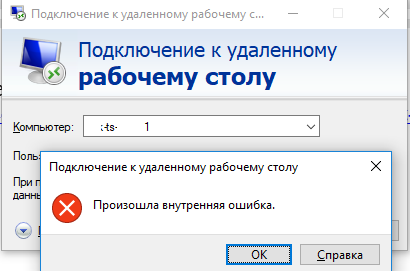
Столкнулся со странным сообщением “
Произошла внутренняя ошибка
/
An internal error has occurred
” при RDP подключении к недавно развернутому серверу RDSH на Windows Server 2012 R2 из Windows 10. Буквально вчера RDP подключение к серверу работало нормально, но после установки и настройки RemotApp приложений и перезагрузки сервера, я не могу удаленно подключиться к его рабочему столу. Служба Remote Desktop Services судя по всему работает, так как пароль пользователя при подключении запрашивается.
Как я понял, сообщение RDP консоли “Произошла внутренняя ошибка” может появляться в различных случаях и иметь совершенно различные причины, связанные как с сервером Remote Desktop, так и с клиентом. В этой статье я постарался собрать все варианты решения и сценарий, который помог мне.
В первую очередь, убедитесь, что на RDS сервере доступен RDP порт 3389, и подключение не блокируется файерволом (Test-NetConnection rdsserver –port 3389).
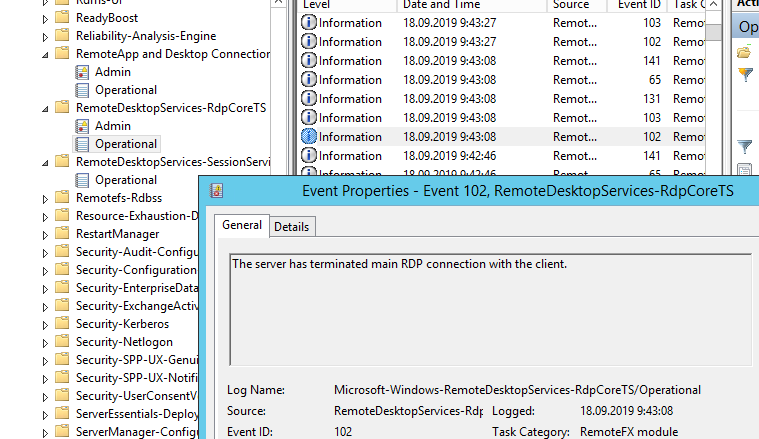
Изучив логи RDP подключений на удаленном RDS сервере, я не увидел никаких особенных ошибок. В журнале Microsoft-Windows-RemoteDesktopServices-RdpCoreTS/Operational видно, что RDP сессия создается:
The server accepted a new TCP connection from client 10.10.1.60:64379.
Connection RDP-Tcp#3 created
Но потом без какой-либо ошибки RDP сеанс завершается:
The server has terminated main RDP connection with the client.
The disconnect reason is 0
Проверьте состояние службу Remote Desktop Services на удаленном сервере и перезапустите ее. Вы можете удаленно перезапустить службу через консоль Services.msc (Connect to another computer), но гораздо проще проверить состояние службы и перезапустить ее через PowerShell:
(Get-Service TermService -ComputerName msk-ts1).status
Служба запушена (Running), перезапустим ее:
Get-Service TermService -ComputerName msk-ts1| Restart-Service –force –verbose

Но проблему это не решило.
Какие еще варианты решения проблемы мне удалось найти в сети:
- Если у вас на удаленном сервере установлен КриптоПРО, он может быть источником проблем с rdp подключением. Попробуйте отключить проверку контрольных целостности файлов (проверки контрольных сумм) в КриптоПро через реестр. Перейдите в ветку реестра
HKLM\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\Session Manager\CProIntegrity
и измените значение параметра CheckMode на 0. Перезагрузите сервер. - Если в журнале событий TerminalServices-RemoteConnectionManager вы встретите событие с EventID 1057 (The RD Session Host Server has failed to create a new self signed certificate to be used for RD Session Host Server authentication on SSL connections), перейдите в каталог
C:\ProgramData\Microsoft\Crypto\RSA
, переименуйте папку Machinekeys в Machinekeys_bak и перезапустите службу TermService. - Также нашел информацию, что RDP проблема “Произошла внутренняя ошибка” встречалась в Windows 10 1809, если на удаленном компьютере включена политика Configure H.264/AVC hardware encoding for Remote Desktop connections (находится в секции GPO: Computer Configuration -> Administrative Templates -> Windows Components -> Remote Desktop Services -> Remote Desktop Session Host -> Remote Session Environment). Для решения этой проблемы достаточно отключить UDP протокол для RDP, создав в ветке реестра
HKLM\SOFTWARE\Policies\Microsoft\Windows NT\Terminal Services\Client
параметр
fClientDisableUDP
со значением 1. - В комментариях Ivan оставил очень полезный фикс.
Проблема с ошибкой RDP может быть в наличии некоего счетчика учитывающего максимальное количество подключений в Windows.
В десктопных версиях Windows — 100, в Windows Server -3000. Для сброса счетчика достаточно перезагрузить компьютер, или просто увеличить лимит через реестр:
REG ADD "HKLM\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\Terminal Server" /v MaxOutstandingConnections /t REG_DWORD /d 65536
Ни один из рассмотренных выше сценариев не был применим в моем случае. Я совершенно случайно обнаружил, что с других компьютеров нет проблем с подключением к этому RDS серверу. Значить проблема только с моим компьютером, а не с сервером.
Я очистил историю RDP подключений в ветке
HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Software\Microsoft\Terminal Server Client\Servers
и сбросил кэш RDP в каталоге
C:\Users\%Username%\AppData\Local\Microsoft\Terminal Server Client\Cache
(перед удалением закройте все запущенные сеансы mstsc.exe):
del "C:\Users\%Username%\AppData\Local\Microsoft\Terminal Server Client\cache"

После этого перезагрузил свой компьютер, и ошибка RDP подключения исчезла!
Что вызывает Internal Error удаленного рабочего стола в Windows
Различные факторы могут вызвать сообщение внутренней ошибке при подключении к удаленному рабочему столу. К этим факторам относятся неправильные настройки подключения к удаленному рабочему столу, проблемы с сетью, настройки безопасности, конфигурация брандмауэра Windows и проблемы с самой службой удаленного рабочего стола.
Как решить проблему Internal Error удаленного рабочего стола
Чтобы подключиться к серверу через VNC, мы сначала должны попасть в панель управления сервером. Чтобы попасть в панель управления сервером, из личного кабинета мы должны в разделе Услуги нажать на Виртуальные серверы, затем на сам сервер, а затем на кнопку Перейти.
Когда откроется панель, нажимаем на кнопку Управление, затем на Виртуальные машины, после этого мы нажимаем на сам сервер и как последний шаг, мы нажимаем на кнопку VNC и авторизируемся на наш сервер.
Чтобы решить проблему с невозможности подключиться на наш сервер через RDP, мы открываем Windows Defender Firewall
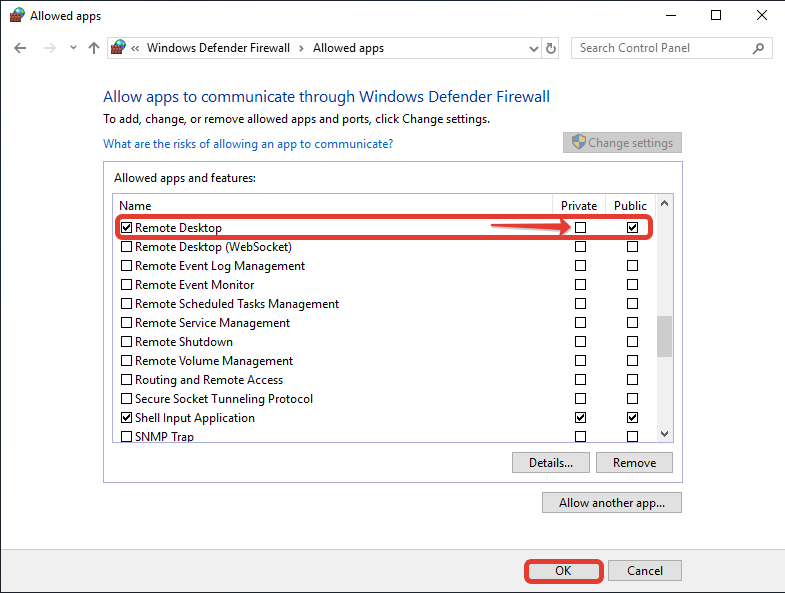
После того как сам фаерволл открылся, нажимаем на Allow an app or feature through Windows Defender Firewall.
В новом окне мы ищем Remote Desktop и также включаем галочку чтобы как на Public (публичной сети), так и на Private (приватная сеть) был доступ к RDP. Нажимаем на галочку, затем на кнопку ОК и перезагружаем сам сервер, затем пробуем войти по RDP.
Инструкция выше мне не помогла, что мне делать чтобы исправить работу RDP?
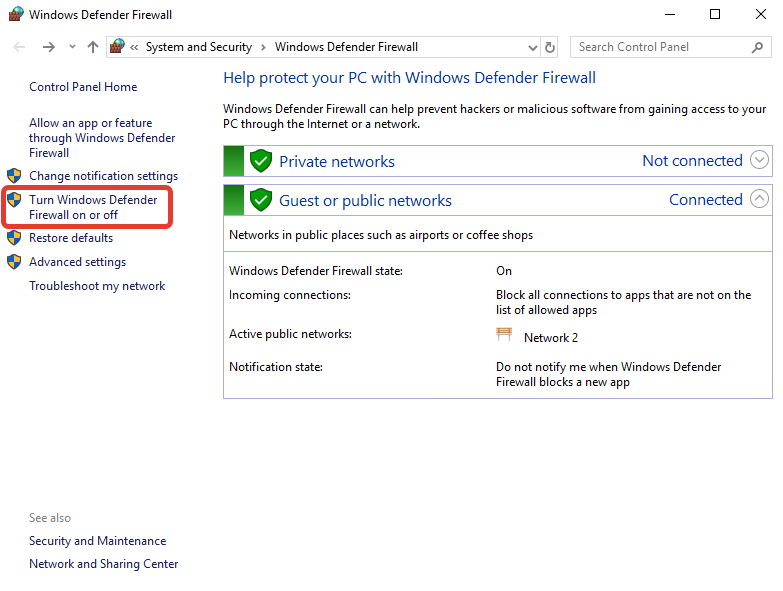
К сожалению если к Вашем серверу по RDP приходит много запросов на подбор паролей, Ваш фаервол может не пускать вас на сервер, даже после действия выше. В таком случае мы должны выключить сам фаервол.
Чтобы это сделать, снова открываем сам фаервол и нажимаем на кнопку Turn Windows Defender Firewall on or of
А затем выключаем сам фаерволл как для пользователей, так и для администратора, нажав на кнопку в оба раздела Turn off Windows Defender Firewall (not recommended)
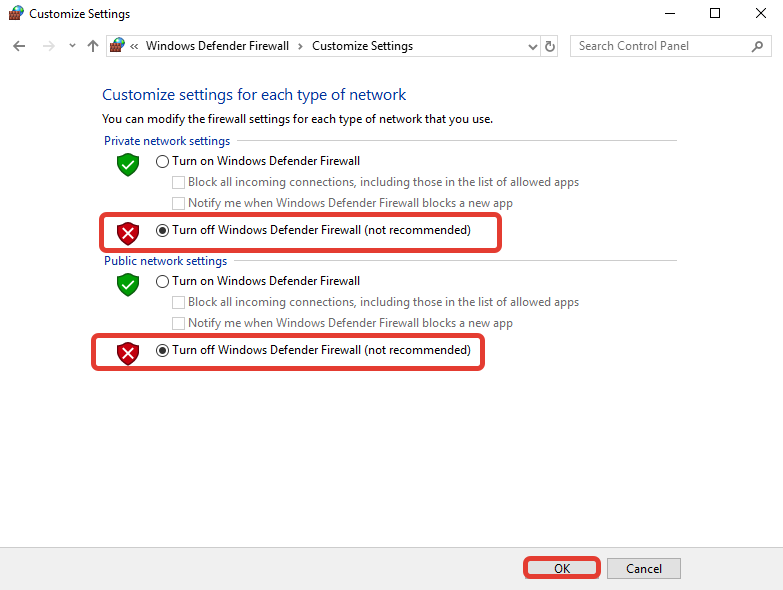
Нажимаем на кнопку ОК, перезагружаем сервер и проверяем.
Если данный вариант не сработал для вас, внизу вы можете нажать на ссылку и посмотреть инструкцию, как можно сменить RDP порт как это лучший вариант обеспечить безопасность сервера.
https://firstbyte.ru/manuals/kak-zamenit-rdp-port-v-windows-server-2012-2016-2019-2022/
Yesterday I was faced with an error while trying to connect to a Windows 2016 Server hosed in AWS (EC2):
An internal error has occurred.
The only “change” that had been made recently was the installation of .NET Framework 4.8.
I found some articles pointing to possible solutions, but without access to the console it was going to prove difficult to diagnose and resolve!
My first port of call was checking the event log. Fortunately windows event viewer supports connecting to a remote computer:

When trying to establish a Remote Desktop Connection an error was appearing in the System log (coming from Schannel):
A fatal error occurred when attempting to access the TLS server credential private key. The error code returned from the cryptographic module is 0x8009030D. The internal error state is 10001.
Google found a few suggestions (including some changes to my local client registry) but no initial joy. Then I found this TechNet article which sounded a bit more promising: https://social.technet.microsoft.com/Forums/en-US/0d2da30b-4876-45c1-99d1-1e89a12c1e86/an-internal-error-has-ocurred-error-when-i-try-to-rdp-onto-a-2012-r2-server?forum=winserver8gen
The challenge was then figuring out how to apply this change remotely… Initially I didn’t even have the Group Policy Object Editor available on my machine (Windows 10 Home). But a quick script was able to add it:
dir /b %SystemRoot%\servicing\Packages\Microsoft-Windows-GroupPolicy-ClientExtensions-Package~3*.mum >List.txt
dir /b %SystemRoot%\servicing\Packages\Microsoft-Windows-GroupPolicy-ClientTools-Package~3*.mum >>List.txt
for /f %%i in ('findstr /i . List.txt 2^>nul') do dism /online /norestart /add-package:"%SystemRoot%\servicing\Packages\%%i"
pause
You need to save the script with a .bat extension and run/execute. Great now we can launch the local policy editor, but no apparent option to connect to a remote computer!
Some more googling… great it looks like when using Microsoft Management Console (mmc) you can add the component and have the option to connect to a remote computer (there is also a command line argument):
gpedit.msc /gpcomputer:Computername
But damn, Access Denied and no prompt/option to enter credentials! Fortunately, I commonly need to launch applications (such as SQL Server Management Studio, Visual Studio etc) with remote credentials so I have a trick up my sleeve!
runas /netonly /user:remote-machine\username cmd
We now have a shell running with the remote administrator’s credentials. From here we can launch mmc or gpedit.msc and connect to the remote computer!
I was successfully able to change the remote policy. Under Computer Configuration, Administrative Templates, Windows Components, Remote Desktop Services, Remote Desktop Session Host, Security, set Require use of specific secuirty layer for remote (DGP) connections to Enabled and select RDP from the Security Layer options dropdown.
I wasn’t able to quickly find a way to execute gpupdate on the remote machine (I know I could have used something like psexec, but didn’t have that to hand), but was able to reboot the server gracefully simply by executing:
shutdown /r /m \\remote-machine /t 0
Voila! We’re back in business.
I think some of the credential issues could also been able averted by creating a user on my local computer with the same username/password as the remote administrator account. Then logging in to my local computer with that account.
Good luck!
In some cases, when connecting to a remote computer or RDS host via Remote Desktop Connection (RDP), users may encounter an “An internal error has occurred” error. This error can occur for a number of reasons related to both the RDP/RDS server and the client settings, and usually shows after user credentials are entered in the mstsc.exe window or immediately after the Connect button is clicked.

As there are several possible causes for this internal RDP error, try the following tips one by one until you find a solution that will help you.
Check the Remote Desktop Settings on the Client Device
If the “An internal error has occurred” error is only showing on one computer and other clients are successfully connecting to the Remote Desktop host, you need to check the settings on the current client device.
Reset the DNS client cache on your computer by running the following command from an elevated command prompt:
ipconfig /flushdns
If you have entered the hostname or FQDN of the remote computer in the RD Client window, try to establish an RD connection using an IP address. If the Remote Desktop IP connection is successful, use the nslookup command to check that the DNS settings on your computer are correct:
nslookup yourRDShost
Hint. If the DNS settings are not configured correctly, the Remote Desktop can’t find your computer error will appear.
Then check that the default RDP port (TCP/3389) is available on the remote server and the connection is not blocked by a firewall. Open the PowerShell console and run the command:
Test-NetConnection yourRDShost -port 3389
This command will return TcpTestSucceeded: True if the RDP port is not blocked.

If you are using a VPN to connect to a remote network, try disabling the VPN connections and try reconnecting to the RDP host. You can find and disable all active native Windows VPN connections using PowerShell:
foreach ($item in get-vpnconnection | where { $_.ConnectionStatus -eq "Connected" })
{
Rasdial $item.Name /disconnect
}
If you are using third-party VPN software, disconnect VPN sessions from its interface.
Open the properties of your RDP connection in Remote Desktop Connection windows (mstsc.exe) and make sure the ‘Reconnect if the connection is dropped‘ option is enabled on the Experience tab.

Also, try to disable the Server Authentication warning in the Advanced tab of the RDC client. Set the If server authentication fails to Connect and don’t warn me.
Check the Security Event Log for the following event ID 5379:
Credential Manager credentials were read.
This event occurs when a user performs a read operation on stored credentials in Credential Manager.
Your RDP client may have tried to use saved RDP credentials to connect. You should try removing the saved password from Windows Credential Manager:
- Open the Windows Credentials via the Control Panel. Or by running the command:
rundll32.exe keymgr.dll,KRShowKeyMgr
- Delete the saved RDP logon credentials for your remote host. Find the entry that starts with TERMSRV\your_rdp_host_name or TERMSRV\your_rdp_IP_address and click the Remove button;
Use the following batch script to clear the RDP cache on the client:
@echo off reg delete "HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Software\Microsoft\Terminal Server Client\Default" /va /f reg delete "HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Software\Microsoft\Terminal Server Client\Servers" /f reg add "HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Software\Microsoft\Terminal Server Client\Servers" attrib -s -h %userprofile%\documents\Default.rdp del %userprofile%\documents\Default.rdp del /f /s /q /a %AppData%\Microsoft\Windows\Recent\AutomaticDestinations del /f /s /q /a "%userprofile%\AppData\Local\Microsoft\Terminal Server Client\Cache"
Save this code to the reset_mstsc_cache.bat file and run it as an administrator.

Next, check the settings on the RDP host side if none of these tips work.
Check the Remote Desktop Host Settings
If the Remote Desktop connection error occurs on all clients, the simplest way to resolve the problem is to reboot the remote RDP/RDS host.
If you cannot restart the RD host immediately, you should try to restart the Remote Desktop Service (along with the Remote Desktop Services UserMode Port Redirector). You can do this with the following commands running in the elevated cmd.exe:
net stop termservice net start termservice
Or you can restart Remote Desktop Services from the services.msc console.

If the problem disappeared after a restart, but it reappears after a while, then you need to try to change the settings of the RD Session host.
Use GPO to Fine-tune the RD Host Settings
Try to change some Group Policy settings using the Local GPO editor (gpedit.msc) or domain Group Policy Management Console (gpmc.msc).
- Disable UDP protocol for RDP connections. Navigate to Computer Configuration > Administrative Templates > Windows Components > Remote Desktop Services > Remote Desktop Session Host > Connections, enable the policy Select RDP transport protocols and set Select Transport Type = Use only TCP. This will completely disable the use of UDP for RDP connections;
- The error “An internal RD error has occurred” often only occurs on clients that are connected to the network via a VPN tunnel. It seems that the problem is caused by the fragmentation of the UDP packets in the VPN tunnel. To disable RDP over UDP on a specific client only, enable the following GPO option on that computer: Off UDP on Client = Enabled under Computer configuration > Administrative Templates > Windows Components > Remote Desktop Services > Remote Desktop Connection Client > Turn Off UDP on Client = Enabled;
- Enable FIPS compliant algorithms: Computer configuration > Windows Settings > Security Settings > Local Policies > Security Options > System cryptography: Use FIPS compliant algorithms for encryption, hashing, and signing = Enabled;
- Disable the hardware encoding and enforced AVC:444 mode on the RDP server side: Computer configuration > Administrative Templates > Windows Components > Remote Desktop Services > Remote Desktop Session Host > Remote Session Environment > Prioritize H.264/AVC 444 Graphics mode for Remote Desktop Connection = Disabled;
- Try to adjust the RDP security level to RDP mode. Enable the policy ‘Require use of specific security layer for remote connections’ under the GPO section Computer configuration > Administrative Templates > Windows Components > Remote Desktop Services > Remote Desktop Session Host > Security and set the Security level to RDP (according to the article). Restart the remote host to apply this setting.
After changing the local Group Policy settings on a remote server, you need to apply them on the client and server using the gpupdate command.
Check Network Level Authentication
To secure RDP connections, Network Level Authentication (NLA) is enabled by default on the RD host. In some cases, NLA can prevent RD connections from legacy or incompatible devices. You can temporarily disable NLA and see if the insecure remote desktop connection works as one of the troubleshooting steps.

Network Settings on Remote Desktop Host
If you are using NIC Teaming (bonding) on your Windows Server host, make sure that the receive side scaling is disabled.
- Open the Device Manager console (devmgmt.msc);
- Expand the Network adapters and open the properties of the Microsoft Network Adapter Multiplexor Driver;
- Go to the Advanced tab and set Receive Side Scaling to Disabled.
You can try to change the maximum outstanding connections limit on your RDP server via the registry. Set the following registry value via regedit.exe:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\Terminal Server DWORD: MaxOutstandingConnections VALUE: 10000
Or with PowerShell:
New-ItemProperty -Path "HKLM:\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\Terminal Server" -Name MaxOutstandingConnections -Value 10000 -PropertyType DWORD -Force
Check the current MTU size in your Windows with the command:
netsh interface ipv4 show subinterfaces

RDS Certificates
When you use a smart card certificate to authenticate on the Remote Desktop server, you may encounter the following events in the RemoteDesktopServices-RdpCoreT log on the Windows Server 2019/2016 RDS host:
Warning Event 226, RemoteDesktopServices-RdpCoreTS
General: RDP_TCP: An error was encountered when transitioning from StateUnknown in response to Event_Disconnect (error code 0x80070040)
Warning Event 142, RemoteDesktopServices-RdpCoreT
General: TCP socket READ operation failed, error 64
Make sure your certificate has not been revoked.
Next, try to recreate the RDP certificate:
- Open the local computer certificates MMC snap-in (run the certlm.msc command);
- Go to the following certificate section: Remote Desktop > Certificates;
- Right-click your self-signed certificate RDP cert and delete it (if there are several RDP certs, remove them all);
- Restart the Remote Desktop Services as described above.
RDP and TLS Encryption
If you have disabled the legacy Transport Layer Security (TLS) 1.0 and TLS 1.1 protocols on your RD host, this may cause an Internal error when attempting to establish an RD connection to an RDS farm with the Connection Broker. The reason for this problem is that the Windows Internal Database (WID), which is used by default on an RDCB host running Windows Server 2016/2012 R2, only supports TLS 1.0.
To solve the problem, you can:
- Use an external Microsoft SQL Server with TLS 1.2 support for the RD Connection Broker database.
- Or you need to enable the TLS 1.0 protocol on RDCB:
reg add "HKLM\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\SecurityProviders\SCHANNEL\Protocols\TLS 1.0\Server" /v Enabled /t REG_DWORD /d 1 /f
Now check if your RDP client connects to the remote host without errors.
Cyril Kardashevsky
I enjoy technology and developing websites. Since 2012 I’m running a few of my own websites, and share useful content on gadgets, PC administration and website promotion.
Home » OS’s » Windows » RDP An Internal Error Has Occurred Fix and workarounds

Microsoft Remote Desktop Protocol RDP makes it easy to remotely control and administer servers and clients. However, sometimes there are issues. If you have see the RDP An Internal Error has occurred issue, this post will look at some common fixes for the problem.
Table of contents
- What causes the Internal Error for Windows?
- Things to check on the target computer
- Check the domain
- Delete MachineKeys
- Reconnect the Domain
- RD Gateway settings
- Allow the Windows Firewall to Connect to RDP
- Change the Startup Status of RDP service
- Configure your network address for DHCP instead of Static
- Enable Persistent Bitmap Caching
- Monitor Windows System Logs
- Change Remote Desktop Connection App Settings
- Update Remote Desktop Connection Client
- Check Proxy Server Settings
- Update Windows Server
- Troubleshoot Network Connectivity
- Wrapping up
What causes the Internal Error for Windows?
There may be incorrect Remote Desktop Connection settings, network issues, security settings, Windows Firewall configuration problems that interfere, and problems with the Remote Desktop Service itself.

Things to check on the target computer
To enable remote connections on the target computer, follow these steps:
-
Go to your system properties (right-click on This Computer and select properties)
-
Click on Remote settings in the System Properties window.
-
Under Remote Desktop, select Allow remote connections to this computer.
-
Click Apply and then OK

Check the domain
Make sure that the client computer and the remote computer are part of the same domain or workgroup. This can help make sure to avoid issues with authentication. Certain security policies are applied when a computer is a member of the domain that could cause issues if the other computer isn’t a domain member as well.

Restart Remote Desktop Service
You can try to restart the Remote Desktop Service on your RDP server and this can sometimes resolve the RDP error. To do this, follow these steps:
-
Press Windows Key + R to open the Run dialog.
-
Type services.msc and press Enter.
-
Find Remote Desktop Services in the list of services.
-
Right-click and select Remote Desktop Services and select “Restart.”

Change RDP Security Settings
To change RDP security settings, follow these steps:
-
Open the Local Group Policy Editor by pressing Windows Key + R, and typing gpedit.msc, and pressing Enter.
-
Go to Computer Configuration > Administrative Templates > Windows Components > Remote Desktop Services > Remote Desktop Session Host > Security.
-
Double-click on Require use of specific security layer for remote (RDP) connections and select Enabled.
-
In the Options section, select the appropriate security layer from the drop-down menu, such as RDP Security Layer or Negotiate.
-
Click Apply and then OK.
If you have settings defined here, make sure of what those are and if there are security settings that may cause issues connecting.

Below, you can change the Require use of specific security layer for remote (RDP) connections setting.

Delete MachineKeys
Corrupt or outdated MachineKeys can cause RDP internal errors. To delete MachineKeys, follow these steps:
-
Press Windows Key + R to open the Run dialog.
-
Type
%ProgramData%\Microsoft\Crypto\RSA\MachineKeysto find the machine keys folder and press Enter. -
Back up the MachineKeys folder by copying the folder and pasting it in a backup location
-
Delete all files in the original MachineKeys folder.
-
Restart the computer and try the Remote Desktop Connection again.

Reconnect the Domain
If the remote computer is part of a domain, try removing it from the domain and then rejoining it. This can resolve potential authentication issues.
An easy way to do this with PowerShell is using the command shown below:
test-computersecurechannel -repair -credential <your user>
RD Gateway settings
In the Remote Desktop Connection app, go to the Advanced tab and click Settings under Connect from anywhere.
Make sure that the correct RD Gateway server name is entered, and select Use my RD Gateway credentials for the remote computer. You may need to make changes to the settings here.

Allow the Windows Firewall to Connect to RDP
Make sure you have setup the Windows Firewall to not block RDP connections. To do this:
-
Press Windows Key + R and type firewall.cpl, then press Enter.
-
Click on Allow an app or feature through Windows Firewall.
-
Locate Remote Desktop in the list and ensure that it is allowed for both Private and Public networks.

Disable Network Level Authentication
Disabling Network Level Authentication is something that can sometimes resolve RDP internal errors. To do this, uncheck the box Allow connections only from computers running Remote Desktop with Network Level Authentication.

Disable VPN Connections
If you have a VPN connection enabled, try to disable any active VPN connections and connect to the remote computer again. VPN can capture and try to route traffic a certain way that may cause issues if the computer you are trying to remote into is located on your local network.
Change the Startup Status of RDP service
Make sure the Remote Desktop Protocol service has the correct startup status. Go to the services console by typing services.msc. Set the startup type to Automatic for this service.

Configure your network address for DHCP instead of Static
If your computer has a static IP address, try disabling it and switching to DHCP. This can resolve RDP internal errors caused by network issues or IP conflicts.
-
Press Windows Key + R, type ncpa.cpl, and press Enter to open the Network Connections window.
-
Right-click on your network adapter and select Properties.
-
Double-click on Internet Protocol Version 4 (TCP/IPv4).
-
Select Obtain an IP address automatically and Obtain DNS server address automatically.
-
Click OK and restart your computer.

Change the MTU Value
MTU settings that aren’t right can cause something called fragmentation of your TCP packets where the packets get fragmented and have to be retransmitted which isn’t good and can cause issues for connections.
-
Open an admin Command Prompt by right-clicking on the Start button and selecting Command Prompt (Admin).
-
Type
netsh interface ipv4 show subinterfaces. You will see the MTU value. -
Note the name of the network interface you are using for RDP.
-
Type
netsh interface ipv4 set subinterface "Interface Name" mtu=1458 store=persistentand press Enter -
Restart your computer and then you can try the RDP connection again

Enable Persistent Bitmap Caching
Enabling persistent bitmap caching can improve the performance of your Remote Desktop Connection and possibly resolve RDP internal errors.
-
Open the Remote Desktop Connection app.
-
Click on Show Options to access advanced settings.
-
In the Experience tab, check the box Persistent bitmap caching.
-
Click Connect to establish the RDP connection.

Monitor Windows System Logs
Monitoring Windows System Logs can provide possible information or error messages about the cause of the RDP an internal error has occurred issue. To access the Event Viewer and check the logs, follow these steps:
-
Press Windows Key + R, type eventvwr.msc, and press Enter to open the Event Viewer.
-
In the left pane, navigate to Windows Logs > System.
-
Look for events related to Remote Desktop Services or any errors that occurred around the time the issue was encountered.
You may also want to check the Windows Logs > Application section for any related events or errors.

Change Remote Desktop Connection App Settings
In some cases, adjusting the settings of the Remote Desktop Connection app may resolve the internal error. To do this:
-
Open the Remote Desktop Connection app.
-
Click on Show Options to access advanced settings.
-
In the Display tab, adjust the screen resolution and color depth settings.
-
In the Local Resources tab, configure the settings for audio, keyboard, and local devices.
-
In the Experience tab, select the appropriate connection speed from the drop-down menu and enable or disable specific performance options.

You can try and experiment with these settings to find the settings and configuration that may help with the internal error.
Update Remote Desktop Connection Client
An outdated Remote Desktop Connection client may cause internal errors. To update the client, follow these steps:
-
Press Windows Key + R, type appwiz.cpl, and press Enter to open the Programs and Features window.
-
Look for Remote Desktop Connection or Microsoft Remote Desktop in the list of installed programs.
-
Follow the on-screen instructions to update the client if an update is available.
Check Proxy Server Settings
A misconfigured proxy server providing an Internet connection can interfere with RDP connections and this may be something that is causing internal errors.
-
Press Windows Key + I to open the Windows Settings app.
-
Click on Network & Internet.
-
In the left pane, select Proxy.
-
Make sure you have the right settings configured for your proxy settings
Update Windows Server
There may be pending Windows updates that could resolve the issue or just updates pending in general that need a reboot. To update your server, follow these steps:
-
Press Windows Key + I to open the Settings app.
-
Click on Update & Security.
-
In the Windows Update tab, click on Check for updates and follow the on-screen instructions to install any available updates.

Troubleshoot Network Connectivity
Network connectivity issues can cause RDP internal errors. To troubleshoot your network connection:
-
Check the physical connections (the wire) between your computer, and modem/router, etc
-
Use the ping command to test the connection between your and remote computers. So use something like
ping mycomputer.domain.comorping 192.168.1.2 -
Check your router or switch for any configuration issues like VLAN configuration problems or other settings that could cause problems.

Wrapping up
The “RDP an internal error has occurred” issue can be a tricky one to pinpoint. However, you can use the methods listed in the post to troubleshoot RDP connectivity, the service, domain joins, and other problems that can lead to this issue.
Brandon Lee is the Senior Writer, Engineer and owner at Virtualizationhowto.com, and a 7-time VMware vExpert, with over two decades of experience in Information Technology. Having worked for numerous Fortune 500 companies as well as in various industries, He has extensive experience in various IT segments and is a strong advocate for open source technologies. Brandon holds many industry certifications, loves the outdoors and spending time with family. Also, he goes through the effort of testing and troubleshooting issues, so you don’t have to.






