Python is a versatile and widely used programming language, known for its simplicity and easy-to-understand syntax. When you’re setting up a Python development environment, one of the first tasks is locating where Python is installed on your machine. This information is crucial for configuring different tools and managing libraries and environments.
Python is normally installed in the system’s default program files directory. On Windows, it’s typically found in the “C:\PythonXX” folder. On Linux or Mac, it’s often in “/usr/local/bin/pythonX.X”. You can check your Python installation path by running “python –version” or “which python” in the command line.

This article will help you understand how to find the Python installation location on your system, focusing on different methods and operating systems. This knowledge will assist you in setting up your programming environment correctly and provide a better understanding of how Python interacts with your machine.

Let’s get into it!
Python Installation Locations
On various operating systems like Windows, macOS, or Linux, Python’s installation location can vary due to user preferences or installation packages from different sources.

In this section, we’ll look at the installation location of Python for different operating systems. Specifically, we’ll look at the following:
- Python Installation location on Windows
- Python Installation location on MacOS
- Python Installation location on Linux
1. Python Installation Location on Windows
By default, Python installations on Windows are located in the C:\ directory or C:\Users\<User>\AppData\Local\Programs.
The common installation paths for both 32-bit and 64-bit versions may reside in the C:\PythonXX folder, where XX stands for the Python version (e.g., C:\Python27 for Python 2.7).
In newer installations, the 64-bit version is often located in the C:\Program Files\PythonXX folder, while the 32-bit version is in the C:\Program Files (x86)\PythonXX folder.

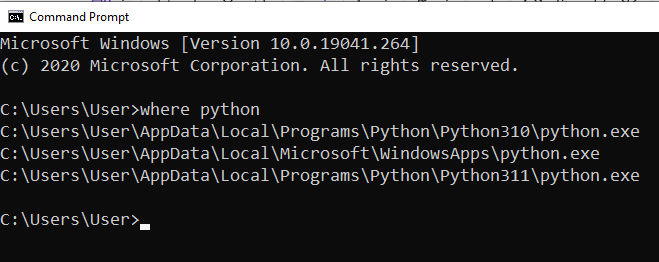
To find the exact location of your Python installation on Windows, you can use the command prompt by typing where python and press Enter. This command will display the file paths of any installed Python versions on your system.
The following image demonstrates this prompt:
2. Python Installation Location on MacOS
On macOS, Python is typically installed in the /Library/Frameworks/Python.framework/Versions directory, with different versions contained in their respective subfolders (e.g., /Library/Frameworks/Python.framework/Versions/3.9 for Python 3.9).
Alternatively, Python installations managed by Homebrew are located in /usr/local/Cellar/python.
To check the exact path of your Python installation, you can open the terminal and type which python or which python3. Pressing “Enter” will display the file path of the active Python version on your system.
3. Python Installation Location on Linux
In most Linux distributions, Python is installed by default and can be found in the /usr/bin/ directory. The installed versions usually include both Python 2 and Python 3.
For Python 2.x, the executable is named python, while for Python 3.x, it’s named python3.
For systems with multiple Python installations or custom installation paths, you can find the location by typing which python or which python3 in the terminal and pressing Enter.
The command will show the file path of the active Python version on your system.
In the next section, we’ll go over how you can use built-in Python modules to locate the Python folder in your system.
How to Use Python’s os and sys Modules to Locate Python Folder
Python’s os and sys modules are built-in modules that allow you to interact with the operating system.

To locate where Python is installed, follow the steps given below:
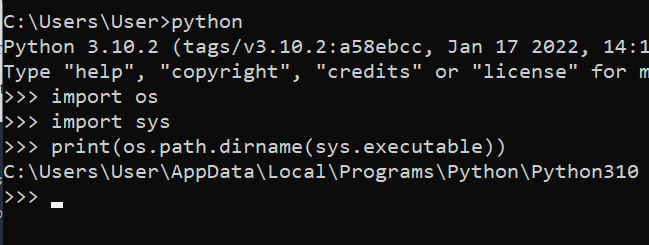
- Run Python interpreter by typing python in the terminal or command prompt.
- Execute the following commands:
import os
import sys
print(os.path.dirname(sys.executable))
This Python script is used to print the directory of the Python interpreter being used to execute the script. os.path.dirname(sys.executable) gets the path of the currently running Python interpreter.
The output is given below:
How to Check the Location of Python Executables
When you are working in Python, you’ll want to install libraries from time to time. In most cases, you might want to check the path of a certain library.

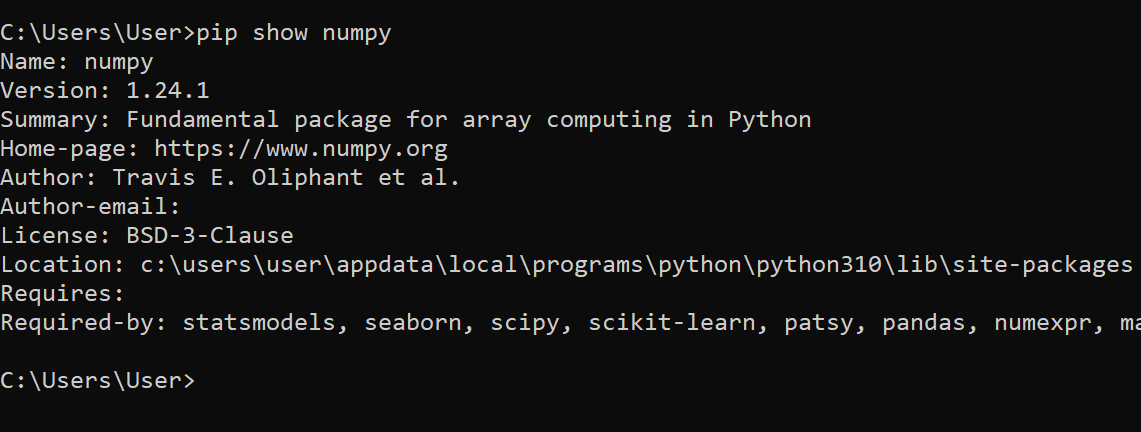
You can check the path of a Python library or executable with the pip package manager. To do this, open up CMD and run the following code:
pip show <package name>Let’s say I want to check the location of NumPy library on my operating system. To do this, I’ll type the following prompt in CMD:
pip show numpyThe output is given below:
How to Configure Python Path
When you first install Python on Windows, it’s important that you configure the path environment variable.
This means you should let your operating system know the path of your installation folder, which will allow the interpreter to refer to this path when running Python files.

We’ve listed a step-by-step guide to setting your environment variable and variables below:
Windows
- Right-click on ‘My Computer’ or ‘This PC,’ and select ‘Properties.’
- Click on ‘Advanced system settings.’
- Go to the ‘Advanced’ tab and click on ‘Environment Variables.’
- In the ‘System variables’ section, locate the ‘Path’ variable, select it, and click on ‘Edit.’
- Add the path to the Python executable (e.g., C:\Python<version>\Scripts;C:\Python<version>), and click ‘OK.’
macOS and Linux
- Open the terminal (Terminal on macOS, and Ctrl + Alt + T on Linux).
- Edit the shell configuration file (~/.bashrc for bash shell, ~/.zshrc for zsh shell).
- Add the following line: export PATH=”/path/to/python-<version>/bin:$PATH”
- Save the file and restart the terminal for the changes to take effect.
How to Verify Python Version and Installation
Before starting any Python project, it’s essential to know the version of Python installed on the system as well as its location.
It’ll help you ensure compatibility between packages, libraries, and other tools.

This section will guide you through verifying your Python version and installation using various Python-related commands and performing cross-platform checks.
1. Python-related Commands
To find the version of Python installed on any platform, you can use the python –version command in the terminal or command prompt.
It returns the Python 2 version installed on your system. To check for the Python 3 version, you can use the python3 –version command instead. These commands help you determine which Python interpreter you are currently using.
In case you are using both Python 2 and Python 3 versions, you can verify the compatibility of a specific module by importing it into the Python interpreter.
For example, to check if the re module is compatible, you can try running the following command:
import re
print(re.__version__)When you run the above command, you’ll get an output similar to the following:
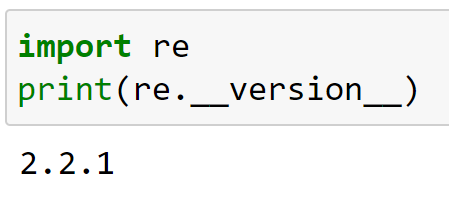
An output like the above suggests that Python’s re module is compatible with your current Python version.
If you’d like to learn how to switch to the latest version of Python, check out our quick and easy guide on how to update Python.
2. Cross-platform Verification
To find where Python is installed on your system, you can use the following Python code snippet for a cross-platform solution:
import sys
print(sys.executable)
This code will print the location of the Python interpreter executable. Depending on your operating system, this might differ.
The output is given below:
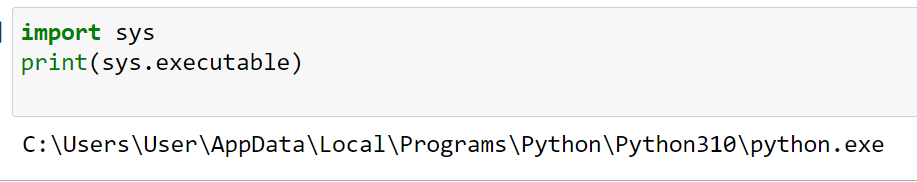
By knowing this location, you can ensure that you are using the correct Python interpreter for your projects.
Troubleshooting Common Python Issues
In this section, we’ll talk about some common issues that you may face when working with Python paths.

Let’s get into it!
1. Path-related Problems
For beginners, one common problem when using Python is related to file paths.
When Python is installed, its location may not be added automatically to the system environment variables PATH.
This could result in the “Python not found” error when trying to run Python scripts or access the Python shell.
To troubleshoot this issue, you can:
- Ensure Python is installed correctly by checking the installation folder, typically found in:
- Windows: C:\Python{version}
- macOS and Linux: /usr/local/bin/python{version}
- Add Python to the PATH variable to make it accessible system-wide:
- Windows: Open the Control Panel, navigate to System and Security > System > Advanced system settings > System Environment Variables, and edit the PATH variable to include the Python installation folder.
- macOS and Linux: Open the terminal and add the Python installation directory to the PATH variable using the export command, such as export PATH=/usr/local/bin/python{version}:$PATH.
- Save and restart the terminal or Command Prompt to apply the changes.
After following the steps above correctly, you’ll no longer run into any errors with running Python files.
2. Version Compatibility
Different Python versions might lead to version compatibility issues, especially when working with third-party modules and libraries.
To overcome this, you can:
- Check your Python version by running python –version in the terminal or Command Prompt.
- Verify the compatibility of a package by checking its documentation or the PyPI page. Packages usually list compatible Python versions.
- Use a virtual environment to manage and isolate dependencies for different projects.
By addressing path-related problems and ensuring version compatibility, you can resolve some of the most common Python issues.
To learn more about error resolution in Python, check the following video out:
Final Thoughts
Understanding where Python is installed on your system is a fundamental aspect of becoming an efficient programmer.
It allows you to manage your programming environment effectively and is key when dealing with using multiple versions of Python versions or when installing modules.
It also helps you in cases when you want to use specific versions for different projects, or when you need to install packages globally or just for one project.
Furthermore, knowing the path of your Python installation can also help you troubleshoot issues related to your environment setup or version conflicts and fine-tune your coding environment to your liking.
It’s an essential step in setting up an integrated development environment, and it makes using code editors or Python-related software smoother and more efficient!
Frequently Asked Questions
In this section, we’ve listed some frequently asked questions that most beginners have related to the Python installation directory.

Where is Python install location on Windows?
Python is installed in the default location C:\PythonXY where XY represents the version number.
For example, C:\Python39 for Python 3.9. It might also get installed under C:\Users\YourUsername\AppData\Local\Programs\Python\PythonXY for per-user installations.
How to find Python location in CMD?
To find the Python installation path in CMD, you can use the following command:
python -c
import os, sys
print(os.path.dirname(sys.executable))This command imports the os and sys modules and prints the directory of the Python executable.
Where is Python’s location in Windows 10?
On Windows 10, Python’s default location is C:\PythonXY or C:\Users\YourUsername\AppData\Local\Programs\Python\PythonXY for per-user installations.
How to check if Python is installed?
To check if Python is installed, open a command prompt or terminal and type in:
python --versionIf Python is installed, the command will display the version of Python.
If it’s not installed, you’ll get an error or the Microsoft Store may open for Python installations in certain cases on Windows.
How to find Python package’s installation location?
Python packages are generally installed in a subfolder of the Python installation. The specific location depends on whether you’re using a virtual environment or not.
To find the installation location of a package, open a terminal or command prompt and type:
pip show package-nameReplace “package-name” with the name of the package you want to find the location for. The output will show the package’s location along with other information.
If you are unable to find Python being installed on your Windows (10/11) operating system and wondering how to locate the folder, well there are a few things that you can try.
Option 1: Make use of the where command
If you make use of the Command Prompt or PowerShell you can try to make use of the where command.
The where command can be used to display the location of files that match the given search pattern.
Example:
C:/> where python
C:/> C:\Users\Code2care\AppData\Local\Programs\Python\Python39-32\python-exeOption 2: Using the which command
If you make use of bash or git bash on Windows, you can try the which command.
# man witch
which – locate a program file in the user's pathExample:
which pythonOprion 3: Using Python code
This may sound funny, but you can write your own Python script or execute code snippets to find out the location of your Python installation on your Windows device using the os module.
Example:
>>> import os
>>> import sys
>>> os.path.dirname(sys.executable)
'C:\Users\Code2care\AppData\Local\Programs\Python\Python39-32\python-exe'Option 4: Check the Environment Variables
Python is often added to the system’s PATH environment variable during installation. You can check if the Python installation directory is listed in the PATH variable by following these steps,
- Go to Start menu and search for «Environment Variables«
- Click on «Edit the system environment variables» option.
- In System Properties -> «Environment Variables» button.
- Look for Path under «System variables»
- Click edit and check if the Python installation directory is included.
Option 6: Search Manually
Most commonly Python setup is installed under C: drive «Program Files» or «Program Files (x86)» based on 32/64 bit versions. You can try to go to this location and try to find out.
You can download this article in various formats for your convenience. Choose from the options below:
Facing issues? Have Questions? Post them here! I am happy to answer!
Provide Feedback For This Article
We take your feedback seriously and use it to improve our content. Thank you for helping us serve you better!

«Discover how to locate the Python installation path on your Windows system using two effective methods: the traditional Command Prompt and the modern Terminal. Whether you’re troubleshooting or setting up environment variables, this guide provides clear, step-by-step instructions with visuals to help you find the information you need. Explore now!»
By CodeWithHarry
Updated: 5 April 2025
Locating the installation path of Python on your Windows system is essential for various tasks such as setting up environment variables or troubleshooting issues. In this guide, I will show you two methods to help you find the Python installation path, first using the Command Prompt (cmd) and the newer terminal.
Method 1: Using Command Prompt (CMD)
This classic method involves utilizing Windows’ Command Prompt to find where Python is installed.
Step 1: Open Command Prompt
Press Win + R to open the run window, type cmd, and press Enter.

Step 2: Use the where Command
In the Command Prompt window, type the following command:
where pythonPress Enter, and the system will display the paths where Python is installed.

Method 2: Using Terminal
The terminal is a powerful scripting environment and newer command-line shell, offering a more modern approach to interacting with your system. If you use the terminal, the following steps will help you find where Python is installed!
Follow the steps below:
Step 1: Open Terminal
You can open Terminal by searching for it in the Start menu and selecting «Terminal».
Step 2: Use the Get-Command Command
In the Terminal window, type the following command:
(Get-Command python).PathPress Enter, and Terminal will reveal the paths where Python is installed.

Conclusion
Both the Command Prompt and Terminal methods are effective ways to find the Python installation path on your Windows system. While the Command Prompt is more traditional, Terminal offers a modern and powerful alternative.
Whether you’re troubleshooting an issue, setting up an environment variable, or simply curious about your Python installation, these methods provide you with the information you need.
Feel free to drop a comment if you have any questions or require further assistance.
Happy coding!
Tags
howtofindpythoninstallationpath
Пройдите тест, узнайте какой профессии подходите
Работать самостоятельно и не зависеть от других
Работать в команде и рассчитывать на помощь коллег
Организовывать и контролировать процесс работы
Быстрый ответ
Для Unix/Linux/Mac:
Для Python версии 2.x:
Для Windows:
В Python скрипте или интерактивном режиме:
Вышеуказанные команды позволяют определить путь к исполняемому файлу Python. sys.executable возвращает полный путь в любом Python-окружении.

Подробные возможности с помощью модуля sys
Модуль sys раскрывает и другую важную информацию:
- sys.exec_prefix указывает путь к папке со стандартными библиотеками Python.
- sys.path выводит список каталогов, где Python ищет модули.
Пример кода:
Заметка: если исполняемый файл Python не добавлен в системный PATH, команды типа which или where могут не работать.
Управление несколькими версиями Python
Если у вас установлено несколько версий Python и используются виртуальные окружения, поиск может усложниться. Для облегчения задачи применяются следующие команды:
Для Unix/Linux/Mac:
Эта команда выведет все пути к исполняемым файлам python3.
Для Windows: в PowerShell:
В виртуальных окружениях сначала активируйте их, затем команда sys.executable покажет точный путь:
Типичные проблемы при поиске установки Python
Вы можете столкнуться с такими неприятностями:
- Python 2 против Python 3: Может быть получен путь к неподходящей версии, если обе версии установлены.
- Различия командных оболочек: Установки
PATHв разных оболочках могут влиять на результаты командwhichилиwhere. - Символические ссылки: Временами
whichвозвращает путь к символической ссылке, а не к реальному файлу установки.
Визуализация
Представьте себя детективом (🕵️♂️), ищущим скрытого Python:
Каждый инструмент с отличающейся точностью указывает на местоположение Python, где бы он ни прятался.
Уровень эксперта: Раскрытие Python
Вот ещё команды, позволяющие раскрыть установленные версии Python:
Поиск абсолютного пути Pythonistic
Для пользователей Unix readlink поможет определить реальное расположение исполняемого файла Python:
Python и ваша оболочка
У пользователям Bash могут быть интересны команды, связанные с историей использования Python:
P.S.: Это как отправиться на поиски сокровищ в собственном терминале — кто знает, что можно обнаружить!
Переменные окружения под лупой
Переменные окружения, как PATH, PYTHONHOME и PYTHONPATH, могут предоставить дополнительную информацию:
Полезные материалы
- sys — Системно-зависимые параметры и функции – официальная документация Python.
- os — Работа с операционной системой – официальная документация Python.
- Github Gist: Python – inspect – Получение пути вызова – скрипт для вывода обширной информации о путях Python.
- Super User: Добавляем Python в системный путь Windows – инструкция по добавлению Python в системные переменные Windows.
- Работа с файлами в Python – Real Python – обучающий материал по использованию файлов в Python.
- Reddit – Погружение в различные темы – обсуждение по поиску путей Python.
Python’s interpreter, libraries, and scripts can reside in multiple locations on a system. So, finding where Python is installed helps with:
- Locating the
pythonexecutable to launch the interpreter - Editing module files under the Python install’s
site-packages - Modifying scripts under the
scriptsfolder of a Python environment - Switching between multiple Python versions using virtual environments
- Troubleshooting issues related to Python installations
The methods for finding Python’s install location vary across operating systems. In detail, we’ll explore platform-specific techniques on Windows, Linux/Unix, and macOS. Let’s jump right in
Finding Python Location on Windows
There are several easy methods to find where Python is installed on Windows. Using the where command or checking Python’s sys path returns the location.
Also read: Pipenv: The New Packaging Tool For Python
Using the where Command
The easiest way is to use the where command within the Command Prompt (CMD). Simply open CMD and type:
Here’s an example output showing the path to the Python interpreter:
C:\Users\gurpreet\AppData\Local\Programs\Python\Python310\python.exe
So for the sample product data table we imported earlier, we can launch Python from this location:
C:\Users\gurpreet\AppData\Local\Programs\Python\Python310\python.exe
import pandas as pd
print(pd.read_csv('products.csv'))
The where command also works in PowerShell:
PS C:\> where python C:\Users\gurpreet\AppData\Local\Programs\Python\Python310\python.exe
On Windows, Python gets added to your system’s PATH environment variable. So running python launches the interpreter from any location.
But where python returns the actual install location on disk.
Also read: [Fix] Bash: Python3: command not found When Installing discord.py on Windows
Checking Python’s sys.executable
Another method is using Python’s built-in sys module to print the path to the currently running executable:
import sys print(sys.executable)
Output:
C:\Users\gurpreet\AppData\Local\Programs\Python\Python310\python.exe
You can also directly run this oneliner from CMD or PowerShell instead of launching Python first:
python -c "import sys; print(sys.executable)"
So, if you have multiple Python versions installed (eg. Python 2.7, 3.7, 3.10 etc), sys.executable points to the specific executable.
This helps when switching between Python installs using virtual environments.
Additional Ways of Finding Python Path on Windows
Some other methods for locating where Python is installed on Windows include:
- Searching for
python.exeusing Windows search - Running
pip listto see packages installed in Python’ssite-packages - Checking the start menu Python folder’s location
- Using
Get-Command pythonin PowerShell
So in summary, where python, sys.executable, and Windows search makes finding Python installs easy on Windows.
Next, let’s look at Linux/Unix systems.
Finding Python on Linux/Unix
On Linux and Unix-based operating systems like Ubuntu, Debian, CentOS etc, there are simple terminal commands for finding where Python is installed.
The which, type -a, and readlink commands come in handy here.
Using the which Command
Most Linux/Unix systems have Python pre-installed and available globally via the shell.
You can find where it’s located by using which python:
which python3 /usr/bin/python3
This returns the path to the global Python executable in use.
For our product data example, we can run:
/usr/bin/python3
import pandas as pd
print(pd.read_csv('products.csv'))
To find all installed Python versions, use:
which -a python /usr/bin/python /usr/bin/python3 /usr/local/bin/python /home/preet/virtualenvs/analytics/bin/python
So which python helps locate not just the active Python interpreter, but also all available versions on your Linux/Unix system.
Using type -a
Another option is using the type command with the -a flag:
type -a python python is /usr/bin/python python is /usr/bin/python3 python is /usr/local/bin/python python is /home/preet/virtualenvs/analytics/bin/python
This displays all commands matching the name python across directories in your $PATH.
Using readlink
Sometimes Python executables are symbolically linked in the /usr/bin or /usr/local/bin folders to their actual location.
For example:
which python3 /usr/bin/python3
We can find where this symlink points to using readlink:
readlink -f /usr/bin/python3 /usr/local/lib/python3.8/bin/python3
This shows the actual install location to be /usr/local/lib/python3.8/.
In summary, using which, type, and readlink allows locating both global and virtual environment Python installs on Linux and Unix.
Finding Python on macOS
On macOS, Python generally gets installed into the /Library/ or ~/Library/ folders.
The Finder app provides an easy way to find these locations.
You can also use terminal commands like which and sys.executable covered earlier.
Let’s go through the Finder approach first.
Using Finder
To find where Python is installed on your Mac:
1. Launch Finder and hit Command + Shift + G
This opens the Go to Folder dialog box.
2. Enter paths like /Library/Frameworks/Python.framework or ~/Library/Python
The /Library path contains Python versions installed system-wide for all users. This includes major versions like:
/Library/Frameworks/Python.framework/Versions/3.11 /Library/Frameworks/Python.framework/Versions/2.7
While the ~/Library path has Python installs scoped to your user account. Typically, you’ll find virtual environments here:
~/Library/Python/3.11/bin
3. Drill down the folders to see the bin/ directory containing python3.
So using Finder provides a graphical way to explore Python install locations on macOS.
Additional Ways of Finding Python
As on Linux/Unix, which python finds the active Python version:
which python3 /usr/local/bin/python3
And sys.executable prints the currently running one:
python3 -c "import sys; print(sys.executable)" /Users/preet/virtualenvs/analytics/bin/python
These terminal commands work the same on macOS as on Linux.
In summary, Finder and shell commands both provide easy methods for finding Python on macOS.
Quick Reference of All Methods By OS
Here’s a quick comparison table summarizing the different techniques across operating systems:
| Operating System | Method | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Windows | where python | where python |
| Windows | sys.executable | python -c “import sys; print(sys.executable)” |
| Windows | Get-Command | Get-Command python |
| Linux/Unix | which python | which python3 |
| Linux/Unix | type -a python | type -a python |
| Linux/Unix | readlink -f | readlink -f /usr/bin/python |
| macOS | Finder (Ctrl + Shift + G) | /Library/Frameworks/Python.framework |
| macOS | which python | which python3 |
| Cross-platform | sys.executable | python -c “import sys; print(sys.executable)” |
This covers some easy, go-to approaches for finding Python installs across different OS environments.
Summary
Finding where Python is installed is essential for managing multiple versions and virtual environments.
We learned platform-specific techniques for locating Python on Windows, Linux/Unix and macOS systems:
- Windows – Using
where python, PowerShell’sGet-Command, andsys.executable - Linux/Unix – Leveraging the
which,type -a, andreadlinkterminal commands - macOS – Finding Python through Finder and shell commands like
which
These methods help pinpoint the exact folder containing Python installs.
Knowing the install location allows running Python or its packages, modifying installed scripts, switching between environments, and debugging issues, if any.
Whether you just started with Python or have been using it for a while, finding where Python lives on your OS is an important troubleshooting skill.
So next time you need to locate Python, use this guide to find its path across Windows, Linux and macOS platforms.
References: StackOverflow
