Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP) enables users to establish a secure connection to remote computers over a network, allowing them to access files, applications, and system resources as if they were physically present.
Microsoft developed RDP primarily for Windows, but it also works for Linux, macOS, Android, and iOS devices, making it a versatile solution for remote access across different operating systems.
This article will show you how to connect to an Ubuntu system from Windows using RDP.

Prerequisites
- A client Windows machine.
- A host machine with Ubuntu installed.
- Sudo or root privileges on the host machine.
How to Connect to Ubuntu Remote Desktop From Windows
The RDP client is preinstalled on Windows. However, the Ubuntu system must be configured before it accepts incoming RDP connections.
Follow the steps in the sections below.
Install xrdp on Ubuntu
xrdp is an RDP server for Linux that listens for and accepts RDP connections from clients. Ubuntu systems usually do not have xrdp installed by default.
To install xrdp on Ubuntu, take the following steps:
1. Update the Ubuntu packages list:
sudo apt update2. Install xrdp with the following command:
sudo apt install xrdp -y
3. Check the xrdp server status:
sudo systemctl status xrdp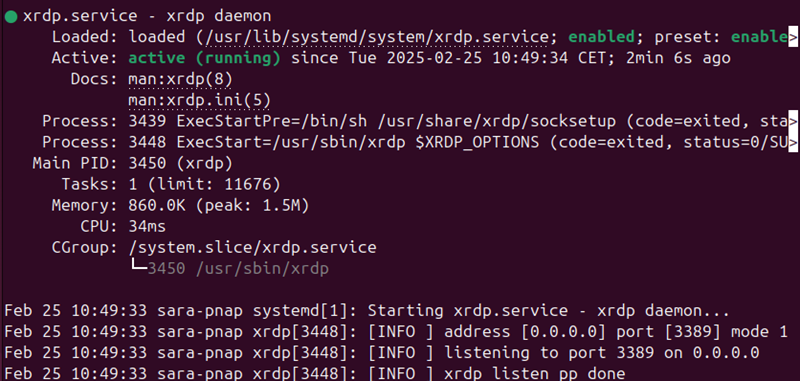
The output confirms the xrdp is active.
Configure xrdp Port (Optional)
The <strong>xrdp</strong> server listens for incoming RDP connections on port number 3389. Using a non-standard port for RDP connection is a form of protection through obscurity. It is not a robust security measure, but it protects a system from rudimentary brute-force attacks.
To instruct xrdp to listen on a different port, take the following steps:
1. Use a text editor, like Vim, to edit the xrdp configuration file, xrdp.ini:
sudo vim /etc/xrdp/xrdp.ini2. Locate the port directive in the [Globals] section and set the desired value. In this example, the RDP port is 49952:
port=49952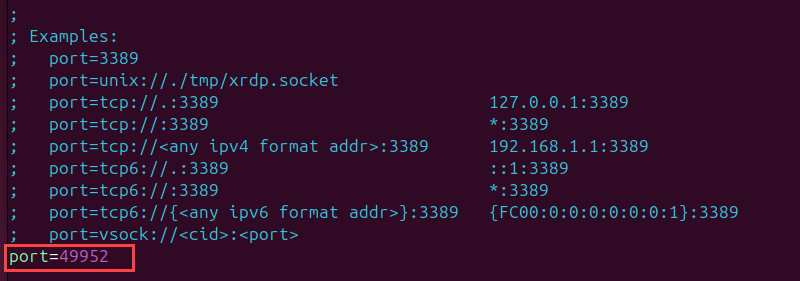
3. Save the changes and exit the file.
4. Restart the xrdp server to apply the changes:
sudo systemctl restart xrdpThere is no confirmation message after the server restarts.
Open a Port for Incoming Traffic in ufw
An active firewall on the Ubuntu system, such as ufw, can block traffic on specific ports. Configure the firewall and allow traffic on the desired port to ensure successful RDP connections.
Take the following steps:
1. Check the ufw firewall status:
sudo ufw status
If the firewall is inactive, use the following command to turn on ufw:
sudo ufw enable2. Allow traffic on port 3389 or choose a different port for your RDP connection. The following command allows RDP connections on port 49952:
sudo ufw allow 49952/tcp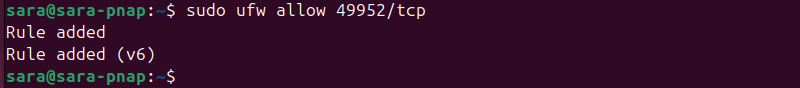
Modify the command to open a different port number for RDP connections.
3. Reload the ufw firewall tool to apply the changes:
sudo ufw reload
Note: If you want to access the Ubuntu machine from outside its local network, configure port forwarding on the router or adjust external firewalls.
Configure Remote Desktop Connection on Windows
To initiate an RDP connection to a remote Ubuntu system from Windows, take the following steps:
1. Type rdp in the Windows search box.
2. Open the Remote Desktop Connection app.
3. Enter the IP address or name of the remote Ubuntu system in the Computer field.
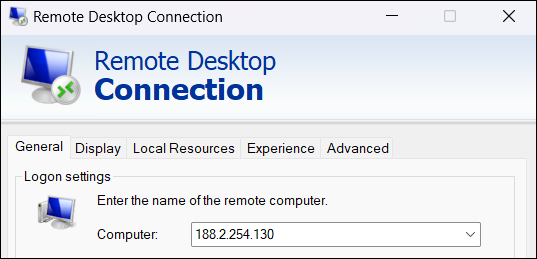
If you change the default port number for RDP connections on Ubuntu, enter the port number after the IP address in the following format:
IP_address:port_number4. Type the username of the Ubuntu user for the RDP connection.
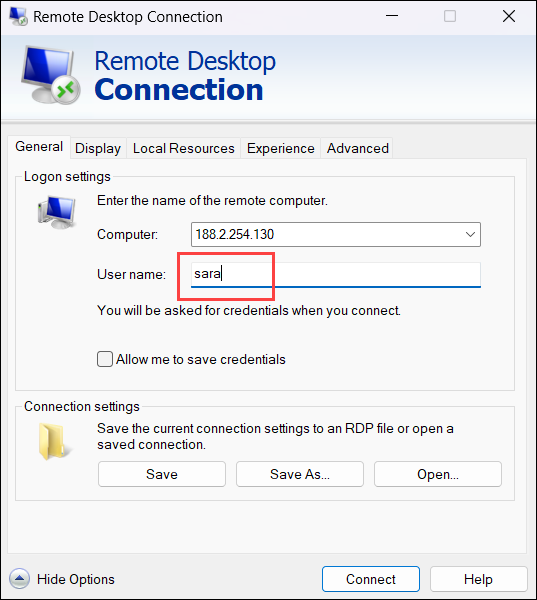
5. (Optional) Save the connection details for future use.
6. (Optional) The Remote Desktop Connection (RDP) app in Windows enables users to configure the RDP session. The main configuration options are split into several sections:
- Display. Adjust the size and color settings of the remote desktop window.
- Local Resources. Decide which local devices (keyboards, audio, and printers) to share with the remote system.
- Experience. Modify visual effects like desktop background and font smoothing based on network speeds.
- Advanced. Fine-tune server authentication settings, set up a Remote Desktop Gateway server, and more.
7. Click Connect.
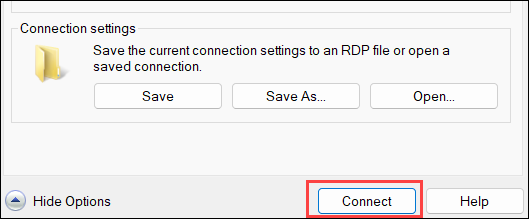
Log in to Ubuntu System
Enter the password for the Ubuntu RDP user and click OK.
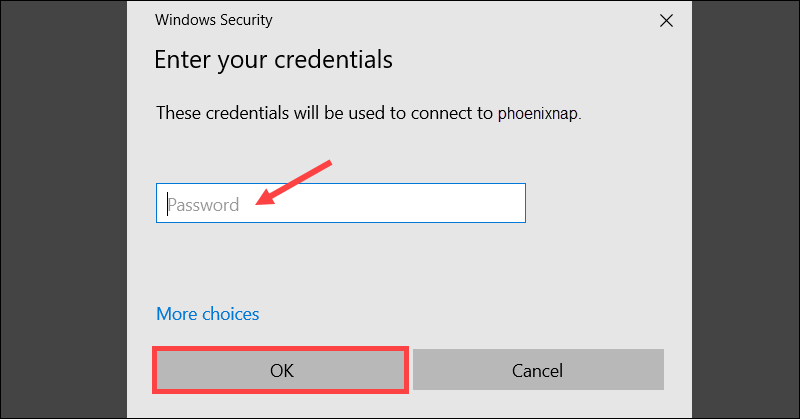
You are now able to interact with the Ubuntu machine via the established RDP session.

Ubuntu RDP From Windows: Extra Tips + Best Practices
To set up a smooth and secure RDP connection from Windows to Ubuntu, focus on more than basic configuration. Optimize hardware, internet speed, and security settings to improve performance and responsiveness.
The following text explains best practices and useful tips for RDP from Windows to Ubuntu.
Minimum vs. Optimal Hardware Requirements
The RDP connection quality from Windows to Ubuntu depends on the system’s hardware capabilities and the type of tasks and applications running on the Ubuntu system.
The Ubuntu system should meet the following requirements:
| REQUIREMENTS | MINIMAL | RECOMMENDED |
|---|---|---|
| CPU | Single-core 1 GHz+ | Dual-core 2 GHz+ |
| RAM | 2 GB+ | 8 GB+ |
| Storage | 25 GB+ | 50 GB+ (SSD) |
| Network | Basic NIC | Stable broadband (Ethernet NIC) |
| Graphics | Integrated graphics or entry-level GPU | Dedicated GPU |
Ideal Internet Speed for RDP Connections
Certain tasks require a minimal level of responsiveness and visual quality. The table offers an overview of minimal and recommended bandwidth per connection for general RDP tasks:
| Tasks | LOCAL NETWORK | INTERNET |
|---|---|---|
| Text editing | 1 Mbps | 1 Mbps |
| Web browsing | 5 Mbps | 2-5 Mbps |
| Video streaming | 10-15 Mbps | 5-10 Mbps |
Beyond bandwidth, factors such as server load, network latency, and packet loss impact RDP performance. For the best experience, prioritize low-latency connections and stable network conditions.
xrdp Black Screen Issue Troubleshooting
Users sometimes encounter a black screen when using xrdp with specific Ubuntu configurations. The screen appears after establishing an RDP session and prevents users from interacting with the Ubuntu system.
To try and resolve the black screen issue, use the tips from the sections below.
Check Log Files
Log files provide valuable information about potential errors. Access the /var/log/xrdp.log using the following command:
sudo vim /var/log/xrdp.log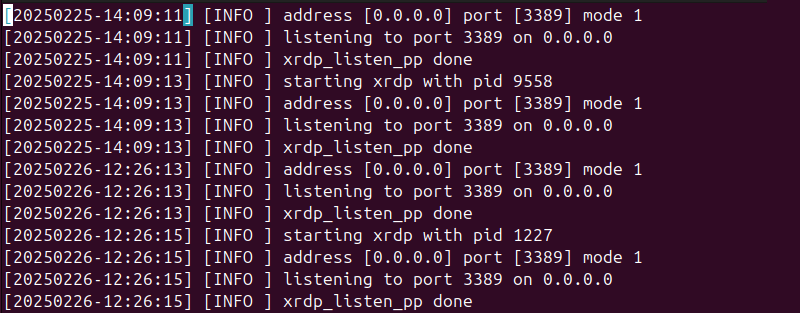
Look for warnings and error messages on the log timeline.
The /var/log/xrdp-sesman.log file contains entries about session startups and shutdowns, operational messages, and warnings. Use the following command to access the log:
sudo vim /var/log/xrdp-sesman.log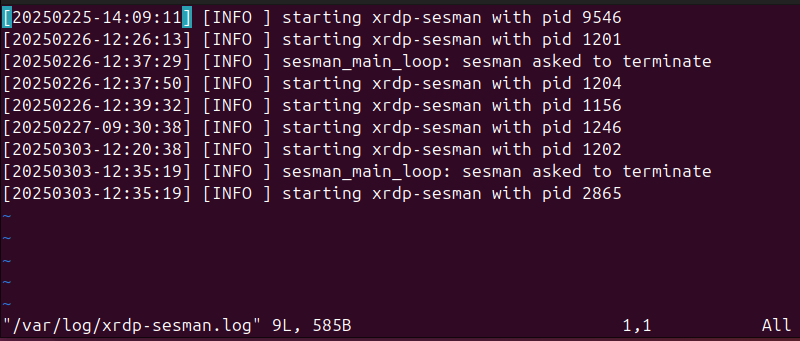
Check for errors occurring when a new session is initiated and for other backend-related issues.
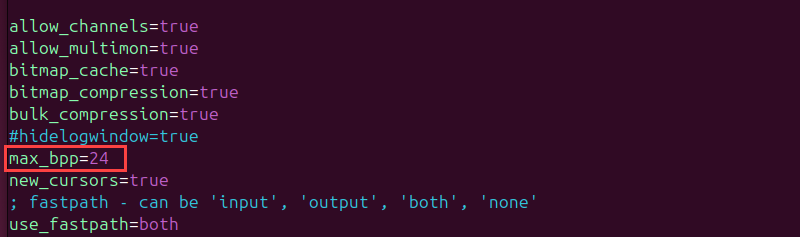
Set max_bpp in xrdp.ini File
The bits per pixel (bpp) value defines the number of bits used to represent the color of a single pixel. High bpp values increase the data that needs to be transferred, which affects performance and causes compatibility issues.
Use the following command to access the xrdp.ini configuration file and check the max_bpp value:
sudo vim /etc/xrdp/xrdp.iniSet the max_bpp value in the [Globals] section to 24, as the default value of 32 bpp sometimes causes issues. If there are other max_bpp values under individual sections, adjust them as well.
Save the changes and restart the xrdp service to ensure the changes take effect.
Reinstall xrdp
A straightforward way to resolve configuration or compatibility issues is to reinstall xrdp.
Run the following to remove the xrdp package and delete its configuration files:
sudo apt remove --purge xrdp -yInitiate a fresh xrdp installation from Ubuntu repositories with:
sudo apt install xrdp -yAfter the installation, modify the xrdp configuration files again.
Install a Different Desktop Environment
The default Ubuntu GNOME desktop occasionally has compatibility issues with xrdp. Install an alternative Ubuntu GUI, such as the XFCE desktop environment, and attempt to establish an RDP connection.
Security Measures
Secure an RDP session from Windows to Ubuntu to prevent unauthorized access and data breaches. Proper security measures include hardening the Windows client and Ubuntu host, restricting network access, and enforcing strong authentication policies.
The following sections present key steps to enhance security.
Windows
- Update Windows regularly to ensure the Remote Desktop Connection app is up-to-date with the latest security patches.
- Limit the number of simultaneous active RDP sessions.
- Disconnect from an RDP session when it is not being used and set timeouts for idle sessions.
Network
- Use a firewall to restrict RDP access to specific IP addresses.
- Change the default RDP port (3389) to a non-standard port number.
- Use a VPN to encrypt the data transfer between client and host machines.
- Alternatively, use SSH port forwarding to create an encrypted tunnel for the RDP session if a VPN is not an option.
Linux
- If you use xrdp, edit the /etc/xrdp/sesman.ini file to specify which users can establish an RDP connection.
- Create dedicated accounts for RDP to restrict access to critical systems or data.
- Implement two-factor authentication for RDP sessions. xrdp does not natively support 2FA but can be integrated with other authentication tools.
- Temporarily lock user accounts after multiple unsuccessful login attempts.
- Enforce strong password policies for RDP user accounts.
Reduce Resolution and Color Depth for Performance Boost
Enhance the RDP session performance by adjusting the color depth and screen size from the Windows RDP client.
To reduce the resolution and color depth, access the Remote Desktop Connection app and:
1. Open the Display tab.
2. Drag the Display configuration slider left to reduce the resolution. For optimal performance on slower connections, 1280×720 resolution is a good choice.
3. Expand the dropdown in the Colors section and choose High Color (16-bit) to reduce the color depth.
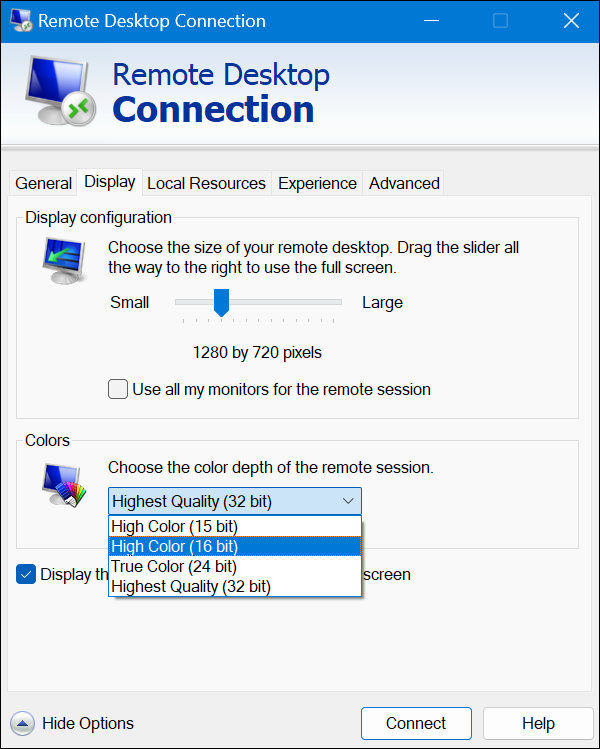
Reducing the screen size and color depth is especially beneficial for low-bandwidth or unreliable network connections.
Conclusion
This tutorial explained how to initiate an RDP session from your Windows system to a remote Ubuntu machine. It also elaborated on useful tips and best practices for a high-quality and secure connection.
Next, learn how to SSH to a remote server from Windows, Linux, or Mac.
Was this article helpful?
YesNo
Безлимитные тарифы интернета с высокой скоростью соединения упростили администрирование компьютеров. Сегодня все чаще помощь пользователям оказывается удаленно. Это удобно, ведь не надо тратить время на поездки и возможность подключиться есть практически круглосуточно.
Сегодня поговорим об удаленном подключении к Ubuntu из ОС Windows.
Зачем удаленно подключаться из Windows к Ubuntu
Не так важно, где находится удаленный компьютер – в соседней комнате или в другом регионе. Интернет убирает подобные ограничения, главное – чтобы связь оставалась стабильной на все время настройки. Это одинаково относится к машинам, работающим хоть на операционной системе Windows, хоть на Ubuntu. Последние используются, например, для развертывания сервера CS или Minecraft.
Причины, по которым требуется удаленное подключение:
- ручной запуск обновлений на компьютере с Ubuntu;
- настройка системы без подключения локального монитора, клавиатуры;
- работа с машиной, расположенной по другому адресу.
Пользователю доступно три варианта коннекта с компьютеров, работающих на ОС Windows. Выбор зависит от удобства и предпочтений: SSH через приложение PuTTY, встроенная поддержка RDP и виртуальная сеть VNC (понадобится предварительная настройка клиента). В любом случае перед работами понадобится выяснить IP-адрес компьютера, к которому предстоит подключаться.
Комьюнити теперь в Телеграм
Подпишитесь и будьте в курсе последних IT-новостей
Подписаться
Как выяснить IP-адрес компьютера с установленной ОС Ubuntu
Если есть физический доступ к компьютеру с установленной Ubuntu, на нем открывается терминал (комбинация клавиш Ctrl+Alt+T) и вводится команда ifconfig. В отображенном перечне данных имеет значение строка, начинающаяся с inet addr. Если используется подключение через Wi-Fi, то рядом будет его маркер в виде «wlan0». При проводном соединении фраза будет заменена на «eth0». Рядом отображается актуальный IP-адрес машины.
Второй способ заключается в применении функций графического интерфейса. Последовательность действий: найти значок подключения на панели, кликнуть правой кнопкой мышки, выбрать пункт «Сведения о подключении». Там и указан постоянный IP-адрес компьютера. Если доступа к нему нет, то можно выяснить данные через маршрутизатор. В панели управления отображаются активные пользователи вместе с их «контактами».
Подключение к Linux через SSH
Перед подключением на компьютер с Windows устанавливается приложение PuTTY. Это популярный инструмент для организации SSH-соединения, которое предоставит удаленный доступ к командной строке Ubuntu. Важно понимать, что этот режим требует определенного опыта в управлении, ведь здесь нет привычной мыши и «окошек», а все команды передаются в текстовом виде. Отчеты предоставляются в таком же виде.
По умолчанию возможность коннекта через SSH в Ubuntu отключена. Так что предварительно эту систему требуется настроить. Активация функции выполняется вводом команды sudo apt install openssh-server (в той же консоли, где ранее был взят IP-адрес). Логин и пароль подключения будут те же, что используются при входе в операционную систему.
Из-за неудобства управления в текстовой среде этот вариант востребован для удаленной активации более удобных инструментов. Например, тех же протоколов RDP или VNC. В них также пригодится IP-адрес, поэтому получить минимальные навыки работы в консоли все равно рекомендуется. Это упростит решаемые задачи, если по каким-то причинам не удается соединение в других режимах.
Подключение из Windows через RDP
Способ подключения через службу Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP) распространен при работе с машинами на платформе Windows. Популярность инструмента объясняется просто – его поддержка встроена во все виды и версии операционных систем. Все, что понадобится для подключения, уже известно: это IP-адрес, логин и пароль от Ubuntu. Запускается утилита через поиск, называется она «Подключение к рабочему столу».
На компьютере-клиенте требуется установка приложения xrdp.
- Необходимо открыть окно термина нажатием комбинации клавиш Ctrl+Alt+T.
- Ввести текстовую команду sudo apt install xrdp и нажать «Ввод».
- Провести активацию программы командой sudo systemctl enable xrdp.
После установки надо ввести на компьютере-сервере данные доступа и нажать кнопку «Подключить». Если поставить галочку «Разрешить мне сохранять учетные данные», последующие входы будут выполняться без дополнительных вопросов. Но в первый раз пароль всегда вводится вручную. При желании создается отдельный конфигурационный файл (востребовано, когда много компьютеров с удаленным управлением).
После подключения пользователь видит рабочий стол компьютера на Ubuntu. Работа с его окнами не отличается от локального управления – функционируют все настроенные горячие клавиши, перетаскивание мышью. В некоторых версиях Ubuntu, например, 18.04 LTS, RDP не работает, пока не выйдешь из текущего пользователя. Подобные фишки обычно известны системным администраторам.
Подключение через VNC
Есть другой вариант удаленного рабочего стола – сеть Virtual Network Computing (VNC). Она тоже требует предварительной настройки обеих машин. Так, на компьютер с Ubuntu инсталлируется ПО, открывающее доступ к управлению.
Последовательность действий:
- Открыть окно терминала.
- Ввести команду sudo apt update.
- Установить сервер: sudo apt install tightvncserver.
- Активировать его: sudo tightvncserver.
Система предложит ввести пароль для подключения. Он понадобится при активации удаленного соединения, поэтому стоит записать (запомнить) внесенные данные.
На этом все! TightVNC Server готов к работе, остается следом настроить компьютер на Windows. Программа доступна на официальном сайте разработчика в двух версиях: 32 и 64-бит.
После инсталляции и запуска достаточно ввести IP-адрес хоста и пароль доступа, введенный после активации сервера на Ubuntu. Схема работы VNC аналогична предыдущему примеру: пользователь видит перед собой удаленный рабочий стол и управляет функциями операционной системы, как будто сидит за компьютером локально.
Learn the steps to connect the remote Ubuntu 24.04 Noble or 22.04 LTS Jammy JellyFish desktop from Windows 11 or 10 using RDP (remote desktop protocol).
Steps to access Ubuntu 24.04/20.04 remotely from Windows 10 or 111. Perform a System update2. Install XRDP on Ubuntu 22.043. Start & Enable XRDP Service4. Open port 3389 in the firewall5. Log out of Ubuntu 24.04 or 22.046. Connect Ubuntu 24.04 or 22.o4 remotely using Windows 10 or 11Ubuntu remote desktop black screen- issue
Windows has a convenient feature called Remote Desktop Connection, which uses the RDP protocol to connect a PC remotely. Although it is straightforward to use when establishing a remote desktop connection from Windows to Windows systems, the same goes for the Linux system. This is because the RDP protocol is not installed in Linux by default. In this situation, we have to configure the Linux system to enable RDP manually; we know how to do that in this guide.
What is XRDP?
XRDP is a free and open-source program that implements Microsoft RDP (Remote Desktop Protocol) to easily access Linux systems remotely with a GUI. With XRDP, you can log on to the remote Linux computer and create a desktop session as if you had logged on to a local computer.
Steps to access Ubuntu 24.04/20.04 remotely from Windows 10 or 11
The steps given here can be used on other versions of Ubuntu, such as 20.0/18.04, including Linux Mint, MX Linux, and more…
1. Perform a System update
In this tutorial, we will use the system’s default repository and APT package manager. To rebuild the APT cache, run the system update command once.
sudo apt update
2. Install XRDP on Ubuntu 22.04
As we know, Ubuntu doesn’t have RDP installed like Windows OS. Hence, we need to install XRDP, the open-source implementation of RDP, on our Linux system. The good thing is that we don’t need to add any third-party repository because it can be installed using the system’s default one.
sudo apt install xrdp
3. Start & Enable XRDP Service
To start and also make the service of XRDP enable automatically with system boot, use the given commands:
To start it:
sudo systemctl start xrdp
Enable it:
sudo systemctl enable xrdp
Check the status:
systemctl status xrdp
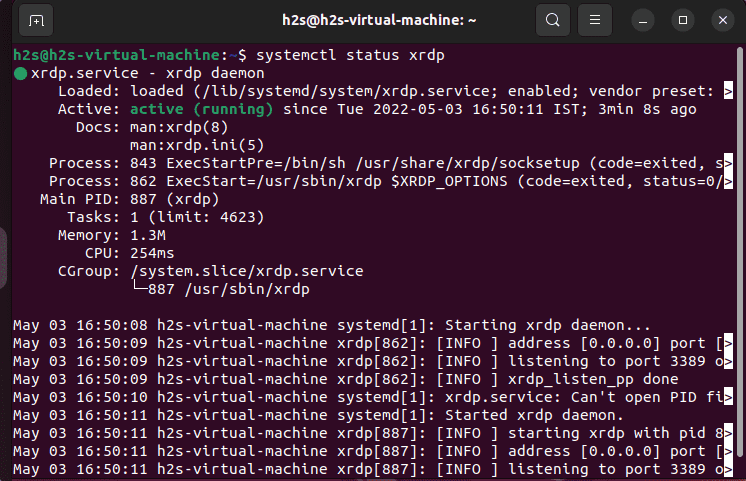
4. Open port 3389 in the firewall
Open port 3389 on your system’s firewall to let the other systems in the network access Ubuntu 22.04 Jammy remotely over RDP.
sudo ufw allow from any to any port 3389 proto tcp
Next, find the IP address of your Ubuntu system and note it down somewhere. For that on your terminal run:
ip a
5. Log out of Ubuntu 24.04 or 22.04
Once the installation is completed, log out of your Ubuntu 24.04 or 22.04 system. Otherwise, you will get a black screen issue on Windows while connecting Ubuntu remotely using XRDP.
To log out, click the Power-off icon and select the logout option.
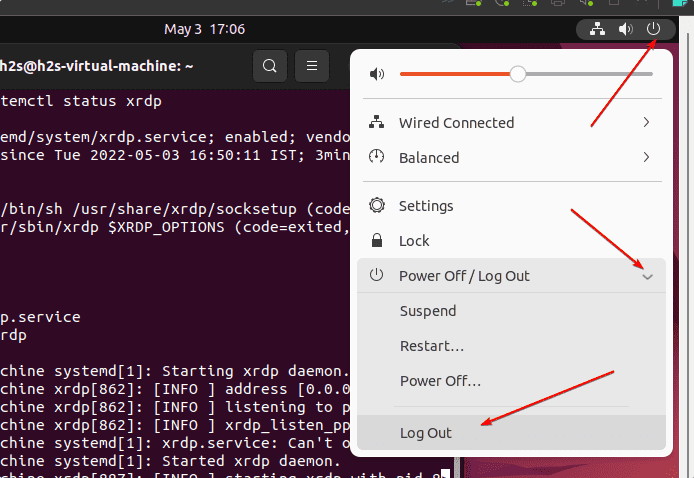
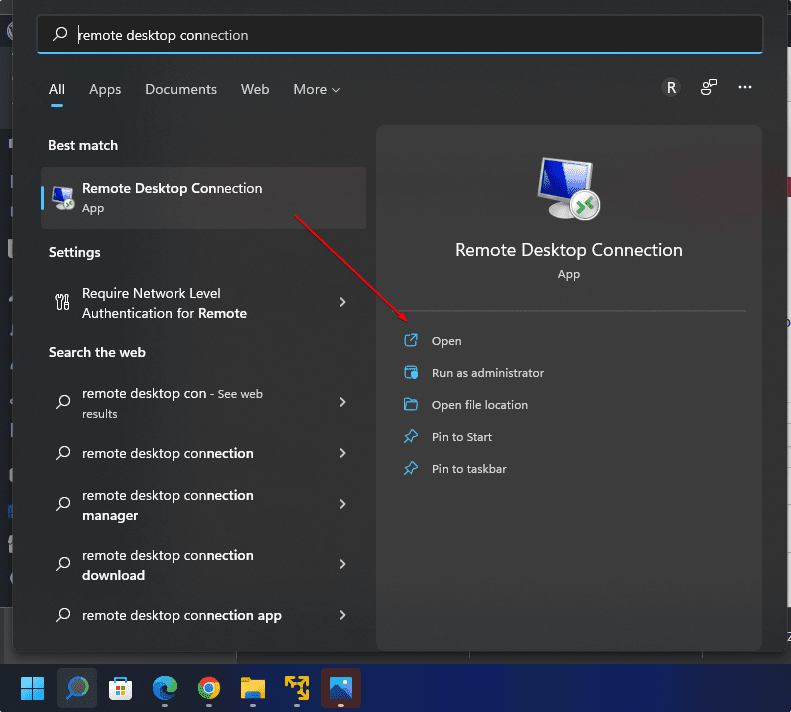
6. Connect Ubuntu 24.04 or 22.o4 remotely using Windows 10 or 11
Finally, go to the Windows 10 or 11 system you are using and click on the Search icon. Type “Remote Desktop Connection” as its icon appears, and click to open the same.
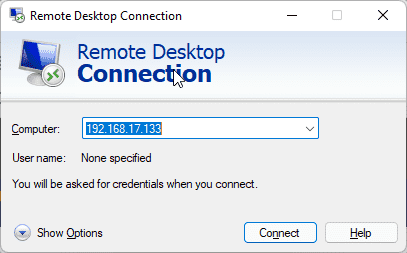
In the Windows “Remote Desktop Connection” app, enter the IP address of your Ubuntu system that you noted down and click on the “Connect” button.
For example, our Ubuntu 22.04 IP address was 192.168.17.133
When the message appears, “The identity of the remote computer cannot be verified. Do you want to connect anyway?“
Click the Yes button.
The XORG window will open. To graphically control your remote Ubuntu 24.04 or 22.04, enter the username and password of the remote Ubuntu 24.04 or 22.04 you want to connect over RDP.
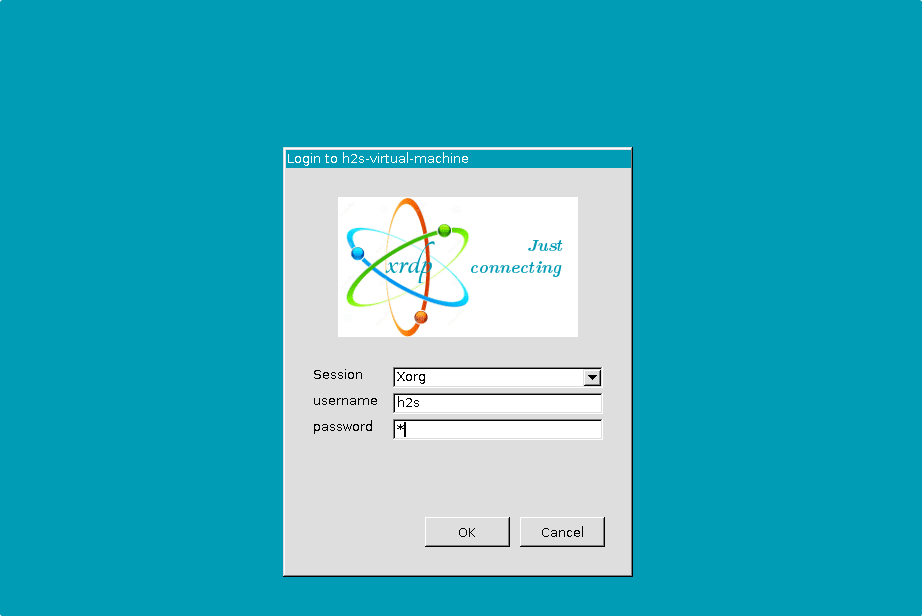
The system will again ask for your system’s password.
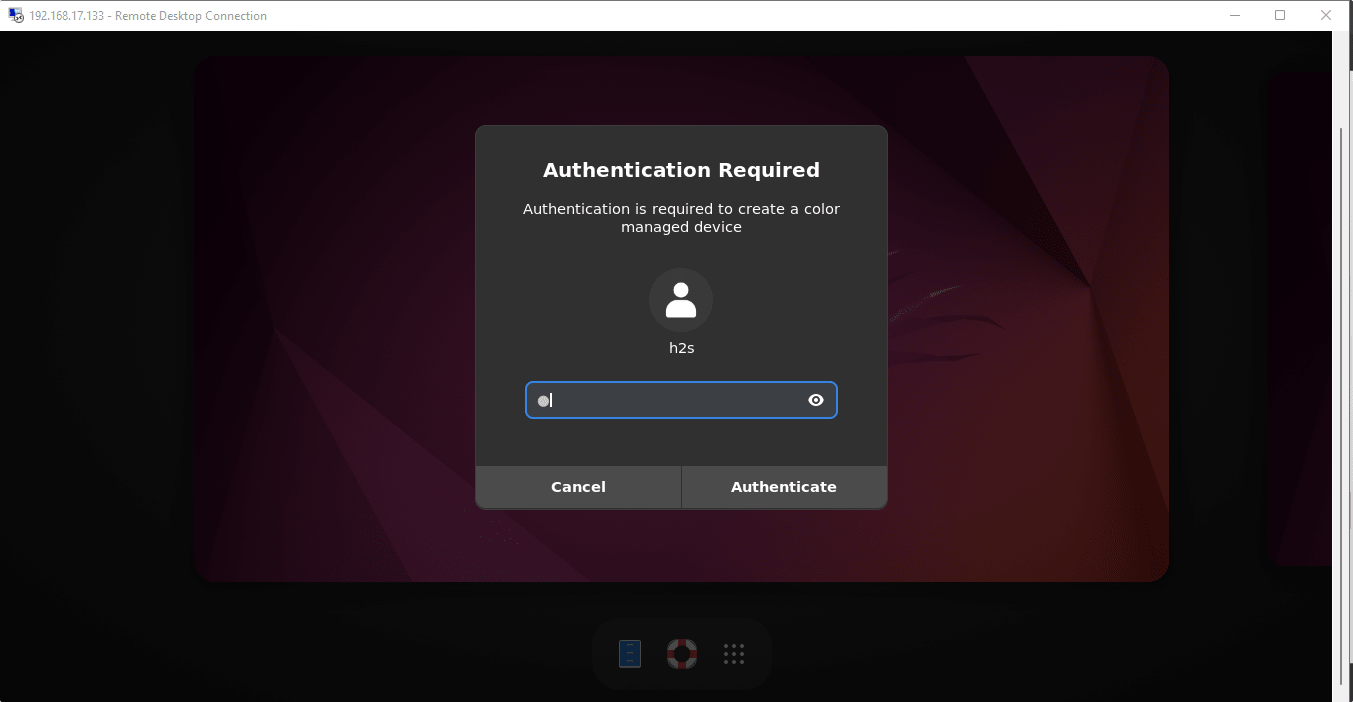
Finally, using the Remote desktop protocol, the remote Ubuntu 24.04 or 22.04 LTS graphical screen will be on your Windows system.
Ubuntu remote desktop black screen- issue
The issue of getting a black screen or automatically shutting down the Remote desktop connection application on Windows appears if you have not logged out of your remote Ubuntu 22.04 system that you want to connect to. Because using RDP, here we can only open a single session.
Other Articles:
• Commands to Install Xrdp Server on Debian 11 Bullseye Linux
• How to Install 7-Zip on Ubuntu 22.04 LTS
• How to Download Youtube videos on Ubuntu 22.04
• Install VMware Workstation Player on Ubuntu 22.04 LTS
Last Updated :
20 Feb, 2024
systemRemote Desktop from Windows helps to access a different operating system in Windows itself. Windows & Ubuntu operating systems can be used simultaneously with the help of Remote Desktop Access. Remote Desktop Access on Ubuntu from the Windows process will be discussed in this article by following simple steps on both Ubuntu & Windows.

Table of Content
- Method 1: Get Remote Access Using Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP)
- Method 2: Get Remote Access Using Virtual Network Computing (VNC)
- Method 3: Get Remote Access Using Third-party Software
Why Do We Use a Remote Desktop Connection?
There are many situations where we require remote desktop access of a computer system. Some of the cases are mentioned below.
- Remote Access: Enables accessing a computer from anywhere.
- File Retrieval: Access files and documents remotely.
- Tech Support: IT support resolves issues without physical presence.
- Collaboration: Multiple users work on the same project simultaneously.
- Resource Utilization: Use powerful software/resources remotely, saving local device resources.
Pre-Requisite to Establish Remote Desktop Access.
Before establishing the Remote desktop access on Ubuntu, you need to meet a few requirements :
- Enable Port Forwarding on the remote device’s router
- Find Ubuntu’s IP Address
- Install SSH on the Ubuntu box.
Let’s see how to do this quickly!
Enable Port Forwarding:
To access a remote Access on another network (e.g., your work network), you need to Enable Port Forwarding on the router where your Ubuntu PC is located.
- Log into your router’s web interface using a web browser.
- Look for the port forwarding section or NAT settings.
- Create a new port forwarding rule for port 3389 (Remote Desktop’s default port).
- Enter the local IP address of your Ubuntu machine.
- Save the changes and restart the router if necessary to apply the configuration.
Find Ubuntu’s IP Address:
- Launch the Terminal application on your Ubuntu machine.
- Type ‘ ifconfig ‘ and press Enter to display network interface details.
- Look for the IPv4 address associated with the network interface you are using (like eth0 or en0).
Install SSH:
- Launch Terminal on your Ubuntu machine.
- Type ‘sudo apt-get update‘ to update package lists.
- Type ‘sudo apt-get install openssh-server‘ and press Enter.
- Complete the installation process and set up SSH on your Ubuntu system.
How to Set Up Remote Desktop Access From Windows to Ubuntu?
Once you are equipped with all the prerequisites to establish Remote Desktop Access. You are ready to move on and start the actual process of Set Up Remote Desktop Access From Windows to Ubuntu.
Method 1: Get Remote Access Using Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP)
On the Ubuntu Operating System
Step 1: To develop Remote Desktop from Windows, first open the terminal open a terminal (Ctrl + Alt + T) of Ubuntu & execute the following command in the terminal. It will help to install the XRDP application in Ubuntu that helps to combine different operating systems. It will take some time to install the application.
Command: sudo apt install xrdp -y
.png)
Step 2: After installation of the application, run the following two commands. One of the commands will help to start the application that is installed on the device. The second command will help to enable the application on the machine.
Commands:
sudo systemctl start xrdp
sudo systemctl enable xrdp
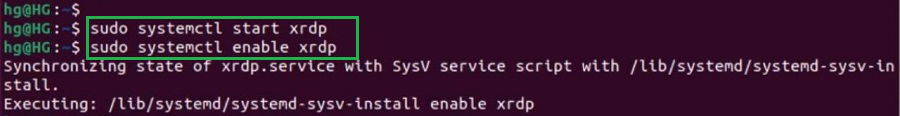
Step 3: After running the above commands, again execute the following command to show the status of the XRDP application. The status of the application is now running.
Command: sudo systemctl status xrdp
.png)
Step 4: At last, execute the following command in the Ubuntu terminal. It will provide configurational details of the machine. Find out the IP Address of the Ubuntu operating system.
Command: ifconfig
.png)
Hence, we have completed the operations required in the Ubuntu operating system.
On Windows Operating System
Step 1: To complete Remote Access Ubuntu from Windows, first open the Remote Desktop Connection in the Windows OS & provide the IP Address of the Ubuntu operating system. It will be the same operating system that was noted down earlier. After that, click on the Connect button.

Step 2: In the next tab, click on the Yes button present there to connect Ubuntu from Windows.
.png)
Step 3: Now provide the username & password. It will be the same username & password used to enter into the Windows operating system. If there is no password present in the Windows operating system, keep it blank here. Then click on OK to finish the operation.

Hence, we have completed the operations required to establish remote desktop access to Ubuntu From Windows
Method 2: Get Remote Access Using Virtual Network Computing (VNC)
Virtual Network Computing allows desktop sharing on computer network. So to connect your Windows to Ubuntu PC, follow these steps.
Step 1: Install VNC Server on Ubuntu:
- 1. Open Terminal and type ‘sudo apt-get update‘.
sudo apt-get update
- 2. Install the VNC server with ‘sudo apt-get install tightvncserver’.
sudo apt-get install tightvncserver
Step 2: Install VNC Viewer on Windows:
- Download and install a VNC Viewer application on your Windows computer.
Step 3: Start VNC Server on Ubuntu:
- Type ‘vncserver‘ in the Terminal and set a password.
vncserver
Step 4: Connect from Windows:
- Open VNC Viewer on Windows.
- Enter Ubuntu’s IP address and the password you set.
- Click Connect to establish remote access to Ubuntu from Windows.

Method 3: Get Remote Access Using Third-party Software
Remote desktop Software allows you to connect and get remote access on computer in another location. You can easily control a connected PC via an internet connection with 2 simple steps.
Step 1: Install Software on Ubuntu and Windows:
- Choose a tool like TeamViewer, NoMachine, or Chrome Remote Desktop
- Go to their official websites and download the software for both Ubuntu and Windows.
Step 2: Launch the Software and Connect:
- Open the software on both devices.
- Enter the partner’s ID (displayed on Ubuntu) in the Windows software.
- Click Connect to establish remote access from Windows to Ubuntu.
Just like this you can use any of the above-mentioned methods and can Set Up Remote Desktop Access from Windows to Ubuntu.
Also Read
- How to control your PC by your Smartphone?
- How do I use SSH to connect to a remote server in Linux?
- How to Run Linux Software on Windows — GeeksforGeeks
A list of the best remote desktop clients for Ubuntu and other Linux distros.
Remote desktop clients allow you to connect to any other desktop/server and perform tasks remotely. It’s one of the important aspects of IT support and other commercial use cases. In Linux, there are many remote desktop clients available. Some of them are free, while others are paid versions. All of these clients support popular remote desktop protocols (RDP) such as VNC, RDP and others.
This article looks at some of the best free remote desktop clients for Ubuntu and other distros. The list includes free and open-source apps and some free-to-use but proprietary apps.
Note: You need a remote desktop server (such as Xrdp) in your target system to establish a remote connection successfully. Then only you can connect using the following apps. It’s a two-way process. If you want to get more insight, refer to one of our case studies: Connecting to Ubuntu from Windows via RDP.
GNOME Connections
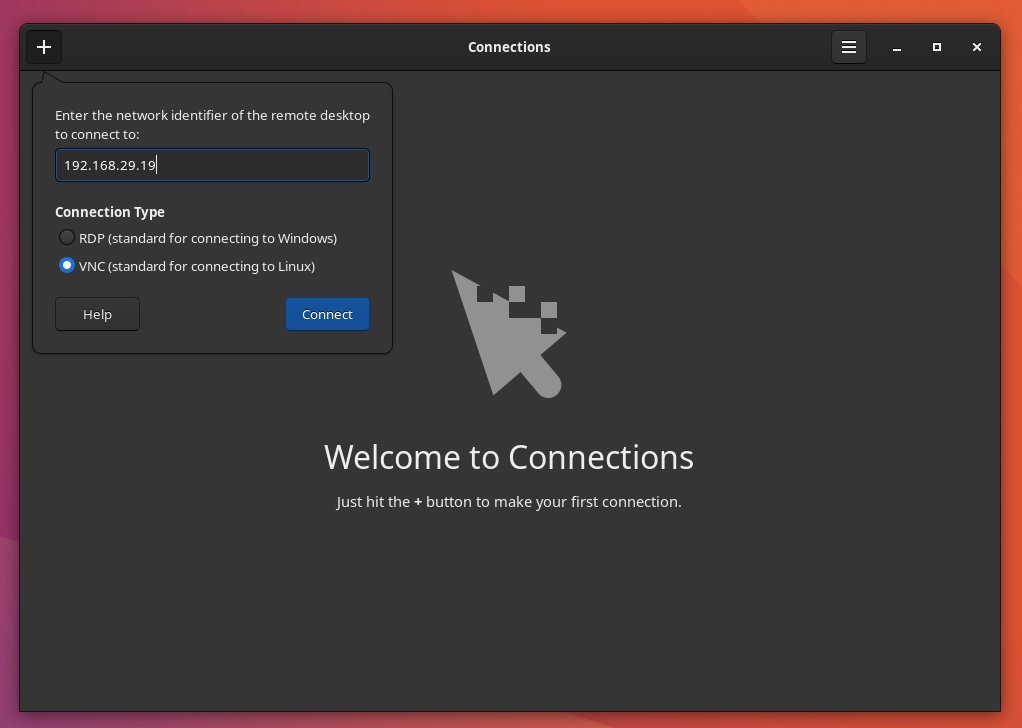
The first remote desktop client is a native GNOME app – “GNOME Connections”. This GTK-based app brings a simple user interface. It’s a perfect app for beginners. It’s also a perfect way quickly set up and connect in a minute (if you know the IP and other details).
In addition, it comes with clear instructions on whether you want to connect to a Linux machine or Windows. GNOME Connections support VNC (for Linux) and RDP (for Windows) protocols.
Installing this app is super easy with Flatpak. Set up your system to use Flatpak and install it using the following command.
flatpak install flathub org.gnome.Connections
More information
- Source code and home page
KRDC

The next app is KRDC, a KDE app that allows you to view and control remote desktop sessions on another machine. It supports VNC and RDP protocol. You can also control the resolutions and passwords; of course, it integrates well with your Plasma desktop.
So, this is it if you are looking for a native-KDE app for a remote desktop. For the KDE Plasma desktop, it should be installed by default.
If not, the ideal way to install it is using Flatpak. Set up your system to use Flatpak, and then use the following command to install.
flatpak install flathub org.kde.krdc
More information
- Home page
- Documentation
- Source code
Remmina
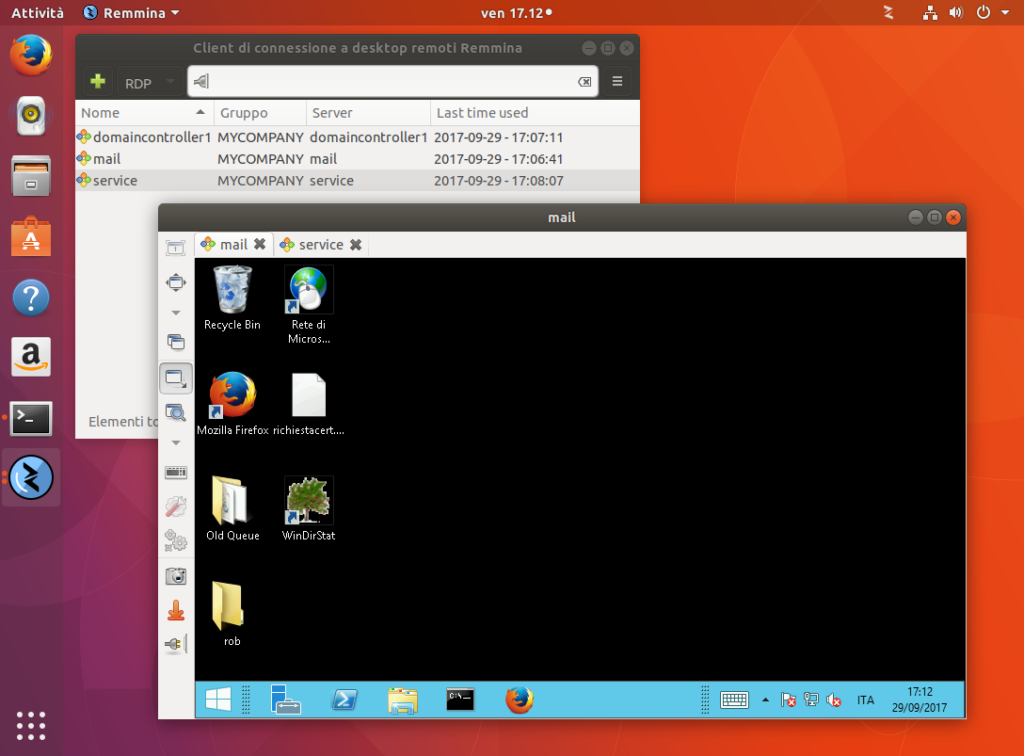
Remmina is one of the oldest remote desktop clients for Linux systems. Probably the “go-to” client when you are in need. This free and open-source app is available Linux as well as for macOS. It supports many remote protocols, such as RDP, VNC, NX, X2GO, SPICE, HTTPS and SSH.
Moreover, it is powerful with its simple yet profound user interface and is super-active in development and bug fixes.
This app is already in all the major distro’s repositories. You can search for “remmina” in your Software app in Ubuntu and related apps in other distros. And hit install.
Alternatively, you can also use the following commands to install.
Furthermore, you can also set up your system for Flatpak and install it as Flatpak using the following command.
flatpak install flathub org.remmina.Remmina
More information
- Home page
- Source code
TigerVNC
TigerVNC is a free and open-source “platform-neutral” implementation of the VNC (Virtual Network Computing) protocol that comes with both client and server packages. You can use this remote desktop when there is a need for high performance because it works best and is optimized for 3D/Video data over a remote connection.
Furthermore, it still provides a 32-bit installer, along with the usual 64-bit and a command line interface. The client program name for TigerVNC is vncviewer and options are present here.
You can get the pre-compiled deb and RPM packages from the Sourceforge page here.
More information
- Home page
- Documentation
- Source code
X2Go
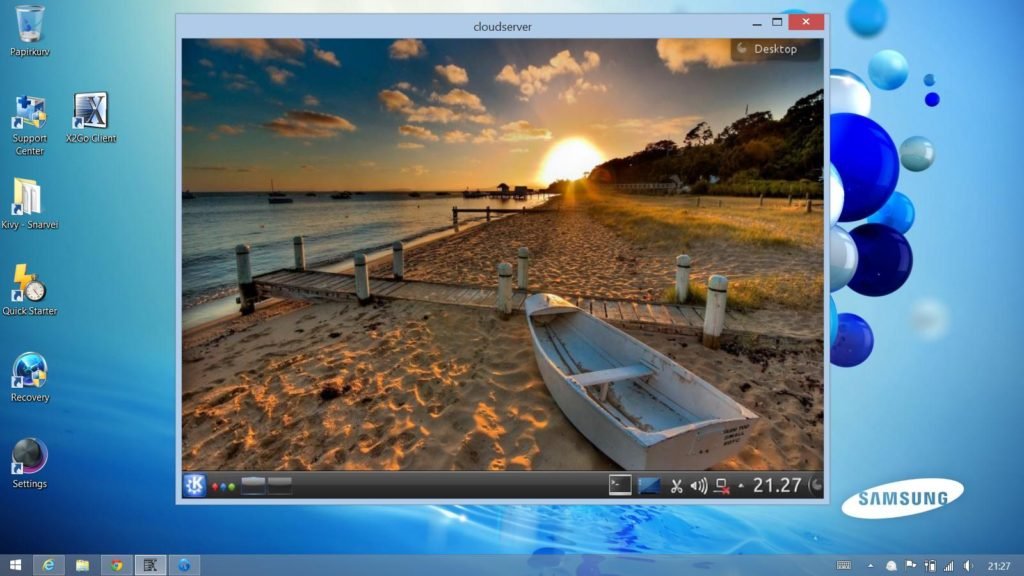
X2Go is a Linux-based remote desktop software based on NX technology which is developed by NoMachine. It is a collection of client and server packages that enables you to connect to remote machines via proxy.
For the remote client part – it comes with two options. You can use either the X2Go client or Pyhoca-GUI (based on Python). All of these are bundled together in the repositories available for Linux. In addition, all the components are also available for Windows and macOS.
You can download this software’s client and server parts from the below page.
Download X2Go
Chrome Remote Desktop
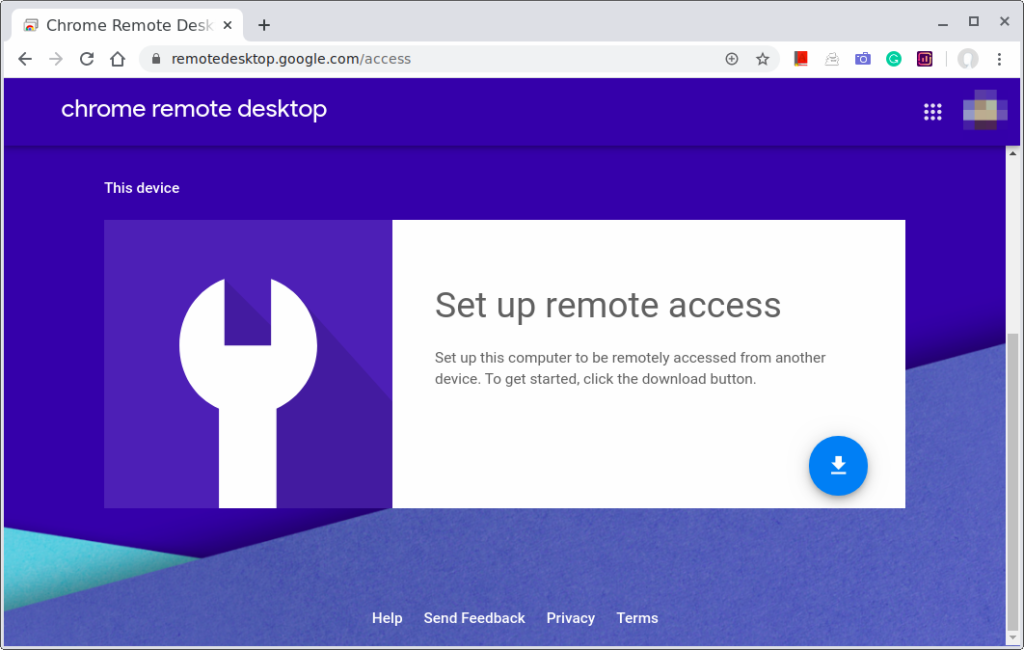
If you prefer a remote connection over a web browser or have limitations in installing an RDP server, you can try out a remote connection via Google Chrome.
The Chrome Remote Desktop service is created by Google and is available over the internet. This service runs via WebRTC protocol over a browser and uses some proprietary technology.
Once launched, a server component is downloaded from the host machine and uses Chrome to provide the functionality. And in the client machine uses a Google Chrome Extension to enable your remote connection.
You can open the below URL to access this service via Chrome and WebRTC-supported browser.
https://remotedesktop.google.com/
Furthermore, it provides an on-the-fly PIN-based authentication mechanism for remote viewing of your systems. And it is limited to being used by up to 100 clients only.
More remote clients
The above list should suffice for most of the common use cases. However, if you are still hungry for more remote desktop clients, here’s a list I have prepared for you with a brief of their nature.
Free and open-source
- TurboVNC (Free and open-source)
- UltraVNC (Free and open-source)
- FreeRDP (Free + require compilation + support Wayland)
Commercial closed source and requires a license to use
- Thincast (Free to use; Flatpak package; Available for Raspberry Pi; Closed source & Proprietary license)
- NoMachine (Free for personal; Paid for business; Popular, available for Linux, Windows, macOS, Raspberry Pi)
- AnyDesk (Free for personal; Paid for business; closed source)
- VNC Connect (Paid; closed source)
- TightVNC (requires a license with an email address to be used in Linux)
- itopia (Free with a trial version; Flatpak)
Wrapping Up
This article lists some of the latest remote desktop clients for Ubuntu and other Linux distributions. Some of them are free and easy to use. You can use them for remote support, studying, and other use cases. IN addition, I also mentioned WebRTC-based remote service, which doesn’t require any installation except a browser extension.
Furthermore, for the benefit of everyone, I have mentioned some of the commercial ones as well. Because if you are a small and medium enterprise, you might want to check the paid version apps with support.
Finally, which one of the remote client software is your “go-to” app? Let me know in the comment box below.
