
Да-да, это очередной гайд по настройке Windows. Здесь не будет настроек, которые относятся к внешнему виду и прочей мишуры. Это так же не является каким-то ультимативным гайдом, но здесь я попытался собрать именно те твики и настройки, которые работают. Здесь нет бессмысленного переписывания не нужных и старых твиков – в основном это попытка собрать оптимизации, которые служат для уменьшения задержек, инпут-лага и троттлинга путём отключение таймера HPET в Windows, настройки и приоритизации прерываний устройств и их драйверов, а так же отключение энергосберегающих функций. Благодаря этим настройкам система становится более отзывчивой, пропадают фризы и микролаги в Windows и ресурсоёмких приложениях, а так же увеличивается плавность в играх. Кроме этого данный гайд так же может решить проблемы с задержками при движении мыши, заиканием звука при использовании других устройств и прочие неприятности связанные с задержками между устройствами.

Содержание
🎓 Перед тем как начать
- Вступление
- На какой версии Windows это работает?
- Я готов, что дальше?
- Как всё не сломать или вернуть как было
- А можно всё это настроить одной кнопкой?
🔌 Драйверы и системные библиотеки
- Драйверы
- Системные библиотеки
🚥 Оптимизация задержек
- Отключение таймера HPET
- Включение MSI mode
- Приоритизация прерываний
- Приоритизация драйверов
- Распараллеливание драйверов по ядрам
🔨 Оптимизация Windows
- Настройка схемы электропитания
- Настройки системных устройств
- Настройка Windows
🔩 Настройки устройств
- Настройка мыши и клавиатуры
- Настройка видеокарты
- Отключение GameBar, GameDVR
- Настройки игр
- Настройки лаунчеров
- Настройка Oculus VR
🎯 Дополнительные настройки
- Оптимизация загрузки
- Настройка аудио
📝 Прочее
- Экспериментальные твики
- Плохие твики
🔗 Ссылки
- Утилиты используемые в гайде
- Полезные ссылки и референсы
🔮 Тесты и выводы

✨ Если у вас есть конкретные рекомендации как улучшить или изменить данный гайд или какие-то предложения и пожелания, то можете написать обо всём в Issues.
Для работы проектов iXBT.com нужны файлы cookie и сервисы аналитики.
Продолжая посещать сайты проектов вы соглашаетесь с нашей
Политикой в отношении файлов cookie
Операционные системы Windows похожи на швейцарский нож, предназначенный для выполнения самых разнообразных задач. Однако те настройки, что используются по умолчанию в ОС, могут идеально подходить одному пользователю и совершенно не устраивать другого. В этом небольшом материале вы узнаете, как существенно уменьшить время ввода в Windows 10/11 и стать быстрее всех в соревновательных играх.

Прежде чем переходить к редактированию скрытых настроек ОС, необходимо отключить встроенные алгоритмы сглаживания и доведения мыши, которые по умолчанию применяются в Windows.
1. Нажимаем Win+R и вводим команду control mouse.
2. В открывшемся окне выставляем настройки, как показано на скриншотах ниже.
П. С. Вы также можете дополнительно уменьшить время ввода с клавиатуры, введя команду сontrol keyboard и переведя все ползунки в правую сторону.
После отключения ненужных алгоритмов доведения и сглаживания необходимо заставить Windows переложить обработку ввода с первого ядра процессора на любое свободное. Всё дело в том, что, несмотря на появление многоядерных CPU и умения нынешних программистов качественно распараллеливать код, Windows 10/11 продолжает выполнять обработку большинства системных задач на первом ядре CPU, создавая очередь ввода и задержку. Убедиться в правдивости моих слов вы можете самостоятельно, скачав и запустив LatencyMon 7.31.
1. Скачиваем и запускаем от имени администратора утилиту intPolicy.
2. В появившемся окне программы находим xHCI-совместимый хост-констроллер USB (Название может отличаться).
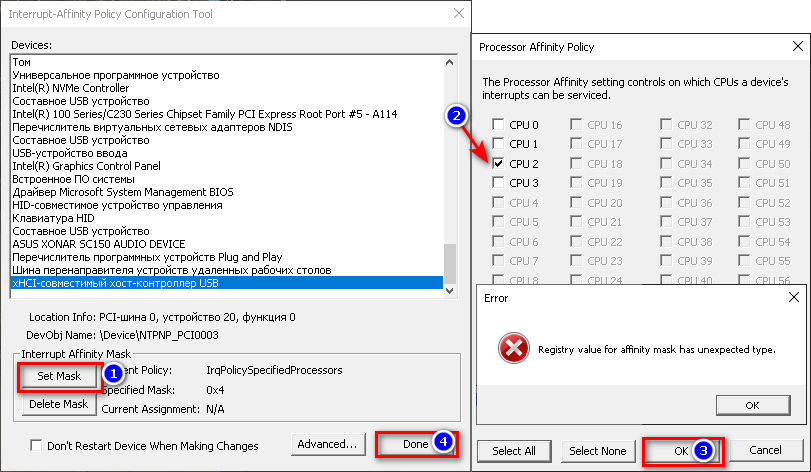
3. Кликам по найденному устройству и переходим в раздел выбора ядра (Set Mask).
4. Выбираем свободное ядро (0 — это первое ядро процессора, а 1 — его виртуальный поток). Нажимаем ОK и Done. Если всё было сделано правильно, то у вас на пару секунд отключится клавиатура и мышь.
5. Перезагружаем ПК.
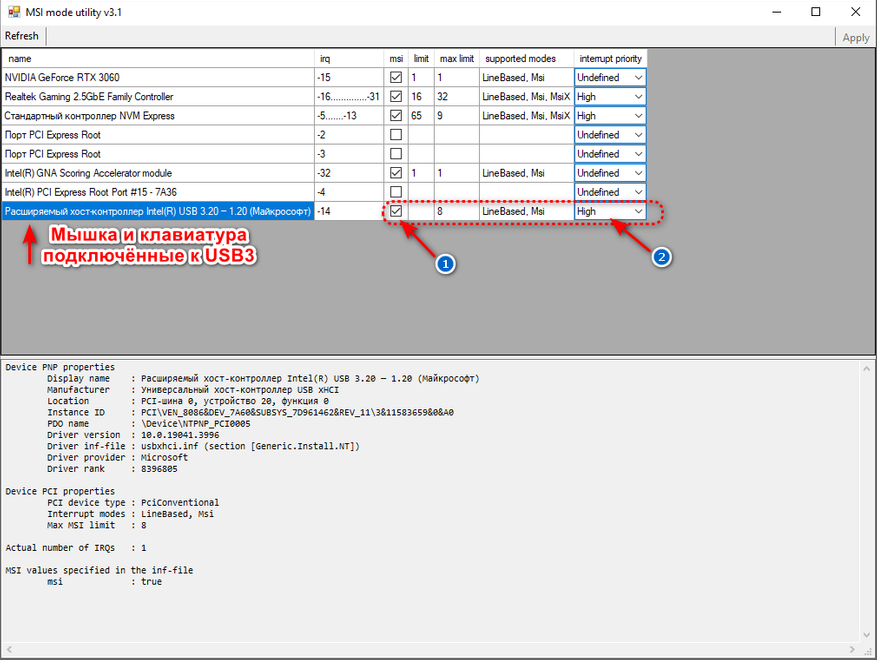
Заставляем Windows использовать альтернативный способ опроса подключённых к ПК устройств — Message Signaled Interrupts (MSI). Не стану забивать вам голову лишней технической информацией, а только скажу, что он давно применяется в серверных системах и значительно уменьшает латентность. Более подробно о MSI вы можете почитать тут.
1. Скачиваем утилиту MSI v3.1 и запускаем её от имени администратора.
2. Находим в интерфейсе программы контроллер USB и ставим напротив него галку и назначаем высокий приоритет (High).
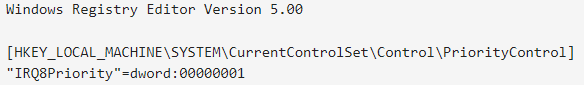
3. Применяем твик прерывания таймера системных часов, используя команду regedit или скачиваем и запускаем от имени администратора уже заранее готовый файл.
Теперь осталось запретить Windows принудительно отключать USB-устройства. Дело в том, что любой алгоритм сохранения электроэнергии не совершенен, а применяемый для USB и вовсе мешает датчикам клавиатуры и мыши.
1. Нажимаем Win+R и вводим команду devmgmt.msc.
2. В появившемся окне переходим в раздел «Вид» и нажимаем «Показать скрытые устройства».
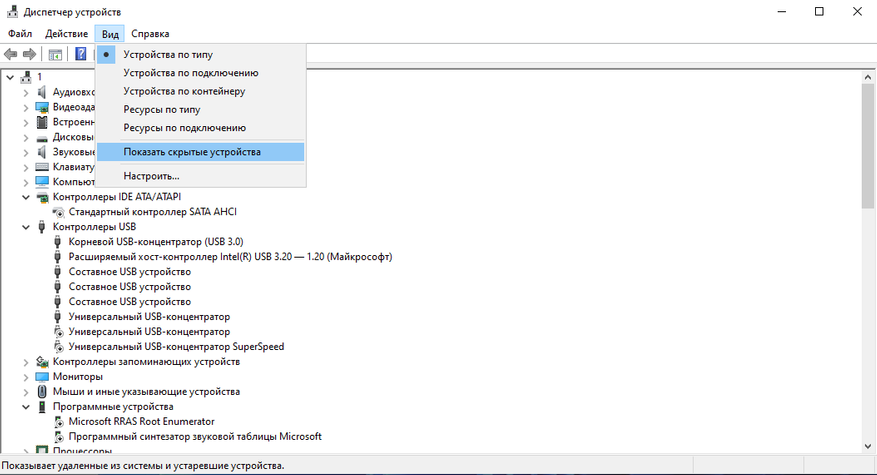
3. Осторожно удаляем все серые устройства.
4. Для оставшихся устройств через правый клик убираем галочки в разделе управления.
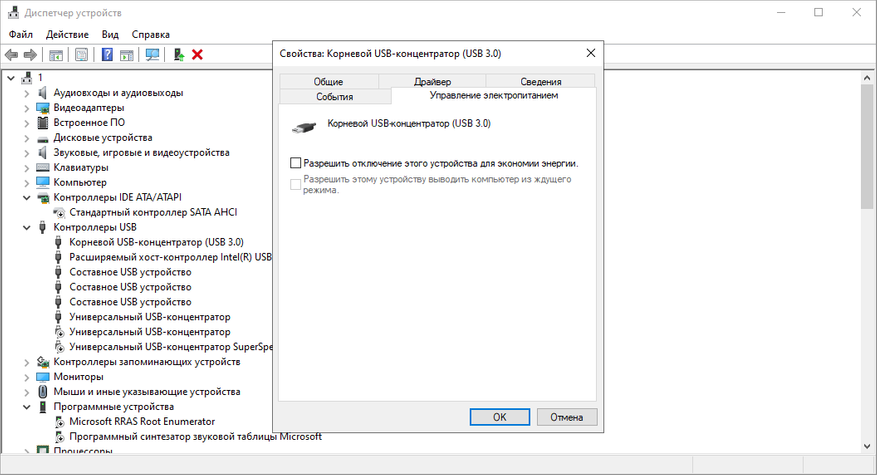
П. С. Вы можете дополнительно уменьшить латентность ввода, отключив все неиспользуемые устройства: USB-порты, перечислитель виртуальных дисков (Майкрософт), перечислитель виртуальных сетевых адаптеров NDIS, шина перенаправителя устройств удаленных рабочих столов, Intel(R) Management Engine Interface и т. п.
Последний пункт относится к спорным настройкам ОС и может не подходить всем пользователям Windows. Имейте это ввиду!
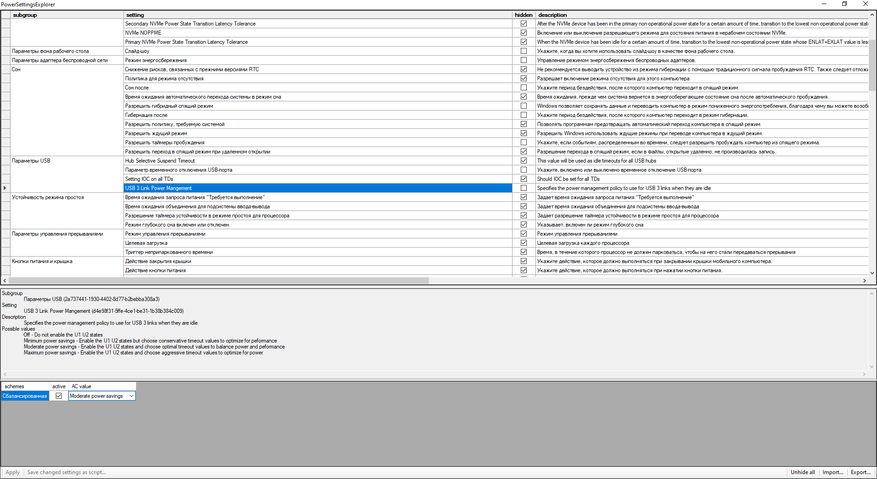
1. Скачиваем и запускаем от имени администратора программу Power Settings Explorer. Она нам понадобится для активации скрытых настроек электропитания Windows.
2. В интерфейсе ПО находим USB3 Link Power Management, «Разрешить состояния снижения питания» и снимаем c них галочки.
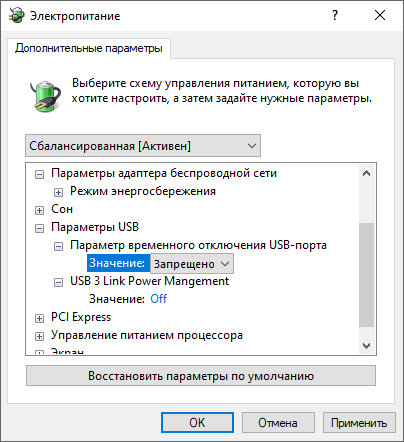
3. Нажимаем Win+R и вводим команду powercfg.cpl. В появившемся окне переходим в раздел «Настройка схемы электропитания» и уверенно нажимаем на «Изменить дополнительные параметры питания».
4. В разделе «Параметры USB» запрещаем Windows отключать питание USB-портов и регулировку подачи электроэнергии (На уровне BIOS и так всё регулируется правильно).
Вот, собственно, и всё! И хотя среднестатистическому пользователю Windows представленная инструкция может показаться очередным ребячеством, которая не стоит потраченного времени. Для всех тех, в ком ещё не погасло пламя огня, при игре в соревновательные шутеры, она обязательно окажется полезной. Уважайте свободу, используйте только проверенное ПО и ни в коем случае не позволяйте компаниям диктовать вам свои условия. С вами был Павел. Ещё увидимся!
П. С. Ещё больше уменьшить задержку ввода вы можете, воспользовавшись отдельной инструкцией по настройке и отключению системного таймера в Windows.
Reducing latency and improving performance in Windows 10 is important for ensuring a smooth and efficient user experience. Here are some steps you can take to achieve this:
1. Update your drivers: Outdated drivers can cause performance issues. Make sure to regularly update your graphics card, sound card, chipset, and other drivers to the latest versions compatible with Windows 10. You can usually find the latest drivers on the manufacturer’s website.
2. Optimize startup programs: Too many programs launching at startup can slow down your system. Open the Task Manager by pressing Ctrl+Shift+Esc and navigate to the Startup tab. Disable any unnecessary programs from launching at startup.
3. Adjust power settings: Windows 10 offers power plans that can affect performance. Open the Control Panel, navigate to Power Options, and select the High-Performance power plan. This helps maximize system performance but might increase power consumption.
4. Disable visual effects: Windows 10 includes various visuals effects that can consume system resources. Open the Control Panel, go to System, click on Advanced system settings, and select the Settings button under the Performance section. Choose the «Adjust for best performance» option or manually disable specific visual effects.
5. Check for malware and viruses: Malware and viruses can significantly impact system performance. Ensure your Windows Defender or any third-party antivirus software is up to date and perform regular scans to keep your system clean.
6. Uninstall unnecessary software: Over time, you may accumulate software that you no longer use. Uninstalling unnecessary programs frees up system resources and improves performance. Open the Control Panel, go to Programs and Features, and uninstall any programs that you don’t need.
7. Disable unnecessary services: Windows 10 runs several background services that may not be required for normal usage. To manage these services, open the Services console by pressing Win+R, typing «services.msc,» and pressing Enter. Analyze the list of services and disable those that are unnecessary for you.
8. Upgrade hardware: If you’re still experiencing performance issues after optimizing software settings, it might be time to consider upgrading your hardware. Upgrading your RAM, adding a solid-state drive (SSD), or upgrading your graphics card can significantly improve system performance.
Remember, implementing these steps may vary depending on your specific system configuration and requirements. It’s also a good practice to regularly maintain your system, keep it up to date with the latest Windows updates, and ensure all software is compatible with Windows 10.
Video Tutorial:Does lower latency mean faster?
What causes high PC latency?
High PC latency can be caused by various factors, and identifying the root cause is crucial for troubleshooting and resolving the issue. Here are some potential reasons for high PC latency:
1. Outdated hardware: Aging or insufficient hardware components like the processor, RAM, or storage can lead to high PC latency. Upgrading these components or ensuring that they meet the system requirements of the software being used can help alleviate latency issues.
2. Insufficient or misconfigured RAM: If a system does not have enough random access memory (RAM), it may struggle to efficiently manage multiple processes or handle large data sets, resulting in high latency. Additionally, misconfigured RAM, such as incorrect voltage or clock settings, can lead to performance degradation.
3. CPU throttling: Modern CPUs often dynamically adjust their clock speeds to optimize power consumption and manage heat generation. However, aggressive throttling or misconfigured power settings can impact a system’s performance and increase latency. Adjusting power management settings or ensuring proper cooling can address this issue.
4. Software conflicts and resource-intensive applications: Conflicts between different software applications or resource-intensive programs can cause high latency. It’s important to identify and resolve conflicts by updating software, closing unnecessary background processes, or using tools like task managers to monitor resource usage.
5. Driver issues: Outdated or incompatible device drivers can significantly impact system performance and introduce latency. Ensuring all device drivers are up to date, either through manual updates or using dedicated software, can help mitigate latency problems.
6. Malware or viruses: Malicious software can often run stealthily in the background, consuming system resources and introducing latency. Performing regular malware scans using reliable antivirus software can help detect and remove any malicious programs.
7. Background processes and services: Numerous background processes and services running simultaneously can hog system resources and increase latency. Reviewing and disabling unnecessary startup programs, scheduled tasks, or services can help reduce latency by freeing up system resources.
8. Storage issues: Slow hard disk drives (HDD) or fragmented files can result in increased latency. Upgrading to a solid-state drive (SSD) or optimizing HDD performance, such as defragmenting the drive or optimizing file indexing, can improve latency.
9. Network issues: If a PC relies heavily on network connectivity, high latency can be caused by network congestion, router issues, or problematic network settings. Troubleshooting network components or contacting your Internet service provider (ISP) can help address these issues.
10. Operating system-related factors: System-specific factors like outdated operating systems, unapplied updates, or incompatible software versions can contribute to high PC latency. Regularly updating the operating system and keeping software up to date can minimize latency problems.
Identifying the specific cause of high PC latency often requires a systematic approach of elimination or further investigation. Monitoring system performance, checking software and hardware compatibility, and applying the necessary updates are essential steps towards resolving latency issues effectively.
What does reducing latency do?
Reducing latency is a crucial aspect of improving overall performance and user experience in various technological applications. Here’s why reducing latency matters:
1. Improved Responsiveness: Latency refers to the delay between when a command or action is initiated and when it is actually executed or observed. By minimizing latency, devices and systems can respond more quickly to user input, resulting in a more immediate and responsive experience. This is especially important in real-time applications like video streaming, online gaming, or virtual reality, where any delay can impact the user’s immersion and engagement.
2. Enhances Communication: In communication systems like voice or video calls, reducing latency is vital to maintaining a natural and seamless conversation. Lower latency ensures that there is minimal delay between the spoken words or video frames being transmitted, making conversations feel more natural and allowing for uninterrupted flow.
3. Optimizes Data Transfer: Latency can significantly impact data transfer rates, especially in scenarios that involve large file transfers or cloud computing. Minimizing latency increases the speed at which data can be transmitted, improving efficiency and reducing the time required for tasks like uploading or downloading files.
4. Enables Real-Time Decision Making: Many technologies rely on real-time processing and decision making, such as autonomous vehicles, industrial automation, or live financial trading. By reducing latency, these systems can quickly analyze and respond to incoming data, enabling more immediate actions and faster decision-making processes.
5. Enhances User Experience: In general, reducing latency across various applications leads to an overall better user experience. Whether it’s web browsing, app usage, or interacting with smart home devices, lower latency ensures smoother interactions, reduces frustration, and makes technology feel more seamless and intuitive.
6. Supports Emerging Technologies: As new technologies continue to evolve, reducing latency becomes increasingly important. For example, in augmented reality (AR) or mixed reality (MR) experiences, low latency is essential to ensure that virtual graphics align with real-world visuals, preventing motion sickness and maintaining the illusion of immersion.
Overall, reducing latency is crucial for a wide range of technologies to operate smoothly, offering fast and responsive interactions, enhancing communication, optimizing data transfer, enabling real-time decision making, and delivering an enhanced user experience.
Reducing latency and improving performance is crucial in today’s tech landscape, especially in the context of smartphones and other smart devices. Here are several reasons why it is important to focus on reducing latency and improving performance:
1. Enhanced User Experience: Faster response times and smoother performance greatly contribute to a positive user experience. Users expect seamless interactions with their devices, whether it’s navigating through apps, browsing the web, or playing games. By minimizing latency and optimizing performance, you can provide a smooth and enjoyable user experience.
2. Increased Productivity: For professionals relying on their smartphones for work, reducing latency and enhancing performance can significantly boost productivity. Quick access to applications, instant loading of files, and seamless multitasking capabilities can make a substantial difference in completing tasks efficiently.
3. Competitive Advantage: In today’s competitive market, companies need to differentiate themselves from others. By prioritizing latency reduction and superior performance, you can gain a competitive edge. Consumers are more likely to choose devices that offer smoother, faster, and more responsive experiences.
4. User Retention: In the age of countless options, user loyalty depends on overall satisfaction. If a device or application consistently lags or underperforms, users are more likely to switch to competitors offering better performance. By reducing latency, you can increase user retention rates and minimize churn.
5. Gaming and Multimedia: With the growing popularity of mobile gaming and multimedia consumption, reducing latency and improving performance become even more critical. Gamers require minimal latency to ensure smooth gameplay, while media enthusiasts expect buffer-free streaming and fast content loading.
Steps to Reduce Latency and Improve Performance:
1. Optimize Software: Regular software updates play a vital role in improving performance. Developers should focus on refining algorithms, optimizing code, and eliminating bottlenecks to minimize latency and enhance overall device performance.
2. Hardware Enhancements: Enhancing the hardware components of a smartphone, such as processors, RAM, and storage, can improve performance. Upgrading to faster processors, increasing RAM capacity, and utilizing faster storage technologies can lead to a noticeable reduction in latency.
3. Network Optimization: Collaborating with network providers and optimizing cellular and Wi-Fi connectivity can significantly reduce latency. Implement features like 5G support, leveraging low-latency network protocols, and ensuring efficient data transmission to enhance performance.
4. Battery Optimization: A device’s performance can be affected by its battery life. Efficient power management techniques help prevent performance degradation due to power-related constraints. Enhancing battery life and optimizing power consumption can positively impact latency and device performance.
5. User Feedback and Testing: Actively seeking user feedback and conducting rigorous testing scenarios can provide valuable insights into areas where latency and performance improvements are required. Incorporating user feedback and conducting performance benchmarking can guide development decisions.
By prioritizing latency reduction and performance optimization, smartphone manufacturers can deliver superior user experiences, gain a competitive advantage, and inspire loyalty among customers.
How can I reduce latency and improve my computer performance?
Reducing latency and improving computer performance involves optimizing various aspects of your system. Here are some steps you can take:
1. Upgrade your hardware: Upgrading components like your CPU, RAM, and storage can significantly improve overall performance. A faster processor and more RAM will handle demanding tasks more efficiently, while an SSD will reduce data access times.
2. Optimize software and settings: Regularly update your operating system and software to ensure you have the latest features and improvements. Adjust settings to prioritize performance, such as disabling unnecessary startup programs, animations, and visual effects.
3. Manage background processes: Close resource-intensive applications that run in the background, consuming system resources and potentially causing latency. Use task manager tools to identify and terminate unnecessary processes.
4. Maintain disk health: Regularly clean up your hard drive by removing temporary files, uninstalling unused applications, and running disk cleanup utilities. A cluttered disk with fragmented data can impact performance.
5. Utilize solid-state drives (SSDs): Consider using SSDs instead of traditional hard drives for faster data access. SSDs have no moving parts and offer faster boot times, application launches, and file transfers.
6. Update your drivers: Keep your drivers, including graphics and audio, up to date to ensure compatibility with the latest software and improve system stability and performance.
7. Manage startup programs: Limit the number of programs that start automatically when your computer boots up. Unnecessary startup programs consume resources and may lead to increased latency.
8. Upgrade your internet connection: If latency issues are evident during online activities, consider upgrading your internet connection to a higher speed package with lower ping times.
9. Clear cache and browsing history: Internet browsers store temporary files and browsing history, which can accumulate over time. Regularly clear your cache and browsing history to free up system resources and potentially enhance browser performance.
10. Consider overclocking: Overclocking is a technique where you increase the clock speed of your CPU or GPU to achieve higher performance. However, it requires expertise and potential risks, so it’s crucial to research and follow proper guidelines.
Remember, these steps may vary depending on your specific hardware and software configuration. It’s always a good idea to research and consult professional advice if you’re unsure about any specific optimizations for your computer.
Should I turn on reduce latency?
When considering whether to turn on reduce latency on your device, there are a few factors to take into account. Here are some important points to consider:
1. Gaming or real-time applications: If you frequently use your device for real-time applications such as online gaming or video conferencing, enabling reduce latency can be beneficial. This feature optimizes network performance by prioritizing low latency, ensuring a smoother and more responsive experience.
2. Battery consumption: Keep in mind that enabling reduce latency may increase power consumption on your device. This is because it prioritizes responsiveness, requiring more frequent data exchanges and potential network activity. If you are concerned about battery life, you might choose to keep reduce latency turned off unless specifically needed.
3. Network stability: If you often experience connectivity issues or have a less stable network connection, turning on reduce latency can help mitigate some of these problems. However, it’s important to note that this feature may not completely resolve severe network-related issues, especially if the problem lies with your internet service provider or network infrastructure.
4. Personal preferences: Ultimately, the decision to enable or disable reduce latency should be based on your personal preferences and usage patterns. Some users may prioritize a seamless and responsive experience, while others may prefer to conserve battery life. Consider your specific needs and weigh the trade-offs before making a decision.
It’s worth mentioning that the availability and options for reduce latency settings may vary across different devices and operating systems. Therefore, it’s recommended to consult your device’s user manual or check the specific settings on your device to determine how to enable or disable reduce latency.
What causes PC latency?
PC latency, or the delay between when an action is performed on a PC and when the corresponding response occurs, can be caused by several factors. Understanding these factors can help in troubleshooting and resolving latency issues. Here are some common causes of PC latency:
1. Insufficient processing power: If the PC’s CPU is underpowered for the tasks it’s handling, it may struggle to keep up with the demands, resulting in latency. This can be caused either by outdated hardware or running resource-intensive applications.
2. Lack of memory (RAM): A PC with insufficient RAM may experience latency as it struggles to store and retrieve data quickly. When the system runs out of RAM, it relies on slower storage options like hard drives, leading to delays in data access.
3. High disk usage: If the PC’s disk (HDD or SSD) is constantly operating at a high usage level, it can create latency. This may occur due to background processes, excessive read/write operations, or fragmentation on traditional hard drives.
4. Outdated or incompatible drivers: Drivers are software components that allow the operating system to communicate with various hardware devices. Using outdated or incompatible drivers can result in latency issues as the PC struggles to communicate effectively with hardware components.
5. Network congestion: If the PC is connected to a network with high traffic or limited bandwidth, latency can occur when requesting or sending data over the network. This can be more noticeable during activities like online gaming or streaming where real-time data transmission is crucial.
6. Background processes and software: Certain applications and processes running in the background can consume system resources, causing latency. Antivirus scans, system updates, or resource-intensive software can lead to delays in responsiveness.
7. Malware or viruses: PC latency can also arise from malware or viruses infecting the system. These malicious programs can consume resources, overload the CPU, or perform unwanted actions, resulting in latency issues.
8. Hardware issues: Faulty hardware components, such as a failing hard drive or overheating CPU, can cause latency. These issues may require professional inspection and repair.
To address PC latency, you can take the following steps:
1. Upgrade hardware: Upgrade the CPU, add more RAM, or switch to faster storage options like SSDs to improve performance.
2. Keep drivers up to date: Regularly update drivers to ensure compatibility and improve performance.
3. Manage background processes: Identify and close unnecessary background processes or applications that consume system resources. Use task manager tools to monitor resource usage.
4. Use reliable security software: Install reputable antivirus software and keep it up to date to prevent malware or virus-related latency issues.
5. Optimize network connection: Troubleshoot network issues, such as congestion or limited bandwidth, by performing speed tests, restarting routers, or contacting your internet service provider.
6. Monitor system temperature: Ensure that your PC is not overheating by regularly cleaning dust from fans, checking proper airflow, and using cooling solutions if necessary.
By addressing these potential causes and taking the appropriate steps, you can mitigate PC latency and improve overall system performance.
Deferred Procedure Call (DPC) manages the execution of low-priority tasks related to hardware and device drivers. While its purpose is to defer less time-sensitive operations so that critical tasks get processed first, when high, it can lead to performance issues, particularly in real-time tasks like audio-video streaming or editing. In today’s blog, we will guide you on how to fix high DPC latency on both Windows 11 and 10. Let’s get started.

Table of Contents
When hardware needs attention or a device driver requires service, it generates an interrupt to alert the CPU. Now Windows OS executes an interrupt service routine (ISR) to respond to them. DPCs defer certain tasks that are related to these interrupts to a later time. High-priority ones are processed before low-priority ones. When one driver takes longer than usual to perform its task, it simultaneously delays the task of other drivers as well, which ultimately can make the PC appear sluggish. In technical terms, this is what we call DPC latency.
Here are some of the common reasons for high DPC latency on Windows:
- Outdated or Faulty Drivers
- Excessive Background Processes
- Overloaded CPU
- Misconfigured System Settings
- Faulty Hardware Components
Quick Answer
Update the graphics and audio drivers on the PC. If that does not help, change the power plan.
1. Launch the Control Panel and select Large icons from the View by drop down menu.
2. Click on Power Options and select High Performance power plan.
Method 1: Switch to New Power Plan
High Performance or Ultimate Performance power plans maximize the processing power of the CPU, which then runs at higher clock speeds consistently. Hence, it can respond more swiftly to handle the Deferred Procedure Calls.
1. Launch the Control Panel, expand the View by dropdown menu in the top right corner, and select Large icons.
2. Click on Power Options and select the High performance or Ultimate performance option.

However, do note that, as this will use more power, it would result in rapid depletion of the battery. If that’s not feasible for you, consider the other methods mentioned below.
Method 2: Update Graphics and Audio Drivers
Graphics and audio drivers handle a significant amount of data and real-time processing. If these drivers are outdated or malfunctioning, they might struggle to keep up with the demands of processing tasks, resulting in high DPC latency. To update these drivers, you can follow our guide on How to Update Graphics Drivers in Windows 11 and How to Update Audio Drivers in Windows 11.

Method 3: Modify Registry
Certain hardware processes can contribute to latency issues. Modifying these settings via the Registry may influence how these processes interact with the system and fix the occurrence of high DPC latency in Windows 11.
Note: Make a backup of registry keys to restore to previous settings in case of manual errors during modification.
1. Press the Win + R keys to open the Run dialog box.
2. Type regedit and click OK. If prompted, select Yes in the UAC prompt.
3. In the Registry Editor, go to the following path:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\Video\{DEB039CC-B704-4F53-B43E-9DD4432FA2E9}\0000
4. Right-click on the 0000 key, click on New, and then select DWORD (32-bit) Value from the context menu.
If you encounter any errors at this step, you can follow our guide on Fix Cannot create key error writing to the registry.

5. Name the DWORD value key as PerfLevelSrc.
6. Double-click on the PerfLevelSrc key and modify its Value data to 3322.
7. Similarly create three more DWORD values named: PowerMizerEnable, PowerMizerLevel, and PowerMizerLevelAC.
8. Set the Value data for PowerMizerLevel and PowerMizerLevelAC as 1.
9. Click OK to save the changes made to the Registry and Restart your PC.
Method 4: Disable Dynamic Ticking
Dynamic Ticking is a feature in Windows that adjusts the timing of the system clock. System adjustments in clock timing can potentially cause irregularities in the handling of Deferred Procedure Calls. Here’s how to disable it:
1. Run Command Prompt as administrator.
2. Type the following command and press Enter: bcdedit /set disabledynamictick yes

3. Once the command is executed successfully, Restart the PC.
Method 5: Disable IPv6
IPv6 and IPv4 are two different network protocols. Enabling both simultaneously might occasionally lead to conflicts and increased network processing overhead, hence a higher DPC latency. Here’s how to disable IPv6:
1. Press the Windows key + R to open the Run dialog box.
2. Type ncpa.cpl in the text field and press Enter to open the Network Connections window.
3. Right-click on the network connection you’re using (such as Ethernet or Wi-Fi) and choose Properties from the dropdown menu.
4. In the list of items, uncheck Internet Protocol Version 6 (TCP/IPv6), click OK to confirm the changes, and close the properties window.
Method 6: Disable Windows Firewall
Windows Defender continuously performs real-time scanning for malware and other threats. Now the scanning process involves system resources and might occasionally contribute to the discussed issue. By temporarily disabling the firewall the burden on system resources can be reduced and for that, you can follow our guide on How to Disable Windows 11 Firewall.

Method 7: Uninstall Bonjour App (If Applicable)
Bonjour is a networking protocol developed by Apple primarily used for discovering devices and services on a local network. If you’ve connected any Apple device with your Windows PC earlier, you might find this app installed on the system. However, it can run background processes that might cause additional CPU usage and network activity, which can cause higher DPC latency.
1. Open the Control Panel and click on Uninstall a program under Programs.
2. Look for Bonjour in the list of installed programs. Right-click on it and then click Uninstall.

3. Once uninstalled, Restart your computer to ensure the changes take effect.
Method 8: Turn off D0 Packet Coalescing
D0 Packet Coalescing is an energy-saving feature that works by combining smaller packets of data into larger ones before transmitting them. By turning off this feature, you prevent the bundling of data packets, allowing quicker transmission of smaller packets which can fix the high DPC latency issues on Windows 11.
1. Launch the Device Manager and expand the Network Adapters category.
2. Right-click on your network adapter and select Properties from the context menu.
3. Look for properties related to packet coalescing, such as Interrupt Moderation or Packet Coalescing, select it, and choose Disable.
Method 9: Use TCP Optimizer
TCP Optimizer allows users to adjust various network settings to optimize internet connectivity and performance. By fine-tuning these settings, it’s possible to improve network efficiency and reduce potential bottlenecks that could contribute to DPC latency issues.
1. Download TCP Optimizer from the official website and once installed, run it as administrator.
2. Select the Optimal option in the bottom right corner and then click the Apply changes button.

TCP Optimizer will prompt you to Restart your computer to implement the new settings. Save any work and Restart the system.
Method 10: System Restore
If the error persists, the last way is to perform a system restore on the PC, and for that, you can follow our guide on How to Use and Create System Restore in Windows 11.
How Do I Check My DPC Latency?
You can use the DPC latency checker for Windows 11/10 to check whether your PC is facing the discussed issue.
1. Visit the official website of Resplendence’s LatencyMon page and click on the Download button in the top navigation bar.
2. Scroll down and under System Monitoring Tools, select LatencyMon 7.31 (or any latest version) to download it to the PC.
3. Install the downloaded .exe file.
4. Open the LatencyMon app and click on the Start monitor button (green triangular icon) in the top-left corner.
5. Let the monitoring run for several minutes to gather sufficient data and then click on the Stop monitor button (square icon).
6. Go to the Stats tab. Here, you can check all your statistics.

- If the DPC and ISR routines are under 2000µs, your PC can handle real-time audio dropouts.
- If it’s between 2000-4000, it’s not ideal.
- If it exceeds 4000µs, it’s a severe issue.
In general, DPC latency is considered high if it exceeds 2000µs. High DPC latency can mess up your audio on the computer. You might notice problems like video stuttering, inconsistent performance with your mouse or keyboard, or more commonly, audio issues such as dropouts, clicks, and popping sounds.
Is DPC latency better On Windows 10 or 11?
Both Windows 10 and 11 can experience DPC latency issues. Its performance between both versions might vary depending on individual system configurations, hardware, and software.
We hope our guide helped you fix high DPC latency on both Windows 11 and Windows 10. If you have any queries or suggestions for us, feel free to let us know in the comments section. Stay connected to TechCult for more such troubleshooting guides.
If you are an online gamer, your utmost priority would be to minimize latency as much as possible. Any sign of latency can exacerbate your experience and can cost your precious K/D Ratio. In this post, we will learn how to reduce latency for gaming on a Windows 11/10 PC.

Follow the instructions below to reduce latency when gaming on your Windows 11/10 computer.
- Reduce the resolution of your game
- Use an Ethernet cable
- Set up the Ultimate Performance Power Plan
- Lock all driver DPC to one core
- Force your CPU to run at full throttle at all times
- Close all the network-consuming application
- Use NVIDIA Low Latency Mode
Let us discuss them in detail.
1] Reduce the resolution of your game
First, you need to reduce the resolution of the game you are playing. Doing so will not only put less pressure on your GPU when it’s trying to render those pixels but also require a lot less bandwidth.
Every game has a method of lowering the resolution, but most do so through the in-game settings. Do that, and you will notice an improved latency.
Read: How to use NVIDIA Reflex to fix Low Latency in games
2] Use an Ethernet cable

If one aims to attain seamless Internet without disruption, one should always opt for Ethernet cables. Also, if you share a WiFi connection with family or housemates, it might be hard to ask them to stop using the internet when you’re gaming. You can try playing games when they’re out or connecting your device to the router with an Ethernet cable. I would pick the latter option.
3] Set up the Ultimate Performance Power Plan
Microsoft created a mode to maximize hardware performance. By default, it’s available on workstations only and not on systems with a battery. Enabling it on devices with a battery will drain the battery faster. However, since most of us play the game when our device is plugged in, there is no harm in switching to Ultimate Performance Power mode. So, go ahead and enable the Ultimate Performance Plan.
4] Lock all Driver DPC to one core
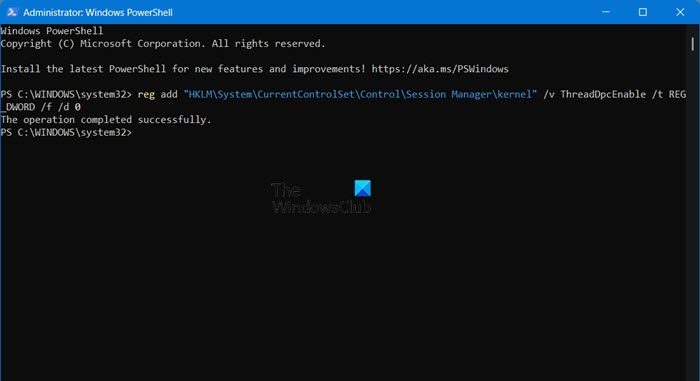
Locking all Driver Deferred Procedure Calls (DPCs) to a single core can help manage DPC latency issues, especially in systems where certain drivers cause high latency. To tweak DPC, we will make changes to your registry, therefore, take a backup of it beforehand.
To do so, open PowerShell as an administrator and then run the following command.
reg add "HKLM\System\CurrentControlSet\Control\Session Manager\kernel" /v ThreadDpcEnable /t REG_DWORD /f /d 0
Consider lowering mouse sensitivity in games if it’s set to 5 or higher. However, you may still encounter issues with mice that have built-in acceleration, causing difficulties in making precise adjustments. This can be identified by using a mouse without built-in acceleration.
4] Force your CPU to run at full throttle at all times
Even though it is not recommended, if you have a decent cooling system, you can enable it when gaming. Once you are done gaming, you can disable it. Also, we would recommend you refrain from enabling it on a laptop, as their cooling systems are usually fragile. That being said, open PowerShell as an administrator and then run the following commands (one by one) to enable this feature.
powercfg.exe /setacvalueindex SCHEME_CURRENT SUB_PROCESSOR IdleDisable 1 powercfg.exe /setactive SCHEME_CURRENT
To disable it, run the below command.
powercfg.exe /setacvalueindex SCHEME_CURRENT SUB_PROCESSOR IdleDisable 0 powercfg.exe /setactive SCHEME_CURRENT
After making the changes, start your game and you will notice a difference.
5] Close all the network-consuming application

You can terminate all the apps and services that are not necessary but are consuming your network. This will allow your computer to channel all its bandwidth to ensure your games are not choppy. To do so, open the Task Manager, go to the Network tab, right-click on the apps that are high up there on the list, and select End Task.
6] Use NVIDIA Low Latency Mode
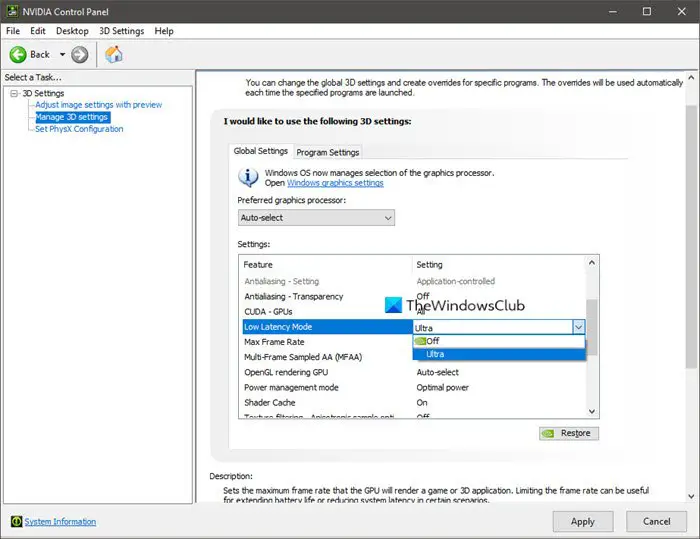
If you have an NVIDIA driver, you can look to enable NVIDIA Low Latency Mode. Low latency modes have the most impact when your game is GPU-bound and frame rates are between 60 and 100 FPS. Enabling this setting allows for high-frame-rate gaming responsiveness without sacrificing graphical fidelity. However, it won’t improve your experience if your game is CPU-bound or if you have very high or very low FPS. Additionally, if you’re experiencing input latency or mouse lag, this setting won’t solve that problem, as these issues are often a result of low frame rates (FPS).
That’s it!
Is 40 ms latency good for gaming?
Yes, a latency of 40ms is good for gaming. We aim for a low ping, as low as we can go. If that means gaming next to the router, so be it. However, we recommend you check the above suggestions to reduce gaming latency.
Read: Tips to improve Windows gaming performance
Why is my PC latency so high?
Various factors affect your computer’s latency. Mostly, your router’s bandwidth is either low or fluctuating, which is why you are experiencing high ping. You can optimize your PC for online gaming and follow the suggestions mentioned earlier to remedy the situation.
Also Read: Best AI Games for Windows 11.
