Переменные окружения (среды) в Windows содержат различную информацию о настройках системы и среды пользователя. Различают переменные окружения пользователя, системы и процессов.
Самый простой способ просмотреть содержимое переменных окружения в Windows – открыть свойства системы (sysdm.cpl) -> Дополнительно -> Переменные среды. Как вы видите, в открывшемся есть две секции: в верхней содержатся переменные окружения пользователя, в нижнем – системные.
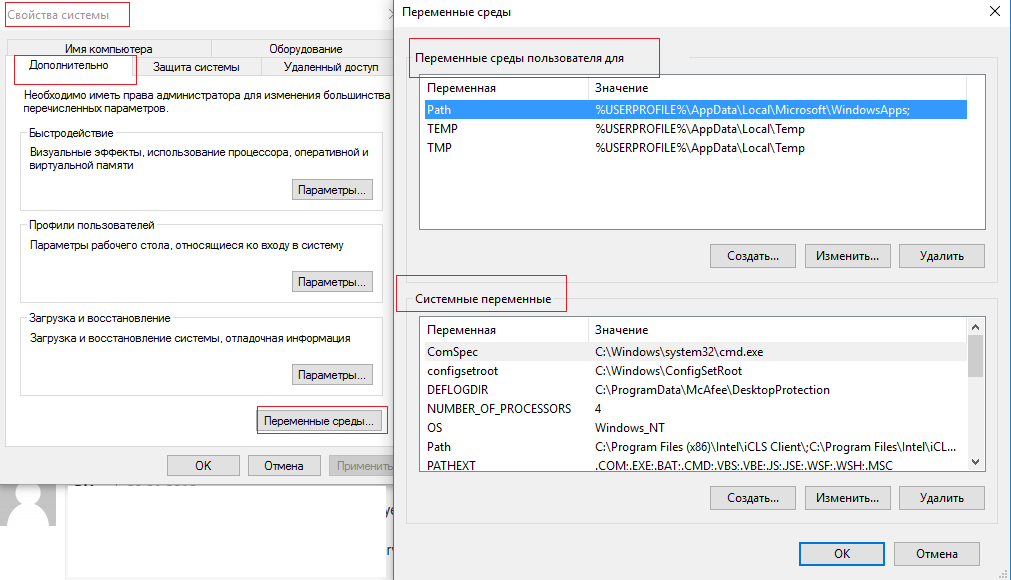
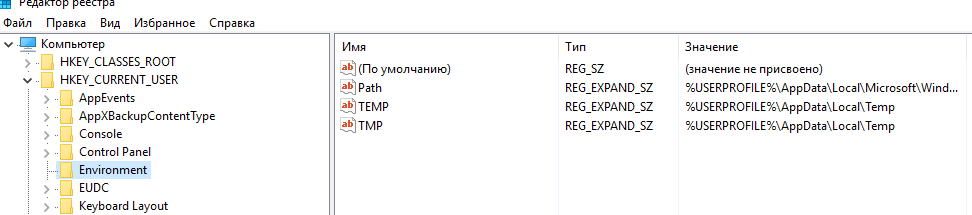
Кроме того, переменные среды хранятся в реестре системы. Пользовательские переменные хранятся в разделе HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Environment. Системные – в HKLM\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\Session Manager\Environment.
Вывести значения всех переменных окружения можно в командной строке Windows. Команда простая:
Set
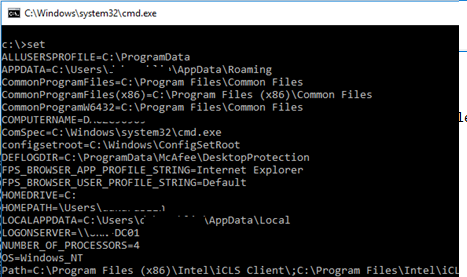
Команда выведет список переменных среды и их значения.
В PowerShell для вывод всех переменных окружения можно использовать команду:
ls env:
Если нужно вывести значение только одной переменной, нужно воспользоваться командой echo, причем имя переменной нужно заключить в знаки процентов. Например,
Echo %systemroot%
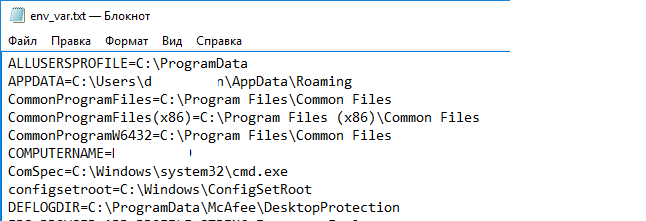
Чтобы сохранить все переменные среды и их значения в текстовый файл, воспользуйтесь командой:
set > c:\tmp\env_var.txt
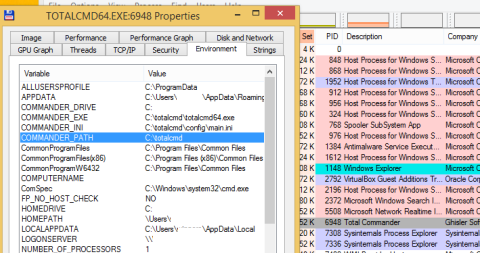
Переменные окружения конкретного процесса можно получить с помощью бесплатной утилиты Process Explorer (от Sysinternals). Достаточно открыть свойства процесса и перейти на вкладку Environment.
What is an environment variable in Windows? An environment variable is a dynamic “object” containing an editable value which may be used by one or more software programs in Windows.
In this note i am showing how to list environment variables and display their values from the Windows command-line prompt and from the PowerShell.
Cool Tip: Add a directory to Windows %PATH% environment variable! Read More →
The environment variables in Windows can be printed using the Windows command-line prompt (CMD) or using the PowerShell.
Windows Command-Line Prompt (CMD)
List all Windows environment variables and their values:
C:\> set
“Echo” the contents of a particular environment variable:
C:\> echo %ENVIRONMENT_VARIABLE%
Windows PowerShell
Print all Windows environment variables (names and values):
PS C:\> gci env:* | sort-object name
Show the contents of a particular environment variable:
PS C:\> echo $env:ENVIRONMENT_VARIABLE
Cool Tip: Set environment variables in Windows! Read More →
Was it useful? Share this post with the world!
Environment variables are key-value pairs a system uses to set up a software environment. The environment variables also play a crucial role in certain installations, such as installing Java on your PC or Raspberry Pi.
In this tutorial, we will cover different ways you can set, list, and unset environment variables in Windows 10.
Prerequisites
- A system running Windows 10
- User account with admin privileges
- Access to the Command Prompt or Windows PowerShell
Check Current Environment Variables
The method for checking current environment variables depends on whether you are using the Command Prompt or Windows PowerShell:
List All Environment Variables
In the Command Prompt, use the following command to list all environment variables:
set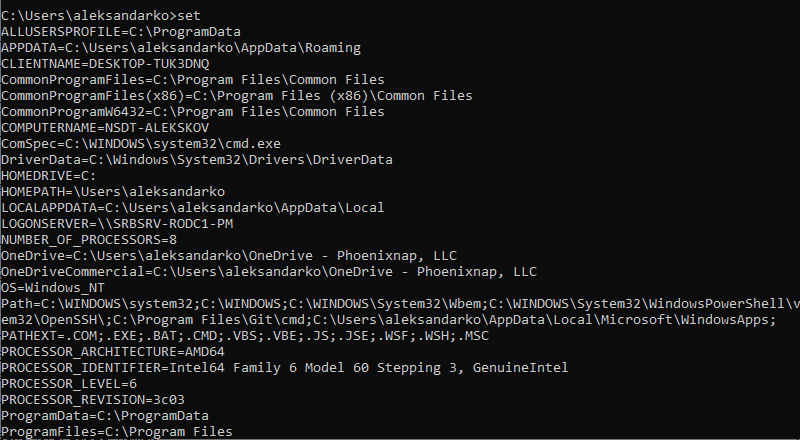
If you are using Windows PowerShell, list all the environment variables with:
Get-ChildItem Env: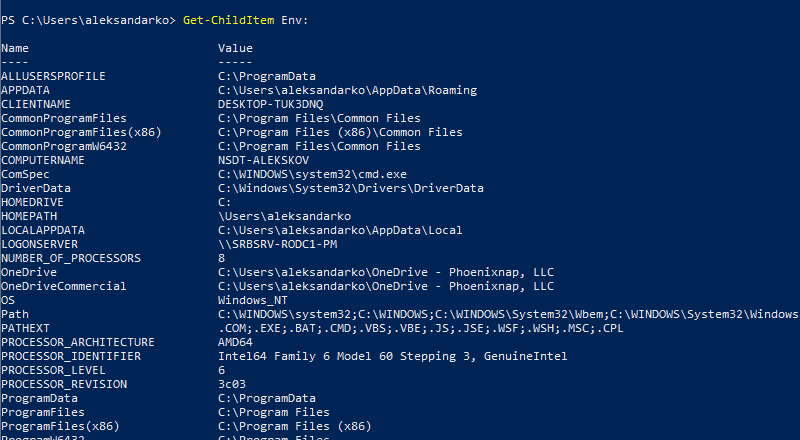
Check A Specific Environment Variable
Both the Command Prompt and PowerShell use the echo command to list specific environment variables.
The Command prompt uses the following syntax:
echo %[variable_name]%
In Windows PowerShell, use:
echo $Env:[variable_name]
Here, [variable_name] is the name of the environment variable you want to check.
Set Environment Variable in Windows via GUI
Follow the steps to set environment variables using the Windows GUI:
1. Press Windows + R to open the Windows Run prompt.
2. Type in sysdm.cpl and click OK.
3. Open the Advanced tab and click on the Environment Variables button in the System Properties window.
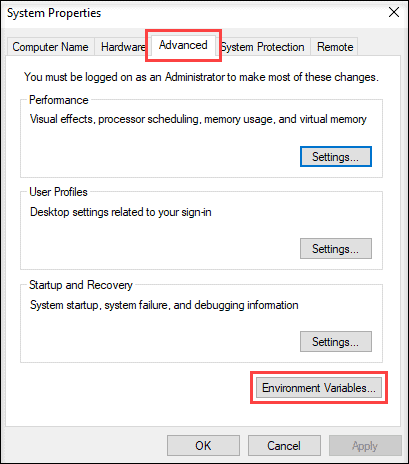
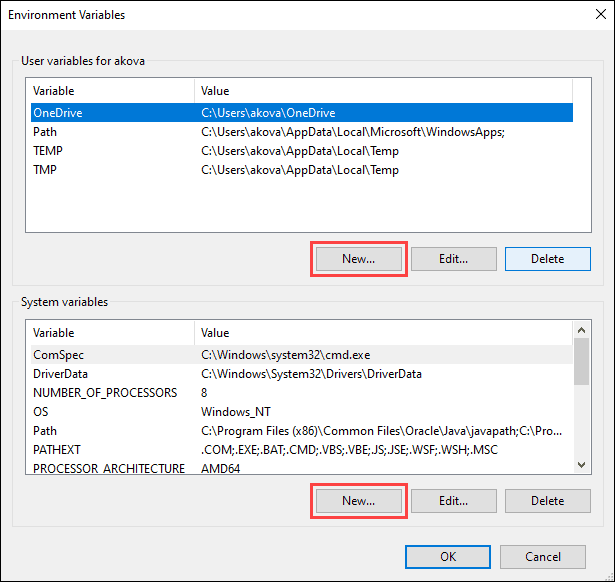
4. The Environment Variables window is divided into two sections. The sections display user-specific and system-wide environment variables. To add a variable, click the New… button under the appropriate section.
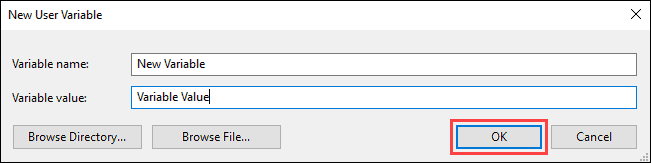
5. Enter the variable name and value in the New User Variable prompt and click OK.
Set Environment Variable in Windows via Command Prompt
Use the setx command to set a new user-specific environment variable via the Command Prompt:
setx [variable_name] "[variable_value]"Where:
[variable_name]: The name of the environment variable you want to set.[variable_value]: The value you want to assign to the new environment variable.
For instance:
setx Test_variable "Variable value"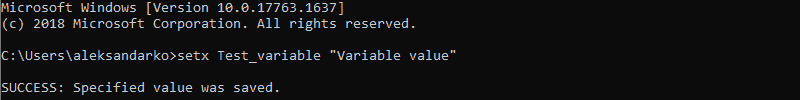
Note: You need to restart the Command Prompt for the changes to take effect.
To add a system-wide environment variable, open the Command Prompt as administrator and use:
setx [variable_name] "[variable_value]" /M
Unset Environment Variables
There are two ways to unset environment variables in Windows:
Unset Environment Variables in Windows via GUI
To unset an environment variable using the GUI, follow the steps in the section on setting environment variables via GUI to reach the Environment Variables window.
In this window:
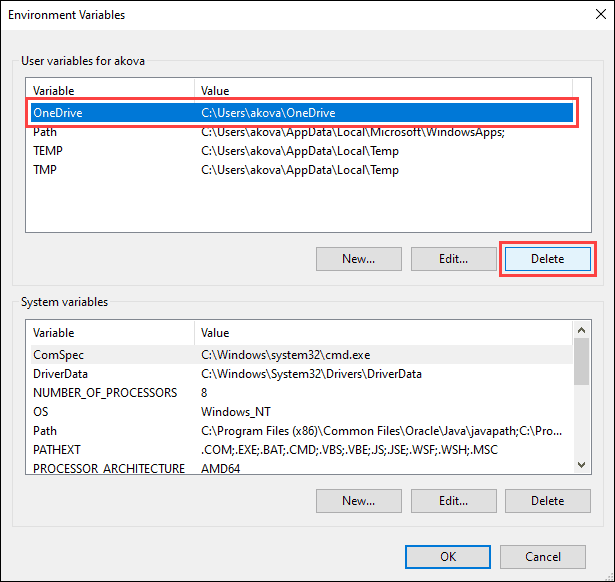
1. Locate the variable you want to unset in the appropriate section.
2. Click the variable to highlight it.
3. Click the Delete button to unset it.
Unset Environment Variables in Windows via Registry
When you add an environment variable in Windows, the key-value pair is saved in the registry. The default registry folders for environment variables are:
- user-specific variables: HKEY_CURRENT_USEREnvironment
- system-wide variables: HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESYSTEMCurrentControlSetControlSession ManagerEnvironment
Using the reg command allows you to review and unset environment variables directly in the registry.
Note: The reg command works the same in the Command Prompt and Windows PowerShell.
Use the following command to list all user-specific environment variables:
reg query HKEY_CURRENT_USEREnvironment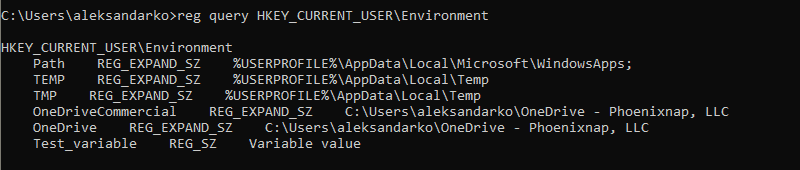
List all the system environment variables with:
reg query "HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESYSTEMCurrentControlSetControlSession ManagerEnvironment"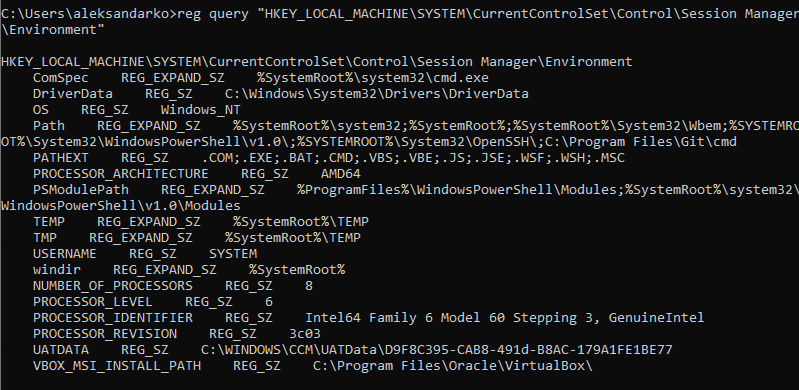
If you want to list a specific variable, use:
reg query HKEY_CURRENT_USEREnvironment /v [variable_name]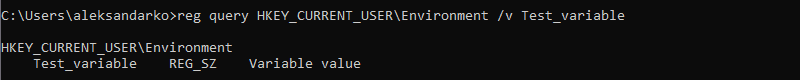
or
reg query "HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESYSTEMCurrentControlSetControlSession ManagerEnvironment" /v [variable_name]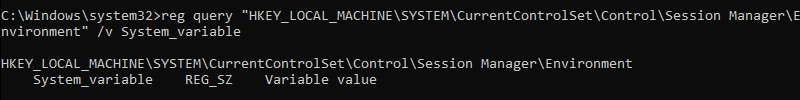
Where:
/v: Declares the intent to list a specific variable.[variable_name]: The name of the environment variable you want to list.
Use the following command to unset an environment variable in the registry:
reg delete HKEY_CURRENT_USEREnvironment /v [variable_name] /f
or
reg delete "HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESYSTEMCurrentControlSetControlSession ManagerEnvironment" /v [variable_name] /f
Note: The /f parameter is used to confirm the reg delete command. Without it, entering the command triggers the Delete the registry value EXAMPLE (Yes/No)? prompt.
Run the setx command again to propagate the environment variables and confirm the changes to the registry.
Note: If you don’t have any other variables to add with the setx command, set a throwaway variable. For example:
setx [variable_name] trash
Conclusion
After following this guide, you should know how to set user-specific and system-wide environment variables in Windows 10.
Looking for this tutorial for a different OS? Check out our guides on How to Set Environment Variables in Linux, How to Set Environment Variables in ZSH, and How to Set Environment Variables in MacOS.
Was this article helpful?
YesNo
If you want to see or check the names and values of Environment Variables in Windows 11 or Windows 10, here is how you can do that. There are mainly four ways to find almost everything about the Environment Variables in Windows 11/10, and this article explains all the possible methods.
What are Environment Variables in Windows 11/10
Environment Variables contain some information related to WindowsApps path, currently logged-in user’s information, Temporary folder’s path, running processes, etc. Although Windows 11/10 comes with a few of those, you can add or modify Environment Variables in Windows PC easily.
However, if you want to find those Environment Variables in Windows 11 or Windows 10, this guide will be handy for you. As said earlier, there are four ways – using the Windows Settings panel, using Command Prompt, using the Registry Editor, and using Windows PowerShell.
To see the names and values of Environment Variables in Windows 11/10, follow these methods:
- Using Windows Settings panel
- Using Command Prompt
- Using Registry Editor
- Using Windows PowerShell
To learn more about these steps, continue reading.
1] Using Windows Settings panel
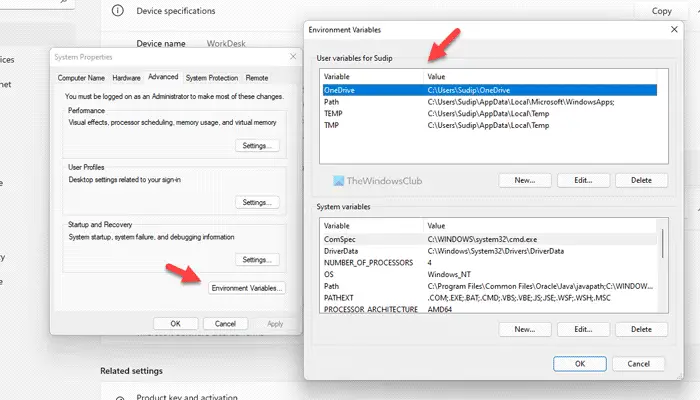
It is the most common method to find the names and values of the Environment Variables in Windows 11/10 PC. Earlier, it was possible to do the same using Control Panel. However, if you are using Windows 11, there is no need to go through the Control Panel since it will eventually open the Windows Settings.
Follow these steps to find the Environment Variables:
- Press Win+I to open Windows Settings.
- Go to System > About.
- Click on the Advanced system settings.
- Click the Environment Variables button.
- Find the Environment Variables.
Next, you need to click on each variable to find the details. It displays a detailed list in the System variables box.
2] Using Command Prompt
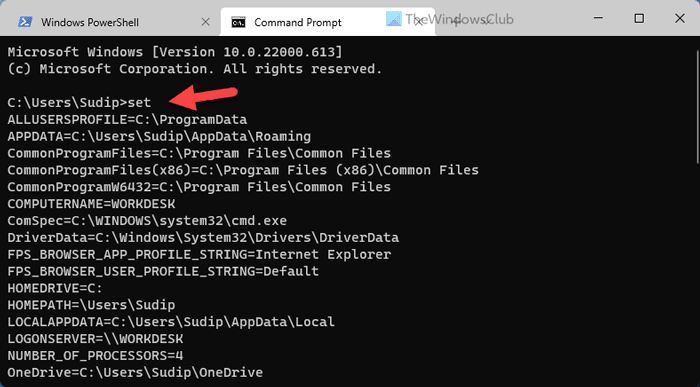
It is probably the easiest method to find almost everything about the Environment Variables on Windows 11/10 PC. For this purpose, we are going to use the Command Prompt instance in Windows Terminal. However, you can open the standalone Command Prompt window and enter the following command:
set
In case you do not know the process to open the Windows Terminal, you can press Win+X and select the Windows Terminal from the WinX menu.
3] Using Registry Editor
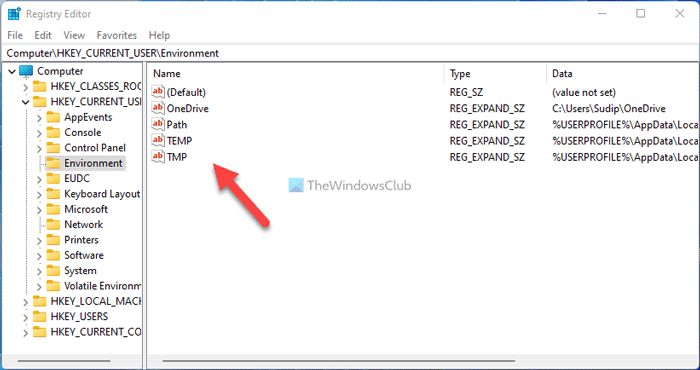
If you do not want to do much with the Environment Variables and want to check them only, you can use the Registry Editor. As these variables depend on the user profile, you need to open the HKEY_CURRENT_USER. To find the names and values of the Environment Variables using Registry Editor, do the following:
- Press Win+R to open the Run prompt.
- Type regedit and hit the Enter button.
- Click on the Yes button in the UAC prompt.
- Navigate to this path: HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Environment
- Find the variables.
In case you want to modify the existing variables using Registry Editor, you need to double-click on each of them and change them according.
4] Using Windows PowerShell
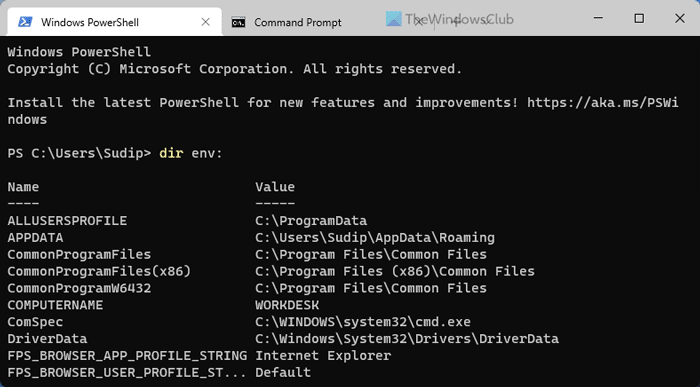
Like, Command Prompt, you can use Windows PowerShell to find the same Environment Variables on your Windows 11 or Windows 10 computer. However, it displays all the Environment Variables of all the users, whereas other methods display only the current user’s variables. That being said, the list could be lengthy since it may contain some variables, such as ComSpec, LOCALAPPDATA, HOMEDRIVE, HOMEPATH, ALLUSERSPROFILE, etc.
If you are fine with the lengthy list, you can use Windows PowerShell and enter this command:
dir env:
Like the Command Prompt method, you can open the standalone Windows PowerShell or the PowerShell instance in the Windows Terminal.
How do I view Environment Variables in Windows 11?
To view the Environment Variables in Windows 11, you can use any of the aforementioned methods. If you do not want to modify existing variables, you can use the Command Prompt method. For that, you can open the Command Prompt or the Command Prompt instance in Windows Terminal and enter this command: set. Then, it displays almost everything about the current user’s Environment Variables on your screen. Similarly, you can use the Windows PowerShell method to get the same thing done. In that case, you have to use this command: dir env:
How do I get a list of Environment Variables?
To get a list of Environment Variables, you have four techniques in your hands. However, using the Windows Settings method is probably the most fruitful method since you can view, add, or modify any Environment Variable without any issue. However, if you want to get a list only, you can use any of the other three methods. To choose one, you can open the Windows Terminal and enter this command in the PowerShell instance: dir env:. If you want to use the Command Prompt instance, you need to execute this command: set.
That’s all! Hope this guide helped.
Read: How to add or edit a PATH Environment Variable in Windows.
