The tasklist is the Windows command we use to list running processes on a Windows system. Often operates together with taskkill to terminate a running process or processes.
Open a command prompt (CMD or PowerShell), type tasklist, and press Enter:
tasklistThe following screenshot shows the default output of the tasklist command. It shows the Image Name (the name of the program that launched the process), process ID (PID), and the Memory Usage of each task.
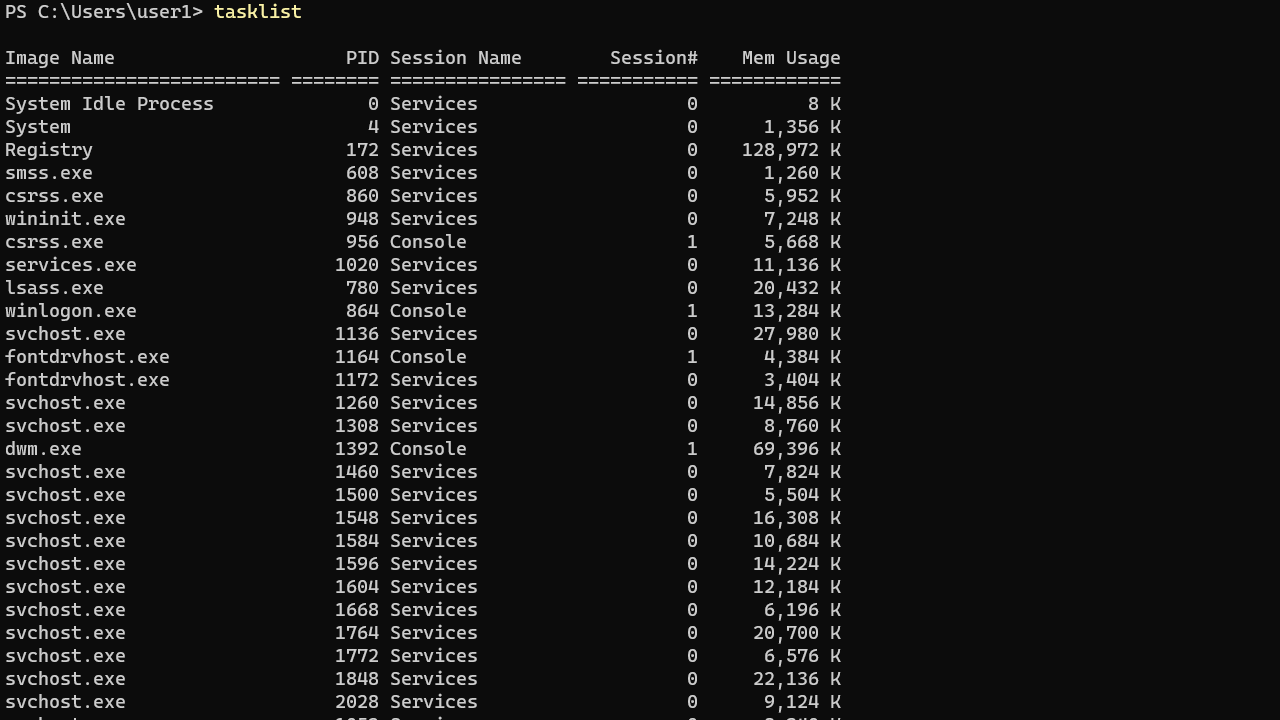
The list can be long, so you may want to pipe the output to the more command (press Enter key to scroll through).
tasklist | moreIf you want to end a process, use the taskkill command to terminate a running process using its process ID (PID) or image name.
taskkill /pid process-ID
taskkill /im image-nameFor example, the following command terminates all instances of the notepad process by its image name.
taskkill /im notepad.exeThe Windows tasklist command supports three output formats: Table (the default), List, and CSV. To change the output format, use the /fo option, as shown in the following example:
tasklist /fo listThe following command saves the current task list into a text file in CSV format:
tasklist /fo csv > tasklist.txtRunning Tasklist Command on a Remote Computer
We can use the tasklist command to list running tasks on a remote computer. Use the /s and /u options to specify the IP Address and username of the remote computer, respectively.
tasklist /s 192.168.1.100 /u user1However, the Firewall must be configured on the remote Windows system to allow the tasklist command. Click the link below for instructions on how to do it.
How to allow tasklist command from Windows Firewall
Command Options
The tasklist command has multiple options, which you can see by typing tasklist /?.
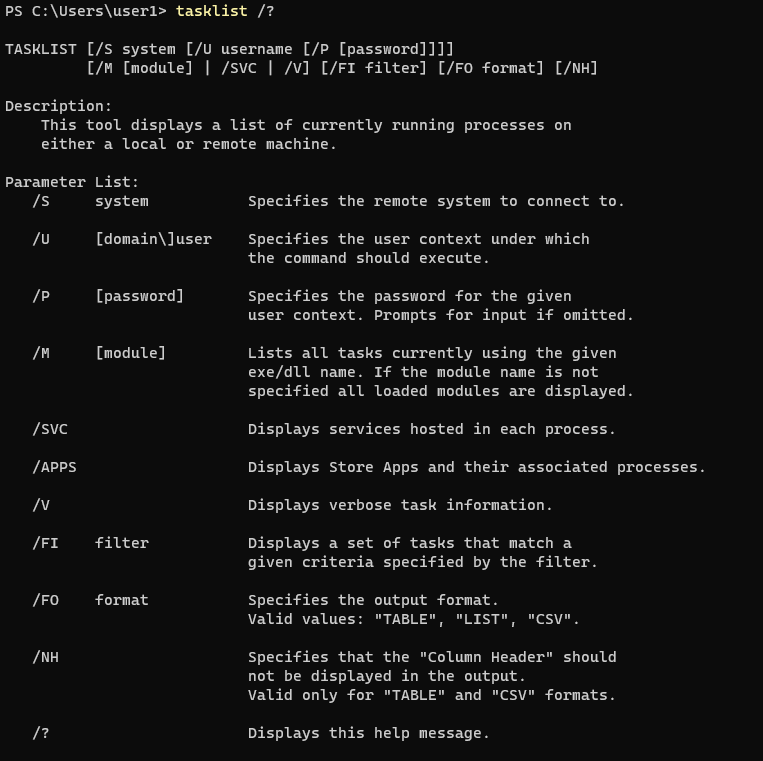
Examples
Use the /V option to display additional information, such as the program’s username and total CPU time:
tasklist /vShow the list of dll files used by each process:
tasklist /mDisplay the services provided by each process:
tasklist /svcUsing Filters to List Tasks That Match a Given Criteria
Using the /fi option, you can filter the command output to display the tasks that match the given criteria. The following section presents some examples.
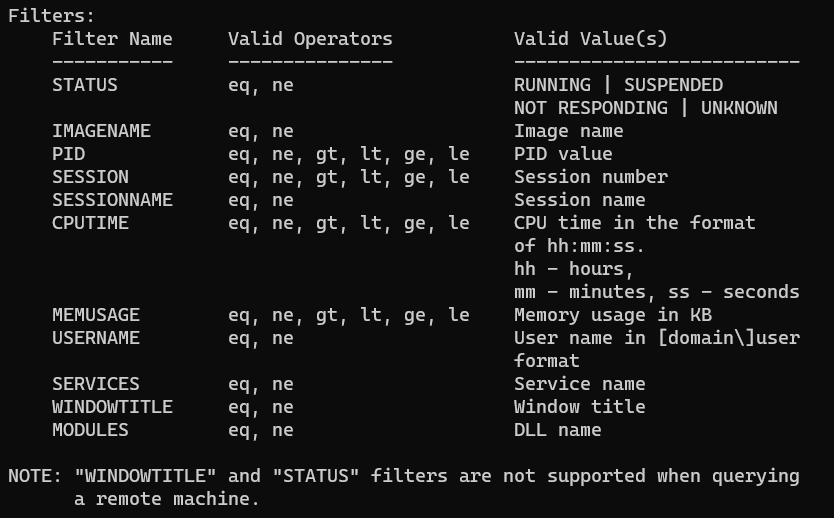
List running processes:
tasklist /fi "status eq running"List tasks that not responding:
tasklist /fi "status eq not responding"List the process that has PID of 0:
tasklist /fi "pid eq 0"List all processes owned by the user user1:
tasklist /fi "username eq user1"Display the services are related the svchost process(es):
tasklist /svc /fi "imagename eq svchost.exe"Show the processes using more than 10MB of memory:
tasklist /fi "memusage gt 10240"You can get a list of all filters by running the tasklist /? command.
Бывают ситуации, когда нужно посмотреть/завершить запущенные процессы из командной строки. Это бывает нужно если вы управляете компьютером удаленно из командной строки, либо если компьютер сильно загружен, и очень много времени уходит на запуск диспетчера задач. Еще бывает такое, что через диспетчер задач процесс не завершается. В этих случаях вам может помочь способ просмотра и завершения задач из командной строки, о чем я и расскажу ниже.
Для того что бы посмотреть запущенные процессы, существует утилита командной строки – tasklist, пример результата ее выполнения ниже на скриншоте. Из нее нам нужно запомнить имя процесса или PID, если несколько процессов запущенны с одним именем.

Для того что бы завершить задачу, можно воспользоваться утилитой taskkill, я его обычно использую с ключами /f /pid или /f /im, где после ключ /pid нужно указать ID процесса, после /im его имя
Например завершим все запущенные процессы google chrome, для этого нужно набрать команду:
taskkill /f /im chrome*
Что бы завершить один процесс internet explorer нужно набрать:
taskkill /f /pid 5192
Видео по теме
Способов управлять процессами в Windows предостаточно, и командная строка занимает в них далеко не первое место. Однако иногда бывают ситуации, когда все остальные инструменты кроме командной строки недоступны, например некоторые вредоносные программы могут блокировать запуск Task Manager и подобных ему программ. Да и просто для общего развития полезно знать способы управления компьютером из командной строки.
Для управления процессами в командной строке есть две утилиты — tasklist и taskkill. Первая показывает список процессов на локальном или удаленном компьютере, вторая позволяет их завершить. Попробуем …
Если просто набрать команду tasklist в командной строке, то она выдаст список процессов на локальном компьютере.
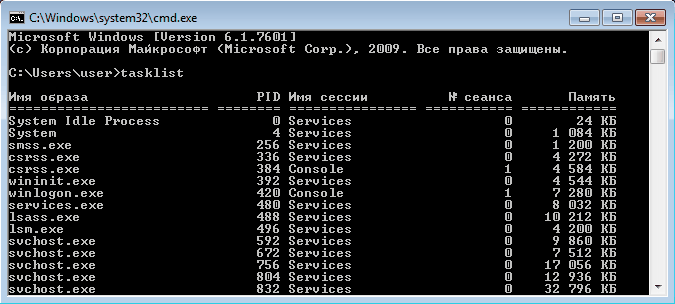
По умолчанию информация выводится в виде таблицы, однако ключ /fo позволяет задать вывод в виде списка или в формате CSV, а ключ /v показывает более подробную информацию о процессах, например команда tasklist /v /fo list выведет подробное описание всех процессов в виде списка.
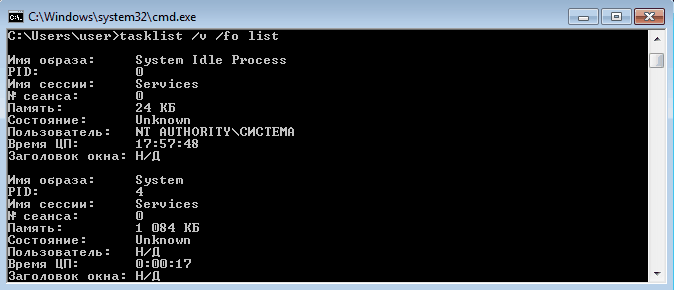
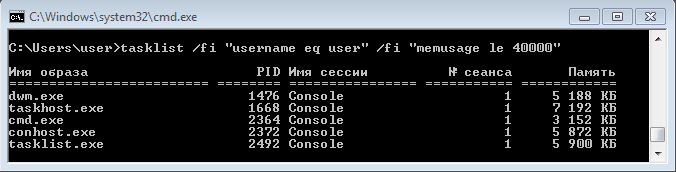
Список получится довольно большой, поэтому попробуем уточнить запрос. Для этого используем ключ /fi , который позволяет использовать фильтры для вывода данных, например команда tasklist /fi ″username eq user″ /fi ″memusage le 40000″ выводит список процессов пользователя user, которые потребляют не больше 40Мб памяти.
Найдя процессы, которые необходимо завершить, воспользуемся командой taskkill. Завершать процессы можно по имени, идентификатору процесса (PID) или задав условия с помощью фильтров. Для примера запустим несколько экземпляров блокнота (notepad.exe) и попробуем завершить его разными способами.
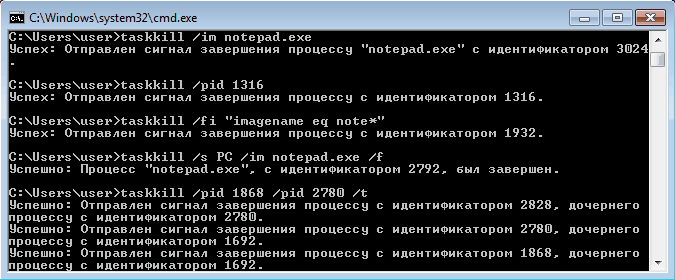
Ключ /f завершает процесс принудительно, а /t завершает все дочерние процессы.
Полную справку по командам tasklist и taskkill можно получить, введя их с ключом /?
Теперь пустим в ход тяжелую артиллерию — PowerShell. Его можно запустить не выходя из командной строки. Для получения списка процессов используем командлет Get-Process.
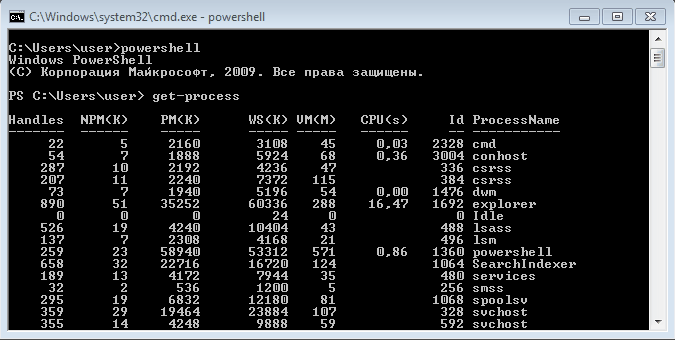
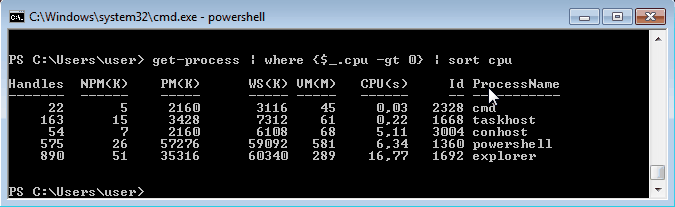
Чтобы не выводить весь список процессов можем воспользоваться командлетом Where-Object, который задает фильтр для выводимой информации. Для примера выведем список процессов, которые загружают процессор и отсортируем их по возрастанию нагрузки с помощью команды:
Get-Process | where {$_.cpu -gt 0} | sort cpu
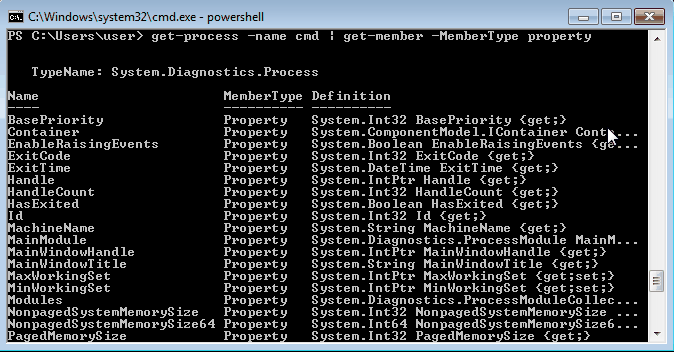
С помощью PowerShell мы можем получить любую информацию о любом процессе. В качестве примера возьмем процесс cmd и выведем список его свойств командой:
Get-Process -Name cmd | Get-Member -Membertype property
Выбираем те свойства, что нам интересны ( в примере имя и ID процесса, путь к файлу, используемые модули и время запуска) и выводим их в виде списка командой:
Get-Process -Name cmd | Format-List name, id, path, modules, starttime
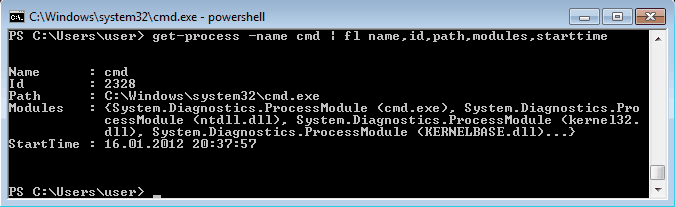
Таким образом мы можем посмотреть когда и кем был запущен процесс, сколько он потребляет ресурсов, где находится исполняемый файл и еще много различной информации.
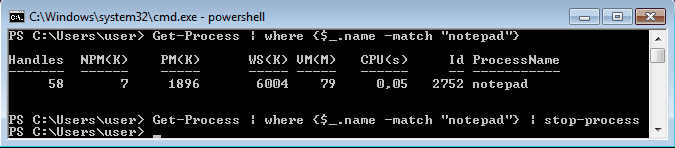
Для завершения процесса в PowerShell есть командлет Stop-Process. Он завершает указанный процесс по его имени или идентификатору. Однако мы поступим по другому и передадим результат выполнения командлета Get-Process по конвейеру:
Get-Process | where {$_.name -match ″notepad″} | Stop-Process
Get-Process не может показать процессы на удаленном компьютере, для этого воспользуемся командлетом Get-WmiObject , например посмотрим процессы на удаленном компьютере PC командой:
Get-WmiObject win32_process -computername PC | ft name, processid, description

Для боле полного ознакомления с PowerShell можно воспользоваться встроенной справкой, для вызова справки нужно набрать Get-Help ″имя командлета″
Ну и для полноты обзора рассмотрим еще одно средство для управления процессами из командной строки. Это утилиты Pslist и Pskill входящие в состав пакета PSTools от компании Sysinternals.
Эти утилиты не требуют специальной установки, достаточно просто скопировать их на диск. Для запуска нужно зайти в папку с утилитами и ввести в командной строке необходимую команду.
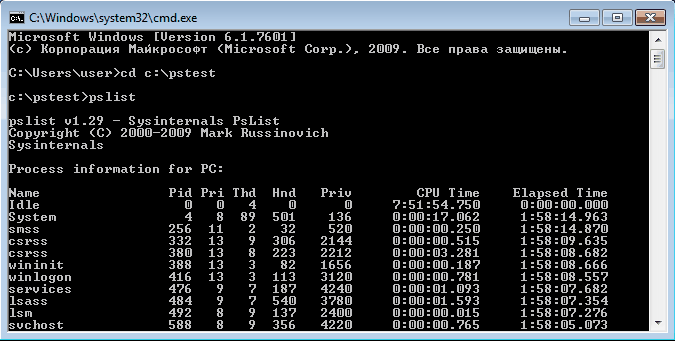
Pslist может выводить информацию о процессах по имени или ID, например командой pslist notepad -x выведем подробную информацию о нашем «многострадальном» блокноте.
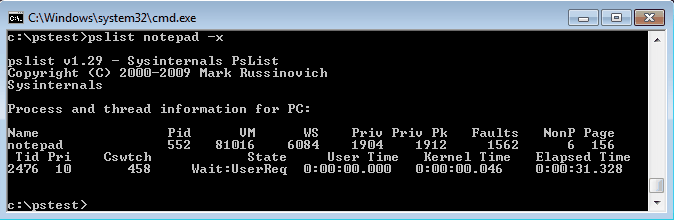
Особенностью утилиты Pslist является режим task-manager. В этом режиме информация автоматически обновляется, причем можно задать время работы и интервал обновления. Запускается режим ключом -s , например командой tasklist -s -r 10 запускаем режим программу в режиме task-manager с обновлением раз в 10 сек.
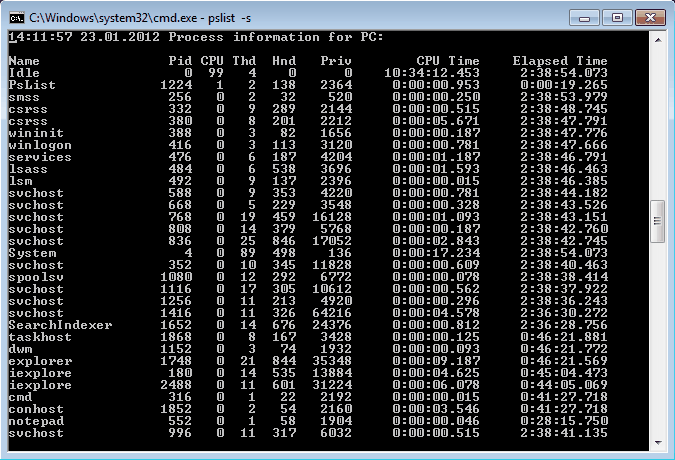
Завершение процесса программой pskill предельно просто, вводим команду и имя (или ID) процесса и все.
Справку по утилитам Pslist и Pskill можно посмотреть, введя команду с ключом /?
И еще, все манипуляции с процессами необходимо выполнять с правами администратора, для этого командную строку требуется запускать с повышением привилегий.
In Windows, we can get the list of processes running on the system from command prompt also. We can use ‘tasklist‘ command for this purpose.
Using this command we can selectively list the processes based on criteria like the memory space used, running time, image file name, services running in the process etc. Below you can find the syntax and examples for various cases.
Get the list of all the process running on the system
tasklist
Get the list of process using memory space greater than certain value.
tasklist /fi "memusage gt memorysize"
Memory size should be specified in KB
For example, to get the list of processes occupying more than 30MB of memory, we can run the below command.
tasklist /fi "memusage gt 30000"
Find the list of processes launched by a user
tasklist /fi "username eq userName"
Find the memory usage of a specific process
tasklist /fi "pid eq processId"
Example:
c:\>tasklist /fi "pid eq 6544" Image Name PID Session Name Session# Mem Usage ========================= ======== ================ =========== ============ WmiPrvSE.exe 6544 Services 0 8,936 K
Find the list of not responding processes
tasklist /fi "status eq not responding"
example:
c:\>tasklist /fi "status eq not responding" Image Name PID Session Name Session# Mem Usage ========================= ======== ================ =========== ============ rundll32.exe 3916 Console 1 7,028 K
Get the list of services running in a process
tasklist /svc /fi "pid eq processId"
Example:
c:\>tasklist /svc /fi "pid eq 624"
Image Name PID Services
========================= ======== ============================================
lsass.exe 624 EFS, KeyIso, Netlogon, ProtectedStorage,
SamSs, VaultSvc
c:\>
Get list of processes running for more than certain time
tasklist /fi "cputime gt hh:mm:ss"
example:
Get the list of processes that have been running from more than an hour and 20 minutes.
c:\>tasklist /fi "cputime gt 01:20:00" Image Name PID Session Name Session# Mem Usage ========================= ======== ================ =========== ============ System Idle Process 0 Services 0 24 K SynTPEnh.exe 4152 Console 1 8,080 K firefox.exe 1740 Console 1 857,536 K c:\>
Find processes that are running a specified image file:
tasklist /fi "imagename eq imageName"
Example:
c:\>tasklist /fi "imagename eq firefox.exe" Image Name PID Session Name Session# Mem Usage ========================= ======== ================ =========== ============ firefox.exe 1740 Console 1 812,160 K c:\>
Find the process running a specific service
tasklist /fi "services eq serviceName"
example:
c:\>tasklist /fi "services eq webclient" Image Name PID Session Name Session# Mem Usage ========================= ======== ================ =========== ============ svchost.exe 1052 Services 0 20,204 K c:\>
Related Posts:
How to kill a process from windows command line.
All processes in Windows can be listed on the command-line prompt (CMD) using the tasklist command.
The tasklist command in Windows is the Linux ps command equivalent.
In this note i am showing how to list all processes on the command-line prompt (CMD) in Windows using the tasklist command, how to sort the process list and how to find a specific process by name.
Cool Tip: List services in Windows from the CMD & PowerShell! Read more →
Get the list of all running processes in Windows:
C:\> tasklist
Sort the list of processes by name:
C:\> tasklist /NH | sort
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
/NH |
Hide column names (header) from result set output |
Filter the list of processes by a process name (case insensitive):
C:\> tasklist /NH | findstr /I myProcess
Cool Tip: Kill a hanging process in Windows from the CMD! Read more →
Was it useful? Share this post with the world!
