В Windows одновременно можно одновременно установить и запустить несколько версий .NET Framework. При разработке или развертывания нового приложения, основанного на библиотеках .NET, иногда нужно предварительно узнать какие версии и пакеты обновления .Net Framework уже установлены на компьютере пользователя или на сервере. Вы можете получить список версий .NET Framework, установленных на компьютере, несколькими способами.
Содержание:
- Информация об установленных версиях .NET Framework в реестре
- Как узнать версию .NET Framework с помощью PowerShell?
- Проверить версию .Net Framework на удаленных компьютерах
- Вывести версии .NET Framework в командной строке
Информация об установленных версиях .NET Framework в реестре
При установке или обновлении любой версии .NET Framework, изменения записываются в реестр Windows.
Откройте редактор реестра (regedit.exe) и перейдите в раздел HKLM\ SOFTWARE\Microsoft\NET Framework Setup\NDP. В этой ветке хранится информация обо всех версиях .NET на компьютере. Разверните любой раздел и обратите внимание на следующие параметры (для .Net 4.x нужно развернуть ветку Full):
- Install — флаг установки (если равен 1, значит данная версия .Net установлена на компьютере);
- Install Path — каталог, в который установлена данная версия .Net;
- Release — номер релиза .Net;
- Version — полный номер версии .Net Framework.
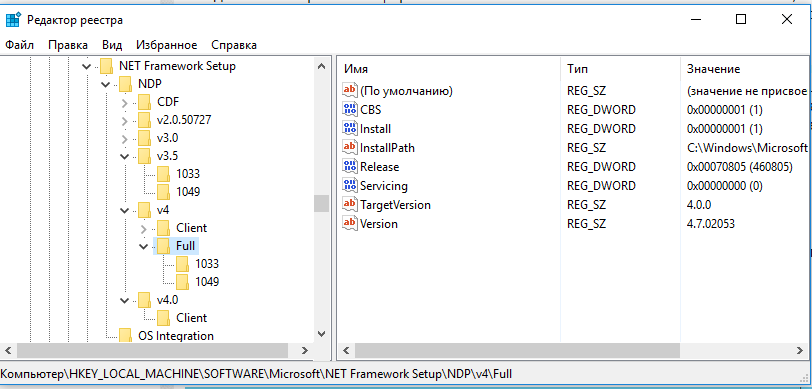
Примечание. Для .NET 4.0 и выше, если подраздел Full отсутствует, это значит, что данная версия Framework на компьютере не установлена.
К примеру, в данном примере видно, что на компьютере установлены .NET Framework v2.0.50727, 3.0, 3.5 и 4.7 (релиз 460805).
Обратите внимание, что в серверных ОС начиная с Windows Server 2012, все базовые версии .Net (3.5 и 4.5) является частью системы и устанавливаются в виде отдельного компонента (Установка .NET Framework 3.5 в Windows Server 2016, в Windows Server 2012 R2), а минорные (4.5.1, 4.5.2 и т.д.) устанавливаются уже в виде обновлений через Windows Update или WSUS.
С помощью следующей таблицы вы можете установить соответствие между номером релиза и версией .NET Framework (применимо к .NET 4.5 и выше).
| Значение DWORD параметра Release | Версия .NET Framework |
| 378389 | .NET Framework 4.5 |
| 378675 | NET Framework 4.5.1 на Windows 8.1 / Windows Server 2012 R2 |
| 378758 | .NET Framework 4.5.1 на Windows 8, Windows 7 SP1, Windows Vista SP2 |
| 379893 | .NET Framework 4.5.2 |
| 393295 | .NET Framework 4.6 на Windows 10 |
| 393297 | .NET Framework 4.6 |
| 394254 | .NET Framework 4.6.1 на Windows 10 1511 |
| 394271 | .NET Framework 4.6.1 |
| 394802 | .NET Framework 4.6.2 на Windows 10 1607 |
| 394806 | .NET Framework 4.6.2 |
| 460798 | .NET Framework 4.7 на Windows 10 1703 |
| 460805 | .NET Framework 4.7 |
| 461308 | .NET Framework 4.7.1 на Windows 10 1709 |
| 461310 | .NET Framework 4.7.1 |
| 461808 | .NET Framework 4.7.2 на Windows 10 1803 |
| 461814 | .NET Framework 4.7.2 |
| 528372 | .NET Framework 4.8 на Windows 10 2004, 20H2, и 21H1 |
| 528040 | .NET Framework 4.8 на Windows 10 1903 и 1909 |
| 528449 | .NET Framework 4.8 в Windows Server 2022 и Windows 11 |
| 528049 | .NET Framework 4.8 (остальные версии Window) |
.NET Framework 4.8 сегодня — самая последняя доступная версия .NET Framework.
Как узнать версию .NET Framework с помощью PowerShell?
Можно получить информацию об установленных версиях и релизах NET Framework на компьютере с помощью PowerShell. Проще всего получить эти данные напрямую из реестра с помощью командлетов
Get-ChildItem
и
Get-ItemProperty
(подробнее о работе с записями реестра из PowerShell).
Чтобы вывести таблицу по всем версиям .Net Framework на компьютере, выполните команду:
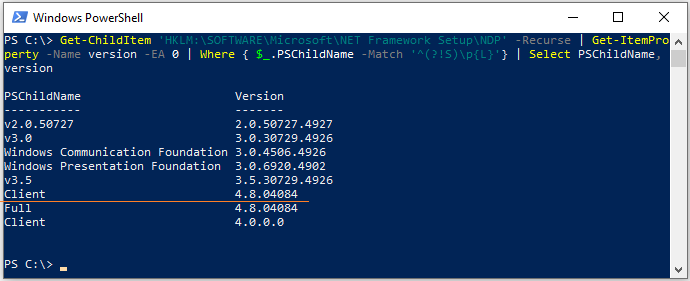
Get-ChildItem ‘HKLM:\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\NET Framework Setup\NDP’ -Recurse | Get-ItemProperty -Name version -EA 0 | Where { $_.PSChildName -Match ‘^(?!S)\p{L}’} | Select PSChildName, version
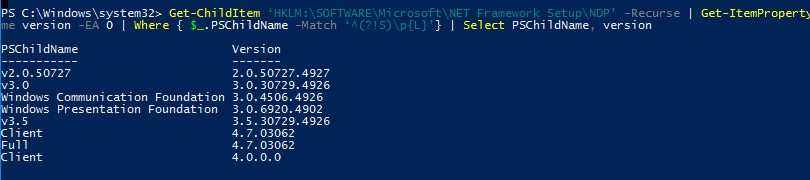
На этом компьютере установлены версии .Net 2.0, 3.0, 3.5 и 4.7.
Начиная с версии .Net v4.0 более новая версия Framework перезаписывает (заменяет) старую версию. Т.е. если на компьютере был установлен .NET Framework 4.7, то при установке .NET Framework 4.8, старая версия пропадет.
Можно вывести только номер релиза (для версий .Net 4.x):
(Get-ItemProperty ‘HKLM:\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\NET Framework Setup\NDP\v4\Full’ -Name Release).Release
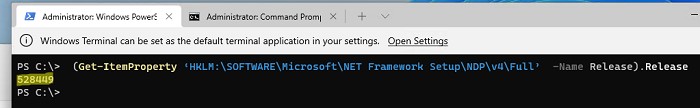
Согласно таблице, номер 528449 соответствует версии .Net Framework 4.8 в Windows 11.
Проверить версию .Net Framework на удаленных компьютерах
Вы можете удаленно получить список версий .Net Framework, установленных на компьютерах в вашей сети помощью PowerShell.
Ниже представлен небольшой PowerShell скрипт, который получает список компьютеров из текстового файла и проверяет на всех версию .Net Framework. Для запуска команд на удаленных компьютерах используется WinRM командлет Invoke-Command.
Function GetNetFramework {
Get-ChildItem 'HKLM:\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\NET Framework Setup\NDP' -recurse |
Get-ItemProperty -name Version,Release -EA 0 |
Where { $_.PSChildName -match '^(?![SW])\p{L}'} |
Select PSChildName, Version, Release, @{
name="Product"
expression={
switch -regex ($_.Release) {
"378389" { [Version]"4.5" }
"378675|378758" { [Version]"4.5.1" }
"379893" { [Version]"4.5.2" }
"393295|393297" { [Version]"4.6" }
"394254|394271" { [Version]"4.6.1" }
"394802|394806" { [Version]"4.6.2" }
"460798|460805" { [Version]"4.7" }
"461308|461310" { [Version]"4.7.1" }
"461808|461814" { [Version]"4.7.2" }
"528040|528049|528449|528372" { [Version]"4.8" }
{$_ -gt 528449} { [Version]"Undocumented version (> 4.8)" }
}
}
}
}
$result=@()
$servers= Get-Content C:\PS\servers.txt
foreach ($server in $servers)
{
$result+=Invoke-Command -ComputerName $server -ScriptBlock $function:GetNetFramework
}
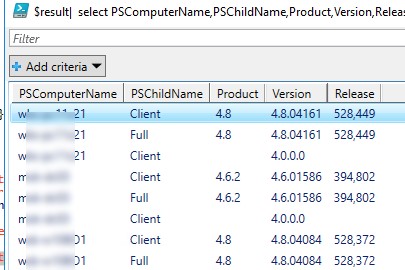
$result| select PSComputerName,@{name = ".NET Framework"; expression = {$_.PSChildName}},Product,Version,Release| Out-GridView
Скрипт выводит табличку (через Out-GridView) со списком версий .Net Framework, установленных на удаленных компьютерах.
Также вы можете задать список компьютеров, на которых нужно проверить .NET так:
$servers= @("pc1","pc2","pc3","pc4","pc5")
Или выбрать список компьютеров из домена с помощью командлета Get-ADComputer из модуля AD PowerShell. Следующая команда выберет все активные хосты Windows Server в домене:
$servers= Get-ADComputer -Filter 'operatingsystem -like "*Windows server*" -and enabled -eq "true"'
Вывести версии .NET Framework в командной строке
Все версии.NET Framework устанавливаются в следующие каталоги Windows:
-
%SystemRoot%\Microsoft.NET\Framework -
%SystemRoot%\Microsoft.NET\Framework64
Вы можете просто открыть этот каталог и увидеть список установленных версий .NET. Каждой версии соответствует отдельный каталог с символом v и номером версии в качестве имени папки. Можно вывести список установленных версий .NET Framework из команды строки:
dir %WINDIR%\Microsoft.Net\Framework\v* /O:-N /B
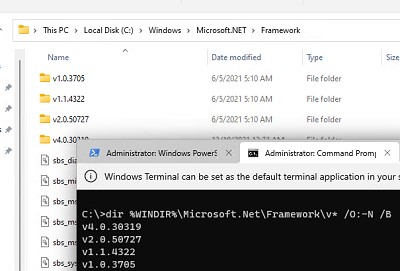
Команда выведет все установленные версии кроме 4.5, т.к. .NET Framework 4.5 устанавливается в подкаталог v4.0.xxxxx.
Содержание
Как определить установленные версии .NET Framework
В этой заметке рассмотрены разные способы определения установленных версий .NET Framework на ОС Windows и Windows Server.
Проверка в проводнике Windows
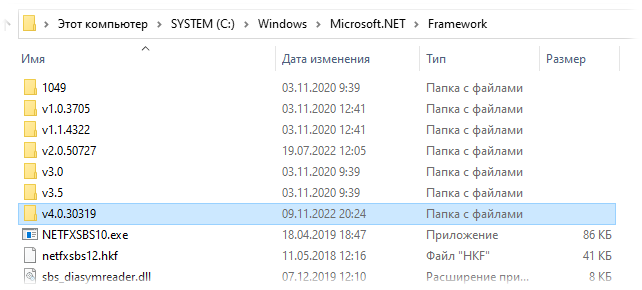
Проверка с помощью Проводника Windows (File Explorer) заключается в изучении содержимого каталога C:\Windows\Microsoft.NET\Framework.
В этом каталоге найдите подкаталог с самой большой версией, например v4.0.30319.
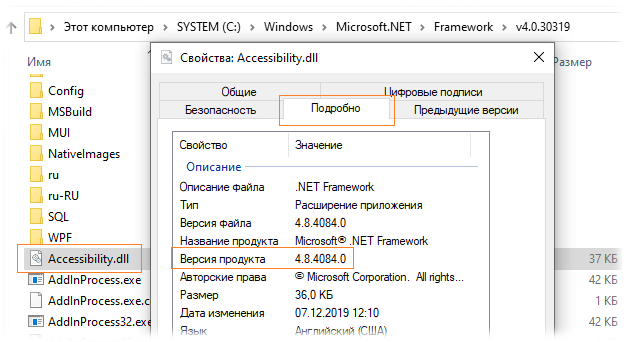
В подкаталоге откройте свойства любой библиотеки с расширением *.dll и на вкладке «Подробно» версия будет указана в поле «Версия продукта». В нашем примере это версия 4.8.4084.0.
Проверка в системном реестре
Информацию об установленных версиях .NET Framework из системного реестра Windows можно извлечь разными способами.
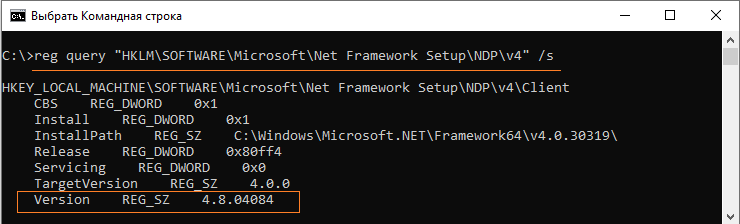
Запрос с помощью утилиты командной строки reg с опросом ключа реестра HKLM\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Net Framework Setup\NDP:
reg query "HKLM\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Net Framework Setup\NDP" /s
Запрос с помощью командлетов PowerShell:
Get-ChildItem 'HKLM:\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\NET Framework Setup\NDP' -Recurse ` | Get-ItemProperty -Name version -EA 0 ` | Where { $_.PSChildName -Match '^(?!S)\p{L}'} ` | Select PSChildName, version
Проверено на следующих конфигурациях:
| Версия ОС |
|---|
| Microsoft Windows 10 21H2 (19044) |
Автор первичной редакции:
Алексей Максимов
Время публикации: 10.11.2022 11:32
Here are the steps to check the .NET framework version installed on your computer.
- Right-click the Windows icon and then click Run.
- Write ‘regedit’ in the text box and then hit ‘Enter’ key on the keyboard.
- Expand the following key.
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\NET Framework Setup\NDP\v4\Full
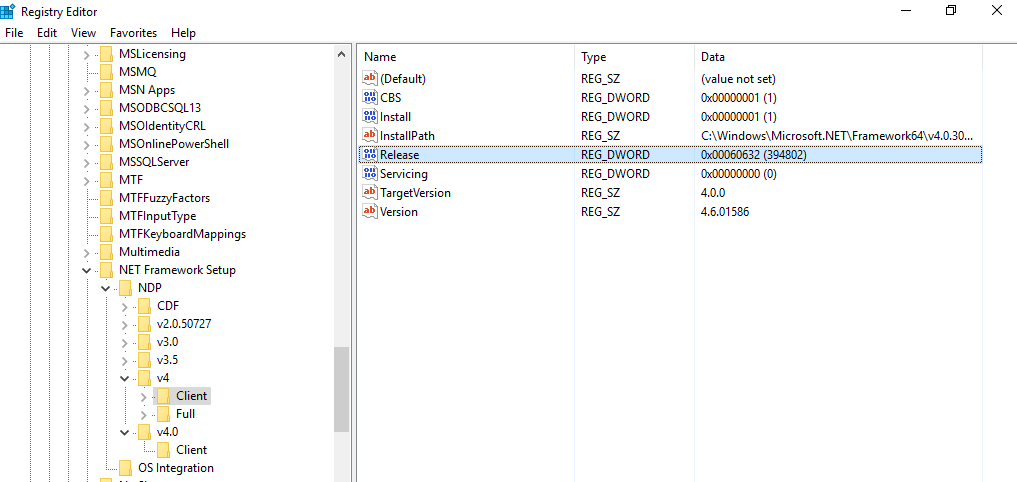
Check for a DWORD value named Release in right column. The following table indicates the value of released DWORD and the installed .NET Framework version.
| Value of the Released DWORD | Version |
|---|---|
| 378389 | .NET Framework 4.5 |
| 378675 | .NET Framework 4.5.1 installed with Windows 8.1 or Windows Server 2012 R2 |
| 378758 | .NET Framework 4.5.1 installed on Windows 8, Windows 7 SP1, or Windows Vista SP2 |
| 379893 | .NET Framework 4.5.2 |
With the release of each new version of .NET Framework, users are bound to install as many framework versions as possible as some applications require .NET Framework version 3.5 and some will work only on version 2.0. Microsoft does not give an easy way to check which versions of .NET Framework are installed on a Windows system.
Nope, you can’t check it from Apps and Features or Programs and Features!
We have already share a software called .NET Framework detector which can list down the frameworks installed and supported by your system. Although it is an easier way to check but sometimes it becomes difficult to install the software on every system if you are a developer or a network admin.
Table of Contents
Windows 10 Version 1803 has .NET Framework 4.7.2 installed by default. There are a few ways we can check which versions of .NET Framework are installed using command line. Let’s go through them one by one.
How to check .NET Framework Version Using Command Line
1- Using Windows directory
Here we are going to check which .Net Framework is installed on your computer through command line.
Simply open command Prompt from the start and then type any of the following commands
dir %windir%\Microsoft.NET\Framework /AD

It will show the list of all the directories with all the versions installed along with the latest ones.
Once you are in the directory then to check which latest version is installed type
.\MSBuild.exe -version
For example, if I want to check the exact version for .NET Framework 4, I will run the following commands in sequence:
dir %windir%\Microsoft.NET\Framework /AD cd %windir%\Microsoft.NET\Framework\v4.0.30319 .\MSBuild.exe -version
2- Using WMIC
You can list down the default (latest one) .NET Framework being used by the system using the WMIC command:
wmic product get description | findstr /C:.NET
If you want a list of all versions installed on your computer, you can also use the following command:
dir /b %windir%\Microsoft.NET\Framework\v*
This command is basically a rip-off of the first method we used above. This will not give you the exact version number as you still have to use the MSBuild command as listed above to get the exact version number.
Which method do you use for checking the installed .NET Framework version?
Use PowerShell to detect which versions of .NET Framework are installed on a machine by querying the Windows registry.
Determine the .NET Framework and ASP.NET Framework version installed
To get an accurate list of the .NET Framework versions installed on a computer, you can view the registry or query the registry in code. Note that the .NET Framework consists of two main components, which are versioned separately:
- A set of assemblies, which are collections of types and resources that provide the functionality for your apps. The .NET Framework and assemblies share the same version number.
- The common language runtime (CLR), which manages and executes your app’s code. The CLR is identified by its own version number (see Versions and Dependencies).
To get an accurate list of the .NET versions installed on a computer, you can view the registry or query the registry in code.
Read the full how to ‘determine Which .NET Framework Versions Are Installed’ on docs.microsoft.com: How to: Determine Which .NET Framework Versions Are Installed
In PowerShell use the Get-ItemProperty cmdlet to get the installed .NET version:
(Get-ItemProperty "HKLM:Software\Microsoft\NET Framework Setup\NDP\v4\Full").Version
Check for a DWORD value named Release. The existence of the Release DWORD indicates that the .NET Framework 4.5 or newer has been installed on that computer.
(Get-ItemProperty "HKLM:Software\Microsoft\NET Framework Setup\NDP\v4\Full").Release
| .NET Framework version | Value of the Release DWORD |
|---|---|
| .NET Framework 4.5 | All Windows operating systems: 378389 |
| .NET Framework 4.5.1 | On Windows 8.1 and Windows Server 2012 R2: 378675. On all other Windows operating systems: 378758 |
| .NET Framework 4.5.2 | All Windows operating systems: 379893 |
| .NET Framework 4.6 | On Windows 10: 393295. On all other Windows operating systems: 393297 |
| .NET Framework 4.6.1 | On Windows 10 November Update systems: 394254. On all other Windows operating systems (including Windows 10): 394271 |
| .NET Framework 4.6.2 | On Windows 10 Anniversary Update and Windows Server 2016: 394802. On all other Windows operating systems (including other Windows 10 operating systems): 394806 |
| .NET Framework 4.7 | On Windows 10 Creators Update: 460798. On all other Windows operating systems (including other Windows 10 operating systems): 460805 |
| .NET Framework 4.7.1 | On Windows 10 Fall Creators Update and Windows Server, version 1709: 461308. On all other Windows operating systems (including other Windows 10 operating systems): 461310 |
| .NET Framework 4.7.2 | On Windows 10 April 2018 Update and Windows Server, version 1803: 461808. On all Windows operating systems other than Windows 10 April 2018 Update and Windows Server, version 1803: 461814 |
| .NET Framework 4.8 | On Windows 10 May 2019 Update: 528040. On all others Windows operating systems (including other Windows 10 operating systems): 528049. On Windows 11 and Windows Server 2022: 528449 |
| .NET Framework 4.8.1 | On Windows 11 2022 Update and Windows 11 2023 Update: 533320. All other Windows operating systems: 533325 |
(table copied from the earlier mentioned docs.microsoft.com article)
About .NET Framework versions: Did you know you can use the /clr parameter of AppCmd to target multiple ASP.NET CLR versions with AppCmd? CLR stands for Common Language Runtime. Pretty neat heh? 
Is .NET and .NET Core installed? What are the versions?
If you want to know whether .NET and / or .NET Core is installed and, if yes, the available versions, you can use the dotnet executable and PowerShell. Here are a couple of options for you.
Dotnet executable
On Stack Overflow, Andriy Tolstoy lists a way to list the .NET Core runtimes available, and the SDK’s:
(dir (Get-Command dotnet).Path.Replace('dotnet.exe', 'shared\Microsoft.NETCore.App')).Name
(dir (Get-Command dotnet).Path.Replace('dotnet.exe', 'sdk')).Name
Its output is for example:
PS C:\Users\janreilink> (dir (Get-Command dotnet).Path.Replace('dotnet.exe', 'shared\Microsoft.NETCore.App')).Name
2.1.30
3.1.20
3.1.31
3.1.32
5.0.11
5.0.17
6.0.11
6.0.13
6.0.14
7.0.2
PS C:\Users\janreilink> (dir (Get-Command dotnet).Path.Replace('dotnet.exe', 'sdk')).Name
3.1.426
5.0.402
5.0.408
5.0.414
6.0.114
6.0.406
7.0.102
Of course dotnet also has a simple --list-runtimes command argument:
PS C:\Users\janreilink> dotnet --list-runtimes
Microsoft.AspNetCore.All 2.1.30 [C:\Program Files\dotnet\shared\Microsoft.AspNetCore.All]
Microsoft.AspNetCore.App 2.1.30 [C:\Program Files\dotnet\shared\Microsoft.AspNetCore.App]
Microsoft.AspNetCore.App 3.1.20 [C:\Program Files\dotnet\shared\Microsoft.AspNetCore.App]
Microsoft.AspNetCore.App 3.1.31 [C:\Program Files\dotnet\shared\Microsoft.AspNetCore.App]
Microsoft.AspNetCore.App 3.1.32 [C:\Program Files\dotnet\shared\Microsoft.AspNetCore.App]
Microsoft.AspNetCore.App 5.0.11 [C:\Program Files\dotnet\shared\Microsoft.AspNetCore.App]
Microsoft.AspNetCore.App 5.0.17 [C:\Program Files\dotnet\shared\Microsoft.AspNetCore.App]
Microsoft.AspNetCore.App 6.0.11 [C:\Program Files\dotnet\shared\Microsoft.AspNetCore.App]
Microsoft.AspNetCore.App 6.0.13 [C:\Program Files\dotnet\shared\Microsoft.AspNetCore.App]
Microsoft.AspNetCore.App 6.0.14 [C:\Program Files\dotnet\shared\Microsoft.AspNetCore.App]
Microsoft.AspNetCore.App 7.0.2 [C:\Program Files\dotnet\shared\Microsoft.AspNetCore.App]
Microsoft.NETCore.App 2.1.30 [C:\Program Files\dotnet\shared\Microsoft.NETCore.App]
Microsoft.NETCore.App 3.1.20 [C:\Program Files\dotnet\shared\Microsoft.NETCore.App]
Microsoft.NETCore.App 3.1.31 [C:\Program Files\dotnet\shared\Microsoft.NETCore.App]
Microsoft.NETCore.App 3.1.32 [C:\Program Files\dotnet\shared\Microsoft.NETCore.App]
Microsoft.NETCore.App 5.0.11 [C:\Program Files\dotnet\shared\Microsoft.NETCore.App]
Microsoft.NETCore.App 5.0.17 [C:\Program Files\dotnet\shared\Microsoft.NETCore.App]
Microsoft.NETCore.App 6.0.11 [C:\Program Files\dotnet\shared\Microsoft.NETCore.App]
Microsoft.NETCore.App 6.0.13 [C:\Program Files\dotnet\shared\Microsoft.NETCore.App]
Microsoft.NETCore.App 6.0.14 [C:\Program Files\dotnet\shared\Microsoft.NETCore.App]
Microsoft.NETCore.App 7.0.2 [C:\Program Files\dotnet\shared\Microsoft.NETCore.App]
Microsoft.WindowsDesktop.App 3.1.20 [C:\Program Files\dotnet\shared\Microsoft.WindowsDesktop.App]
Microsoft.WindowsDesktop.App 3.1.31 [C:\Program Files\dotnet\shared\Microsoft.WindowsDesktop.App]
Microsoft.WindowsDesktop.App 3.1.32 [C:\Program Files\dotnet\shared\Microsoft.WindowsDesktop.App]
Microsoft.WindowsDesktop.App 5.0.11 [C:\Program Files\dotnet\shared\Microsoft.WindowsDesktop.App]
Microsoft.WindowsDesktop.App 5.0.13 [C:\Program Files\dotnet\shared\Microsoft.WindowsDesktop.App]
Microsoft.WindowsDesktop.App 5.0.17 [C:\Program Files\dotnet\shared\Microsoft.WindowsDesktop.App]
Microsoft.WindowsDesktop.App 6.0.4 [C:\Program Files\dotnet\shared\Microsoft.WindowsDesktop.App]
Microsoft.WindowsDesktop.App 6.0.6 [C:\Program Files\dotnet\shared\Microsoft.WindowsDesktop.App]
Microsoft.WindowsDesktop.App 6.0.7 [C:\Program Files\dotnet\shared\Microsoft.WindowsDesktop.App]
Microsoft.WindowsDesktop.App 6.0.11 [C:\Program Files\dotnet\shared\Microsoft.WindowsDesktop.App]
Microsoft.WindowsDesktop.App 6.0.13 [C:\Program Files\dotnet\shared\Microsoft.WindowsDesktop.App]
Microsoft.WindowsDesktop.App 6.0.14 [C:\Program Files\dotnet\shared\Microsoft.WindowsDesktop.App]
Microsoft.WindowsDesktop.App 7.0.2 [C:\Program Files\dotnet\shared\Microsoft.WindowsDesktop.App]
Yes, I need to do some cleanup 
Dotnet-core-uninstall
Have dotnet-core-uninstall.exe installed? It’s a pain, but I recommend it. You can feed the dotnet uninstall tool all kinds of arguments, it can remove the hosting-bundle, runtime, aspnet-runtime, major versions and minor versions. And it can report installed versions, sweet! See:
PS C:\Users\janreilink> &'C:\Program Files (x86)\dotnet-core-uninstall\dotnet-core-uninstall.exe' list
This tool cannot uninstall versions of the runtime or SDK that are
- SDKs installed using Visual Studio 2019 Update 3 or later.
- SDKs and runtimes installed via zip/scripts.
- Runtimes installed with SDKs (these should be removed by removing that SDK).
The versions that can be uninstalled with this tool are:
.NET Core SDKs:
.NET Core Runtimes:
7.0.3 x86
7.0.3 x64
6.0.14 x86
6.0.14 x64
ASP.NET Core Runtimes:
7.0.3 x86
7.0.3 x64
6.0.14 x86
6.0.14 x64
.NET Core Runtime & Hosting Bundles:
7.0.3
6.0.14
The tool has extensive documentation, read .NET uninstall tool and How to remove the .NET Runtime and SDK at Microsoft Learn.
PowerShell and the Windows Registry
On Microsoft’s Technet Script Center gallery, you may find an additional How to determine ASP.NET Core installation on a Windows Server by PowerShell recipe contributed by OneScript Team:
$DotNETCoreUpdatesPath = "Registry::HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Wow6432Node\Microsoft\Updates\.NET Core"
$DotNetCoreItems = Get-Item -ErrorAction Stop -Path $DotNETCoreUpdatesPath
$NotInstalled = $True
$DotNetCoreItems.GetSubKeyNames() | Where { $_ -Match "Microsoft .NET Core.*Windows Server Hosting" } | ForEach-Object {
$NotInstalled = $False
Write-Host "The host has installed $_"
}
If ($NotInstalled) {
Write-Host "Can not find ASP.NET Core installed on the host"
}
An shorter version is:
$DotNetCoreItems = Get-Item -ErrorAction Stop -Path "Registry::HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Wow6432Node\Microsoft\Updates\.NET Core"
$DotNetCoreItems.GetSubKeyNames() | Where { $_ -Match "Microsoft .NET Core.*Windows Server Hosting" } | ForEach-Object {
Write-Host ".NET Core versions found: $_"
}
HTH, this was how to list installed ASP.NET versions using PowerShell.
