Время на прочтение5 мин
Количество просмотров35K
В данной статье мы продолжаем рассказывать про работу с Windows Server Core 2019. В прошлых постах мы рассказали как готовим клиентские виртуальные машины на примере нашего нового тарифа VDS Ultralight с Server Core за 99 рублей. Затем показали как работать с Windows Server 2019 Core и как установить на него GUI. Сегодня мы поговорим про управление с помощью Windows Admin Center.

Фото: ТАСС
Головной болью было, наверное, по соображениям безопасности, разделять роли серверов. Заводить несколько машин, чтобы физически разделить контроллер домена и файловый сервер.
Благо нам на помощь пришла виртуализация, и теперь изолированно друг от друга могут работать несколько служб, которые из соображений безопасности не могут работать на том же сервере. Виртуализация принесла массу удобства, развертывание виртуальных машин из одного шаблона экономит время специалистам, и физически, все в одной коробке с мощным железом.
Машин все меньше, а серверов все больше, даже у меня, для «просто посмотреть» образовалось два контроллера домена, файловый сервер, сервер под Java приложения и еще пачка веб серверов, поэтому давайте поговорим о том, как можно эффективно управлять серверами на Windows, не отрывая левой руки от кофе.
— С помощью Powershell!
Конечно да, но… нет. Продукт позиционируется как удобный инструмент управления гигантской инфраструктурой. Понятно, что это не совсем так, для таких случаев есть Powershell ISE и скрипты, поэтому хотелось бы рассмотреть действительно полезные юзкейсы. Если у вас есть свой опыт, которым вы вы хотели поделиться, мы можем добавить его в эту статью.
TL;DR
Windows Admin Center лучше подходит для управления стоковыми компонентами. На текущий момент только RSAT может управлять установленными ролями.
Используя WAC, можно улучшить безопасность вашей инфраструктуры, если будете использовать его как шлюз.
Сводная таблица того, он умеет и не умеет:
Управление системой
Управление ролями
Превью — установка бета версий компонентов для WAC, не входит в состав сборки. Перечислять все не нужно, потому что буквально все компоненты управляются только с помощью RSAT.
Нюансы
Powershell в Windows Admin Center не имеет своей среды сценариев аналогичной Powershell ISE.
Windows Admin Center не поддерживает Powershell ниже 5.0, на старых машинах обязательно нужно ставить новый Powershell, если хотите использовать его.
Главным минусом Windows Admin Center в микро инстансах является потребление оперативной памяти сервера. Он создает четыре сессии по 50-60 мегабайт каждая, и каждая эта сессия остается даже после закрытия Windows Admin Center.
Та же самая проблема и с Powershell через Enter-PSSession, он так же создает новую сессию, и если просто закрыть окно терминала, сессия весом и 70 мегабайт так и останется на удалённом сервере, если её не закрыть её перед выходом с помощью Exit-PSSession или Remove-Pssession.
При использовании Windows Admin Center с этим придется мириться, он отнимет около 170 мегабайт ОЗУ, RSAT таким не страдает.

(См. wsmprovhost.exe)
Упрощаем работу
Максимальное удобство управления достигается если ваша рабочая станция, на которой установлен WAC находится в домене. Он берет учетные данные пользователя, который зашел в систему, подключение к серверам осуществляется по одному щелчку мыши.
Импортировать список серверов можно с помощью txt файла, перечислив имена серверов переносом строки, как и в RSAT.
Что тоже радует, ранее, чтобы интегрировать в AD виртуальную машину на Server Core, приходилось делать это через sconfig, а это значит нужен прямой доступ к его экрану. В случае с хостингами приходилось делать все это через VNC. Теперь, при переходе на главную страницу можно нажать «Изменить идентификатор компьютера» и ввести в домен.
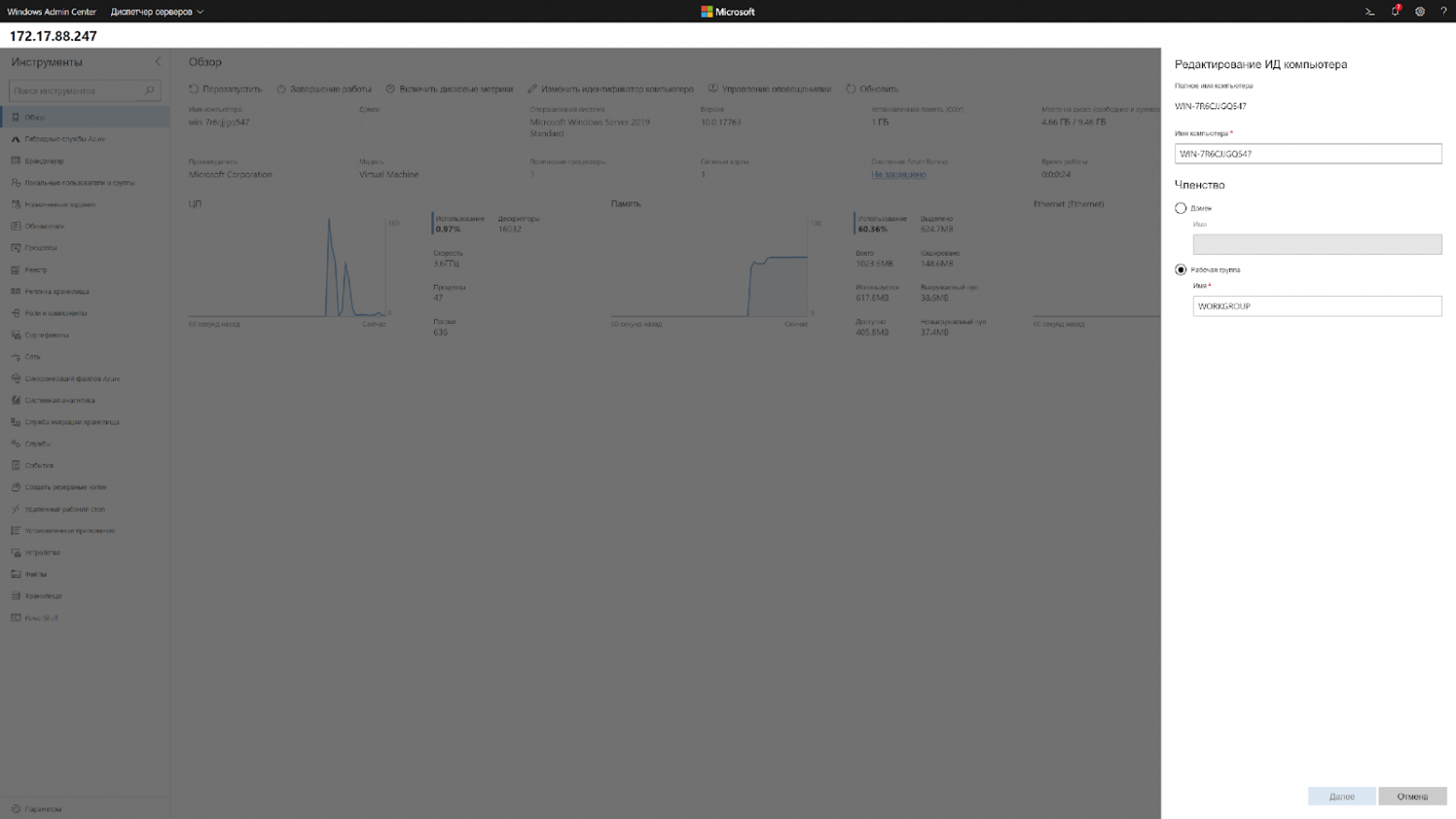
Кстати, чтобы ввести в домен Windows Server 2019, больше не требуется делать Sysprep, потому что Sysprep тоже нужно было завершать через VNC.
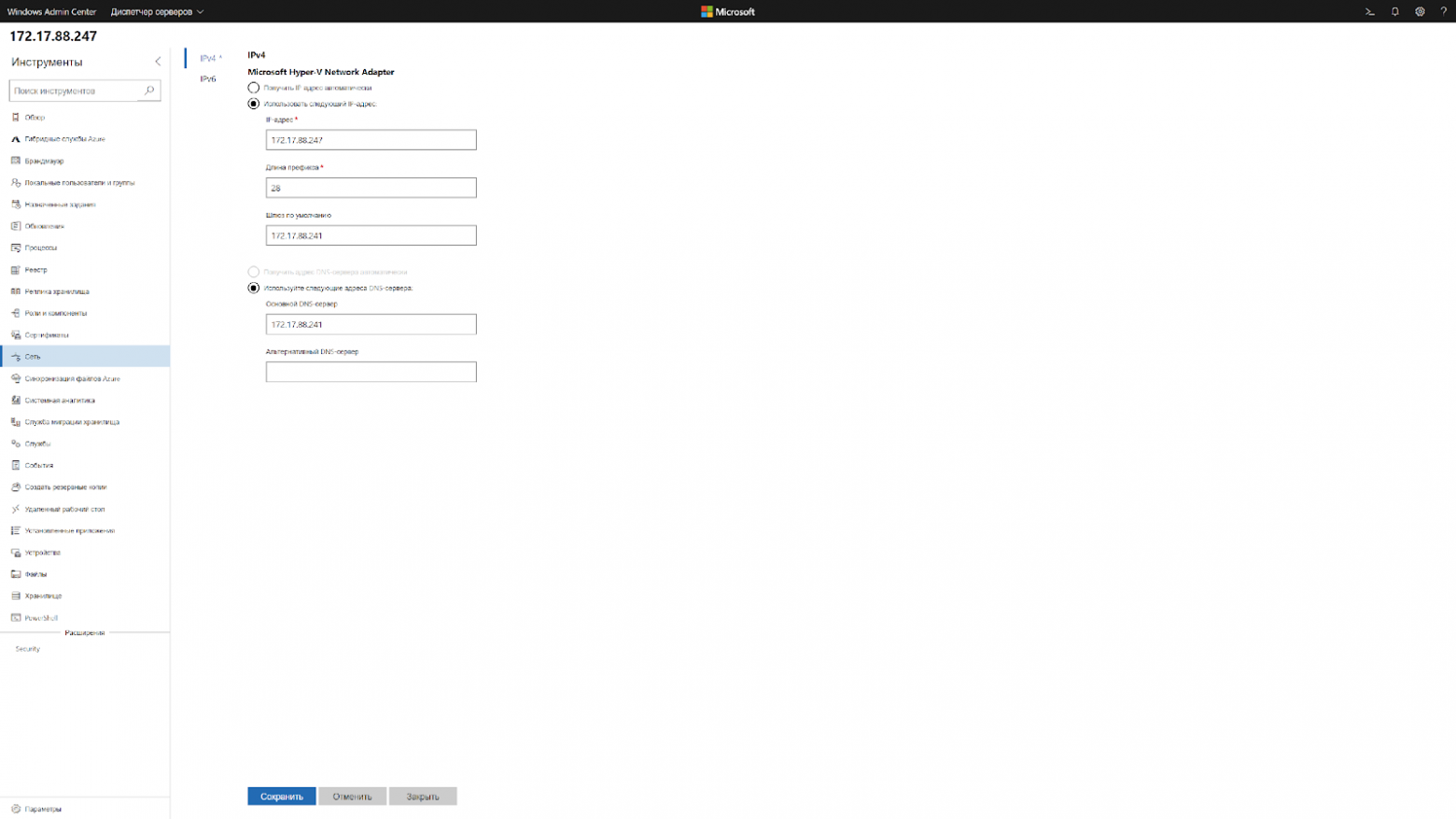
Чтобы изменить сетевые настройки теперь нужно сделать два клика. Подключаешься к серверу и меняешь.
Это выходит так же быстро, как и через WinRM, только одной рукой.
Повышаем безопасность
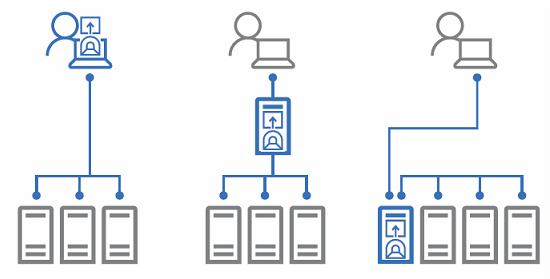
На текущий момент есть четыре типа развертывания. Локальный, в качестве шлюза, установка на один из продакшн серверов и в составе кластера.
*Картинка с сайта майкрософт
Установка в качестве шлюза, на отдельный сервер, наиболее безопасный и рекомендуемый вариант. Это аналог схемы с VPN, когда доступ к управлению имеется только с определенного IP адреса или участка сети.
Согласитесь, гораздо удобнее держать на одной вкладке видосы и мемасы, а на другой Windows Admin Center, нежели целиком терять подключение к ютубу из-за входа в защищенную сеть.
Как же обезопасить все свои N серверов? С помощью следующего скрипта:
## Список серверов через запятую ##
$servers = Get-Content -Path .\Servers.txt
## Список правил через перенос строки ##
$rules = Get-Content -Path .\Rules.txt
## IP адрес нашего гейта с установленным WAC ##
$gate = "1.1.1.1"
$MySecureCreds = Get-Credential
foreach ($server in $servers.Split("`n")) {
foreach ($line in $rules.Split("`n")) {
Invoke-Command -ComputerName $server -ScriptBlock {
Set-NetFirewallRule -Name $Using:line -RemoteAddress $Using:gate
} -Credential $MySecureCreds
}
}
# список правил, RULES.txt#
RemoteDesktop-UserMode-In-TCP
RemoteDesktop-UserMode-In-UDP
WINRM-HTTP-In-TCP
WINRM-HTTP-In-TCP-PUBLIC
# список ваших серверов, SERVERS.txt#
1.1.1.1, 1.1.1.2, 1.1.1.3Этот скрипт изменит стандартные правила брандмауэра таким образом, что вы сможете использовать RDP и WinRM только с определенного IP адреса, понадобится для организации безопасного доступа к инфраструктуре.
Powershell в Windows Admin Center не имеет своей среды сценариев аналогичной Powershell ISE, можно только вызывать готовые скрипты.

Кстати, вот так выглядит RDP на Windows Server Core.

Выводы
На текущий момент Windows Admin Center не способен заменить RSAT, однако в нём уже присутствуют функции, которых нет у RSAT. Добавляются старые оснастки, которые не так удобны для управления через браузер.
Странным является приоритет разработки, наиболее активно добавляются функции интегрированные с Azure, хостингом от Майкрософт, вместо реально полезных функций.
К сожалению, пока что, управлять всеми функциями Windows Server с удобствами можно только подключившись к нему по RDP.
Не смотря на все минусы, у Windows Admin Center есть свой SDK, с помощью которого можно писать свои собственные модули и управлять своим собственным ПО через него, что однажды сделает его лучше RSAT.

-
What is a Windows Server Core Control Panel?
-
Importance of the Control Panel in managing Windows Server Core
-
Windows Server Core Control Panel vs Other Management Tools
-
7 Use cases for Windows Server Core Control Panel
-
Understanding the Role of the Control Panel in Windows Server Core
-
9 Advantages of Using Windows Server Core Control Panel
-
Common Issues with Windows Server Core Control Panel
-
FAQs
-
Summary
What is a Windows Server Core Control Panel?
The Windows Server Core Control Panel is a streamlined and command-line-driven tool. It is designed to control server core installations of Windows.
The Windows server core control panel is a simple tool. Unlike the full-screen interface, Server Core uses a command line interface. This helps reduce resource use and improve security. The dashboard allows admins to manage server functions like:
-
Network settings
-
Security
-
User accounts.
This tool is ideal for environments that prioritize performance and server security. Reducing the vulnerability also strengthens security. The control settings work with other tools and utilities. This makes managing local and distant servers easy.
Importance of the Control Panel in managing Windows Server Core
1. Simplifies Server Management Without a Visual Interface

One major challenge with the Windows operating system is the lack of a screen interface. This can be difficult for administrators who are not used to working with command-line tools. The dashboard helps by offering a simple, menu-driven interface. It is easier to perform tasks such as:
-
Setting up network settings
-
Managing user accounts
-
Installing updates
-
Activating licenses
Even admins with limited experience in command-line interfaces can use the control settings effectively.
2. Reduces Resource Consumption
The Windows operating system is designed to be lightweight. It helps save system resources. Unlike complete visual interface-based tools like Server Manager. This consumes lots of CPU and memory. The dashboard runs through Command Prompt or Windows PowerShell, providing several benefits:
-
More resources for critical tasks like database operations or hosting apps.
-
Faster performance due to reduced graphical elements.
This is especially useful in resource-constrained environments, such as virtualized setups. It uses virtualizers or situations where hardware resources are limited.
3. Enhances Security
Security is one of the main reasons many organizations prefer server-core setups. It is over the traditional Windows operating system. Server Core cuts down on unnecessary services, reducing the potential vulnerability. The control settings further strengthen security by:
-
Allowing administrators to set up Windows Firewall using sconfig or PowerShell cmdlets. It allows only authorized traffic.
-
Removing unnecessary services and components to minimize vulnerabilities.
-
Streamlining patch management allows for the easy application of essential security updates with minimal downtime.
The dashboard helps ensure that Windows’ server basic setup stays secure. It keeps the system running smoothly.
4. Streamlines Configuration Tasks
The control settings provide an easy way to set up key server settings. It does not need complex scripts. For example:
| Task | How It’s Done Using the Control Settings |
|---|---|
| Network Configuration | Set static IPs, DNS servers, and gateways via sconfig. |
| Firewall Settings | Set up Windows Firewall rules to secure the server environment. |
| Domain Membership | Join or leave Active Directory domains using menu options. |
| System Updates | Install critical updates directly from the menu (Option 5 in sconfig). |
These simple options save time and reduce the risk of errors. It is compared to command-line configurations.
5. Supports Remote Management

In modern IT setups, remote control is essential. The dashboard makes remote management easy by:
-
Integrating with tools like the Microsoft Management Console (MMC) and its snap-ins. For example, Active Directory Users and Computers.
-
Supporting remote access through command tool sessions or Remote Desktop Services (RDS).
-
Enabling centralized management with a management dashboard. It enhances the control setting features.
This flexibility allows administrators to manage local and distant servers effectively. This makes handling significant, distributed environments easier.
6. Improves Maintenance and Troubleshooting
Routine maintenance and troubleshooting are important to keep servers healthy. The dashboard simplifies these tasks by providing quick access to essential utilities:
-
Apply patches and updates quickly using sconfig.
-
Monitor performance data and system health without extra software.
-
Manage user accounts and permissions from the command line or management tool snap-ins.
Its lightweight design also reduces downtime during maintenance, keeping servers available and responsive.
7. Reduces Complexity in Multi-Server Environments
Managing multiple server-core setups can quickly become complex. The dashboard reduces this complexity by integrating smoothly with other management tools like:
-
Windows PowerShell
-
Management tool snap-ins
-
Windows Admin Center.
This integration offers a unified management experience, allowing administrators to:
-
Set up settings across multiple servers using scripts or centralized tools.
-
Monitor performance data for all servers from one interface (e.g., management dashboard).
-
Keep the server environment simple and organized.
This approach helps organizations manage their server systems efficiently while minimizing complexity.
Windows Server Core Control Panel vs Other Management Tools
| Aspect | Windows Server Core Control Panel | Other Management Tools (Server Manager, Windows Admin Center) |
|---|---|---|
| Interface | Its functionality uses a command-line interface (CLI). It is simple for core server management. | Other tools, like the management dashboard, offer a visual interface. It is easier for those familiar with visual management. |
| Security Focus | Server Core setups and the dashboard reduce unnecessary services. It makes the server more secure by cutting down the vulnerability. | These expose more services. It increases the attack surface and makes the server more vulnerable to threats. |
| Resource Consumption | It is lightweight and uses fewer resources. This helps the core server focus on essential tasks. | Visual interface tools like Server Manager use more CPU and memory. It can slow down the server, especially in virtual environments. |
| Remote Control | You can manage your server core remotely using the command tool. | Other tools like Windows Admin Center allow remote control. It is easier to monitor and set up servers remotely. |
| Ease of Use | It requires some experience with command-line tools. This can be tricky for beginners. | They are easier to use, especially for those familiar with the Windows operating system. |
7 Use cases for Windows Server Core Control Panel
1. Amazon Web Services (AWS): Remote Server Management
Amazon Web Services (AWS) manages distant servers for clients globally. It offers scalable and secure cloud solutions. Their infrastructure allows seamless management of resources.
-
Use Case: AWS uses the dashboard to remotely manage the server’s basic setup. It helps set up settings and run diagnostics.
-
Key Advantage: The command tool allows AWS to manage servers efficiently. It helps to use scripts and cmdlets.
2. Microsoft Azure: Virtualized Environments (Hyper-V)

Microsoft Azure uses the Windows operating system to host Hyper-V. It manages many virtual machines (VMs).
-
Use Case: The panel helps manage network settings, resources, and security. It is for server-basic setup running a virtualizer.
-
Key Advantage: Server Core helps Azure manage multiple VMs. It is without using too many resources.
3. Dropbox: Cloud Infrastructure
Dropbox uses a minimal Windows setup to manage its cloud storage infrastructure. It helps to ensure efficient data handling and quick scalability. This allows them to maintain smooth operations.
-
Use Case: The control settings help control Server Core setups. It helps to ensure smooth operation and scalability across Dropbox’s services.
-
Key Advantage: Server Core uses fewer resources. It allows Dropbox to handle large data loads efficiently.
4. Ford Motor Company: On-Premises Server Management
Ford Motor Company uses the Windows operating system for servers. It helps to control production lines and business operations.
-
Use Case: The panel allows Ford’s IT team to manage server installations. It keeps the systems running smoothly.
-
Key Advantage: Server Core uses fewer resources. It is ideal for on-site production environments where efficiency is essential.
5. Facebook: Data Centers

Facebook uses a minimal Windows setup to manage servers in its data centers. It ensures high efficiency and security. By minimizing unnecessary services, Facebook can optimize resource usage.
-
Use Case: It helps manage and set up the basic setup of servers in Facebook’s data centers. It monitors performance and applies updates.
-
Key Advantage: It reduces the number of services running, improving security and efficiency.
6. Bank of America: High-Security Environments
Bank of America uses the Windows operating system to manage sensitive financial data. It ensures enhanced security and compliance with industry standards.
-
Use Case: The panel helps set up security settings. It helps to manage firewalls and apply updates for the server’s basic setup.
-
Key Advantage: Server Core minimizes unnecessary services, enhancing security for sensitive data.
7. Smith & Johnson Law Firm: Small to Medium Business (SMB) IT Management
Smith & Johnson Law, a mid-sized law firm, uses the Windows operating system. It helps to store and manage client data securely.
-
Use Case: The panel helps the IT team manage the basic setup of their server. It sets up network settings and applies updates remotely.
-
Key Advantage: Server Core is an affordable, low-maintenance solution for SMBs. It requires secure data storage.
Understanding the Role of the Control Panel in Windows Server Core
| Function | Details |
|---|---|
| Simplified Configuration | It makes setting up network configuration, domain membership, firewall settings, and system updates easy. This simplifies tasks for users who may not be familiar with command-line operations. |
| Security Configurations | The dashboard helps set up Windows Firewall, update security, and manage services. This ensures that Windows operating systems are secure by reducing unnecessary services. |
| Resource Management | It helps manage system resources efficiently. This helps to avoid using extra graphical elements and is essential in environments. It must save resources like virtualized setups. |
| Task Automation | It helps automate regular tasks like: — Running start commands — Managing user accounts — Setting up roles. This reduces the work needed to keep server core environments running smoothly. |
9 Advantages of Using Windows Server Core Control Panel
1. Reduced Resource Usage
The Windows operating dashboard uses fewer resources without a visual interface. This is great for environments with limited hardware or high-density virtualization setups.
-
Lower Disk Space Usage: A Server Core installation takes up much less disk space.
-
Optimized Memory and CPU Usage: They are available without a graphical interface. It is for essential tasks, such as databases or virtual machines.
-
Ideal for Resource-Constrained Environments: This setup is perfect for environments with limited hardware.
2. Enhanced Security
Security is one of the top benefits of using a minimal Windows setup. The control settings help manage security settings and reduce vulnerabilities.
-
Reduced Attack Surface: By removing unnecessary services and components. The attackers can target fewer areas.
-
Minimized Patching Requirements: Fewer components mean fewer updates, reducing downtime and security risks.
-
Built-in Firewall Management: The dashboard makes it easy to set up firewalls. This helps to secure network traffic.
-
Fewer Risks: The absence of GUI services reduces vulnerabilities from desktop-related features.
3. Simplified Maintenance

The control settings make maintenance tasks easier by reducing system complexity.
-
Fewer Updates: With fewer services, updates and patches are needed.
-
Easier Troubleshooting: The simplified setup makes finding and fixing issues easier.
-
Consistency Across Servers: Standard configurations across multiple servers make managing large environments easier.
4. Improved Performance
The lightweight nature of the Windows operating system improves performance. It helps to use fewer system resources.
| Feature | Impact on Performance |
|---|---|
| No GUI Overhead | Faster boot times and reduced system load. |
| Streamlined Configuration | Faster execution of tasks with command-line tools. |
| Optimized Resource Usage | More resources are available for applications. |
Server Core is ideal for high-performance applications like web hosting or database management.
5. Streamlined Management with SConfig
The Server Configuration Tool (SConfig) is an easy-to-use interface. It is for managing minimal Windows setup and allows administrators to handle updates.
-
Set up Network Settings: Easily adjust IP addresses, DNS, and more.
-
Manage User Accounts: Quickly manage user accounts and permissions.
-
Install Updates & Enable Remote Control: Perform these tasks with minimal effort.
6. Remote Control Capabilities
The dashboard supports remote control, which is key for modern IT environments. Admins can manage servers from any location.
-
MMC Integration: Works with Microsoft Management Console and snap-ins. It includes a virtualizer manager for remote server management.
-
Windows Admin Center: Manage multiple servers from a single interface.
-
PowerShell Remoting: Use PowerShell to set up and manage servers remotely.
7. Reduced Downtime

The control settings help reduce downtime by making updates faster. It helps to require fewer reboots.
-
Quick Updates: Updates can be applied without affecting server performance.
-
Fewer Reboots: Server Core setups need fewer reboots, which means less downtime.
-
Increased Uptime: This improves overall system availability, which is essential in production environments.
8. Flexibility Across Use Cases
The dashboard in the Windows operating system is flexible. This supports many different use cases. It can efficiently manage virtual machines, web hosting, and high-security environments.
| Use Case | How the Control Panel Helps |
|---|---|
| Virtualization | Manages virtual machines efficiently using Hyper-V. |
| High-Security Environments | Reduces risks while maintaining necessary functionality. |
| Web Hosting | Configures IIS servers with minimal overhead for better performance. |
This flexibility makes Server Core suitable for both on-premises and cloud-based deployments.
9. Cost Efficiency
The dashboard helps lower costs. It helps to reduce resource consumption and simplify server management.
-
Lower Hardware Requirements: Server Core uses fewer resources. It needs less hardware, which saves money.
-
Increased Productivity: Reduced downtime means more productive time for servers.
-
Simplified Management: The panel makes management more effortless. This helps to cut training costs and reduce the need for third-party tools.
-
Maximized ROI: These savings help maximize IT investments.
Common Issues with Windows Server Core Control Panel
| Issue | Details |
|---|---|
| Lack of GUI | Server Core has no desktop experience. It is harder for administrators to use visual interface tools. |
| Recovery Options | It lacks visual interface recovery tools, making recovery difficult. You may need to connect to the server core remotely to fix issues. |
| Software Compatibility | Some third-party apps need a screen interface to work. Without it, Server Core may not run these apps or may require adjustments to do so. |
| App Support | Many apps require a visual interface to run. Without it, some apps might not work with Server Core or may need special adjustments. |
| Local Management | It does not have a user interface for local management. You must use the management tool snap-in to manage the server core remotely. |
| Remote Access | It relies on remote control. Setting up PowerShell Remoting can be more complex than managing a server screen interface system. |
| Diagnostics | It offers fewer diagnostic tools, making troubleshooting harder. You may need to use the following information or right-click the snap-in to view more details. |
| Configuration | Setting up network settings and services takes longer because there is no GUI. You will need to use the command at a command prompt. |
| Patching | Patching in Server Core can be more complex. Fewer tools are available to handle updates, so you may need to run the following command or use scripts. |
FAQs
1. What does the Windows Server Core Control Settings do?
The Windows operating system is a command-line tool. It helps control server core setups. This simplifies tasks like configuring network settings and applying updates without a GUI.
2. Can I manage a Server Core server remotely?
You can control the Server Core remotely through the management dashboard or PowerShell. These tools let you set up and monitor the server from another computer.
3. What is the difference between using Server Core vs. Server Manager?
Server Core is a minimalist installation with no visual interface. It is focused on performance and security. The hosting server manager is more user-friendly. It has a visual interface but uses more resources.
4. What are the benefits of using Server Core for virtualization in environments?
Server Core is lightweight and perfect for Hyper-V environments. It uses fewer resources, leaving more for virtual machines and improving overall performance.
5. How can I ensure a secure Server Core setup in a production environment?
Disable unused services, configure Windows Firewall and apply security patches regularly. It is for a secure setup and keeps Server Core safe from threats.
Summary
The Windows Server Core Control Panel is a command-line tool. This tool manages a server-core computer, focusing on performance and security. Consider the following features:
-
Simplifies Server Management Without a GUI: Manages servers easily without a graphical interface.
-
Reduces Resource Consumption: Uses fewer resources for better performance.
-
Enhances Security: Reduces vulnerabilities and improves protection.
Explore the Hosting Control Panel and manage your Windows Server Core with ease.
В 2017 году Microsoft анонсировала работы по разработке бесплатного HTML5 веб-интерфейса для администрирования и централизованного управления серверами Windows Server. Проект получил кодовое название Project Honolulu. В апреле 2018 года Microsoft выпустила RTM решение и теперь данный продукт официально называется Windows Admin Center.
Идея Microsoft заключается в замене традиционных MMC консолей и других графических инструментов управления серверами Windows возможностью управления из браузера через единый веб интерфейс (по аналогии с веб-клиентом управления VMware vCenter). Admin Center разворачивается локально и может быть использован в том числе для управления серверами, изолированных от Интернета.
На данный момент проект Гонолулу находится в стадии preview и доступен как часть программы Windows Server Insider. В текущей версии из веб-интерфейса возможно выполнить около 80% типовых задач администрирования серверами Windows Server. По информации от Microsoft, RTM версия продукта будет доступна в марте 2018 года (вместе с выходом обновления 1803).
Содержание:
- Особенности, требования и ограничения Windows Admin Center
- Установка Windows Admin Center в Windows 10/ Windows Server 2016
- Использование консоли Admin Center для управления серверами Windows
Особенности, требования и ограничения Windows Admin Center
Windows Admin Center поддерживает управление следующими версиями ОС: Windows Server 2016, Windows Server 2012 / R2, Hyper-V 2016/2012R2/2012, Windows 10, северами Azure, а также Core редакциями. Возможно также управление целыми кластерами: Failover Clusters, Hyper-V Clusters и виртуальными машинами Hyper-V на них.
На управляемый хост не нужно устанавливать никаких агентов или дополнительных расширений. Коммуникация осуществляется выполняется через Remote PowerShell и WMI over WinRM с помощью RESTful API. На управляемых серверах должен быть установлен как минимум Management Framework (WMF) 5.0 (Powershell 5.0). На Windows Server 2012 / R2 WMF 5.0 нужно становить отдельно.
Узнать поддерживаемую версию Powershell можно с помощью команды:
$PSVersionTable
Сам веб интерфейс Windows Admin Centerнаписан на HTML 5 и корректно работает в Edge и Chrome (Internet Explorer пока полностью не поддерживается).
В последней доступной версии Windows Admin Center прямо из окна браузера поддерживается RDP подключение через веб-интерфейс и консоль PowerShell.
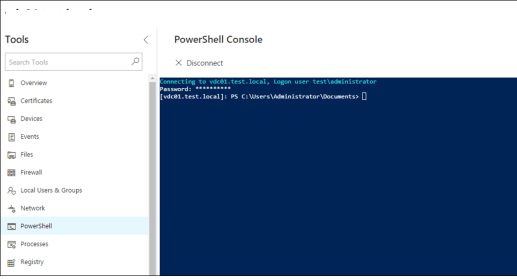
На Windows Server 2016 можно установить Windows Admin Center в режиме шлюза (Gateway Mode), в этом режиме возможно удаленно подключаться к консоли управление с других компьютерах. На Windows 10 / Windows Server 2012 клиент устанавливается в режиме Desktop Mode (консоль доступна только с локального компьютера).
Для авторизации на удаленных серверах можно вручную вводить данные для авторизации, или использовать Local Administration Password Solution (LAPS).
Установка Windows Admin Center в Windows 10/ Windows Server 2016
Установить Windows Admin Center можно на Windows 10 или на Windows Server (2016 и 1709) в режиме Gateway. Чтобы скачать msi дистрибутив Windows Admin Center (около 30 Мб), можно на странице https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/windows-server/manage/windows-admin-center/understand/windows-admin-center
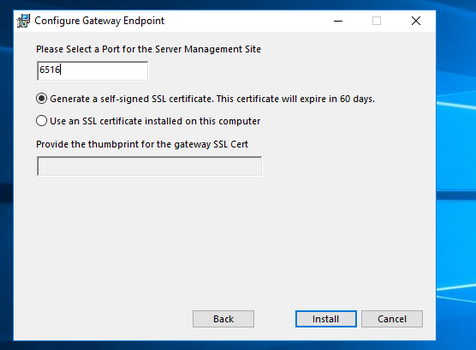
Установить дистрибутив Windows Admin Center можно из командной строки (с самоподписанным сертификатом сроком действия 60 дней)
msiexec /i HonoluluTechnicalPreview1712-05002.msi /qn /L*v log.txt SME_PORT=6516 SSL_CERTIFICATE_OPTION=generate
Либо с помощью обычного мастера установки. По умолчанию для управления используется порт 6515 (можно изменить). На Windows Server компонент Admin Center устанавливается в виде отдельной службы.
После установки веб интерфейс консоли Honolulu можно открыть, перейдя по адресу:
https://ip_сервера:6516
или с помощью значка на рабочем столе.
Использование консоли Admin Center для управления серверами Windows
По умолчанию в веб-консоли добавлен только один локальный сервер.
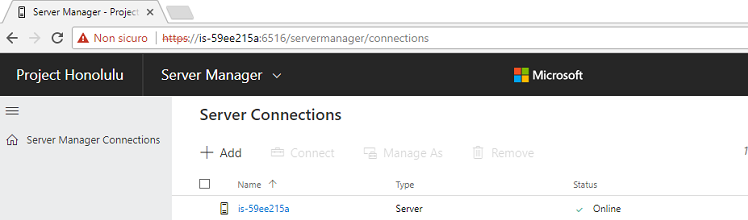
С помощью кнопки Add можно добавить
- Отдельный сервер (Server Manager)
- Отказоустойчивый кластер (Failover Cluster Manager)
- Кластер Hyper-V (Hyper-Converged Cluster Manager)
В нашем случае у нас только один сервер. Выберем его, чтобы открыть веб консоль управления. На этой странице отображаются характеристики сервера, а также его состояние в реальном времени (производительность, нагрузка и т.д.). прямо из этой панели можно выключить или перезагрузить сервер, изменить его имя.
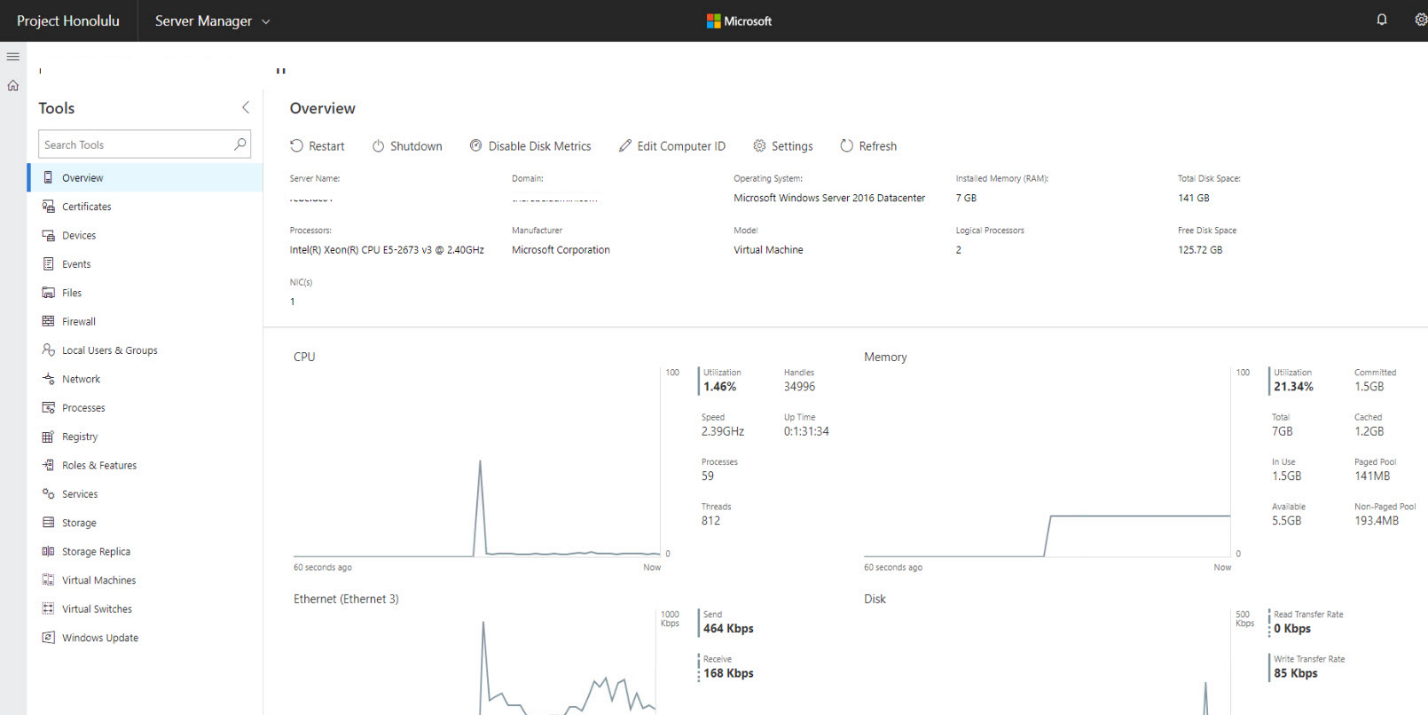
В левом сайдбаре представлен список доступных функций, которыми можно управлять из веб-интерфейса. Кратко пробежимся по основным:
Список возможностей веб консоли Windows Admin Center пока не дотягивает до полноценного функционала всех инструментов управления Windows, однако со временем доступный функционал веб интерфейса будет существенно расширен. В дальнейшем Microsoft планирует опубликовать SDK, позволяющий партнерам расширять функционал консоли Admin Center.
When it comes to hosting Windows-based servers, a hosting control panel is an essential tool for managing server resources, websites, and other services efficiently. A control panel provides a user-friendly interface for managing tasks such as domain management, email configuration, and file management, making it easier for system administrators, developers, and web hosting providers to maintain their servers.
What is a Windows Server Hosting Control Panel?
A Windows Server Hosting Control Panel is a software tool designed to simplify the management of Windows-based web hosting environments. It allows users to control server settings, manage websites, databases, and email accounts, monitor server performance, and more—all through a graphical interface. Instead of dealing with command-line interfaces, a control panel allows administrators to perform complex tasks with just a few clicks.
Top Features of Windows Server Hosting Control Panels
- User-Friendly Interface: Most control panels offer an intuitive graphical user interface (GUI), making it easier for administrators to perform various tasks without needing deep technical knowledge.
- Website and Domain Management: Hosting control panels typically allow users to manage multiple websites and domains from a single interface. This includes adding, deleting, or modifying domains, and configuring DNS settings.
- Email Management: Many control panels include integrated tools for managing email accounts and services. This includes setting up email addresses, creating email forwarding rules, and monitoring email server performance.
- Database Management: Control panels often include built-in database management tools for working with SQL databases. Administrators can create, delete, and modify databases, and perform backups and restores.
- Security Features: Advanced security tools like SSL certificate management, firewall configurations, and user access control are typically integrated into hosting control panels to enhance the security of hosted services.
- Resource Monitoring: Control panels offer real-time monitoring of server resources such as CPU usage, RAM, disk space, and network traffic. This allows administrators to identify performance bottlenecks and address them promptly.
- Backup and Restore: Control panels often provide automated backup solutions to protect data and websites. This feature can be a lifesaver in case of data loss or server failure.
- Support for Multiple Web Applications: Many control panels are designed to integrate with various web applications, including content management systems (CMS) like WordPress, Joomla, and Drupal, e-commerce platforms like Magento, and development tools like PHP and Python.
Popular Windows Server Hosting Control Panels
There are several popular control panels used in Windows hosting environments. Each has unique features suited to different types of users, ranging from small businesses to large enterprises.
1. Plesk
Plesk is one of the most widely used control panels for Windows-based hosting. It provides a complete suite of features, including website management, email management, database management, and security tools. Plesk supports multiple operating systems, including Windows and Linux, making it versatile for users with diverse hosting environments.
Key Features:
- Multi-language support
- Advanced security tools
- Supports multiple PHP versions
- Automatic updates and patches
- One-click app installation for popular applications
2. cPanel (with WHM)
Although cPanel is primarily known for its Linux hosting capabilities, it also offers a version for Windows hosting environments. The cPanel/WHM combo is highly popular for its simplicity and extensive features, allowing users to manage websites, emails, databases, and more.
Key Features:
- Easy-to-use interface
- Built-in website and domain management tools
- Supports multiple PHP versions
- One-click app installation
- Extensive customer support and documentation
3. Windows Server IIS (Internet Information Services)
Windows Server IIS is not a full-fledged hosting control panel in the same sense as Plesk or cPanel, but it is an important tool for managing Windows server environments. IIS is a web server that includes features for managing websites, web applications, and security configurations. It is often used in combination with other tools to enhance server management.
Key Features:
- Web application management tools
- Supports ASP.NET, PHP, and other frameworks
- Security management and firewall configuration
- Integrated with Windows authentication and Active Directory
4. Helm
Helm is another popular control panel that provides a comprehensive suite of features for Windows hosting. It allows users to manage hosting accounts, email, databases, and websites. Helm is known for its scalability and robust support for large hosting environments.
Key Features:
- Flexible billing and account management system
- User-friendly GUI
- Multi-server support
- Built-in support for managing databases and email services
5. ZPanel
ZPanel is a free, open-source hosting control panel that offers a simple interface for managing Windows-based servers. It includes essential features like domain and email management, as well as security tools, making it a great option for small businesses or individuals on a budget.
Key Features:
- Free and open-source
- Simple, user-friendly interface
- Basic domain and website management tools
- Backup and restore functionalities
- Integrated FTP and file management tools
Benefits of Using a Windows Server Hosting Control Panel
- Simplifies Server Management: With a control panel, users can manage complex server tasks through an easy-to-use interface, saving time and reducing the learning curve for system administrators.
- Increased Efficiency: Control panels automate many routine tasks, such as backup creation, server updates, and performance monitoring, allowing administrators to focus on more important tasks.
- Better Security: Many control panels come with built-in security features, such as SSL certificate management, firewall configurations, and security monitoring, which can help protect hosted services from cyber threats.
- Customization: Windows server control panels allow for significant customization, making it possible to tailor the hosting environment to meet specific needs, whether for small businesses or large enterprises.
- Improved Support: Control panels typically offer a wealth of customer support resources, including documentation, community forums, and dedicated support teams, making it easier to resolve issues.
Conclusion
Windows Server hosting control panels provide an essential platform for managing server resources, websites, and applications. Whether you’re managing a small business website or a large enterprise server, these control panels offer an intuitive interface and powerful features to make server management easier, more efficient, and more secure. Popular control panels like Plesk, cPanel, and Helm provide a range of tools and functionalities to support various hosting needs. Ultimately, choosing the right hosting control panel depends on your specific requirements, budget, and the size of your infrastructure.
How to Install and Configure Windows Admin Center on Windows Server 2019. One of the newest features of Microsoft that was introduced with Windows Server 2019 is Admin Center. This console, also known as the Honolulu Project, provides a web-based environment for controlling and managing servers as well as clients
With Admin Center you can easily manage all systems.
In this article, we are going to teach you how to install and configure Windows Admin Center in Windows Server 2019 and Windows 10.
Note: Admin Center can only be installed on Windows Server 2016 and above and Windows 10, but it also has the ability to control Windows Server 2012, Windows Server 2016, Windows Server 2019 and Windows 10.
Follow us with the tutorial to install Admin Center on Windows Server 2019 and Windows 10.
Table of Contents
Prerequisites
To download Admin Center, go to the Admin Center site and download the version you want.
How to Install the Windows Admin Center
1. Double click on the executable application just downloaded and proceed with the prompts as shown below. Then Click on Next.
2. In the next step, you can Use Microsoft update or not.
– Click Next.
3. Click Next again.
4. Choose a port or you can use the default one then click Install.
5. Follow the installation process to the end.
6. Finally, click on Finish.
Load the browser and run Admin Center
You are now able to load Admin Center via your browser and begin using it to add the systems you intend to administer.
a) Go to your browser and load the address below:
https://localhost(or IP).
b) Then select the certificate from the prompt and click OK.
c) Admin Center will now load as shown below:
How to Add a Server to manage with Windows Admin Center
The only available system when it finally loads is the localhost. You are now ready to add more from this point.
1. Click on the + Add button.
You can either add Servers, Windows PCs, Failover clusters, and others.
2. Choose the one that befits your scenario.
3. You can now add one by one, import a list, or search from Active Directory.
This is quite flexible.
4. The server you added will be added to the All Connections section.
5. By click on any of the servers, copious amounts of information and functionality get populated.
You will be able to connect to the server via Powershell, Remote Desktop. Then you will view its registry, CPU Performance, Disks and volume status, Installed Memory, Services, events, Installed Apps, Roles, and Features installed, files among many others.
6. You can fully administer your servers from this one Admin Center Node.
We hope you have taken advantage of the Admin Center installation tutorial on Windows Server 2019 and Windows 10 at the end.
Dear user, we hope you would enjoy this tutorial, you can ask questions about this training in the comments section, or to solve other problems in the field of Eldernode training, refer to the Ask page section and raise your problem in it as soon as possible. Make time for other users and experts to answer your questions.
Goodluck.
