If you use Qt’s Maintenance Tool to manage your installations of Qt, you will find it hard to install older versions of Qt. More precisely, unmaintained versions are no longer listed and can no longer be installed with the tool. You can keep these old versions; if you uninstall them, you will not have access to them again, as, by default, the installer only shows versions from 6.5 to 6.9 (as of December 2024), which means 21 months of Qt. Enabling the archives will get you more versions: as of now, you can go back up to Qt 6.2 (33 months of Qt) and 5.15, but not 6.0 or 6.1… or anything before 5.15.


What if you need access to more versions? You can still download the source code and build it (that is all the KDE Free Qt Foundation guarantees). The Qt Company hosts an extensive archive that goes back to Qt 1.41 — that should be enough, unless you are interested in archaeology: Qt 1.41 was out in 1998.
But that’s not convenient. Compiling Qt requires a lot of time, especially if you need all its modules. The Qt Company used to provide binaries for all these versions; may we still access them as open-source users? The “new” archive lets you download the offline installers for Qt 4.0 to 5.14. And that’s all you’ll have for Qt 4.0 until 5.8 (included).
That’s better, but what about Qt 6.0 and 6.1? Many versions of Qt 5 were available in the online installer (with its first release in 2015, the same year Qt 5.5 was out): is there a way to manage them with the same convenience as recent versions? Yes, but to some extent.
This blog post focuses on binaries for Windows.
The Maintenance Tool has a Settings page, accessible only from the start screen:

There, you can add user-defined repositories in the Repositories tab by clicking the Add button:

For Qt 5.9 until 6.8, you need to use two repositories per version you want to make available in the tool. For instance, for Qt 6.1.3:
- https://download.qt.io/online/qtsdkrepository/windows_x86/desktop/qt6_613/
- https://download.qt.io/online/qtsdkrepository/windows_x86/desktop/qt6_613_src_doc_examples/

Now, when you choose to add packages, you will have access to Qt 6.1.3!

That’s cumbersome if you need to install many versions, but it works.
tl;dr
Use a software like mitmproxy to modify the (https)-request to iapi.qt.io/api/v2/repositories so it’s response lists the old Qt directorys that are still on the servers.
If you never used mitmproxy before here is the guide that shows you how it’s done.
why?
This guide was written because I’ve written a plugin for x64dbg and wanted to build it with the same Qt version (5.6.x) that was used to build the official x64dbg releases. Just to be sure that everything is compatible.
But since Qt 5.6 is not supported anymore it disappeared from the Qt Maintenance Tool. You can still download Qt 5.6 installers from the official Website, but those are seperate x86 and x64 installers. It’s not possible to install both in the same directory, so it’s not possible to have one instance of Qt Creator installed with x86 and x64 toolchain.
At this point I already googled a lot, lost some hairs and bitten my desk.
how?
Install mitmproxy and run the webinterface gui. Since we need to modify https traffic, we need to install a cert. Mitmproxy makes it very easy. Just open a webbrowser and configure it to use 127.0.0.1:8080 (default) as http-proxy. Then open http://mitm.it in it to download the cert. Windows will open an installation dialog if you try to open the cert file, just leave all settings as they are, enter no passwort and click though the wizard.
Start the Qt Maintenance Tool now, if you haven’t installed Qt Creator yet you can use the following method on the Qt web installer as well. If you’re using a VirtualBox guest for your build environment make sure that you activated 3D acceleration because Qt Creator needs OpenGL.
We want mitmproxy to intercept a request, to do this we can just paste the regex iapi\.qt\.io\/api\/v2\/repositories.+ to the form field with the pause symbol.
Click on the «Settings» button to make the maintenance tool or online installer use mitmproxy as proxy. Login with your credentials and click next. The installer should hang while showing Fetching repositorys…, on mitmproxy you should see an orange highlighted request with a pause symbol. Click on the Resume button on the Flow tab. This will send the reqeust to the server and pause again on the response. If it paused on the response click on the pencil symbol on the Response tab.

Now I added the following snippet to the json response, you can copy&paste the response to https://beautifier.io to autoindent the json for easier editing.
{
"action": "add",
"categories": ["Latest releases", "Archive"],
"name": "Qt Windows-x86 Desktop Qt5.6.3 online repository",
"releasedate": "2017-06-30T11:00:00.000Z",
"url": "http://download.qt.io/online/qtsdkrepository/windows_x86/desktop/qt5_563"
}, {
"action": "add",
"categories": ["Latest releases", "Archive"],
"name": "Qt Windows-x86 Qt5.6.3 src online repository",
"releasedate": "2017-06-30T11:00:00.000Z",
"url": "http://download.qt.io/online/qtsdkrepository/windows_x86/desktop/qt5_563_src_doc_examples"
},
I just copied the entrys of Qt version 5.9.1 and edited the path to the 5.6.3 release, I also edited the name. You can open http://download.qt.io/online/qtsdkrepository/windows_x86/desktop/ in your webbrowser to see all available directories. Note that I added "Latest releases" on the line "categories": ["Latest releases", "Archive"], to the categories, so it will be shown without setting a filter in the installer, but thats optional.
Click the «finish edit» symbol in the upper right corner and hit Resume agian. Click on Packet manager in the maintenance tool, now you should be able to install your favourite packages.

- How do I install Qt offline?
- How do I download Qt maintenance tool?
- How do I get Qt open source?
- Is Qt GUI free?
- Is Qt free to download?
- Is Qt a horror game?
- How do I download Python Qt?
- What is the download size of Qt?
- Is Qt free for commercial use?
- Is Qt for Android free?
- Is Qt open source?
- How do I install Qt executable?
- What is qt4?
How do I install Qt offline?
You could dowload the offline installer, the online installer require a qt account. Offline installer link. First you should download and install the qt creator and then download and install the qt source package, if you do not want to use the qt-creator then you do not have to dowload that.
How do I download Qt maintenance tool?
Download the Qt Online Installer from the Qt website and use that to install a version of Qt for Android. The Qt Maintenance Tool will then be available at /opt/Qt/MaintenanceTool .
How do I get Qt open source?
Go to https://www.qt.io/download-open-source/ and click on Download Now, make sure that you are downloading the Qt installer for Linux.
Is Qt GUI free?
Yes, it really is free. This is because the Qt Open Source Edition uses the GNU GPL, which forbids the imposition of any license restrictions on software based on the Open Source Edition that would make it non-free.
Is Qt free to download?
Download a free trial of the Qt framework, tools for desktop and embedded development, Qt Design Studio, plus other enterprise add-ons like Qt Digital Advertising platform.
Is Qt a horror game?
except everything is cute and cuddly (but still very weird) It’s a truly unusual twist on the classic horror mini-game. took on a life of its own as a small, extremely creepy, slow-burn horror game. …
How do I download Python Qt?
First use the installer from the qt-project website, from qt to install PyQt. Next you want to install a Python version 3.3 or newer. Check the box to add all of the PyQt5 extras. It’s not necessary to compile everything from source, you can install all the required packages with the installer.
What is the download size of Qt?
On the official Qt website They say that the size should be less than 3.3 GB. So if you realy want to use the offline installer, you should take that road.
Is Qt free for commercial use?
Qt for Device Creation is a product available only under a commercial license. This allows you to, for example, control your device’s user experience, and build proprietary functionality on top of Qt and to lock down your device.
Is Qt for Android free?
Qt on Android is now protected by the KDE Free Qt Foundation agreement. If you want to know more about Free Software, please read https://www.gnu.org/philosophy/free-sw.htm first.
Is Qt open source?
The Qt framework is available under both open source and commercial licenses. This dual-licensing model is based on the principal of quid pro quo – roughly meaning “something for something.”
How do I install Qt executable?
an exe is formed in your build folder->release folder, copy that exe somewhere, click on it, It will tell you what necessary dll’s file it requires, copy it one after another i.e copy the dll, then again click on it and so on… Search the dll’s in where your qt is installed. Copy them where is your exe is.
What is qt4?
It is a cross-platform frontend for platform-native build systems, like GNU Make, Visual Studio and Xcode. CMake is also a popular alternative to build Qt projects, Qt 4 support has been integrated years ago and Qt 5 provided support early. A new player entered the game recently: The Qt Build Suite a.k.a Qbs.
- Forum
- Other
- General Programming
- How to uninstall Qt, when MaintenanceTool.exe doesn’t exist?
-
6th January 2024, 20:10
#1
How to uninstall Qt, when MaintenanceTool.exe doesn’t exist?
Problem is in the title, but yeah, I can’t uninstall Qt 4 because Maintenance.exe doesn’t exist…. and Qt takes over 10Gt space, so I need to uninstall it. Needed it for school and won’t need it for another year. If someone knows how to work around this problem, please help. Thank you. Google haven’t helped my situation.
-
12th January 2024, 00:51
#2
Re: How to uninstall Qt, when MaintenanceTool.exe doesn’t exist?
The Qt tools and libraries are usually installed in a directory tree rooted in a single directory. If you are on Windows, look at the Properties for the Qt Creator or Qt Assistant application icons on your Desktop. Go to the directory that contains those EXE files and then up the hierarchy until you reach the root Qt directory. You can delete that and Qt will be gone.
Of course, if you have used other directories for developing your projects, those won’t be deleted along with Qt, but the Maintenance tool won’t do that either.
<=== The Great Pumpkin says ===>
Please use CODE tags when posting source code so it is more readable. Click «Go Advanced» and then the «#» icon to insert the tags. Paste your code between them.
-
10th September 2024, 03:43
#3
Re: How to uninstall Qt, when MaintenanceTool.exe doesn’t exist?
You can:
— Open «Control Panel».
— Select «Programs» > «Programs and Features».
— Find Qt in the list of installed programs.
— Select Qt and click «Uninstall».*** Spam URL removed by moderator ***
Do not post links to commercial sites. Next time you will be banned.
Last edited by d_stranz; 10th September 2024 at 16:23.
Reason: removed URL
-
21st September 2024, 05:06
#4
Re: How to uninstall Qt, when MaintenanceTool.exe doesn’t exist?
If you want to uninstall Qt but can’t find the MaintenanceTool.exe file, you can follow these steps. On Windows, you can go to Control Panel, select Programs and uninstall Qt from the list. Otherwise, you can navigate to the Qt installation folder (usually C:\Qt), delete the entire folder and remove the related environment variables. On Linux, if you installed Qt via the package manager, use the command sudo apt remove qt5-default or sudo dnf remove qt5 to uninstall. If installing manually, you just need to delete the installation directory (usually /opt/Qt or ~/Qt).
-
25th December 2024, 15:34
#5
Re: How to uninstall Qt, when MaintenanceTool.exe doesn’t exist?
Hello, you can probably verify that you are installing the correct file extension. The file extension typically ends in.a or.lib for static libraries and.dll or.so for dynamic libraries.
Last edited by cubnecktie; 25th December 2024 at 15:39.
Similar Threads
-
Replies: 6
Last Post: 4th November 2016, 03:44
-
Replies: 2
Last Post: 27th February 2011, 16:32
-
Replies: 0
Last Post: 9th December 2009, 17:46
-
Replies: 2
Last Post: 24th March 2008, 05:37
Tags for this Thread
Bookmarks
Bookmarks
Posting Permissions
- You may not post new threads
- You may not post replies
- You may not post attachments
- You may not edit your posts
- BB code is On
- Smilies are On
- [IMG] code is On
- [VIDEO] code is On
- HTML code is Off
Forum Rules
Qt is a trademark of The Qt Company.
Попробовал на днях Boot to Qt и был слегка шокирован. Сейчас расскажу, почему.
Couple a days ago I discovered Boot to Qt and was quite shocked. I want to tell you why.
На русском 🇷🇺
В дополнение к официальному манулу решил написать своё руководство по установке и настройке Qt for Device Creation для Windows, а также резкий пример использования. Для Linux, в общем-то, должно быть всё то же самое.
О том, что это вообще всё такое, можно посмотреть здесь. Если вкратце, то это подготовленный загрузочный образ Линукса для embedded устройства плюс весь необходимый инструментарий для запуска приложения прямо из IDE Qt Creator. При включении девайс загрузит не рабочий стол Линукса, а сразу Qt приложение. То есть, написал что-то в Qt Creator — можешь сразу запустить это на подключённом девайсе не отходя от кассы.
Хочу предупредить, что для возможности вести разработку с Qt for Device Creation (а именно такой требуется пакет) у вас должна быть соответствующая лицензия, так как этот пакет не доступен для Open Source лицензий (GPL, LGPL). Точнее, доступны не все компоненты, например интересующий нас Boot to Qt. Ну и если у вас коммерческий проект, то Open Source вам не подходит (в большинстве случаев). Лицензию можно приобрести тут: https://www.qt.io/contact-us/
Большей частью инструкция повторяет эти шаги, но с моими комментариями и скриншотами. И хотя шаги для Linux пропущены, для них должно быть всё примерно то же самое.
И да, на Mac OS это всё (возможность работать с устройством) пока недоступно, можно только в Linux (x64) и Windows.
Предварительная подготовка
Итак, для начала я поставил на всякий случай и JRE, и JDK. Затем поставил Android Studio (в основном, нужен Android Debug Bridge) и VirtualBox (для эмулятора).
Теперь можно ставить Qt. Если вы ставите его впервые, то сначала нужно загрузить установщик через Qt Account:
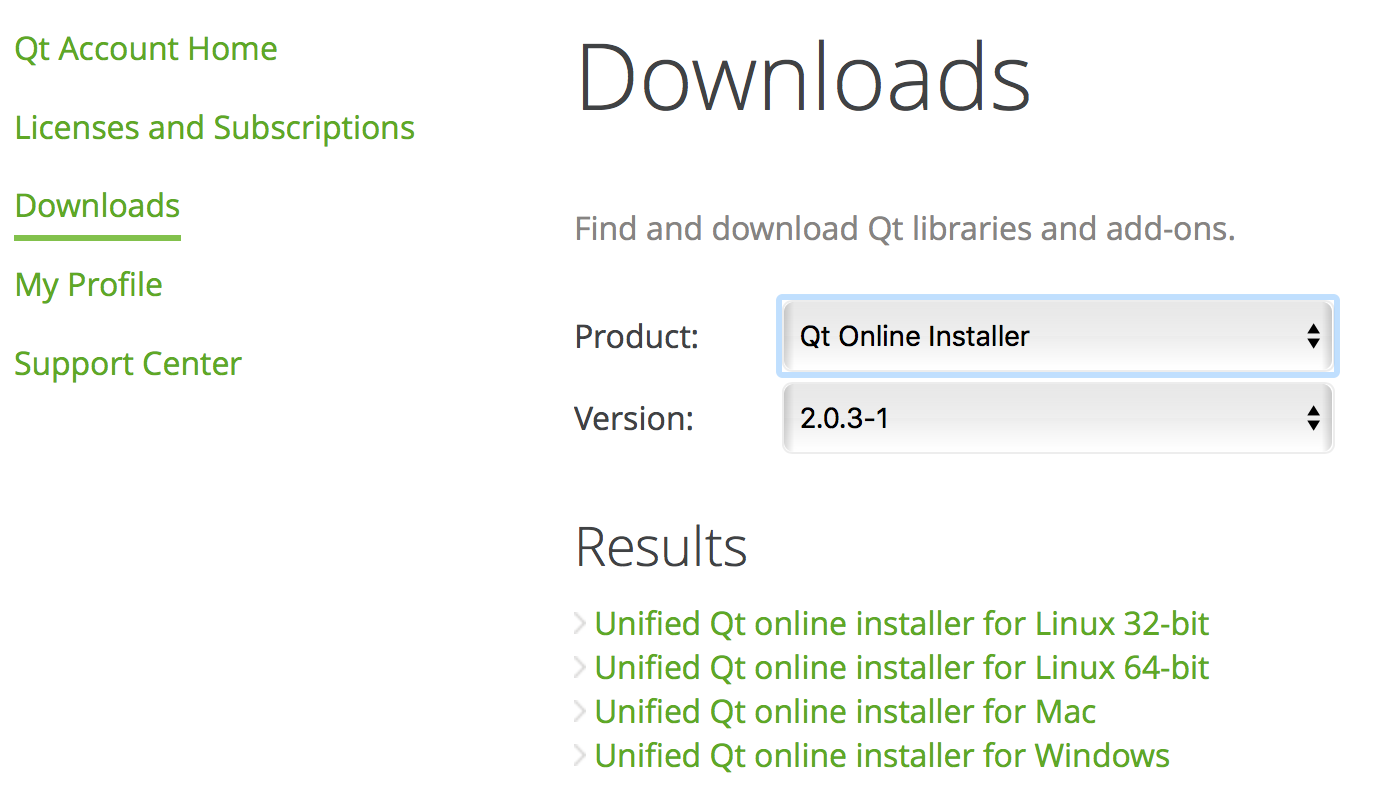
Я бы рекомендовал онлайн-установщик, но можно выбрать и оффлайн вариант.
Если Qt у вас уже установлен, весь заново ставить не нужно, потребуется только доставить новые компоненты через Qt Maintenance Tool (установщик Qt, должен лежать в том же каталоге, имя файла: MaintenanceTool.exe).
Итак, запускаем установщик (или Maintenance Tool), вводим данные своего Qt Account и выбираем Add or remove components.
Помимо прочих нужно развернуть ветку Qt Embedded и выбрать интересующий девайс. У меня под рукой устройство типа такого, потому я выбрал соответсвующий пункт:
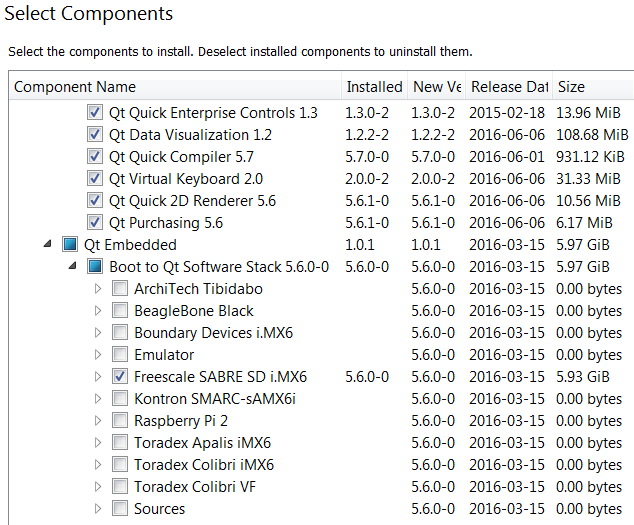
Хотя, по ходу, надо было выбирать Boundary Devices. Но тут это не так важно. Короче, визард поставит всё выбранное.
Создание загрузочного раздела
Теперь нужно подготовить SD карту, поставить на неё Boot to Qt. Вставляем карту в комп, запускаем Qt Creator, выбираем в меню Tools -> Flash Boot To Qt device. Запустится мастер, спросит про образ:
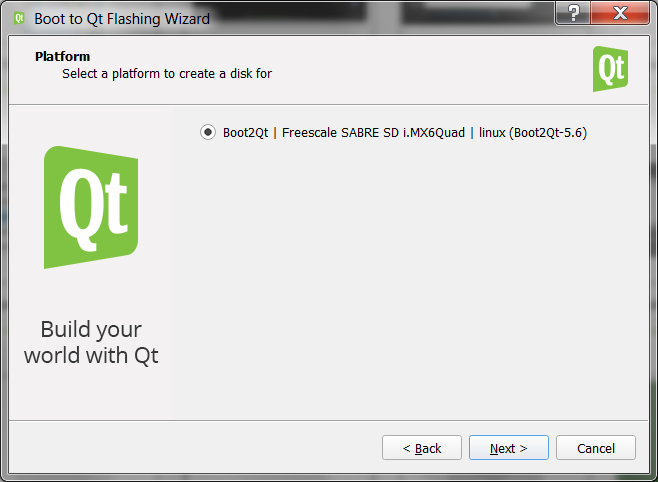
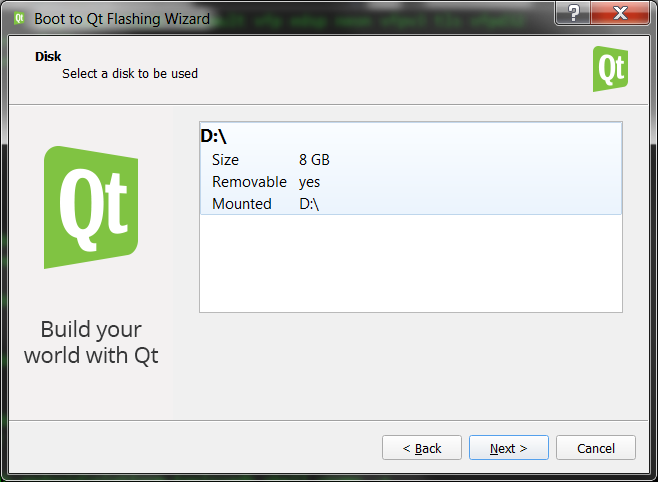
а потом спросит про карту, на которую его нужно залить:
После окончания “прошивки” карты её можно извлечь, вставить в устройство и запустить его (включить в розетку):
If video doesn’t play in your browser, you can download it here.
Как видим, устройство загрузилось с установленного нами на карту образа и явило графический интерфейс на тачскрине, представленный в виде демонстрационного приложения Qt (это не моё, оно идёт в комплекте).
Настройка Qt Creator
Теперь осталось настроить Qt Creator для запуска приложений на устройстве. Оставляем устройство запущенным, присоединяем его через Micro-USB к компьютеру, ждём определения устройства системой, пока она поставит драйвера. Когда всё поставится и определится, можно проверить доступность присоединённого устройства через ADB, у меня он установлен по пути C:\programs\sdk-android\platform-tools\adb.exe:
Команда:
должна выдать что-то вроде:
c:\programs\sdk-android\platform-tools>adb devices
List of devices attached
* daemon not running. starting it now on port 5037 *
* daemon started successfully *
b2qt-sabre-0019b8010384 deviceЗначит, коннект есть. Теперь запускаем Qt Creator и идём в настройки, там Devices. Находим наше устройство:
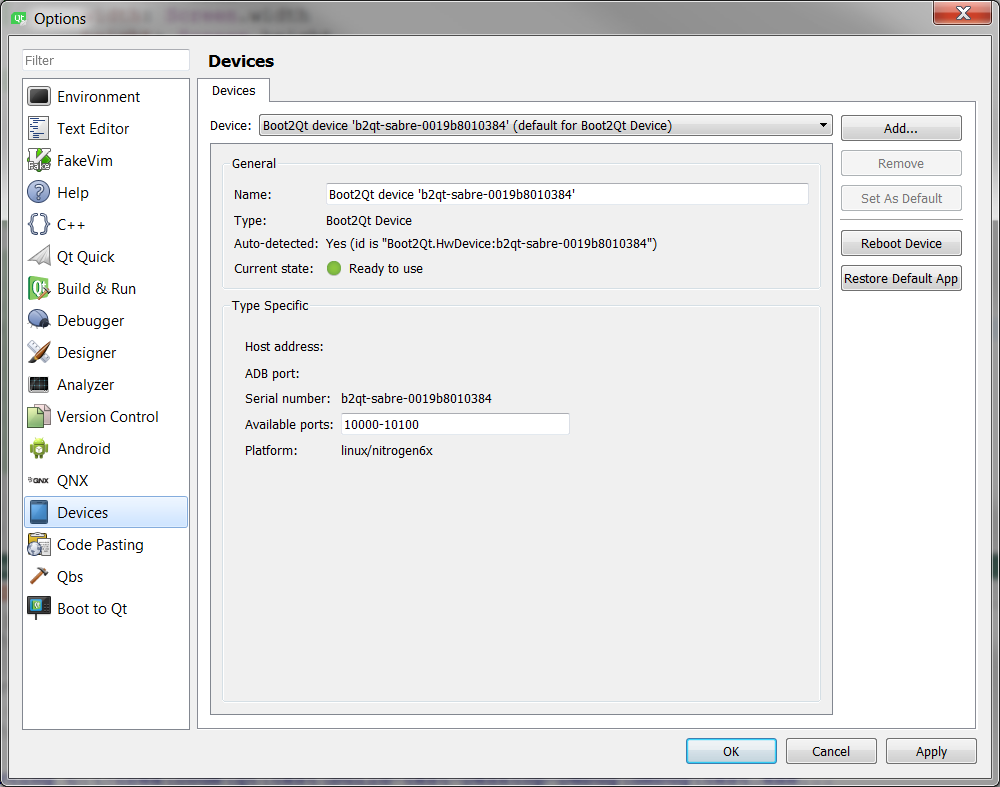
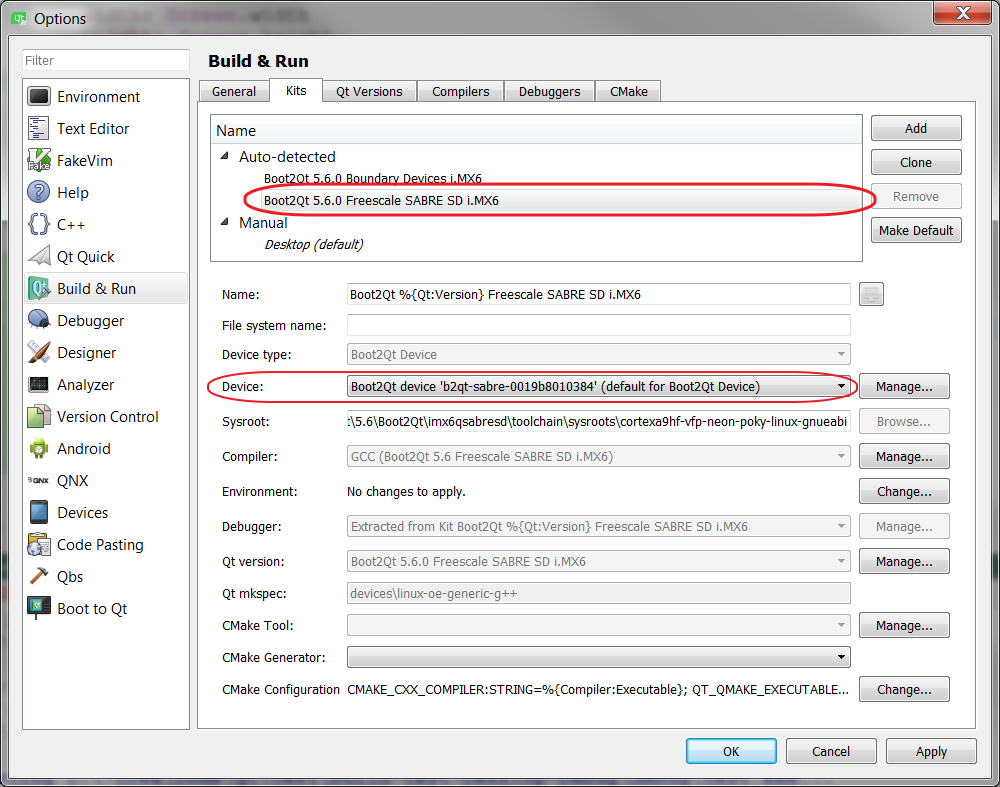
Видим, что оно там есть и его статус Connected. Теперь идём в раздел Build & Run. Там на вкладке Kits среди Auto-detected должен быть Boot2Qt, который мы выбирали при установке. Нужно нажать на него и выбрать из выпадающего списка Device наше устройство:
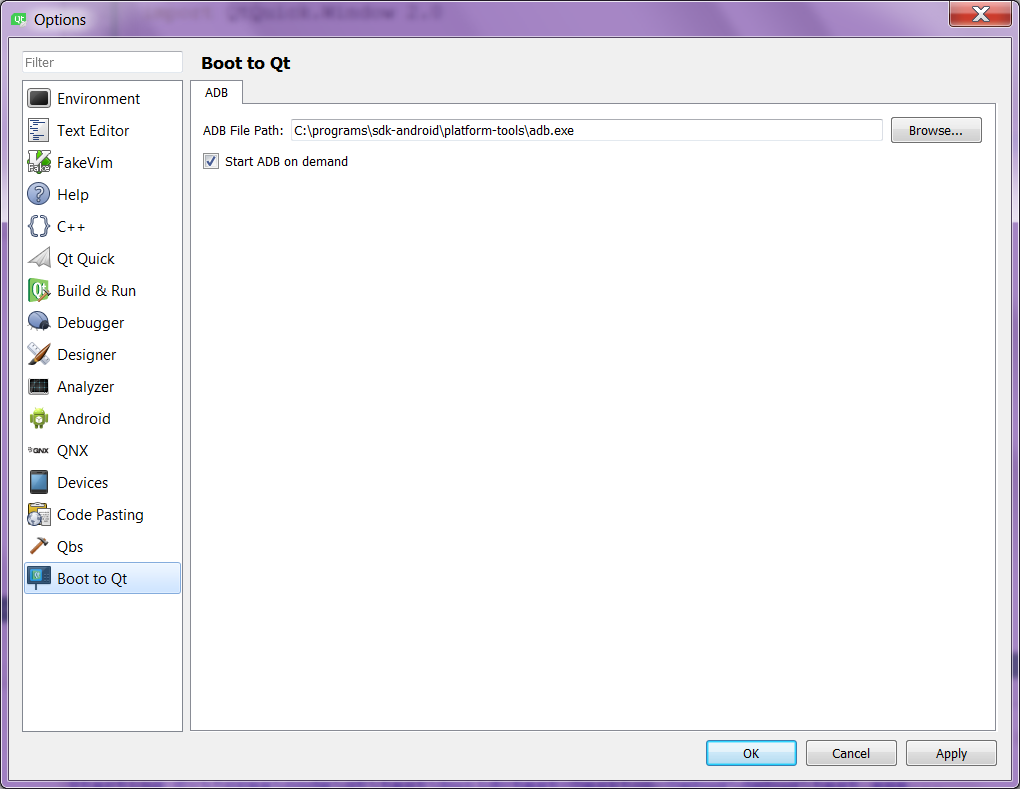
Также надо указать путь до ADB в разделе Boot to Qt:
На этом настройка закончена.
Резкий пример приложения
Запилим простейшее приложение и запустим его сразу же на устройстве.
Это будет окно на весь экран с четырьмя цветными квадратами по углам. При нажатии на каждый всё окно будет заливаться соответствующим цветом. Фрагмент кода для одного из квадратов:
Rectangle {
id: rectGreen
Layout.alignment: Qt.AlignLeft | Qt.AlignBottom
color: "green"
Layout.preferredWidth: 150
Layout.preferredHeight: 150
MouseArea {
anchors.fill: parent
onClicked: {
root.color = rectGreen.color;
}
}
}Полный исходный код проекта выложен в репозитории.
Для наглядности снял видео запуска приложения из Qt Creator на десктопе и сразу на устройстве:
If video doesn’t play in your browser, you can download it here.
Как видите, удобство просто зверское. Всего лишь один переключатель, и вы можете запустить ваше приложение не только на компьютере, где идёт разработка, но сразу и на устройстве. Более того, возможна также и пошаговая отладка (да, прямо во время выполнения кода на устройстве) с использованием профайлеров, но об этом я расскажу в других статьях.
Вот ещё статья про всё то же самое, но с Raspberry Pi, включая сборку самого девайса с тачскрином.
In english 🇬🇧
In addition to the official manual I decided to write my own manual about how to install and set up Qt for Device Creation for Windows, and also to show some quick example of usage. For Linux it would be the same steps (in general).
More detailed you can read about it here. Shortly saying, it’s a pre-build boot image of Linux for embedded device plus all necessary toolchain for launching applications right from IDE Qt Creator. When you turn on the device, it will boot not to the Lunix Desktop, but straight to Qt application. So, you write something in Qt Creator and you can execute it on the connected device right away.
I want to warn you from the start, that to be able to develop with Qt for Device Creation (that’s the name of the package) you should have corresponding license, as this package is not available for Open Source licenses (GPL, LGPL). More precisely, not all components are available, for example Boot to Qt itself. And if you have a commercial project, then Open Source is definatelly not for you (in most cases). You can purchase a license here: https://www.qt.io/contact-us/
Mostly, this manual repeats these steps, but with my comments and screenshots. Though steps for Linux are missing, basically it should be all the same.
And by the way, all that (ability to work with device) is not available for Mac OS yet, it’s only Linux (x64) and Windows now.
Preparations
So, for starters I installed both JRE and JDK just for a case. Then I installed Android Studio (in general, for the Android Debug Bridge) and VirtualBox (for device emulator).
Now you can install Qt. If you are installing it for the first time, then get the installer from your Qt Account:

I would recommend online-installer, but you can choose offline-installer as well.
If you already have Qt, then you don’t have to re-install it — just add new components via Qt Maintenance Tool (Qt installer, it should be in the same folder under the name MaintenanceTool.exe).
Ok, start the installer (or Maintenance Tool), input your Qt Account credentials and choose Add or remove components.
Among the others find the branch Qt Embedded and choose corresponding device. I have a board (like this, so I chose this:

I guess, I should have chosen Boundary Devices, but this time it doesn’t really matter. So, wizard will install all selected components.
Flashing SD card
Now you need to flash the SD card (put Boot to Qt to it). Insert the card to you workstation, start Qt Creator and find in the menu Tools -> Flash Boot To Qt device. The wizard will launch and ask you about the image:

and then it will ask to choose the card to flash the image to:

After flashing being done you can eject the card, insert it to the device and start the device (turn on the power):
If video doesn’t play in your browser, you can download it here.
As you can see, the device booted from the SD card with our image and showed GUI of Qt demo application (it’s not mine, it comes pre-installed with the image) on the touchscreen.
Setting up Qt Creator
Now you need to set up the Qt Creator for launching applications on the device. Leave the device running and connect it to your workstation via Micro-USB cable. Wait till it will be detected by computer and drivers will be installed. When it’s done, you can check its availability with ADB. I have it installed here: C:\programs\sdk-android\platform-tools\adb.exe.
The command:
should give you something like this:
c:\programs\sdk-android\platform-tools>adb devices
List of devices attached
* daemon not running. starting it now on port 5037 *
* daemon started successfully *
b2qt-sabre-0019b8010384 deviceSo, it’s connected. Now start Qt Creator and go to the Options, then to the Devices. Find your device:

You can see that it’s there and its status is Connected. Now go to the Build & Run. There you can find Kits and among the Auto-detected ones there should be a Boot2Qt that we chose during the installation. Click on it and choose our device from the Device dropdown list:

You also need to set the path to ADB at Boot to Qt tab:

Now Qt Creator is ready.
Let’s create a simpliest application and launch it right on the device.
It would be a full-screen window with 4 color squares in its corners. When you click on any of them, the window will be filled with the corresponding color. Here’s a code for one of the squares:
Rectangle {
id: rectGreen
Layout.alignment: Qt.AlignLeft | Qt.AlignBottom
color: "green"
Layout.preferredWidth: 150
Layout.preferredHeight: 150
MouseArea {
anchors.fill: parent
onClicked: {
root.color = rectGreen.color;
}
}
}Full source code of the project is available in the repository.
For clarity I made a video of launching the application from Qt Creator both on desktop and on the device:
If video doesn’t play in your browser, you can download it here.
As you can see, it’s incredibly convinient. Just one switch and you can launch your application not only on the computer, where all the development happens, but on right on the device as well. And there is more: it also allows you step-by-step debugging (yes, right when the app is running on the device) and using profilers, but I’ll tell about it in the next articles.
And here’s an article about all the same but with Raspberry Pi, including device assembly with a touchscreen.
