Windows Server 2008 r2, работа, служба терминалов, служба удаленных рабочих столов
Установка сервера удалённых рабочих столов
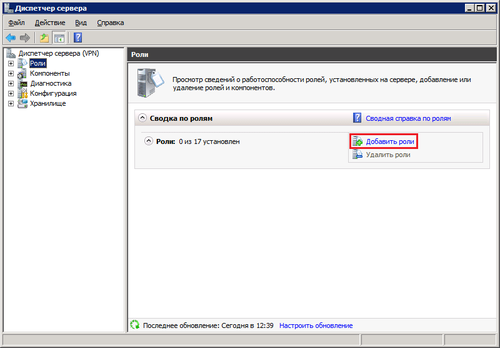
Входим на сервер с правами администратора.
Открывем «Дисппетчер сервера» -> Роли -> Добавить роль:
В списке доступных ролей сервера выбираем «Службы удалённых рабочих столов»:

В списке «Службы роли» отмечаем «Узел сеансов удалённых рабочих столов» и «Лицензирование удалённых рабочих столов». Этих служб достаточно для поддержания базовой функциональности.

Желательно устанавливать сервер терминалов до установки пользовательских приложений.
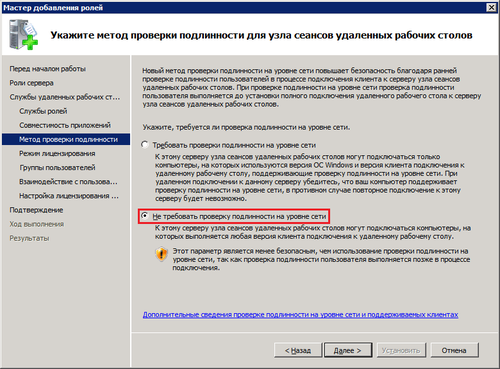
Метод проверки подлинности. «Требовать проверку подлинности на уровне сети» — эта опция обеспечивает повышенную безопасность, но в этом режиме к серверу не смогут подключаться пользователи с устаревшими клиентами (rdp 5.х и ниже), а также пользователи подключающиеся через Эксплорер (remote desktop web connection). Чтобы обеспечить поддержку клиентов всех версий, выбирайте опцию «Не требовать проверку подлинности на уровне сети».
Режим лицензирования. Желательно заранее определиться с режимом лицензирования: «на пользователя» или «на устройство». Лицензии «на пользователя» эффективны, если в организации большое количество мобильных пользователей, которым требуется доступ к серверу как из корпоративной сети, так и из удаленной (дом, другой офис). Лицензии «на устройство» эффективны, если пользователи жестко привязаны к своим рабочим местам.

Группы пользователей. Здесь вы можете сразу указать группы или отдельных пользователей, которым будет разрешен доступ к серверу терминалов. Это можно будет сделать и позднее, просто добавив нужных пользователей в группу «Пользователи удаленного рабочего стола».

Настройка сервера лицензий Windows Server 2008 r2. Если сервер не входит в домен, то вариантов особо нет:

Обзор выбранных опций перед установкой.
Далее нажимаем кнопку Установить. Система один раз перезагрузится, после чего установка будет продолжена. В итоге вы должны увидеть жизнеутверждающий экран «Установка прошла успешно»
Активация сервера терминалов
Открываем Пуск -> Администрирование -> Службы удалённых рабочих столов -> «Диспетчер лицензирования удалённых рабочих столов». В списке выбираем сервер лицензий. Делаем правый клик, и в меню выбираем пункт «Активировать сервер»:

Запускается мастер активации сервера Windows Server 2008 r2
На следующем шаге выбираем метод подключения. Можно смело выбирать «Автоподключение»:
Сведения об организации. Вводим имя, фамилию и название организации
Дополнительные сведения. Можно заполнить, а можно и проигнорировать
Через несколько секунд ваш сервер будет успешно активирован
Теперь можно преступить к установке лицензий. Следует отметить, что после активации сервера лицензий нет необходимости сразу покупать и устанавливать лицензии. При отсутствии полноценных лицензий сервер работает в демо-режиме. Пользователям выдаются временные лицензии на 120 дней.
Установка лицензий
Запускаем мастер установки лицензий. Это можно сделать сразу после активации сервера лицензий, выбрав соответствующую опцию
Далее выбираем тип соглашения. В моем случае это «Enterprise Agreement». Номер соглашения можно найти в поисковике по запросу «Enrollment Number». Например, работают: 4965437 (3325596;6565792;4526017;5296992)

Выбираем версию продукта, тип лицензии (должен совпадать с ранее выбранным типом лицензий сервера лицензий), количество лицензий

Нажимаем Далее. Если данные верны, лицензии будут успешно установлены.
Попутные вопросы:
Как разрешить новому пользователю доступ к удаленному рабочему столу?
Откройте Диспетчер сервера -> Конфигурация -> Локальные пользователи -> Пользователи. Откройте свойства пользователя, которому необходим доступ, закладка «Членство в группах». Добавьте группу «Пользователи удаленного рабочего стола»:

Можно ли под одним аккаунтом создать несколько независимых сеансов подключения?
Можно, но по умолчанию эта опция отключена (для экономии ресурсов). Откройте Диспетчер сервера -> Роли -> Конфигурация служб терминалов -> Изменить настройки (на той же странице). Двойной клик на опции открывает окно, где можно выполнить изменения:

Какой порт использует RDP по умолчанию и как его изменить?>
По умолчанию используется порт TCP 3389. Изменить его можно отредактировав реестр. Откройте ветку
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\System\CurrentControlSet\Control\TerminalServer\WinStations\RDP-tcp
и измените параметр PortNumber.
Взято отсюда
| Previous | Table of Contents | Next |
| Configuring and Managing RAID 5 on Windows Server 2008 R2 | Installing Applications for Windows Server 2008 R2 Remote Desktop Services |
<google>BUY_WINSERV_2008R2</google>
Remote Desktop Services (formerly known as Terminal Services and often abbreviated to RD Services) allow either individual applications or entire desktop sessions to be run on remote server systems, but displayed and interacted with on local client systems. In effect, while the applications and desktops appear to be running on the local machine they are actually running in virtual sessions on the remote server with only the display graphics and keyboard and mouse information passing between the two systems. This allows one or more Windows Server 2008 R2 systems (referred to as Remote Desktop Session Hosts) to provide the applications and desktops for any number of desktop systems. This has a number of advantages in terms of ensuring that all users have the same version of a particular application and also in terms of reducing administrative overheads. With remote desktop services, for example, if an application needs to be upgraded it only needs to be upgraded on the host server, not on every desktop in the enterprise.
There are a number of different Remote Desktop Services configuration options, many of which will be covered in subsequent chapters. In this chapter the configuration of the basic Remote Desktop Services role and installing applications for use by Remote Desktop Services users will be covered.
Contents
Contents
|
||
Installing Remote Desktop Services
Windows Server 2008 R2 Remote Desktop Services may be installed from the Server Manager tool. Within Server Manager, click on Roles in the left hand pane and click on Add Roles in the resulting screen to invoke the Add Roles Wizard. If the introductory screen appears, click on Next to list the available roles. On the Select Server Roles screen, select Remote Desktop Services and click on Next to select the specific services required. For the purposes of this chapter just the basic Remote Desktop Session Host option needs to be selected (the other options will be covered in subsequent chapters):

After clicking Next a warning screen will appear recommending that any applications intended to be accessed by remote desktop users not be installed until the Remote Desktop Services role has been installed. In fact, the installation of applications for Remote desktop Services requires some special steps which will be covered in detail in a later chapter. Having read this information, click Next to proceed to the authentication selection screen. Selecting Require Network Level Authentication will prevent users running on older operating systems without Network Level Authentication from accessing Remote Desktop Services. Network Level Authentication essentially performs authentication before the remote session is established. If less strict authentication is acceptable or some users are running older operating systems then the Do not require Network level Authentication option will need to be selected before clicking Next to proceed.
The Specify Licensing Mode screen allows the licensing method to be defined. If Configure later is selected a 120 day grace period allows the system to be used without providing licenses. If this option is selected the licensing must be configured within 120 days. In the case of Per Device mode, this allows a specified number of devices to connect to the service at any one time regardless of who the users are. On the other hand, Per User restricts access to specified users, regardless of the device from which they are connecting.
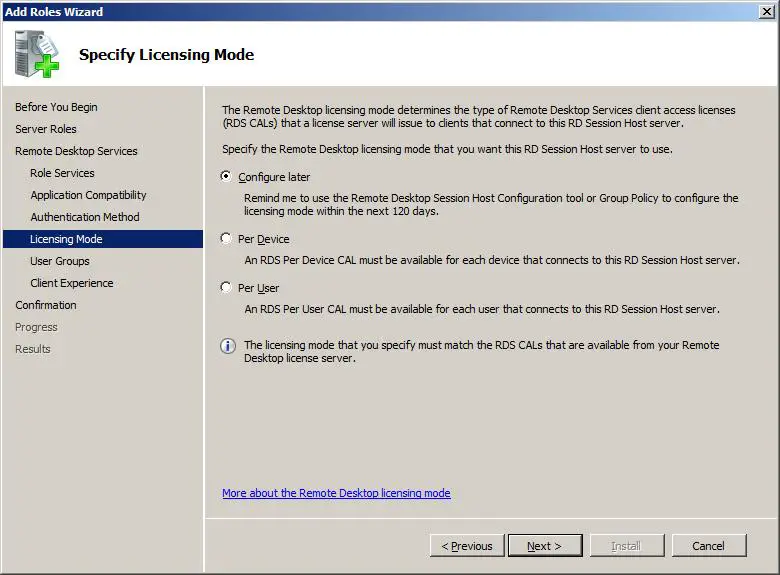
For the purposes of this tutorial, select the Configure later option and click Next to proceed.
Next, the users and groups allowed to access the RD Session Host need to be specified, although users may be added and removed at any time by changing the members of the Remote Desktop Users Group. Click on Add… to add additional users.
The final configuration screen allows the user experience to be configured. This essentially controls whether or not audio, video and desktop effects (such as the Aero user interface) are enabled on the user’s remote desktops. The reason that these features are not enabled by default is that they consume considerable amounts of bandwidth and place an extra load on the RD Session Hosts. Unless you specifically need users to be able to stream audio (both to and from the session host) and video to the remote desktops and use the latest graphics intensive desktop effects it is recommended that these features remain disabled:
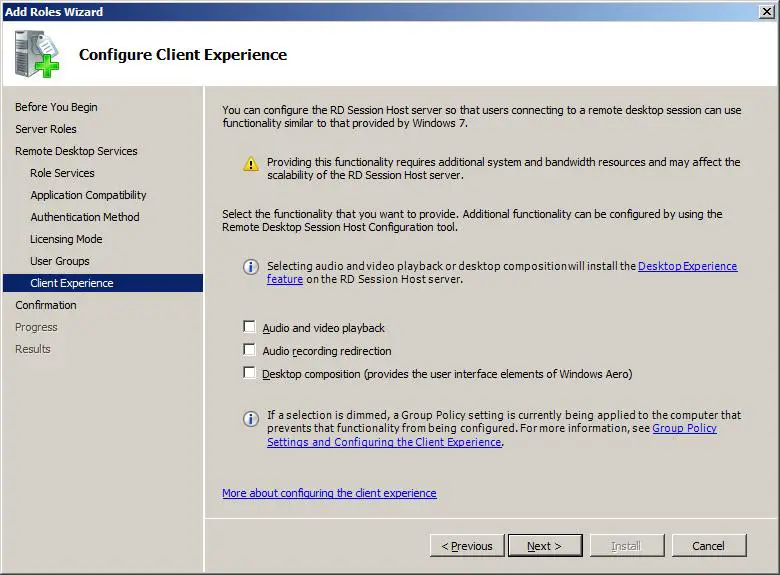
Clicking Next proceeds to the Confirmation screen. Read carefully any warnings that are displayed. Typically the wizard will recommend any currently installed applications should be re-installed before remote access is provided to users (steps to achieve this are outlined in the next chapter). Click Install to begin the installation process. Partway through the installation it will be necessary to restart the Windows Server 2008 R2 system. Once rebooted, be sure to log in as the same administrative user to complete the Remote Desktop Services configuration process. Once the process is complete, a screen similar to the following will appear:
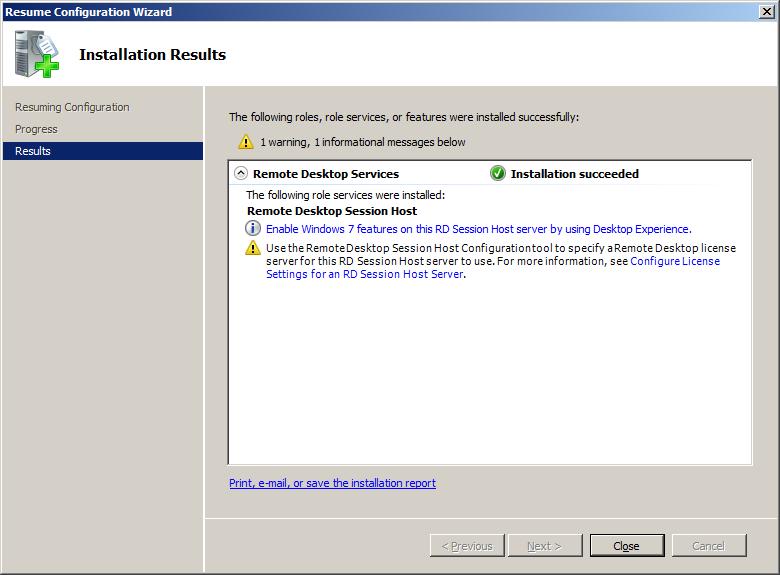
Adding Users to the Remote Desktop Users Group
The default configuration for Remote Desktop Users Group is to allow all members of the Administration group to connect remotely. Active Directory also contains a Remote Desktop Users group to which users may be added to provide Remote Desktop access privileges. To provide users with remote desktop and application access through Remote Desktop Services, open Control Panel -> System and Security -> System -> Remote settings and click on the Select Users button to invoke the Remote Desktop Users dialog illustrated in the following figure:
<google>ADSDAQBOX_FLOW</google>
Note that users with administrative privileges do not need to be added to this list, by default they already have Remote Desktop access. To add additional users click on the Add… button to display the Select Users dialog. Enter the name of the user in the text box entitled Enter object names to select and click on Check names to list names that match the name entered. Select the appropriate name from the list. The following example shows user Bill on server winserver-2:

Click on OK to apply the change. The new user will now appear in the list of users with Remote Desktop access on the Remote Users screen. Click OK to close this screen and click on Apply in the System Settings screen. The specified user will now have Remote Desktop Services access to the system.
Accessing Remote Desktop Services from the Client
With Remote Desktop Services installed and configured on the server, the next step is to ensure the services can be accessed from a remote client. Remote Desktop Services provides both remote desktop and remote application access. Under remote desktop access an entire desktop session running on the server is displayed on the client. The user then interacts with the desktop to launch and interact with applications (details on installing applications for use with Remote Desktop Services is covered in Installing Applications for Windows Server 2008 R2 Remote Desktop Services). In the case of remote applications, the remote application running on the server appears in its own window on the client desktop, to all intents and purposes looking like a local application to the user. Remote applications are covered in detail in Configuring RemoteApps on Windows Server 2008 R2.
With the appropriate configuration tasks completed on the remote system the next step is to launch the Remote Desktop Client on the local system.
To invoke the Remote Desktop Client select Start -> All Programs -> Accessories -> Remote Desktop Connection or enter the following in the Run dialog or at a command prompt:
mstsc
Once launched, the following initial screen will appear requesting details of computer to which the client is to connect:
<google>WIN28BOX</google>
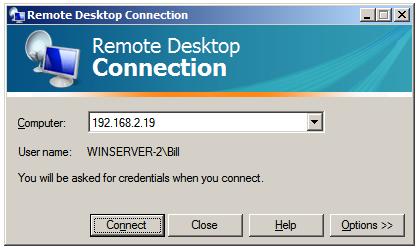
This can either be an IP address or a computer name. If previous connections have been established the User name field will be populated with the user name used in the preceding session. If you need to log in as a different user this option will be provided on the next screen which appears after the Connect button is pressed:
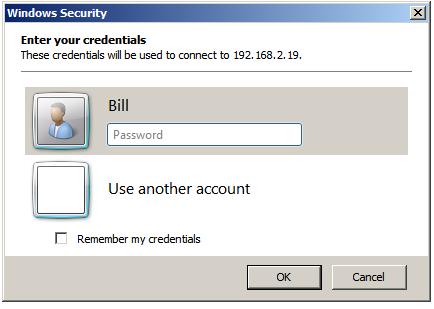
In this screen enter the password for the selected user (note that remote desktop access is only available for user accounts which are password protected). If a user other than the one displayed is required, simply click on the Use another account link and enter the necessary details. Click on OK to establish the connection. After a short delay the remote desktop will appear on the local computer screen.
Remote Desktop Client Configuration Options
The Options>> button displayed on the initial screen of the Remote Desktop Client provides six tabs, each containing a range of configuration options:
- General — Allows login credentials to be configured and session information to be saved.
- Display — Configures the resolution and color settings to be used when displaying the remote desktop on the local system.
- Local Resources — Specifies which local resources (sound, disk drives, printers etc) are to be made accessible to the remote system during the Remote Desktop session. This page also provides options to control the situations under which special key combinations such as Ctrl-Alt-Del are interpreted by the local or remote systems.
- Programs — Allows specified programs to be automatically invoked each time a remote sessions is established.
- Experience — Controls which desktop features are enabled or disabled for the Remote Desktop session. For example, over a slow dial-up connection it is unwise to have the desktop background displayed and font smoothing enabled. Either select the connection type and speed to see recommended settings, or use Custom to configure you own settings. This particular screen also provides the option to have connected automatically re-established in the event that a session is dropped.
- Advanced — Enables and disables remote server verification. This ensures that the remote server to which you are connected is indeed the server you wanted. Also available are RD Gateway settings. By default the Remote Desktop Client is configured to automatically detect RD Gateway settings.
Logging out from a Remote Desktop Session
When the Remote Desktop Client is exited by pressing the ‘X’ on the control panel the remote session continues to run on the server even though no client is connected. Next time the user connects the desktop session will appear exactly as it was left before.
To end the session select Start in the remote desktop session, click on the right arrow button in the bottom right hand corner of the menu and select Log Off. This will close down the remote desktop session and close the remote desktop client.
Running Multiple Remote Desktops
Multiple concurrent remote desktops can be run and managed within a single window using the MMC Remote Desktops snap-in. This may either be snapped into the MMC or launched from the command-line or a Run dialog by typing:
tsmmc.msc
Once launched, right click on the Remote desktops item in the tree in the left hand panel and select Add a new connection from the menu. Once selected, the Add New Connection dialog will be displayed as follows:
In this dialog enter either the IP address or the computer name of the remote system to which the connection is to be established, together with the User name and the name to be assigned to this connection (this is essentially the name by which this connection will be listed and administered from this point on inside the Remote Desktops snap-in). For an administrative session (as opposed to a virtual session) set the Connect with /admin box. Click OK to add the session to the snap-in. Once added, the session will appear in the left hand panel under Remote Desktops. Repeat these steps to add connections to any additional remote systems required.
To establish a remote desktop connection, simply right click on the name of the session on the left panel and select the Connect option from the popup menu. The remote session will subsequently appear in the main window. To start another session right click on the required session name and once again select Connect. To switch between sessions simply click on the name of the session in the left hand panel and the corresponding desktop will be displayed. The following figure illustrates two sessions running in Remote Desktops:
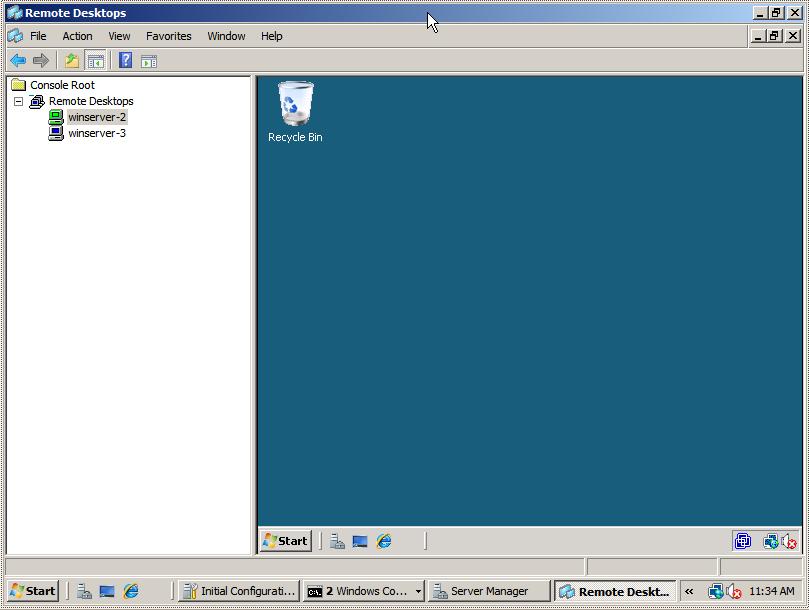
To change configuration options for each session right click on the desired session in the left hand panel and select Properties. This panel has a number of tabs which enable credentials, screen size and program start properties to be defined.
Having configured Remote Desktop Services on a Windows Server 2008 R2 system, the next step is to install applications suitable for remote access as outlined in the next chapter.
<google>BUY_WINSERV_2008R2_BOTTOM</google>
Microsoft’s Remote Desktop Services Virtual Desktop Infrastructure product offers a lot of benefits, but not every IT administrator knows where to start.
As a virtual desktop administrator, you should learn the ins and outs of this VDI product to make the most of it. Learn step by step how to get Remote Desktop Services (RDS) and some of the basic RDS components up and running.
Step 1: Begin the installation
Launch Server Manager and select Server Roles. Once the roles manager screen is up, check the box for Remote Desktop Services. Some other boxes may already be checked, but this is fine — the only box you need to worry about for this step is the Remote Desktop Services box. Click the next button in the bottom right corner to proceed.
Now you should see an introduction to RDS. Select the next button at the bottom of the page.
Step 2: Select Remote Desktop Services roles you want to install
RDS includes several components and settings (Figure 1). These components can be on one machine or many.
- Remote Desktop Session Host. This is the name for Terminal Server.
- Remote Desktop Virtualization Host. This component integrates with Microsoft Client Hyper-V. This allows for the pooling of virtual machines on Hyper-V so they can serve as virtual desktops.
- Remote Desktop Connection Broker. This component bridges the user with a virtual Windows desktop, remote application or Remote Desktop Session Host session.
- Remote Desktop Licensing. This is the modern name of Terminal Server licensing server that also includes licensing for Windows Server.
- Remote Desktop Gateway. This provides a single connection point for clients to connect to a specific virtual desktop, remote app or Remote Desktop Session Host session.
- Remote Desktop Web Access. This provides clients an interface to access their virtual desktop, remote app or Remote Desktop Session Host sessions.
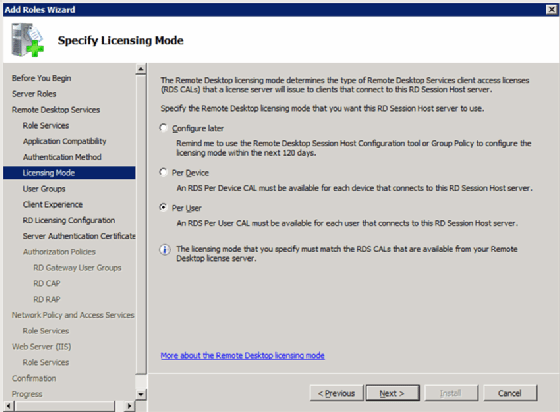
Step 3: Pick the license mode
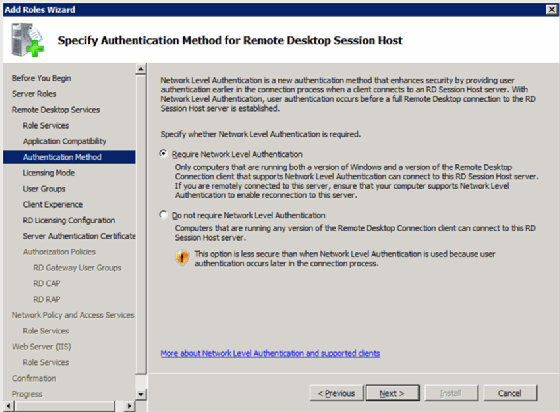
As with past Terminal Server licensing, there are two license options: per-device and per-user (Figure 2).
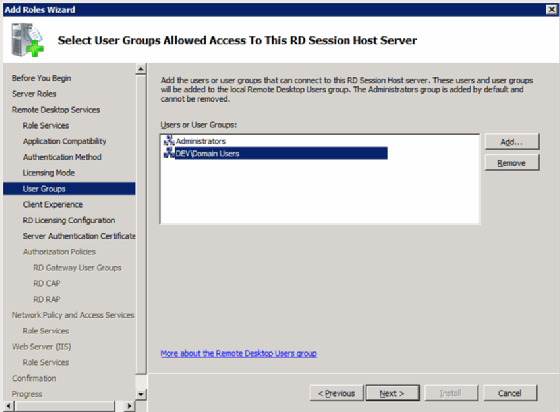
Step 4: Allow access to Remote Desktop Session Host (not required)
Select which users to grant access to the local Remote Desktop Session Host. This server component is not required for RDS to work. If you choose to install the Remote Desktop Session Host, you will get this prompt (Figure 3).
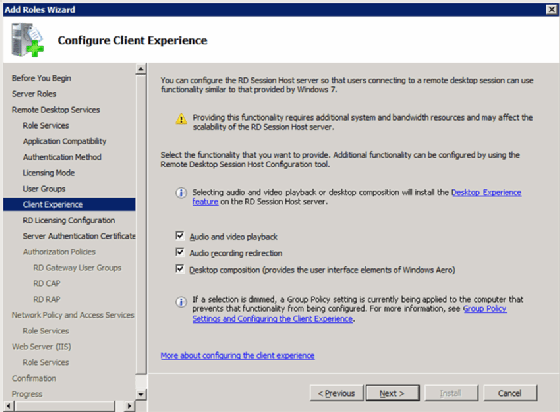
Step 5: Configure the client experience
The next screen is called Configure Client Experience (Figure 4). This is where you set the defaults for the end-user experience with the VDI system and remote desktop.
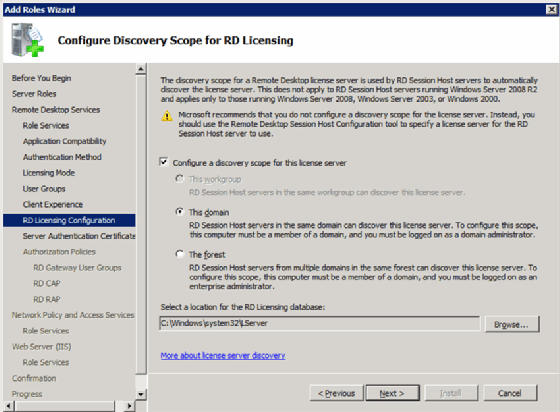
Step 6: Configure license scope
Just as with Terminal Server of the past, you can configure the scope of the Remote Desktop Session Host license server. You have the following two options:
- Domain. This limits the licensing to only servers in the domain (Figure 5).
- Active Directory Forest. This allows any Remote Desktop Session Host server in the Active Directory Forest — the highest-level container in a set of servers — to attain a license.
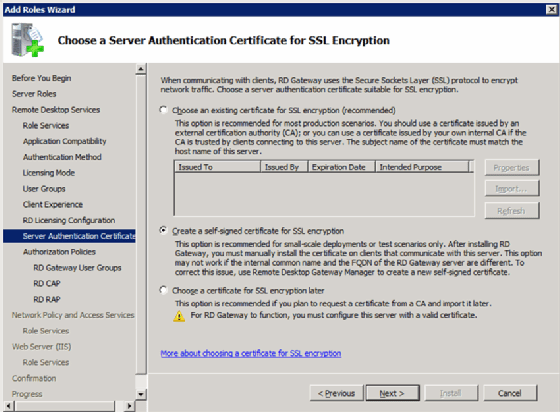
Step 7: Assigning the SSL certificate for Remote Desktop Gateway
The Remote Desktop Gateway uses Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) to tunnel and encrypt traffic from the client. This functionality requires a certificate. There are two options for certificates:
- Specify a certificate from the certificate store.
- Produce a self-signed certificate.
In either case, the client must trust the certificate (Figure 6).
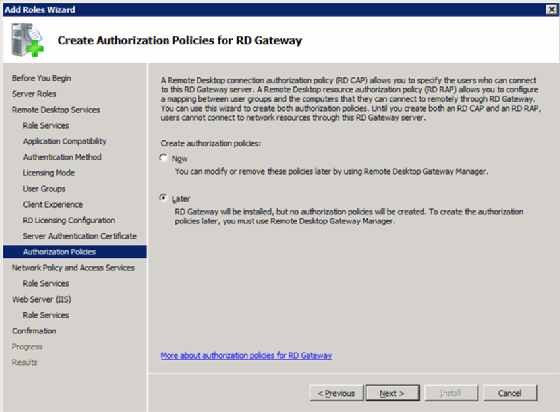
Step 8: Configure network access protection (optional)
These next few screens go beyond the scope of RDS but are related, so this article will just cover the basics.
Create authorization policies
This is where you would configure a policy that states who is allowed to establish a desktop connection to the Remote Desktop Gateway
(Figure 7).
Install and configure network access and protection policies
You can use this to configure and enforce network access policies such as Internet Protocol Security (IPsec) and network access protection from the client (Figure 8).
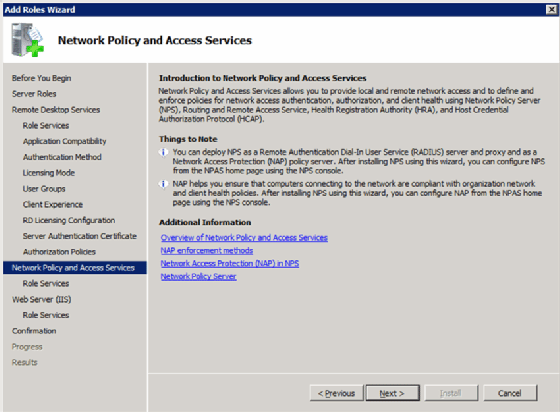
You can also use this feature to define different policies based on users’ connectivity (Figure 9).
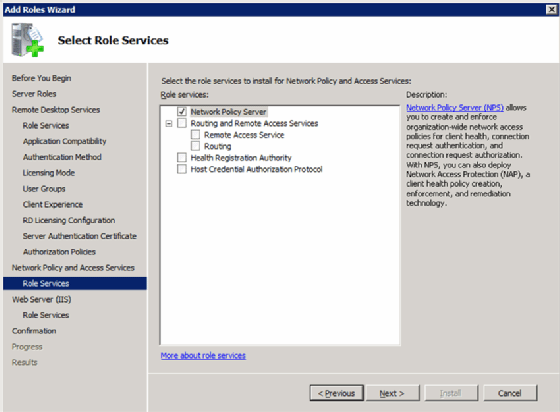
Step 9: Install IIS and Remote Desktop Web Access
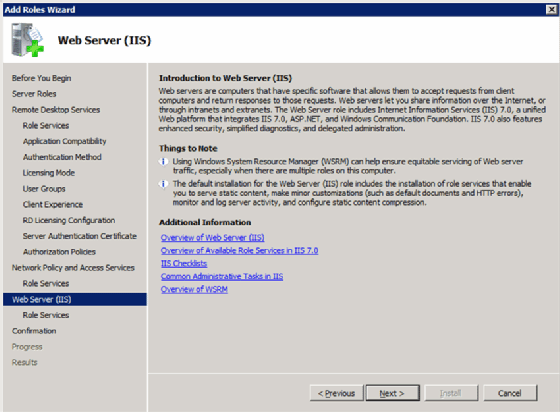
Remote Desktop Web Access requires Internet Information Services (IIS), so the next two screens are for installing and configuring IIS. First, there is the overview screen (Figure 10).
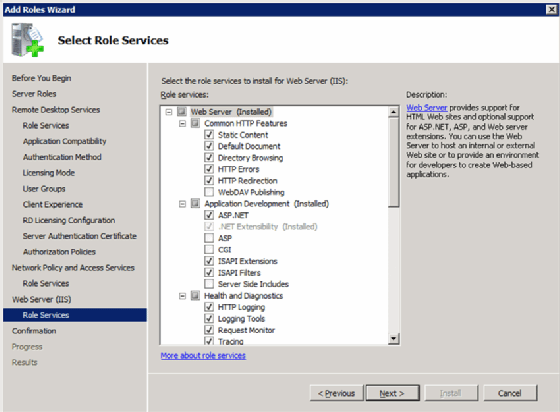
The second screen is the configuration screen (Figure 11).
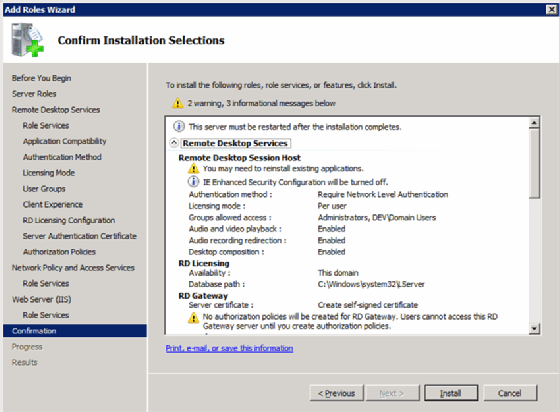
Step 10: The final steps
At this point, you’re done. The last two screens just let you know what you’re installing (Figure 12).
There is also the final screen that lets you know whether any additional steps like rebooting are required (Figure 13).
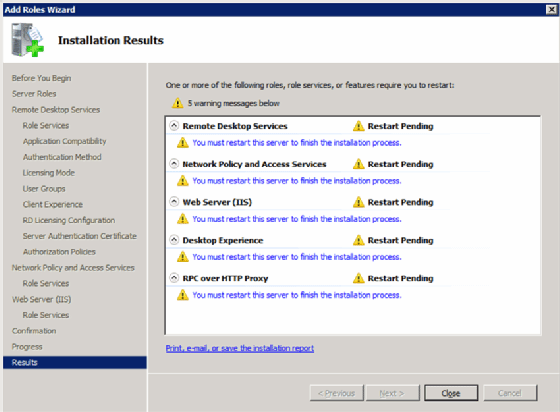
Now that you have installed and configured RDS, you can start using Remote Desktop Session Host and Remote Desktop Gateway Manager.
Remote Desktop is a useful feature that allows users to access their Windows Server 2008 R2 system from another computer. This can be particularly helpful for IT administrators or individuals who need to manage their server remotely. If you’re wondering how to enable Remote Desktop on your Windows Server 2008 R2, follow these steps:
Step 1: Open the Start menu on your server and click on «Control Panel.«
Step 2: In the Control Panel window, select «System and Security.«
Step 3: Under the System and Security section, click on «System.«
Step 4: In the System window, select «Remote settings» from the left sidebar.
Step 5: In the System Properties window that opens, navigate to the «Remote» tab.
Step 6: In the Remote tab, you will find two options: «Allow connections from computers running any version of Remote Desktop (less secure)» and «Allow connections only from computers running Remote Desktop with Network Level Authentication (more secure).» Choose the option that best suits your security requirements.
Step 7: Click on «Apply» and then «OK» to save your changes.
Now that you have enabled Remote Desktop on your Windows Server 2008 R2, you can access it remotely using a Remote Desktop client from another computer on the same network or through the internet. Simply launch the Remote Desktop client, enter the IP address or hostname of the server, and provide your credentials to establish a connection.
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| 1. Allows remote management of Windows Server 2008 R2, providing flexibility and convenience. | 1. Potential security risks if not configured properly or accessed from untrusted devices. |
| 2. Provides access to server resources and applications from anywhere with an internet connection. | 2. Requires a stable and reliable network connection for optimal performance. |
| 3. Helps streamline server administration and troubleshooting tasks. | 3. May require additional configuration and firewall settings to allow remote connections. |
Enabling Remote Desktop on Windows Server 2008 R2 can greatly enhance your ability to manage and access your server remotely. However, it is important to ensure that proper security measures are in place to protect your system from unauthorized access. Consider configuring firewall settings and utilizing strong passwords to maintain the security of your remote connections.
Video Tutorial:How to enable RDP via command line?
How to install RSAT on Windows Server 2008 R2?
Installing RSAT (Remote Server Administration Tools) on Windows Server 2008 R2 is a straightforward process. Here are the steps:
1. Verify the compatibility: Before proceeding with the installation, ensure that your system meets the requirements to run RSAT. Make sure you have administrative rights and that your server is running Windows Server 2008 R2.
2. Download RSAT: Visit the Microsoft Download Center website and search for «Remote Server Administration Tools for Windows Server 2008 R2.» Locate the appropriate version, either 32-bit or 64-bit, depending on your system architecture. Download the RSAT package.
3. Run the installer: Once the download is complete, navigate to the download location and run the installer. The installation wizard will open.
4. Select the desired tools: In the installation wizard, you’ll be presented with a list of available tools. Choose the specific tools within RSAT that you want to install. You can select multiple tools by holding the Ctrl key while clicking.
5. Complete the installation: After selecting the desired tools, click on the «Install» button to begin the installation process. The installer will extract and install the selected tools on your system.
6. Configure RSAT: Once the installation is complete, you need to configure RSAT to enable and access the installed tools. This involves navigating to the «Control Panel» and finding the «Programs» section. Locate the «Turn Windows features on or off» option and click on it.
7. Enable RSAT features: In the «Windows Features» dialog box, scroll down to find the «Remote Server Administration Tools» section. Expand it to reveal more options. Check the box corresponding to the specific tools you installed in step 4. Click «OK.«
8. Restart if necessary: In some cases, enabling or disabling certain Windows features may prompt a system restart. If required, restart your server to apply the changes and make the RSAT tools accessible.
9. Access RSAT: Once the server restarts (if necessary), you can access the RSAT tools by searching for them in the Start Menu or from the Administrative Tools folder. Each tool will have its own interface and usage instructions.
Remember to refer to official documentation, such as Microsoft’s documentation for RSAT, for more detailed steps or troubleshooting guidance if needed.
To enable Windows Server Remote Desktop, follow these steps:
1. Log in to your Windows Server using an administrative account.
2. Click on the «Start» menu and type «Remote Desktop» in the search bar.
3. In the search results, click on the «Remote Desktop Connection» application to open it.
4. In the Remote Desktop Connection window, type the name or IP address of the server you want to connect to in the «Computer» field.
5. Click on the «Show Options» button to expand additional settings.
6. In the expanded options, you can configure settings like display, local resources, and experience. Make the necessary adjustments based on your preferences or requirements.
7. Once you’ve made the appropriate settings, click on the «Connect» button to start the remote desktop session.
8. If it’s your first time connecting to the server, you may be prompted to verify the server’s identity or enter your credentials. Follow the on-screen instructions to complete the connection.
9. After successful authentication, you should now have remote access to the Windows Server desktop.
Please note that enabling Remote Desktop on a Windows Server may have security implications, so it’s vital to ensure proper security measures are in place, such as strong passwords, firewall configurations, and limiting access to authorized users. It’s also recommended to keep your server and Remote Desktop client software up to date to mitigate potential risks.
How to run as administrator command line Windows Server 2008 R2?
Running commands as an administrator on Windows Server 2008 R2 allows users to perform administrative tasks and make system-level changes. Here’s how you can do it:
1. Launch the Command Prompt: Click on the «Start» button, type «cmd» in the search box, and press Enter to open the Command Prompt.
2. Run as administrator: Right-click on the Command Prompt icon in the search results and select «Run as administrator.» If prompted for permission, click «Yes.«
3. User Account Control (UAC) prompt: If UAC is enabled, a prompt may appear asking for confirmation to run the Command Prompt as an administrator. Click «Yes» to continue.
4. Elevated Command Prompt: After successfully running Command Prompt as an administrator, the title bar of the Command Prompt window should display «Administrator: Command Prompt» to indicate that you have elevated privileges.
5. Execute commands: You can now run any command that requires administrative privileges. Simply type the desired command and press Enter to execute it.
Note: Exercise caution while running commands as an administrator, as system-level changes can affect the stability and performance of the Windows Server if not executed correctly. It’s advisable to have a good understanding of the commands you intend to run and their potential impact on the system.
It’s important to keep in mind that this answer is written as a tech blogger and not as an technical blogger.
How to check Remote Desktop users in Windows Server 2008?
To check Remote Desktop users in Windows Server 2008, you can follow these steps:
1. Open the «Start» menu and go to «Administrative Tools» and then select «Remote Desktop Services.«
2. Under «Remote Desktop Services,» choose «Remote Desktop Session Host Configuration.«
3. In the console tree, expand the «Connections» folder.
4. Right-click on the name of your RDP connection (e.g., «RDP-Tcp«) and select «Properties.«
5. In the «Properties» window, go to the «Permissions» tab.
6. Here, you can see the list of users who have permissions to connect through Remote Desktop to your Windows Server 2008.
7. You can further modify the permissions by clicking the «Advanced» button and selecting «Advanced Permissions.«
Please note that these steps are specifically for Windows Server 2008, and the process may vary slightly on different Windows Server versions.
How to enable Remote Desktop in Windows Server 2008?
To enable Remote Desktop in Windows Server 2008, you can follow the steps below:
1. Open the Start menu and go to «Control Panel«.
2. In the Control Panel, click on «System and Security» or «System and Maintenance» depending on your Control Panel view.
3. In the new window, find and click on «System«. This will open the System Properties.
4. In the System Properties window, click on the «Remote settings» link on the left-hand side. This will open the Remote tab.
5. Under the Remote Desktop section, you will see two options: «Don’t allow connections to this computer» and «Allow connections from computers running any version of Remote Desktop (less secure)«. Select the second option if you want to allow remote connections.
6. If you want to restrict remote connections to specific users, click on the «Select Users» button and add the desired users to the list.
7. Click «OK» to save the changes.
8. If you have a firewall enabled, make sure to allow Remote Desktop connections through the firewall. Check your firewall settings or consult the Windows Server 2008 documentation for specific instructions on how to do this.
After applying these steps, Remote Desktop should be enabled on your Windows Server 2008. You can now access the server remotely using a Remote Desktop client.
How do I enable remote management in Windows Server 2008 R2?
Enabling remote management in Windows Server 2008 R2 involves several steps. Here’s how you can accomplish it:
1. Launch Server Manager: Log in to the Windows Server 2008 R2 machine, click on the Start button, and open the Server Manager console.
2. Add the Remote Server Administration Tools (RSAT) feature: In the Server Manager window, click on the «Features» section in the left-hand pane. Then, click on the «Add Features» link in the main pane. A new window will open, and you need to select the «Remote Server Administration Tools» checkbox. Click «Next» to proceed.
3. Select the desired remote management tools: In the Remote Server Administration Tools window, expand the «Role Administration Tools» section and then expand the «AD DS and AD LDS Tools» option. Here, you can select the specific tools you want to enable for remote management, such as «Active Directory Administrative Center» or «Group Policy Management.» Once you’ve made your selections, click «Next.«
4. Confirm the installation selections: Review the summary of your installation selections and click «Install» to begin the installation process. The required files and features will be downloaded and installed on your Windows Server machine.
5. Enable remote management: After the installation completes, return to the Server Manager window, and in the left-hand pane, expand the «Configuration» section and select «Local Server.» In the main pane, locate the «Remote Management» option and click on the disabled status.
6. Configure remote management settings: A new window called «System Properties» will open. Click on the «Remote» tab and select the checkbox labeled «Allow remote connections to this computer.» You can also choose to enable remote management settings for specific users or groups by clicking on the «Select Users» button.
7. Firewall configuration: By default, the Windows Firewall blocks remote management connections. To allow remote management connections, you need to configure the firewall to permit them. In the Server Manager window, click on «Configuration» in the left-hand pane, and then select «Windows Firewall with Advanced Security.» From there, you can create inbound and outbound rules to allow remote management traffic.
8. Test remote management: Once you’ve completed the above steps, you can test remote management by connecting to the Windows Server 2008 R2 machine from another computer using remote management tools like Windows PowerShell or Remote Desktop.
It’s important to note that these instructions assume you have administrative access to the Windows Server 2008 R2 machine and are familiar with basic Windows Server administration concepts. Additionally, ensure that remote management is in compliance with your organization’s security policies and guidelines.
Enabling remote desktop on Windows Server 2008 R2 allows you to access and manage your server remotely from any location. This can be particularly useful if you need to make changes to your server’s settings or troubleshoot issues without physically being in front of the machine. In this blog post, we will guide you through the steps to enable remote desktop on Windows Server 2008 R2 and provide some additional tips to enhance your remote desktop experience.
Video Tutorial:
There are several reasons why you would want to enable remote desktop on your Windows Server 2008 R2. Here are a few:
1. Remote management: Enabling remote desktop allows you to manage your server from anywhere with a network connection. This can save you time and effort by eliminating the need to physically be present at the server location.
2. Troubleshooting: If you encounter any issues with your server, enabling remote desktop allows you to troubleshoot and resolve the problem remotely. This can be particularly useful if the server is in a remote or hard-to-reach location.
3. Flexibility: Enabling remote desktop gives you the flexibility to work on your server from any device with a remote desktop client. This means you can use your laptop, tablet, or even your smartphone to access and manage your server.
Now that we understand why enabling remote desktop on Windows Server 2008 R2 is important, let’s explore how to do it.
Method 1: Enabling Remote Desktop via the GUI
Enabling remote desktop using the graphical user interface (GUI) is the easiest way to do it. Here are the steps:
1. Open the “Start” menu and go to “Control Panel”.
2. Click on “System and Security”, then “System”.
3. In the left-hand pane, click on “Remote settings”.
4. In the “System Properties” window, go to the “Remote” tab.
5. Under the “Remote Desktop” section, select the option “Allow connections from computers running any version of Remote Desktop (less secure)”.
6. Click on “Apply” and then “OK” to save the changes.
Pros:
1. Easy and straightforward process to enable remote desktop.
2. Allows for remote management and troubleshooting of the server.
3. Provides flexibility to work on the server from various devices with a remote desktop client.
Cons:
1. Selecting the less secure option may pose a slight security risk.
2. Limited control over user access and permissions.
Method 2: Enabling Remote Desktop via Group Policy
If you have a group of servers that need remote desktop enabled, using group policy is an efficient way to do it. Here’s how:
1. Open the “Group Policy Management” console.
2. Create a new GPO or select an existing one.
3. Right-click on the GPO and choose “Edit”.
4. Navigate to “Computer Configuration” > “Policies” > “Administrative Templates” > “Windows Components” > “Remote Desktop Services” > “Remote Desktop Session Host” > “Connections”.
5. Locate the policy setting called “Allow users to connect remotely using Remote Desktop Services” and double-click on it.
6. Select the “Enabled” option and click on “Apply” and then “OK” to save the changes.
Pros:
1. Allows for centralized management of remote desktop settings.
2. Enables consistent configuration across multiple servers.
3. Provides granular control over user access and permissions.
Cons:
1. Requires advanced knowledge of group policy management.
2. May require additional configuration and troubleshooting if the policy is not applied correctly.
Method 3: Enabling Remote Desktop via Command Line
If you prefer using the command line, you can enable remote desktop on Windows Server 2008 R2 using the “reg” command. Here’s how:
1. Open the Command Prompt as an administrator.
2. Type the following command and press Enter: reg add “HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESYSTEMCurrentControlSetControlTerminal Server” /v fDenyTSConnections /t REG_DWORD /d 0 /f
3. Type the following command and press Enter: netsh advfirewall firewall set rule group=”Remote Desktop” new enable=Yes
4. Close the Command Prompt.
Pros:
1. Provides a quick way to enable remote desktop without using the GUI.
2. Allows for automation and scripting.
Cons:
1. Requires familiarity with the command line interface.
2. Limited visibility of other remote desktop settings.
Method 4: Enabling Remote Desktop via PowerShell
PowerShell is a powerful scripting language that can be used to enable remote desktop on Windows Server 2008 R2. Here’s an example of how to do it:
1. Open PowerShell as an administrator.
2. Type the following command and press Enter: Set-ItemProperty -Path ‘HKLM:SystemCurrentControlSetControlTerminal Server’ -name “fDenyTSConnections” -Value 0
3. Type the following command and press Enter: Enable-NetFirewallRule -DisplayGroup “Remote Desktop”
4. Close PowerShell.
Pros:
1. Offers automation capabilities for remote desktop enablement.
2. Can be combined with other PowerShell scripts for advanced configuration.
Cons:
1. Requires familiarity with PowerShell scripting.
2. Limited visibility of other remote desktop settings.
What to Do If You Can’t Enable Remote Desktop
If you encounter any issues while trying to enable remote desktop on Windows Server 2008 R2, here are some potential fixes:
1. Check firewall settings: Ensure that the necessary firewall rules are in place to allow remote desktop connections.
2. Verify network connectivity: Make sure that the server has a stable network connection and can communicate with other devices on the network.
3. Check group policy settings: Confirm that the group policy settings are applied correctly and not blocking remote desktop connections.
4. Restart the Remote Desktop Services: Restarting the Remote Desktop Services can sometimes resolve issues with remote desktop connectivity.
Bonus Tips
Here are three bonus tips to enhance your remote desktop experience on Windows Server 2008 R2:
1. Use strong passwords: Ensure that you have strong passwords in place for all user accounts on the server to prevent unauthorized access.
2. Enable network-level authentication: Network-level authentication provides an additional layer of security by requiring users to authenticate before establishing a remote desktop session.
3. Use Remote Desktop Gateway: If your server is behind a firewall or requires access over the internet, consider setting up a Remote Desktop Gateway for secure remote access.
5 FAQs
Q1: How do I access a remote desktop session on Windows Server 2008 R2?
A: To access a remote desktop session on Windows Server 2008 R2, you will need a remote desktop client such as Remote Desktop Connection (RDC) or a third-party remote desktop application.
Q2: Can I connect to Windows Server 2008 R2 from a Mac?
A: Yes, you can connect to Windows Server 2008 R2 from a Mac using the Microsoft Remote Desktop application available in the Mac App Store.
Q3: Can multiple users connect simultaneously to a Windows Server 2008 R2 using remote desktop?
A: Yes, Windows Server 2008 R2 supports multiple concurrent remote desktop sessions, depending on the licensing and configuration of the server.
Q4: How can I improve the performance of a remote desktop session?
A: To improve the performance of a remote desktop session, you can reduce the display settings, disable unnecessary visual effects, and optimize your network connection.
Q5: Can I copy files between my local machine and the remote desktop session?
A: Yes, you can copy files between your local machine and the remote desktop session by using the clipboard or the shared drives feature in the remote desktop client.
Final Thoughts
Enabling remote desktop on Windows Server 2008 R2 is a valuable capability that allows you to manage your server from anywhere, improve troubleshooting efficiency, and increase flexibility in server management. Whether you choose to enable remote desktop via the GUI, group policy, command line, or PowerShell, following the steps outlined in this blog post will help you achieve your desired remote desktop configuration. Don’t forget to implement the bonus tips and refer to the FAQs for additional guidance.{“@context”:”https://schema.org”,”@type”:”FAQPage”,”mainEntity”:[{“@type”:”Question”,”name”:” How do I access a remote desktop session on Windows Server 2008 R2?”,”acceptedAnswer”:{“@type”:”Answer”,”text”:” To access a remote desktop session on Windows Server 2008 R2, you will need a remote desktop client such as Remote Desktop Connection (RDC) or a third-party remote desktop application.”}},{“@type”:”Question”,”name”:” Can I connect to Windows Server 2008 R2 from a Mac?”,”acceptedAnswer”:{“@type”:”Answer”,”text”:” Yes, you can connect to Windows Server 2008 R2 from a Mac using the Microsoft Remote Desktop application available in the Mac App Store.”}},{“@type”:”Question”,”name”:” Can multiple users connect simultaneously to a Windows Server 2008 R2 using remote desktop?”,”acceptedAnswer”:{“@type”:”Answer”,”text”:” Yes, Windows Server 2008 R2 supports multiple concurrent remote desktop sessions, depending on the licensing and configuration of the server.”}},{“@type”:”Question”,”name”:” How can I improve the performance of a remote desktop session?”,”acceptedAnswer”:{“@type”:”Answer”,”text”:” To improve the performance of a remote desktop session, you can reduce the display settings, disable unnecessary visual effects, and optimize your network connection.”}},{“@type”:”Question”,”name”:” Can I copy files between my local machine and the remote desktop session?”,”acceptedAnswer”:{“@type”:”Answer”,”text”:” Yes, you can copy files between your local machine and the remote desktop session by using the clipboard or the shared drives feature in the remote desktop client.”}}]}
