Version numbering
Since version 3.0.0, QEMU uses a time based version numbering scheme:
- major
- incremented by 1 for the first release of the year
- minor
- reset to 0 with every major increment, otherwise incremented by 1 for each release from git master
- micro
- always 0 for releases from git master, incremented by 1 for each stable branch release
The implication of this is that changes in major version number
do not have any bearing on the scope of changes
included in the release. Non-backward compatible changes may be made
in any master branch release, provided they have followed the
deprecation
policy which calls for warnings to be emitted for a minimum of two
releases prior to the change.
Время на прочтение6 мин
Количество просмотров179K
Хотим мы того или нет, но программы, для которых необходима Windows, никуда из офисов не исчезли. В ситуации, когда их использование безальтернативно, лучше иметь виртуальную ОС, например для того, чтобы подключиться к аудио-конференции через Skype for Business.
В этой статье я расскажу, как можно с минимальными издержками установить гостевую ОС Windows на гипервизоре QEMU с помощью графического интерфейса virt-manager. Мы нанесем на карту все подводные камни и рифы, а жучков аккуратно посадим в банку.
Подготовка
Самый первый шаг — настройка параметров ядра. Обязательна поддержка KVM и vhost-net, желательна поддержка туннельных интерфейсов[1] и сетевого моста[2]. Полный список на Gentoo вики-странице QEMU.
Подготовьте дисковое пространство. Я выделил 70 GiB, и Windows 8.1 за пару месяцев использовала почти 50 GiB так, что для обновления до 10-й версии места на диске не хватило.
Далее, нам понадобится набор редхатовских драйверов virtio-win. Если у вас установлен RedHat, достаточно запустить
[root@server ~]# yum install virtio-winи образ iso будет записан в каталог /usr/share/virtio-win/. Также можно его скачать с репозитариев Fedora.
Убедитесь, что поддержка аппаратной виртуализация включена в BIOS/UEFI. Без этого KVM не будет активирован, а virt-manager выдаст вот такую ошибку.

В качестве проверки можно прочитать файл устройства.
(2:506)$ ll /dev/kvm
crw-rw----+ 1 root kvm 10, 232 ноя 9 02:29 /dev/kvmЕсли файл не обнаружен, а опции ядра выставлены верно, значит дело в настройках BIOS/UEFI.
Устанавливаем нужные пакеты.
(5:519)$ sudo emerge -av qemu virt-managerДля RedHat 7 достаточно установить только virt-manager, так как QEMU устанавливается по умолчанию.
[root@server ~]# yum install virt-managerДебианщикам надо установить пакет qemu.
root# aptitute install qemuМожно теперь переходить к установке.
Запуск и инсталляция
Запускаем virt-manager и создаем новую виртуальную машину из локального хранилища.

Указываем путь к установочному iso образу Windows.

Далее, на 3-м и 4-м шаге будет выбор количества CPU, объем RAM и размер дискового пространства, после чего на 5-м шаге следует выбрать дополнительные конфигурации перед настройкой.

Окно дополнительных настроек нужно для того, чтобы выполнить финт ушами. Его смысл в том, чтобы добавить виртуальный флопарь с драйверами из набора virtio-win. Это даст возможность изменить тип жесткого диска: удалить диск с шиной IDE и добавить его же, но с шиной VirtIO. Подробно, в доках RedHat.
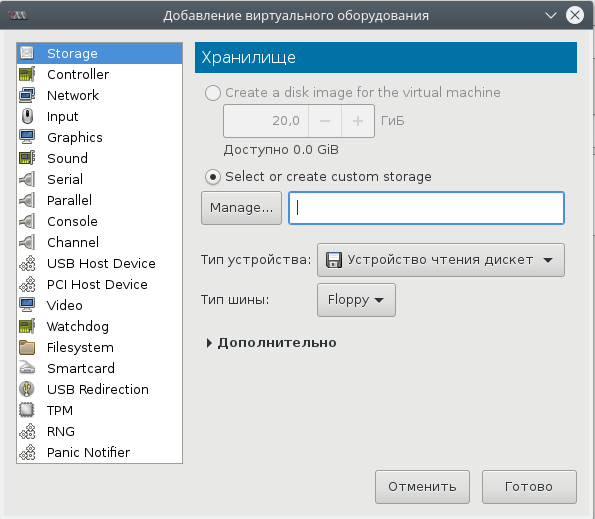
Прописываем драйвер /usr/share/virtio-win/virtio-win.vfd и добавляем виртуальный флоппи-диск. Затем переходим на вкладку [Шина] Диск № и проделываем финт с заменой шины диска: удаляем с IDE и добавляем с VirtIO.
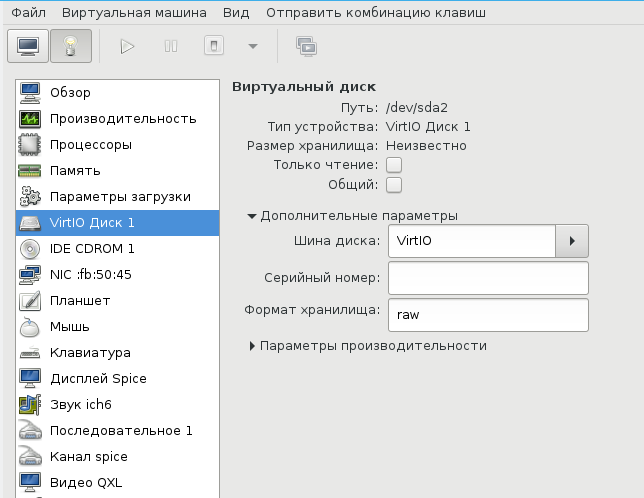
Чуть не забыл сказать, для чего нужен этот фокус. Специалисты утверждают, что с шиной VirtIO, производительность диска ощутимо выше.
В принципе, уже можно начинать инсталляцию, но мы забыли добавить CD-ROM с драйверами virtio-win, а они нам пригодятся, когда диспетчер устройств засверкает желтыми иконками вопросительного знака.
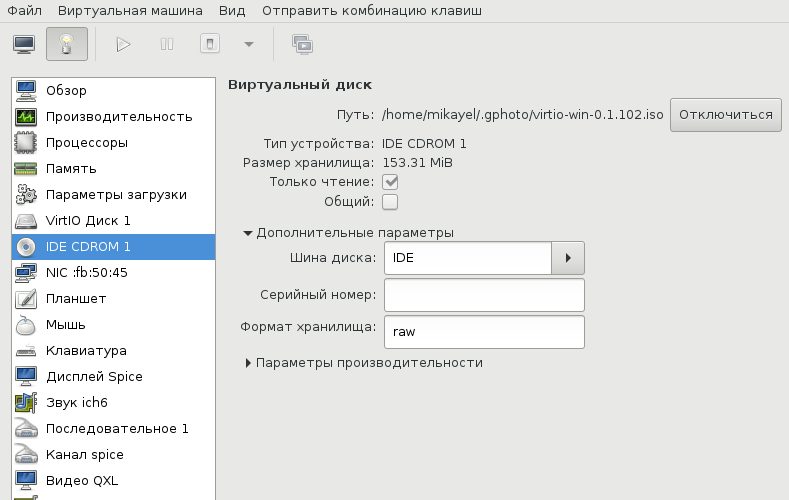
Ну вот теперь можно начать установку.
Ну хорошо, начали мы установку. А что, если установщик Windows попросит сменить диск? Мне из-за этого пришлось пару раз прервать и начать всю карусель заново, но с вами такого уже не случится.
(qemu) change ide1-cd0 /tmp/windows_8.1_x64_disk2.isoДрайвера и доводка
По окончанию процесса установки диспетчер устройств недосчитается некоторых драйверов. Предположительно, это могут быть:
Ethernet Controller
PCI Simple Communication Controller
SCSI ControllerНужно скормить им драйвера из набора virtio-win, что подключены через IDE CD-ROM в предыдущем разделе.
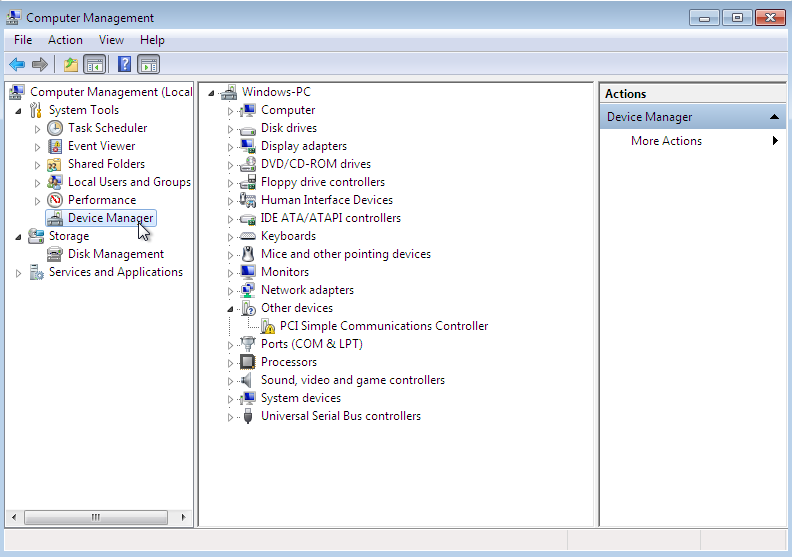
Делается это стандартно: правой кнопкой на желтый знак вопроса, обновить драйвера, путь к файлам.
Вот весь список, а это соседняя страница RedHat доков, где установка драйверов показана подробнее.
- Balloon, the balloon driver, affects the PCI standard RAM Controller in the System devices group.
- vioserial, the serial driver, affects the PCI Simple Communication Controller in the System devices group.
- NetKVM, the network driver, affects the Network adapters group. This driver is only available if a virtio NIC is configured. Configurable parameters for this driver are documented in Appendix E, NetKVM Driver Parameters.
- viostor, the block driver, affects the Disk drives group. This driver is only available if a virtio disk is configured.
Оборудование
Тут постепенно начинается область безграничных возможностей и 101 способов сделать по-своему, поэтому я покажу, как это работает у меня, а вы можете настроить более точно под свои нужды.
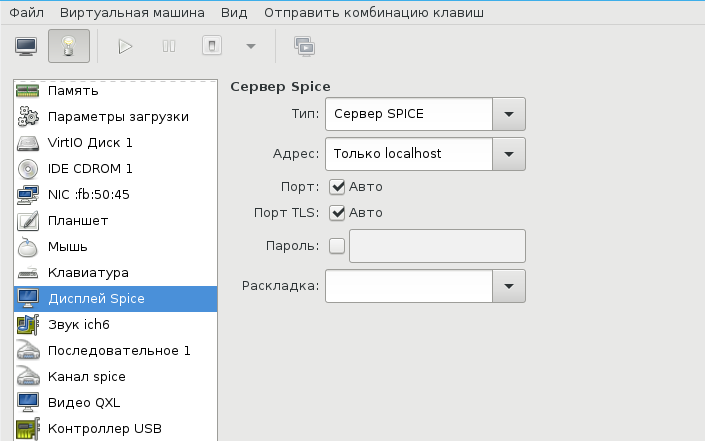
У меня выбран дисплей Сервер Spice и звуковое устройство ich6. Нет, конечно, если у вас уйма времени и желание во всем разобраться до самых тонкостей — дерзайте и пробуйте альтернативные подходы, но у меня звук взлетел, вернее завибрировал, только с такими настройками. Во второй части, посвященной прогулке по граблям и отлову багов, я расскажу об этом подробнее. В закладке видео я выставил QXL, ибо с этой опцией, благодаря волшебному драйверу, мне удалось добиться нормального разрешения экрана.
Подключаться к ВМ можно разнообразно.
- Через графический интерфейс virt-manager
- Выбрать дисплей VNC-сервер и подключаться через vnc-клиента
- Установить Spice-клиента и подключаться через него
- К Windows можно подключиться через rdp, если включен терминальный сервер
У меня вариант 3, для Gentoo это программа spice-gtk
$ eix spice-gtk
[I] net-misc/spice-gtk
Доступные версии: 0.31 ~0.32-r1 ~0.32-r2 **9999 {dbus gstaudio gstreamer gstvideo gtk3 +introspection libressl lz4 mjpeg policykit pulseaudio python sasl smartcard static-libs usbredir vala webdav PYTHON_SINGLE_TARGET="python2_7 python3_4" PYTHON_TARGETS="python2_7 python3_4"}
Установленные версии: 0.31(16:05:41 18.06.2016)(gtk3 introspection pulseaudio python usbredir -dbus -gstreamer -libressl -lz4 -policykit -sasl -smartcard -static-libs -vala -webdav PYTHON_SINGLE_TARGET="python2_7 -python3_4" PYTHON_TARGETS="python2_7 python3_4")
Домашняя страница: http://spice-space.org https://cgit.freedesktop.org/spice/spice-gtk/
Описание: Set of GObject and Gtk objects for connecting to Spice servers and a client GUIСеть
Сеть для ВМ можно настроить по-разному, на Хабре умельцы уже об этом писали. Я перепробовал несколько способов, и в конце простота опять взяла вверх. Сама ВМ запускается из под рута[3], но графический интерфейс spice-gtk — из под обычного непривилегированного пользователя. Это позволяет решить дилемму: для сетевых опций нужны права рута, а для звукового демона pulseaudio, рут запрещен. Я пробовал навешать все права на обычного пользователя, но ничего не получалось, то pulse не пульсирует, то сеть не создается, там много а тут мало. В итоге решил так и доволен. Буду рад, если в комментариях будет найден лучший способ.
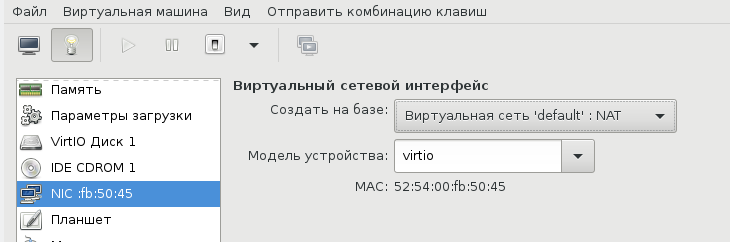
Такой простой выбор сетевых опций дает результат превосходящий ожидания. Создаются 3 дополнительных сетевых интерфейса: virbr0, virbr0-nic, vnet0.
$ ip addr
...
4: virbr0: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc noqueue state UP group default qlen 1000
link/ether 52:54:00:cc:2a:1e brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff
inet 192.168.102.1/24 brd 192.168.102.255 scope global virbr0
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
5: virbr0-nic: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST> mtu 1500 qdisc pfifo_fast master virbr0 state DOWN group default qlen 1000
link/ether 52:54:00:cc:2a:1e brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff
11: vnet0: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc pfifo_fast master virbr0 state UNKNOWN group default qlen 1000
link/ether fe:54:00:fb:50:45 brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff
inet6 fe80::fc54:ff:fefb:5045/64 scope link
valid_lft forever preferred_lft foreverВ iptables создается свод правил, вот основные:
$ sudo iptables -L
...
Chain FORWARD (policy ACCEPT)
target prot opt source destination
ACCEPT all -- anywhere 192.168.102.0/24 ctstate RELATED,ESTABLISHED
ACCEPT all -- 192.168.102.0/24 anywhere Windows ВМ:
C:\Users\user>ipconfig
Windows IP Configuration
Ethernet adapter Ethernet 2:
Connection-specific DNS Suffix . :
Link-local IPv6 Address . . . . . : fe80::90c3:a458:6645:7b9a%7
IPv4 Address. . . . . . . . . . . : 192.168.102.203
Subnet Mask . . . . . . . . . . . : 255.255.255.0
Default Gateway . . . . . . . . . : 192.168.102.1
Tunnel adapter isatap.{BD8F0DA4-92A8-42BD-A557-23AC89AED941}:
Media State . . . . . . . . . . . : Media disconnected
Connection-specific DNS Suffix . :
Tunnel adapter IPHTTPSInterface:
Connection-specific DNS Suffix . :
IPv6 Address. . . . . . . . . . . : 2620:0:a13:8a7:51af:79ae:92b8:828a
Temporary IPv6 Address. . . . . . : 2620:0:a13:8a7:b49d:81fe:e509:16e7
Link-local IPv6 Address . . . . . : fe80::51af:79ae:92b8:828a%15
Default Gateway . . . . . . . . . :Повторяю, все это libvirtd создает сам, ничего для этого делать не надо. В результате имеем нормальный роутинг между хостом и ВМ, можно обмениваться файлами по ssh / scp. Можно пойти дальше и создать шару на Windows, а на Linux хосте настроить samba, но мне это показалось избыточным.
В завершение
Трудно рассказать в одной статье обо всех аспектах Windows + QEMU/KVM, поэтому завершим в следующей. А там будет самый смак, командный интерфейс, разрешение экрана максимум 1024×768, Сцилла pulseaudio и Харибда сети, команда virsh и настройка ВМ из конфиг файла, фейл с tpm, двоичный синтаксис устройств и прочие тихие радости.
- ↑TUN/TAP interfaces
- ↑Ethernet bridging
- ↑От английского root
Если эта публикация вас вдохновила и вы хотите поддержать автора — не стесняйтесь нажать на кнопку
LINUX
Setting up a Windows 10 virtual machine (VM) using KVM (Kernel-based Virtual Machine) and QEMU (Quick Emulator) can seem like a daunting task if you’re new to virtualization. However, with the right guidance and tools, you can create a powerful and efficient virtual environment. This article provides a comprehensive, step-by-step guide to help you successfully set up a KVM/QEMU Windows 10 VM on a Linux host.
Table of Contents
-
Prerequisites
-
Installing KVM and QEMU
-
Configuring KVM
-
Downloading Windows 10 ISO
-
Creating a Windows 10 VM
-
Installing Windows 10 on the VM
-
Optimizing Your Windows 10 VM
-
Common Troubleshooting Tips
-
Conclusion
Prerequisites
Before you start, ensure you have the following:
-
A Linux host operating system (Ubuntu, CentOS, Fedora, etc.)
-
At least 4 GB of RAM (8 GB recommended) and sufficient disk space (at least 20 GB for the Windows VM)
-
Administrative access to install packages and configure settings
-
Basic knowledge of command-line operations
Installing KVM and QEMU
Step 1: Check if your CPU supports virtualization
Run the following command to check if your CPU supports virtualization:
egrep -c '(vmx|svm)' /proc/cpuinfo
A value greater than 0 indicates your CPU can support KVM.
Step 2: Install KVM and QEMU
For Ubuntu, use these commands:
sudo apt update
sudo apt install qemu-kvm libvirt-daemon-system libvirt-clients bridge-utils virt-manager
For CentOS, run:
sudo yum install qemu-kvm libvirt libvirt-python libguestfs-tools virt-manager
After the installation, confirm that the KVM modules are loaded:
Step 3: Add your user to the KVM group
Make sure your user account has the necessary permissions:
sudo usermod -aG kvm $USER
Log out and back in for the changes to take effect.
Configuring KVM
Enable the libvirt service to allow managing VMs seamlessly:
sudo systemctl enable --now libvirtd
Check the status of the libvirt service:
sudo systemctl status libvirtd
Downloading Windows 10 ISO
-
Visit the official Microsoft website.
-
Download the Windows 10 disk image (ISO file).
-
Make sure to save the ISO in a directory accessible to your virtual machine.
Creating a Windows 10 VM
Step 1: Create a disk image for the VM
Run the following command to create a virtual disk image for your Windows 10 installation:
qemu-img create -f qcow2 ~/win10.img 50G
This command creates a 50 GB disk image named win10.img in your home directory.
Step 2: Use virt-install to create the VM
You can launch a new VM using virt-install, specifying the appropriate parameters:
virt-install \
--name win10 \
--ram 4096 \
--disk path=~/win10.img,size=50 \
--vcpus 2 \
--os-type windows \
--os-variant win10 \
--network network=default \
--graphics vnc \
--cdrom /path/to/windows10.iso
Explanation of parameters:
-
--name: Name of the VM (Windows 10). -
--ram: Amount of RAM assigned to the VM. -
--disk: Path and size of the virtual disk. -
--vcpus: Number of virtual CPUs to allocate. -
--os-type: Operating system type. -
--os-variant: Optimization specifics for the OS version. -
--network: Networking mode; typically, the default network. -
--graphics: Graphics display type (VNC in this example). -
--cdrom: Path to the Windows 10 ISO.
Step 3: Access the VM
Once the VM has been created, access it using a VNC viewer, or use virt-manager for a graphical interface:
Select your VM and open the console to start the installation process.
Installing Windows 10 on the VM
Follow the on-screen instructions once the Windows 10 installer loads:
-
Choose the language, time, and keyboard preferences.
-
Select “Install Now.”
-
Enter the product key (if required) or select “I don’t have a product key”.
-
Choose the “Custom: Install Windows only (advanced)” option.
-
Select the virtual disk (unallocated space) for installation.
After the installation completes, you will need to go through Windows setup (user accounts, privacy settings, etc.).
Optimizing Your Windows 10 VM
After installing Windows 10, optimizing the performance of your VM is crucial. Here are some tips:
-
Install VirtIO Drivers: For better disk and network performance, install the VirtIO drivers. Download the drivers from the Fedora Project site and load them during Windows setup.
-
Adjust Resource Allocation: Use
virt-managerto fine-tune the RAM and CPU allocation based on your use-case. -
Disable Unnecessary Services: Inside Windows, you can disable services that are not needed for your specific tasks.
Common Troubleshooting Tips
-
Boot Issues: If the VM fails to boot, double-check that the ISO is correctly attached to the VM and verify the disk settings.
-
Network Issues: Ensure that your network settings in
virt-manageror when usingvirt-installcorrectly link to an active network bridge. -
No VNC Connection: If you can’t connect via VNC, ensure that your VNC viewer is correctly configured and the firewall rules on the host allow VNC connections.
Conclusion
Setting up a KVM/QEMU Windows 10 VM can greatly enhance your productivity by allowing you to run Windows applications seamlessly on a Linux host. By following the steps outlined above, you will have a fully functional Windows 10 environment optimized for performance.
If you encounter issues during the setup or have specific questions, the virtualization community is robust and finding help online is just a search away. Happy virtualizing!
Suggested Articles
LINUX
LINUX
LINUX
LINUX
LINUX
LINUX
As virtualization continues to grow in popularity, many users are searching for QEMU KVM for Windows solutions to run virtual machines effectively. With the rise of remote work, cloud computing, and the need for robust testing environments, understanding how to implement QEMU KVM on a Windows system is crucial. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll uncover what QEMU KVM is, its benefits, installation steps, and best practices. #QEMU #KVM #WindowsVirtualization
What is QEMU KVM?
QEMU (Quick Emulator) is a popular open-source virtualization technology, while KVM (Kernel-based Virtual Machine) is a Linux kernel module that allows the Linux kernel to function as a hypervisor. Together, they offers high-performance virtualization.
Though traditionally utilized on Linux systems, QEMU KVM for Windows has gained attention for its ability to create and manage virtual machines on Windows. This combination provides users with the flexibility of running different operating systems alongside their existing Windows environments, offering numerous possibilities for development, testing, and learning. #Virtualization #QEMUKVM
Benefits of Using QEMU KVM for Windows
- Cost-Effective: QEMU KVM is open-source software, which means it’s free to use, making it an economical choice for individuals and businesses.
- High Performance: KVM effectively utilizes hardware virtualization extensions, enabling high performance in guest operating systems.
- Flexibility: Provides the ability to run a variety of guest operating systems and offers a plethora of configuration options.
- Extensive Features: Advanced capabilities such as snapshotting, live migration, and networking make QEMU KVM a robust choice for virtualization.
System Requirements for QEMU KVM on Windows
Before diving into the installation process, it’s essential to ensure your system meets the necessary requirements:
- Operating System: Windows 10/11 with Hyper-V support.
- CPU: Intel VT-x or AMD-V virtualization support.
- RAM: Minimum of 4GB (recommended 8GB or more for optimal performance).
- Disk Space: At least 20GB for installation and additional space for virtual machines.
How to Install QEMU KVM on Windows
Follow these steps to successfully install QEMU KVM on your Windows machine:
Step 1: Enable Hyper-V
- Search for Turn Windows features on or off in the Start menu.
- Check the box for Hyper-V and click OK.
- Restart your computer to apply changes.
Step 2: Download and Install QEMU
- Visit the official QEMU website.
- Choose the Windows version suitable for your architecture (32-bit or 64-bit).
- Follow the installation wizard to complete the setup.
Step 3: Configure QEMU KVM
- Open a command prompt with administrative privileges.
- Navigate to the QEMU installation directory.
- Run the command to create a virtual machine, e.g.,
qemu-system-x86_64 -hda .img
.
Creating Your First Virtual Machine
Now that you’ve installed QEMU KVM for Windows, you can create your first virtual machine:
Step 4: Obtain an ISO File
- Download the ISO file of the operating system you wish to install.
Step 5: Set Up the Virtual Machine
- Use the
qemu-system-x86_64 -boot d -cdrom -m 2048
command.
- Replace with the path to your downloaded ISO file.
Step 6: Start the Virtual Machine
Enter the command, and the virtual machine will boot from your specified ISO. Follow the installation instructions from your operating system. #VirtualMachine #QEMUKVMWindows
Networking Configuration
Networking is essential in a virtualized environment. QEMU KVM offers several options for network configurations:
Using TAP Interfaces
- Install TAP drivers to allow the virtual machines to communicate with the host and each other.
- Configure the virtual machines to use TAP interfaces through QEMU command line options.
Using User Networking
- Simply start QEMU with
-netdev user,id=mynet0
to create a user-mode network stack.
- This option is simpler to set up and is suitable for basic uses.
Best Practices for Using QEMU KVM on Windows
- Regular Backups: Always backup your VM data to avoid data loss.
- Monitor Performance: Keep an eye on system performance and allocate resources intelligently.
- Use Snapshots: Take snapshots of your VMs before making any significant changes.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Users may encounter various issues when configuring QEMU KVM for Windows. Here are some common problems and solutions:
Performance Issues
Check your CPU utilization and resource allocation settings. Ensure that your hardware virtualization settings are enabled in your BIOS/UEFI.
Network Connectivity Problems
Verify the network configuration settings. Ensure that the firewalls are appropriately set to allow traffic from virtual machines.
Conclusion
Using QEMU KVM for Windows is a fantastic way to implement virtualization on your Windows system. With its powerful features, flexibility, and cost-effectiveness, it opens doors to infinite possibilities for developers, IT professionals, and hobbyists alike. By following this guide, you’ll be equipped to leverage QEMU KVM effectively and create robust virtual environments tailored to your needs. #Virtualization #QEMUKVM #HyperV
For additional resources and documentation on QEMU KVM, visit the official QEMU documentation.
Do you want to use QEMU for Windows? This post from MiniTool shows you how to download and install the QEMU software on Windows. It also shows you how to use QEMU on Windows to create an Ubuntu VM.
What Is QEMU
QEMU, short for Quick Emulator, is a free open-source hosted virtual machine manager that can execute hardware virtualization. With the help of KVM (Kernel-based Virtual Machine), QEMU can offer fast running speed. Therefore, it develops fast and is going to replace VirtualBox and VMware on Linux.
Tip: On Linux, with the help of quickgui, QEMU can create some macOS, Windows, and Linux virtual machines without downloading the ISO files manually. Please refer to this post: How to Install macOS and Windows 11 Virtual Machines on Ubuntu.
However, on Windows, the advantages of QEMU are not significant, because the KVM technology is not applicable on the Windows host machine. In addition, the quickgui is also not available to Windows. But QEMU develops fast and many people still want to use this VM software on Windows.
QEMU for Windows Download and Install
1. Download QEMU for Windows
To use QEMU for Windows, you should download and install it first. Please refer to the following QEMU download guide:
Step 1: Go to the official QEMU website (https://www.qemu.org). Click the Download button at the top section. You will go to the QEMU download page.
Step 2: Click the Windows tab to get the QEMU Windows version. Click 32-bit or 64-bit according to what OS you are running (for me, I click the 64-bit because my OS is 64-bit).
Step 3: On the new page, click the .exe file to download it. This file is the installer file.
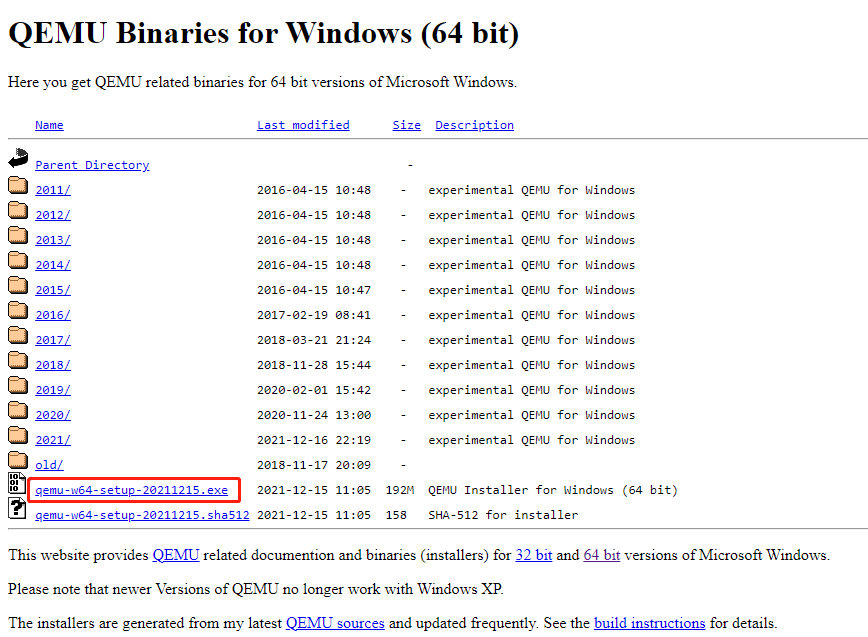
2. Install QEMU for Windows
After the installer file is downloaded, you can double-click it to run directly. Before doing that, I recommend you to create a partition separately for it. For any virtual machine software, I will recommend you create a separate partition to store the software and the VM files so that you can manage them better.
To create a separate partition, you can use the shrink feature in the Windows Disk Management tool. But this tool can’t help you move the location of partitions, so I recommend you to use MiniTool Partition Wizard.
If the free space of one partition is not enough, you can move/resize another partition to get more unallocated space and then gather the unallocated space together to create one partition. Here is the guide:
MiniTool Partition Wizard FreeClick to Download100%Clean & Safe
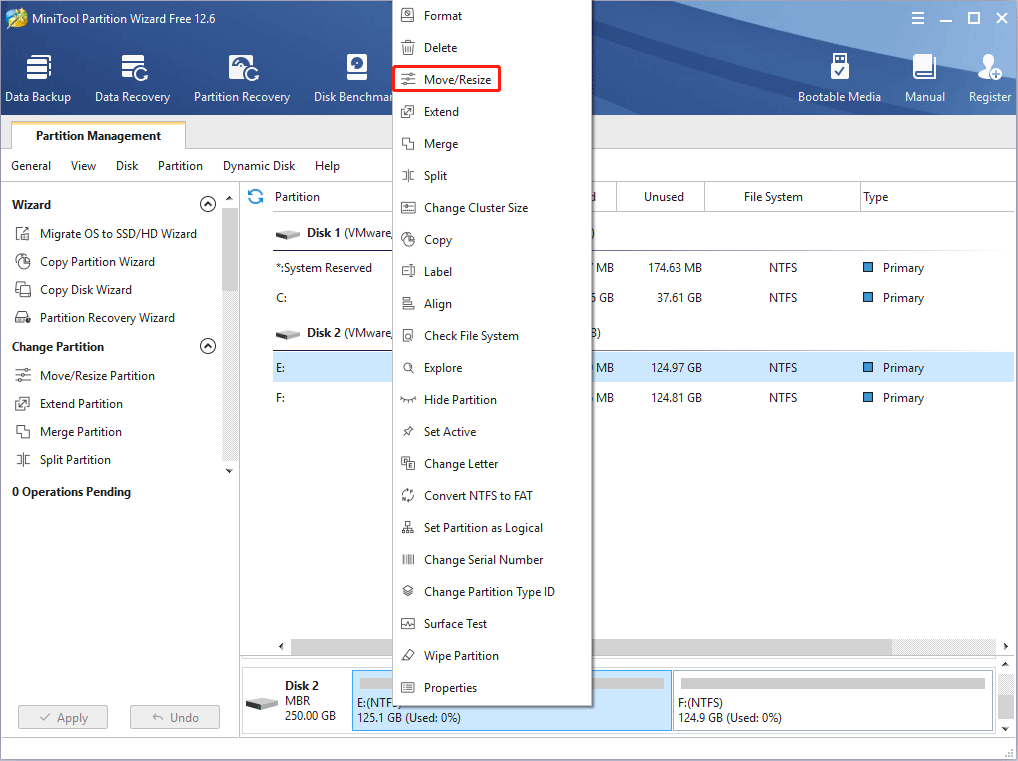
Step 1: Launch MiniTool Partition Wizard and go to its main interface. Right-click a partition and choose Move/Resize.
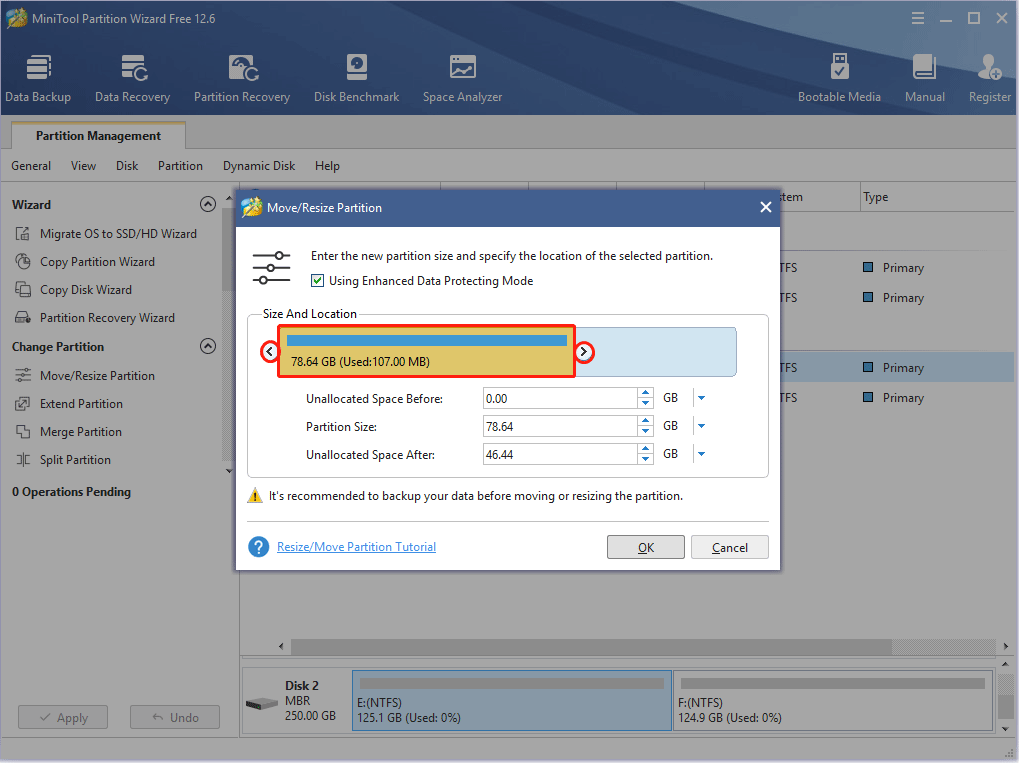
Step 2: Drag the two arrows on the two sides of the partition to shrink the partition, and then drag the block to move the location of the partition. Then, click the OK button. In this way, you can get unallocated space.
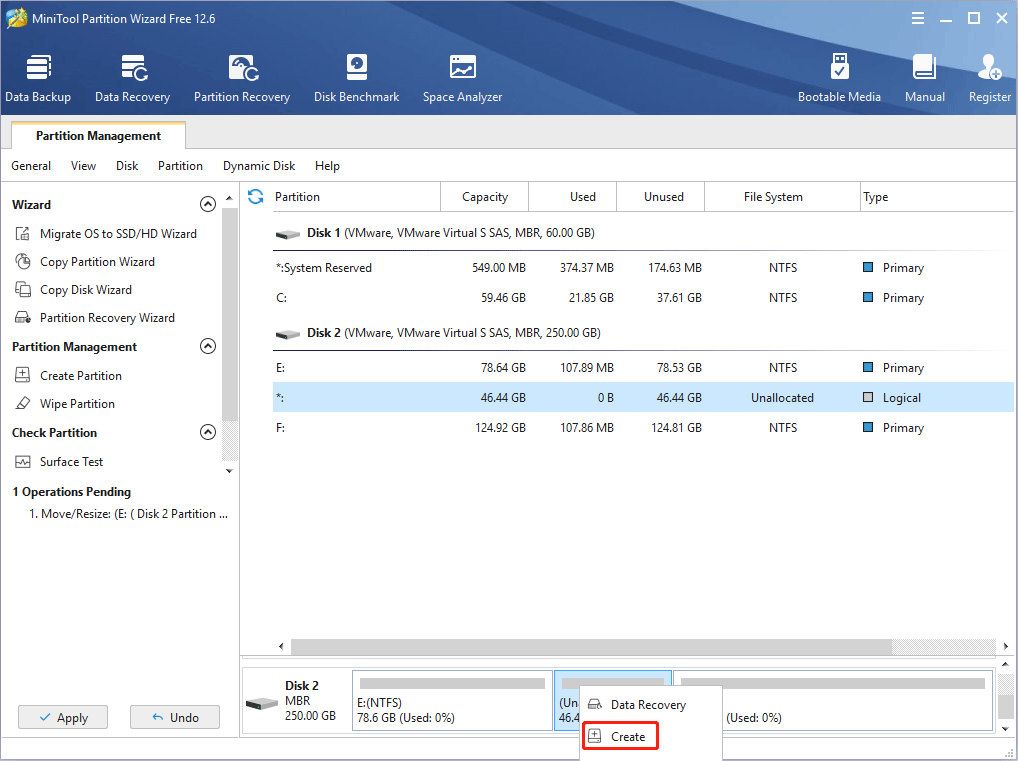
Step 3: Right-click the unallocated space and choose the Create button.
Step 4: Set parameters for the new partition. You can keep all of them to the default value if you don’t have specific demands. Then, click the OK button.
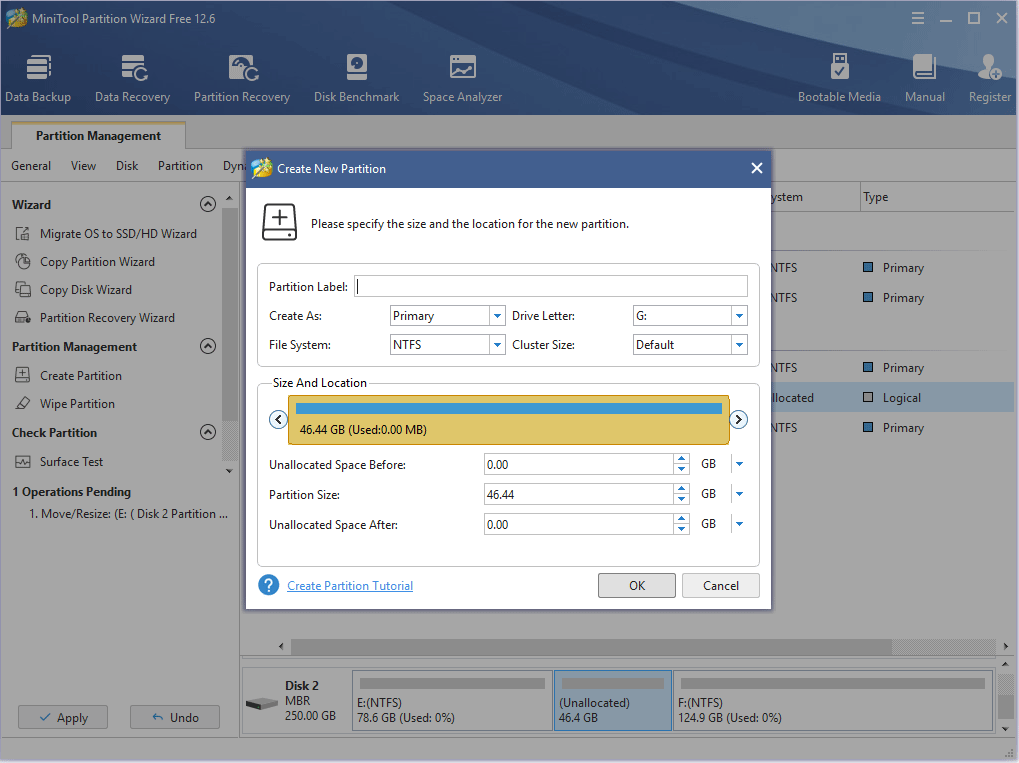
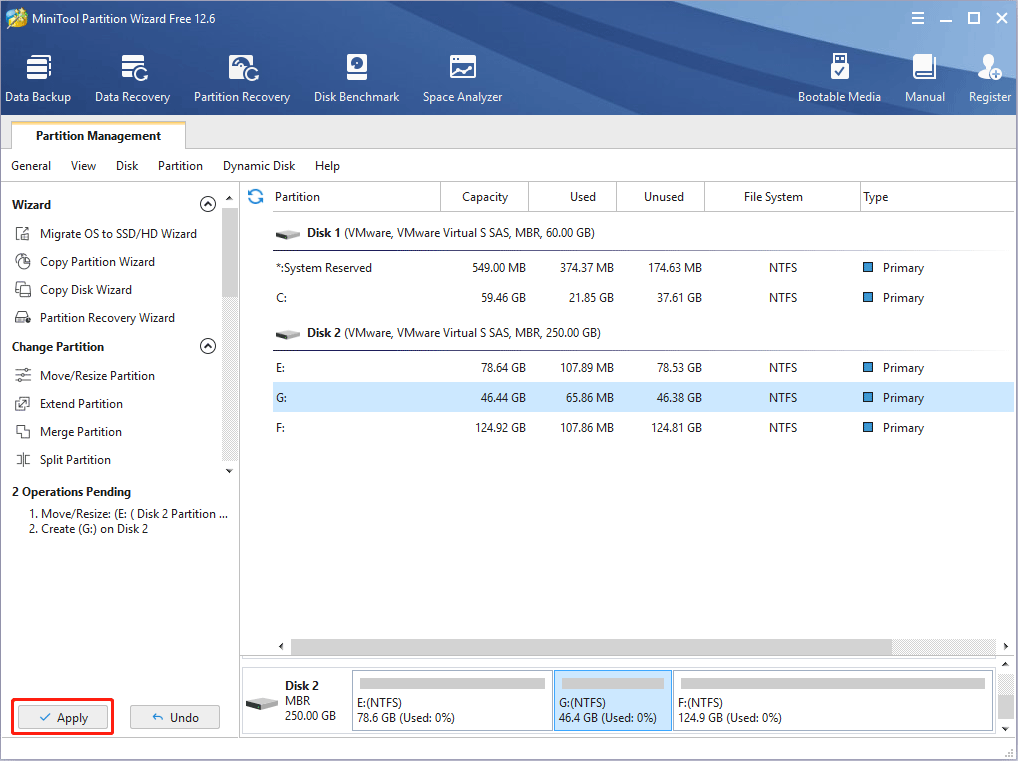
Step 5: Click the Apply button to execute pending operations.
How to Merge Unallocated Space in Windows 10 for a Large Drive
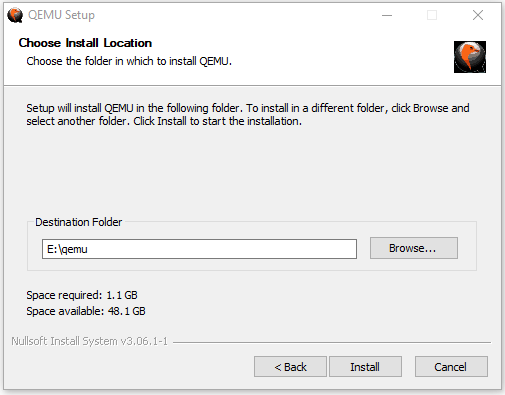
After the new partition is created, you can then double-click the QEMU installer file to install this VM software. You just need to follow the on-screen instructions to complete the installation.
Tip: When you are asked to choose the install location, please choose the newly-created partition (taking E drive as an example).
How to Use QEMU on Windows
After installing the QEMU Windows version, you may want to know how to use QEMU to create a virtual machine. Here are 2 ways and the 2nd way is better.
Way 1. Create a Virtual Machine Using Commands
QEMU doesn’t come with a GUI. If you don’t install a GUI manually, you need to use commands to run QEMU. Here is the guide on how to use QEMU on Windows to create a VM via commands (taking Ubuntu as an example).
Step 1: Download the Ubuntu ISO file from the official website.
Step 2: Add QEMU path into Environment Variables.
- Open File Explorer, go to the QEMU installation location, and then copy the path (E:\qemu).
- Right-click This PC / Computer, choose Properties, and then click Advanced system settings.
- Under the Advanced tab, click Environment Variables.
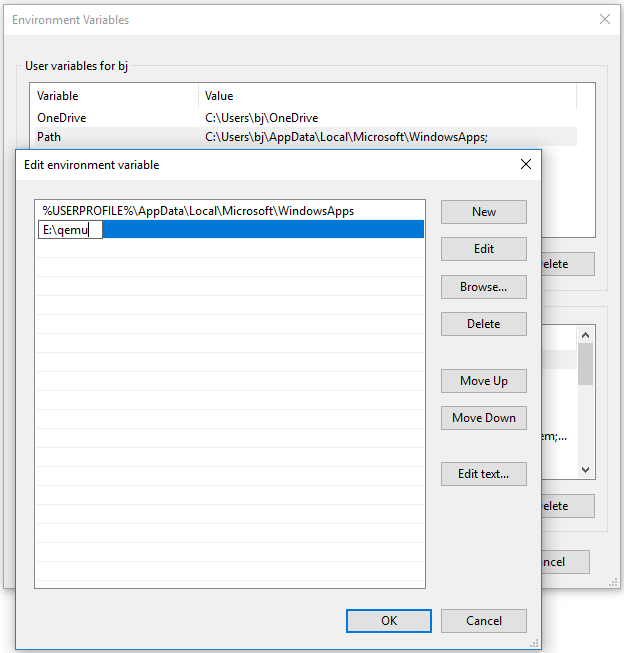
- In the User variables box, double-click the Path variable, click New, and then paste the QEMU path.
- Click the OK button to save changes, and then click the OK button again to save and exit the Environment Variables
Tip:
1. If you use Windows 7, the adding process may be a little different.
2. If there is no Path variable under the User box, you can create one, or you can add the QEMU path into the System variables.
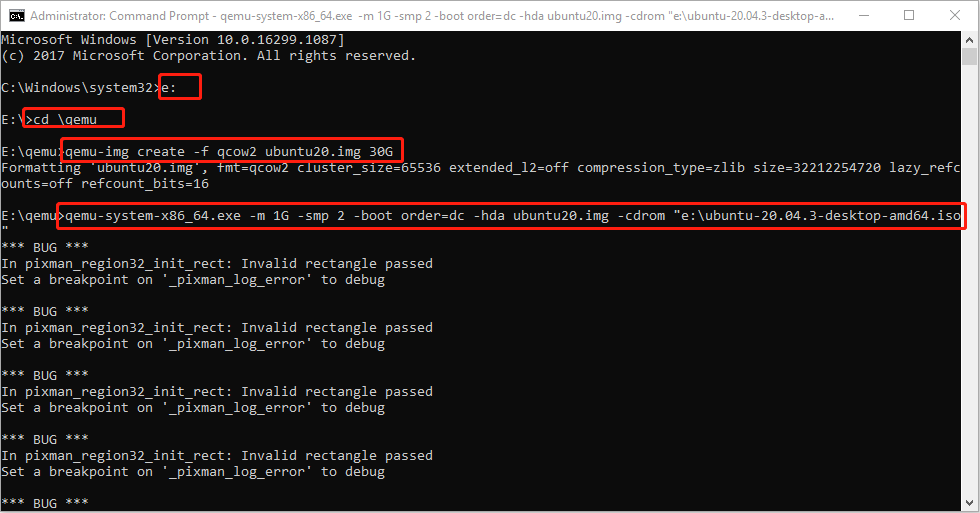
Step 3: Run Command Prompt as administrator and then execute the following commands.
- E: (this will open the e drive where QEMU is installed).
- cd \qemu (this will open the qemu folder).
- qemu-img create -f qcow2 ubuntu20.img 30G (this will create a virtual hard drive of 30GB).
- qemu-system-x86_64.exe -m 1G -smp 2 -boot order=dc -hda ubuntu20.img -cdrom “e:\ubuntu-20.04.3-desktop-amd64.iso” (this will run Ubuntu using CD/ROM).
Tip:
1. If you want to install other VMs (macOS, ARMs, etc.), the qemu-system may vary greatly.
2. The above commands are not perfect. If you have better commands, you can run them.
3. The QEMU installation path and the location of the Ubuntu ISO file in the above commands should be changed accordingly.
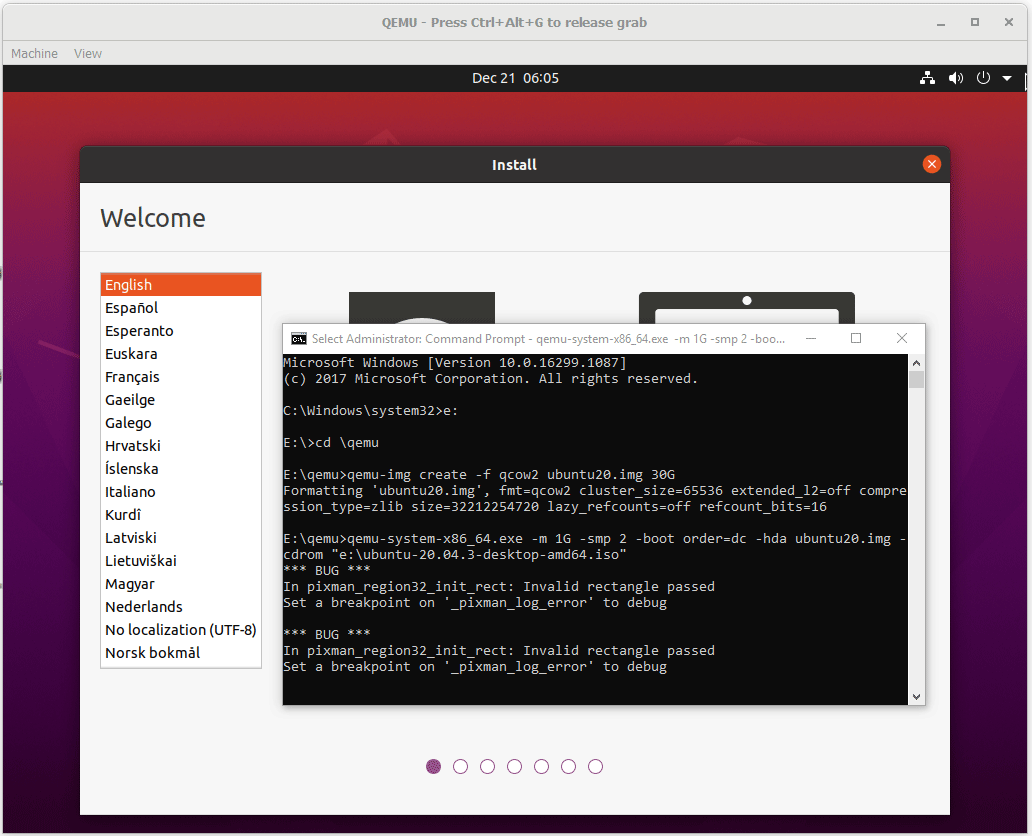
Step 4: Go through the Ubuntu installation process. Although there may be many bugs, I launch Ubuntu 20 successfully and then just need to complete the installation process.
How to Install Linux (Ubuntu) on Windows 10 [Ultimate Guide 2022]
Way 2. Create a Virtual Machine Using QtEmu
As you can see, creating a VM using QEMU via commands is a tough job. You need to search for various tutorials online. In addition, once errors occur, you may have no idea how to solve them. Therefore, I recommend you to use QtEmu, an open-source GUI for QEMU Windows.
How to use QEMU on Windows via QtEmu? Here is the guide:
Step 1: Download the Ubuntu ISO file and QtEmu. The QtEmu official website is https://qtemu.org and the QtEmu source is placed on https://gitlab.com/qtemu/gui. Go to the GitLab source page, scroll down to find the Downloads section, and click the first link to download the QtEmu installer.
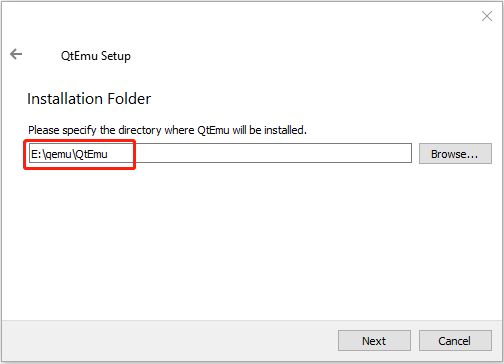
Step 2: Double-click the QtEmu installer file and go through the installation process. When you are asked to specify the installation location (where to create the QtEmu folder), please install the QtEmu under the QEMU folder. For me, I type: E:\qemu\QtEmu.
Step 3: After QtEmu is installed, go to E:\qemu\QtEmu. Right-click the qtemu.exe file and choose Send to > Desktop (create shortcut). Then, create a folder named VMs under the E drive to store all VM files to be created.
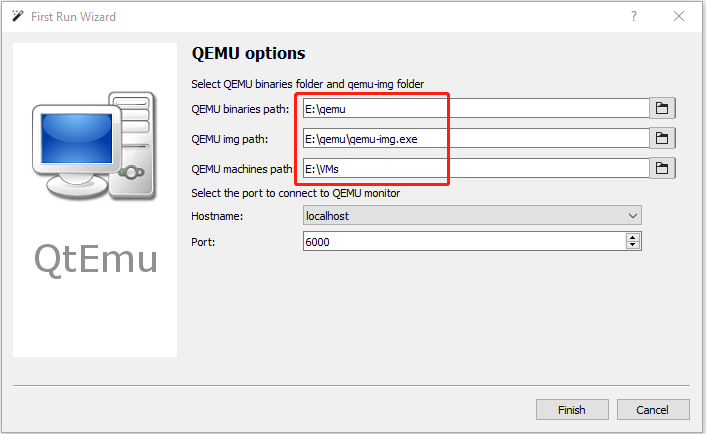
Step 4: Double-click the QtEmu shortcut to launch this software. In the QEMU options window, please set QEMU binaries path to E:\qemu, set QEMU img path to E:\qemu, and set QEMU machines path to E:\VMs. Then, click the Finish button.
Step 5: Click Machine > New Machine. Then, give a name to the new machine (Ubuntu20), choose OS type (GNU/Linux), choose OS version (Ubuntu), and then click Next.
Step 6: On the Filter page, if you don’t need to specify certain motherboard chipsets, you can click the Next button directly to skip this step.
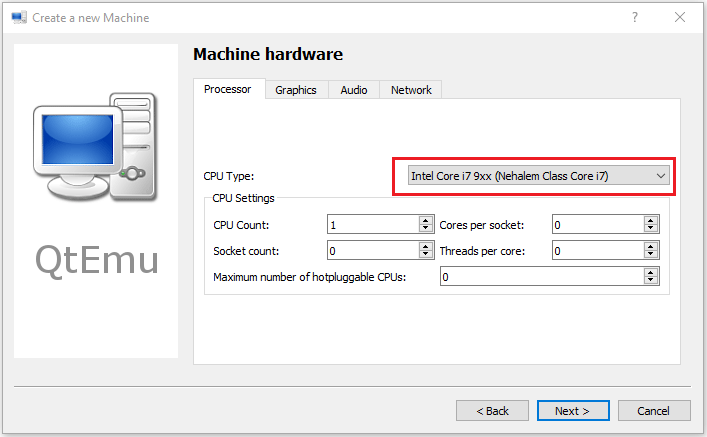
Step 7: Select a correct CPU Type, and set CPU, Graphics, Audio, and Network parameters. If all is OK, click the Next button.
Tip: The Ubuntu 20 version requires a 64-bit CPU. If you choose a 32-bit CPU, the VM may not boot.
What Is the Difference Between 32 Bit and 64 Bit (x86 vs x64)
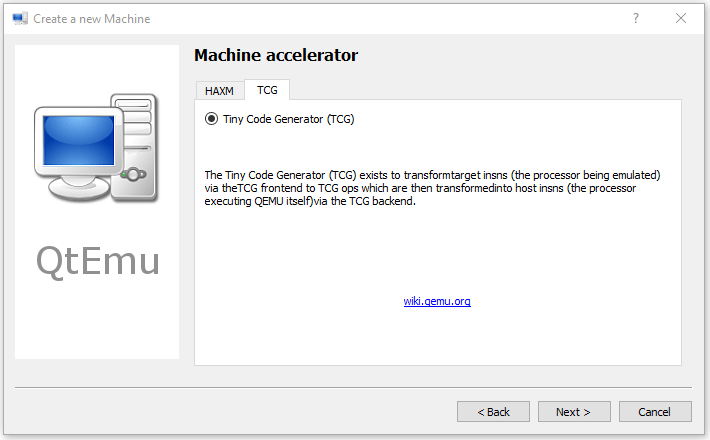
Step 8: Select the machine accelerator. HAXM is chosen by default. However, some computers may not support this technology. Therefore, I recommend you uncheck HAXM and then choose TCG instead. Then, click Next.
Tip: Some people report that nothing happens when they play the VM. The culprit is likely to be the HAXM. To ensure the VM can work on most PCs, TCG is recommended.
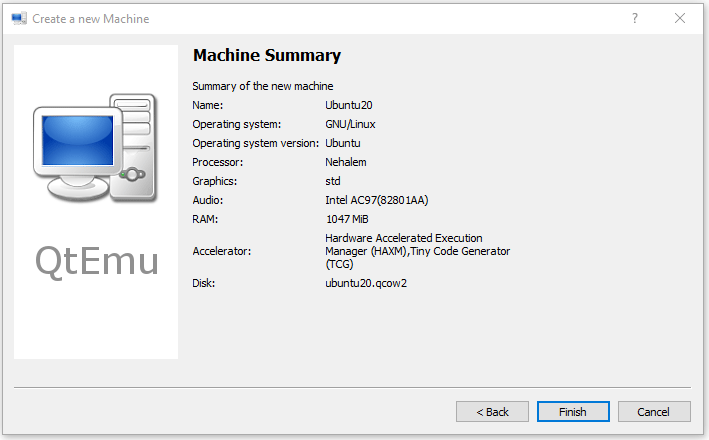
Step 9: Follow the on-screen wizard to set memory size, create a new virtual hard disk, set disk size and type, and then check the VM summary.
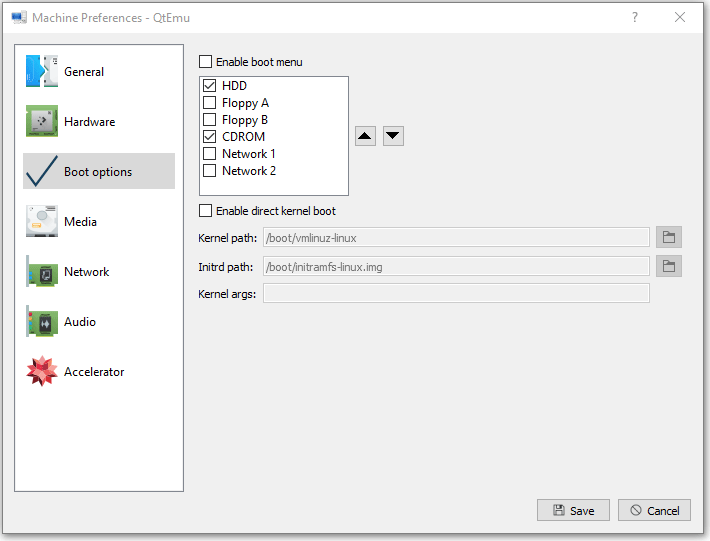
Step 10: Right-click on the newly-created VM and choose Machine Settings. Go to the Boot options tab, and tick CDROM.
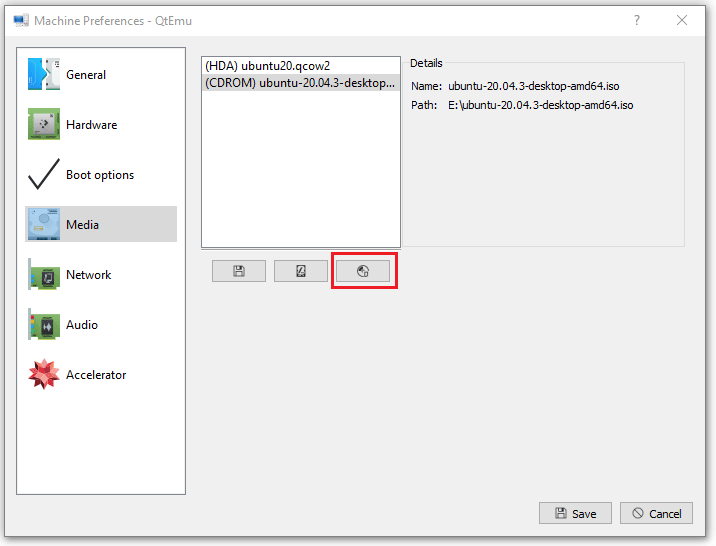
Step 11: Go to the Media tab, click the disc icon, and select the Ubuntu ISO file. Then, click Save.
Step 12: Select the VM and then click the Play icon. Then, you may need to go through the Ubuntu installation process. After the installation process is completed, you can enjoy the VM.
Best Virtual Machine for Windows, Linux, and Mac Systems
Here is a post talking about how to download, install, and use QEMU on Windows. If you are interested in this software, this post may help you.Click to Tweet
Bottom Line
Is this post helpful to you? Do you have other ideas about how to run QEMU on Windows? Please leave a comment in the following zone for sharing. In addition, if you have difficulty in moving or resizing partitions, please feel free to contact us via [email protected]. We will get back to you as soon as possible.
