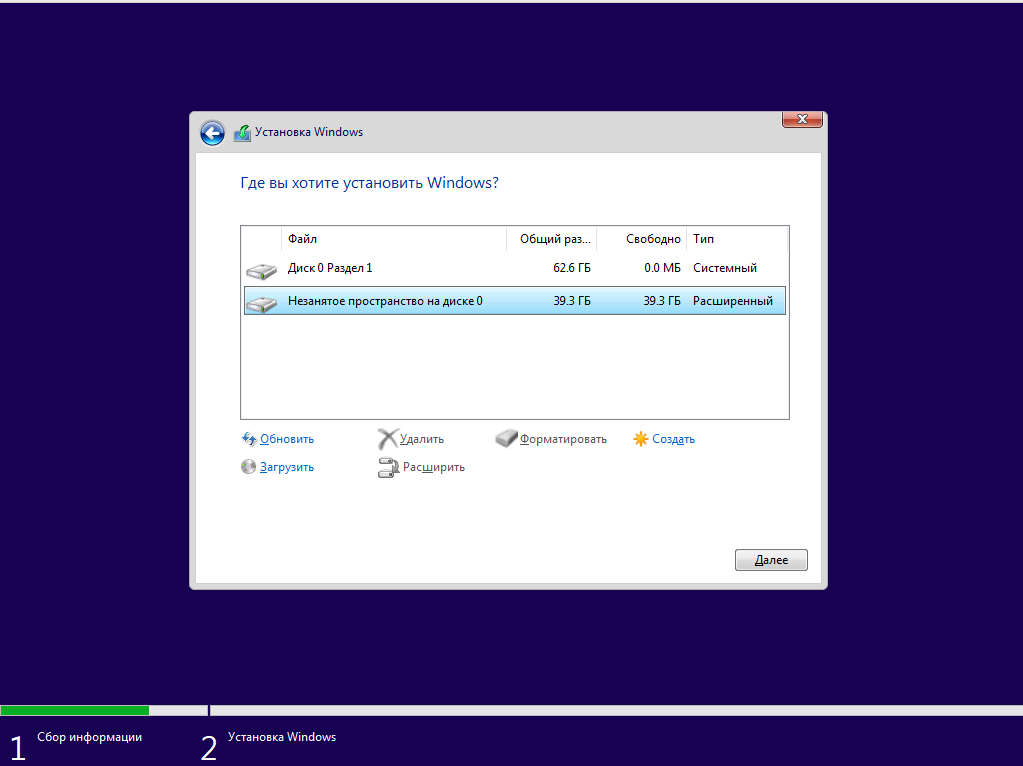
Теперь надо разобраться, как поставить Windows после Linux. Я не буду рассматривать все шаги установщика Windows. Вы их и так знаете. На шаге выбора раздела для установки кликните по свободному месту, которое подготовили раньше. Система не будет показывать расширенных разделов и других дополнительных параметров диска, только размер, это для неё нормально.
Затем нажмите кнопку Создать и выберите размер раздела. Можно согласиться с тем, что предлагает установщик:
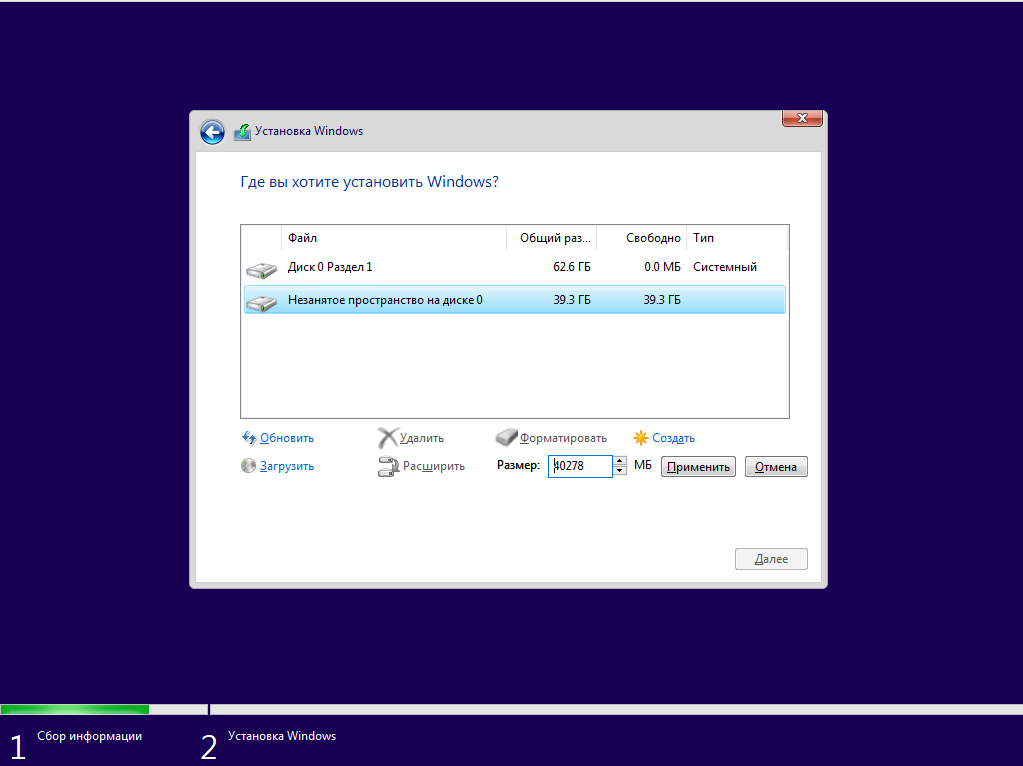
Затем согласитесь на создание дополнительных разделов для системных файлов:
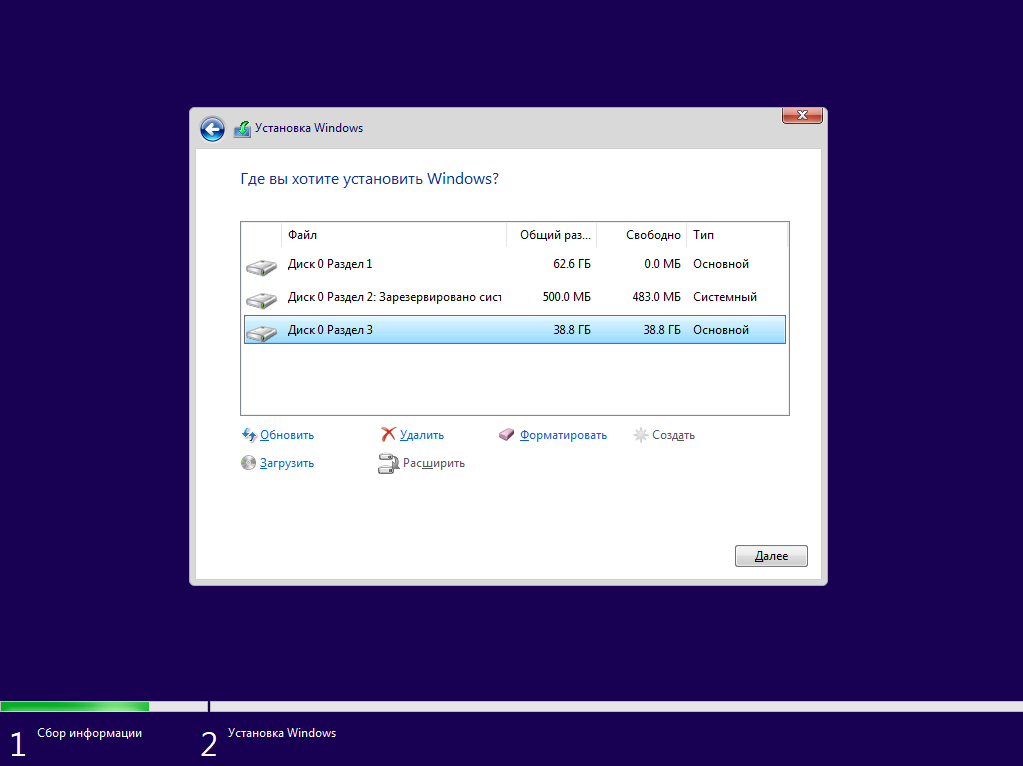
Дальше выбирайте только что созданный системный размер и нажимайте Далее. Осталось дождаться завершения установки.
3. Восстановление загрузчика Linux
После того, как вы окажетесь на рабочем столе Windows, работа с Windows будет завершена, и вам надо снова загрузиться с LiveCD Ubuntu или дистрибутива Linux, который у вас установлен. Дальше мы будем выполнять действия, описанные в статье о восстановлении загрузчика Grub.
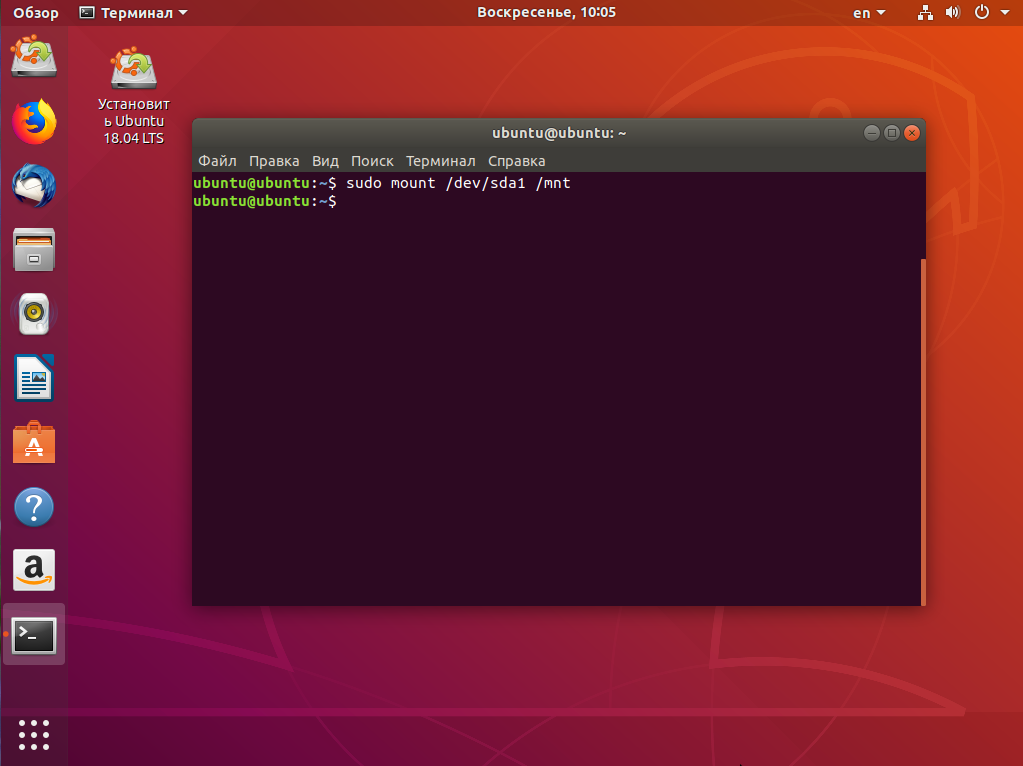
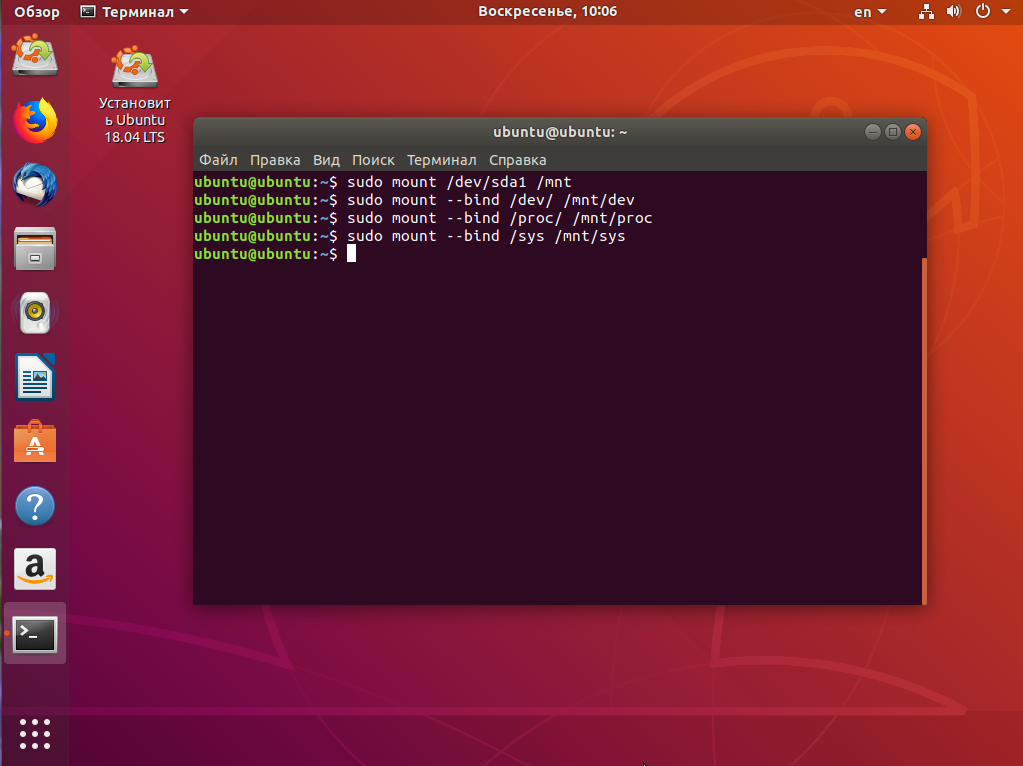
Сначала нам нужно примонтировать корневой раздел с Linux, в моём случае это /dev/sda1:
sudo mount /dev/sda1 /mnt
Если раздел /boot у вас также существует отдельно, его тоже надо примортировать. Затем подключаем подсистемы взаимодействия с ядром в папку /mnt, куда мы раньше примонтировали корень:
sudo mount --bind /dev/ /mnt/dev/
sudo mount --bind /proc/ /mnt/proc/
sudo mount --bind /sys/ /mnt/sys/
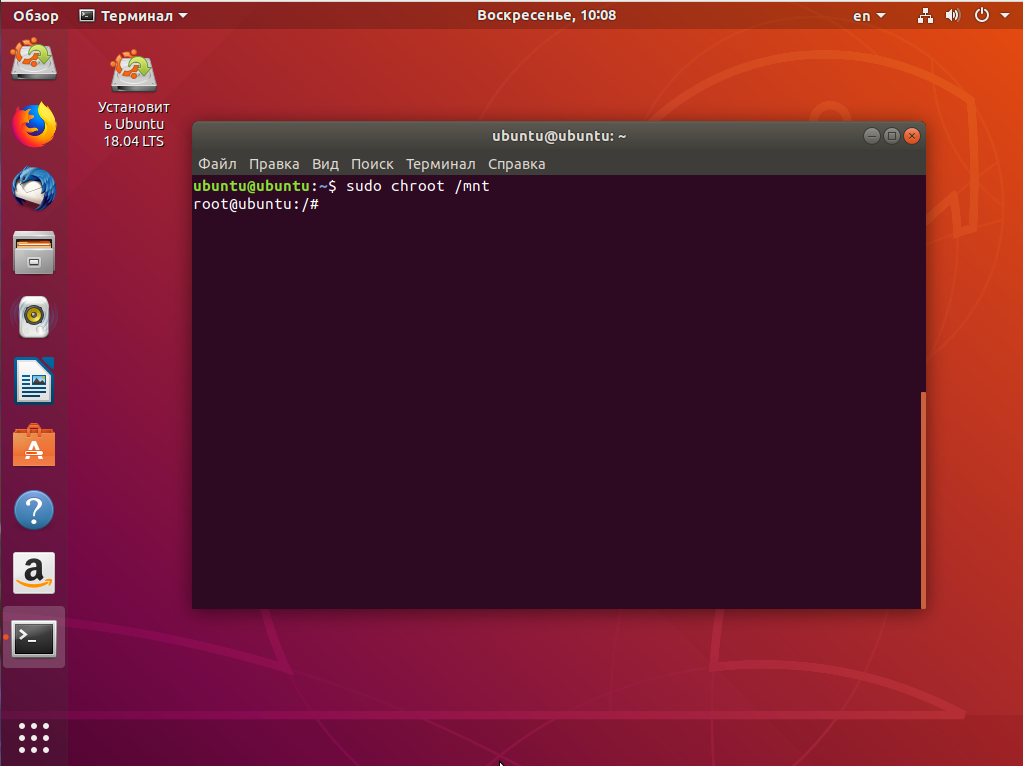
И переходим в окружение нашего установленного ранее Linux с помощью команды chroot:
sudo chroot /mnt/
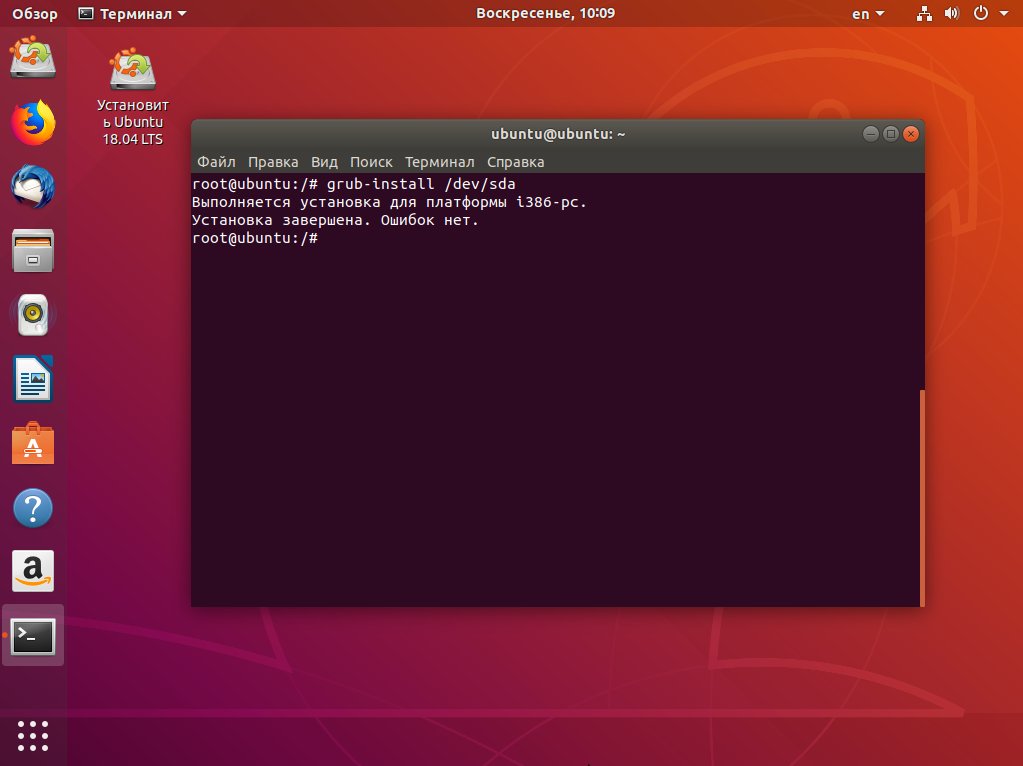
Далее мы можем заняться восстановлением загрузчика. Сначала установим его на диск:
grub-install /dev/sda
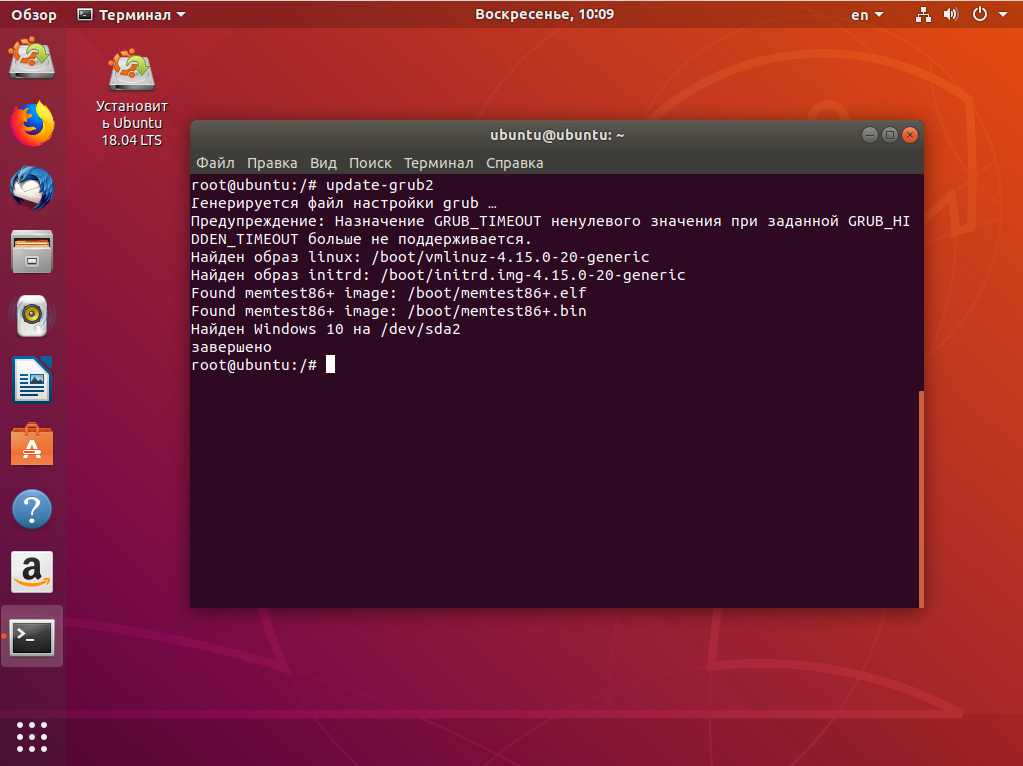
Затем создадим новый конфигурационный файл, в котором уже будет наша только что установленная Windows:
update-grub2
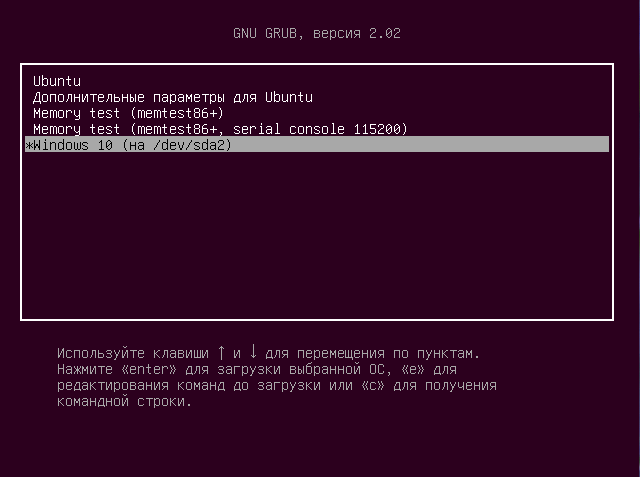
Дальше осталось перезагрузить компьютер:
Теперь в качестве загрузчика будет использоваться Grub2 и в списке операционных систем отобразится Ubuntu и Windows, чего мы и добивались:
Выводы
В этой статье мы рассмотрели, как выполняется установка Windows после Linux. Это довольно нетипичная ситуация, но для многих пользователей информация может быть полезной. А вы используете Windows рядом с Linux? Напишите в комментариях!
Статья распространяется под лицензией Creative Commons ShareAlike 4.0 при копировании материала ссылка на источник обязательна .
