Understanding the EFI Partition in Windows 11
If you’re a Windows 11 user, you may have come across the term «EFI partition». The EFI (Extensible Firmware Interface) partition is a crucial part of the system that contains essential files for the boot process. It serves as the bridge between the firmware and the operating system during the boot-up sequence. Mounting the EFI partition can be necessary in various situations, such as modifying the bootloader, repairing boot-related issues, or accessing EFI boot files. In this guide, we will explore how to mount the EFI partition in Windows 11 step by step.
Why Mount the EFI Partition in Windows 11?
Before diving into the process of mounting the EFI partition, it’s important to understand why you would need to do this in the first place. Here are some common reasons:
- Repairing boot-related issues: Mounting the EFI partition allows you to access the EFI boot files and repair any issues that may be preventing your system from booting correctly.
- Modifying the bootloader: If you want to add or remove operating systems from the boot menu, customize the boot order, or make any changes to the bootloader, you’ll need to mount the EFI partition.
- Accessing EFI boot files: Sometimes, you may need to access specific EFI boot files for troubleshooting or other purposes. Mounting the EFI partition gives you direct access to these files.
- Performing advanced system configurations: Mounting the EFI partition can be useful when performing advanced system configurations that require modifying or updating EFI-related files.
Step-by-Step Guide to Mount the EFI Partition
Now that you understand the importance of mounting the EFI partition, let’s walk through the step-by-step process:
Step 1: Open Disk Management
To begin, you’ll need to open the Disk Management utility in Windows 11. You can do this by right-clicking on the Start button and selecting «Disk Management» from the menu. Alternatively, you can press the Windows key + X key and choose «Disk Management» from the Power User menu.
Step 2: Identify the EFI Partition
In the Disk Management window, look for a partition labeled as «EFI System Partition» or «ESP». The EFI partition is typically a small partition with a few hundred megabytes in size. Take note of the disk number and the partition number of the EFI partition for the next steps.
Step 3: Open Command Prompt as Administrator
Next, you’ll need to open the Command Prompt with administrative privileges. Right-click on the Start button and select «Windows PowerShell (Admin)» from the menu. If you see «Command Prompt (Admin)» instead, you can choose that option as well.
Step 4: Mount the EFI Partition
In the Command Prompt window, type the following command:
The command is:
mountvol X: /s
Replace «X» with any unused drive letter that you want to assign to the mounted EFI partition. This drive letter will be used to access the EFI partition from Windows Explorer or any other file manager.
Using the Mounted EFI Partition
Now that you have successfully mounted the EFI partition, you can access it like any other drive from Windows Explorer. Here are a few things you can do with the mounted EFI partition:
- Browse the contents: You can explore the files and folders within the EFI partition to view the boot files and other EFI-related components.
- Make changes to the bootloader: If you want to modify the bootloader, add or remove operating systems from the boot menu, or customize the boot order, you can make the necessary changes directly from the mounted EFI partition.
- Back up EFI boot files: It’s always a good idea to create a backup of your EFI boot files. With the EFI partition mounted, you can easily copy and store these files in a safe location.
- Perform repairs or updates: If you encounter boot-related issues in the future, having the EFI partition mounted makes it easier to perform repairs or updates to the bootloader or EFI files.
Alternative Methods for Mounting the EFI Partition
In addition to the method outlined above, there are a few alternative methods you can use to mount the EFI partition in Windows 11:
Using DiskPart
DiskPart is a command-line utility in Windows that allows you to manage disks, partitions, and volumes. Here’s how you can use DiskPart to mount the EFI partition:
Step 1: Open Command Prompt as Administrator
Open the Command Prompt as an administrator using the method mentioned earlier.
Step 2: Launch DiskPart
Type «diskpart» in the Command Prompt and press Enter to launch the DiskPart utility.
Step 3: List the Disks and Partitions
Once inside DiskPart, type «list disk» to view the available disks and identify the disk number containing the EFI partition. Then, type «select disk X» (replace «X» with the appropriate disk number) to select the disk.
After selecting the disk, type «list partition» to view the partitions on the selected disk. Identify the partition number of the EFI partition.
Step 4: Assign a Drive Letter
With the EFI partition selected, type «assign letter=X» (replace «X» with the desired drive letter) to assign a drive letter to the EFI partition. The EFI partition will now be mounted and accessible from Windows Explorer.
Using Third-Party Tools
There are also third-party tools available that provide a graphical interface for managing partitions and volumes. These tools often include features for easily mounting and accessing the EFI partition. Some popular tools include EaseUS Partition Master, AOMEI Partition Assistant, and MiniTool Partition Wizard.
It’s important to note that when using third-party tools, caution should be exercised, and it’s recommended to create a backup of your system before making any changes to disk partitions or volumes.
In Conclusion
Mounting the EFI partition in Windows 11 is a useful skill to have, especially if you need to repair boot-related issues, modify the bootloader, or access EFI boot files. By following the step-by-step guide outlined in this article, you can easily mount the EFI partition and gain access to its contents. Remember to exercise caution when making changes to the EFI partition and create backups to ensure the safety of your system.

Mounting the EFI Partition in Windows 11
Mounting the EFI partition in Windows 11 allows you to access and modify the files stored in this crucial partition. Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you:
Method 1: Using Disk Management
- Press the Windows key + R to open the Run dialog box.
- Type «diskmgmt.msc» and press Enter to open Disk Management.
- Find the EFI partition, usually labeled as «EFI System Partition,» and note its drive letter.
- Right-click on the EFI partition and select «Change Drive Letter and Paths.»
- Click on «Add» and choose a drive letter for the EFI partition.
- Click «OK» to mount the EFI partition with the assigned drive letter.
Method 2: Using Command Prompt
- Press the Windows key + X and select «Command Prompt (Admin)» or «Windows PowerShell (Admin).»
- Type «diskpart» and press Enter to open the DiskPart command-line utility.
- Use the following commands:
| list disk | Show a list of drives. |
select disk X
Key Takeaways — How to Mount Efi Partition in Windows 11
Frequently Asked QuestionsHere are some commonly asked questions about mounting the EFI partition in Windows 11. 1. How can I mount the EFI partition in Windows 11?To mount the EFI partition in Windows 11, follow these steps: To start, open the Command Prompt as an administrator. You can do this by right-clicking the Start button and selecting «Command Prompt (Admin)» from the menu. Once the Command Prompt window opens, type «diskpart» and press Enter. Next, type «list disk» and press Enter to display a list of all available disks on your computer. Identify the disk number that corresponds to your EFI partition. Once you have identified the disk number, type «select disk [disk number]» (replace [disk number] with the actual disk number) and press Enter. In the next step, type «list partition» and press Enter to display a list of partitions on the selected disk. Locate the EFI partition in the list. After you have identified the EFI partition, type «select partition [partition number]» (replace [partition number] with the actual partition number) and press Enter. Finally, type «assign letter=Z» and press Enter to assign a drive letter to the EFI partition. The EFI partition will now be mounted and accessible in Windows Explorer. 2. Why would I want to mount the EFI partition in Windows 11?Mounting the EFI partition in Windows 11 can be useful for various reasons: 1. Accessing or modifying boot-related files: The EFI partition contains important files related to the boot process, such as bootloaders and configuration files. By mounting the EFI partition, you can access and modify these files if needed. 2. Troubleshooting boot issues: If you are experiencing boot issues, mounting the EFI partition can help you analyze and troubleshoot the problem. You can check for any corrupted or missing files in the EFI partition and make necessary repairs. 3. Customizing the boot menu: Mounting the EFI partition allows you to customize the boot menu options in Windows 11. You can add or remove entries, change the default boot option, or modify the boot order. 3. Can I mount the EFI partition in Windows 11 without using Command Prompt?While using Command Prompt is the most common method for mounting the EFI partition in Windows 11, there are alternative methods available: 1. Using Disk Management: You can also mount the EFI partition using Disk Management. Open Disk Management by right-clicking the Start button and selecting «Disk Management» from the menu. Locate the EFI partition, right-click it, and select «Change Drive Letter and Paths.» Then, click «Add» and assign a drive letter to the EFI partition. 2. Using third-party software: There are third-party software applications available that provide a graphical interface for mounting the EFI partition. These tools can make the process more user-friendly and intuitive. 4. Is it safe to mount the EFI partition in Windows 11?Mounting the EFI partition in Windows 11 is generally safe, as long as you are cautious and know what you are doing. However, it is important to be mindful of the following: 1. Modify files with caution: When accessing and modifying files in the EFI partition, make sure you know what you are changing. Modifying or deleting critical files can cause boot issues and render your system unbootable. 2. Create backups: Before making any changes to the EFI partition, it is highly recommended to create backups of the important files and the entire partition. This ensures that you can restore the system in case anything goes wrong. 3. Follow instructions carefully: When using Command Prompt or any other method to mount the EFI partition, follow the instructions precisely. Mistakes or incorrect commands could have unintended consequences. 5. Can I unmount the EFI partition in Windows 11?Yes, you can In conclusion, mounting the EFI partition in Windows 11 is an essential step for managing system boot and firmware settings. By accessing the EFI partition, users can modify bootloader configurations, update firmware, and troubleshoot boot-related issues. Mounting the EFI partition in Windows 11 can be done through the Disk Management tool or using Command Prompt. Both methods involve locating the EFI partition, assigning it a drive letter, and accessing its contents. However, it is crucial to exercise caution when making changes to the EFI partition to avoid damaging the system’s boot files. Always create a backup and consult reliable resources or seek expert advice if needed.
|
The easiest way to mount an EFI partition in Windows 10 is to use the Disk Management tool. To do this, follow these steps:
1. Press the Windows key + R to open the Run dialog box.
2. Type diskmgmt.msc and press Enter.
3. Right-click on the EFI partition and select Mount.
4. Follow the prompts to complete the operation.
How do I mount an EFI folder in Windows 10?
Where is EFI partition mounted?
The EFI partition is mounted at /boot/efi.
How do I access my EFI System Partition?
The EFI System Partition (ESP) is a small (usually FAT32-formatted) partition on a data storage device that is used by computers adhering to the Unified Extensible Firmware Interface (UEFI). The ESP is intended to contain files that are used by the computer to initialize and boot the operating system.
To access the ESP, you will need to open the Disk Management tool in Windows. To do this, press the Windows key + R, type diskmgmt.msc into the Run dialog, and press Enter.
In the Disk Management tool, you should see the ESP listed as a separate partition. You can then right-click on the ESP and select the option to mount it. Once the ESP is mounted, you can access it like any other drive in Windows.
There are a few different ways to mount a Windows EFI partition, depending on what operating system you’re using.
If you’re using a Windows operating system, you can use the Disk Management tool to mount the EFI partition. To do this, open the Disk Management tool (press the Windows key + R, type diskmgmt.msc, and press Enter), right-click on the EFI partition, and select the «Mount» option.
If you’re using a Linux operating system, you can use the mount command to mount the EFI partition. For example, if your EFI partition is /dev/sda1, you would use the following command:
sudo mount /dev/sda1 /mnt/efi
If you’re using a MacOS operating system, you can use the diskutil command to mount the EFI partition. For example, if your EFI partition is /dev/disk0s1, you would use the following command:
sudo diskutil mount /dev/disk0s1
How do I fix mount the EFI system partition failed?
There are a few things that could cause this issue.
First, check to make sure that the EFI system partition is indeed present and intact on the drive. If it is not, you will need to recreate it.
Next, check the boot order in the BIOS and make sure that the EFI system partition is listed first.
If those two things check out, try running the bootrec utility from a Windows Recovery Environment. This will scan the drive for any missing or corrupt boot files and attempt to repair them.
If none of these things work, you may need to reinstall Windows.
How do I add an EFI partition?
There are a few different ways to add an EFI partition, but the most common is to use a tool like gdisk to create a new partition and then format it as FAT32. Once the partition is created, you can then mount it to a directory and add it to your /etc/fstab file so that it will be automatically mounted at boot.
Does EFI partition need to be first?
There is no requirement for the EFI partition to be first on a drive, but it is often recommended to keep it at the beginning of the drive for organizational purposes. If you do choose to keep the EFI partition at the beginning of the drive, you will need to ensure that your computer’s BIOS is configured to boot from that location.
Where is the EFI directory located?
The EFI directory is located on the EFI System Partition (ESP). The ESP is a partition on your hard drive that is used to store boot data.
Does Windows 10 need Reserved Partition?
There is no reserved partition on Windows 10.
Can not find room for the EFI System Partition?
If you cannot find room for the EFI System Partition on your hard drive, you may need to delete or resize an existing partition to make room. To do this, you will need to use a partition manager. Once you have made room for the EFI System Partition, you can create it using the Windows Disk Management tool.
How do I fix system reserved partition Windows 10?
If you are using Windows 10, you can fix the system reserved partition by following these steps:
1. Press the Windows key + R to open the Run dialog box.
2. Type «diskpart» and press Enter.
3. Type «list volume» and press Enter.
4. Type «select volume X» where X is the number of your system reserved partition.
5. Type «assign letter=Y» where Y is the drive letter you want to assign to the system reserved partition.
6. Type «exit» and press Enter.
Your system reserved partition should now be accessible from Windows Explorer.
Does Windows 10 need EFI partition?
No, Windows 10 does not require an EFI partition. However, if you are using an EFI-based computer, you will need to create an EFI partition in order to install Windows 10.
Is EFI partition necessary?
The answer to this question depends on the specific computer system and operating system in question. In general, however, an EFI partition is not necessary and can be safely removed without affecting the normal operation of the computer.
How to Mount EFI in Windows 11
The EFI (Extensible Firmware Interface) system is a standard interface between a computer’s firmware and its operating system. It is used to boot the operating system and manage hardware devices. In Windows 11, the EFI system is located on a partition called the EFI System Partition (ESP). This partition is typically hidden by default, but you can mount it to view its contents.
There are a few reasons why you might want to mount the EFI system partition. For example, you may need to access the EFI Boot Manager to change the boot order of your system. Or, you may need to troubleshoot a problem with your computer’s firmware.
In this article, I will show you how to mount the EFI system partition in Windows 11. I will also provide a brief overview of the EFI system and its role in the boot process.
What is the EFI System Partition?
The EFI System Partition (ESP) is a small partition (typically 100 MB) that is created when you install Windows 11. The ESP contains the EFI firmware, which is responsible for booting the operating system. It also contains the boot loader, which is a small program that loads the operating system into memory.
The ESP is typically hidden by default, but you can mount it to view its contents. To do this, you can use the Disk Management tool or the Command Prompt.
How to Mount the EFI System Partition
There are two ways to mount the EFI System Partition in Windows 11:
- Using the Disk Management tool:
1. Open the Disk Management tool by pressing Windows+X and selecting Disk Management.
2. Right-click the EFI System Partition and select Mount.
3. In the Mounted Location box, type a drive letter for the EFI System Partition.
4. Click OK.
- Using the Command Prompt:
1. Open the Command Prompt by pressing Windows+R and typing cmd.
2. Type the following command:
mountvol X: /s
where X is the drive letter you want to use for the EFI System Partition.
What is the EFI Boot Manager?
The EFI Boot Manager is a small program that is stored on the EFI System Partition. The EFI Boot Manager is responsible for loading the operating system into memory.
When you start your computer, the EFI Boot Manager is the first program that is executed. The EFI Boot Manager scans the EFI System Partition for bootable operating systems. When it finds a bootable operating system, it loads the operating system into memory.
How to Access the EFI Boot Manager
To access the EFI Boot Manager, you can use the following steps:
1. Restart your computer.
2. Press the F2 key or the Delete key repeatedly during the boot process.
3. The EFI Boot Manager will be displayed.
4. Use the arrow keys to select the operating system you want to boot.
5. Press Enter to boot the operating system.
In this article, I showed you how to mount the EFI system partition in Windows 11. I also provided a brief overview of the EFI system and its role in the boot process.
If you have any questions about mounting the EFI system partition, please leave a comment below.
| Column 1 | Column 2 | Column 3 |
|---|---|---|
| Title | Description | Link |
| How to Mount EFI in Windows 11 | This guide will show you how to mount the EFI partition in Windows 11. | Link |
| Troubleshooting EFI Mount Problems in Windows 11 | This guide will help you troubleshoot problems mounting the EFI partition in Windows 11. | Link |
The EFI system partition (ESP) is a small partition on a hard drive that contains the files necessary for the computer to boot from the hard drive. The ESP is typically located at the beginning of the hard drive, and it is formatted with the FAT32 file system. The ESP contains the following files:
- Boot loader: The boot loader is a small program that loads the operating system into memory.
- EFI drivers: EFI drivers are required for the operating system to communicate with the hardware.
- EFI configuration file: The EFI configuration file contains information about the hardware on the computer.
If you need to access the files on the EFI system partition, you can mount it using the Disk Management tool in Windows 11.
How to mount the EFI system partition in Windows 11
To mount the EFI system partition in Windows 11, follow these steps:
1. Open the Disk Management tool by pressing Windows+R and typing diskmgmt.msc.
2. In the Disk Management window, right-click the EFI system partition and select Mount.
3. In the Mount Partition dialog box, select the Mount in the following empty NTFS folder option and click Browse.
4. Navigate to the location where you want to mount the EFI system partition and click OK.
5. The EFI system partition will be mounted as a drive letter. You can now access the files on the EFI system partition by opening the drive letter in File Explorer.
In this article, we showed you how to mount the EFI system partition in Windows 11. If you need to access the files on the EFI system partition, you can use the steps in this article to mount the partition.
Additional resources
- [How to Mount an EFI System Partition in Windows 10](https://www.windowscentral.com/how-mount-efi-system-partition-windows-10)
- [How to Access the EFI System Partition in Windows](https://www.howtogeek.com/197645/how-to-access-the-efi-system-partition-in-windows/)
- [What is the EFI System Partition?](https://www.dell.com/support/kbdoc/en-us/000124339/what-is-the-efi-system-partition)
The EFI (Extensible Firmware Interface) system is a standard interface between a computer’s operating system and its firmware. It is used to boot the operating system and manage hardware devices. In Windows 11, the EFI system is located in the \EFI\ folder on the system drive.
If you need to access the EFI system for troubleshooting or other purposes, you can mount it as a drive in Windows 11. This guide will show you how to mount the EFI system in Windows 11.
Prerequisites
To mount the EFI system in Windows 11, you will need:
- A Windows 11 computer
- Administrator privileges
Steps
To mount the EFI system in Windows 11, follow these steps:
1. Open the Run dialog box by pressing Windows+R.
2. Type diskmgmt.msc and press Enter.
3. Right-click on the EFI System Partition and select Mount.
4. In the Mount Drive Letter or Path dialog box, select a drive letter for the EFI system and click OK.
The EFI system will now be mounted as a drive in Windows 11. You can access it by opening the File Explorer and navigating to the drive letter you selected.
This guide has shown you how to mount the EFI system in Windows 11. By following these steps, you can access the EFI system for troubleshooting or other purposes.
Here are some additional resources that you may find helpful:
- [How to Access the EFI System in Windows 10](https://www.windowscentral.com/how-access-efi-system-windows-10)
- [What is the EFI System Partition?](https://www.howtogeek.com/197989/what-is-the-efi-system-partition-and-how-do-i-use-it/)
- [How to Repair the EFI System Partition in Windows](https://www.tenforums.com/tutorials/163056-repair-efi-system-partition-windows-10-a.html)
Q: What is the EFI partition?
A: The EFI partition is a small partition on a hard drive that contains the files necessary for the computer to boot from that drive. It is typically 100 MB in size and is located at the beginning of the hard drive.
Q: Why do I need to mount the EFI partition?
A: You may need to mount the EFI partition if you need to access the files on it, or if you need to make changes to the partition’s settings. For example, you may need to mount the EFI partition if you are trying to install a new operating system or if you are trying to change the boot order of your computer.
Q: How do I mount the EFI partition?
A: To mount the EFI partition, you can use the following steps:
1. Open the Disk Management tool.
2. Right-click on the EFI partition and select Mount.
3. Select the drive letter that you want to assign to the EFI partition.
4. Click OK.
The EFI partition will now be mounted and you will be able to access it from File Explorer.
Q: What are the common problems when mounting the EFI partition?
A: There are a few common problems that you may encounter when mounting the EFI partition. These include:
- The EFI partition may not be visible in Disk Management.
- You may not be able to assign a drive letter to the EFI partition.
- You may receive an error message when trying to mount the EFI partition.
If you encounter any of these problems, you can try the following solutions:
- Make sure that the EFI partition is formatted as FAT32.
- Make sure that the EFI partition is not in use by another operating system.
- Try mounting the EFI partition in a different way. For example, you can try using the Diskpart command-line tool or a third-party partitioning tool.
Q: How can I prevent problems when mounting the EFI partition?
You can prevent problems when mounting the EFI partition by following these tips:
- Make sure that the EFI partition is formatted correctly.
- Make sure that the EFI partition is not in use by another operating system.
- Back up the EFI partition before making any changes to it.
By following these tips, you can help to ensure that the EFI partition is mounted correctly and that you do not encounter any problems.
In this blog post, we discussed how to mount the EFI partition in Windows 11. We covered the steps on how to do this using the Disk Management tool and the Command Prompt. We also provided some tips on troubleshooting common problems.
We hope this blog post was helpful. If you have any questions, please feel free to leave a comment below.
Author Profile
-
Hatch, established in 2011 by Marcus Greenwood, has evolved significantly over the years. Marcus, a seasoned developer, brought a rich background in developing both B2B and consumer software for a diverse range of organizations, including hedge funds and web agencies.
Originally, Hatch was designed to seamlessly merge content management with social networking. We observed that social functionalities were often an afterthought in CMS-driven websites and set out to change that. Hatch was built to be inherently social, ensuring a fully integrated experience for users.
Now, Hatch embarks on a new chapter. While our past was rooted in bridging technical gaps and fostering open-source collaboration, our present and future are focused on unraveling mysteries and answering a myriad of questions. We have expanded our horizons to cover an extensive array of topics and inquiries, delving into the unknown and the unexplored.
Latest entries
В этой статье мы покажем, как вручную восстановить случайно удаленный загрузочный EFI раздел Windows на компьютере с UEFI. Этот простой способ ручного пересоздания загрузочного EFI и MSR разделов Windows позволит вам загрузить ОС после случайного форматирования или удаления загрузочного EFI раздела. Инструкции в статье актуальны для всех версий Windows (в том числе Windows 10 и 11, и Windows Server).
Если вы случайно (или не очень случайно, например при попытке удалить с диска OEM разделы производителя) удалили или отформатировали загрузочный EFI раздел на компьютере с UEFI (не BIOS), ваша Windows 11/10/8.1 /7 перестанет загружаться и будет циклически предлагать выбрать загрузочное устройство (
Reboot and select proper boot device or insert boot media in selected
или
Windows Boot Manager: No media
). Далее мы покажем, как восстановить загрузку Windows при удалении раздела диска с загрузчиком Boot Manager без переустановки ОС.
Предупреждение. Инструкция предполагает работу с разделами диска и не предназначена новичкам. В случае неверной интерпретации команд, вы можете случайно удалить все данные на жестком диске. Также настоятельно рекомендуется создать резервную копию важных данных на отдельном носителе.
Содержание:
- Структура разделов GPT диска для Windows
- Что будет, если в Windows отсутствует раздел EFI?
- Как вручную создать EFI и MSR разделы на GPT диске?
- Восстановление EFI загрузчика и BCD в Windows
Структура разделов GPT диска для Windows
Рассмотрим, как должна выглядеть таблица разделов загрузочного жесткого диска Windows с GPT разметкой на UEFI компьютере. Как минимум должны присутствовать следующие разделы:
- Системный раздел EFI (Extensible Firmware Interface, или EFI System Partition — ESP) с загрузчиком – 100 Мб (тип раздела — EFI);
- Резервный раздел Майкрософт (Microsoft Reserved) – 128 Мб (тип раздела — MSR);
- Основной раздел Windows – раздел с Windows.
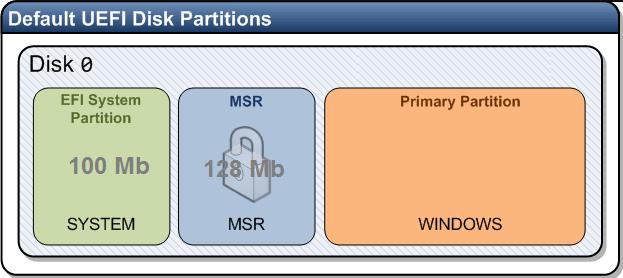
Это именно минимальная конфигурация. Эти разделы создает установщик Windows при чистой установке системы на неразмеченный диск.
Производители компьютеров или сами пользователи могут дополнительно создавать собственные разделы, содержащие, к примеру раздел Recovery со средой восстановления Windows в файле winre.wim (Windows RE), раздел с резервным образом системы от производителя (позволяет откатится к исходному состоянию компьютера), пользовательские разделы и т.д.
Раздел EFI c файловой системой FAT32 является обязательным на дисках с GPT разметкой на UEFI системах и имеет GUID
c12a7328-f81f-11d2-ba4b-00a0c93ec93b
. Стандартный размер EFI раздела 100Мб (на дисках расширенного формата с секторами 4Кб /4K Native / размер EFI раздела 260Мб).
MSR раздел раздел (Microsoft System Reserved) на GPT диске используется для упрощения управления разделами и используется для служебных операций (например, при конвертировании диска из простого в динамический). Это резервный раздел c GUID
e3c9e316-0b5c-4db8-817d-f92df00215ae
, которому не назначается код раздела. На этом разделе нельзя хранить данные пользователя. В Windows 10 и 11 размер MSR раздела – всего 16 Мб (в Windows 8.1 размер MSR раздела – 128 Мб), файловая система – NTFS. MSR раздел должен находиться между разделами EFI (ESP) и первичным разделом с операционной системой Windows.
На основном разделе с файловой системой NTFS находится установленная Windows, программы и данные пользователя. Также на диске могут присутствовать дополнительные разделы с данными.
Что будет, если в Windows отсутствует раздел EFI?
На EFI разделе (по аналогии с разделом System Reserved на дисках с MBR разметкой) хранится хранилище конфигурации загрузки (BCD) и ряд файлов, необходимых для загрузки Windows. При загрузке компьютера среда UEFI загружает загрузчик (EFI\Microsoft\Boot\bootmgfw.efi) с раздела EFI (ESP) и передает управление ему. Исполняемый файл bootmgfw.efi выполняет запуск основного загрузчика Windows Boot Manager, который загружает данные конфигурации из BCD. После загрузки BCD начинается загрузка Windows через winload.efi.
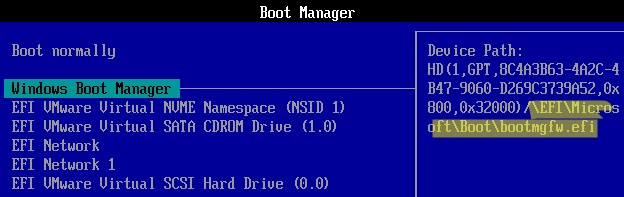
При загрузке UEFI компьютера он ищет системный раздел EFI на всех подключенных дисках. Если раздел EFI удален или поврежден, вы не сможете загрузить Windows с такого диска. Появится ошибка UEFI:
could not locate \efi\boot\bootx64.efi – not found
, пустой UEFI Shell с предложением выбрать загрузочное устройство.
Также вы не сможете загрузить Windows, если EFI раздел отформатирован в файловой системе NTFS. Даже при чистой установке Windows в таком случае вы получите ошибку:
Windows detected that the EFI system partition was formatted as NTFS. Format the EFI system partition as FAT32, and restart the installation.
Установлено, что системный раздел EFI отформатированный в NTFS. Отформатируйте системный раздел EFI в формате FAT32 и перезапустите программу установки.
Как вручную создать EFI и MSR разделы на GPT диске?
Т.к. Windows не загружается корректно, нам понадобится загрузочное устройство с Windows 10/11 или любой другой загрузочный диск (см. как создать загрузочную USB флешку c Windows для UEFI компьютера). Загрузите компьютера с установочного диска и на экране начала установки нажмите комбинацию клавиш Shift+F10. Должно открыться окно командной строки
Запустите утилиту управления дисками и разделами:
Diskpart
Выведите список жестких дисков в системе:
list disk
В этом примере к компьютеру подключен только один disk 0. Звездочка (*) в столбце Gpt означает, что на диск создана таблица разделов GPT).
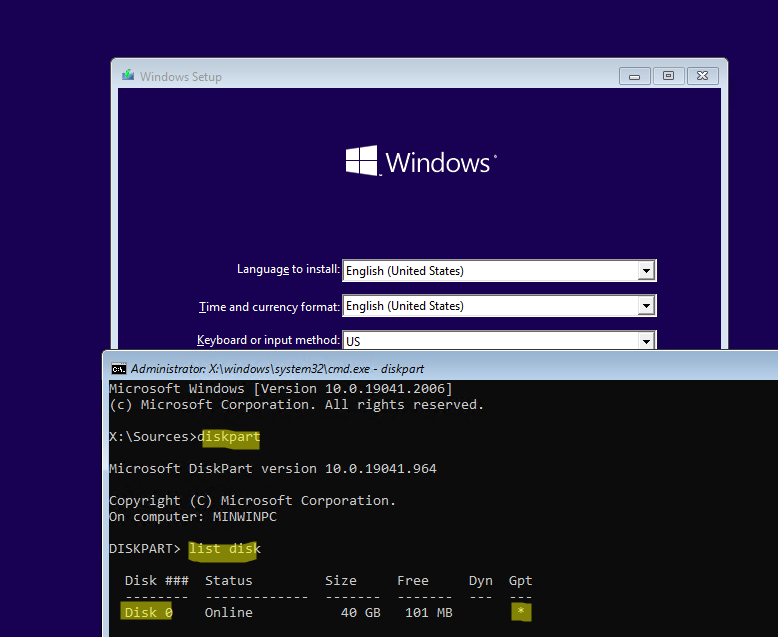
Если в столбце GPT отсутствует *, значит на диске MBR таблица разделов. Вам нужно убедиться, что ранее вы загружали компьютер в нативном UEFI режиме (иначе следовать данной инструкции бессмысленно). Если вы уверены, что тип таблицы разделов сменился, возможно его нужно стоит переконвертировать из MBR в GPT.
Выберите этот диск:
Select disk 0
Выведите список разделов на диске:
List partition
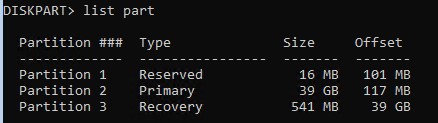
В нашем примере в системе осталось всего 3 раздела:
- Раздел Reserved (MSR) — 16 Мб
- Системный раздел с Windows – 30 Гб
- Recovery (раздел восстаовления0) – 541 Мб
Как вы видите, раздел EFI (может называться System) отсутствует (удален).
Совет. Если на разделе EFI были повреждены только файлы среды EFI, а сам раздел остался на месте, вы можете пропустить процесс пересоздания разделов с помощью diskpart. В большинстве случаев достаточно восстановить загрузчик по статье Восстановление EFI загрузчика в Windows . Если у вас компьютер с BIOS и MBR диск, вы можете пересоздать BCD так.
Наша задача удалить оставшийся MSR раздел, так чтобы на диске осталось неразмечено как минимум 228 Мб свободного места (для разделов MSR и EFI). Вы можете удалить оставшийся раздел с помощью графической утилиты GParted или непосредственно из командной строки (именно так и поступим).
Важно! Здесь будьте максимально внимательными и не удалите случайно раздел с Windows или разделы с пользовательскими данными (если таковые имеются).
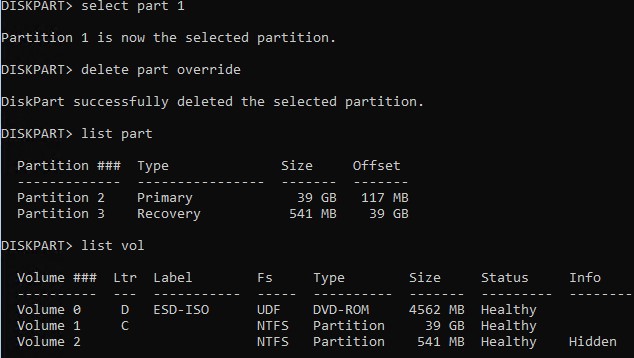
Выберите раздел для удаления:
Select partition 1
И удалите его:
Delete partition override
Убедитесь, что остался только Primary раздел с Windows размером 30 Гб (в нашем случае) и раздел восстановления:
List partition
Теперь вы можете вручную создать разделы EFI и MSR для размещения загрузчика Windows. Для этого в контексте утилиты diskpart последовательно выполните команды:
Выберите диск:
select disk 0
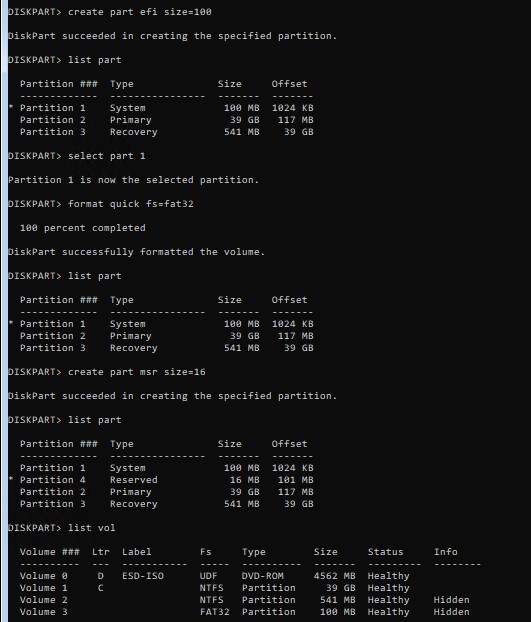
Создайте EFI раздел размером 100 Мб, отформатируйте его в файловой системе FAT32 и назначьте ему букву диска:
create partition efi size=100
Убедитесь, что в diskpart выбран раздел 100 Мб с именем System (звездочка напротив строки Partition 1):
list partition
select partition 1
format quick fs=fat32 label="System"
assign letter=G
Теперь нужно создать MSR раздел размером 16 Мб (для Windows 10 и 11):
create partition msr size=16
list partition
list vol
В нашем случае основному разделу с Windows уже назначена буква диска C:. Если это не так, назначьте ему букву следующим образом:
select vol 1
assign letter=C
exit
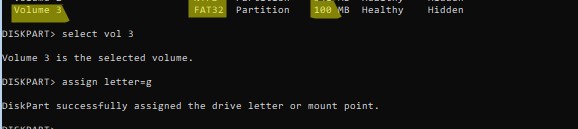
Назначьте букву диска вашему EFI разделу:
Select vol 3
Assign letter=G
Закройте diskpart:
exit
При создании EFI или MSR раздела может появится ошибка
No usable free extent could be found. It may be that there is insufficient free space tocreate a partition at the specified size and offset. Specify different size and offset values or don't specify either to create the maximum sized partition. It may be that the disk is partitioned using the MBR disk partitioning format and the disk contains either 4 primary partitions, (no more partitions may be created), or 3 primary partitions and one extended partition, (only logical drives may be created).
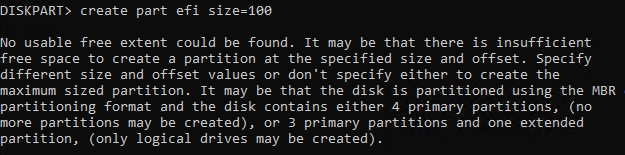
В этом случае вам нужно уменьшить раздел основного раздела с Windows на 128 Мб(в нашем примере это volume 1):
select volume 1
shrink desired=128 minimum=128
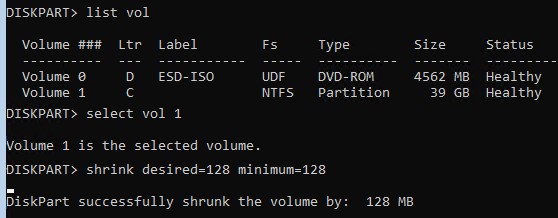
После этого создайте разделы EFI и MSR как описано выше.
Восстановление EFI загрузчика и BCD в Windows
После того, как вы создали минимальную структуру разделов для GPT диска на компьютере с UEFI, нужно скопировать загрузочные файлы EFI на ваш диск и создать конфигурационный файла загрузчика (BCD).
Теперь с помощью утилиты bcdboot.exe скопируйте файлы среды загрузки UEFI из системного каталога Windows в загрузочный EFI раздел и пересоздайте конфигурацию загрузчика BCD. Выполните команду:
bcdboot c:\windows /s G: /f UEFI
Boot files successfully created.
В результате на EFI разделе будет создана структура каталогов. На системном разделе EFI должны обязательно присутствовать следующие файлы:
- \EFI\Microsoft\Boot\bootmgfw.efi
- \EFI\Microsoft\Boot\bootmgr.efi
- \EFI\Microsoft\Boot\memtest.efi
- \EFI\Microsoft\Boot\BCD
- \EFI\Microsoft\Boot\Fonts\wgl4_boot.ttf
- \EFI\Boot\bootx64.efi
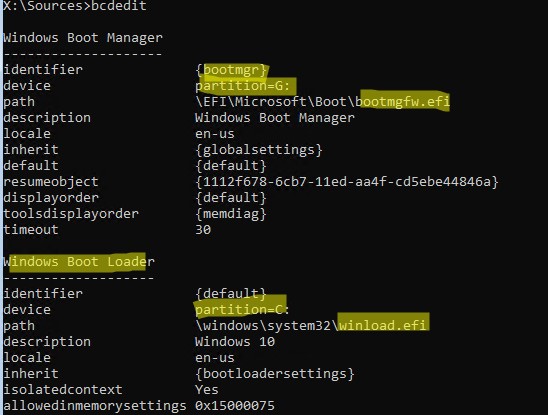
Выведите текущую конфигурацию загрузчика Windows Boot Manager. В разделе {bootmgr} должна появиться запись, которая указывает на раздел с файлом управления загрузкой UEFI (
\EFI\MICROSOFT\BOOT\bootmgfw.efi
). В этом примере это
partition=G
, или
partition=\Device\HarddiskVolume2
(если вы не назначили букву EFI разделу).
Загрузчик UEFI затем должен передать управление файлу загрузчика Windows Boot Loader
\Windows\system32\winload.efi
на partition=C:
Перезагрузите компьютер (для перезагрузки из среды WinPE нужно выполнить команду wpeutil reboot) и извлеките загрузочную флешку.
Опционально! Вы можете вручную выполнить действия, которые выполняет команда bcdboot. Далее мы покажем, как самостоятельно скопировать системные файлы EFI и пересоздать BCD.
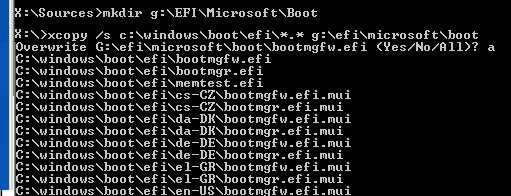
Скопируйте загрузочные файлы среды EFI из каталога вашего диска, на который установлена ваша Windows:
mkdir G:\EFI\Microsoft\Boot
xcopy /s C:\Windows\Boot\EFI\*.* G:\EFI\Microsoft\Boot
Пересоздайте конфигурацию загрузчика Windows:
g:
cd EFI\Microsoft\Boot
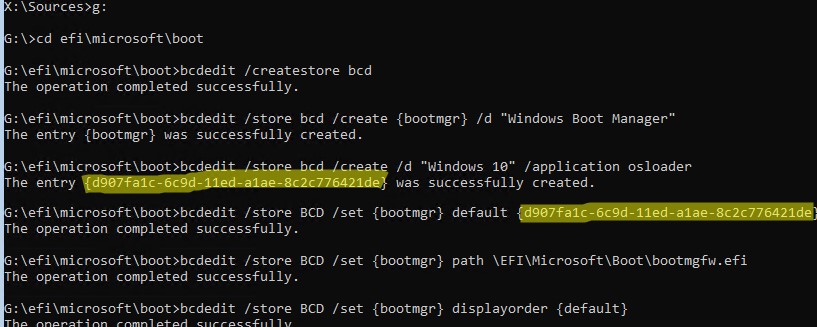
bcdedit /createstore BCD
bcdedit /store BCD /create {bootmgr} /d “Windows Boot Manager”
bcdedit /store BCD /create /d “Windows 10” /application osloader
Команда возвращает GUID созданной записи. Этот GUID нужно подставить в следующей команде вместо
{your_guid}
.
bcdedit /store BCD /set {bootmgr} default {your_guid}
bcdedit /store BCD /set {bootmgr} path \EFI\Microsoft\Boot\bootmgfw.efi
bcdedit /store BCD /set {bootmgr} displayorder {default}
Дальнейшие команды bcdedit выполняются в контексте {default}:
bcdedit /store BCD /set {default} device partition=c:
bcdedit /store BCD /set {default} osdevice partition=c:
bcdedit /store BCD /set {default} path \Windows\System32\winload.efi
bcdedit /store BCD /set {default} systemroot \Windows
exit
Если с первого раза Windows не загрузился, выполните следующие действия:
- Отключите питание компьютера;
- Отключите (физически) жесткий диск;
- Включите ПК, дождитесь появления окна с ошибкой загрузки Operating System not found. Выключите компьютер;
- Подключите диск обратно.
Если это не помогло, опять загрузитесь с установочной USB флешки и выполните команду:
bootrec /rebuildbcd
Перезагрузите компьютер
Затем в нашем случае (тестирование проводилось на виртуальной машине VMWare с UEFI средой) пришлось добавить новый загрузочный пункт меню, выбрав файл EFI\Microsoft\Boot\bootmgrfw.efi на EFI разделе.
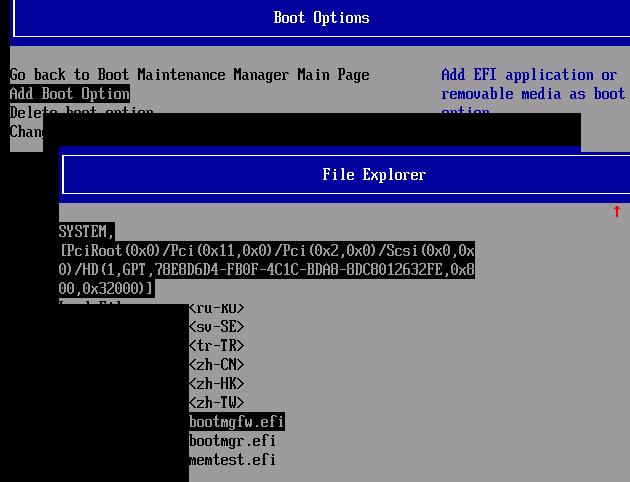
В некоторых UEFI меню по аналогии нужно изменить приоритет загрузочных разделов.
После всех рассмотренных манипуляций Windows должна загрузиться корректно.
Совет. Если что-то не заработало, рекомендуем проверить, что загрузочный флаг (boot flag) установлен только у раздела EFI. Проще всего в этом убедится с помощью LiveCd GParted.
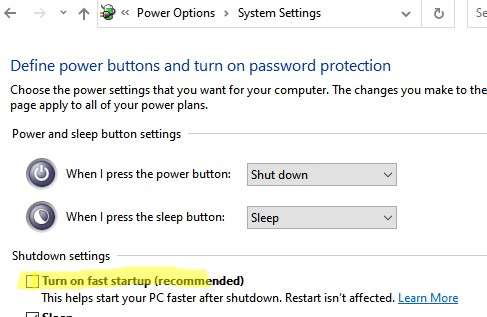
В некоторых случаях после пересоздания разделов EFI и MSR и восстановления BCD Windows может перестать корректно выключаться. Если у вас проявляется эта проблема, чтобы исправить ее нужно отключить функцию быстрого запуска в Windows в настройках электропитания компьютера:
- Откройте панель управления электропитанием
powercfg.cpl
; - Выберите Choose what the power buttons does;
- Нажмите кнопку Change settings that are currently unavailable и отключите опцию «Turn on fast startup» в разделе «Shutdown settings».