Below is a list of common Windows file name extensions and formats.
|
Extension |
Format |
|---|---|
|
aac, adt, adts |
Windows audio file |
|
accdb |
Microsoft Access database file |
|
accde |
Microsoft Access execute-only file |
|
accdr |
Microsoft Access runtime database |
|
accdt |
Microsoft Access database template |
|
aif, aifc, aiff |
Audio Interchange File format file |
|
aspx |
ASP.NET Active Server page |
|
avi |
Audio Video Interleave movie or sound file |
|
bat |
PC batch file |
|
bin |
Binary compressed file |
|
bmp |
Bitmap file |
|
cab |
Windows Cabinet file |
|
cda |
CD Audio Track |
|
csv |
Comma-separated values file |
|
dif |
Spreadsheet data interchange format file |
|
dll |
Dynamic Link Library file |
|
doc |
Microsoft Word document before Word 2007 |
|
docm |
Microsoft Word macro-enabled document |
|
docx |
Microsoft Word document |
|
dot |
Microsoft Word template before Word 2007 |
|
dotx |
Microsoft Word template |
|
eml |
Email file created by Outlook Express, Windows Live Mail, and other programs |
|
eps |
Encapsulated Postscript file |
|
exe |
Executable program file |
|
flv |
Flash-compatible video file |
|
gif |
Graphical Interchange Format file |
|
htm, html |
Hypertext markup language page |
|
ini |
Windows initialization configuration file |
|
iso |
ISO-9660 disc image |
|
jar |
Java architecture file |
|
jpg, jpeg |
Joint Photographic Experts Group photo file |
|
m4a |
MPEG-4 audio file |
|
mdb |
Microsoft Access database before Access 2007 |
|
mid, midi |
Musical Instrument Digital Interface file |
|
mov |
Apple QuickTime movie file |
|
mp3 |
MPEG layer 3 audio file |
|
mp4 |
MPEG 4 video |
|
mp4 |
MPEG 4 video |
|
mpeg |
Moving Picture Experts Group movie file |
|
mpg |
MPEG 1 system stream |
|
msi |
Microsoft installer file |
|
mui |
Multilingual User Interface file |
|
|
Portable Document Format file |
|
png |
Portable Network Graphics file |
|
pot |
Microsoft PowerPoint template before PowerPoint 2007 |
|
potm |
Microsoft PowerPoint macro-enabled template |
|
potx |
Microsoft PowerPoint template |
|
ppam |
Microsoft PowerPoint add-in |
|
pps |
Microsoft PowerPoint slideshow before PowerPoint 2007 |
|
ppsm |
Microsoft PowerPoint macro-enabled slideshow |
|
ppsx |
Microsoft PowerPoint slideshow |
|
ppt |
Microsoft PowerPoint format before PowerPoint 2007 |
|
pptm |
Microsoft PowerPoint macro-enabled presentation |
|
pptx |
Microsoft PowerPoint presentation |
|
psd |
Adobe Photoshop file |
|
pst |
Outlook data store |
|
pub |
Microsoft Publisher file |
|
rar |
Roshal Archive compressed file |
|
rtf |
Rich Text Format file |
|
sldm |
Microsoft PowerPoint macro-enabled slide |
|
sldx |
Microsoft PowerPoint slide |
|
swf |
Shockwave Flash file |
|
sys |
Microsoft DOS and Windows system settings and variables file |
|
tif, tiff |
Tagged Image Format file |
|
tmp |
Temporary data file |
|
txt |
Unformatted text file |
|
vob |
Video object file |
|
vsd |
Microsoft Visio drawing before Visio 2013 |
|
vsdm |
Microsoft Visio macro-enabled drawing |
|
vsdx |
Microsoft Visio drawing file |
|
vss |
Microsoft Visio stencil before Visio 2013 |
|
vssm |
Microsoft Visio macro-enabled stencil |
|
vst |
Microsoft Visio template before Visio 2013 |
|
vstm |
Microsoft Visio macro-enabled template |
|
vstx |
Microsoft Visio template |
|
wav |
Wave audio file |
|
wbk |
Microsoft Word backup document |
|
wks |
Microsoft Works file |
|
wma |
Windows Media Audio file |
|
wmd |
Windows Media Download file |
|
wmv |
Windows Media Video file |
|
wmz, wms |
Windows Media skins file |
|
wpd, wp5 |
WordPerfect document |
|
xla |
Microsoft Excel add-in or macro file |
|
xlam |
Microsoft Excel add-in after Excel 2007 |
|
xll |
Microsoft Excel DLL-based add-in |
|
xlm |
Microsoft Excel macro before Excel 2007 |
|
xls |
Microsoft Excel workbook before Excel 2007 |
|
xlsm |
Microsoft Excel macro-enabled workbook after Excel 2007 |
|
xlsx |
Microsoft Excel workbook after Excel 2007 |
|
xlt |
Microsoft Excel template before Excel 2007 |
|
xltm |
Microsoft Excel macro-enabled template after Excel 2007 |
|
xltx |
Microsoft Excel template after Excel 2007 |
|
xps |
XML-based document |
|
zip |
Compressed file |
Windows, как и любая другая операционная система, поддерживает работу с разнообразными файловыми системами. Каждая из них предусматривает свои ключевые особенности и нюансы, о которых необходимо знать каждому ПК-пользователю.
Далее предстоит изучить файловые системы Windows. Необходимо выяснить, что они собой представляют, какими бывают, для чего используются. Особое внимание будет уделено NTFS как наиболее распространенной файловой системе. Информация, представленная далее, рассчитана на широкую публику. Она пригодится и обычному ПК-пользователю, и IT-специалисту.
Файловая система – это…
Данные обычно записываются, хранятся, обрабатываются на различных цифровых носителях в виде файлов. Далее, в зависимости от типа того или иного документа, осуществляется кодирование в виде знакомых каждому расширений – .exe, .pdf, .doc и других, а затем производится его открытие и обработка в соответствующем программном обеспечении.
Файловая система (file system или ФС) – это порядок, определяющий способ хранения, организации и именования данных на информационных носителях компьютеров и другого оборудования. Она будет определять формат содержимого, а также способ физического хранения данных, которые группируются в файлы.
Файловая система используется для связи хранилища (информации) с прикладным программным обеспечением, организуя доступ к конкретным документам через функционал взаимодействия программ API. Приложение, при обращении к файлам, знает только их имена, атрибуты и размеры. Все остальные сведения относительно типа носителя, на котором записан обрабатываемый документ, а также информация о структуре хранения данных, может быть получена от драйвера файловой системы.
Основные функции
Файловая система отвечает за оптимальное логическое распределение данных на определенном физическом носителе. Ее драйвер организует взаимодействие между:
- информационным хранилищем;
- операционной системой;
- прикладным программным обеспечением.
Грамотный выбор файловой системы для определенных пользовательских задач оказывает прямое воздействие на скорость обработки данных, принципы распределения и иные функциональные возможности, необходимые для стабильной работы компьютерных систем.
К основным функциям файловых систем относят:
- определение максимального объема данных, который может поддерживать тот или иной информационный носитель;
- создание, чтение и удаление файлов;
- поиск документов;
- определение структуры файла;
- организация каталогов;
- защита документов от системных сбоев и попыток получения несанкционированного доступа;
- назначение и изменение атрибутов файлов (размера, времени создания/изменения, владельца и создателя документа, максимальная длина имени файла и так далее);
- размещение и упорядочивание информации в виде файлов на выбранном носителе.
Эти функции характерны не только файловой системе NTFS, но и другим ФС. Другие функции рассматриваемый элемент не выполняет.
Задачи файловой системы
Функциональные возможности файловых систем направлены на решение определенного спектра задач. К ним относят:
- присвоение документам имен;
- поддержка устойчивости системы файлов ко всевозможным ошибкам и сбоям;
- содержание параметров документа, необходимых для корректного взаимодействия с другими объектами системы (ядром, приложениями и так далее);
- формирование программного интерфейса для взаимодействия приложений с документами;
- отображение логической модели файловой системы на физическую организацию информационного хранилища.
Во многопользовательских системах обеспечивается защита файлов от несанкционированного доступа, а также предоставляются возможности для совместной работы. Если один документ открыт пользователем, для других он будет временно доступен в режиме «только для чтения».
Все данные о файлах хранятся в специальных областях раздела – томах. Их структура полностью зависит от типа используемой файловой системы. Справочник файлов дает возможность ассоциировать числовые идентификаторы уникальных документов и дополнительные сведения о них с непосредственным содержимым файла, находящегося в другом области тома.
У операционных систем Windows встречаются различные файловые системы. К ним можно отнести:
- NTFS;
- FAT;
- ReFS.
Далее каждая из них будет рассмотрена более подробно. Особое внимание предстоит уделить файловой системе NTFS.
FAT – таблица распределения файлов
FAT – это самая первая ФС, которая появилась в Windows. Она была разработана по договоренности Билла Гейтса с первым наемным сотрудником Microsoft Марком Макдональдом в 1977 году. Ключевой задачей FAT стала работа с информацией в Microsoft 8080/x80 на базе платформы MDOS/MIDAS.
FAT перетерпела за время своего существования несколько модификаций: FAT12, FAT16, FAT32. Последняя до сих пор используется на большинстве внешних накопителей. Модификации отличаются друг от друга объемом доступной для хранения информации. Цифры 12, 16 и 32 указывают на количество бит, используемых для перечисления блока файловой системы.
FAT32 – это фактический стандарт в Windows. Он устанавливается на большинстве сменных носителей по умолчанию. FAT32 может использоваться не только на современных компьютерах, но и на устаревшем оборудовании/консолях, оснащенных USB-разъемом.
FAT32 предусматривает логическое разделение на три области:
- табличная форма указателей;
- место, зарезервированное для служебных структур;
- непосредственное пространство записи содержимого документов.
Пользуясь файловой системой FAT32, необходимо помнить о недостатке этого стандарта – ограничение размера документов на диске до 4 Гб, а всего раздела – до 8 Гб. Из-за соответствующей особенности FAT32 обычно устанавливается на USB-накопители и иные внешние информационные хранилища.
Для устранения ограничений упомянутого стандарта Microsoft создали обновленную файловую систему – exFAT. Она дает возможность хранить документы большего размера. Число перезаписей секторов, ответственных за непосредственное хранение файлов, здесь значительно снижено. Стандарт exFAT поддерживает совместимость с Android, macOS, Windows. Для Linux необходимо воспользоваться вспомогательным программным обеспечением.
ReFS
ReFS – это свежая разработка от компании Microsoft. Она доступна для серверов Windows 8 и 10. Архитектура тут представлена преимущественно в виде B + -tree. ReFS обладает высокой отказоустойчивостью. Это обусловлено наличием следующих функций:
- Copy-on-Write (CoW) – никакие метаданные не будут изменяться без копирования;
- информация записывается на новое дисковое пространство, а не поверх существующих документов;
- при модификации новая копия хранится на свободном дисковом пространстве, после чего система формирует ссылку из метаданных на новую версию.
ReFS – это файловая система, которая обеспечивает надежное хранение документов. А еще – гарантирует быстрое и легкое восстановление данных в случае необходимости.
NTFS
NTFS – это файловая система новой технологии. Стандарт, который достоин более детального изучения. Он был разработан с целью устранения недостатков FAT.
Первая реализация NTFS встретилась в Windows NT в 1995 году. С тех пор она используется в качестве основной файловой системы семейства Windows. Этот стандарт может расширить максимальный размер файла до 16 ГБ. NTFS поддерживает возможность формирования разделов диска до 16 Эб.
Свойства
NTFS – это файловая система, которая поддерживает следующие свойства:
- работа с большими документами;
- надежность за счет использования журналирования;
- простая процедура восстановления данных;
- управление доступом и безопасностью;
- поддержка шифрования и сжатия;
- поддержка дополнительных атрибутов.
Все эти особенности будут рассмотрены далее более подробно. Они помогут лучше изучить файловую систему NTFS и ее особенности.
Структура
NTFS предусматривает следующую структуру:
- Загрузочный сектор. Это самый первый сектор на диске. Он включает в себя информацию о файловой системе, а также позволяет операционной системе запуститься на устройстве. поддерживает код загрузчика и таблицу разделов.
- Мастер файловой таблицы (MFT). Так называется центральная структура NTFS, включающая данные обо всех файлах и папках на диске. Каждый документ и каталог предусматривают наличие собственной записи в MFT, которая содержит метаданные: имя файла, атрибуты, ссылки на физические блоки информации.
- Атрибуты файлов и папок. В NTFS они используются для хранения дополнительных данных о файлах и папках. Пример – информация о владельце документа, времени создания и изменения, пользовательские сведения. За счет соответствующей особенности NTFS получает инструменты гибкого управления и организации файлов.
- Аллокационные единицы (кластеры). Они представлены информационными блоками, на которые разбивается диск. Каждый кластер NTFS обладает фиксированным размером и содержит данные документов или метаданные. Изучаемый стандарт задействует алгоритмы сжатия и фрагментации для эффективного использования дискового пространства.
- Журнал файловой системы (NTFS journal). Представлен механизмом, записывающим любые изменения, происходящие в пределах используемого диска. С его помощью удастся восстановить файловую систему NTFS при сбоях и ошибках. Журнал также отвечает за целостность данных и защиту от информационных потерь.
Такой состав NTFS позволяет обеспечить эффективное управление данными и возможность их восстановления, а также обезопасить имеющиеся документы. Windows за счет NTFS будет эффективно работать с имеющимися элементами и папками, обеспечивая высокий уровень производительности и надежности.
Журналирование
NTFS использует журналирование. Оно присуще всем современным операционным системам. За счет журналирования NTFS и другие ФС при системной сбое или аварийном завершении работы можно восстановить до последнего рабочего состояния. Документы утрачены не будут.
Работа с информацией за счет журналирования в NTFS осуществляется по принципу транзакций: операция будет совершена полностью или не совершаться вовсе. Примером может послужить запись системного документа на диск. Компьютер с NTFS создает пометки в метафайле MFT и ведет мини-журнал процесса копирования. Это происходит до тех пор, пока документ не будет записан полностью на необходимый раздел диска. Если устройство в процессе записи перезагружается, при следующем включении система обратится к журналу NTFS, узнает о совершенных и несовершенных транзакция, а затем оставит лишь те, что помечены как завершенные. Остальные транзакции вычеркиваются, а файлы удаляются или возвращаются на место.
Такая схема эффективна только с системными документами. Это связано с тем, что пользовательская информация может быть повреждена или вовсе удалиться при системном сбое. NTFS и другие использующие журналирование стандарты допускают проверку при помощи контрольных точек восстановления – их компьютер создает время от времени. Соответствующие точки можно использовать для отказа до прежних состояний ОС.
Шифрование
Шифрование – это отдельная надстройка над ФС устройства. Она дает возможность закрыть пользовательские данные от посторонних практически на аппаратном уровне. В NTFS шифрование имеет значимую роль. Защищенные таким образом файлы не получится просмотреть на другом компьютере, а также после смены операционной системы или материнской платы.
NTFS в Windows формирует ключи и сертификаты, актуальные только для той сборки системы, на которой было подключено соответствующее шифрование. Рассматриваемый стандарт также выделяется:
- поддержкой крупных томов и документов;
- несколькими уровнями безопасности;
- возможностью сжатия;
- поддержкой огромного количества файлов;
- возможностью распределения прав доступа.
NTFS ориентирована на работу с операционной системой, а также на взаимодействие с носителями с большим объемом и несколькими разделами.
Преимущества и недостатки NTFS
NTFS – стандарт организации файлов и папок, который предусматривает следующие преимущества:
- Надежность. NTFS гарантирует целостность информации и высокую надежность.
- Огромные возможности хранения. Стандарт поддерживает большие размеров документов и разделов: 16 Эб и 256 Тб соответственно.
- Безопасность.
- Управление дисками. NTFS позволяет организовать эффективное управление жестким диском и его разделами. У него есть функции динамического разделения дискового пространства, сжатия файлов и создания теневых копий.
- Поддержка многопользовательской среды.
Изучая информацию о файловой системе NTFS, необходимо обратить внимание и на ее недостатки. К ним можно отнести:
- Скорость работы. NTFS может работать чуть медленнее, чем другие файловые системы.
- Сложность. Структура и механизмы стандарта более сложные. За счет этого у пользователей могут возникать проблемы в процессе отладки и восстановления данных.
- Совместимость. У NTFS нет полной совместимости с отдельными операционными системами. Из-за соответствующей особенности не исключены проблемы при обмене документами между разными ОС.
Несмотря на это, NTFS пользуется спросом в Windows. Лучше изучить особенности этого стандарта помогут дистанционные компьютерные курсы. Они рассчитаны на срок от нескольких месяцев до года. Весь образовательный процесс сопровождается богатой практикой и формированием портфолио. В конце курса каждый успешно завершивший его получит электронный сертификат, подтверждающий приобретенные навыки и знания.
Хотите освоить современную IT-специальность? Огромный выбор курсов по востребованным IT-направлениям есть в Otus!
Расширение файла
В этом уроке я расскажу, что такое расширение и какие бывают типы файлов в Windows. А в конце дам таблицу наиболее популярных форматов с подробным описанием.
Содержание:
- Что такое формат и расширение
- Как узнать расширение
- Как изменить расширение
- Как назначить программу запуска
- Таблица форматов
Что такое формат и расширение
Формат или тип — это информация о файле, по которой система понимает, какого он вида и в какой программе его открыть. Для этого у каждого файла есть расширение.
Расширение — это несколько английских букв и/или цифр. Находятся они сразу после названия и разделяются точкой.
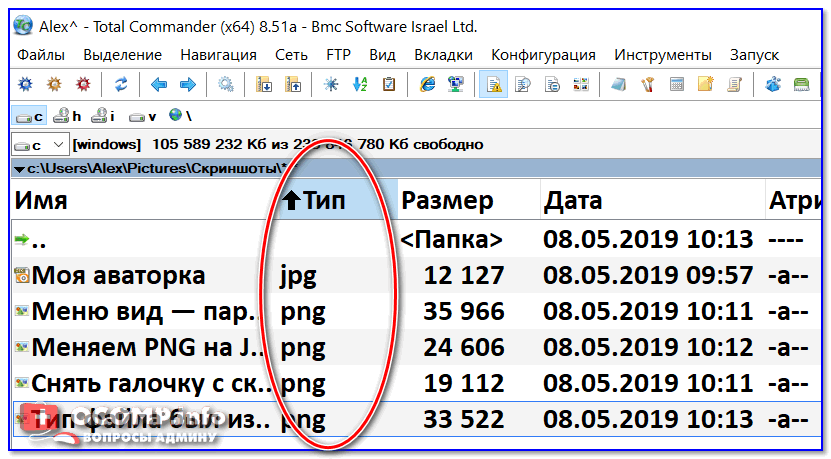
На картинке показан файл с расширением mp3. Про него компьютер знает, что это аудио и открывать его нужно в программе-проигрывателе. Значок, которым он отмечен – это иконка программы запуска.
Есть текстовые файлы — они открываются в программе для работы с текстом. Есть музыкальные и видео — они запускаются в проигрывателях. Есть графические (фото, картинки) – они открываются в программах для просмотра изображений. И еще много других типов. У каждого из них свой значок, точнее, значок приложения, в котором он будет открыт.
Если у файла вместо иконки белый лист, значит, компьютер не подобрал для него подходящую программу.
При его открытии появится окно с выбором приложения. Компьютер предлагает пользователю самостоятельно указать программу для запуска.
На заметку. В Windows есть разнообразные системные иконки.
Как правило, такими значками отмечены файлы, которые нужны для корректной работы компьютера. Их много в системном локальном диске. Такие объекты нельзя удалять или переименовывать, иначе приложения, за которые они отвечают, могут работать со сбоями.
Как узнать расширение
Система компьютера может быть настроена таким образом, что расширения у всех файлов показаны.
Или наоборот: так, что показаны только имена, без форматов.
Эту настройку можно изменить.
В Windows 10 открыть любую папку, нажать на пункт «Вид» вверху и поставить или убрать птичку с пункта «Расширения имен файлов».
Или так: Вид → Параметры → вкладка «Вид» → пункт «Скрывать расширения для зарегистрированных типов файлов».

В Windows 7 чуть сложнее:
- Открыть любую папку.
- Нажать на «Упорядочить значки» вверху.
- Выбрать «Параметры папок и поиска».
- В появившемся окошке перейти на вкладку «Вид».
- Внизу списка поставить или убрать галочку с пункта «Скрывать расширения для зарегистрированных типов файлов».
Или так: Пуск → Панель управления → Оформление и персонализация → Параметры папок.

Если расширения нет
Если у объекта нет расширения, компьютер не может подобрать программу для его запуска. Это происходит, когда пользователь случайно или намеренно удаляет расширение из имени. А еще может быть из-за вируса.
Решить эту проблему легко, если знаешь тип объекта. Например, знаешь, что это фотография. Тогда нужно просто переименовать файл, добавить после названия точку и указать формат. Вот как это сделать:
- Настроить компьютер на показ расширений (см. выше).
- Правой кнопкой мыши по файлу – Переименовать.
- Сразу после названия напечатать точку и расширение.
- Нажать Enter.
Наиболее популярные форматы:
- Документы – doc, docx или pdf
- Таблицы – xls, xlsx
- Архивы – zip или rar
- Фотографии – jpg или png
- Музыка – mp3 или wav
- Видео – mp4 или avi
Другие типы можно посмотреть в конце в таблице.
Если формат неизвестен. Чтобы открыть файл, необязательно вручную прописывать расширение. Можно просто запустить его и в окошке выбрать подходящую программу. Если вы правильно ее укажите, объект откроется.
Или щелкните по нему правой кнопкой мыши, выберите «Открыть с помощью…». Или «Открыть с помощью» → «Выбрать другое приложение».
Узнать тип файла можно через сервис open-file.ru. Просто перетяните объект в окошко, и сайт определит формат.
Как изменить расширение
Изменить расширение можно через переименование:
- Настроить компьютер на показ расширений (см. выше).
- Щелкнуть правой кнопкой мыши по файлу – Переименовать.
- Стереть старое расширение после точки и напечатать новое.
- Нажать Enter.
Появится окошко, в котором система предупредит о последствиях. Ведь если вы неправильно укажите формат, файл может не открыться. Например, у вас документ с расширением doc, а вы меняете его на pdf.

После нажатия на кнопку «Да» новый тип будет назначен. А также добавится значок программы для его запуска. Но обычно после такой ручной смены расширения файл перестает открываться. Потому что он технически остался тем же, что и был.
Вернуть старое расширение можно таким же образом – через переименование. Или щелкнув правой кнопкой мыши по пустому месту и выбрав пункт «Отменить переименование».

Так как же правильно изменить расширение? Для этого нужно сделать конвертацию – преобразование в другой формат. Это делается через специальные программы или онлайн-сервисы.
Вбиваем в поисковик Яндекс или Гугл запрос «из … в …». Например, из word в pdf.

В моем случае Яндекс предложил несколько онлайн сервисов. Все они интуитивно понятны: загружаем документ на сайт → сервис преобразовывает его в pdf → скачиваем результат на компьютер.
Но в некоторых случаях лучше использовать программу. Например, если нужно конвертировать видео большого размера.
Как назначить программу запуска
Каждому типу файла система назначает приложение для его запуска. И помечает иконкой этой программы. Например, текстовые (txt) будут по умолчанию открыты в Блокноте. А музыкальные (mp3) – в проигрывателе Windows Media.
Когда вместо значка показан белый лист, значит, система не понимает, в какой программе открыть объект. И при его запуске предлагает самостоятельно выбрать приложение из тех, что установлены на компьютере.
Если поставить птичку на пункт «Всегда использовать это приложение», то в последующем все объекты данного типа будут запускаться в выбранной программе.
Но не всегда нужная программа установлена на компьютере. Бывает, ее просто нет — тогда файл открыть никак не получится. В этом случае нужно установить подходящее приложение.
Для каждого популярного формата есть своя бесплатная программа:
- PDF – Foxit Reader
- ZIP и RAR – 7-Zip
- DOC, DOCX, XLS, XLSX и другие документы MS Office – OpenOffice
- MP3, MP4, MKV и другие аудио/видео – Media Player Classic
Другие форматы и программы для них смотрите в таблице.
Выбор программы по умолчанию
А бывает, объекты определенного типа открываются в неподходящей программе. Тогда можно указать другое приложение для их запуска.
1. Щелкните правой кнопкой мыши по файлу. Выберите «Открыть с помощью…» или «Открыть с помощью» → «Выбрать другое приложение».

2. В окошке кликните левой кнопкой мыши по нужной программе и поставьте птичку на пункт «Всегда использовать это приложение». Нажмите ОК.
Вот и всё – теперь объекты данного формата будут по умолчанию запускаться в назначенной программе.
Таблица популярных форматов
| РАСШИРЕНИЕ | ТИП ФАЙЛА | ПРОГРАММА |
|---|---|---|
| .jpg .png .bmp .gif .tif | Изображение | Фотографии (Windows 8/10) Средство просмотра фотографий (Windows 7) FastStone Image Viewer Paint |
| .doc .docx | Документ | Microsoft Word OpenOffice LibreOffice |
| .xls .xlsx | Электронная таблица | Microsoft Excel OpenOffice LibreOffice |
| PDF-документ | Acrobat Reader Foxit Reader |
|
| .txt | Текстовый файл | Блокнот Notepad++ |
| .zip .rar .7z .gzip | Архив | WinZip WinRAR 7-Zip |
| .mp3 .wav .midi .aac | Аудиофайл | Windows Media Player Media Player Classic VLC Media Player |
| .mp4 .avi .mkv .wmv .flv .mpeg | Видеофайл | Windows Media Player Media Player Classic VLC Media Player |
| .html .htm .mht | Cтраница из интернета | Google Chrome Яндекс.Браузер Mozilla Firefox Opera |
| .ppt .pptx | Презентация | Microsoft PowerPoint OpenOffice |
| .mdb .accdb | База данных | Microsoft Access |
| .iso | Образ оптического диска | UltraISO Alcohol 120% 7-Zip |
| .cdr | Векторное изображение | CorelDRAW CDR Viewer |
| .torrent | Торрент-файл | uTorrent BitTorrent |
| .djvu | Сканированный документ (книга, журнал и пр.) |
WinDjView |
| .fb2 .epub .mobi | Электронная книга | FBReader |
This is a list of file formats used by computers, organized by type. Filename extension is usually noted in parentheses if they differ from the file format’s name or abbreviation. Many operating systems do not limit filenames to one extension shorter than 4 characters, as was common with some operating systems that supported the File Allocation Table (FAT) file system. Examples of operating systems that do not impose this limit include Unix-like systems, and Microsoft Windows NT, 95-98, and ME which have no three character limit on extensions for 32-bit or 64-bit applications on file systems other than pre-Windows 95 and Windows NT 3.5 versions of the FAT file system. Some filenames are given extensions longer than three characters. While MS-DOS and NT always treat the suffix after the last period in a file’s name as its extension, in UNIX-like systems, the final period does not necessarily mean that the text after the last period is the file’s extension.[1]
Some file formats, such as .txt or .text, may be listed multiple times.
- ?Q? – files that are compressed, often by the SQ program.
- 7z – 7-zip compressed file
- ACE – ace: ACE compressed file
- ALZ – ALZip compressed file
- ARC – pre-Zip data compression
- ARJ – ARJ compressed file
- BZ2 – bzip2
- CAB – A cabinet file is a library of compressed files stored as one file. Cabinet files are used to organize installation files that are copied to the user’s system.[2]
- CPT, SEA – Compact Pro (Macintosh)
- EGG – Alzip Egg Edition compressed file
- EGT – EGT Universal Document also used to create compressed cabinet files, replaces .ecab
- ECAB, EZIP – EGT Compressed Folder used in advanced systems to compress entire system folders, replaced by EGT Universal Document
- ESS – EGT SmartSense File, detects files compressed using the EGT compression system.
- FLIPCHART – Used in Promethean Flipchart Software.
- FUN – A FUN file is a file that has been encrypted by Jigsaw ransomware, which is malware distributed by cybercriminals. It contains a file, such as a .JPG, .DOCX, .XLSX, .MP4, or .CSV file, that has been renamed and encrypted by the virus.
- GZ – gzip Compressed file
- JAR – jar ZIP file with manifest for use with Java applications.
- LAWRENCE – LBR Lawrence Compiler Type file
- LBR – LBR Library file
- LZH – LHA Lempel, Ziv, Huffman
- LZ – lzip Compressed file
- LZO – lzo
- LZMA – lzma Lempel–Ziv–Markov chain algorithm compressed file
- LZX – LZX
- MBW – MBRWizard archive
- MCADDON — Plugin for Minecraft Bedrock
- BIN – BIN MacBinary
- OAR – OAR: OAR archive
- PAK – Enhanced type of .ARC archive
- PAR, PAR2 – PAR Parchive
- PAF – PAF Portable Application File
- PEA – PEA PeaZip archive file
- PYK – PYK compressed file
- RAR – RAR Rar Archive, for multiple file archive (rar to .r01-.r99 to s01 and so on)
- RaX – Archive file created by RaX
- SITX – SIT StuffIt (Macintosh)
- TAR – TAR: group of files, packaged as one file
- WAX – Wavexpress – A ZIP alternative optimized for packages containing video, allowing multiple packaged files to be all-or-none delivered with near-instantaneous unpacking via NTFS file system manipulation.
- XZ – xz compressed files, based on LZMA/LZMA2 algorithm
- Z – Unix compress file
- ZOO – zoo: based on LZW
- ZIP – zip: popular compression format
Application packages
edit
- ABB – Android App Bundle – is the Android (and Android TV) application publishing file format (required by Google Play) taking over from APK
- APK – Android package: Applications installable on Android (also installable in derivatives and e.g. Windows 11); also a package format of the Alpine Linux distribution.
- APPX – Microsoft Application Package (.appx)
- APP – HarmonyOS APP Packs file format for HarmonyOS apps installable from AppGallery and third party OpenHarmony based app distribution stores.
- DMG — A format that Macintosh devices use for all applications third-party applications and some direct Apple Inc. applications.
- DEB – Debian install package
- HPKG – Haiku application package format
- IPG – Format in which Apple Inc. packages their iPod games. Can be extracted through Winrar
- RPM – Red Hat package/installer for Fedora, RHEL, and similar systems.
- SIS, SISX – SIS/SISX: Symbian Application Package
- XAP – Windows Phone Application Package
Physical recordable media archiving
edit
- ADF – for archiving Amiga floppy disks
- ADZ – The GZip-compressed version of ADF.
- B5T – BlindWrite 5 image file
- B6T – BlindWrite 6 image file
- BWT – BlindWrite 4 image file
- BIN – Raw binary format, often paired with CUE
- CDI – DiscJuggler image file
- CUE – CDRWrite CUE image file
- CIF – Easy CD Creator .cif format
- C2D – Roxio-WinOnCD .c2d format
- DAA – PowerISO .daa format
- D64 – An archive of a Commodore 64 floppy disk.
- DAA – DAA: Closed-format, Windows-only compressed disk image
- DMG – Macintosh disk image files
- DMS – a disk-archiving system native to the Amiga.
- DSK – For archiving floppy disks from a number of other platforms, including the ZX Spectrum and Amstrad CPC.
- ESD – ESD: Electronic Software Distribution, a compressed and encrypted WIM File
- FFPPKG – FreeFire Profile Export Package
- GHO, GHS – GHO Norton Ghost
- IMG – Raw disk image, for archiving DOS formatted floppy disks, hard drives, and larger optical media.
- ISO – Generic format for most optical media, including CD-ROM, DVD-ROM, Blu-ray, HD DVD and UMD.
- MDS – Daemon Tools native disc image format used for making images from optical CD-ROM, DVD-ROM, HD DVD or Blu-ray. It comes together with MDF file and can be mounted with DAEMON Tools.
- MDX – Daemon Tools format that allows getting one MDX disc image file instead of two (MDF and MDS).
- NRG – Proprietary optical media archive format used by Nero applications.
- SDI – used for archiving and providing «virtual disk» functionality.
- SWM – Splitted WIM File, usually found on OEM Recovery Partition to store preinstalled Windows image, and to make Recovery backup (to USB Drive) easier (due to FAT32 limitations)
- TIB – TIB Acronis True Image backup
- WIM – WIM A compressed disk image for installing Windows Vista or higher, Windows Fundamentals for Legacy PC, or restoring a system image made from Backup and Restore (Windows Vista/7)
- Msi – Windows installation file
- Vdhx – Virtual disk created by Hyper-V (Hyper-V runs on Microsoft Windows)
Computer-aided design
edit
Computer-aided is a prefix for several categories of tools (e.g., design, manufacture, engineering) which assist professionals in their respective fields (e.g., machining, architecture, schematics).
Computer-aided design (CAD)
edit
Computer-aided design (CAD) software assists engineers, architects and other design professionals in project design.
- 3DXML – Dassault Systemes graphic representation
- 3MF – Microsoft 3D Manufacturing Format[3]
- ACP – VA Software VA – Virtual Architecture CAD file
- AMF – Additive Manufacturing File Format
- AEC – DataCAD drawing format[4]
- AEDT – Ansys Electronic Desktop – Project file
- AR – Ashlar-Vellum Argon – 3D Modeling
- ART – ArtCAM model
- ASC – BRL-CAD Geometry File (old ASCII format)
- ASM – Solidedge Assembly, Pro/ENGINEER Assembly
- BIN, BIM – Data Design System DDS-CAD
- BREP – Open CASCADE 3D model (shape)
- C3D – C3D Toolkit File Format
- C3P – Construct3 Files
- CCC – CopyCAD Curves
- CCM – CopyCAD Model
- CCS – CopyCAD Session
- CAD – CadStd
- CATDrawing – CATIA V5 Drawing document
- CATPart – CATIA V5 Part document
- CATProduct – CATIA V5 Assembly document
- CATProcess – CATIA V5 Manufacturing document
- CGR – CATIA V5 graphic representation file
- CKD – KeyCreator CAD parts, assemblies, and drawings
- CKT – KeyCreator template file
- CO – Ashlar-Vellum Cobalt – parametric drafting and 3D modeling
- DAB – AppliCad 3D model CAD file
- DRW – Caddie Early version of Caddie drawing – Prior to Caddie changing to DWG
- DFT – Solidedge Draft
- DGN – MicroStation design file
- DGK – Delcam Geometry
- DMT – Delcam Machining Triangles
- DXF – ASCII Drawing Interchange file format, AutoCAD
- DWB – VariCAD drawing file
- DWF – Autodesk’s Web Design Format; AutoCAD & Revit can publish to this format; similar in concept to PDF files; Autodesk Design Review is the reader
- DWG – Popular file format for Computer Aided Drafting applications, notably AutoCAD, Open Design Alliance applications, and Autodesk Inventor Drawing files
- EASM – SolidWorks eDrawings assembly file
- EDRW – eDrawings drawing file
- EMB – Wilcom ES Designer Embroidery CAD file
- EPRT – eDrawings part file
- EscPcb – «esCAD pcb» data file by Electro-System (Japan)
- EscSch – «esCAD sch» data file by Electro-System (Japan)
- ESW – AGTEK format
- EXCELLON – Excellon file
- EXP – Drawing Express format
- F3D – Autodesk Fusion 360 archive file[5]
- FCStd – Native file format of FreeCAD CAD/CAM package
- FM – FeatureCAM Part File
- FMZ – FormZ Project file
- G – BRL-CAD Geometry File
- GBR – Gerber file
- GCODE — G-code Geometric code. Instructions for 3D printers.
- GLM – KernelCAD model
- GRB – T-FLEX CAD File
- GRI – AppliCad GRIM-In file in readable text form for importing roof and wall cladding job data generated by business management and accounting systems into the modelling/estimating program
- GRO – AppliCad GRIM-Out file in readable text form for exporting roof and wall cladding data job material and labour costing data, material lists generated by the modelling/estimating program to business management and accounting systems
- IAM – Autodesk Inventor Assembly file
- ICD – IronCAD 2D CAD file
- IDW – Autodesk Inventor Drawing file
- IFC – buildingSMART for sharing AEC and FM data
- IGES – Initial Graphics Exchange Specification
- DGN, CEL – Intergraph Standard File Formats Intergraph
- IO – Stud.io 3D model
- IPN – Autodesk Inventor Presentation file
- IPT – Autodesk Inventor Part file
- JT – Jupiter Tesselation
- MCD – Monu-CAD (Monument/Headstone Drawing file)
- MDG – Model of Digital Geometric Kernel
- model – CATIA V4 part document
- OCD – Orienteering Computer Aided Design (OCAD) file
- PAR – Solidedge Part
- PART – A file used with Stud.Io
- PIPE – PIPE-FLO Professional Piping system design file
- PLN – ArchiCad project
- PRT – NX (recently known as Unigraphics), Pro/ENGINEER Part, CADKEY Part
- PSM – Solidedge Sheet
- PSMODEL – PowerSHAPE Model
- PWI – PowerINSPECT File
- PYT – Pythagoras File
- RLF – ArtCAM Relief
- RVM – AVEVA PDMS 3D Review model
- RVT – Autodesk Revit project files
- RFA – Autodesk Revit family files
- RFT — Autodesk Revit Revit Family Template
- RXF – AppliCad annotated 3D roof and wall geometry data in readable text form used to exchange 3D model geometry with other systems such as truss design software
- S12 – Spirit file, by Softtech
- SCAD – OpenSCAD 3D part model
- SCDOC – SpaceClaim 3D Part/Assembly
- SKB – Google SketchUp backup File
- SKP – Sketchup
- SLDASM – SolidWorks Assembly drawing
- SLDDRW – SolidWorks 2D drawing
- SLDPRT – SolidWorks 3D part model
- dotXSI – For Softimage
- STATE – A file used by the IaC tool to record information about what has been deployed by the tool.
- STEP – Standard for the Exchange of Product model data
- STL – Stereo Lithographic data format used by various CAD systems and stereo lithographic printing machines.
- STD – Power Vision Plus – Electricity Meter Data (Circuitor)
- TCT – TurboCAD drawing template
- TCW – TurboCAD for Windows 2D and 3D drawing
- UNV – I-DEAS I-DEAS (Integrated Design and Engineering Analysis Software)
- VC6 – Ashlar-Vellum Graphite – 2D and 3D drafting
- VLM – Ashlar-Vellum Vellum, Vellum 2D, Vellum Draft, Vellum 3D, DrawingBoard
- VS – Ashlar-Vellum Vellum Solids
- WRL – Similar to STL, but includes color. Used by various CAD systems and 3D printing rapid prototyping machines. Also used for VRML models on the web.
- X_B – Parasolids binary format
- X_T – Parasolids
- XE – Ashlar-Vellum Xenon – for associative 3D modeling
- ZOFZPROJ – ZofzPCB 3D PCB model, containing mesh, netlist and BOM
Electronic design automation (EDA)
edit
Electronic design automation (EDA), or electronic computer-aided design (ECAD), is specific to the field of electrical engineering.
- BRD – Board file for EAGLE Layout Editor, a commercial PCB design tool
- BSDL – Description language for testing through JTAG
- CDL – Transistor-level netlist format for IC design
- CPF – Power-domain specification in system-on-a-chip (SoC) implementation (see also UPF)
- DEF – Gate-level layout
- Detailed Standard Parasitic Format – Detailed Standard Parasitic Format, Analog-level Parastic component of interconnections in IC design
- EDIF – Vendor neutral gate-level netlist format
- FSDB – Analog waveform format (see also Waveform viewer)
- GDSII – Format for PCB and layout of integrated circuits
- HEX – ASCII-coded binary format for memory dumps
- LEF – Library Exchange Format, physical abstract of cells for IC design
- Liberty (EDA) – Library modeling (function, timing) format
- MS12 – NI Multisim file
- OASIS – Open Artwork System Interchange Standard
- OpenAccess – Design database format with APIs
- PSF – Cadence proprietary format to store simulation results/waveforms (2GB limit)
- PSFXL – Cadence proprietary format to store simulation results/waveforms
- SDC – Synopsys Design Constraints, format for synthesis constraints
- SDF – Standard for gate-level timings
- SPEF – Standard format for Parasitic component of interconnections in IC design
- SPI, CIR – SPICE Netlist, device-level netlist and commands for simulation
- SREC, S19 – S-record, ASCII-coded format for memory dumps
- SST2 – Cadence proprietary format to store mixed-signal simulation results/waveforms
- STIL – Standard Test Interface Language, IEEE1450-1999 standard for Test Patterns for IC
- SV – SystemVerilog source file
- S*P – Touchstone/EEsof Scattering parameter data file – multi-port blackbox performance, measurement or simulated
- TLF – Contains timing and logical information about a collection of cells (circuit elements)
- UPF – Standard for Power-domain specification in SoC implementation
- V – Verilog source file
- VCD – Standard format for digital simulation waveform
- VHD, VHDL – VHDL source file
- WGL – Waveform Generation Language, format for Test Patterns for IC
Files output from Automatic Test Equipment or post-processed from such.
- Standard Test Data Format
- 4DB – 4D database Structure file
- 4DC – 4D database Structure file (compiled in legacy mode)
- 4DD – 4D database Data file
- 4DIndy – 4D database Structure Index file
- 4DIndx – 4D database Data Index file
- 4DR – 4D database Data resource file (in old 4D versions)
- 4DZ – 4D database Structure file (compiled in 4D Project mode)
- ACCDB – Microsoft Database (Microsoft Office Access 2007 and later)
- ACCDE – Compiled Microsoft Database (Microsoft Office Access 2007 and later)
- ADT – Sybase Advantage Database Server (ADS)
- APR – Lotus Approach data entry & reports
- BOX – Lotus Notes Post Office mail routing database
- CHML – Krasbit Technologies Encrypted database file for 1 click integration between contact management software and the Chameleon Software
- DAF – Digital Anchor data file
- DAT – DOS Basic
- DAT – Intersystems Caché database file
- DB – Paradox
- DB – SQLite
- DBF – db/dbase II,III,IV and V, Clipper, Harbour/xHarbour, Fox/FoxPro, Oracle
- DTA – Sage Sterling database file
- EGT – EGT Universal Document, used to compress sql databases to smaller files, may contain original EGT database style.
- ESS – EGT SmartSense is a database of files and its compression style. Specific to EGT SmartSense
- EAP – Enterprise Architect Project
- FDB – Firebird Databases
- FDB – Navision database file
- FP, FP3, FP5, FP7 – FileMaker Pro
- FRM – MySQL table definition
- GDB – Borland InterBase Databases
- GTABLE – Google Drive Fusion Table
- KEXI – Kexi database file (SQLite-based)
- KEXIC – shortcut to a database connection for a Kexi databases on a server
- KEXIS – shortcut to a Kexi database
- LDB – Temporary database file, only existing when database is open
- LIRS – Layered Intager Storage. Stores intageres with characters such as semicolons to create lists of data.
- MDA – Add-in file for Microsoft Access
- MDB – Microsoft Access database
- ADP – Microsoft Access project (used for accessing databases on a server)
- MDE – Compiled Microsoft Database (Access)
- MDF – Microsoft SQL Server Database
- MYD – MySQL MyISAM table data
- MYI – MySQL MyISAM table index
- NCF – Lotus Notes configuration file
- NSF – Lotus Notes database
- NTF – Lotus Notes database design template
- NV2 – QW Page NewViews object oriented accounting database
- ODB – LibreOffice Base or OpenOffice Base database
- ORA – Oracle tablespace files sometimes get this extension (also used for configuration files)
- PCONTACT – WinIM Contact file
- PDB – Palm OS Database
- PDI – Portable Database Image
- PDX – Corel Paradox database management
- PRC – Palm OS resource database
- SQL – bundled SQL queries
- REC – GNU recutils database
- REL – Sage Retrieve 4GL data file
- RIN – Sage Retrieve 4GL index file
- SDB – StarOffice’s StarBase
- SDF – SQL Compact Database file
- SQLITE – SQLite
- UDL – Universal Data Link
- waData – Wakanda (software) database Data file
- waIndx – Wakanda (software) database Index file
- waModel – Wakanda (software) database Model file
- waJournal – Wakanda (software) database Journal file
- WDB – Microsoft Works Database
- WMDB – Windows Media Database file – The
CurrentDatabase_360.wmdbfile can contain file name, file properties, music, video, photo and playlist information.
Big Data (Distributed)
edit
- Avro – Data format appropriate for ingestion of record based attributes. Distinguishing characteristic is schema is stored on each row enabling schema evolution.
- Parquet – Columnar data storage. It is typically used within the Hadoop ecosystem.
- ORC – Similar to Parquet, but has better data compression and schema evolution handling.
- AI – Adobe Illustrator
- AVE, ZAVE – Aquafadas
- CDR – CorelDRAW
- CHP, pub, STY, CAP, CIF, VGR, FRM – Ventura Publisher – Xerox (DOS / GEM)
- CPT – Corel Photo-Paint
- DPE – Package of AVE documents made with Aquafadas digital publishing tools.
- DTP – Greenstreet Publisher, GST PressWorks
- FM – Adobe FrameMaker
- GDRAW – Google Drive Drawing
- ILDOC – Broadvision Quicksilver document
- INDD – Adobe InDesign
- MCF – FotoInsight Designer
- PDF – Adobe Acrobat or Adobe Reader
- PMD – Adobe PageMaker
- PPP – Serif PagePlus
- PSD – Adobe Photoshop
- PUB – Microsoft Publisher
- QXD – QuarkXPress
- SLA, SCD – Scribus
- XCF – XCF: File format used by the GIMP, as well as other programs
These files store formatted text and plain text.
- 0 – Plain Text Document, normally used for licensing
- 1ST – Plain Text Document, normally preceded by the words «README» (README.1ST)
- 600 – Plain Text Document, used in UNZIP history log
- 602 – Text602 (T602) document
- ABW – AbiWord document
- ACL – MS Word AutoCorrect List
- AFP – Advanced Function Presentation
- AMI – Lotus Ami Pro
- ANS – American National Standards Institute (ANSI) text
- ASC – ASCII text
- AWW – Ability Write
- BBeB – Broad Band EBook
- CCF – Color Chat 1.0
- CSV – ASCII text as comma-separated values, used in spreadsheets and database management systems
- CWK – ClarisWorks-AppleWorks document
- DBK – DocBook XML sub-format
- DITA – Darwin Information Typing Architecture document
- DOC – Microsoft Word document
- DOCM – Microsoft Word macro-enabled document
- DOCX – document, Office Open XML, there are at least 4 quite different versions of Microsoft’s DOCX: 1) ECMA-376, 2)ISO/IEC 29500 Transitional, 3) ISO/IEC 29500 Strict, 4) Microsoft-specific Compatibility Mode variants.
- DOT – Microsoft Word document template
- DOTX – Office Open XML text document template
- DWD – DavkaWriter Heb/Eng word processor file
- EGT – EGT Universal Document
- EPUB – EPUB open standard for e-books
- EVTX – Windows XML EventLog files are system log files used by the Windows operating system[6]
- EZW – Reagency Systems easyOFFER document[7]
- FDX – Final Draft
- FTM – Fielded Text Meta
- FTX – Fielded Text (Declared)
- GDOC – Google Drive Document
- GUIDE – AmigaGuide
- HTML, HTM – HyperText Markup Language
- HWP – Haansoft (Hancom) Hangul Word Processor document
- HWPML – Haansoft (Hancom) Hangul Word Processor Markup Language document
- KPUB – Kobo ebook format
- LOG – Text log file
- LWP – Lotus Word Pro
- MBP – metadata for Mobipocket documents
- MD – Markdown text document
- ME – Plain text document normally preceded by the word «READ» (READ.ME)
- MCW – Microsoft Word for Macintosh (versions 4.0–5.1)
- Mobi – Mobipocket documents
- NB – Mathematica Notebook
- NB – Nota Bene Document (Academic Writing Software)
- NBP – Mathematica Player Notebook
- NEIS – 학교생활기록부 작성 프로그램 (Student Record Writing Program) Document
- NT – N-Triples RDF container (.nt)
- NQ – N-Quads RDF container (.nq)
- ODM – OpenDocument master document
- ODOC – Synology Drive Office Document
- ODT – OpenDocument text document
- OSHEET – Synology Drive Office Spreadsheet
- OTT – OpenDocument text document template
- OMM – OmmWriter text document
- PAGES – Apple Pages document
- PAP – Papyrus word processor document
- PER – Canadian Forces Personnel Appraisal System (CFPAS) Personnel Evaluation Report (PER)
- PDR – Canadian Forces Personnel Appraisal System (CFPAS) Personnel Development Report (PDR)
- PDAX – Portable Document Archive (PDA) document index file
- PDF – Portable Document Format
- PROTONDOC – Proton Docs file shortcut
- QUOX – Question Object File Format for Quobject Designer or Quobject Explorer
- Radix-64 – Need helps!!!
- RTF – Rich Text document
- RPT – Crystal Reports
- SDW – StarWriter text document, used in earlier versions of StarOffice
- SE – Shuttle Document
- STW – OpenOffice.org XML (obsolete) text document template
- Sxw – OpenOffice.org XML (obsolete) text document
- TeX – TeX
- TMDX – SoftMaker TextMaker
- INFO – Texinfo
- Troff – Unix OS document processing system
- TXT – ASCII or Unicode plain text file
- UOF – Uniform Office Format
- UOML – Unique Object Markup Language
- VIA – Revoware VIA Document Project File
- WPD – WordPerfect document
- WPS – Microsoft Works document
- WPT – Microsoft Works document template
- WRD – WordIt! document
- WRF – ThinkFree Write
- WRI – Microsoft Write document
- XHTML, XHT – XHTML eXtensible HyperText Markup Language
- XML – eXtensible Markup Language
- XPS – XPS: Open XML Paper Specification
- MYO – MYOB Limited (Windows) File
- MYOB – MYOB Limited (Mac) File
- TAX – TurboTax File
- YNAB – You Need a Budget (YNAB) File
- Tax2010 – Tax filling software
Financial data transfer formats
edit
- IFX – Interactive Financial Exchange XML-based specification for various forms of financial transactions
- OFX – Open Financial Exchange, open standard supported by CheckFree and Microsoft and partly by Intuit; SGML and later XML based
- QFX – proprietary pay-only format used only by Intuit
- QIF – Quicken Interchange Format open standard formerly supported by Intuit
- ABF – Adobe Binary Screen Font
- AFM – Adobe Font Metrics
- BDF – Bitmap Distribution Format
- BMF – ByteMap Font Format
- BRFNT – Binary Revolution Font Format
- FNT – Bitmapped Font – Graphics Environment Manager (GEM)
- FON – Bitmapped Font – Microsoft Windows
- MGF – MicroGrafx Font
- OTF – OpenType Font
- PCF – Portable Compiled Format
- PFA – Printer Font ASCII
- PFB – Printer Font Binary – Adobe
- PFM – Printer Font Metrics – Adobe
- FOND – Font Description resource – Mac OS
- SFD – FontForge spline font database Font
- SNF – Server Normal Format
- TDF – TheDraw Font
- TFM – TeX font metric
- TTF, TTC – TrueType Font
- UFO – Unified Font Object is a cross-platform, cross-application, human readable, future proof format for storing font data.
- WOFF – Web Open Font Format
These file formats allow for the rapid creation of new binary file formats.
- IFDS – Incredibly Flexible Data Storage file format. File extension and the magic number does not have to be IFDS.[8]
Geographic information system
edit
- ASC – ASCII point of interest (POI) text file
- APR – ESRI ArcView 3.3 and earlier project file
- DEM – USGS DEM file format
- E00 – ARC/INFO interchange file format
- GeoJSON – Geographically located data in object notation
- TopoJSON – Extension of GeoJSON with topology encoded in arcs for web development
- GeoTIFF – Geographically located raster data
- GML – Geography Markup Language file[9]
- GPX – XML-based interchange format
- ITN – TomTom Itinerary format
- MXD – ESRI ArcGIS project file, 8.0 and higher
- NTF – National Transfer Format file
- OV2 – TomTom POI overlay file
- SHP – ESRI shapefile
- TAB – MapInfo TAB format
- GeoTIFF – Geographically located raster data: text file giving corner coordinate, raster cells per unit, and rotation
- DTED – Digital Terrain Elevation Data
- KML – Keyhole Markup Language, XML-based
Graphical information organizers
edit
- 3DT – 3D Topicscape, the database in which the meta-data of a 3D Topicscape is held, it is a form of 3D concept map (like a 3D mind-map) used to organize ideas, information, and computer files
- ATY – 3D Topicscape file, produced when an association type is exported; used to permit round-trip (export Topicscape, change files and folders as desired, re-import to 3D Topicscape)
- CAG (file format) – Linear Reference System
- FES (file format) – 3D Topicscape file, produced when a fileless occurrence in 3D Topicscape is exported to Windows. Used to permit round-trip (export Topicscape, change files and folders as desired, re-import them to 3D Topicscape)
- MGMF – MindGenius Mind Mapping Software file format
- MM – FreeMind mind map file (XML)
- MMP (file format) – Mind Manager mind map file
- MUP – File type used by MindMup to export editable Mind Maps
- TPC (file format) – 3D Topicscape file, produced when an inter-Topicscape topic link file is exported to Windows; used to permit round-trip (export Topicscape, change files and folders as desired, re-import to 3D Topicscape)
- ACT – Adobe Color Table. Contains a raw color palette and consists of 256 24-bit RGB colour values.
- ASE – Adobe Swatch Exchange. Used by Adobe Substance, Photoshop, Illustrator, and InDesign.[10]
- GPL – GIMP palette file. Uses a text representation of color names and RGB values. Various open source graphical editors can read this format,[11] including GIMP, Inkscape, Krita,[12] KolourPaint, Scribus, CinePaint, and MyPaint.[13]
- PAL – Microsoft RIFF palette file
- ICC, ICM – Color profile conforming the specification of the ICC.
Raster or bitmap files store images as a group of pixels.
- ART – America Online proprietary format
- BLP – Blizzard Entertainment proprietary texture format
- BMP – Microsoft Windows Bitmap formatted image
- BTI – Nintendo proprietary texture format
- C4 – JEDMICS image files, a DOD system
- CALS – JEDMICS image files, a DOD system
- CD5 – Chasys Draw IES image
- CIT – Intergraph is a monochrome bitmap format
- CPT – Corel PHOTO-PAINT image
- CLIP – CLIP STUDIO PAINT format
- CPL – Windows control panel file
- DDS – DirectX texture file
- DIB – Device-Independent Bitmap graphic
- DjVu – DjVu for scanned documents
- EGT – EGT Universal Document, used in EGT SmartSense to compress PNG files to yet a smaller file
- EXIF – Exchangeable image file format (Exif) is a specification for the image format used by digital cameras
- GIF – CompuServe’s Graphics Interchange Format
- GIFV – Graphics Interchange Format Video, a format used for short, looping videos that combines the advantages of GIFs and videos, with better playback quality and lower file sizes[14]
- GRF – Zebra Technologies proprietary format
- ICNS – format for icons in macOS. Contains bitmap images at multiple resolutions and bitdepths with alpha channel.
- HEIC – High-Efficiency Image Codec
- ICO – a format used for icons in Microsoft Windows. Contains small bitmap images at multiple resolutions and bitdepths with 1-bit transparency or alpha channel.
- IFF, ILBM, LBM – IFF ILBM
- JNG – a single-frame MNG using JPEG compression and possibly an alpha channel
- JPEG, JFIF, JPG, JPEG – Joint Photographic Experts Group; a lossy image format widely used to display photographic images
- JP2 – JPEG2000
- JPS – JPEG Stereo
- JXL – JPEG XL, an image format designed for professional photography and web images; supports wide color gamut, high dynamic range, animations, and a max resolution of 1,073,741,823 x 1,073,741,824
- KRA – Krita image file
- LBM – Deluxe Paint image file
- MAX – ScanSoft PaperPort document
- MIFF – ImageMagick’s native file format
- MNG – Multiple-image Network Graphics, the animated version of PNG
- MSP – a format used by old versions of Microsoft Paint; replaced by BMP in Microsoft Windows 3.0
- NEF – Nikon camera raw format; photos have this on some Nikon cameras if the quality RAW is selected in camera settings
- NITF – A U.S. Government standard commonly used in Intelligence systems
- OTB – Over The Air bitmap, a specification designed by Nokia for black and white images for mobile phones
- PBM – Portable bitmap
- PC1 – Low resolution, compressed Degas picture file
- PC2 – Medium resolution, compressed Degas picture file
- PC3 – High resolution, compressed Degas picture file
- PCF – Pixel Coordination Format
- PCX – a lossless format used by ZSoft’s PC Paint, popular for a time on DOS systems.
- PDD – Adobe PhotoDeluxe image
- PDN – Paint.NET image file
- PGF – Progressive Graphics File
- PGM – Portable graymap
- PI1 – Low resolution, uncompressed Degas picture file
- PI2 – Medium resolution, uncompressed Degas picture file; also Portrait Innovations encrypted image format
- PI3 – High resolution, uncompressed Degas picture file
- PICT, PCT – Apple Macintosh PICT image
- PNG – Portable Network Graphic (lossless, recommended for display and edition of graphic images)
- PNJ – a sub-format of the MNG file format, used for encapsulating JPEG files[15]
- PNM – Portable anymap graphic bitmap image
- PNS – PNG Stereo
- PPM – Portable Pixmap (Pixel Map) image
- procreate – Procreate’s drawing file
- PSB – Adobe Photoshop Big image file (for large files)
- PSD – Adobe Photoshop Document
- PSP – Paint Shop Pro image
- PX – Pixel image editor image file
- PXM – Pixelmator image file
- PXR – Pixar Image Computer image file
- PXZ – a compressed layered image file used for the image editing website, pixlr.com
- QFX – QuickLink Fax image
- RLE – a run-length encoding image
- SCT – Scitex Continuous Tone image file
- SGI, RGB, INT, BW – Silicon Graphics Image
- TGA, TARGA, ICB, VDA, VST, PIX – Truevision TGA (Targa) image
- TIFF, TIF – Tag(ged) Image File Format; usually lossless, but many variants exist, including lossy ones.
- TIFF/EP, TIF, TIFF – Tag Image File Format / Electronic Photography, ISO 12234-2; tends to be used as a basis for other formats rather than in its own right.
- VTF – Valve Texture Format
- WEBP – WebP, an image format designed for the web that can provide both lossless and lossy compression.
- XBM – X Window System Bitmap
- XCF – GIMP image (from Gimp’s origin at the eXperimental Computing Facility of the University of California)
- XPM – X Window System Pixmap
- ZIF – Zoomable/Zoomify Image Format (a web-friendly, TIFF-based, zoomable image format)
- CR2 – Canon camera raw format; photos have this on some Canon cameras if the quality RAW is selected in camera settings
- DNG – «Digital Negative» a type of raw image file format used in digital photography.
- RAW – General term for minimally processed image data (acquired by a digital camera)
Vector graphics use geometric primitives such as points, lines, curves, and polygons to represent images.
- 3DV file – 3-D wireframe graphics by Oscar Garcia
- AMF – Additive Manufacturing File Format
- AWG – Ability Draw
- AI – Adobe Illustrator Document
- CGM – Computer Graphics Metafile, an ISO Standard
- CDR – CorelDRAW Document
- CMX – CorelDRAW vector image
- DP – Drawing Program file for PERQ[16]
- DRAWIO – Diagrams.net offline diagram
- DXF – ASCII Drawing Interchange file Format, used in AutoCAD and other CAD-programs
- E2D – 2-dimensional vector graphics used by the editor which is included in JFire
- EGT – EGT Universal Document, EGT Vector Draw images are used to draw vector to a website
- EPS – Encapsulated Postscript
- FS – FlexiPro file.x
- GBR – Gerber file
- ODG – OpenDocument Drawing
- MOVIE.BYU – 3D Vector file for polygons, coordinates and more complex shapes
- RenderMan – Displays Shading in both 2D and 3D scapes
- SVG – Scalable Vector Graphics, employs XML
- 3DMLW – Scene description languages (3D vector image formats)
- STL – Stereo Lithographic data format (see STL (file format)) used by various CAD systems and stereo lithographic printing machines. See above.
- WRL – Virtual Reality Modeling Language, VRML Uses this extension for the creation of 3D viewable web images.
- X3D – XML-based file for communicating 3D graphics
- SXD – OpenOffice.org XML (obsolete) Drawing
- TGAX – Texture format used by Zwift
- V2D – voucher design used by the voucher management included in JFire
- VDOC – Vector format used in AnyCut, CutStorm, DrawCut, DragonCut, FutureDRAW, MasterCut, SignMaster, VinylMaster software by Future Corporation
- VSD – Vector format used by Microsoft Visio
- VSDX – Vector format used by MS Visio and opened by VSDX Annotator
- VND – Vision numeric Drawing file used in TypeEdit, Gravostyle.
- WMF – Windows Meta File
- EMF – Enhanced (Windows) MetaFile, an extension to WMF
- ART – Xara–Drawing (superseded by XAR)
- XAR – Xara–Drawing
3D graphics are 3D models that allow building models in real-time or non-real-time 3D rendering.
- 3DMF – QuickDraw 3D Metafile (.3dmf)
- 3DM – OpenNURBS Initiative 3D Model (used by Rhinoceros 3D) (.3dm)
- 3MF – Microsoft 3D Manufacturing Format (.3mf)[3]
- 3DS – legacy 3D Studio Model (.3ds)
- ABC – Alembic (computer graphics)
- AC – AC3D Model
- AMF – Additive Manufacturing File Format
- AN8 – Anim8or Model
- AOI – Art of Illusion Model
- ASM – PTC Creo assembly
- B3D – Blitz3D Model
- BBMODEL Blockbench Model
- BLEND – Blender
- BLOCK – Blender encrypted blend files
- BMD3 – Nintendo GameCube first-party J3D proprietary model format (.bmd)
- BDL4 – Nintendo GameCube and Wii first-party J3D proprietary model format (2002, 2006–2010) (.bdl)
- BRRES – Nintendo Wii first-party proprietary model format 2010+ (.brres)
- BFRES – Nintendo Wii U and later Switch first-party proprietary model format
- C4D – Cinema 4D (.c4d)
- Cal3D – Cal3D (.cal3d)
- CCP4 – X-ray crystallography voxels (electron density)
- CFL – Compressed File Library
- COB – Caligari Object
- CORE3D – Coreona 3D Coreona 3D Virtual File(.core3d)
- CTM – OpenCTM
- DAE – COLLADA
- DFF – RenderWare binary stream, commonly used by Grand Theft Auto III-era games as well as other RenderWare titles
- DN – Adobe Dimension CC file format
- DPM – DeepMesh
- DTS – Torque Game Engine (DTS (file format))
- EGG – Panda3D Engine
- FACT – Electric Image (.fac)
- FBX – Autodesk FBX
- G – BRL-CAD geometry
- GLB – a binary form of glTF required to be loaded in Facebook 3D Posts
- GLM – Ghoul Mesh
- glTF – the JSON-based standard developed by Khronos Group
- HEC – Hector Game Engine – Flatspace model format
- IO – Bricklink Stud.io 2.0 Model File
- IOB – Imagine (3D modeling software)
- JAS – Cheetah 3D file
- JMESH – Universal mesh data exchange file based on JMesh specification (.jmsh for text/JSON based, .bmsh for binary/UBJSON based)
- LDR – LDraw Model File
- LWO – Lightwave Object
- LWS – Lightwave Scene
- LXF – LEGO Digital Designer Model file
- LXO – Luxology Modo (software) file
- M3D – Model3D, universal, engine-neutral format
- MA – Autodesk Maya ASCII File
- MAX – Autodesk 3D Studio Max file
- MB – Autodesk Maya Binary File
- MPD – LDraw Multi-Part Document Model File
- MD2 – MD2: Quake 2 model format
- MD3 – MD3: Quake 3 model format
- MD5 – MD5: Doom 3 model format
- MDX – Blizzard Entertainment’s own model format
- MESH – New York University(.m)
- MESH – Meshwork Model (.mesh)
- MIOBJECT – Mine-Imator object file
- MIPARTICLE – Mine-Imator particle file
- MIMODEL – Mine-Imator model file
- MM3D – Misfit Model 3d
- MPO – Multi-Picture Object – This JPEG standard is used for 3d images, as with the Nintendo 3DS
- MRC – MRC: voxels in cryo-electron microscopy
- NIF – Gamebryo NetImmerse File
- NWC – Navisworks — cached version of the converted model geometry
- NWD – Navisworks — publish format
- NWF – Navisworks — working format for projects
- OBJ – Wavefront .obj file
- OFF – OFF Object file format
- OGEX – Open Game Engine Exchange (OpenGEX) format
- PLY – PLY: Polygon File Format / Stanford Triangle Format
- PRC – Adobe PRC (embedded in PDF files)
- PRT – PTC Creo part
- POV – POV-Ray document
- R3D – Realsoft 3D (Real-3D)
- RWX – RenderWare Object
- SIA – Nevercenter Silo Object
- SIB – Nevercenter Silo Object
- SKP – SketchUp file
- SLDASM – SolidWorks Assembly Document
- SLDPRT – SolidWorks Part Document
- SMD – Valve Studiomdl Data format
- U3D – Universal 3D format
- USD – Universal Scene Description
- USDA – Universal Scene Description, human-readable text format
- USDC – Universal Scene Description, binary format
- USDZ – Universal Scene Description, a zip-compressed container
- VIM – Revizto visual information model format (.vimproj)
- VRML97 – VRML Virtual reality modeling language (.wrl)
- VUE – Vue scene file
- VWX – Vectorworks
- WINGS – Wings3D
- W3D – Westwood 3D Model
- X – DirectX 3D Model
- X3D – Extensible 3D
- Z3D – Zmodeler
- ZBMX – Mecabricks Blender Add-On
- Alias – Alias (Mac OS)
- JNLP – Java Network Launching Protocol, an XML file used by Java Web Start for starting Java applets over the Internet
- LNK – binary-format file shortcut in Microsoft Windows 95 and later
- APPREF-MS – File shortcut format used by ClickOnce
- NAL – ZENworks Instant shortcut (opens a .EXE not on the C:\ drive)
- URL – INI file pointing to a URL bookmarks/Internet shortcut in Microsoft Windows
- WEBLOC – Property list file pointing to a URL bookmarks/Internet shortcut in macOS
- SYM – Symbolic link
- DESKTOP – Desktop entry on Linux Desktop environments
- Harwell-Boeing – a file format designed to store sparse matrices
- MML – MathML – Mathematical Markup Language
- ODF – OpenDocument Math Formula
- SXM – OpenOffice.org XML (obsolete) Math Formula
- G3K – an obscure, uncommon format used by the CASIO graphing calculators to store keylogs
- 8BF – files plugins for some photo editing programs including Adobe Photoshop, Paint Shop Pro, GIMP and Helicon Filter.
- A – a static library on Unix-like systems
- A – Objective C native static library
- a.out – (no suffix for executable image, .o for object files, .so for shared object files) classic Unix object format, now often superseded by ELF
- APK – Android Package
- APP – A folder found on macOS systems containing program code and resources, appearing as one file.
- APP – file extension are executable application packages for running apps on HarmonyOS, OpenHarmony and Oniro devices.
- BAC – an executable image for the RSTS/E system, created using the BASIC-PLUS
COMPILEcommand[17] - BPL – a Win32 PE file created with Delphi or C++Builder containing a package.
- Bundle – a Macintosh plugin created with Xcode or make which holds executable code, data files, and folders for that code.
- CLASS – Compiled Java bytecode
- COFF – (no suffix for executable image, .o for object files) Unix Common Object File Format, now often superseded by ELF
- COM – Simple executable format used by CP/M and DOS.
- DCU – Delphi compiled unit
- DLL – Dynamic library used in Windows and OS/2 to store data, resources and code.
- DOL – the format used by the GameCube and Wii, short for Dolphin, which was the codename of the GameCube.
- EAR – archives of Java enterprise applications
- ELF – (no suffix for executable image, .o for object files, .so for shared object files) used in many modern Unix and Unix-like systems, including Solaris, other System V Release 4 derivatives, Linux, and BSD)
- EXE – DOS executable (.exe: used in DOS)
- EXE – New Executable (used in multitasking («European») MS-DOS 4.0, 16-bit Microsoft Windows, and OS/2)
- EXE – Portable Executable used in Microsoft Windows and some other systems
- IPA – file extension for apple IOS application executable file. Another form of zip file.
- JAR – archives of Java class files
- JEFF – a file format allowing execution directly from static memory[18]
- KO – Loadable kernel module
- LIB – a static library on Microsoft platforms
- LIST – variable list
- Mach-O – (no suffix for executable image, .o for object files, .dylib and .bundle for shared object files) Mach-based systems, notably native format of macOS, iOS, iPadOS, watchOS, tvOS and visionOS
- NLM – NetWare Loadable Module the native 32-bit binaries compiled for Novell’s NetWare Operating System (versions 3 and newer)
- O – un-linked object files directly from the compiler
- OBJ – object file on Windows
- RLL – used in Microsoft operating systems together with a DLL file to store program resources
- S1ES – Executable used for S1ES learning system.
- SO – shared library, typically ELF
- VAP – Value Added Process the native 16-bit binaries compiled for Novell’s NetWare Operating System (version 2, NetWare 286, Advanced NetWare, etc.)
- WAR – an archive of a Java Web application
- XAP – Windows Phone package
- XBE – XBE is Xbox executable
- XCOFF – (no suffix for executable image, .o for object files, .a for shared object files) extended COFF, used in AIX
- XEX – XEX is Xbox 360 executable
- XPI – PKZIP archive that can be run by Mozilla web browsers to install software.
- XSD – XML Schema Definition, used for planning and organizing XML documents.
Object extensions:
- OCX – Object Control extension
- TLB – Windows Type Library
- VBX – Visual Basic extension
Page description language
edit
- DVI – DVI are Device independent format
- EGT – Universal Document can be used to store CSS type styles
- PLD – PLD are PhotoLine Document files
- PCL – PCL Manages printer language
- PDF – PDF are Portable Document Format
- PS, GZ – PostScript [clarification needed]
- SNP – SNP are Microsoft Access Report Snapshot
- XPS – XPS
- XSL-FO – XSL-FO (Formatting Objects)
- Configurations, Metadata
- CSS – CSS are Cascading Style Sheets
- XSLT, XSL – XML Style Sheet
- TPL – Web template
Personal information manager
edit
- MNB – MyInfo notebook
- MSG – Microsoft Outlook task manager
- ORG – Lotus Organizer PIM package
- ORG – Emacs Org-Mode Mindmanager, contacts, calendar, email-integration
- PST, OST – Microsoft Outlook email communication
- SC2 – Microsoft Schedule+ calendar
- GSLIDES – Google Drive Presentation
- KEY, KEYNOTE – Apple Keynote Presentation
- NB – Mathematica Slideshow
- NBP – Mathematica Player slideshow
- ODP – OpenDocument Presentation
- OTP – OpenDocument Presentation template
- PEZ – Prezi Desktop Presentation
- POT – Microsoft PowerPoint template
- PRDX – SoftMaker Presentations
- PPS – Microsoft PowerPoint Show
- PPT – Microsoft PowerPoint Presentation
- PPTX – Office Open XML Presentation, there are at least 4 quite different versions of Microsoft’s PPTX: 1) ECMA-376, 2)ISO/IEC 29500 Transitional, 3) ISO/IEC 29500 Strict, 4) Microsoft-specific Compatibility Modes.
- PRZ – Lotus Freelance Graphics
- SDD – StarOffice’s StarImpress
- SHF – ThinkFree Show
- SHOW – Haansoft(Hancom) Presentation software document
- SHW – Corel Presentations slide show creation
- SLP – Logix-4D Manager Show Control Project
- SSPSS – SongShow Plus Slide Show
- STI – OpenOffice.org XML (obsolete) Presentation template
- SXI – OpenOffice.org XML (obsolete) Presentation
- THMX – Microsoft PowerPoint theme template
- WATCH – Dataton Watchout Presentation
Project management software
edit
- MPP – Microsoft Project
Reference management software
edit
Formats of files used for bibliographic information (citation) management.
- BIB – BibTeX
- ENL – EndNote
- RIS – Research Information Systems RIS (file format)
Scientific data (data exchange)
edit
- FITS – Flexible Image Transport System, a standard data format for astronomy
- Silo – a storage format for visualization developed at Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory
- SPC – SPC, spectroscopic data
- EAS3 – binary format for structured data
- EOSSA – Electro-Optic Space Situational Awareness format
- OST – (Open Spatio-Temporal) extensible, mainly images with related data, or just pure data; meant as an open alternative for microscope images
- CCP4 – CCP4, X-ray crystallography voxels (electron density)
- MRC – MRC, voxels in cryo-electron microscopy
- HITRAN – spectroscopic data with one optical/infrared transition per line in the ASCII file (.hit)
- ROOT – hierarchical platform-independent compressed binary format used by ROOT
- SDF – Simple Data Format (SDF), a platform-independent, precision-preserving binary data I/O format capable of handling large, multi-dimensional arrays.
- MYD – Everfine LEDSpec software file for LED measurements
- CSDM – (Core Scientific Dataset Model) model for multi-dimensional and correlated datasets from various spectroscopies, diffraction, microscopy, and imaging techniques (.csdf, .csdfe).[19]
- NetCDF – Network common data format
- HDR, HDF, h4, h5 – Hierarchical Data Format
- SDXF – SDXF, (Structured Data Exchange Format)
- CDF – Common Data Format
- CGNS – CGNS, CFD General Notation System
- FMF – Full-Metadata Format
- GRIB – Grid in Binary, WMO format for weather model data
- BUFR – WMO format for weather observation data
- PP – UK Met Office format for weather model data
- NASA-Ames – Simple text format for observation data. First used in aircraft studies of the atmosphere.
- CML – Chemical Markup Language (CML) (.cml)
- MOL, SD, SDF – Chemical table file (CTab)
- DX, JDX – Joint Committee on Atomic and Molecular Physical Data (JCAMP)
- SMI – Simplified molecular input line entry specification (SMILES)
- G6, S6 – graph6, sparse6, ASCII encoding of Adjacency matrices
Molecular biology and bioinformatics:
- AB1 – In DNA sequencing, chromatogram files used by instruments from Applied Biosystems
- ACE – A sequence assembly format
- ASN.1 – Abstract Syntax Notation One, is an International Standards Organization (ISO) data representation format used to achieve interoperability between platforms. NCBI uses ASN.1 for the storage and retrieval of data such as nucleotide and protein sequences, structures, genomes, and PubMed records.
- BAM – Binary Alignment/Map format (compressed SAM format)
- BCF – Binary compressed VCF format
- BED – The browser extensible display format is used for describing genes and other features of DNA sequences
- CAF – Common Assembly Format for sequence assembly
- CRAM – compressed file format for storing biological sequences aligned to a reference sequence
- DDBJ – The flatfile format used by the DDBJ to represent database records for nucleotide and peptide sequences from DDBJ databases.
- EMBL – The flatfile format used by the EMBL to represent database records for nucleotide and peptide sequences from EMBL databases.
- FASTA – The FASTA format, for sequence data. Sometimes also given as FNA or FAA (Fasta Nucleic Acid or Fasta Amino Acid).
- FASTQ – The FASTQ format, for sequence data with quality. Sometimes also given as QUAL.
- GCPROJ – The Genome Compiler project. Advanced format for genetic data to be designed, shared and visualized.
- GenBank – The flatfile format used by the NCBI to represent database records for nucleotide and peptide sequences from the GenBank and RefSeq databases
- GFF – The General feature format is used to describe genes and other features of DNA, RNA, and protein sequences
- GTF – The Gene transfer format is used to hold information about gene structure
- MAF – The Multiple Alignment Format stores multiple alignments for whole-genome to whole-genome comparisons [1]
- NCBI – Structured ASN.1 format used at National Center for Biotechnology Information for DNA and protein data
- NEXUS – The Nexus file encodes mixed information about genetic sequence data in a block structured format
- NeXML – XML format for phylogenetic trees
- NWK – The Newick tree format is a way of representing graph-theoretical trees with edge lengths using parentheses and commas and useful to hold phylogenetic trees.
- PDB – structures of biomolecules deposited in Protein Data Bank, also used to exchange protein and nucleic acid structures
- PHD – Phred output, from the base-calling software Phred
- PLN – Protein Line Notation used in proteax software specification
- SAM – SAM, Sequence Alignment Map format, in which the results of the 1000 Genomes Project will be released
- SBML – The Systems Biology Markup Language is used to store biochemical network computational models
- SCF – Staden chromatogram files used to store data from DNA sequencing
- SFF – Standard Flowgram Format
- SRA – format used by the National Center for Biotechnology Information Short Read Archive to store high-throughput DNA sequence data
- Stockholm – The Stockholm format for representing multiple sequence alignments
- Swiss-Prot – The flatfile format used to represent database records for protein sequences from the Swiss-Prot database
- VCF – Variant Call Format, a standard created by the 1000 Genomes Project that lists and annotates the entire collection of human variants (with the exception of approximately 1.6 million variants).
- DCM – Digital Imaging and Communications in Medicine (DICOM)
- NIfTI – Neuroimaging Informatics Technology Initiative
- NII – single-file (combined data and meta-data) style
- NII.GZ – gzip-compressed, used transparently by some software, notably the FMRIB Software Library (FSL)
- GII – single-file (combined data and meta-data) style; NIfTI offspring for brain surface data
- IMG, HDR – dual-file (separate data and meta-data, respectively) style
- IMG, HDR – Analyze data, meta-data
- BRIK, HEAD – AFNI data, meta-data
- MGH – uncompressed, Massachusetts General Hospital imaging format, used by the FreeSurfer brain analysis package
- MGZ – zip-compressed, Massachusetts General Hospital imaging format, used by the FreeSurfer brain analysis package
- MINC – Medical Imaging NetCDF format
- MNC – previously based on NetCDF; since version 2.0, based on HDF5
Biomedical signals (time series)
edit
- ACQ – AcqKnowledge format for Windows/PC from Biopac Systems Inc., Goleta, CA, USA
- ADICHT – LabChart format from ADInstruments Pty Ltd, Bella Vista NSW, Australia
- BCI2000 – The BCI2000 project, Albany, NY, USA
- BDF – BioSemi data format from BioSemi B.V. Amsterdam, Netherlands
- BKR – The EEG data format developed at the University of Technology Graz, Austria
- CFWB – Chart Data Format from ADInstruments Pty Ltd, Bella Vista NSW, Australia
- DICOM – Waveform An extension of Dicom for storing waveform data
- ecgML – A markup language for electrocardiogram data acquisition and analysis
- EDF, EDF+ – European Data Format
- FEF – File Exchange Format for Vital signs, CEN TS 14271
- GDF – The General Data Format for biomedical signals
- HL7aECG – Health Level 7 v3 annotated ECG
- MFER – Medical waveform Format Encoding Rules
- OpenXDF – Open Exchange Data Format from Neurotronics, Inc., Gainesville, FL, USA
- SCP-ECG – Standard Communication Protocol for Computer assisted electrocardiography EN1064:2007
- SIGIF – A digital SIGnal Interchange Format with application in neurophysiology
- WFDB – Format of Physiobank
- XDF – eXtensible Data Format
Other biomedical formats
edit
- HL7 – Health Level 7, a framework for exchange, integration, sharing, and retrieval of health information electronically
- xDT – a family of data exchange formats for medical records
- CBF – Common Biometric Format, based on CBEFF 2.0 (Common Biometric ExFramework).
- EBF – Extended Biometric Format, based on CBF but with S/MIME encryption support and semantic extensions
- CBFX – XML Common Biometric Format, based upon XCBF 1.1 (OASIS XML Common Biometric Format)
- EBFX – XML Extended Biometric Format, based on CBFX but with W3C XML Encryption support and semantic extensions
Programming languages and scripts
edit
- A – an external file extension for C/C++
- ADB – Ada body
- ADS – Ada specification
- AHK – AutoHotkey script file
- APPLESCRIPT – applescript: see SCPT
- AS – Adobe Flash ActionScript File
- AU3 – AutoIt version 3
- AWK – AWK
- B – (B file) Similar to .a, but less compressed.
- BAT – Batch file
- BAS – QBasic & QuickBASIC
- BTM – Batch file
- CLASS – Compiled Java binary
- CLS – ooRexx class file
- CLJS – ClojureScript
- CMD – Batch file
- command — A shell script, specifically associated with the Terminal on macOS
- Coffee – CoffeeScript
- C – C
- CIA – Nintendo 3DS Software Installation File, short for «CTR Importable Archive»
- CPP – C++
- CS – C#
- DART – Dart (programming language)
- FS – F#
- EGG – Chicken
- EGT – EGT Asterisk Application Source File, EGT Universal Document
- ERB – Embedded Ruby, Ruby on Rails Script File
- GO – Go
- GD — GDscript (Godot)
- HTA – HTML Application
- HX — Haxe source code file
- HXML — Haxe project configuration file
- IBI – Icarus script
- ICI – ICI
- IJS – J script
- INO – Arduino sketch (program)
- IPYNB – IPython Notebook
- ITCL – Itcl
- JS – JavaScript and JScript
- JSFL – Adobe JavaScript language
- JSX — JSX (JavaScript)
- KT – Kotlin
- LUA – Lua
- M – Mathematica package file
- MRC – mIRC Script
- NCF – NetWare Command File[20][21] (scripting for Novell’s NetWare OS)
- NUC – compiled script
- NUD – C++ External module written in C++
- NUT – Squirrel
- NQP – Raku language Not Quite Perl, or Raku bootstrapping language[22]
- O – Compiled and optimized C/C++ binary
- PDE – Processing (programming language), Processing script
- PHP – PHP
- PHP? – PHP (? = version number)
- PL – Perl
- PM – Perl module
- PS1 – Windows PowerShell shell script
- PS1XML – Windows PowerShell format and type definitions
- PSC1 – Windows PowerShell console file
- PSD1 – Windows PowerShell data file
- PSM1 – Windows PowerShell module file
- PY – Python
- PYC – Python byte code files
- PYO – Python
- R – R scripts
- R – REBOL scripts
- RAKU – Raku language Raku script (compiled into memory)[22]
- RAKUMOD – Raku language Raku module (precompiled)
- RAKUDOC – Raku language Raku documentation file (a slang or sublanguage of Raku)
- RAKUTEST – Raku language Unit test files in Raku
- RB – Ruby
- RDP – RDP connection
- RED – Red scripts
- REX, REXX – Rexx and ooRexx script file
- RXS, REXG, REXP – ooRexx script file
- RS – Rust (programming language)
- SB, SB2, SB3 – Scratch
- SCPT – Applescript
- SCPTD – See SCPT.
- SDL – State Description Language
- SH – Shell script
- SPRITE3 – Scratch 3.0 exported sprite file
- SPWN – SPWN source file
- SYJS – SyMAT JavaScript
- SYPY – SyMAT Python
- TCL – Tcl
- TNS – Ti-Nspire Code/File
- TS – TypeScript
- TSCN — Used to store Godot scenes
- UP − Pocket Up project
- VBS – Visual Basic Script
- XAML – Used in programs like Visual Studio to create exe files.
- XPL – XProc script/pipeline
- EBUILD – Gentoo Linux’s portage package.
Authentication and general encryption formats are listed here.
- OMF – OpenPGP Message Format used by Pretty Good Privacy, GNU Privacy Guard, and other OpenPGP software; can contain keys, signed data, or encrypted data; can be binary or text («ASCII armored»)
Certificates and keys
edit
- GXK – Galaxkey, an encryption platform for authorized, private and confidential email communication[citation needed]
- SSH – OpenSSH private key, Secure Shell private key; format generated by ssh-keygen or converted from PPK with PuTTYgen[23][24][25]
- PUB – OpenSSH public key, Secure Shell public key; format generated by ssh-keygen or PuTTYgen[23][24][25]
- PPK – PuTTY private key, Secure Shell private key, in the format generated by PuTTYgen instead of the format used by OpenSSH[23][24][25]
- nSign – nSign public key nSign public key in a custom format[26]
- CER, CRT, DER – Distinguished Encoding Rules stores certificates
- P7B, P7C – PKCS#7 SignedData commonly appears without main data, just certificates or certificate revocation lists (CRLs)
- P12, PFX – PKCS#12 can store public certificates and private keys
- PEM – Privacy-enhanced Electronic Mail: full format not widely used, but often used to store Distinguished Encoding Rules in Base64 format
- PFX – Microsoft predecessor of PKCS#12
This section shows file formats for encrypted general data, rather than a specific program’s data.
- AXX – Encrypted file, created with AxCrypt
- EEA – An encrypted CAB, ostensibly for protecting email attachments
- TC – Virtual encrypted disk container, created by TrueCrypt
- KODE – Encrypted file, created with KodeFile
- nSignE – An encrypted private key, created by nSign[26]
Password files (sometimes called keychain files) contain lists of other passwords, usually encrypted.
- BPW – Encrypted password file created by Bitser password manager
- KDB – KeePass 1 database
- KDBX – KeePass 2 database
Signal data (non-audio)
edit
- ACQ – AcqKnowledge format for Windows/PC from Biopac
- ADICHT – LabChart format from ADInstruments
- BKR – The EEG data format developed at the University of Technology Graz
- BDF, CFG – Configuration file for Comtrade data
- CFWB – Chart Data format from ADInstruments
- DAT – Raw data file for Comtrade data
- EDF – European data format
- FEF – File Exchange Format for Vital signs
- GDF – General data formats for biomedical signals
- GMS – Gesture And Motion Signal format
- IROCK – intelliRock Sensor Data File Format
- MFER – Medical waveform Format Encoding Rules
- SAC – Seismic Analysis Code, earthquake seismology data format[27]
- SCP-ECG – Standard Communication Protocol for Computer assisted electrocardiography
- SEED, MSEED – Standard for the Exchange of Earthquake Data, seismological data and sensor metadata[28]
- SEGY – Reflection seismology data format
- SIGIF – SIGnal Interchange Format
- WIN, WIN32 – NIED/ERI seismic data format (.cnt)[29]
- 8SVX – Commodore-Amiga 8-bit sound (usually in an IFF container)
- 16SVX – Commodore-Amiga 16-bit sound (usually in an IFF container)
- AIFF, AIF, AIFC – Audio Interchange File Format
- AU – Simple audio file format introduced by Sun Microsystems
- AUP3 – Audacity’s file for when you save a song
- BWF – Broadcast Wave Format, an extension of WAVE
- CDDA – Compact Disc Digital Audio
- DSF, DFF – Direct Stream Digital audio file, also used in Super Audio CD
- RAW – Raw samples without any header or sync
- WAV – Microsoft Wave
- CWAV – file read by the Nintendo 3DS for Home-screen sound effects
- QAU, QUEYEAUDIO — Queye Audio file, adapted from WAVE with specific metadata, generally for artists to submit music to their labels.
- QAU0 — Proprietary version of the Queye Audio file, without metadata.
- RA, RM – RealAudio format
- FLAC – Free lossless codec of the Ogg project
- LA – Lossless audio
- PAC – LPAC
- APE – Monkey’s Audio
- OFR, OFS, OFF – OptimFROG
- RKA – RKAU
- SHN – Shorten
- TAK – Tom’s Lossless Audio Kompressor[30]
- THD – Dolby TrueHD
- TTA – Free lossless audio codec (True Audio)
- WV – WavPack
- WMA – Windows Media Audio 9 Lossless
- BCWAV – Nintendo 3DS Home-screen BGM file
- BRSTM – Binary Revolution Stream[31]
- DTS, DTSHD, DTSMA – DTS (sound system)
- AST – Nintendo Audio Stream
- AW – Nintendo Audio Sample used in first-party games
- PSF – Portable Sound Format, PlayStation variant (originally PlayStation Sound Format)
- AC3 – Usually used for Dolby Digital tracks
- AMR – For GSM and UMTS based mobile phones
- MP1 – MPEG Layer 1
- MP2 – MPEG Layer 2
- MP3 – MPEG Layer 3
- SPX – Speex (Ogg project, specialized for voice, low bitrates)
- GSM – GSM Full Rate, originally developed for use in mobile phones
- WMA – Windows Media Audio
- AAC – Advanced Audio Coding (usually in an MPEG-4 container)
- MPC – Musepack
- VQF – Yamaha TwinVQ
- OTS – Audio File (similar to MP3, with more data stored in the file and slightly better compression; designed for use with OtsLabs’ OtsAV)
- SWA – Adobe Shockwave Audio (Same compression as MP3 with additional header information specific to Adobe Director)
- VOX – Dialogic ADPCM Low Sample Rate Digitized Voice
- VOC – Creative Labs Soundblaster Creative Voice 8-bit & 16-bit Also output format of RCA Audio Recorders
- DWD – DiamondWare Digitized
- SMP – Turtlebeach SampleVision
- OGG – Ogg Vorbis
- MOD – Soundtracker and Protracker sample and melody modules
- MT2 – MadTracker 2 module
- S3M – Scream Tracker 3 module
- XM – Fast Tracker module
- IT – Impulse Tracker module
- SNG – Goat Tracker module
- NSF – NES Sound Format
- MID, MIDI – Standard MIDI file; most often just notes and controls but occasionally also sample dumps (.mid, .rmi)
- FTM – FamiTracker Project file
- BTM – BambooTracker Project file
- FUR – Furnace Tracker Project file
- ABC – ABC Notation sheet music file
- DARMS – DARMS File Format also known as the Ford-Columbia Format
- ETF – Enigma Transportation Format abandoned sheet music exchange format
- GP – Guitar Pro sheet music and tablature file
- KERN – Kern File Format sheet music file
- LY – LilyPond sheet music file
- MEI – Music Encoding Initiative file format that attempts to encode all musical notations
- MIDI – MIDI file format that is a music sheet for instruments
- MUS, MUSX – Finale sheet music file
- MXL, XML – MusicXML standard sheet music exchange format
- MSCX, MSCZ – MuseScore sheet music file
- SMDL – Standard Music Description Language sheet music file
- SIB – Sibelius sheet music file
Other file formats pertaining to audio
edit
- ASF – Advanced Systems Format
- CUST – DeliPlayer custom sound format
- GYM – Genesis YM2612 log
- JAM – Jam music format
- MNG – Background music for the Creatures game series, starting from Creatures 2
- NIFF – Notation Interchange File Format
- PTB – Power Tab Editor tab
- PVD – Portable Voice Document used for Oaisys & Mitel call recordings
- RMJ – RealJukebox Media used for RealPlayer
- SF2 – Polyphone Soundfont 2
- SF3 – Polyphone Soundfont 3
- SF4 – Polyphone Soundfont 4
- SID – Sound Interface Device – Commodore 64 instructions to play SID music and sound effects
- SPC – Super NES sound format
- TXM – Track ax media
- VGM – Stands for «Video Game Music», log for several different chips
- YM – Atari ST/Amstrad CPC YM2149 sound chip format
- AIMPPL – AIMP Playlist format
- ASX – Advanced Stream Redirector
- RAM – Real Audio Metafile For RealAudio files only.
- XPL – HDi playlist
- XSPF – XML Shareable Playlist Format
- ZPL – Groove Music Playlist format from Microsoft
- M3U – Multimedia playlist file
- PLS – Multimedia playlist, originally developed for use with the museArc
- QAUA – «Queye Audio Album», set of Queye Audio files with album metadata.
Audio editing and music production
edit
- ALS – Ableton Live set
- ALC – Ableton Live clip
- ALP – Ableton Live pack
- ATMOS, AUDIO, METADATA – Dolby Atmos Rendering and Mastering related file
- AUP – Audacity project file
- AUP3 – Audacity 3.0 project file
- BAND – GarageBand project file
- CEL – Adobe Audition loop file (Cool Edit Loop)
- CAU – Caustic project file
- CPR – Steinberg Cubase project file
- CWP – Cakewalk by BandLab project file
- DRM – Steinberg Cubase drum file
- DWP – DirectWave Sampler Instrument file (mainly used for FL Studio Mobile)
- DMKIT – Image-Line’s Drumaxx drum kit file
- ENS – Native Instruments Reaktor Ensemble
- FLM – Image Line FL Studio Mobile project file
- FLP – Image Line FL Studio project file
- GRIR – Native Instruments Komplete Guitar Rig Impulse Response
- LOGIC – Logic Pro X project file
- MMP – LMMS project file (alternatively MMPZ for compressed formats)
- MMR – MAGIX Music Maker project file
- MX6HS – Mixcraft 6 Home Studio project file
- NPR – Steinberg Nuendo project file
- OMF, OMFI – Open Media Framework Interchange OMFI succeeds OMF (Open Media Framework)
- PTX – Pro Tools 10 or later project file
- PTF – Pro Tools 7 up to Pro Tools 9 project file
- PTS – Legacy Pro Tools project file
- RIN – Soundways RIN-M file containing sound recording participant credits and song information
- RPP, RPP-BAK – REAPER project file
- REAPEAKS – REAPER peak (waveform cache) file
- SES – Adobe Audition multitrack session file
- SFK – Sound Forge waveform cache file
- SFL – Sound Forge sound file
- SNG – MIDI sequence file (MidiSoft, Korg, etc.) or n-Track Studio project file
- STF – StudioFactory project file. It contains all necessary patches, samples, tracks and settings to play the file
- SND – Akai MPC sound file
- SYN – SynFactory project file. It contains all necessary patches, samples, tracks and settings to play the file
- UST – Utau Editor sequence excluding wave-file
- USTX – OpenUtau project file
- VCLS – VocaListener project file
- VPR – Vocaloid 5 Editor sequence excluding wave-file
- VSQ – Vocaloid 2 Editor sequence excluding wave-file
- VSQX – Vocaloid 3 & 4 Editor sequence excluding wave-file
Recorded television formats
edit
- DVR-MS – Windows XP Media Center Edition’s Windows Media Center recorded television format
- WTV – Windows Vista’s and up Windows Media Center recorded television format
Source code for computer programs
edit
- ADA, ADB, 2.ADA – Ada (body) source
- ADS, 1.ADA – Ada (specification) source
- ASM, S – Assembly language source
- BAS – BASIC, FreeBASIC, Visual Basic, BASIC-PLUS source,[17] PICAXE basic
- BB – Blitz Basic Blitz3D
- BMX – Blitz Basic BlitzMax
- C – C source
- CLJ – Clojure source code
- CLS – Visual Basic class
- COB, CBL – COBOL source
- CPP, CC, CXX, C, CBP – C++ source
- CS – C# source
- CSPROJ – C# project (Visual Studio .NET)
- D – D source
- DBA – DarkBASIC source
- DBPro123 – DarkBASIC Professional project
- E – Eiffel source
- EFS – EGT Forever Source File
- EGT – EGT Asterisk Source File, could be J, C#, VB.net, EF 2.0 (EGT Forever)
- EL – Emacs Lisp source
- FOR, FTN, F, F77, F90 – Fortran source
- FRM – Visual Basic form
- FRX – Visual Basic form stash file (binary form file)
- FTH – Forth source
- GED – Game Maker Extension Editable file as of version 7.0
- GM6 – Game Maker Editable file as of version 6.x
- GMD – Game Maker Editable file up to version 5.x
- GMK – Game Maker Editable file as of version 7.0
- GML – Game Maker Language script file
- GO – Go source
- H – C/C++ header file
- HPP, HXX – C++ header file
- HS – Haskell source
- I – SWIG interface file
- INC – Turbo Pascal included source
- JAVA – Java source
- JS – JavaScript source
- L – lex source
- LGT – Logtalk source
- LISP – Common Lisp source
- M – Objective-C source
- M – MATLAB
- M – Mathematica
- MAP – CodeWarrior linker file
- M4 – m4 source
- ML – Standard ML and OCaml source
- MSQR – M² source file, created by Mattia Marziali
- N – Nemerle source
- NB – Nuclear Basic source
- P – Parser source
- PAS, PP, P – Pascal source (DPR for projects)
- PHP, PHP3, PHP4, PHP5, PHPS, Phtml – PHP source
- PIV – Pivot stickfigure animator
- PL, PM – Perl
- PLI, PL1 – PL/I
- PRG – Ashton-Tate; dbII, dbIII and dbIV, db, db7, clipper, Microsoft Fox and FoxPro, harbour, xharbour, and Xbase
- PRO – IDL
- POL – Apcera Policy Language doclet
- PY – Python source
- R – R source
- raku, rakumod, rakudoc, rakutest, nqp – Raku Language
- RED – Red source
- REDS – Red/System source
- RB – Ruby source
- RESX – Resource file for .NET applications
- RC, RC2 – Resource script files to generate resources for .NET applications
- RKT, RKTL – Racket source
- RS – Rust source
- Resources – Visual Studio Code
- S – CodeWarrior / PowerPC ASM
- SCALA – Scala source
- SCI, SCE – Scilab
- SCM – Scheme source
- SD7 – Seed7 source
- SKB, SKC – Sage Retrieve 4GL Common Area (Main and Amended backup)
- SKD – Sage Retrieve 4GL Database
- SKF, SKG – Sage Retrieve 4GL File Layouts (Main and Amended backup)
- SKI – Sage Retrieve 4GL Instructions
- SKK – Sage Retrieve 4GL Report Generator
- SKM – Sage Retrieve 4GL Menu
- SKO – Sage Retrieve 4GL Program
- SKP, SKQ – Sage Retrieve 4GL Print Layouts (Main and Amended backup)
- SKS, SKT – Sage Retrieve 4GL Screen Layouts (Main and Amended backup)
- SKZ – Sage Retrieve 4GL Security File
- SLN – Visual Studio solution
- SPIN – Spin source (for Parallax Propeller microcontrollers)
- STK – Stickfigure file for Pivot stickfigure animator
- SWG – SWIG source code
- TCL – Tcl source code
- VAP – Visual Studio Analyzer project
- VB – Visual Basic.NET source
- VBG – Visual Studio compatible project group
- VBP, VIP – Visual Basic project
- VBPROJ – Visual Basic .NET project
- VCPROJ – Visual C++ project
- VDPROJ – Visual Studio deployment project
- XPL – XProc script/pipeline
- XQ – XQuery file
- XSL – XSLT stylesheet
- Y – yacc source
- 123 – Lotus 1-2-3
- AB2 – Abykus worksheet
- AB3 – Abykus workbook
- AWS – Ability Spreadsheet
- BCSV – Nintendo proprietary table format
- CLF – ThinkFree Calc
- CELL – Haansoft(Hancom) SpreadSheet software document
- CSV – Comma-Separated Values
- GSHEET – Google Drive Spreadsheet
- numbers – Apple Numbers Spreadsheet
- gnumeric – Gnumeric spreadsheet, a gziped XML file
- LCW – Lucid 3-D
- ODS – OpenDocument spreadsheet
- OTS – OpenDocument spreadsheet template
- QPW – Quattro Pro spreadsheet
- PMDX – SoftMaker PlanMaker
- SDC – StarOffice StarCalc Spreadsheet
- SLK – SYLK (SYmbolic LinK)
- STC – OpenOffice.org XML (obsolete) Spreadsheet template
- SXC – OpenOffice.org XML (obsolete) Spreadsheet
- TAB – tab delimited columns; also TSV (Tab-Separated Values)
- TXT – text file
- VC – Visicalc
- WK1 – Lotus 1-2-3 up to version 2.01
- WK3 – Lotus 1-2-3 version 3.0
- WK4 – Lotus 1-2-3 version 4.0
- WKS – Lotus 1-2-3
- WKS – Microsoft Works
- WQ1 – Quattro Pro DOS version
- XLK – Microsoft Excel worksheet backup
- XLS – Microsoft Excel worksheet sheet (97–2003)
- XLSB – Microsoft Excel binary workbook
- XLSM – Microsoft Excel Macro-enabled workbook
- XLSX – Office Open XML worksheet sheet, there are at least 4 quite different versions of Microsoft’s XLSX: 1) ECMA-376, 2)ISO/IEC 29500 Transitional, 3) ISO/IEC 29500 Strict, 4) Microsoft-specific Compatibility Modes.
- XLR – Microsoft Works version 6.0
- XLT – Microsoft Excel worksheet template
- XLTM – Microsoft Excel Macro-enabled worksheet template
- XLW – Microsoft Excel worksheet workspace (version 4.0)
- TSV – Tab-separated values
- CSV – Comma-separated values
- DB – databank format; accessible by many econometric applications
- DIF – accessible by many spreadsheet applications
- 3GP – the most common video format for cell phones
- AAF – mostly intended to hold edit decisions and rendering information, but can also contain compressed media essence
- AT3 – Sony’s UMD data compression
- GIF – Animated GIF (simple animation; until recently often avoided because of patent problems)
- ASF – container (enables any form of compression to be used; MPEG-4 is common; video in ASF-containers is also called Windows Media Video (WMV))
- AVCHD – Advanced Video Codec High Definition
- AVI – container (a shell, which enables any form of compression to be used)
- BIK – Bink Video file. A video compression system developed by RAD Game Tools
- BRAW – a high bitrate video format used by Blackmagic Design cameras.
- CAM – aMSN webcam log file
- COLLAB – Blackboard Collaborate session recording
- DAT – video standard data file (automatically created when we attempted to burn as video file on the CD)
- DVR-MS – Windows XP Media Center Edition’s Windows Media Center recorded television format
- FLV – Flash video (encoded to run in a flash animation)
- MPEG-1 – M1V Video
- MPEG-2 – M2V Video
- NOA – rare movie format use in some Japanese eroges around 2002
- FLA – Adobe Flash (for producing)
- FLR – (text file which contains scripts extracted from SWF by a free ActionScript decompiler named FLARE)
- SOL – Adobe Flash shared object («Flash cookie»)
- STR – Sony PlayStation video stream
- M4V – video container file format developed by Apple
- MKV – Matroska Matroska is a container format, which enables any video format such as MPEG-4 ASP or AVC to be used along with other content such as subtitles and detailed meta information
- WRAP – MediaForge (*.wrap)
- MNG – mainly simple animation containing PNG and JPEG objects, often somewhat more complex than animated GIF
- MOV – QuickTime container which enables any form of compression to be used; Sorenson codec is the most common; QTCH is the filetype for cached video and audio streams
- MPEG, MPG, MPE – MPEG
- THP – Nintendo proprietary movie/video format
- MPEG-4 – MPEG-4 Part 14, shortened «MP4» multimedia container (most often used for Sony’s PlayStation Portable and Apple’s iPod)
- MXF – Material Exchange Format (standardized wrapper format for audio/visual material developed by SMPTE)
- ROQ – used by Quake III Arena
- NSV – NSV Nullsoft Streaming Video (media container designed for streaming video content over the Internet)
- OGG – container, multimedia
- RM – RealMedia
- SVI – SVI Samsung video format for portable players
- SMK – Smacker video file. A video compression system developed by RAD Game Tools
- SWF – Adobe Flash (for viewing)
- TORRENT – A file that does not hold the video, but simply where the video is located (Can also be used to store the location of a software or audio)
- WMV – Windows Media Video (See ASF)
- WTV – Windows Vista’s and up Windows Media Center recorded television format
- YUV – raw video format; resolution (horizontal x vertical) and sample structure 4:2:2 or 4:2:0 must be known explicitly
- WebM – video file format for web video using HTML5
- ASS, SSA – ASS (also SSA): a subtitles file created by Aegisub, a video typesetting application (also a Halo game engine file)
- SMI – SMI SAMI Caption file (HTML like subtitle for movie files)
- SRT – SubRip Subtitle – file format for closed captioning or subtitles
Video editing, production
edit
- BRAW – Blackmagic Design RAW video file name
- DRP – Davinci Resolve 17 project file
- FCP – Final Cut Pro project file
- MSWMM – Windows Movie Maker project file
- PDS – Cyberlink PowerDirector project
- PPJ, PRPROJ – Adobe Premiere Pro video editing file
- AEP – Adobe After Effects video editing file
- IMOVIEPROJ – iMovie project file
- VEG, VEG-BAK – Sony Vegas project file
- SUF – Sony camera configuration file (setup.suf) produced by XDCAM-EX camcorders
- WLMP – Windows Live Movie Maker project file
- KDENLIVE – Kdenlive project file
- VPJ – VideoPad project file
- MOTN – Apple Motion project file
- IMOVIEMOBILE – iMovie project file for iOS users
- WFP, WVE – Wondershare Filmora Project
- VPROJ – VSDC Free Video Editor project file
List of common file formats of data for video games on systems that support filesystems, most commonly PC games.
These formats are used by the video game osu!.
- OSB – storyboard data
- OSC – osu!stream combined stream data
- OSF2 – free osu!stream song file
- OSG – compressed live gameplay archive (optimized for spectating)
- OSK – compressed skin archive
- OSR – compressed replay archive
- OSU – beatmap data
- OSZ – compressed beatmap archive
- OSZ2 – paid osu!stream song file
These formats are used by the video game Minecraft.
- MCADDON – Bedrock Edition add-ons and resource packs
- MCFUNCTION – functions/scripts
- MCMETA – customizable texture packs
- MCPACK – Bedrock Edition in-game texture packs and full add-ons
- MCR – data for in-game worlds before version 1.2
- MCTEMPLATE – Bedrock Edition world templates
- MCWORLD – Bedrock Edition in-game worlds
- NBS – used by Note Block Studio, a tool that can be used to make songs with note blocks in-game
- EPK – used by Eaglercraft, an AOT compiled port of Minecraft which has been modified to run under TeaVM, a Java emulator for HTML5 & JavaScript, for saving world data, resource packs, profiles and more.
TrackMania/Maniaplanet Engine
edit
Formats used by games based on the TrackMania engine.
- GBX – All user-created content is stored in this file type.
- REPLAY.GBX – Stores the replay of a race.
- CHALLENGE.GBX, MAP.GBX – Stores tracks/maps.
- SYSTEMCONFIG.GBX – Launcher info.
- TRACKMANIAVEHICLE.GBX – Info about a certain car type.
- VEHICLETUNINGS.GBX – Vehicle physics.
- SOLID.GBX – A block’s model.
- ITEM.GBX – Custom Maniaplanet item.
- BLOCK.GBX – Custom Maniaplanet block.
- TEXTURE.GBX – Info about a texture that are used in materials.
- MATERIAL.GBX – Info about a material such as surface type that are used in Solids.
- TMEDCLASSIC.GBX – Block info.
- GHOST.GBX – Player ghosts in Trackmania and TrackMania Turbo.
- CONTROLSTYLE.GBX – Menu files.
- SCORES.GBX – Stores info about the player’s best times.
- PROFILE.GBX – Stores a player’s info such as their login.
- DDS – Almost every texture in the game uses this format.
- PAK – Stores environment data such as valid blocks.
- LOC – A locator. Locators allow the game to download content such as car skins from an external server.
- SCRIPT.TXT – Scripts for Maniaplanet such as menus and game modes.
- XML – ManiaLinks.
Formats used by games based on the Doom engine.
- WAD – Data storage (contains music, maps, and textures)
- DEH – DeHackEd files to mutate the game executable (not officially part of the Doom engine)
- DSG – Saved game
- LMP – A «lump», an entry in a WAD file
- LMP – Saved demo recording
- MUS – Music file (usually contained within a WAD file)
Formats used by games based on the Quake engine.
- BSP – BSP: (For binary space partitioning) compiled map format
- MAP – MAP: Raw map format used by editors like GtkRadiant or QuArK
- MDL, MD2, MD3, MD5 – MDL/MD2/MD3/MD5: Model for an item used in the game
- PAK, PK2 – PAK/PK2: Data storage
- PK3, PK4 – PK3/PK4: used by the Quake II, Quake III Arena and Quake 4 game engines, respectively, to store game data, textures etc. They are actually .zip files.
- DAT – not specific file type, often generic extension for «data» files for a variety of applications, sometimes used for general data contained within the PK3/PK4 files
- FONTDAT – a DAT file used for formatting game fonts
- ROQ – Video format
- SAV – Savegame/Savefile format
Formats used by games based on the Unreal engine.
- FUK – Map File for Postal 2
- U – Unreal script format
- UASSET – An asset format since Unreal Engine 4/5.
- UAX – Animations format for Unreal Engine 2.
- UMAP – Map file type for Unreal Engine and levels.
- UMX – Map format for Unreal Tournament
- UMX – Music format for Unreal Engine 1
- UNR – Map format for Unreal
- UPK – Package format for cooked content in Unreal Engine 3
- USX – Sound format for Unreal Engine 1 and Unreal Engine 2
- UT2 – Map format for Unreal Tournament 2003 and Unreal Tournament 2004
- UT3 – Map format for Unreal Tournament 3
- UTX – Texture format for Unreal Engine 1 and Unreal Engine 2
- UXX – Cache format; these are files a client downloaded from server (which can be converted to regular formats)
Formats used by games based on this engine.
- DMO – Save game
- GRP – Data storage
- MAP – Map (usually constructed with BUILD.EXE)
Formats used by Diablo by Blizzard Entertainment.
- SV – Save Game
- ITM – Item File
Formats used by Bohemia Interactive. Operation:Flashpoint, ARMA 2, VBS2
- LIP – Format that is created from WAV files to create in-game accurate lip-sync for character animations.
- PBO – Binarized file used for compiled models
- SQF – Format used for general editing
- SQM – Format used for mission files
- RBXL – Roblox Studio place file (XML, binary)
- RBXM – Roblox Studio model file (XML, binary)
- RBXLX – Roblox Studio place file (exclusively XML)
- RBXMX – Roblox Studio model file (exclusively XML)
Formats used by Valve. Half-Life 2, Counter-Strike: Source, Day of Defeat: Source, Half-Life 2: Episode One, Team Fortress 2, Half-Life 2: Episode Two, Portal, Left 4 Dead, Left 4 Dead 2, Alien Swarm, Portal 2, Counter-Strike: Global Offensive, Titanfall, Insurgency, Titanfall 2, Day of Infamy
- BSP – Source Engine compiled map file
- DEM – Source Engine demo format
- HL2 – Half-Life 2 save format
- MDL – Source Engine model format
- PCF – Source Engine particle effect file
- SAV – Source Engine save format
- SMD – Source Engine uncompiled model format
- VMF – Valve Hammer Map editor raw map file
- VMT – Source Engine material format.
- VMX – Valve Hammer Map editor backup map file
- VPK – Source Engine pack format
- VTF – Source Engine texture format
Formats used in Metal Gear Rising: Revengeance, Bayonetta, Vanquish (video game), Nier: Automata
- DAT, DTT, EVN, EFF, EFT — Data containers, acts similarly to a folder, but can only have one layer of depth
- WMB — Mesh data
- SCR — Collection of WMBs to makeup levels and scenes.
- WTA — Texture definitions and flags
- WTP — Raw texture data
- WTB — Combination of both WTA and WTP, with WTA first, then WTP after
- TRG — Controls the flow of in-game events and calls functions in code
- BXM — Binary-encoded and compressed XML data
- EST — Effect data for the ESP effects system (Used in Metal Gear Rising: Revengeance and Nier: Automata)
- EF2 — Effect data for the EF2 effects system (Used in Bayonetta 1)
- MOT — Motion capture animation data
- CGB – Pokémon Black and White/Black 2 and White 2 C-Gear skins
- ARC – used to store New Super Mario Bros. Wii level data
- B – used for Grand Theft Auto saved game files
- BBSETTINGS — Blockbench settings
- BBTHEME — Blockbench theme
- BBKEYMAP — Blockbench keybindings
- BOL – used for levels on Poing!PC
- DBPF – The Sims 2, DBPF, Package
- DDZ – a file which can only be used by the «daydreamer engine» created by «fever-dreamer», a program similar to RAGS, it’s mainly used to make somewhat short games.
- DIVA – Project DIVA timings, element coordinates, MP3 references, notes, animation poses and scores.
- ESM, ESP – Master and Plugin data archives for the Creation Engine
- HAMBU – format used by the Aidan’s Funhouse game RGTW for storing map data[32]
- HE0, HE2, HE4 – HE games File
- GCF – format used by the Steam content management system for file archives
- IMG – format used by Renderware-based Grand Theft Auto games for data storage
- LLSP3 – Lego Spike program file
- LOVE – format used by the LOVE2D Engine[33]
- MAP – format used by Halo: Combat Evolved for archive compression, Doom³, and various other games
- MCA – format used by Minecraft for storing data for in-game worlds[34]
- MLOG – A file format intended to be used for Mindustry Logic
- MSAV — A file format used to store Mindustry’s Map and save data.
- MSCH — A file format used to store Mindustry’s Schematic data.
- MPQ – MPQ Archives Used by Blizzard Entertainment
- NBT – format used by Minecraft for storing program variables along with their (Java) type identifiers
- NL2PKG – NoLimits 2 Package
- OEC – format used by OE-Cake for scene data storage
- P3D – format for panda3d by Disney
- PLAGUEINC – format used by Plague Inc. for storing custom scenario information[35]
- POD – format used by Terminal Reality
- RAG, RAGS – Game file, a game playable in the RAGS game-engine, a free program which both allows people to create games, and play games, games created have the format «RAG game file»
- RCT – Used for templates and save files in RollerCoaster Tycoon games
- REP – used by Blizzard Entertainment for scenario replays in StarCraft
- RIQ – Used in Heaven Studio to store custom maps
- Simcity, DBPF, DAT, SC4Lot, SC4Model – All game plugins use this format, commonly with different file extensions (Sim City 4)
- SMZIP – ZIP-based package for StepMania songs, themes and announcer packs.
- SOLITAIRETHEME8 – A solitaire theme for Windows solitaire
- UNI, UNIS – Super Mario UniMaker level data
- USLD – format used by Unison Shift to store level layouts.
- VIV – Archive format used to compress data for several video games, including Need For Speed: High Stakes.
- VOL – video game data package
- VVVVVV – format used by VVVVVV
- CPS – format used by The Powder Toy, Powder Toy save
- STM – format used by The Powder Toy, Powder Toy stamp
- PKG – format used by Bungie for the PC Beta of Destiny 2, for nearly all the game’s assets.
- CHR – format used by Team Salvato, for the character files of Doki Doki Literature Club!
- Z5 – format used by Z-machine for story files in interactive fiction.
- SCWORLD – format used by Survivalcraft to store sandbox worlds.
- SCSKIN – format used by Survivalcraft to store player skins.
- SCBTEX – format used by Survivalcraft to store block textures.
- PRISON – format used by Prison Architect to save prisons
- ESCAPE – format used by Prison Architect to save escape attempts
- WBFS – (Wii Backup File System)
- GBA – Game Boy Advance ROM File
- JKR – format used by Balatro for data storage
- PSS – Sony PlayStation 2 Game Video file and is used to store audio and video data by games for the PlayStation 2 console.
- XD – A format used in a mod (XDBot) for Geometry Dash to save macros, (a format to replay inputs.) This is saved within the Documents section in File Explorer for Windows 10.
- FNFC — Friday Night Funkin’ Chart File.
- ARC – Nintendo U8 Archive (mostly Yaz0 compressed)
- SZS – Nintendo Yaz0 Compressed Archive
List of the most common filename extensions used when a game’s ROM image or storage medium is copied from an original read-only memory (ROM) device to an external memory such as hard disk for back up purposes or for making the game playable with an emulator. In the case of cartridge-based software, if the platform specific extension is not used then filename extensions «.rom» or «.bin» are usually used to clarify that the file contains a copy of a content of a ROM. ROM, disk or tape images usually do not consist of one file or ROM, rather an entire file or ROM structure contained within one file on the backup medium.[36]
- 32X – Sega 32X
- 3DS – Nintendo 3DS
- A26 – Atari 2600
- A52 – Atari 5200
- A78 – Atari 7800
- ADF – Amiga (.adf) (for 880K diskette images)
- ADZ – GZip-compressed version of the above.
- BIN – Odyssey²
- CIA – Nintendo 3DS Installation File (for installing games with the use of the FBI homebrew application)
- CRT – (for cartridge images)
- D64 – (for disk images)
- DMS – Disk Masher System, previously used as a disk-archiving system native to the Amiga, also supported by emulators.
- DSI – Nintendo DSiWare
- DSK – (for disk images)
- FC# – FCEUX Save States (.fc#, where # is any character, usually a number)
- FDS – Famicom Disk System
- FIG – Super Famicom (Japanese releases are rarely .fig, above extensions are more common)
- FRZ, 000-008 – Snes9X Save States
- GB – Game Boy (this applies to the original Game Boy and the Game Boy Color)
- GBA – a Game Boy Advance Game from a ROM Cartridge
- GBC – Game Boy Color
- GCM, ISO – a GameCube disk/game
- GG – Game Gear
- INT – Intellivision
- ISO, WBFS, WAD, WDF – a Wii and WiiU disk/game
- JAG, J64 – an Atari Jaguar game from a Rom Cartridge
- JST – Jnes Save States
- LNX – Atari Lynx
- MIN – Pokémon Mini
- MIN – a Pokémon mini rom/game
- N64, V64, Z64, U64, USA, JAP, PAL, EUR – Nintendo 64
- NDS – a Nintendo DS game from a ROM Cartridge
- NES – Nintendo Entertainment System[37]
- NGC – Neo Geo Pocket Color
- NPC, NGP – Neo Geo Pocket
- NSP – Nintendo Switch EShop Video Game file that stores audio data, video data, game data, and program code for the Nintendo Switch; Also supported by emulators.
- PCE – TurboGrafx-16/PC Engine
- PJ – Project 64 Save States
- PSS – A Sony PlayStation 2 Game Video file and is used to store audio and video data by games for the PlayStation 2 console.
- SAV – Game Boy Advance Saved Data Files
- SG – SG-1000
- SGM – Visual Boy Advance Save States
- SMC, 078, SFC – Super NES (.078 is for split ROMs, which are rare)
- SMD, BIN – Mega Drive/Genesis
- SMS – Master System
- SRM – Super NES Saved Data Files
- T64 – (for tape images without copy protection, considerably smaller than .tap files)
- TAP – Commodore 64 (.tap) (for tape images including copy protection)
- TAP – for tape images without copy protection
- TZX – ZX Spectrum (for exact copies of ZX Spectrum games)
- VB – Virtual Boy
- VEC – Vectrex
- WS – WonderSwan
- WSC – WonderSwan Color
- XCI – Nintendo Switch Video Game cartridge dump file that stores audio data, video data, game data, and program code for the Nintendo Switch; Also supported by emulators.
- Z80, SNA – (for snapshots of the emulator RAM)
- ZST, ZS1-ZS9, Z10-Z99 – ZSNES Save States
- VFD – Virtual Floppy Disk
- VHD – Virtual Hard Disk
- VUD – Virtual Undo Disk
- VMC – Virtual Machine Configuration
- VSV – Virtual Machine Saved State
- LOG – Virtual Machine Logfile
- VMDK, DSK – Virtual Machine Disk
- NVRAM – Virtual Machine BIOS
- VMEM – Virtual Machine paging file
- VMSD – Virtual Machine snapshot metadata
- VMSN – Virtual Machine snapshot
- VMSS, STD – Virtual Machine suspended state
- VMTM – Virtual Machine team data
- VMX, CFG – Virtual Machine configuration
- VMXF – Virtual Machine team configuration
- VBOX – VirtualBox machine
- VDI – VirtualBox virtual disk image
- VBOX-EXTPACK – VirtualBox extension pack
- HDD – Virtual Machine hard disk
- PVS – Virtual Machine preferences/configuration
- SAV – Virtual Machine saved state
- COW – Copy-on-write
- QCOW – QEMU copy-on-write
- QCOW2 – QEMU copy-on-write – version 2
- QED – QEMU enhanced disk format
Static
- DTD – Document Type Definition (standard), MUST be public and free
- HTML, HTM – HyperText Markup Language
- XHTML, XHT – XHTML eXtensible HyperText Markup Language
- MHT, MHTML – MHTML Archived HTML, store all data on one web page (text, images, etc.) in one big file
- MAFF – MAF web archive based on ZIP
Dynamically generated
- ASP – ASP Microsoft Active Server Page
- ASPX – ASPX Microsoft Active Server Page. NET
- ADP – ADP AOLserver Dynamic Page
- BML – BML Better Markup Language (templating)
- CFM – CFM ColdFusion
- CGI – CGI
- IHTML – iHTML Inline HTML
- JSP – JSP JavaServer Pages
- LAS, LASSO, LASSOAPP – Lasso, A file created or served with the Lasso Programming Language
- PL – Perl
- PHP, PHP?, PHTML – PHP ? is version number (previously abbreviated Personal Home Page, later changed to PHP: Hypertext Preprocessor)
- SHTML – SSI HTML with Server Side Includes (Apache)
- STM – SSI HTML with Server Side Includes (Apache)
Markup languages and other web standards-based formats
edit
- ATOM, XML – Atom Another syndication format.
- EML – EML Format used by several desktop email clients.
- JSONLD – JSON-LD A JSON-based serialization for linked data.
- KPRX – KPRX A XML-based serialization for workflow definition generated by K2.
- MARKDOWN, MD – Markdown Plain text formatting syntax, which is popularly used to format «readme» files.
- METALINK, MET – Metalink A format to list metadata about downloads, such as mirrors, checksums, and other information.
- MHTML – Mime HTML (Hyper-Text Markup Language) code file
- PS – PS A XML-based serialization for test automation scripts called PowerScripts for K2 based applications.
- RSS, XML – RSS Syndication format.
- SE – Shuttle Another lightweight markup language.
- ZIM – ZIM: an open file format that stores wiki content for offline usage
- AXD – cookie extensions found in temporary internet folder
- BDF – Binary Data Format – raw data from recovered blocks of unallocated space on a hard drive
- CBP – CD Box Labeler Pro, CentraBuilder, Code::Blocks Project File, Conlab Project
- CEX – SolidWorks Enterprise PDM Vault File
- COL – Nintendo GameCube proprietary collision file (.col)
- CREDX – CredX Dat File
- DDB – Generating code for Vocaloid singers voice (see .DDI)
- DDI – Vocaloid phoneme library (Japanese, English, Korean, Spanish, Chinese, Catalan)
- DUPX – DuupeCheck database management tool project file
- FTM – Family Tree Maker data file
- FTMB – Family Tree Maker backup file
- GA3 – Graphical Analysis 3
- GED – GEDCOM (GEnealogical Data COMmunication) format to exchange genealogy data between different genealogy software
- HLP – Windows or CP/M help file
- IGC – flight tracks downloaded from GPS devices in the FAI’s prescribed format
- INF – similar format to INI file; used to install device drivers under Windows, inter alia.
- JAM – JAM Message Base Format for BBSes
- KMC – tests made with KatzReview’s MegaCrammer
- KCL – Nintendo GameCube/Wii proprietary collision file (.kcl)
- KTR – Hitachi Vantara Pentaho Data Integration/Kettle Transformation Project file
- LNK – Microsoft Windows format for Hyperlinks to Executables
- LSM – LSMaker script file (program using layered .jpg to create special effects; specifically designed to render lightsabers from the Star Wars universe) (.lsm)
- MCR – a macro recording file for Super Macro software
- MELSAVE – Melon Playground build save file
- MELMOD – Melon Playground mod file
- MELMAP — Melon Playground Map file
- NARC – archive format used in Nintendo DS games
- NTH – NTH: Nokia Theme Used by Nokia Series 40 cellphones
- OER – AU OER Tool, Open Educational Resource editor
- PA – Used to assign sound effects to materials in KCL files
- PIF – Used to run MS-DOS programs under Windows
- POR – So called «portable» SPSS files, readable by PSPP
- PXZ – Compressed file to exchange media elements with PSALMO
- RISE – File containing RISE generated information model evolution
- SCR – Windows Screen Saver file
- TOPC – TopicCrunch SEO Project file holding keywords, domain, and search engine settings (ASCII)
- XLF – Utah State University Extensible LADAR Format
- XMC – Assisted contact lists format, based on XML and used in kindergartens and schools
- ZED – My Heritage Family Tree
- ZONE – Zone file a text file containing a DNS zone
- FX – Microsoft DirectX plain text effects and properties for the associated file and are used to specify the textures, shading, rendering, lighting and other 3D effects
- MIFRAMES – Mine-imator keyframes file (.miframes)
- MILANGUAGE – Mine-Imator language data file
- MIDATA – Mine-Imator data file
- BCA – Short for Burst Cutting Area Holds the information of the circular area near the center of a DVD, HD DVD or Blu-ray Disc, it is usually 64 bytes in size. (.bca)
- ANI – Animated cursor
- CUR – Cursor file
- Smes – Hawk’s Dock configuration file
General data formats
edit
These file formats are fairly well defined by long-term use or a general standard, but the content of each file is often highly specific to particular software or has been extended by further standards for specific uses.
- CSV – comma-separated values
- HTML – hyper text markup language
- CSS – cascading style sheets
- INI – a configuration text file whose format is substantially similar between applications
- JSON – JavaScript Object Notation is an openly used data format now used by many languages, not just JavaScript
- TSV – tab-separated values
- XML – an open data format
- YAML – an open data format
- ReStructuredText – an open text format for technical documents used mainly in the Python programming language
- MD – Markdown an open lightweight markup language to create simple but rich text, often used to format README files
- AsciiDoc – an open human-readable markup document format semantically equivalent to DocBook
- YNI – a configuration file similar to YAML
Generic file extensions
edit
These are filename extensions and broad types reused frequently with differing formats or no specific format by different programs.
- BAK, BK – Bak file various backup formats: some just copies of data files, some in application-specific data backup formats, some formats for general file backup programs
- BIN – binary data, often memory dumps of executable code or data to be re-used by the same software that originated it
- DAT – data file, usually binary data proprietary to the program that created it, or an MPEG-1 stream of Video CD
- DSK – file representations of various disk storage images
- RAW – raw (unprocessed) data
- SZH – files that are associated with zero unique file types (the most prevalent being the Binary Data format)
- CNF, CONF, CFG – configuration file substantially software-specific
- LOG – logfiles usually text, but sometimes binary
- TEXT, TXT, ASC – human-readable plain text, usually no more specific
Differences and patches
edit
- DIFF – text file differences created by the program diff and applied as updates by patch
Incomplete transfers
edit
- !UT – Partially complete uTorrent download
- CRDOWNLOAD – Partially complete or incomplete Google Chrome or Microsoft Edge download
- OPDOWNLOAD – Partially complete or incomplete Opera download
- PART – PART partly complete Mozilla Firefox or Transmission download
- PARTIAL – PARTIAL partly complete Internet Explorer or Edge Legacy download
- TEMP, TMP – Temporary file sometimes in a specific format, but often just raw data in the middle of processing
- Pseudo-pipelines, Pseudo-pipeline – Pseudo-pipeline file used to simulate a software pipe
- List of filename extensions
- MIME#Content-Type, a standard for referring to file formats
- List of motion and gesture file formats
- List of file signatures, or «magic numbers»
- List of open-source file formats
- ^ «Filename extension definition». The Linux Information Project. Retrieved 1 February 2019.
- ^ «What Is a Cabinet (.cab) File?». microsoft.com. Microsoft.
- ^ a b «3D printing with Windows 10». microsoft.com. Microsoft.
- ^ «www.datacad.com – DataCAD Revision History». datacad.com.
- ^ «How to export a design in Fusion 360». Knowledge.autodesk.com. Retrieved 4 August 2019.
- ^ «Windows XML Event Log (EVTX) format». github.com.
- ^ «Reagency Systems – easyOFFER the OREA and TREB real estate forms software solution details». reagency.ca. Archived from the original on 19 June 2020. Retrieved 11 August 2013.
- ^ «Incredibly Flexible Data Storage (IFDS) File Format». Github.com. Retrieved 16 December 2022.
- ^ «GML Format». gephi.org.
- ^ «Create, manage, and import swatches in InDesign». Helpx.adobe.com. Retrieved 24 September 2018.
- ^ «Swatch Book – Inkscape Wiki». Wiki.inkscape.org. Retrieved 24 September 2018.
- ^ «Palette Docker – Krita Manual version 4.1». Docs.krita.org. Retrieved 24 September 2018.
- ^ «v1.2 Palette · mypaint/mypaint Wiki». GitHub.com. Retrieved 24 September 2018.
- ^ «What is graphics interchange format video (GIFV)?». Lenovo.com.
- ^ «How do I open a .pnj file?». FileSuffix.com.
- ^ «Index of /pdf/perq/accent_S5/Accent_UsersManual_1984». Bitsavers.org. Retrieved 4 August 2019.
- ^ a b RSTS-11 System Users Guide (PDF) (DEC-11-ORSUA-D-D (RSTS/E V06A-02) ed.). Digital Equipment Corporation. 1975. pp. 2–16–2–17. Archived from the original (PDF) on 21 March 2011. Retrieved 22 March 2011.
- ^ «Archived copy» (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 15 December 2017. Retrieved 24 March 2018.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link) - ^
Srivastava, Deepansh; Vosegaard, Thomas; Massiot, Dominique; Grandinetti, Philip (January 2020). «Core Scientific Dataset Model: A lightweight and portable model and file format for multi- dimensional scientific data». PLOS ONE. 15 (1): e0225953. Bibcode:2020PLoSO..1525953S. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0225953. PMC 6940021. PMID 31895936. - ^ «Definition of NCF file». PCMAG. Retrieved 29 October 2022.
- ^ Bastiaansen, Rob; Vugt, Sander van (9 May 2006). Novell Cluster Services for Linux and NetWare. Pearson Education. p. 27. ISBN 978-0-672-33283-8. Retrieved 29 October 2022.
- ^ a b «Filename extensions».
- ^ a b c «Setting Up and Using PuTTY». Wipo.int.
- ^ a b c «How to Convert Your Putty .PPK Private Key to a Normal SSH Key You Can Use on an Apple Mac | These things are far too hard». leadingedgescripts.co.uk. Archived from the original on 11 July 2012. Retrieved 15 January 2022.
- ^ a b c Leo Notenboom. «How do I create and use Public Keys with SSH?»
- ^ a b Jayasooriya, Tarith (16 September 2020). «nSign». nsign. Retrieved 12 October 2020.
- ^ «SAC Data File Format». Incorporated Research Institutions for Seismology.
- ^ «Standard for the Exchange of Earthquake Data» (PDF). Data Formats. IRIS (Incorporated Research Institutions for Seismology). Retrieved 5 May 2016.
- ^ «What is WIN system?» (in Japanese). Earthquake Observation Center, Earthquake Research Institute, U. Tokyo, Japan. Archived from the original on 2 April 2016. Retrieved 5 May 2016.
- ^ «TAK». hydrogenaud.io.
- ^ Tim Fisher. «BRSTM File (What It Is & How To Open One)». About.com Tech. Archived from the original on 5 May 2016. Retrieved 20 March 2012.
- ^ «HAMBU File Extension – What is a .hambu file and how do I open it?». fileinfo.com. Retrieved 17 July 2020.
- ^ love2d.org
- ^ «MCA File Extension». FileInfo.com. Retrieved 26 December 2018.
- ^ «FileInfo information about PLAGUEINC file format».
- ^ «.GCM file extension! [Archive] – EmuTalk.net». emutalk.net. 21 June 2004.
- ^ Medley, Sam (20 September 2018). «You can now play your own NES ROMs on Nintendo Switch Online thanks to a new hack». Notebookcheck. Retrieved 9 November 2022.
- File formats at FileInfo.com
- File Extension Database at FileExpert.Net
- fileformats.archiveteam.org
Содержание статьи:
- Типовые вопросы по форматам файлов
- Как увидеть расширение у файлов (Windows их не показывает)
- Сколько всего расширений (типов файлов)
- Таблица популярных расширений файлов
- Как узнать, какой программой открыть незнакомый формат (если Windows не может открыть файл)
- Как поменять расширение у файла
- Как назначить программу для открытия файлов определенного формата по умолчанию
- Как искать файлы конкретного формата
- Вопросы и ответы: 0
Доброго здравия!
Сегодняшняя заметка будет «солянкой» (сборкой) по ответам на популярные типовые вопросы насчет форматов/расширений файлов (тем паче, что часть ответов у меня уже сохранилась в почте, а часть была немного освещена в блоге).
Если вы только знакомитесь с подобной темой — рекомендую читать заметку с самого начала, по порядку (иначе некоторые слова могут быть непонятны).
Теперь ближе к теме…
*
Итак, что же такое формат файла, и его расширение?
Формат файла — способ кодирования информации (структура, как записаны данные). В зависимости от типа информации (текстовый файл, картинка, видео и прочее) — используются разные форматы.
В Windows у файлов есть расширения — неск. англ. букв в конце имени файла (см. скрин ниже: docx, rar, png). Они помогают системе определять к какому формату относится файл, и какой программой его можно открыть (т.е. архив — будет открыт архиватором, музыкальный файл — проигрывателем, документ — в Microsoft Word и т.д.).
Примеры расширений у файлов — архив, картинка, текстовый документ // Windows, раб. стол
👉 Здесь стоит сразу сделать замечание: не у всех на компьютере включено отображение расширений (по умолчанию в некоторых версиях Windows показ расширения у файла отключен, якобы так удобнее).
Собственно, список ответов на типовые вопросы начну как раз с этой темы. Думаю, разумно сначала рассмотреть вопрос вкл. показа расширений…
*
Типовые вопросы по форматам файлов
Как увидеть расширение у файлов (Windows их не показывает)
📌 Вариант 1:
- открыть проводник (сочетание клавиш Win+E) // можно просто перейти в какую-нибудь папку;
- перейти в параметры проводника (в верхнем меню есть кнопка);
- в меню «Вид» снять галочку со скрытия расширений (можно доп. включить показ скрытых файлов);
- сохранить настройки и открыть нужный каталог еще раз: расширения у файлов должны появиться! 👇👌
Примечание: если не получилось найти параметры проводника — можно просто открыть командную строку и ввести команду: reg add «HKCU\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Explorer\Advanced» /v HideFileExt /t REG_DWORD /d 00000000 /f (нажать Enter. После перезагрузить ПК).
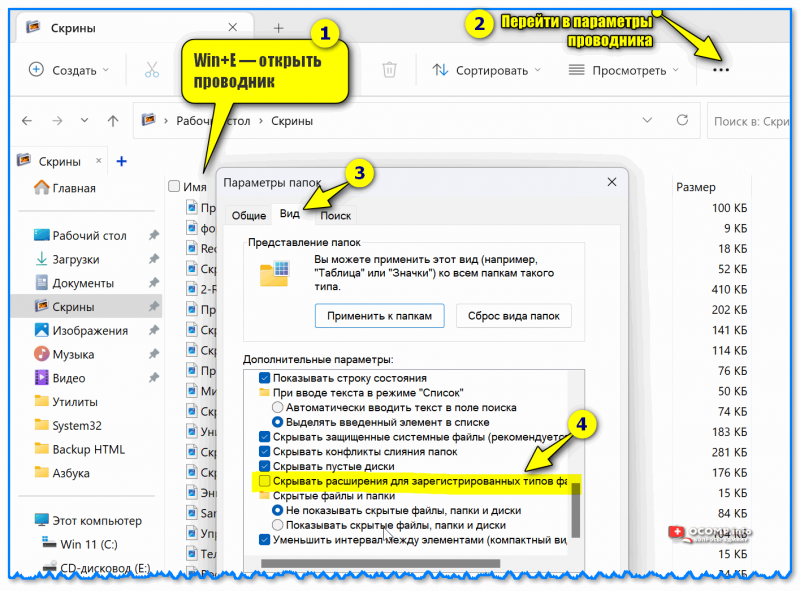
Настройка проводника — включаем показ расширений

Примеры расширений у файлов — архив, картинка, текстовый документ
📌 Вариант 2:
- можно установить на ПК какой-нибудь файловый коммандер (например, Total Commander);
- затем запустить его и открыть нужный каталог — по умолчанию для всех файлов коммандер покажет расширения (кстати, у коммандеров гораздо больше функций по управлению файлами, чем у проводника!).
Тип файлов / Total Commander
*
Сколько всего расширений (типов файлов)
Много!
Вообще, вопрос интересный… На вскидку: можно точно ответить, что их больше нескольких сотен, по крайней мере самых популярных (а вот назвать точное число — не сможет никто (наверное 🙂)).
По идее, никто вам не мешает создать свою программу и сделать так, чтобы она записывала файлы в нужное вам расширение.
И как это посчитать?..
*
Таблица популярных расширений файлов
Примечание: ниже в табличке представлены только самые популярные расширения в Windows. Если расширение вам незнакомо и Windows не может открыть этот файл — см. вот эту часть заметки.
| Расширения | Что за файл | Какой программой открыть |
|---|---|---|
| .jpg
.png .bmp .gif .tif |
Изображения (фото, картинки) |
|
| .doc
.docx |
Документы |
|
| .xls
.xlsx |
Электронная таблица |
|
| PDF-документ |
|
|
| .txt | Текстовый файл |
|
| .zip
.rar .7z .gzip |
Архивы |
|
| .mp3
.wav .midi .aac |
Аудиофайлы (музыка) |
|
| .mp4
.avi .mkv .wmv |
Видеофайлы (фильмы, ролики) |
|
| .html
.htm |
Веб-страница |
|
| .iso | Образ компакт-диска |
|
| .torrent | Торрент-файл |
|
| .djvu | Сканированный документ (книга, журнал и пр.). Аналог PDF (своего рода). |
|
| .fb2
.epub .mobi |
Файл электронной книги |
|
*
Как узнать, какой программой открыть незнакомый формат (если Windows не может открыть файл)
Для начала в Windows нужно включить показ расширений и посмотреть его у проблемного файла. В моем примере ниже, например, расширение у не открывающегося файла «.png1». 👇
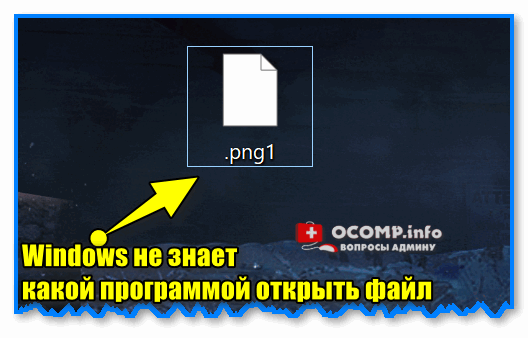
Windows не знает какой программой открыть файл (значок серый)
📌 Далее можно поступить следующим образом:
- во-первых, если вы видите, что расширение задано неправильно — то можно его отредактировать // т.е. переименовать файл (например, вместо «.PNG1» написать «.PNG», а затем попробовать открыть файл);
Переименовать файл
- во-вторых, можно попробовать в сети поискать название программ для работы с файлами такого расширения. Например, для формата «.SVG» Google мне выдал добрый десяток программ (разумеется, установив одну из них — проблема сама-собой решится!), см. пример ниже 👇.
Как и чем открыть SVG — подсказки Google
- в-третьих, можно также попробовать конвертировать этот «проблемный файл» в другой формат (например, картинку можно из PNG перегнать в JPG).
*
Как поменять расширение у файла
Вариант 1
Самый простой вариант — вкл. показ расширений в проводнике Windows, а затем переименовать файл так, как вам нужно. Например, вместо «.PNG» можно картинке дать новое расширение «.BMP» *. 👇
* Важно: этот способ хоть и помогает во множестве случаев, однако при переименовании файла — вы не меняете сам формат файла! Та же картинка: она как была PNG так и останется ей, просто при задании расширения «.BMP» — Windows может работать с файлом в др. программах (что иногда и помогает).
📌 Чтобы изменить не просто расширение, но и сам формат файла — необходимо провести операцию конвертирования…

Переименовать файл
*
Вариант 2 (с конвертированием)
Конвертирование файла — это не просто смена расширения одно на другое, эта операция преобразования из одного формата в другой (аналогия для примера: представьте у вас есть листочек-рукопись, на котором записан рецепт. Если вы его напечатаете на ПК, на принтере — то информация на нем вроде бы будет та же, но формат другой // конвертация… 🙂).
*
👉 Разумеется, для конвертирования файлов нужны спец. приложения, причем, для картинок — это будут одни программы, для видео — другие, для текста — третьи…
У меня на блоге было неск. заметок по этой тематике, чтобы не повторяться — приведу ссылки ниже:
- 📌 видео-конверторы — подборка программ для работы с форматами AVI, MPEG4, WMV, 3GP и др.;
- 📌 Чем заменить Word и Excel (мой Office) — приводил аналоги продуктов от Microsoft, которые помогут преобразовать текстовые файлы в различные форматы;
- 📌 Конвертирование картинок — инструкция по работе с популярными граф. форматами JPG, PNG, GIF и BMP.
*
👉 Кстати!
Если вам нужно конвертировать незнакомые форматы файлов (и вы не можете найти программы для работы с ними) — попробуйте задать в Google запрос вида «конвертировать JPG в GIF» (где вместо JPG и GIF — укажите свои расширения. Вполне возможно, что легко найдете конвертер).
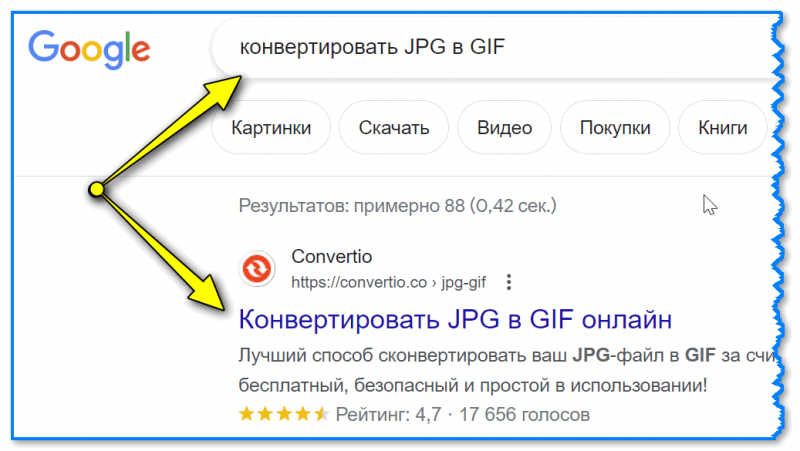
Пример поиска конвертеров в Google
*
Как назначить программу для открытия файлов определенного формата по умолчанию
Если вы делаете двойной клик по файлу и он открывается совсем не в той программе, в которой вам нужно — то в Windows это можно относительно легко поменять: просто задать другую программу по умолчанию…
По теме: как поменять браузер по умолчанию.
*
Вариант 1
Выбрать файл, открыть его свойства, во вкладке «Общие» нажать по кнопке «Изменить» и задать необходимое приложение…
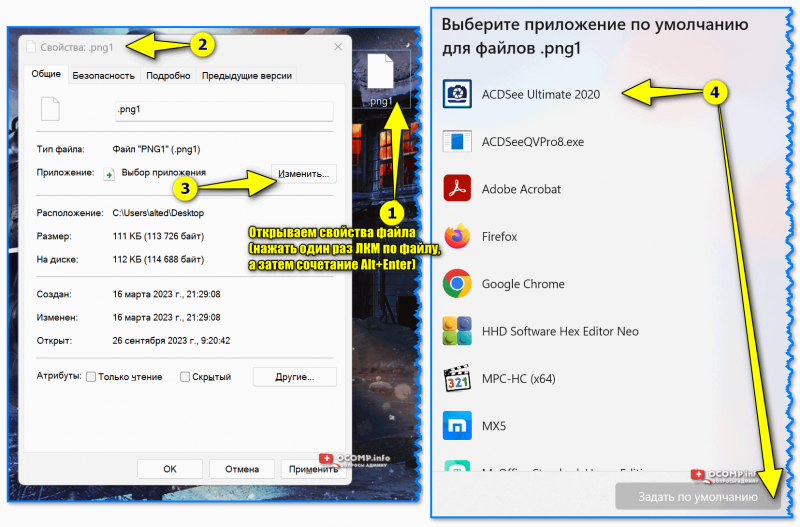
Открываем свойства файла
Вариант 2
Открыть параметры системы (Win+i) и перейти во вкладку «Приложения / приложения по умолчанию» (далее задать нужное).
Параметры Windows 11 — приложения по умолчанию
*
Как искать файлы конкретного формата
Вопрос популярный, и у меня на блоге он уже был (см. ссылку на заметку ниже). Если кратко: то искать можно как в проводнике, так и с помощью спец. приложений (в том же Total Commander, например).
https://ocomp.info/ne-mogu-nayti-fayl-na-diske.html
Кстати, в том же проводнике (Win+E для запуска) в поисковой строке достаточно указать нужное вам расширение и нажать Enter… См. скрин ниже. 👇
Поиск файлов // проводник Windows 11
*
Дополнения по теме — приветствуются в комментариях (заранее благодарю за помощь).
За сим откланяюсь, удачи!
👋