Администратор файлового сервера Windows может вывести список открытых файлов в общей сетевой папке и принудительно закрыть заблокированные файлы, открытые пользователями в монопольном режиме. Если пользователь открыт файл в общей сетевой SMB папке на сервере на чтение и запись и забыл его закрыть (ушел домой, в отпуск), другие пользователи не смогут внести изменения в файл.
В этой статье мы рассмотрим, как получить список открытых файлов на файловом сервере Windows и пользователей, которые их используют, а также способы сброса файловых сессий для разблокировки открытых файлов.
Содержание:
- Вывод списка открытых файлов в сетевой папке Windows
- Кто открыл файл в общей сетевой папке на сервере Windows?
- Принудительно закрыть открытый файл на сервере Windows
- Как удаленно закрыть открытые по сети файлы с помощью PowerShell?
Вывод списка открытых файлов в сетевой папке Windows
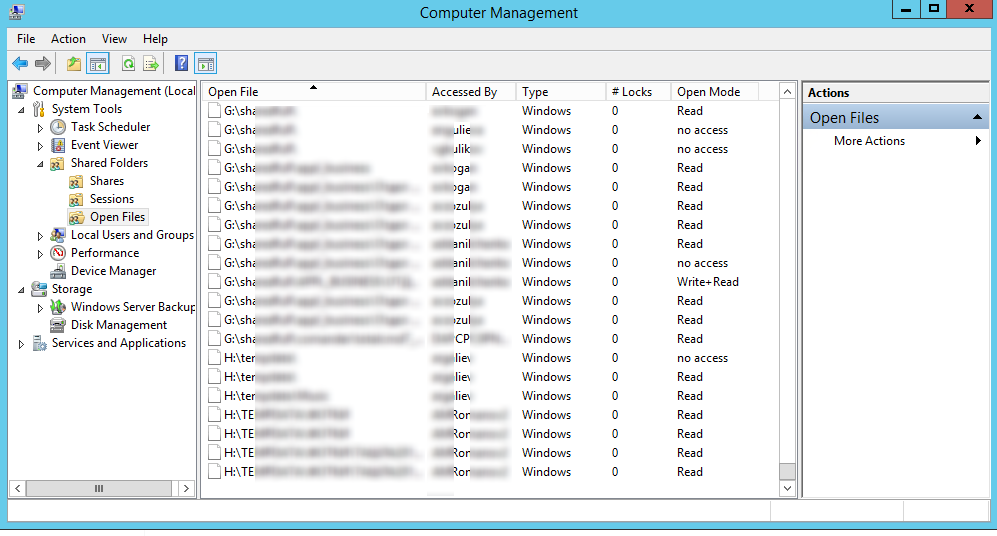
Список открытых по сети файлов в Windows можно получить с помощью графической консоли Computer Management (Управление компьютером).
- Откройте консоль
compmgmt.msc
и перейдите в раздел System Tools -> Shared Folders -> Open files (Служебные программы -> Общие папки -> Открыты файлы); - В правой части окна отображается список открытых файлов. Здесь указаны локальный путь к файлу, имя учетной записи пользователя, количество блокировок и режим, в котором открыт файл (Read или Write+Read).
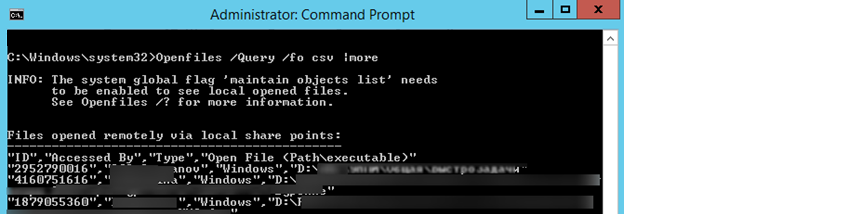
Также вы можете вывести список открытых на сервере файлов из командной строки:
Openfiles /Query /fo csv
Команда возвращает номер сессии, имя пользователя, количество блокировок и полный путь к файлу.
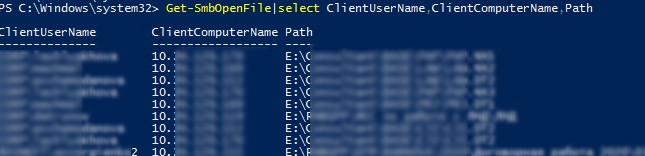
Cо списком открытых файлов на сервере удобнее работать с помощью PowerShell командлета Get-SmbOpenFile:
Get-SmbOpenFile|select ClientUserName,ClientComputerName,Path,SessionID
В выводе команда содержится имя пользователя, имя (IP адрес) удаленного компьютера, с которого открыт файл), имя файла и ID файловой сессии.
Кто открыл файл в общей сетевой папке на сервере Windows?
Чтобы удаленно определить пользователя, который открыл (заблокировал) файл cons.adm в сетевой папке на сервере mskfs01, выполните команду:
Openfiles /Query /s mskfs01 /fo csv | find /i "cons.adm"
Ключ /i используется, чтобы выполнялся поиск без учета регистра в имени файла.
Можно указать только часть имени файла. Например, чтобы узнать, кто открыл xlsx файл, в имени которого есть строка farm, воспользуйтесь таким конвейером:
Openfiles /Query /s mskfs01 /fo csv | find /i "farm"| find /i "xlsx"
С помощью PowerShell также можно получить информацию о пользователе, который открыл файл. Например:
Вывести все открытые по сети exe файлы:
Get-SmbOpenFile | Where-Object {$_.Path -Like "*.exe*"}
Найти открытые файлы по части имени:
Get-SmbOpenFile | Where-Object {$_.Path -Like "*защита*"}
Вывести все файлы, открытые определенным пользователем:
Get-SMBOpenFile –ClientUserName "corp\aaivanov" |select ClientComputerName,Path
Найти файлы, которые открыли с указанного компьютера:
Get-SMBOpenFile –ClientComputerName 192.168.12.170| select ClientUserName,Path
Принудительно закрыть открытый файл на сервере Windows
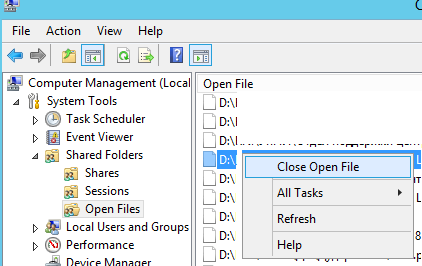
Можно закрыть открытый файл через консоль Computer Management. Найдите файл в списке секции Open Files, выберите в контекстном меню пункт “Close Open File”.
Если на сервере по сети открыты сотни файлов, то найти нужный файл в графической консоли довольно сложно. Лучше использовать инструменты командной строки.
Закрыть файл можно, указав ID его SMB сессии. Получить ID сессии файла:
Openfiles /Query /fo csv | find /i "report2023.xlsx"
Теперь можно принудительно отключить пользователя по полученному идентификатору SMB сессии:
Openfiles /Disconnect /ID 3489847304

SUCCESS: The connection to the open file "D:\path\REPORT2023.XLSX" has been terminated.
Вы разблокировали открытый файл и теперь его могут открыть другие пользователи.
Можно принудительно сбросить все сессии и освободить все файлы, открытые определённым пользователем:
openfiles /disconnect /s mskfs01 /u corp\aivanova /id *
Можно закрыть открытый файл по ID сессии с помощью PowerShell командлета Close-SmbOpenFile.
Close-SmbOpenFile - SessionId 3489847304
Найти и закрыть открытый файл одной командой:
Get-SmbOpenFile | where {$_.Path –like "*report2023.xlsx"} | Close-SmbOpenFile
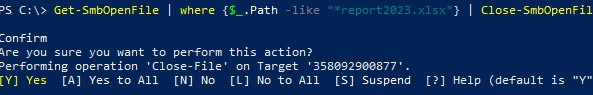
Для подтверждения сброса сессии и освобождения отрытого файла нажмите
Y
->
Enter
.
Чтобы закрыть файл без предупреждения, добавьте параметр
-Force
в последнюю команду.
С помощью Out-GridView можно сделать простую графическую форму для поиска и закрытия файлов. Следующий скрипт выведет список открытых файлов. Администратору нужно с помощью фильтров в таблице Out-GridView найти и выделить нужные файлы, а затем нажать ОК. В результате выбранные файлы будут принудительно закрыты.
Get-SmbOpenFile|select ClientUserName,ClientComputerName,Path,SessionID| Out-GridView -PassThru –title “Select Open Files”|Close-SmbOpenFile -Confirm:$false -Verbose
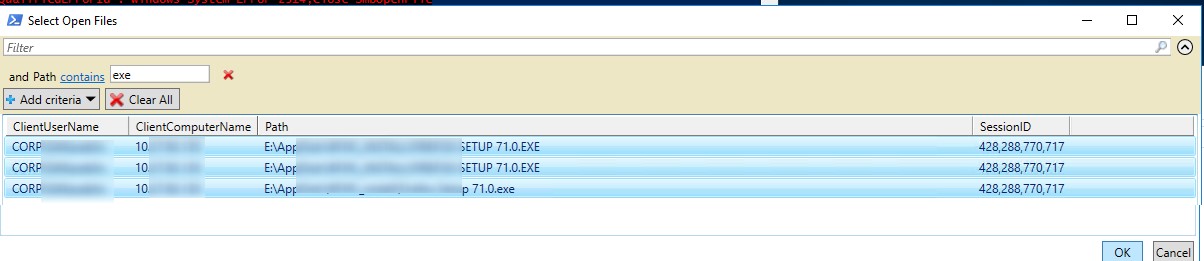
Принудительное закрытие открытого файла на файловом сервере, вызывает потерю несохраненных пользователем данных. Поэтому команды openfiles /disconnect и
Close-SMBOpenFile
нужно использовать с осторожностью.
Как удаленно закрыть открытые по сети файлы с помощью PowerShell?
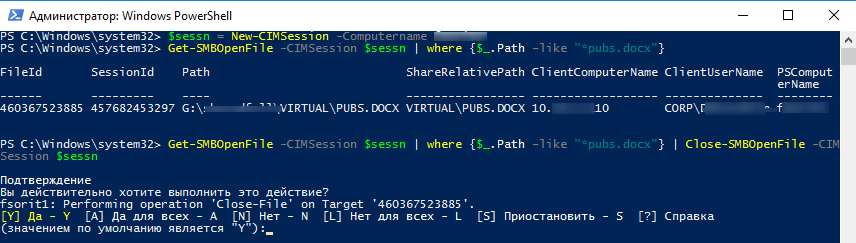
Командлеты Get-SMBOpenFile и Close-SmbOpenFile можно использовать чтобы удаленно найти и закрыть открытые файлы. Сначала нужно подключиться к удаленному SMB серверу Windows через CIM сессию:
$sessn = New-CIMSession –Computername mskfs01
Также вы можете подключаться к удаленному серверам для запуска команд через командлеты PSRemoting: Enter-PSSession или Invoke-Command .
Следующая команда найдет сессию для открытого файла
*pubs.docx
и завершит ее.
Get-SMBOpenFile -CIMSession $sessn | where {$_.Path –like "*pubs.docx"} | Close-SMBOpenFile -CIMSession $sessn
Подтвердите закрытие файла, нажав
Y
. В результате вы разблокировали открытый файл. Теперь его могут открыть другие пользователи.
С помощью PowerShell вы можете закрыть и осведомить на файловом сервере все файлы, открытые определенным пользователем (пользователь ушел домой и не освободил файлы). Например, чтобы сбросить все файловые сессии для пользователя ipivanov, выполните:
Get-SMBOpenFile -CIMSession $sessn | where {$_.ClientUserName –like "*ipivanov*"}|Close-SMBOpenFile -CIMSession $sessn
Can’t take ownership of folder as DomainAdmin – Access denied.
Once in a while you as an admin it’s possible that you come across a folder on the fileserver where you need to set permissions for other users, but you as DomainAdmin have no permssions to. When you want to set the permissions you get’Access denied’. Most of the time there is a simple fix, […]
DeploymentSettings or RDS arguments empty for (new) remote desktop collection
I needed to create a additional collection on the connection broker for a test environment. When the pool was created on the connection broker, when download the .rdp file from the RDWeb the .rdp file would be missing a lot of details and the computername field also would be empty. I’ve tried a lot of […]
The OpenFiles command helps
you track open shared files on any system of a network. This utility has
a number of purposes, but the most important is to ensure that a system
has no shared files open before shutting it down. Even though Windows
performs an orderly shutdown on the server, the client may have data
stored in a local cache that could get lost when the server shuts down.
You could also use this utility to look for signs of unwanted intrusion
(either locally or from a remote source). A shared file that you can’t
account for could indicate the activities of a cracker or a disgruntled
employee. The OpenFiles utility has three modes of operation,
DISCONNECT, QUERY, and LOCAL, which are discussed in the sections that
follow.
1. Disconnect
This mode disconnects a
user or closes a file. You can use this mode to force a closure. In some
cases, you might find this necessary when an application terminates
abnormally and leaves the file in an uncertain state. This mode uses the
following syntax:
OPENFILES /Disconnect [/S system [/U username [/P [password]]]]
{[/ID id] [/A accessedby] [/O {Read | Read/Write | Write}]}
[/OP openfile]
The following list describes each of the command line arguments.
Always disconnect
users or close files with care. Pursue every other possible means of
disconnecting the user or closing the file before you use the DISCONNECT
mode. Disconnecting users or closing files using this technique may
corrupt the data file or cause the application to lose data because this
method doesn’t consider any of the data that appears in the application
cache.
/S
system-
Specifies the remote system that you want to check. In most cases, you’ll also need to supply the /U and the /P command line switches when using this switch.
/U[domain\]user
-
Specifies the
username on the remote system. This name may not match the username on
the local system. You’ll need to supply a domain name when working with a
domain controller.
/P[password]
-
Specifies the
password for the given user. You can provide the command line switch
without specifying the password on the command line in cleartext. The
system prompts you for the password. Using this feature can help you
maintain the security of passwords used on your system.
/ID
id-
Specifies the
identifier of the file to disconnect. You may use the * wildcard to
disconnect all currently shared files by identifier. Use the OPENFILES
/Query mode to obtain the list of files currently open on the system,
including the file identifier.
/A
username-
Disconnects all files
opened by a particular user as specified by username. You can use the *
wildcard to disconnect all currently shared files by username. Use the
OPENFILES /Query mode to obtain the list of files currently open on the
system, including the username.
/O {Read | Read/Write | Write}-
Closes all files
opened in a particular mode. The valid values include read, read/write,
and write. You can use the * wildcard to disconnect all currently shared
files by open mode. Use the OPENFILES /Query /V mode to obtain the list
of files currently open on the system, including the open mode. Note
that the standard display doesn’t include the open mode, so you must
specify the /V command line switch.
/OP openfile-
Disconnects
all open file connections created by a particular open filename. You
can use the * wildcard to disconnect all currently shared files by
filename. Use the OPENFILES /Query mode to obtain the list of files
currently open on the system, including the name of the open file.
2. Query
Use this mode to obtain a list of the files currently open on a system. This mode uses the following syntax:
OPENFILES /Query [/S system [/U username [/P [password]]]]
[/FO {TABLE | LIST | CSV}] [/NH] [/V]
The following list describes each of the command line arguments.
/S
system-
Specifies the remote system that you want to check. In most cases, you’ll also need to supply the /U and the /P command line switches when using this switch.
/U[domain\]user
-
Specifies the
username on the remote system. This name may not match the username on
the local system. You’ll need to supply a domain name when working with a
domain controller.
/P[password]
-
Specifies the
password for the given user. You can provide the command line switch
without specifying the password on the command line in cleartext. The
system prompts you for the password. Using this feature can help you
maintain the security of passwords used on your system.
/FO {TABLE | LIST | CSV}-
Defines the
output provided by the utility. The table format is normally the easiest
to view on screen. The table columns define the values for output,
while each row contains one driver entry. The CSV output provides the
best method for preparing the data for entry in a database. Use
redirection to output the CSV data to a file and then import it to
your database. The list format provides one data element per line. Each
group of data elements defines one driver. The utility separates each
driver by one blank line. Some people find the list format more readable
when working in verbose mode since the table format requires multiple
lines for each entry (the lines wrap).
/NH-
Forces the utility
to display the data without a column header. You can only use this
command line switch with the table and CSV formats. Omitting the header
makes it easier to incorporate the data in a report or import it into a
database.
/V-
Displays
detailed file information. The standard display includes the file
identifier, accessed by information, file type, and filename complete
with path. The extended information provided by this command line switch
includes the hostname (server), number of locks, and the mode used to
open the file (read, read/write, or write).
15.9.3. Local
This mode uses the following syntax:
OPENFILES /Local [{ ON | OFF }]
The following describes the command line argument.
{ ON | OFF }-
Enables
or disables the «maintain objects list» system global flag. The state
of this flag determines whether the system tracks the state of local
file handles. Enabling this flag adds overhead, which reduces
performance, and also lets you track the status of shared files on your
system. Calling the OPENFILES /Local mode without using this command
line switch at all displays the current flag status, which is disabled
on Windows systems.
Before rebooting a server, you should see who has open files so you won’t corrupt data or knock a user offline.
Server 2008 has moved where you can view these.
To see the open files, right click on computer. Select Manage. Click Roles – File Services – Share and storage management. Choose Action and then manage open files.
About TCAT Shelbyville IT Department
The Tennessee College of Applied Technology — is one of 46 institutions in the Tennessee Board of Regents System, the seventh largest system of higher education in the nation. This system comprises six universities, fourteen community colleges, and twenty-six Applied Technology Colleges.
|
|

|
|
Правила раздела Windows
1. Указывайте версию Вашей ОС.
2. Запрещается размещать запросы и ссылки на кряки, серийники и т.п., а также вопросы нарушения лицензии ПО и его взлома.
3. Не разрешается давать советы из разряда «Поставь Linux».
4. Переустановка ОС — крайнее и безотказное лекарство, которое знают все. В таких советах никто не нуждается.
5. При публикации скриптов пользоваться тегами code. Тип подсветки кода выбирать строго в соответствии с языком публикуемого кода.
6. Прежде чем задать вопрос, обязательно загляните в FAQ и следуйте написанным рекомендациям для устранения проблемы. И если не помогло, а поиск по разделу не дал результатов — только тогда задавайте вопрос на форуме.
7. Вопросы, связанные с проблемами ПО, задавайте в разделе Программное обеспечение
Как посмотреть список открытых файлов по сети
- Подписаться на тему
- Сообщить другу
- Скачать/распечатать тему
|
|
|
|
Как сделать сабж в Win 2008R2. |
|
AntonGorod |
|
|
Цитата ^D^ima @ Как посмотреть список открытых файлов по сети список открытых файлов, простите где? на файл сервере (роль такая отдельная есть)? |
|
^D^ima |
|
|
Ну да. На сервере открыли файлы из расшаренной папки по SMB. Как с этого сервере посмотреть список открытых файлов. И ещё список открытых файлов опубликованных приложений(WebApp). На 2008 нашел только это: Но там показаны открытые файлы терминальных пользователей. Файлов, открытых по сети, или файлов, открытых опубликованными приложениями нет. Или таких встроенных средств нет? Сообщение отредактировано: ^D^ima — |
|
AntonGorod |
|
|
openfiles /local on Добавлено Цитата ^D^ima @ Но там показаны открытые файлы терминальных пользователей. правильно говорить: файлы открытые в виртуальных окружениях пользователей. Ты эта, посмотри, я команду поменял. Очепятался изначально не много, контрл-в подвел. Сообщение отредактировано: AntonGorod — |
|
nash |
|
|
net file и net file id не поможет? |
|
Демо |
|
|
Также есть утилита в помощь — PSFILE от Руссиновича. |
|
^D^ima |
|
|
Демо |
|
nash |
|
|
Цитата ^D^ima @ Как сделать сабж в Win 2008R2. Цитата ^D^ima @ Файлов, открытых по сети, или файлов, открытых опубликованными приложениями нет. Цитата ^D^ima @ стало быть это открытые по сети файлы, а не локальные Витиевато у вас всё как-то, товарищ. |
|
^D^ima |
|
|
Я думал через «Manage Open Files…» показываются открытые локально файлы, но как оказывается это открытые файлы по сети. |
|
UncleBob |
|
|
Цитата ^D^ima @ Я думал через «Manage Open Files…» показываются открытые локально файлы, но как оказывается это открытые файлы по сети. Цитата ^D^ima @ Как посмотреть список открытых файлов по сети ты бы уже определился |
0 пользователей читают эту тему (0 гостей и 0 скрытых пользователей)
0 пользователей:
- Предыдущая тема
- Windows
- Следующая тема
[ Script execution time: 0,0272 ] [ 15 queries used ] [ Generated: 14.05.25, 02:16 GMT ]