Когда сервер Windows работает в течение длительного периода времени, приложения и функции операционной системы могут работать нестабильно. Нестабильная операционная система может иметь сбои приложений, зависание приложений или утечки памяти. Иногда даже важные системные функции перестают отвечать.

Простым решением является перезагрузка. В этом руководстве вы узнаете, как перезапустить Windows Server 2016 с несколькими параметрами команды.
Перезагрузить Windows Server через графический интерфейс
Интерфейс Windows Server 2016 представляет собой графический интерфейс, который упрощает многие задачи.
Нажмите: меню Пуск -> Кнопка питания -> Перезагрузить.
Как перезагрузить Windows Server с помощью командной строки
В некоторых случаях у вас может не быть установлен компонент GUI. Или ваша операционная система столкнулась с проблемой, и все, что вы можете получить доступ, это командная строка.
Шаг 1: Откройте командную строку
- Нажмите Ctrl + Alt + Del.
- Система должна показать меню — щелкните Task Manager (Диспетчер задач).
- В окне Task Manager (Диспетчер задач) нажмите More Details (Подробнее).
- Откройте меню File (Файл) и выберите Run new task (Запустить новое задание).
- В поле введите
cmd.exe–, затем установите флажок, чтобы создать задачу с правами администратора. Нажмите ОК. - Должно появиться черное окно с белым текстом.
Шаг 2. Перезагрузите операционную систему Windows Server.
В окне командной строки введите команду перезагрузки Windows Server и нажмите клавишу Enter:
shutdown –r
Параметр –r заставляет Windows перезагружаться, а не просто выключаться.
Перезапуск из PowerShell
Windows PowerShell напоминает расширенную версию командной строки. Он основан на .NET Framework и включает язык сценариев. PowerShell полезен для работы под операционной системой Windows.
Шаг 1. Запустите PowerShell
- Нажмите Ctrl + Alt + Del и выберите Task Manager (Диспетчер задач).
- Откройте меню File (Файл) и выберите Run new task (Запустить новое задание).
- В командной строке введите
powershell.exeи установите флажок, чтобы начать с правами администратора. Нажмите ОК. - Должно открыться новое окно с темно-синим фоном. Вы можете понять, что находитесь в окне PowerShell, если подсказка начинается с
PS.
Шаг 2: перезагрузите систему
В окне PowerShell введите следующую команду и нажмите Enter:
Restart-Computer
По умолчанию вы получите 5-секундный обратный отсчет, затем система перезагрузится. Вы можете добавить опцию, чтобы отложить перезапуск на более чем 5 секунд по умолчанию:
Restart-Computer –delay 15
Перезагрузка удаленного сервера Windows с помощью PowerShell
Шаг 1. Запустите PowerShell
Если вы находитесь в командной строке, введите команду:
PowerShell
Подсказка добавит PS в начале, и ваши набранные команды должны появиться в желтом цвете.
Шаг 2. Перезагрузитесь удаленно
В окне PowerShell введите следующее:
Restart-Computer –ComputerName “NAME_OF_SYSTEM”
Замените NAME_OF_SYSTEM на имя компьютера, который вы хотите перезагрузить. Не забудьте поставить кавычки.
Примечание. Предполагается, что ваши текущие учетные данные те же, что и для удаленной системы. Обычно это может выглядеть как имя пользователя администратора, и один и тот же пароль для обеих систем. Это также может работать, если обе системы находятся в одном домене, а ваша учетная запись пользователя имеет соответствующие разрешения.
As a system administrator, one of the essential skills you need to master is the ability to efficiently manage and troubleshoot servers. This includes knowing how to restart a Windows Server using command-line tools. This article delves into various methods and tricks to restart Windows Server using the command line, a crucial technique for quick and effective server management.
To reboot a Windows server using the command line, you can employ the /r switch with the shutdown command. This article provides various examples of how to use command line instructions to restart Windows systems.
- Restart Computer: For restarting a local Windows system, use the following command:
shutdown /r - Restart Forecefully: To restart the local system and force all running applications to close, include the
/fswitch:shutdown /r /f - Adding a Timer: Optionally, you can add a delay to the restart process. For instance, below command will restart the server after 60 seconds.
shutdown /r /t 60 - Restart Remote Computer: If you need to restart a remote system, include the system’s hostname with the
/mswitch:shutdown /r /f /m \\REMOTE-PC - Adding Comments: Additionally, you can add a comment to document the reason for the reboot using the
/cswitch. For instance, if you are restarting the system after installing software, the command would be:shutdown /r /f /m \\REMOTE-PC /c "Post Installing Software"
These commands offer a streamlined and efficient way to manage system restarts directly from the command line.
Using PowerShell
For those who prefer PowerShell, the process is similar but uses different commands:
- Open PowerShell: Search for it in the start menu or type powershell in the Run dialog.
- Restart-Computer Command: Use the command
Restart-Computer. This straightforward command initiates an immediate restart of the server.Restart-Computer - Adding Parameters: Similar to Command Prompt, you can add parameters like
-Delayto set a timer for the restart.Restart-Computer -Delay 60 - Restart Remote Server: If you need to restart a server remotely, you can use the following command in PowerShell:
Restart-Computer -ComputerName [ServerName] -ForceReplace
[ServerName]with the actual name of the server. The-Forceparameter ensures that all running applications are closed immediately.
Conclusion
Mastering the command line for restarting Windows Server is a vital skill for any system administrator. It provides a quick, reliable, and scriptable method to manage servers, especially in complex or remote environments. By incorporating these tips and tricks into your routine, you can significantly streamline your server management tasks.
Remember, while the command line is a powerful tool, always proceed with caution and ensure you have backups and a recovery plan in place for unforeseen circumstances.

This article provides a step-by-step guide on how to reboot a server/machine using the command line on Linux and Windows operating systems. It provides necessary commands and options for Linux users and Windows users.
Table Of Contents
- Why is Rebooting the Operating System Necessary?
- Rebooting Linux Operating System
- How to Reboot a Linux OS using the Commandline?
- Rebooting Windows Operating System
- How to Reboot a Windows using Commandline?
- Rebooting Best Practices (For Servers)
- Scale Your Business with Veeble VPS Hosting
Why is Rebooting the Operating System Necessary?
- Rebooting an operating system is essential for various reasons, like software updates, troubleshooting, and resolving system conflicts.
- It allows the operating system and all its components to be refreshed and reloaded, resolving issues due to memory leaks, software bugs, or other system-level problems.
- Rebooting improves overall server performance and stability by clearing temporary files, cached data, and other system-generated information.
- It may be necessary to apply critical security updates or patches to protect the server against the latest threats.
Rebooting Linux Operating System
Linux is a widely used operating system for servers, and rebooting a Linux OS is a common task for system administrators and end users. The process of rebooting a Linux can vary depending on the specific distribution and the user’s familiarity with the command line interface (CLI).
One of the most common ways to reboot a Linux OS is by using the reboot command. This command can be executed directly in the terminal or shell prompt, and it will initiate the reboot process. The “reboot” command can also be used with various options to customize the reboot process, such as specifying a delay before the reboot or providing a message to users before the system goes down.
In addition to the “reboot” command, Linux users can also use the shutdown command to reboot the server. The “shutdown” command provides more options and flexibility, allowing users to specify the time and reason for the reboot, as well as the desired behavior after the reboot is complete (e.g., power off, halt, or reboot).
How to Reboot a Linux OS using the Commandline?
To reboot a Linux OS using the command line, follow these steps:
- Log in to the Linux machine using a terminal or secure shell (SSH) client.
- Open a terminal or command prompt.
- Type the following command to reboot the server:
sudo reboot- Enter your administrative password when prompted.
- The server will begin the reboot process, and you will be logged out of the session.
- Wait for the server to finish the reboot process, which may take a few minutes.
- Once the reboot is complete, you can log back into the server and verify that it is running correctly.

Alternatively, you can use the shutdown command to reboot the server:
- Log in to the Linux server using a terminal or SSH client.
- Open a terminal or command prompt.
- Type the following command to reboot the server:
sudo shutdown -r now- Enter your administrative password when prompted.
- The server will begin the reboot process, and you will be logged out of the session.
- Wait for the server to finish the reboot process, which may take a few minutes.
- Once the reboot is complete, you can log back into the server and verify that it is running correctly.

Common Commands Used in Linux Rebooting
In addition to the “reboot” and “shutdown” commands, several other commands can be used to manage the reboot process on a Linux server. Here are some of the most common commands:
| Command | Function |
|---|---|
| shutdown -r now | Immediately reboots the server. |
| shutdown -t +5 | It reboots the server in 5 minutes. |
| shutdown -r 23:00 | Reboots the server at 11:00 p.m. |
| shutdown -c | Cancels a scheduled reboot. |
| init -6 | It reboots the server (used in older Linux distributions). |
| systemctl reboot | systemctl reboot: Reboots the server (used in modern Linux distributions). |
| reboot -f | Forces an immediate reboot, bypassing any shutdown procedures. |
| reboot -w | Performs a “warm reboot,” which skips the POST (Power-On Self-Test) process. |
Rebooting Windows Operating System
Rebooting a Windows operating system is a similar process to rebooting a Linux OS, but the commands and options may differ.
One of the primary ways to reboot a Windows server is by using the shutdown command. This command can be executed directly in the command prompt or PowerShell, and it provides various options for controlling the reboot process. The “shutdown” command can be used to initiate an immediate reboot, schedule a reboot for a specific time, or even perform a remote reboot on a different machine.
In addition to the shutdown command, Windows OS can also be rebooted using the graphical user interface (GUI). This can be done by navigating to the Start menu, selecting the Power button, and then choosing the “Restart” option. This method is often preferred by users who are more comfortable with a graphical interface, but it may not provide the same level of control and flexibility as the command-line approach.
How to Reboot a Windows using Commandline?
To reboot a Windows server using the command line, follow these steps:
- Log in to the Windows server using an administrator account.
- Open the command prompt or PowerShell.
- Type the following command to reboot the server:
shutdown /r /t 0
- The server will begin the reboot process immediately.
- Wait for the server to finish the reboot process, which may take a few minutes.
- Once the reboot is complete, you can log back in to the server and verify that it is running correctly.
Alternatively, you can use the following command to schedule a reboot at a specific time:
- Log in to the Windows server using an administrator account.
- Open the command prompt or PowerShell.
- Type the following command to schedule a reboot at after 3600 seconds:
shutdown /r /t 3600
- The server will reboot in 1 hour (3600 seconds).
- If you need to cancel the scheduled reboot, use the following command:
shutdown /a- Once the reboot is complete, you can log back into the server and verify that it is running correctly.
Common Commands Used in Windows Rebooting
In addition to the shutdown command, there are several other commands that can be used to manage the reboot process on a Windows server. Here are some of the most common commands:
| Command | Function |
|---|---|
| shutdown /r | Reboots the server immediately. |
| shutdown /r /t <seconds> | Reboots the server after the specified number of seconds. |
| shutdown /s | Shuts down the server immediately. |
| shutdown /s /t <seconds> | Shuts down the server after the specified number of seconds. |
| shutdown /a | Cancels a scheduled shutdown or reboot. |
| shutdown /h | Puts the server into hibernation mode. |
| shutdown /l | Logs off the current user. |
| shutdown /m \\<computer_name> | Reboots a remote server. |
| shutdown /i | Opens the Shutdown Windows dialog box. |
| shutdown /d <reason_code> | Provides a reason code for the shutdown or reboot. |
Rebooting Best Practices (For Servers)
Rebooting a server is crucial for minimal disruption to the system and its users. To ensure a smooth process, follow these best practices:
- Plan and schedule the reboot during a maintenance window or a time when the server’s downtime will have minimal impact on users and business operations. 🗓️🕒
- Inform all relevant stakeholders about the planned reboot, including the scheduled time, expected downtime, and potential impact on services or applications. 📢📅
- Back up critical data and configurations before rebooting the server. 💾🔐
- Test the reboot process on a non-production server or in a development environment to identify potential issues. 🧪🖥️
- Monitor the server’s status and logs during the reboot to identify and address potential problems. 📊🔍
- Verify the server’s functionality after the reboot. ✅🔧
- Keep detailed records of the reboot process for future reference or troubleshooting. 📝📂
- Automate the reboot process whenever possible to ensure consistency, reduce human error risk, and make the process more efficient. 🤖🔄
- Prioritize critical servers and have a well-defined rollback plan in place in case of unexpected issues or problems. 🚨📋
This article provides a comprehensive guide on how to reboot a server using the command line in Linux and Windows environments, ensuring efficient and minimal disruption to the system and users.
Scale Your Business with Veeble VPS Hosting
Unlock the full potential of your business with Veeble VPS hosting. Our team of experts is available 24/7 to help you with any questions or issues you may have.
Choose Your Plan
Restarting a Windows Server is crucial for applying updates, troubleshooting issues, and maintaining system performance. Regular restarts help ensure a server runs the latest software, resolves conflicts, and clears temporary files.
This tutorial explains how to restart a Windows server using different methods.

Prerequisites
- A system running Windows Server.
- Access to the Command Prompt.
- Access to PowerShell.
Why Restart a Windows Server?
Restarting a Windows server is essential for applying critical updates and patches that enhance security and performance. It helps resolve software conflicts and clears out temporary files, which improves system stability and speed. It also closes running processes that slow the system down and starts them up again. Restarting is also helpful in troubleshooting network connectivity issues and application errors.
Note: A full Windows server restart clears all processes, ensuring a fresh start. However, using Fast Boot reduces downtime by speeding up the startup process. Still, Fast Boot only applies after a complete shutdown, never when restarting the system. Fast Boot is also more relevant to client versions of Windows, while server environments often prioritize full resets for stability and performance. So, use Fast Boot for personal computers or lightweight server tasks and avoid it for critical servers, troubleshooting, and security-sensitive environments. To set up Fast Boot, access Power Options in Windows settings.
Shutdown vs. Restart
Restarting a Windows server closes all applications and processes, shuts down the system, and immediately powers it back on, ensuring a complete reset of all system components. However, shutting down powers it off completely.
Use shutdown for regular power-offs, especially when Fast Boot is enabled for faster startups. Use restart when applying updates, troubleshooting, or needing a complete system reset to clear temporary issues.
Soft vs. Hard Restart
A soft restart is the standard method for restarting Windows. It involves using the operating system’s built-in restart command or restarting through the Start menu, which closes all running applications and processes before restarting the system.
On the other hand, a hard restart, also known as a hard reboot or force restart, involves forcibly cutting power to the system by holding down the power button until the system shuts down or disconnecting the power source and then turning it back on again. This method is used when the system becomes unresponsive and cannot be restarted using the usual soft restart method.
How to Restart a Windows Server
There are several ways to restart a Windows server, such as the Command Prompt, PowerShell, or via the GUI. The following text presents a few ways to do that.
Note: Save all work before restarting your server to avoid losing any data or halting the process.
Restart the Windows Server with the GUI
The Windows Graphical User Interface simplifies many tasks, including restarting servers. To restart the Windows server via GUI, take the following steps:
1. Click the Start menu.
2. Select the Power button.
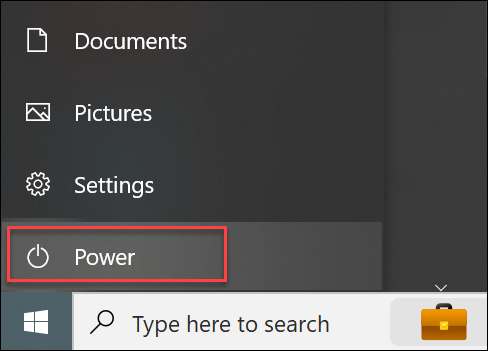
3. Click Restart.
Restart Windows Server via Command Prompt
If the GUI is not installed or working, other options exist for restarting your Windows server. One of them is to use the Windows shutdown command. The Windows shutdown command allows you to shut down, restart, log off, or hibernate your computer from the command line. Its syntax is:
shutdown [options]The shutdown command has plenty of options, but the one relevant to this tutorial is -r. The –r option tells Windows to restart instead of shutting down.
To restart the Windows server, access the Command Prompt and enter:
shutdown –r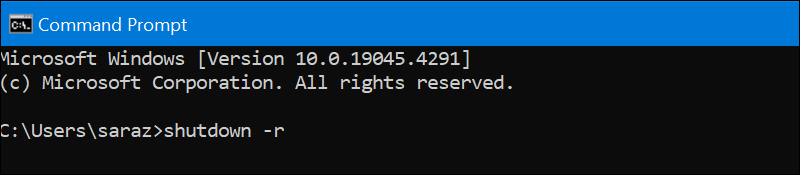
The command has no output, but it restarts the server.
Restart Windows Server via Windows Powershell
PowerShell is a robust command-line shell developed by Microsoft. It’s designed for system administration tasks, automation, and managing configurations across Windows-based systems.
The Restart-Computer cmdlet in PowerShell is used to restart a computer. It provides options to specify the computer name, force the restart, wait for the restart to complete, add a delay before the restart, set a timeout period, and provide credentials if necessary. The command syntax with all available options is:
Restart-Computer [-ComputerName] [-Force] [-Wait] [-For ] [-Delay ] [-Timeout ] [-Credential ] [-Protocol ] [-Confirm] [-WhatIf]The command consists of:
[-ComputerName]. Specifies the name of the computer to restart.[-Force]. Forces the restart without prompting for confirmation.[-Wait]. Waits for the restart to complete before returning.[-For]. Specifies how long it takes for the restart to complete (in seconds).[-Delay]. Specifies a delay before initiating the restart (in seconds).[-Timeout]. Specifies a timeout period for the restart operation (in seconds).[-Credential]. Shows a user account with permission to restart the computer.[-Protocol]. Determines the protocol to use for the restart operation.[-Confirm]. Prompts for confirmation before executing the restart.[-WhatIf]. Shows what happens if the restart command runs without actually restarting the computer.
To restart a server, use the command without any options. Access the PowerShell and type the following:
Restart-Computer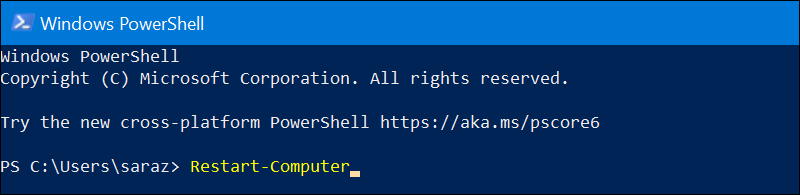
You can delay the restart for longer than the default five seconds. For example, delay the restart for 15 seconds with:
Restart-Computer –delay 15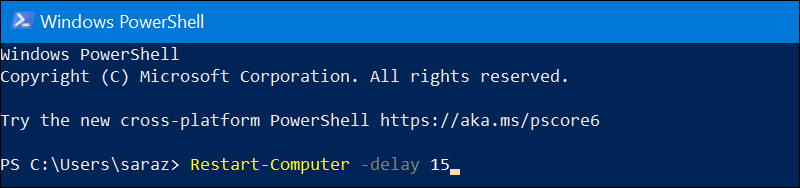
Restart Remote Windows Server
Use PowerShell to restart a remote Windows server. In the PowerShell window, type the following:
Restart-Computer –ComputerName ["NAME_OF_SYSTEM"]Replace ["NAME_OF_SYSTEM"] with the name of a server you want to restart. Make sure to include the quotation marks. For example, to restart a remote machine named «Server01», run the following:
Restart-Computer -ComputerName "Server01"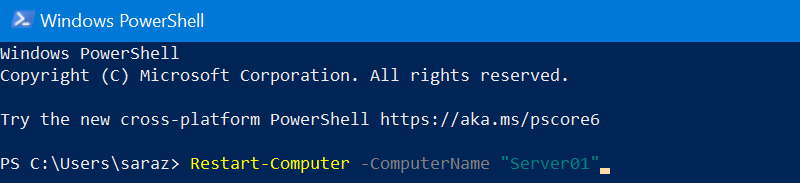
This command initiates a restart of the remote Windows server named «Server01».
Conclusion
Restarting a Windows server is simple, and this article presents several different ways to do it.
Next, learn about the most important Windows cmd commands.
Was this article helpful?
YesNo
We continue to explore the features of Windows Server 2022. It is well known that this is Microsoft’s next solution for enterprise environments. Well, like its predecessors, this version has variants with and without a graphical environment. In addition, it is well known that a common task is to shut down or restart the server. Therefore, this can be done from the start menu. However, in environments without a graphical plug-in, then we can do it from the command line. Read on to find out How to shutdown and reboot Windows Server 2022 with commands.
How to restart Windows Server 2022
The first thing you have to do is to open a CMD as administrator. Then use the following syntax:
shutdown /r /t time
Please replace Time with the time you want to wait for the server to restart.

This means that after 200 seconds, the server will be restarted. On the other hand, it is possible to add a message at restart time. For this purpose, just add the -c parameter:
shutdown /r /t time -c message

The server will restart after the timeout period has elapsed. On the other hand, sometimes there are open programs that prevent a restart. In such a case it is possible to force a shutdown using the following command:
shutdown /r /f
It is even possible to schedule this task for a remote computer. With this in mind, use the following syntax:
shutdown /r /f /m \\Computer
How to shutdown Windows Server 2022 with commands
The commands for shutting down the server are very similar to that for restarting it. In fact, only the first element changes. So use the following syntax:
shutdown /s /t time

To add a message we use the -c parameter as follows:
shutdown /s /t time -c message

To force applications to close we run:
shutdown /s /f
It is also possible to use it with remote computers:
shutdown /s /f /m \\COMPUTER
Ultimately, we have seen how to shutdown and reboot Windows Server 2022 with commands. Consequently, we have an expeditious way to manage these tasks on the server. Bye!
— Advertisement —
Everything Linux, A.I, IT News, DataOps, Open Source and more delivered right to you.
Subscribe
«The best Linux newsletter on the web»
