В современных версиях Windows информация для запуска операционной системы храните в файле конфигурации загрузки BCD (Boot Configuration Data). В этом файле хранятся данные об установленной Windows и параметрах ее загрузки. Если файл BCD удален или поврежден, Windows перестает загружаться. Также вы не сможете загрузить Windows, если повреждена MBR запись на жестком диске. В этой статье мы покажем, как корректно пересоздать файл хранилища данных конфигурации загрузки BCD и
Master Boot Record
(MBR) на примере Windows 10 и 11.
Содержание:
- Ошибка “The boot configuration data file is missing some required information”
- Автоматическое восстановление конфигурации загрузчика Windows
- Идентификация разметки дисков и букв томов
- Восстановление загрузочного сектора MBR в Windows 10/11
- Пересоздание BCD файла загрузчика Windows 10
Ошибка “The boot configuration data file is missing some required information”
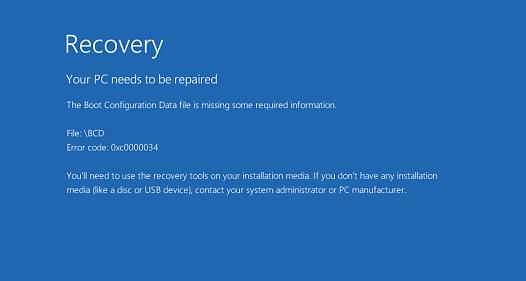
Если файл BCD поврежден, отсутствует, если вы удалили / отформатировали отдельный раздел диска с меткой System Reserved (и размером 500Мб), специальный OEM раздел, то скорее всего при попытке загрузить Windows появится такое сообщение:
Your PC needs to be repaired The Boot Configuration Data file is missing some required information File: \Boot\BCD Error code: 0xc0000034
Также ошибка может выглядеть так:
The Boot Configuration Data for your PC is missing or contain errors. File: \boot\bcd Error Code: 0xc000000f
При повреждении MBR может быть ошибка No operating system found.

Автоматическое восстановление конфигурации загрузчика Windows
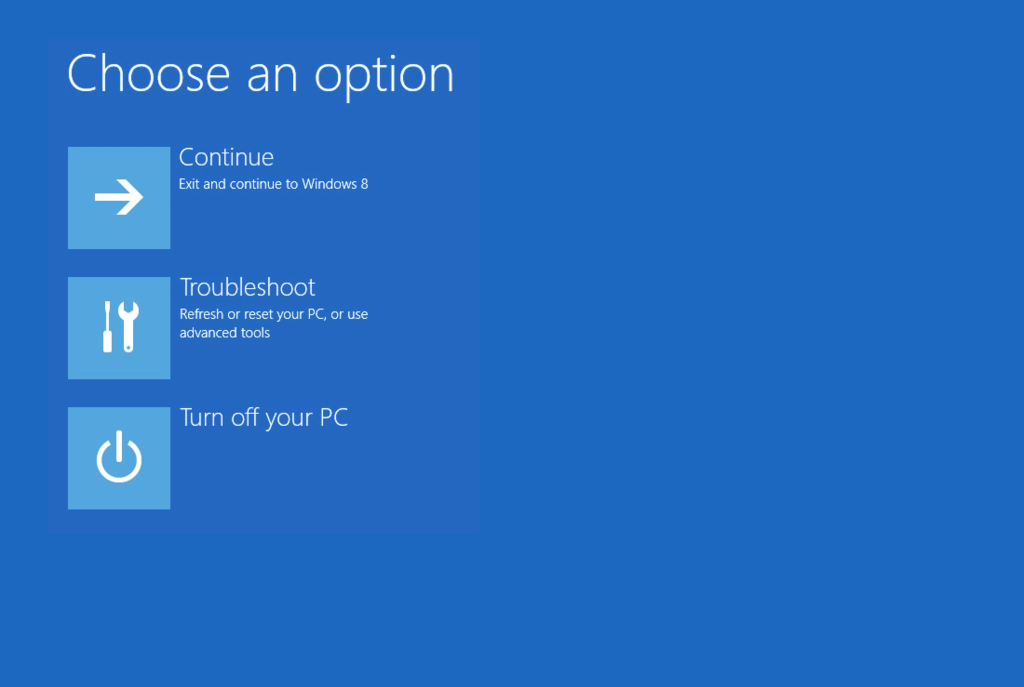
При появлении такой ошибки, в первую очередь попробуйте исправить проблему с загрузкой ОС с помощью режима автоматического восстановления (Startup Repair), который можно запустить из среды восстановления Windows RE.
Совет. Желательно периодически проверять работоспособность среды WinRE, и если она не работает, воспользоваться для ее восстановления методикой из статьи Восстановление среды WinRE в Windows.
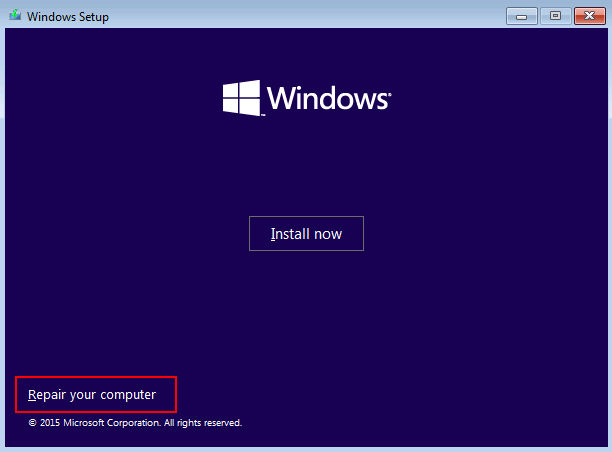
Если автоматическое восстановление с помощью Startup Repair не помогло решить проблему, вам нужно загрузиться с загрузочного или установочного диска с Windows или в среде WinRe (Repair your computer -> Troubleshoot -> Advanced options -> Command Prompt), запустить командную строку и попробовать полностью пересоздать файл конфигурации загрузчика BCD и обновить MBR запись.
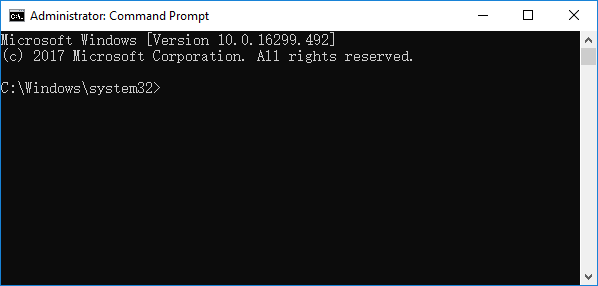
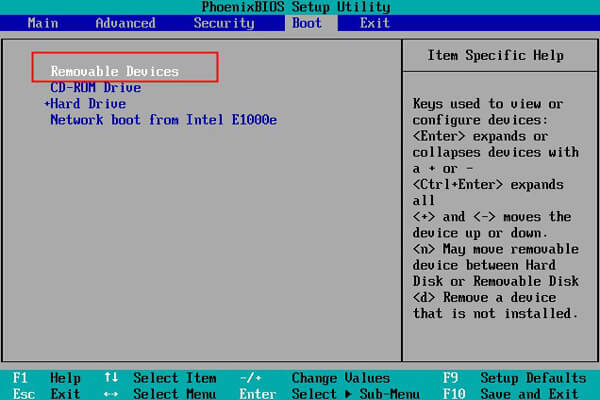
В этом примере я буду использовать установочный диск с Windows 10. Выберите в настройках BIOS первичным загрузочным устройство DVD диск или USB флешку с дистрибутивом Windows (в зависимости от того, с какого устройства вы хотите загрузить компьютер). Загрузитесь с установочного диска и на экране выбора языка установки нажмите сочетание клавиш Shift+F10. Перед вами откроется консоль командной строки.
Попробуйте восстановить BCD файл автоматически, выполнив команду:
bootrec /RebuildBCD
Перезагрузите компьютер и проверьте, загружается ли Windows (не забудьте изменить приоритет загрузочных устройств в BIOS). Если Windows не загружается, еще раз загрузитесь с установочного диска и откройте окно командной строки.
Идентификация разметки дисков и букв томов
Очень важно. Все инструкции, описанные ниже, подходят для обычных компьютеров с BIOS (или загружающихся в режиме UEFI legacy) и MBR таблицей разделов. На компьютерах с UEFI прошивками для пересоздания BCD нужно использовать следующе инструкци: восстановлению EFI загрузчика в Windows 10 или восстановление удаленного EFI раздела в Windows.
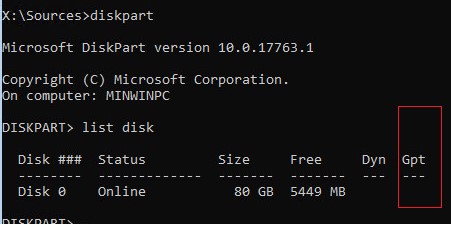
Как понять, используется ли у вас BIOS или UEFI система? Проще всего проверить тип таблицы разделов на диске, на котором установлена Windows: GPT или MBR. Для этого выполните команду:
diskpart
Затем выполните:
list disk
- Если у диска в столбце Gpt указана звездочка (*), значит на диске используется таблица разделов GPT. Это значит, что у вас компьютер с UEFI, и для восстановления загрузчика нужно использовать статью по ссылке выше.
- Если в столбце GPT звездочка отсутствует, значит у вас на диске таблица разделов MBR, и вы можете продолжить следовать данной инструкции.
Далее вам нужно идентифицировать локальные диски и разделы системы (скорее всего назначенные им буквы дисков будут отличаться от дисков, которые вы видели при работе в Windows). Проще всего это сделать с помощью утилиты diskpart. Выполните следующие команды:
diskpart
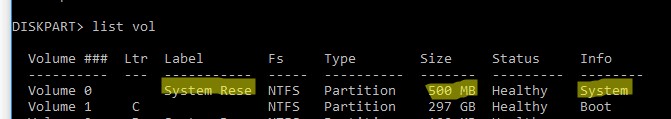
list vol
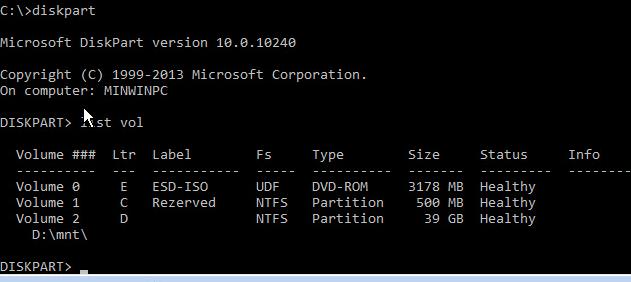
Перед вами появится список разделов в системе, назначенные им буквы дисков и их размер. В нашем случае к компьютеру подключен 1 жесткий диск, на котором имеются всего два раздела:
- Раздел System Reserved размером 500 Мб, которому назначена буква диска C:. На этом небольшом служебном разделе по-умолчанию хранится файл конфигурации загрузки BCD (подробнее)
- NTFS раздел размером 39 Гб, которому назначена буква D:. На этом разделе находится установленная Windows, программы и данные пользователя.
Важно. Запомните буквы дисков, назначенные разделам. Данные буквы дисков будут использоваться в последующих командах.
Восстановление загрузочного сектора MBR в Windows 10/11
С помощью утилиты bootrec.exe можно перезаписать данные в MBR и загрузочном секторе, поместим в них ссылки на загрузчик Windows (bootloader).
Попробуйте перезаписать основную загрузочную запись (MBR) системного раздела для совместимости с загрузчиком Windows (существующая таблица разделов не перезаписывается).
bootrec.exe /fixmbr
Добавьте в загрузочные секторы диска код для загрузки файла bootmgr ( диспетчера загрузки Windows):
bootsect.exe /nt60 all /force
Прежде, чем идти далее, попробуйте автоматически пересоздать конфигурацию загрузчика BCD командами (это самый простой способ для начинающих):
bootrec /FixBoot
– команда создает новый загрузочный сектор на системном разделе (перезаписывает загрузочную запись раздела PBR).
bootrec /ScanOs
– просканировать диски и найти установленные копии Window, которых нет в хранилище конфигурации загрузки
В случае успешного сканирования появится запрос на добавление записей о найденный Windows в BCD:
Scanning all disks for Windows installations. Please wait, since this may take a while... Successfully scanned Windows installations. Total identified Windows installations: 1 [1] D:\Windows Add installation to boot list? Yes/No/All:
bootrec /RebuildBcd
– пересоздать хранилище конфигурации загрузкика, добавить в BCD найденные на компьютере копии Windows/
После этого перезагрузите компьютер и проверьте загрузку Windows. Если ОС не загружается, следуйте инструкции.
Если команда bootsect.exe не найдена, попробуйте указать полный путь к ней:
X:\boot\bootsect.exe /nt60 all /force
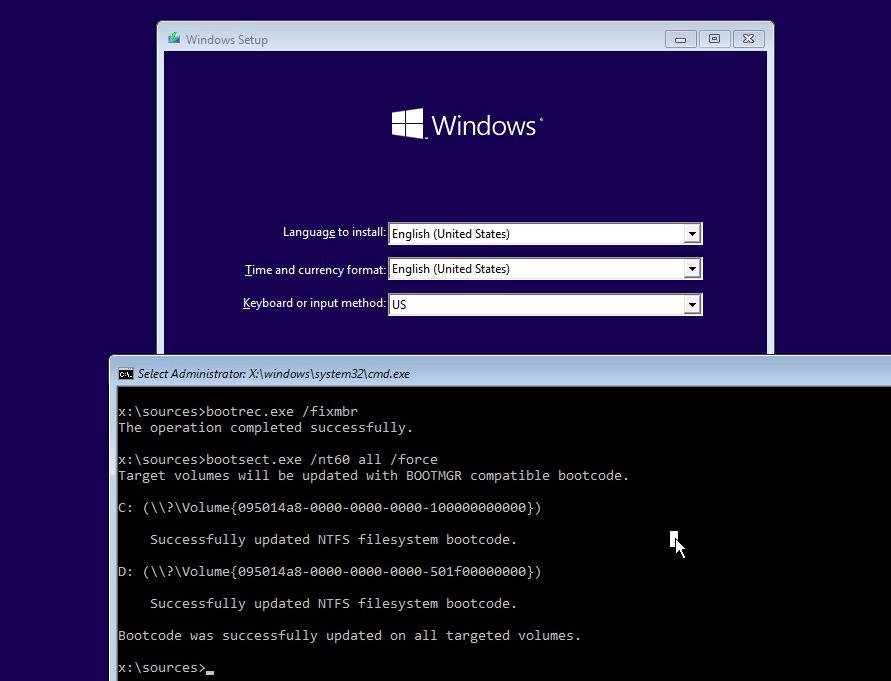
Пересоздание BCD файла загрузчика Windows 10
Далее с помощью команды BCDedit нужно создать новый файл с конфигурацией загрузчика (предполагается, что у вас нет резервной копии BCD).
Ваши дальнейшие действия зависят от того, есть ли на диске отдельный раздел System Reserved или нет. В командной строке выполните:
diskpart
list vol
Проверьте, есть ли на диске компьютера системный раздел System Reserved. Его можно идентифицировать по метке тома, либо более точнее по размеру (500 Мб для Windows 10+, 350 Мб для Windows 8.1 и 100 Мб для Windows 7).
- Если раздела нет (вы случайно удалили его), можно хранить конфигурацию загрузчика BCD на основном диске, где находится каталог Windows. Чтобы создать конфигурационные файл загрузчика BCD и Bootmgr на указанном диске, выполните команду:
bcdboot C:\Windows /S C:
Должно появится сообщение
Boot files successfully created
. - Если раздел System Reserved у вас имеется, удалите старый (поврежденный) файл BCD и создайте вместо него новый:
del c:\boot\bcd
Если разделу System Reserved не назначена буква диска (по-умолчанию), вы можете сами назначить ее с помощью diskpart.
Запустите:
diskpart
Выберите диск (в моем случае в компьютере имеется всего один жесткий диск, а вы можете вывести список дисков командой list disk):
select disk 0
На скриншота выше видно, что раздел с меткой System Reserverd называется Volume 1. Выберите его:
select volume 1
Назначьте букву диска (я назначил букву C:, но вы можете использовать любую другую букву, в этом случае измените путь в следующих командах):
assign letter C:
exit
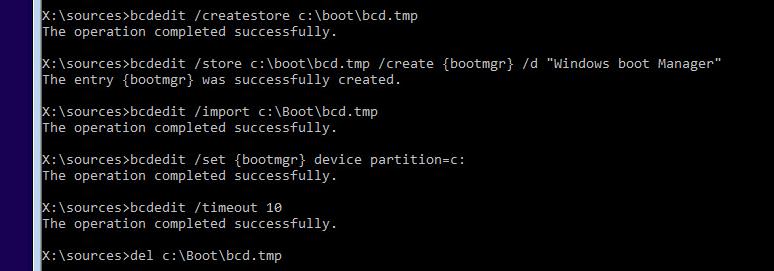
Создайте временный пустой файл bcd.tmp:
bcdedit /createstore c:\boot\bcd.tmp
Создайте запись для диспетчера загрузки bootmgr:
bcdedit.exe /store c:\boot\bcd.tmp /create {bootmgr} /d "Windows Boot Manager"
Импортируйте в BCD настройки из файла bcd.tmp:
bcdedit.exe /import c:\boot\bcd.tmp
Если команда bcdedit возвращает ошибку (
Ошибка создания хранилища. Отказано в доступе, access denied
) при доступе к файлу BCD, попробуйте снять с него атрибуты скрытый, read-only и системный:
attrib C:\Boot\BCD -s -h -r
Укажите, что загрузчик находится на служебном разделе System Reserved (ему назначена буква диска C: )
bcdedit.exe /set {bootmgr} device partition=c:
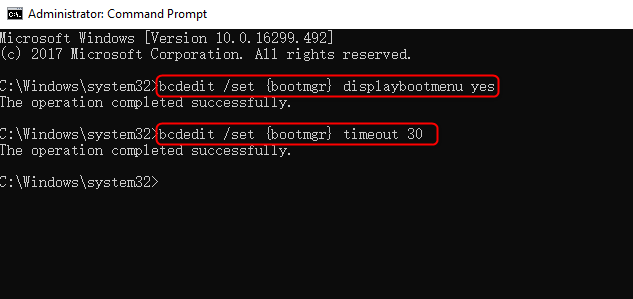
Настройте время ожидания при выборе ОС:
bcdedit.exe /timeout 10
Удалите временный файл:
del c:\boot\bcd.tmp
Итак, вы создали пустой BCD файл с параметрами загрузчика. Теперь в него нужно добавить записи об установленных на диске Windows .
Создайте в хранилище BCD новую запись для Windows 10:
bcdedit.exe /create /d "Windows 10" /application osloader
Команда должна вернуть уникальный идентификатор (GUID) данной записи загрузчика:
The entry {8a7f03d0-5338-11e7-b495-c7fffbb9ccfs} was successfully created.

Укажем, что bootmgr должен использовать данную запись по-умолчанию (после истечения времени ожидания при выборе ОС, для загрузки будет используется именно эта запись).
bcdedit /default {8a7f03d0-5338-11e7-b495-c7fffbb9ccfs}
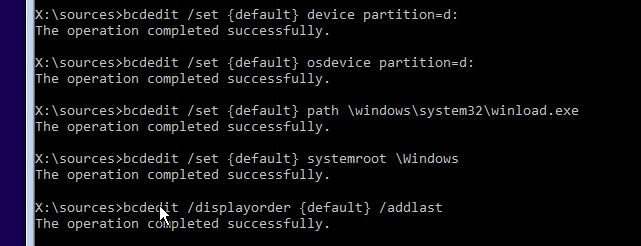
Теперь в новой записи загрузчика осталось указать пути к имеющейся на диске установленной копии Windows 10. Ранее мы определили, что в среде WinPE диску с установленной Windows присвоена буква D:. Используйте эту букву диска в следующих командах:
bcdedit.exe /set {default}device partition=d:
bcdedit.exe /set {default} osdevice partition=d:
bcdedit.exe /set {default} path \Windows\system32\winload.exe
bcdedit.exe /set {default} systemroot \Windows
Осталось сделать данную загрузочную запись в BCD видимой (по умолчанию она скрыта):
bcdedit.exe /displayorder {default} /addlast
Итак, мы полностью пересоздали загрузчик Windows 10 (обновили файл BCD и перезаписали загрузочный сектор MBR).
Теперь нужно сделать раздел, на котором находится файл BCD с конфигурацией загрузчика активным (BIOS передает управлению загрузчику ОС с активным MBR раздел). Допустим, разделы на вашем диске распределены так.
- Volume 0 – загрузочная/установочная флешка (ISO образ) диск, с которого вы загрузили компьютер
- Volume 1 – раздел System Reserved с BCD загрузчиком (размер 500 Мб)
- Volume 2 – раздел с файлами Windows (здесь находятся каталог Windows, Program Files, Users и т.д.)
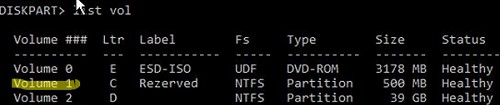
В этом примере нужно сделать активным раздел Volume 1 (в вашем случае определите номер раздела самостоятельно). Сделать раздел активным можно с помощью diskpart:
diskpart
list disk
sel disk 0
list vol
select volume 1
(файлы bootmgr и «\Boot\BCD» находятся на этом разделе)
active
exit
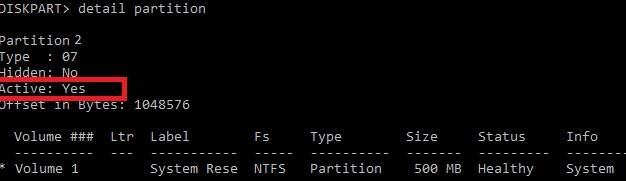
Проверьте, что раздел volume 1 теперь активный:
select vol 1
detail partition
Все верно (
Active: Yes
).
Теперь вы можете перезагрузить компьютер и убедится, что Windows загружается в штатном режиме.