SSH-server based on the OpenSSH package is part of the operating system in all modern versions of Windows. In this article, we’ll show you how to install and configure the OpenSSH server on Windows 10/11 and Windows Server 2022/2019 and connect to it remotely via a secure SSH connection (just like in Linux 🙂).
Contents:
- How to Install OpenSSH Server on Windows
- Configuring SSH Server on Windows
- Sshd_config: OpenSSH Server Configuration File
- How to Connect to a Remote Windows Computer via SSH?
- Checking SSH Connection Logs in Windows
How to Install OpenSSH Server on Windows
The OpenSSH Server package is a part of all modern versions of Windows 10 (starting with 1803), Windows 11, and Windows Server 2022/2019 as a Feature on Demand (FoD). To install the OpenSSH server, open the elevated PowerShell prompt and run the command:
Get-WindowsCapability -Online | Where-Object Name -like ‘OpenSSH.Server*’ | Add-WindowsCapability –Online
Or using DISM:
dism /Online /Add-Capability /CapabilityName:OpenSSH.Server~~~~0.0.1.0
If your computer is directly connected to the Internet, the OpenSSH.Server package will be downloaded and installed on Windows.
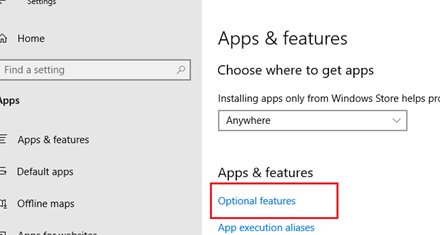
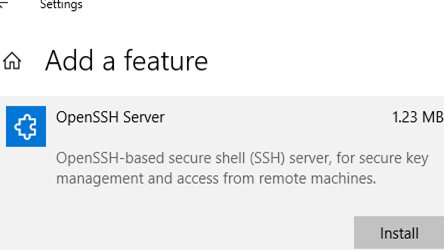
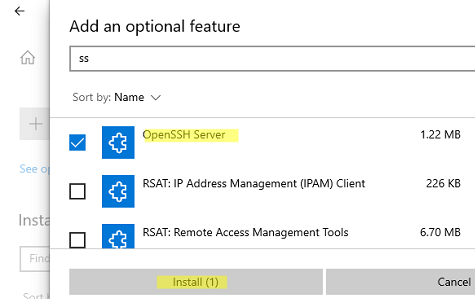
You can also install OpenSSH on Windows 10/11 through the modern Settings panel (Settings -> Apps and features -> Optional features -> Add a feature). Find Open SSH Server in the list and click Install.
On computers in disconnected (offline) environments, you can install the OpenSSH Server from the Feature on Demand ISO image (available in your account on the Microsoft websites: MSDN or my.visualstudio.com). Download the ISO and extract its contents to the E:\FOD folder (you can only extract the file OpenSSH-Server-Package~31bf3856ad364e35~amd64~~.cab) and install the Windows feature from the local repository:
Add-WindowsCapability -Name OpenSSH.Server~~~~0.0.1.0 -Online -Source E:\FOD
An MSI installer for OpenSSH for Windows is also available in the official Microsoft repository on GitHub (https://github.com/PowerShell/Win32-OpenSSH/releases/). For example, for Windows 10 x64, you need to download and install the OpenSSH-Win64-v8.9.1.0.msi package. The following PowerShell command will download the MSI file and install the OpenSSH client and server on your computer:
Invoke-WebRequest https://github.com/PowerShell/Win32-OpenSSH/releases/download/v8.9.1.0p1-Beta/OpenSSH-Win64-v8.9.1.0.msi -OutFile $HOME\Downloads\OpenSSH-Win64-v8.9.1.0.msi -UseBasicParsing
msiexec /i $HOME\Downloads\OpenSSH-Win64-v8.9.1.0.msi
You can install an OpenSSH server in previous Windows versions as well (Windows 8.1, Windows Server 2016/2012R2/2012). Check the example on how to install and configure Win32-OpenSSH in the article “How to Configure SFTP Server (SSH FTP) on Windows?”.
To make sure the OpenSSH server has been installed, run the command:
Get-WindowsCapability -Online | ? Name -like 'OpenSSH.Ser*'
State : Installed

Configuring SSH Server on Windows
After installing the OpenSSH server on Windows, two services are added:
- ssh-agent (OpenSSH Authentication Agent) – can be used to manage private keys if you have configured SSH key authentication;
- sshd (OpenSSH SSH Server).
You need to change the startup type of the sshd service to automatic and start the service using PowerShell:
Set-Service -Name sshd -StartupType 'Automatic'
Start-Service sshd

Use the netstat command to make sure that the SSH server is running and waiting for the connections on TCP port 22:
netstat -na| find ":22"

Make sure that Windows Defender Firewall allows inbound connections to Windows through TCP port 22:
Get-NetFirewallRule -Name *OpenSSH-Server* |select Name, DisplayName, Description, Enabled
Name DisplayName Description Enabled ---- ----------- ----------- ------- OpenSSH-Server-In-TCP OpenSSH SSH Server (sshd) Inbound rule for OpenSSH SSH Server (sshd) True
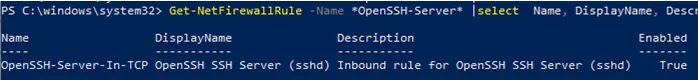
If the rule is disabled (Enabled=False) or missing, you can create a new inbound rule using the New-NetFirewallRule cmdlet:
New-NetFirewallRule -Name sshd -DisplayName 'OpenSSH Server (sshd)' -Enabled True -Direction Inbound -Protocol TCP -Action Allow -LocalPort 22
By default, key OpenSSH components are located in these folders:
- OpenSSH Server executables:
C:\Windows\System32\OpenSSH\(sshd.exe, ssh.exe, ssh-keygen.exe, sftp.exe, etc.) - The sshd_config file (created after the first service start of the service):
C:\ProgramData\ssh - The authorized_keys file and keys can be stored in the user profile folder:
%USERPROFILE%\.ssh\
Sshd_config: OpenSSH Server Configuration File
You can change your OpenSSH server settings in the config file: %programdata%\ssh\sshd_config. This is a plain text file with a set of directives. You can use any text editor for editing:
start-process notepad C:\Programdata\ssh\sshd_config
For example, to deny SSH connection for a specific domain user account (or all users in the specified domain), add these directives to the end of the file:
DenyUsers woshub\[email protected] DenyUsers corp\*
To allow SSH connection to the specific domain security group only:
AllowGroups woshub\sshadmins
You can allow access to a local user group:
AllowGroups sshadmins
By default, all Windows users can connect to OpenSSH. Directives in the sshd_config files are processed in the following order: DenyUsers, AllowUsers, DenyGroups, AllowGroups.
You can deny SSH login for the accounts with administrator privileges. In this case, if you need to perform any privileged actions in your SSH session, you will have to use runas.
DenyGroups Administrators
The following directives allow you to access Windows using SSH private keys or a password.
PubkeyAuthentication yes PasswordAuthentication yes
You can change the default TCP/22 port on which OpenSSH Server connections are accepted in the sshd_config configuration file using the Port directive.
After making any changes to the sshd_config file, you need to restart the sshd service
restart-service sshd
How to Connect to a Remote Windows Computer via SSH?
Now you can try to connect to your Windows 10 computer using the SSH client (I’m using putty in this example).
You can use the built-in Windows SSH client to connect to a remote host. To do this, open the command prompt and run the following command:
ssh [email protected]
In this example, max is the username on the remote Windows computer, and 192.168.13.12 is the IP address or DNS name of the computer.
Note that you can use the following username formats when connecting to Windows via SSH:
max@server1– local Windows user[email protected]@server1– Active Directory user or Microsoft/Azure account (use the UserPrincipalName format)woshub\max@server1– NetBIOS name format
In an Active Directory domain, you can use Kerberos authentication in SSH. To do this, you need to enable the following directive in sshd_config:
GSSAPIAuthentication yes
You can now transparently connect to an SSH server from a domain-joined Windows machine with a domain user session. In this case, the user’s password will not be requested, and SSO authentication via Kerberos will be performed:
ssh -K server1
The first time you connect, you will be prompted to add the host to the list of known SSH hosts (C:\Users\your_user\.ssh\known_hosts).
Click Yes, and login under your Windows user account.
If the SSH connection is successful, you will see the cmd.exe shell prompt.
admin@win10pc C:\Users\admin>
You can run different commands, scripts, and apps in the SSH command prompt.
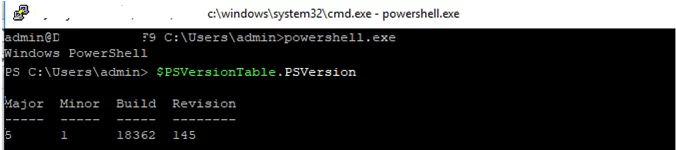
I prefer working in the PowerShell console. To start it, run:
powershell.exe
In order to change the default cmd.exe shell in OpenSSH to PowerShell, make changes to the registry using the following PowerShell command:
New-ItemProperty -Path "HKLM:\SOFTWARE\OpenSSH" -Name DefaultShell -Value "C:\Windows\System32\WindowsPowerShell\v1.0\powershell.exe" -PropertyType String –Force

Restart your SSH connection and make sure that PowerShell is now used as a default SSH shell (this is indicated by the prompt PS C:\Users\admin>).
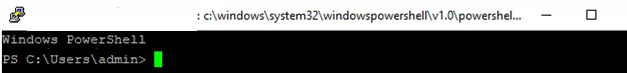
The PowerShell prompt has been started in my SSH session, where the usual functions work: tab autocomplete, PSReadLine syntax highlighting, command history, etc. If the current user is a member of the local administrators’ group, all session commands are executed elevated even if UAC is enabled.
OpenSSH server on Windows can be used in various SSH tunneling scenarios.
Checking SSH Connection Logs in Windows
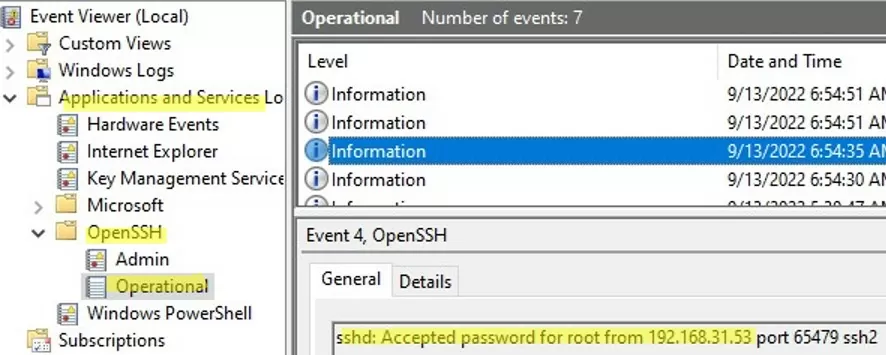
By default in Windows SSH server connection logs are written not to text files, but to a separate event log via Event Tracing for Windows (ETW). Open the Event Viewer console (eventvwr.msc ) and navigate to Application and services logs -> OpenSSH -> Operational.
If you successfully connect to the SSH server using a password, an event will appear in the log:
EventID: 4 sshd: Accepted password for root from 192.168.1.53 port 65749 ssh2
If SSH key authentication was performed, you will see the following event:
sshd: Accepted publickey for locadm from 192.168.1.53 port 61426 ssh2: ED25519 SHA256:FEHDEC/G42FS23209C2KMb4335923pigN31s3qMK322lGibD
If you want the SSH connection logs to be written to a local text file, you need to enable the following parameters in the sshd_config file:
SyslogFacility LOCAL0 LogLevel INFO
Restart the sshd service and make sure that the SSH server logs are now written to a plain text file C:\ProgramData\ssh\logs\sshd.log
You can use a secure SSH connection with PSRemoting to manage remote computers via WinRM.
В современных версиях Windows уже есть встроенный SSH сервер на базе пакета OpenSSH. В этой статье мы покажем, как установить и настроить OpenSSH сервер в Windows 10/11 и Windows Server 2022/2019 и подключиться к нему удаленно по защищенному SSH протоколу (как к Linux).
Содержание:
- Установка сервера OpenSSH в Windows
- Настройка SSH сервера в Windows
- Sshd_config: Конфигурационный файл сервера OpenSSH
- Подключение по SSH к Windows компьютеру
- Логи SSH подключений в Windows
Установка сервера OpenSSH в Windows
Пакет OpenSSH Server включен в современные версии Windows 10 (начиная с 1803), Windows 11 и Windows Server 2022/2019 в виде Feature on Demand (FoD). Для установки сервера OpenSSH достаточно выполнить PowerShell команду:
Get-WindowsCapability -Online | Where-Object Name -like ‘OpenSSH.Server*’ | Add-WindowsCapability –Online
Или при помощи команды DISM:
dism /Online /Add-Capability /CapabilityName:OpenSSH.Server~~~~0.0.1.0
Если ваш компьютер подключен к интернету, пакет OpenSSH.Server будет скачан и установлен в Windows.
Также вы можете установить сервер OpenSSH в Windows через современную панель Параметры (Settings -> Apps and features -> Optional features -> Add a feature, Приложения -> Управление дополнительными компонентами -> Добавить компонент. Найдите в списке OpenSSH Server и нажмите кнопку Install).
На изолированных от интернета компьютерах вы можете установить компонент с ISO образа Features On Demand (доступен в личном кабинете на сайте Microsoft: MSDN или my.visualstudio.com). Скачайте диск, извлеките его содержимое в папку c:\FOD (достаточно распаковать извлечь файл
OpenSSH-Server-Package~31bf3856ad364e35~amd64~~.cab
), выполните установку из локального репозитория:
Add-WindowsCapability -Name OpenSSH.Server~~~~0.0.1.0 -Online -Source c:\FOD
Также доступен MSI установщик OpenSSH для Windows в официальном репозитории Microsoft на GitHub (https://github.com/PowerShell/Win32-OpenSSH/releases/). Например, для Windows 10 x64 нужно скачать и установить пакет OpenSSH-Win64-v8.9.1.0.msi. Следующая PowerShell команда скачает MSI файл и установит клиент и сервер OpenSSH:
Invoke-WebRequest https://github.com/PowerShell/Win32-OpenSSH/releases/download/v8.9.1.0p1-Beta/OpenSSH-Win64-v8.9.1.0.msi -OutFile $HOME\Downloads\OpenSSH-Win64-v8.9.1.0.msi -UseBasicParsing
msiexec /i c:\users\root\downloads\OpenSSH-Win64-v8.9.1.0.msi
Также вы можете вручную установить OpenSSH сервер в предыдущих версиях Windows (Windows 8.1, Windows Server 2016/2012R2). Пример установки Win32-OpenSSH есть в статье “Настройка SFTP сервера (SSH FTP) в Windows”.
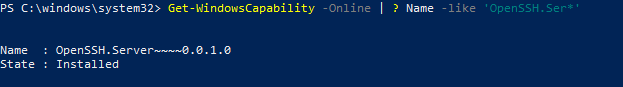
Чтобы проверить, что OpenSSH сервер установлен, выполните:
Get-WindowsCapability -Online | ? Name -like 'OpenSSH.Ser*'
State : Installed
Настройка SSH сервера в Windows
После установки сервера OpenSSH в Windows добавляются две службы:
- ssh-agent (OpenSSH Authentication Agent) – можно использовать для управления закрытыми ключами если вы настроили SSH аутентификацию по ключам;
- sshd (OpenSSH SSH Server) – собственно сам SSH сервер.
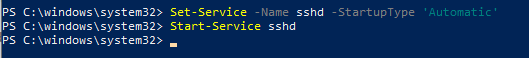
Вам нужно изменить тип запуска службы sshd на автоматический и запустить службу с помощью PowerShell:
Set-Service -Name sshd -StartupType 'Automatic'
Start-Service sshd
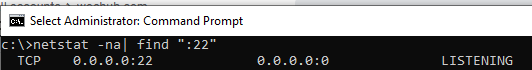
С помощью nestat убедитесь, что теперь в системе запущен SSH сервер и ждет подключений на порту TCP:22 :
netstat -na| find ":22"
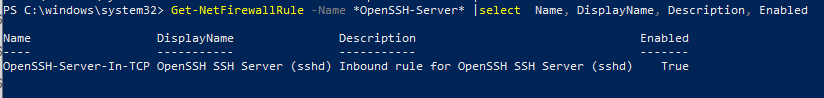
Проверьте, что включено правило брандмауэра (Windows Defender Firewall), разрешающее входящие подключения к Windows по порту TCP/22.
Get-NetFirewallRule -Name *OpenSSH-Server* |select Name, DisplayName, Description, Enabled
Name DisplayName Description Enabled ---- ----------- ----------- ------- OpenSSH-Server-In-TCP OpenSSH SSH Server (sshd) Inbound rule for OpenSSH SSH Server (sshd) True
Если правило отключено (состоянии Enabled=False) или отсутствует, вы можете создать новое входящее правило командой New-NetFirewallRule:
New-NetFirewallRule -Name sshd -DisplayName 'OpenSSH Server (sshd)' -Enabled True -Direction Inbound -Protocol TCP -Action Allow -LocalPort 22
Рассмотрим, где храниться основные компоненты OpenSSH:
- Исполняемые файлы OpenSSH Server находятся в каталоге
C:\Windows\System32\OpenSSH\
(sshd.exe, ssh.exe, ssh-keygen.exe, sftp.exe и т.д.) - Конфигурационный файл sshd_config (создается после первого запуска службы):
C:\ProgramData\ssh - Файлы authorized_keys и ssh ключи можно хранить в профиле пользователей:
%USERPROFILE%\.ssh\
Sshd_config: Конфигурационный файл сервера OpenSSH
Настройки сервере OpenSSH хранятся в конфигурационном файле %programdata%\ssh\sshd_config. Это обычный текстовый файл с набором директив. Для редактирования можно использовать любой текстовый редактор (я предпочитаю notepad++). Можно открыть с помощью обычного блокнота:
start-process notepad C:\Programdata\ssh\sshd_config
Например, чтобы запретить SSH подключение для определенного доменного пользователя (и всех пользователей указанного домена), добавьте в конце файле директивы:
DenyUsers winitpro\[email protected] DenyUsers corp\*
Чтобы разрешить подключение только для определенной доменной группы:
AllowGroups winitpro\sshadmins
Либо можете разрешить доступ для локальной группы:
AllowGroups sshadmins
По умолчанию могут к openssh могут подключаться все пользователи Windows. Директивы обрабатываются в следующем порядке: DenyUsers, AllowUsers, DenyGroups,AllowGroups.
Можно запретить вход под учетными записями с правами администратора, в этом случае для выполнения привилегированных действий в SSH сессии нужно делать runas.
DenyGroups Administrators
Следующие директивы разрешают SSH доступ по ключам (SSH аутентификации в Windows с помощью ключей описана в отдельной статье) и по паролю:
PubkeyAuthentication yes PasswordAuthentication yes
Вы можете изменить стандартный SSH порт TCP/22, на котором принимает подключения OpenSSH в конфигурационном файле sshd_config в директиве Port.
После любых изменений в конфигурационном файле sshd_config нужно перезапускать службу sshd:
restart-service sshd
Подключение по SSH к Windows компьютеру
Теперь вы можете попробовать подключиться к своей Windows 10 через SSH клиент (в этом примере я использую putty).
Вы можете использовать встроенный SSH клиентом Windows для подключения к удаленному хосту. Для этого нужно в командной строке выполнить команду:
ssh [email protected]
В этом примере
alexbel
– имя пользователя на удаленном Windows компьютере, и 192.168.31.102 – IP адрес или DNS имя компьютера.
Обратите внимание что можно использовать следующие форматы имен пользователей Windows при подключении через SSH:
-
alex@server1
– локальный пользователь Windows -
[email protected]@server1
–пользователь Active Directory (в виде UPN) или аккаунт Microsoft/ Azure(Microsoft 365) -
winitpro\alex@server1
– NetBIOS формат имени
В домене Active Directory можно использовать Kerberos аутентификацию в SSH. Для этого в sshd_config нужно включить параметр:
GSSAPIAuthentication yes
После этого можно прозрачно подключать к SSH сервер с Windows компьютера в домене из сессии доменного подключается. В этом случае пароль пользователя не указывается и выполняется SSO аутентификация через Kerberos:
ssh -K server1
При первом подключении появится стандартный запрос на добавление узла в список известных SSH хостов.
Нажимаем Да, и в открывшееся окне авторизуемся под пользователем Windows.
При успешном подключении запускается командная оболочка cmd.exe со строкой-приглашением.
admin@win10tst C:\Users\admin>
В командной строке вы можете выполнять различные команды, запускать скрипты и программы.
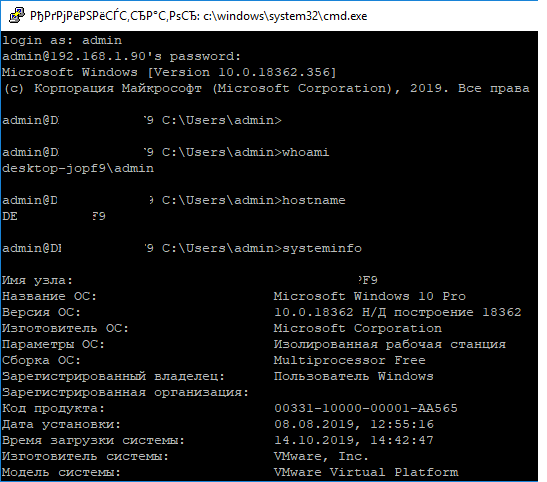
Я предпочитаю работать в командной строке PowerShell. Чтобы запустить интерпретатор PowerShell, выполните:
powershell.exe
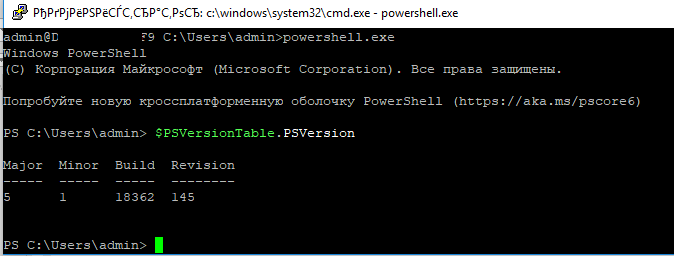
Чтобы изменить командную оболочку (Shell) по умолчанию в OpenSSH с cmd.exe на PowerShell, внесите изменение в реестр такой командой:
New-ItemProperty -Path "HKLM:\SOFTWARE\OpenSSH" -Name DefaultShell -Value "C:\Windows\System32\WindowsPowerShell\v1.0\powershell.exe" -PropertyType String –Force
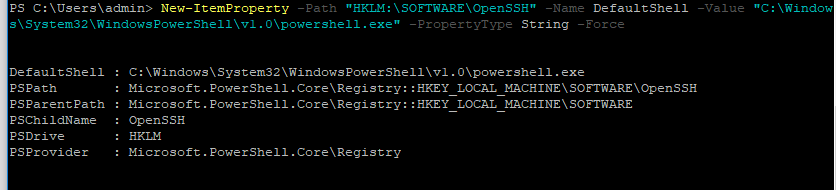
Осталось перезапустить SSH подключение и убедиться, что при подключении используется командный интерпретатор PowerShell (об этом свидетельствует приглашение
PS C:\Users\admin>
).
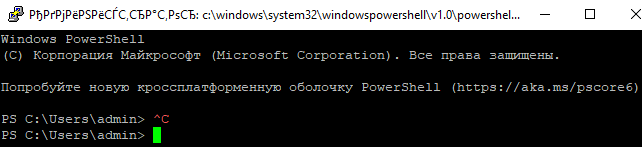
В SSH сессии запустилась командная строка PowerShell, в которой работают привычные функции: авто дополнение, раскраска модулем PSReadLine, история команд и т.д. Если текущий пользователь входит в группу локальных администраторов, то все команды в его сессии выполняются с повышенными правами даже при включенном UAC.
Логи SSH подключений в Windows
В Windows логи подключений к SSH серверу по-умолчанию пишутся не в текстовые файлы, а в отдельный журнал событий через Event Tracing for Windows (ETW). Откройте консоль Event Viewer (
eventvwr.msc
>) и перейдите в раздел Application and services logs -> OpenSSH -> Operational.
При успешном подключении с помощью к SSH серверу с помощью пароля в журнале появится событие:
EventID: 4 sshd: Accepted password for root from 192.168.31.53 port 65479 ssh2
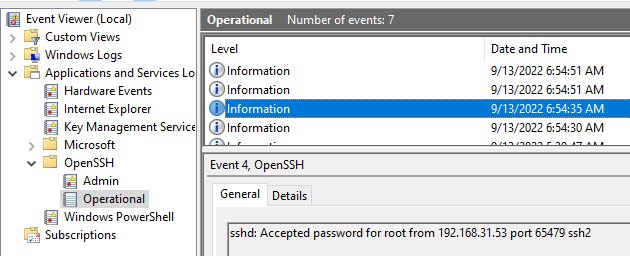
Если была выполнена аутентификация с помощью SSH ключа, событие будет выглядеть так:
sshd: Accepted publickey for locadm from 192.168.31.53 port 55772 ssh2: ED25519 SHA256:FEHDEC/J72Fb2zC2oJNb45678967kghH43h3bBl31ldPs
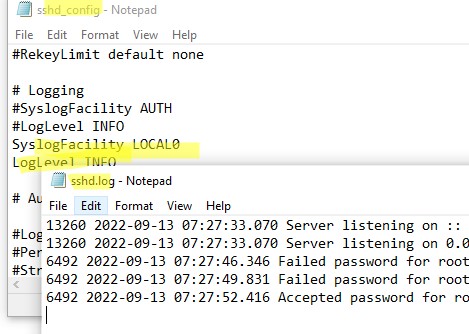
Если вы хотите, чтобы логи писались в локальный текстовый файл, нужно в файле sshd_config включить параметры:
SyslogFacility LOCAL0 LogLevel INFO
Перезапустите службу sshd и провеьте, что теперь логи SSH сервера пишутся в файл C:\ProgramData\ssh\logs\sshd.log
В последних билдах Windows 10 появился встроенный SSH сервер и клиент на базе OpenSSH. Это значит, что теперь вы можете удаленно подключаться к компьютеру Windows 10/11 (Windows Server 2019/2022) с помощью любого SSH клиента, как к Linux. В этой статье мы покажем, как настроить OpenSSH в Windows 10 и подключится к нему с помощью putty или любого другого SSH клиента.
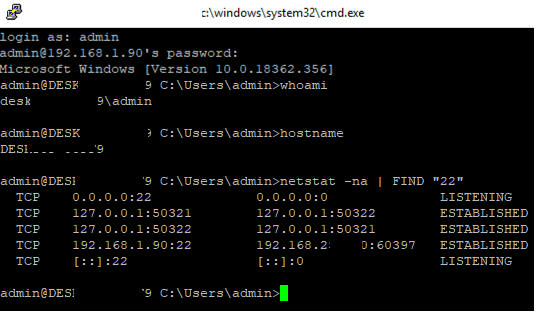
Убедитесь, что ваша версия Windows 10 1809 или выше. Проще всего это сделать, выполнив команду:
winver
Совет. Если у вас более старая версия Windows 10 вы можете обновить ее через Windows Update или с помощью ISO образа с более новой версией Windows 10 (можно создать его с помощью Media Creation Tool). Если вы не хотите обновлять Windows 10, вы можете вручную установить порт OpenSSH для Windows с GitHub — Win32-OpenSSH (https://github.com/PowerShell/Win32-OpenSSH).
Вы можете включить OpenSSH сервера в Windows 10 через панель Параметры:
- Перейдите в Settings -> Apps -> Optional features;
- Нажмите Add a feature, выберите OpenSSH Server и нажмите Install;
Также вы можете установить sshd сервер в Windows с помощью PowerShell:
Add-WindowsCapability -Online -Name OpenSSH.Server*
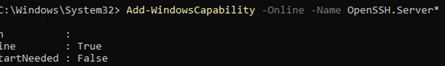
Или с помощью DISM:
dism /Online /Add-Capability /CapabilityName:OpenSSH.Server~~~~0.0.1.0
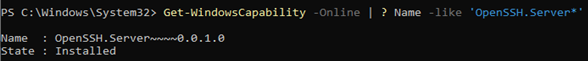
Если вы хотите убедитесь, что OpenSSH сервер установлен, выполните следующую команду:
Get-WindowsCapability -Online | ? Name -like 'OpenSSH.Server*'
Name : OpenSSH.Server~~~~0.0.1.0 State : Installed
Проверьте статус служб ssh-agent и sshd с помощью командлета Get-Service:
Get-Service -Name *ssh*
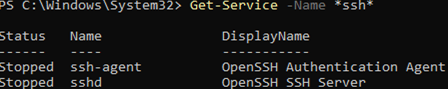
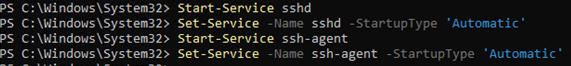
Как вы видите, обе службы находятся в состоянии Stopped и не добавлены в автозагрузку. Чтобы запустить службы и настроить для них автозапуск, выполните команды:
Start-Service sshd
Set-Service -Name sshd -StartupType 'Automatic'
Start-Service ‘ssh-agent’
Set-Service -Name ‘ssh-agent’ -StartupType 'Automatic'
Также нужно разрешить входящие подключения на порт TCP 22 в Windows Defender Firewall:
netsh advfirewall firewall add rule name="SSHD service" dir=in action=allow protocol=TCP localport=22
Теперь вы можете подключиться к Windows 10 с помощью любого SSH клиента. Для подключения из Linux используете команду:
ssh -p 22 admin@192.168.1.90
где, admin – имя локального пользователя Windows, под которым вы хотите подключиться
192.168.1.90 – ip адрес вашего компьютера с Windows 10
После этого откроется окно командной строки Windows.
Совет. Чтобы вместо оболочки cmd.exe при подключении к Windows 10 через SSH запускалась консоль PoweShell, нужно выполнить команду:
New-ItemProperty -Path "HKLM:\SOFTWARE\OpenSSH" -Name DefaultShell -Value "C:\Windows\System32\WindowsPowerShell\v1.0\powershell.exe" -PropertyType String –Force
Так вы измените оболочку, которая стартует через OpenSSH. Теперь при подключении к Windows по SSH у вас будет сразу открываться консоль PowerShell вместо командной строки cmd.exe.
Если вы хотите использовать key-based ssh authentification вместо парольной аутентификации, нужно на вашем клиенте сгенерировать ключ с помощью ssh-keygen.exe.
Затем содержимое файла id_rsa.pub нужно скопировать в файл c:\users\admin\.ssh\authorized_keys в Windows 10.
После этого вы сможете подключаться с вашего Linux клиента к Windows 10 без пароля. Используйте команду:
ssh -l admin@192.168.1.90
Вы можете настроить различные параметры OpenSSH сервера в Windows с помощью конфигурационного файла %programdata%\ssh\sshd_config
Например, вы можете отключить аутентификацию по паролю и разрешить вход только по ключу:
PubkeyAuthentication yes PasswordAuthentication no
How to Install OpenSSH Server/Client on Windows Server 2016 1607 or Before
OpenSSH is the premier connectivity tool for remote login with the SSH protocol. It encrypts all traffic to eliminate eavesdropping, connection hijacking, and other attacks. In addition, OpenSSH provides a large suite of secure tunneling capabilities, several authentication methods, and sophisticated configuration options. Installation of OpenSSH server/client on Windows 2016 1709 onward is really easy. its just few powershell commands away from using it but for older versions it can be a time wasting activity. The easiest way to install is still very long but I would to wrap in few basic steps:
Download OpenSSH
First you need to Download OpenSSH using the attached URL. A zip file will be downloaded on your desired system. Unzip it and copy it under Windows\system32 directory.
Open PowerShell ISE
Open PowerShell ISE with administrative privileges so that you can run the desired commands without any problem. Change the directory to c:\windows\system32\openssh
Run the Commands
First you need to modify the required permission so run the under given command from OpenSSh Directory. The commands are given in the picture below:
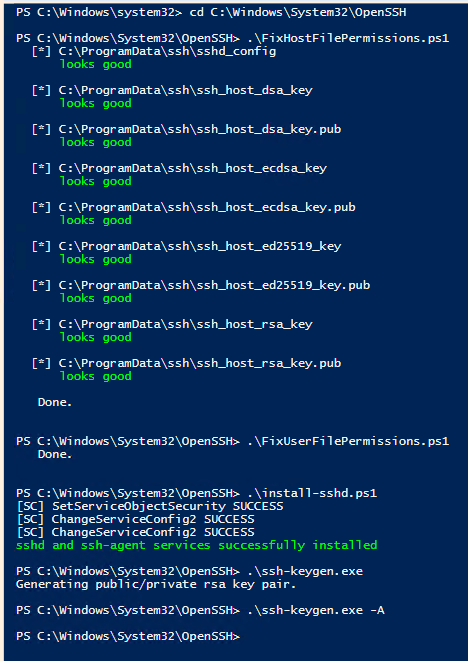
Run the commands in the given order and OpenSSH server will be installed on the Windows Server 2016 1607 or earlier version.
Environment Variables
Copy the directory path and set the system environment variables so that the commands can work without giving the exact path. You can use PowerShell commands to set the path or go to system settings and manually set the path.
Start the services
Change the service startup type from manual to automatic and start the service to use OpenSSH server.
Windows Firewall Settings
SSH works on TCP port 22 so you need to open in-bound port in Windows firewall so that in-coming connections can be accepted. Opening firewall port is pretty simple and I think there is no need to share any command or process to do it.
Thanks for visiting. I hope you like the post.
Время на прочтение3 мин
Количество просмотров100K
Меня всегда удручало подключение к Windows машинам. Нет, я не противник и не сторонник Microsoft и их продуктов. Каждый продукт существует для своей цели, но речь не об этом.
Для меня всегда было мучительно больно подключаться к серверам с Windows, потому что эти подключения либо настраиваются через одно место (привет WinRM с HTTPS) либо работают не очень стабильно (здравствуй RDP к виртуалкам за океаном).
Поэтому, случайно натолкнувшись на проект Win32-OpenSSH, я решил поделиться опытом настройки. Возможно кому-нибудь эта тулза сэкономить кучу нервов.

Варианты установки:
- Вручную
- Через пакет Chocolatey
- Через Ansible, например роль jborean93.win_openssh
Далее я буду рассказывать про первый пункт, так как с остальными и так все более менее понятно.
Отмечу, что данный проект пока что находится на стадии beta, поэтому его не рекомендуют использовать в production.
Итак, скачиваем последний релиз, на текущий момент это 7.9.0.0p1-beta. Есть версии как для 32 так и для 64 битных систем.
Распаковываем в C:\Program Files\OpenSSH
Обязательный момент для корректной работы: права на запись в этой директории должны быть только у SYSTEM и у админской группы.
Устанавливаем сервисы скриптом install-sshd.ps1 находящимся в этой директории
powershell.exe -ExecutionPolicy Bypass -File install-sshd.ps1Разрешаем входящие подключения на 22 порт:
New-NetFirewallRule -Name sshd -DisplayName 'OpenSSH Server (sshd)' -Enabled True -Direction Inbound -Protocol TCP -Action Allow -LocalPort 22Уточнение: апплет New-NetFirewallRule используется на Windows Server 2012 и новее. В наиболее старых системах (либо десктопных) можно воспользоваться командой:
netsh advfirewall firewall add rule name=sshd dir=in action=allow protocol=TCP localport=22
Запускаем сервис:
net start sshdПри запуске будут автоматически сгенерированы хост-ключи (если отсутствуют) в %programdata%\ssh
Автозапуск сервиса при запуске системы мы можем включить командой:
Set-Service sshd -StartupType AutomaticТак же, можно сменить командную оболочку по умолчанию (после установки, по умолчанию — cmd):
New-ItemProperty -Path "HKLM:\SOFTWARE\OpenSSH" -Name DefaultShell -Value "C:\Windows\System32\WindowsPowerShell\v1.0\powershell.exe" -PropertyType String -ForceУточнение: Необходимо указывать абсолютный путь.
Что дальше?
А дальше настраиваем sshd_config, который расположем в C:\ProgramData\ssh. Например:
PasswordAuthentication no
PubkeyAuthentication yesИ создаем в пользовательской папке директорию .ssh, а в ней файл authorized_keys. Туда записываем публичные ключи.
Важное уточнение: права на запись в этот файл, должен иметь только пользователь, в чьей директории лежит файл.
Но если у вас проблемы с этим, всегда можно выключить проверку прав в конфиге:
StrictModes noК слову, в C:\Program Files\OpenSSH лежат 2 скрипта (FixHostFilePermissions.ps1, FixUserFilePermissions.ps1), которые должны
но не обязаны
фиксить права, в том числе и с authorized_keys, но почему-то не фиксят.
Не забывайте перезапускать сервис sshd после для применения изменений.
ru-mbp-666:infrastructure$ ssh Administrator@192.168.1.10 -i ~/.ssh/id_rsa
Windows PowerShell
Copyright (C) 2016 Microsoft Corporation. All rights reserved.
PS C:\Users\Administrator> Get-Host
Name : ConsoleHost
Version : 5.1.14393.2791
InstanceId : 653210bd-6f58-445e-80a0-66f66666f6f6
UI : System.Management.Automation.Internal.Host.InternalHostUserInterface
CurrentCulture : en-US
CurrentUICulture : en-US
PrivateData : Microsoft.PowerShell.ConsoleHost+ConsoleColorProxy
DebuggerEnabled : True
IsRunspacePushed : False
Runspace : System.Management.Automation.Runspaces.LocalRunspace
PS C:\Users\Administrator>Субъективные плюсы/минусы.
Плюсы:
- Стандартный подход к подключению к серверам.
Когда есть немного Windows машин, очень неудобно когда:
Так, сюда мы ходим по ssh, а тут рдп,
и вообще best-practice с бастионами, сначала ssh-туннель, а через него RDP. - Простота настройки
Считаю что это очевидно. - Скорость подключения и работы с удаленной машиной
Нет графической оболочки, экономятся как ресурсы сервера, так и количество передаваемых данных.
Минусы:
- Не заменяет RDP полностью.
Не все можно сделать из консоли, увы. Я имею ввиду ситуации, когда требуется GUI.
Материалы использованные в статье:
Ссылка на сам проект
Варианты установки бессовестно скопированы с Ansible docs.