Maximize Performance of Windows Server 2019: Expert Tips and Tricks
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Background on Windows Server 2019
- Licensing Options for Windows Server 2019
- Long-Term Servicing Channel (LTSC)
- Pros
- Cons
- Semi-Annual Channel
- Pros
- Cons
- Long-Term Servicing Channel (LTSC)
- Choosing the Right Servicing Channel
- Use Cases for the Long-Term Servicing Channel
- Use Cases for the Semi-Annual Channel
- Security Updates and Features
- Release Schedule for Semi-Annual Channel
- Conclusion
🖥️ Introduction
When licensing Windows Server 2019, there are two primary servicing channels to choose from: the Long-Term Servicing Channel (LTSC) and the Semi-Annual Channel. These channels determine the frequency of updates, support lifespan, and availability of new features for your operating system. In this article, we will explore the differences between these channels and discuss their use cases, pros, and cons to help you make an informed decision.
📚 Background on Windows Server 2019
Before delving into the servicing channels, let’s provide some context on Windows Server 2019. It is the latest version of Microsoft’s server operating system, designed to enhance security, improve performance, and offer new features for modern IT environments. As with any Microsoft product, licensing options play a crucial role in determining the level of support and updates you receive.
💼 Licensing Options for Windows Server 2019
Long-Term Servicing Channel (LTSC)
The LTSC is the traditional servicing channel for Windows Server. It follows a long-term support model where a new version of Windows Server is released every two to three years. With the LTSC, you are entitled to five years of mainstream support and can purchase an additional five years of extended support. This gives you a total of 10 years of support, making it an ideal choice for devices with specific purposes, such as MRI machines in hospitals or cash registers in retail environments.
Pros
- Stability: The LTSC provides a stable and predictable environment with only security and non-security updates, offering a robust solution for dedicated-purpose machines.
- Long support lifespan: The 10-year support lifespan ensures your systems receive essential security updates during its operational life.
Cons
- Limited new features: As the LTSC focuses on stability, it does not receive new features or functionality introduced in subsequent versions or updates.
Semi-Annual Channel
The Semi-Annual Channel, closely associated with Windows 10, offers more frequent updates to take advantage of new features and improvements. It is better suited for organizations that want to innovate quickly and leverage the latest capabilities offered by the operating system. Typically, new releases for the Semi-Annual Channel occur twice a year, and each release is supported for 18 months from the initial launch.
Pros
- New features and enhancements: By opting for the Semi-Annual Channel, you gain access to the latest features, improvements, and enhancements introduced in the operating system updates.
- Agile updates: With frequent releases, you can rapidly integrate new capabilities into your infrastructure.
Cons
- Frequent updates: The Semi-Annual Channel requires organizations to keep up with the pace of new releases, which may involve testing and compatibility checks.
- Short support lifespan: Each release is only supported for 18 months, potentially necessitating regular upgrades to remain within the support window.
🔍 Choosing the Right Servicing Channel
The choice between the Long-Term Servicing Channel and the Semi-Annual Channel depends on your specific needs and requirements. Consider factors such as the intended use of the operating system, the level of stability required, and your organization’s ability to adapt to frequent updates.
📝 Use Cases for the Long-Term Servicing Channel
The Long-Term Servicing Channel is well-suited for devices with dedicated purposes, such as ATMs and cash registers in retail environments, as well as machines in Healthcare settings like MRI machines. These devices often require stability and a long support lifespan without the need for regular feature updates.
👨💻 Use Cases for the Semi-Annual Channel
The Semi-Annual Channel is preferable for organizations that want to stay at the forefront of technology and take advantage of the latest features and enhancements. It is particularly useful for businesses that rely on innovative solutions, continuous integration, or agile development methodologies.
🔒 Security Updates and Features
Both the Long-Term Servicing Channel and the Semi-Annual Channel receive security updates. However, the Semi-Annual Channel also includes new features and functionality with each release. It’s essential to assess the importance of receiving new features versus maintaining a stable and predictable environment.
🗓️ Release Schedule for Semi-Annual Channel
The Semi-Annual Channel follows a regular release schedule, typically with updates in the spring and fall. Aligning with the release pattern of Windows 10, each release is supported for 18 months, during which you can enjoy the latest features and capabilities. Planning your system updates accordingly is crucial to take full advantage of the Semi-Annual Channel.
📝 Conclusion
In conclusion, the choice between the Long-Term Servicing Channel and the Semi-Annual Channel ultimately depends on your organization’s requirements, use cases, and preference for stability versus frequent updates. Consider the purpose of your machines, the need for new features, and your ability to adapt to changes before selecting the appropriate servicing channel for your Windows Server 2019 deployment.
Highlights
- Windows Server 2019 offers two primary servicing channels: Long-Term Servicing Channel (LTSC) and Semi-Annual Channel.
- LTSC provides a stable environment with long-term support and no new feature updates.
- The Semi-Annual Channel offers more frequent updates and access to the latest features and enhancements.
- Choose LTSC for dedicated-purpose machines and Semi-Annual Channel for agile organizations and innovation.
- Assess your needs for stability, security updates, and access to new features before selecting a servicing channel.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: Can I switch between the Long-Term Servicing Channel and the Semi-Annual Channel?
A: Yes, it is possible to switch between the channels. However, it involves upgrading or re-installing the operating system, which may require additional steps and considerations.
Q: How often do new releases occur in the Semi-Annual Channel?
A: New releases in the Semi-Annual Channel typically happen twice a year, following the release pattern of Windows 10.
Q: What happens if my supported release in the Semi-Annual Channel reaches its end of life?
A: It is recommended to update to the latest supported release within the Semi-Annual Channel to continue receiving security updates and access to new features.
Resources:
- Windows Server 2019 documentation

Optimizing Windows Server 2019 involves several steps and strategies to ensure that the server operates efficiently and securely. Here are some key areas to focus on:
1. Regular Updates and Patches
- Keep the System Updated: Regularly apply Windows updates to fix bugs, patch vulnerabilities, and improve performance.
- Update Drivers: Ensure that hardware drivers are up to date for optimal performance and security.
2. Performance Tuning
- Hardware Optimization: Use hardware that meets or exceeds the recommended specifications for Windows Server 2019.
- Resource Allocation: Allocate sufficient resources (CPU, memory, storage) based on the server’s role and workload.
- Network Settings: Optimize network settings for better performance, especially if the server handles large data transfers.
3. Role-Based Configuration
- Configure Server Roles: Configure server roles and features according to the specific needs of your environment (e.g., DNS, DHCP, File Server).
- Minimize Server Roles: Limit the server to essential roles to reduce resource usage and potential attack vectors.
4. Security Enhancements
- Firewall and Antivirus: Ensure a robust firewall is in place and antivirus software is installed and updated.
- Least Privilege Principle: Implement the least privilege principle for user accounts and services.
5. Storage Management
- Optimize Disk Usage: Regularly clean up disk space and defragment HDDs (if applicable).
- Storage Spaces: Utilize Storage Spaces for data resilience and performance.
6. Monitoring and Maintenance
- Regular Monitoring: Use tools like Performance Monitor and Event Viewer to track server performance and identify issues.
- Scheduled Maintenance: Perform regular maintenance, including checking for hardware issues and cleaning physical components.
7. Backup and Disaster Recovery
- Regular Backups: Implement a robust backup strategy to protect data.
- Disaster Recovery Plan: Have a disaster recovery plan in place in case of hardware failure or other emergencies.
8. Software and Services
- Unnecessary Services: Disable services that are not needed to free up resources.
- Scheduled Tasks: Review and optimize scheduled tasks for efficiency.
9. Group Policy and User Management
- Group Policy: Use Group Policy to enforce security settings and configurations across your network.
- Active Directory Management: Efficiently manage users and groups if using Active Directory.
10. Power Settings
- Power Plan: Opt for a power plan that balances performance and energy consumption, especially in a data center environment.
11. Virtualization (if applicable)
- Hyper-V Optimization: If using Hyper-V for virtualization, optimize the settings for the host and virtual machines.
12. Documentation and Compliance
- Keep Records: Document configurations and changes for troubleshooting and compliance purposes.
Each environment is unique, so it’s important to tailor these recommendations to your specific needs and regularly review and adjust settings based on performance data and evolving requirements. Additionally, it’s beneficial to stay informed about best practices and new features or updates from Microsoft for Windows Server 2019.
3. Implement Group Policies (Group Policy):
Group Policy is a key feature in Windows Server 2019 that allows you to set and enforce security and management settings in a network environment. Use Group Policy to centrally manage the configuration of your servers and ensure that your organisation’s standards and requirements are met.
3.1 Creating Custom Group Policies
Learn how to create your own custom Group Policies to tailor your server configuration to the specific needs of your organisation. You can set security settings, restrict access to certain functions and customise the user environment according to your requirements.
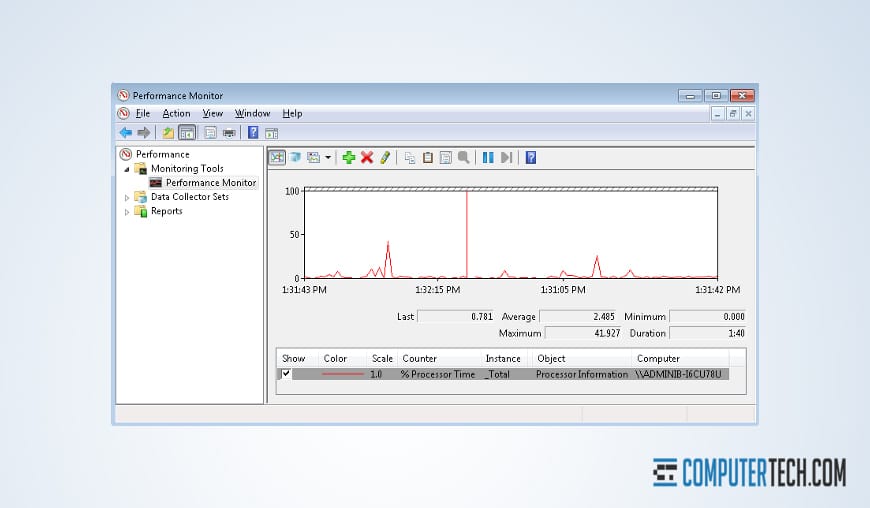
4. Use Monitoring and Performance Tools
Windows Server 2019 offers integrated monitoring and performance tools, such as Performance Monitor and Resource Monitor. Use these tools to monitor server performance, identify bottlenecks, and optimise resource usage. Regular monitoring will help you maintain a healthy and efficient server.
5. Keep your server up to date
It is crucial to keep your server up to date with the latest security patches and updates. Set up automatic updates or set up a regular schedule for installing updates. Keeping your server up to date will protect against known vulnerabilities and improve its overall performance.
Conclusion
Windows Server 2019 offers a wide range of features and tools to efficiently manage your server resources. By leveraging Server Manager, PowerShell, Group Policy, and monitoring and performance tools, you can optimise your Windows Server 2019 management experience. These tips and tricks will help you save time, improve efficiency, and keep your server secure and up-to-date.
Remember that Windows Server 2019 is a versatile and flexible platform, so I encourage you to further explore its features and customise them to your organisation’s needs. Keep a continuous focus on improving and updating your server administration skills to make the most of this powerful platform.
I hope you find these tips and tricks useful in your Windows Server 2019 administration experience! Remember to always research and explore new ways to improve your efficiency and optimise your server environment. Windows Server 2019 is a powerful tool that can help you achieve your business goals.
If you have any further questions, please contact us 
-
An impression many people get is that servers are static and inviolable. They are computers that are orders of magnitude more powerful than your typical desktop, and as such, they rarely if ever experience issues. Problems might be blamed on “the servers” when they have nothing to do with your actual server infrastructure.
The reality is that servers are just big computers, often running specialized software. They can have all of the same sorts of issues that regular computers do, except they tend to be more regimented in their operation. They don’t have a user installing browser toolbars or opening sketchy emails, but they can still be infected with malware just like any other machine.
More importantly, they can have just as many hardware and software issues as any other machine. A server running Windows Server 2012 R2 can have a wide range of configuration problems, settings that hinder performance, and even simple memory leak problems. Likewise, their RAM is still RAM, their hard drives are still hard drives, and their processors are still processors. A fault in any of those components can lead to all manner of problems.
Below, we’ve compiled a list of potential problems you can check for so that you can troubleshoot a slow server. Before you dig in, though, we recommend backing up your data and configurations. Note down any changes you make and when, so you can diagnose if those changes cause problems down the line. And, of course, don’t change anything you don’t have the authority to change; if you need to talk to your IT staff, do that instead.
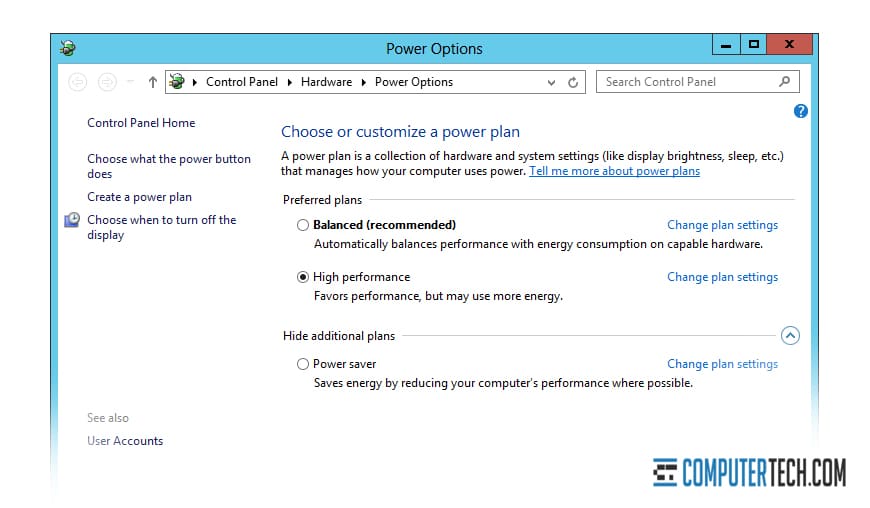
Switch to High-Performance Power
Power plans for servers dynamically scale the clock speed of the processors to meet the needs of the server at any given time. When load changes, this can cause slow performance and delays as the server adjusts. By changing to a high-performance power plan, you can guarantee the processors run at 100% at all times, so all resources are ready and available when needed.
You can set the power plan per-device as a local machine policy, or for all of your servers as part of a group policy. Either way, the option is found in the local computer policy menu under power options.
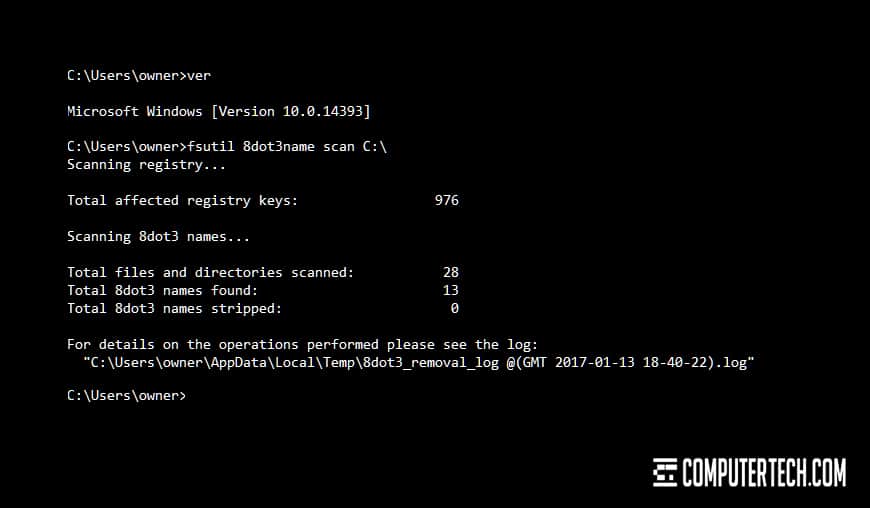
Disable DOS 8.3 Short File Names
Short File Names for DOS 8.3 is a backwards compatibility feature. If you don’t require support for legacy equipment or short names, you can disable this compatibility option to speed up file indexing and creation.
In the command prompt, type fsutil 8dot3name query followed by your volume designation, such as D: – this will show you whether or not you have this option enabled. If it’s enabled, and you’ve confirmed you don’t need it, you can disable it by typing fsutil 8dot3name set d: 1, where d: is your volume name again. You can also strip existing names from compatible files, though doing so might not affect performance.
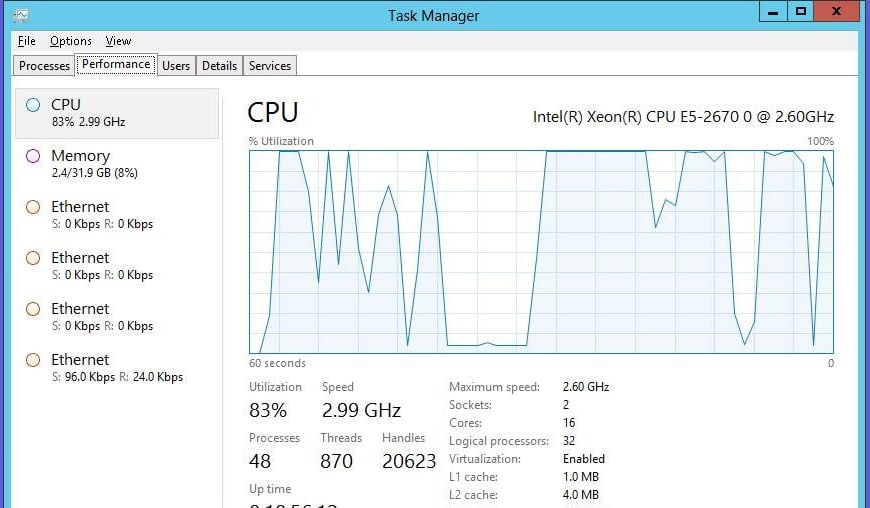
Check for CPU or RAM Consuming Processes
Every Windows computer, whether it’s a server or a PC, has a task manager. Your task manager shows, among other things, all of the processes running on your machine. Along with the process name, it can show additional information, including the RAM and CPU usage that process is consuming at any given time.
A common cause of a slow Windows Server 2012 R2 installation is a process that is consuming exceptionally large amounts of resources. To check this, open up your task manager the usual way, such as with CTRL-SHIFT-ESC or by right-clicking the taskbar and choosing task manager from the menu.
First, check the bottom of the window. Under CPU usage and Physical Memory, there are percentages. Are either of those options maxed out at 100% or otherwise higher than you expect them to be? If so, you may have a problem. Check the Processes tab and sort it by CPU usage or by memory usage, to see which processes are taking up so many resources.
When you identify a problem process, you can investigate what it is and determine if it can be killed and restarted, if it’s malicious software, or what the problem may be. If necessary, contact the employee responsible for the offending application.
You may also want to check the tasks on your virtual machines (if you’re running any). If one of your VMs is maxing out on CPU or memory, and if you’ve configured them to use a flexible amount of processing power, they may be sapping a lot of your server’s resources.
Scan for Malware
Servers are just as vulnerable to malware as personal computers. If they’re accessible to the internet, roving malware can find its access point. If it’s on a network, any infected device on that network could spread malware to it. You will want to have some form of antivirus protection on your server. Usually, Windows Defender is good, but in some cases, you may need something more powerful as an enterprise-grade solution.
If you notice any odd processes consuming resources, or odd behavior, or signs of malware, scan for it. You should also routinely scan, as well as keeping active protection engaged at all times. Avoid making exceptions for individual users or applications, as these can be exploited. Also, keep in mind that some malware is insidious and difficult to spot. Not everything is an obvious piece of ransomware – the truth is, the worst viruses are the ones that are perfectly invisible.
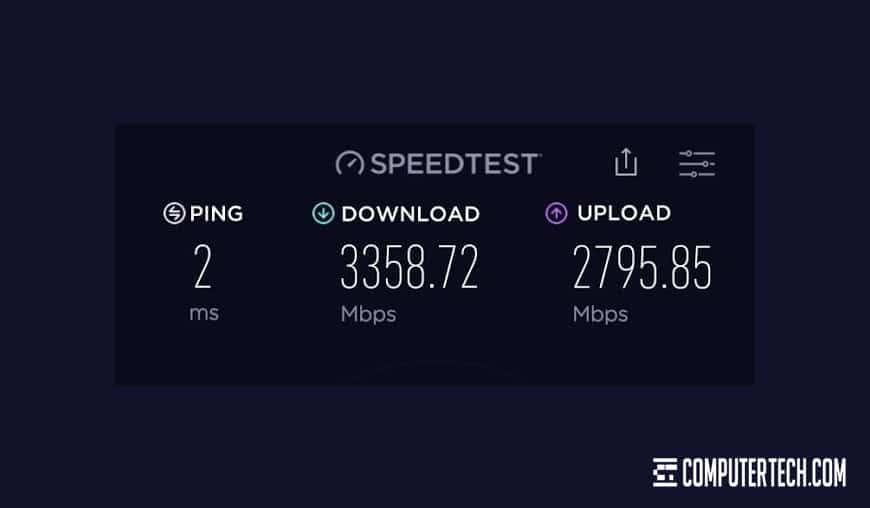
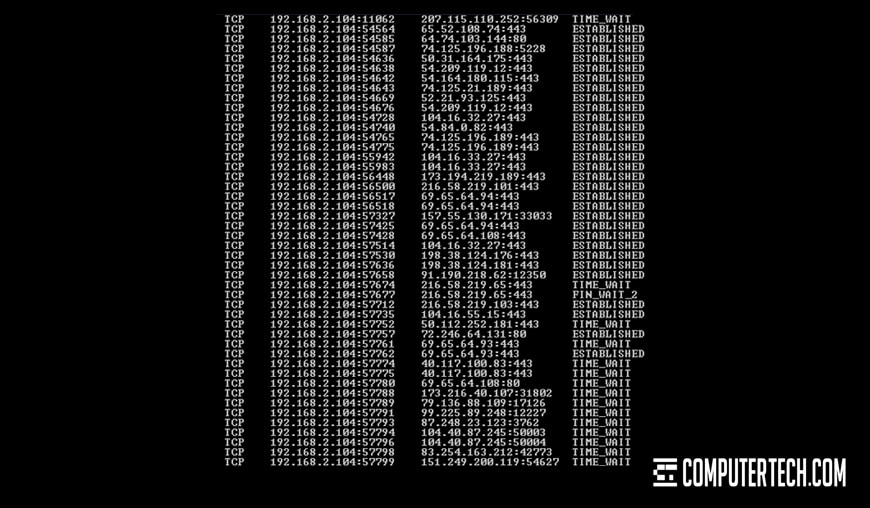
Check Network Speeds
It’s also possible that the cause of slow server speeds has nothing to do with the server itself, and everything to do with the connection used to access it.
There are a lot of different ways in which a server can slow down due to a poor connection.
- Check to make sure all relevant cords are plugged in tight.
- Check any relevant cables to make sure they’re modern, high-speed cables.
- Check with the user reporting problems to make sure they aren’t having personal speed issues.
- Check with the ISP to see if they are having uptime or connection issues.
- Check your network controller to make sure its hardware and software are up to date.
In some cases, you’ll be chasing down reported “slow server speeds” when the actual problem is an issue with the user’s VPN or their ISP. It can also be an issue with DNS. In fact, DNS issues are so common and so varied that many IT workers default to checking for DNS issues before looking elsewhere.
Update Relevant Drivers
If you don’t perform regular maintenance on your servers, it’s possible that you may have an issue that would normally be solved with an update you have not applied. Software issues are common, but you may also consider updating drivers for the hardware in your machine. Driver updates are often overlooked until they cause a problem, but it can be difficult to identify when a problem is caused by a driver issue.
The most relevant drivers to update are typically network card drivers, but graphics and other drivers can cause problems as well.
Before updating any driver, check to make sure the server can be temporarily decommissioned, or that you’re within a designated maintenance window. Driver updates often require a restarted machine, and you don’t want to take down a critical part of your business during operations for a driver update.
Check for Signs of Attack
As mentioned above, servers can be vulnerable to both malware and malicious attack from an outside source. If your server is accessible at all from the internet, it can be subject to attack, even when the way to access it is hidden. There are scripts and bots that exist solely to try every possible IP address in sequence just to see what’s on the other end. Obscurity is not security.
Attacks come and go. A lone bot spamming login attempts can slow down your server as it has to process those attempts. This is why implementing a lockout policy is always a good idea. You may have to deal with unlocking accounts from users who frequently forget their passwords, but it’s better than allowing bots to hammer at your system until they get in.
Additionally, DDoS attacks can eat up server resources and slow down an entire machine. Check network activity and look for unusual spikes or anything that might max out resources. There are many ways to protect a server against a DDoS attack, but it depends on the kind of attack. If you identify an attack, you can investigate further.
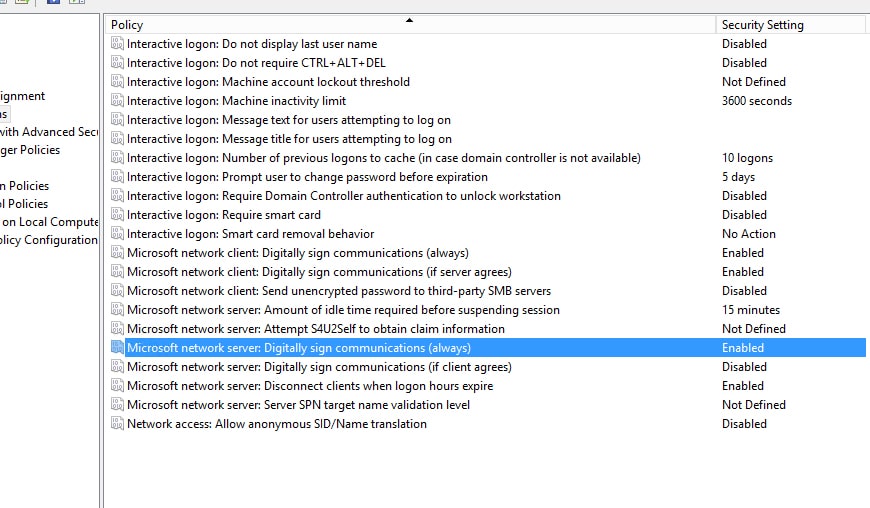
Disable SMB Packet Signing
Server Message Block Packet Signing is a security measure used in Windows servers. Each packet of information passed between a server and a user or back is digitally signed to verify its authenticity. This helps prevent malicious users or devices from inserting themselves in the middle to scrape data or otherwise alter messages.
Unfortunately, in some cases, SMB packet signing can slow down a server, particularly with large file transfers. This is because each packet needs to be signed and authenticated, and this process takes time. Often, it can time out mid-operation as well, further delaying the transfer of a file.
You can check to see if this might be an issue by attempting to transfer a large file and watching the graph of progress. If it’s flat and smooth, this isn’t a problem. If it has abrupt peaks and valleys, time-outs may be the problem.
You can disable packet signing in the security settings for your group policy. Be aware, however, that packet signing is a security measure. Only disable it if you have other security measures in place to prevent man in the middle attacks. A bit more performance isn’t worth a compromised network, after all.
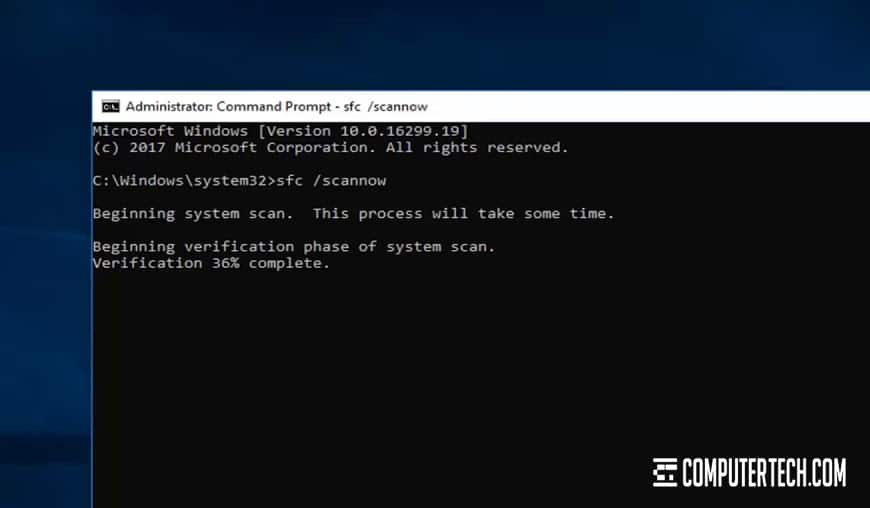
Run SFC /Scannow
Over time and with use, a hard drive – particularly spinning platter drives, though SSDs can have issues as well – degrades. This degradation can result in corrupted blocks of storage, which may or may not be otherwise occupied. Servers can run into issues if system files or other infrequently-accessed files are corrupted, making certain processes error or time out. Sometimes this results in hard-locks or system crashes, and other times it simply causes a time-out or other process failure.
One way to check for such errors is to use the System File Checker. Running SFC with /Scannow will perform a full system scan looking for filesystem errors or corrupted system files. If it finds any, it will offer you the option to repair them, which should help resolve the issue.
Review Hardware for Faults
If your system file scan found faults, you might have a drive that is on the verge of failure. If this is the case, you should consider scanning the entire disc to look for other faults, and repair them. Then, you should swap out the drive. If your drives are properly mirrored, you should be able to hot-swap an individual drive without causing issues. Do not, however, yank a drive if you don’t know that it’s safe to do so. It’s much more common to have a system that needs to be taken down for maintenance and the hardware swapped.
Reference the Performance Tuning Guide
There are approximately a million different settings within the overall Windows Server 2012 R2 system that can be tweaked to improve performance. Often times, the standard settings out of the box are good enough, but in some situations they are no longer adequate. You can tweak and tune these settings to improve the overall performance of your system.
We’re not going to reproduce the entire tuning guide here, because it’s 181 pages long. You can find the full guide in PDF form here.
Consider a Migration to a Cloud Platform
Tweaking and dealing with system issues is a core part of running an on-premises server infrastructure. If you’re continually having issues with them, particularly if those issues are related to hardware limitations, updates, or maintenance, you might benefit from migrating your system to the cloud. We’ve talked extensively about when a cloud system is right for a business, and we’d be more than happy to discuss the entire premise with you if you give us a call.
Contact an Expert for Remote Assistance
If basic troubleshooting hasn’t identified the issue for you, and you don’t want to transfer to a cloud system, it might be worthwhile to contact a company like us to do a remote overview of your system.
Remote assistance can diagnose a lot of potential issues with your server, and we can both offer assistance with fixing them and with managing the servers moving forward. Again, feel free to contact us for more information.
About The Author
Herman
Herman is the lead team member here at Computertech.com. He’s been in IT for over 20 years and has expertise in our various IT Services including Microsoft Azure, Microsoft 365, Microsoft Teams and even Computer Security.
No related posts.
Windows Server 2019 — мощная операционная система, которая может обеспечить надежную и эффективную работу вашего сервера. Однако, как и любая другая операционная система, она может быть протюнена для достижения еще большей производительности.
В данной статье мы рассмотрим несколько методов и стратегий, которые помогут вам оптимизировать работу Windows Server 2019. Мы расскажем о настройке системы для максимальной производительности, использовании инструментов и рекомендаций по улучшению работы операционной системы.
Научитесь оптимизировать производительность вашего сервера с помощью уменьшения загрузки процессора, оптимизации использования памяти, настройки сети и многое другое. Подготовьте ваш сервер к ожидаемым нагрузкам и обеспечьте его стабильную работу.
Содержание
- Оптимизация работы Windows Server 2019
- Улучшение производительности и эффективности системы
- Повышение производительности Windows Server 2019
- 1. Оптимизация настроек энергосбережения
- 2. Оптимизация работа HDD и SSD
- 3. Управление службами и приложениями
- 4. Оптимизация сетевых настроек
- 5. Улучшение производительности журнала событий
- Настройка и оптимизация ресурсов сервера
- Оптимизация сетевых настроек Windows Server 2019
- Ускорение передачи данных и снижение задержек
Оптимизация работы Windows Server 2019
Вот несколько рекомендаций по оптимизации работы Windows Server 2019:
| Пункт | Описание |
|---|---|
| 1 | Отключите неиспользуемые службы и компоненты. |
| 2 | Очистите систему от временных файлов и ненужных данных. |
| 3 | Настройте графический интерфейс сервера для повышения производительности. |
| 4 | Настройте планировщик задач для оптимизации использования ресурсов. |
| 5 | Установите и настройте антивирусное программное обеспечение. |
| 6 | Настройте сетевые параметры для оптимальной работы сети. |
Выполнение этих рекомендаций позволит снизить нагрузку на систему, увеличить производительность и обеспечить стабильную работу сервера.
Оптимизация работы Windows Server 2019 является ключевым фактором для обеспечения высокой производительности и надежности сервера. Следуя рекомендациям по оптимизации, вы сможете максимально эффективно использовать возможности операционной системы и обеспечить бесперебойную работу вашего сервера.
Улучшение производительности и эффективности системы
Windows Server 2019 предлагает ряд возможностей для улучшения производительности и эффективности работы системы. Важно принять во внимание следующие рекомендации:
- Оптимизировать использование ресурсов сервера. Управление ресурсами сервера — это одна из главных составляющих эффективной работы системы. Регулировка размеров выделенной памяти (RAM), задействование правильных количеств процессоров и дискового пространства может повысить производительность и сократить время обработки данных.
- Провести настройку дисковой подсистемы. Разделение дисков на несколько массивов с различными типами дисков (SSD и HDD) позволяет оптимизировать работу сервера и минимизировать время доступа к данным. Конфигурация RAID-массива и оптимизация настроек дисковой подсистемы могут значительно повысить производительность и эффективность обработки данных.
- Использовать оптимизированные сетевые настройки. Интенсивность сетевого трафика на сервере может влиять на производительность и доступность данных. Настройка сетевых параметров, таких как размер MTU (Maximum Transmission Unit), маршрутизация и индексация, может существенно повысить эффективность и производительность работы сервера.
- Настроить мониторинг и анализ системы. Организация системы мониторинга и анализа сервера позволяет оперативно выявлять узкие места, решать проблемы с производительностью и улучшать работу системы в целом. Использование специальных инструментов для мониторинга ресурсов, событий и производительности помогает более эффективно управлять и настраивать сервер.
Правильное настройка сервера и активное использование рекомендаций по улучшению производительности и эффективности системы Windows Server 2019 позволит достичь максимальных результатов и оптимальной работы сервера.
Повышение производительности Windows Server 2019
1. Оптимизация настроек энергосбережения
Одним из первых шагов по улучшению производительности сервера является проверка настроек энергосбережения. На сервере Windows Server 2019 энергосберегающие настройки могут влиять на производительность. Убедитесь, что эти настройки настроены оптимально для сервера, и выключите все функции энергосбережения, которые вам не нужны. Это может помочь увеличить производительность и ускорить работу сервера.
2. Оптимизация работа HDD и SSD
Правильная настройка и оптимизация работы жестких дисков (HDD) и твердотельных накопителей (SSD) также может значительно повысить производительность сервера. Одним из важных аспектов оптимизации является фрагментация дисков. Регулярно выполняйте дефрагментацию дисков для улучшения производительности.
3. Управление службами и приложениями
Часто службы и приложения, которые запускаются на сервере, могут использовать значительное количество ресурсов системы, что может замедлить работу всей системы. Отключите или удалите ненужные службы и приложения, чтобы освободить ресурсы системы и увеличить производительность сервера.
4. Оптимизация сетевых настроек
Сетевые настройки могут оказывать значительное влияние на производительность сервера. Проверьте, что настройки сети корректно настроены и оптимизированы для работы сервера. Настройте TCP/IP параметры, маршрутизацию, фрагментацию пакетов и другие параметры, чтобы повысить производительность сервера.
5. Улучшение производительности журнала событий
История событий (журнал событий) может занимать значительное место на диске и замедлять работу сервера. Проверьте настройки журнала событий и установите ограничение на размер файлов или удалите старые события, которые уже не требуются. Это поможет освободить место на диске и повысить производительность сервера.
| Способ повышения производительности | Описание |
|---|---|
| Оптимизация настроек энергосбережения | Проверка и выключение неиспользуемых функций энергосбережения для улучшения производительности. |
| Оптимизация работа HDD и SSD | Фрагментация дисков, выполнение регулярной дефрагментации для улучшения производительности сервера. |
| Управление службами и приложениями | Отключение или удаление ненужных служб и приложений, чтобы освободить ресурсы системы. |
| Оптимизация сетевых настроек | Настройка сети, TCP/IP параметров и маршрутизации для повышения производительности сервера. |
| Улучшение производительности журнала событий | Настройка журнала событий, установка ограничений на размер файлов или удаление старых событий, чтобы освободить место на диске. |
Настройка и оптимизация ресурсов сервера
Для эффективной работы и повышения производительности сервера Windows Server 2019 необходимо провести настройку и оптимизацию его ресурсов. В этом разделе мы рассмотрим несколько важных шагов, которые помогут вам достичь максимальной эффективности в использовании доступных ресурсов.
1. Настройка памяти
Одним из важных аспектов оптимизации сервера является настройка памяти. Вы можете управлять использованием памяти сервера, чтобы обеспечить оптимальную производительность.
В Windows Server 2019 вы можете настроить размер файла подкачки (paging file), чтобы сбалансировать использование оперативной памяти и дискового пространства. Рекомендуется установить размер файла подкачки равным объему физической памяти (RAM) плюс 10-20%.
2. Оптимизация процессора
Для настройки процессора сервера вы можете использовать такие инструменты как Power Plans (планы электропитания) и настройки планировщика задач. Рекомендуется использовать высокопроизводительные планы электропитания, которые позволяют процессору работать на максимальной производительности.
Также вы можете настроить планировщик задач для приоритетного выполнения некоторых приложений или процессов. Например, вы можете настроить планировщик таким образом, чтобы он давал больше приоритета серверным приложениям, в то время как другие приложения работали на заднем плане.
3. Оптимизация сетевого соединения
Для оптимизации сетевого соединения на сервере Windows Server 2019 вы можете использовать несколько методов.
Во-первых, вы можете настроить параметры сетевых адаптеров, такие как скорость передачи данных и полный дуплекс. Рекомендуется установить скорость передачи и полный дуплекс на максимальные значения, чтобы обеспечить максимальную пропускную способность сети.
Во-вторых, вы можете настроить параметры TCP/IP, такие как размер окна TCP и настройки масштабирования окна. Рекомендуется установить оптимальные значения для этих параметров, чтобы обеспечить оптимальную производительность сети.
Оптимизация сетевых настроек Windows Server 2019
Windows Server 2019 предлагает несколько возможностей для оптимизации сетевых настроек, которые могут повысить производительность сервера и улучшить качество передачи данных в сети.
Вот несколько рекомендаций, которые помогут вам настроить сетевые параметры:
- Используйте правильные сетевые адаптеры: При выборе сетевого адаптера для Windows Server 2019 рекомендуется использовать адаптеры, поддерживающие сетевые стандарты 10 Гб/с или выше. Это поможет увеличить пропускную способность сервера и улучшить скорость передачи данных.
- Настройте сетевые параметры TCP/IP: Для оптимизации работы сети в Windows Server 2019 можно настроить некоторые параметры TCP/IP. Например, установите размер окна TCP больше стандартного значения, чтобы увеличить скорость передачи данных. Также можно изменить значение параметра TTL (Time To Live), чтобы улучшить маршрутизацию пакетов.
- Включите функцию Jumbo Frames: Jumbo Frames позволяет передавать большие пакеты данных по сети, что уменьшает нагрузку на процессор и увеличивает производительность сервера. Но для корректной работы этой функции необходимо, чтобы все устройства в сети поддерживали Jumbo Frames.
- Оптимизируйте настройки сетевых служб: Windows Server 2019 предлагает несколько служб для управления сетью, такие как DNS, DHCP или IPAM. Настройте эти службы таким образом, чтобы они соответствовали потребностям вашего сервера и сети.
При оптимизации сетевых настроек Windows Server 2019 важно помнить, что каждая сеть уникальна, и некоторые рекомендации могут быть не применимы в вашем случае. Поэтому перед внесением изменений в настройки сервера рекомендуется провести тестирование и анализ сети, чтобы оценить их эффективность и безопасность.
Ускорение передачи данных и снижение задержек
Windows Server 2019 предоставляет различные возможности для ускорения передачи данных и снижения задержек в сети. В этом разделе мы рассмотрим несколько полезных методов, которые помогут оптимизировать работу сервера и повысить производительность.
1. Включение TCP Offload Engine (TOE): TOE позволяет перенести некоторые вычислительные задачи сетевого стека TCP/IP на сетевой адаптер, что существенно ускоряет обработку сетевых пакетов. Чтобы включить TOE, необходимо проверить, поддерживает ли сетевой адаптер данную функцию, и включить ее в настройках адаптера.
2. Настройка Jumbo Frames: Jumbo Frames позволяют увеличить размер передаваемых сетевых пакетов, что позволяет снизить нагрузку на сеть и увеличить пропускную способность. Для настройки Jumbo Frames необходимо убедиться, что все устройства в сети поддерживают данную функцию, и включить ее на сервере и на всех подключенных устройствах.
3. Использование сетевых адаптеров с поддержкой RSS и RSC: Receive Side Scaling (RSS) и Receive Segment Coalescing (RSC) – это технологии, позволяющие распределить обработку сетевых пакетов по нескольким ядрам процессора и объединять несколько пакетов в один для уменьшения нагрузки на процессор. Использование адаптеров с поддержкой RSS и RSC позволит снизить задержки и увеличить пропускную способность.
4. Оптимизация параметров TCP/IP: В Windows Server 2019 можно оптимизировать параметры TCP/IP для повышения производительности сети. Некоторые из наиболее важных параметров включают масштабирование TCP-окна, регулировку тайм-аута и использование более эффективных алгоритмов передачи данных.
5. Включение Data Deduplication: Data Deduplication – это технология, позволяющая оптимизировать использование дискового пространства путем удаления дубликатов данных. Включение этой функции на сервере позволит уменьшить объем передаваемых данных и повысить скорость их передачи.
6. Использование кэша на диске: Windows Server 2019 позволяет настроить кэш на диске для ускорения операций чтения и записи данных. Настройка кэша может быть осуществлена как на уровне файла, так и на уровне диска.
Применение этих методов поможет увеличить скорость передачи данных и снизить задержки в сети, что положительно отразится на производительности сервера и пользовательском опыте.